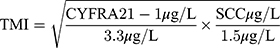Back to Journals » OncoTargets and Therapy » Volume 14
Prognostic Significance of the Combination of Fibrinogen and Tumor Marker Index in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients
Authors Qiao Y, Ma M, Zhang H, Yu Z , Tang P
Received 26 August 2020
Accepted for publication 10 January 2021
Published 17 February 2021 Volume 2021:14 Pages 1101—1111
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S278831
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Takuya Aoki
Yufeng Qiao, Mingquan Ma, Hongdian Zhang, Zhentao Yu, Peng Tang
Department of Esophageal Cancer, Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital, Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Therapy of Tianjin, Tianjin’s Clinical Research Center for Cancer, National Clinical Research Center of Cancer, Tianjin, 300060, People’s Republic of China
Correspondence: Peng Tang
Department of Esophageal Cancer, Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital, Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Therapy of Tianjin, Tianjin’s Clinical Research Center for Cancer, National Clinical Research Center of Cancer, Tianjin, 300060, People’s Republic of China
Tel +86-022-23340123
Fax +86-22-23359984
Email [email protected]
Background: The current study was aimed at comparing the prognostic value of the combination of plasma fibrinogen and tumor marker index (TMI) [F-TMI] system with TMI alone in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) after surgical resection.
Methods: A total of 317 patients with ESCC who underwent surgical resection were retrospectively analyzed. The TMI was calculated as the square root of (CYFRA 21– 1 concentration/3.3 μg/L) × (SCC concentration/1.5 μg/L). The patients were divided into F-TMI scores according to the following criteria: score 2, both elevated fibrinogen and high TMI; score 1, either elevated fibrinogen or high TMI; and score 0, neither abnormality. Univariate and multivariate survival analyses were performed to evaluate the prognostic value of F-TMI or TMI alone.
Results: The five-year overall survival rate of patients with high TMI was significantly lower than that of patients with low TMI (30.8% vs 50.4%, p < 0.001). There was a significant correlation between the F-TMI score with age, tumor size, NLR, PLR, pT status, and pN status. The five-year overall survival rates for patients with F-TMI scores of 2, 1, and 0 were 27.6%, 38.7%, and 63.3%. Multivariate analysis revealed that the F-TMI score (HR 1.297; 95% CI 1.046– 1.609, p = 0.018) was an independent prognostic factor. The F-TMI’s prediction ability was larger than that of fibrinogen, TMI, and the conventional TNM stage.
Conclusion: F-TMI was an independent prognostic factor for patients with ESCC and a more useful prognostic indicator than either of the parameters alone.
Keywords: fibrinogen, tumor marker index, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, prognosis
Introduction
Esophageal cancer is the fifth most common malignancy and the fourth leading cause of cancer-related death in China. More than 90% of esophageal cancer cases is squamous cell carcinoma.1 Despite advances in surgical techniques and multimodal therapy, there is little improvement in the conditions’ prognosis.2 Therefore, it is important to identify reliable prognostic factors to perform prognostic risk stratification and provide personalized treatment.
To date, different studies have reported discrete prognostic factors to predict the long-term survival of patients with esophageal cancer. Amongst them, the squamous cell carcinoma antigen (SCC) and cytokeratin 19 fragment (CYFRA 21–1) have been the most commonly used tumor biomarkers.3,4 However, the sensitivities and specificities of these tumor markers are insufficient in clinical practice. Recently, Muley et al5 introduced an algorithm known as the tumor marker index (TMI) based on CYFRA 21–1 and CEA, which increased the prognostic sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).5,6 In our previous studies, a novel TMI based on SCC and CYFRA 21–1 was proposed, which was found to be a novel marker that could be used to predict the prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) patients.
There has been ample scrutiny over the possible association between malignancies and coagulation.7 Fibrinogen, an acute-phase reactant glycoprotein synthesized in hepatocytes, is involved in blood coagulation and platelet accumulation.8 Several studies have suggested that preoperative fibrinogen was associated with many malignancies’ progression and prognosis.9–11 Studies have also indicated that elevated plasma fibrinogen levels were independently associated with poor outcomes in patients with ESCC.12 However, fibrinogen’s predictive ability or TMI in patients with ESCC is still insufficient when used individually.
Therefore, we hypothesized that the combination of plasma fibrinogen and TMI might increase the prognostic accuracy for ESCC. In this regard, we performed a retrospective study to compare the prognostic value of the combination of fibrinogen and TMI (F-TMI) score with that of TMI alone and assess the usefulness of this combined index in patients with ESCC.
Patients and Methods
Patients
The medical records of 406 patients with histologically confirmed ESCC who underwent esophagectomy at the Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital between January 2008 and March 2013 were reviewed in this retrospective study. All patients were evaluated by physical examination, biochemical tests, coagulation tests, complete blood cell counts, tumor markers, esophagogastroscopy, barium meal, computed tomography (CT) scans of the head, chest, and abdomen, and ultrasound of the neck and abdomen. Positron emission tomography (PET)/CT scanning was performed when necessary. Cardiac and pulmonary function examinations were also performed to assess surgical tolerance.
The patients’ eligibility criteria were as follows: (1) histologically confirmed ESCC; (2) underwent esophagectomy and systematic node dissection. The patients were excluded from the study if they met any of the following criteria: received preoperative chemotherapy or radiotherapy (n = 24), previous history of other malignant tumors (n = 7), with distant metastasis (n = 2), with R1/R2 resection (n = 6), died perioperative period (n = 4), with clinical evidence of inflammation, infection, hematological, autoimmune, or liver disease (n = 25), incomplete clinicopathological and laboratory data (n = 56) and loss of information during the follow-up period (n = 34). Finally, a total of 317 patients were enrolled in the present study. Before surgery, 21 patients (6.6%) had clinical stage I, 155 (48.9%) had stage II, and 141 (44.5%) had stage III disease.
The postoperative pathological tumor stage was evaluated based on the 7th edition of the UICC/AJCC TNM classification of esophageal carcinoma.13 As the role of postoperative adjuvant treatment was controversial during that period, adjuvant therapy was not mandatory. The most frequent adjuvant chemotherapy included fluoropyrimidine‐ plus platinum‐based regimen, paclitaxel- plus platinum‐based regimen, or some irregular regimens. This study complies with the Declaration of Helsinki, was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital. All patients provided written informed consent.
Laboratory Assays
Blood specimens were collected in sodium citrate- or EDTA K2-containing tubes one week before surgery. Serum SCC and CYFRA 21–1 concentration were detected by commercially available enzyme immunoassays with a Cobas Core analyzer (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany). The normal upper limits were 1.5 µg/L and 3.3 µg/L for SCC and CYFRA 21–1, respectively. Plasma fibrinogen concentration was measured based on the Clauss method using an automatic coagulation analyzer (CS-5100; Sysmex Inc., Japan). Blood cell counts, including neutrophil, lymphocyte, and platelet counts, were measured using an automatic hematological analyzer (XE-5000, Sysmex, Kobe, Japan). Thereafter, the NLR, PLR, TMI, and F-TMI were calculated.
Definition of NLR, PLR, TMI, and F-TMI
The values for NLR and PLR were calculated as follows: NLR=neutrophil counts/lymphocyte counts and PLR=platelet counts/lymphocyte counts.
The TMI was calculated by determining the geometric mean of the normalized values of serum CYFRA 21–1 and SCC concentration. Normalization was performed by dividing the individual marker values by the corresponding diagnostic cut-off points, which were 3.3 µg/L for CYFRA 21–1 and 1.5 µg/L for SCC.14
The newly formed F-TMI score was calculated by combining fibrinogen and TMI. In brief, patients with elevated plasma fibrinogen and high TMI were assigned a score of 2. Those with either elevated plasma fibrinogen or high TMI were assigned a score of 1, and those with neither of these abnormalities were assigned a score of 0.
Body mass index (BMI) was calculated according to the standardized definition as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared: weight/height2 (kg/m2). The patients were stratified into three BMI categories: normal weight (BMI 18.5~23 kg/m2), overweight (BMI 23~27.5 kg/m2), and obese (BMI ≥ 27.5 kg/m2) based on the World Health Organization (WHO) recommendation for Asian populations.15
Follow-Up
After surgery, all patients were followed up regularly by means of telephone, email, and medical record, every 3 months during the first two years, every 6 months during the third to fifth years, and then annual thereafter until death or the last follow-up. The follow-up rate in our study was 91.6%. Postoperative follow-up observations involved physical examinations, laboratory blood tests, tumor markers assessment, chest and abdominal CT scans, and endoscopy examinations. Overall survival (OS) was calculated from the date of surgery to death or the final follow-up.
Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 17.0 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Continuous variables are expressed as mean ± standard deviation, and categorical variables are expressed as frequencies and percentages. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to determine the optimal cut-off values of fibrinogen, NLR, PLR, and TMI for prognostic prediction and to compare their predictive ability. Chi-square test or the trend version of the chi-square test was used to analyze the associations between the clinicopathological variables and TMI or F-TMI. Survival analysis was performed using the Kaplan-Meier method, and the difference was compared using the Log rank test. Univariate and multivariate survival analyses were performed using Cox proportional hazard model. The hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) within each subgroup were summarized for the subgroup analysis of overall survival. Two-sided P value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Patient and Disease Characteristics
The enrolled cohort consisted of 261 (82.3%) men and 56 (17.7%) women. The median age was 61 years (range, 33–85 years). A total of 210 (66.2%) patients had a history of smoking. Regarding the tumor site, 18 (5.7%), 220 (69.4%), and 79 (24.9%) patients had tumors located in the upper, middle, and lower thoracic esophageal regions, respectively. Altogether, there were 21 (6.6%), 244 (77.0%), and 52 (16.4%) cases that could be categorized into well, moderately, and poorly differentiated, respectively. Pathologically confirmed lymph node metastasis was found in 141 patients. Based on the 7th edition, TNM staging system, 13 (4.1%) patients presented with stage I, 135 (42.6%) with stage II, and 169 (53.3%) with stage III. A total of 133 (42.0%) patients underwent curative surgery alone, while 184 (58.0%) patients underwent surgery combined with postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy.
Based on the normal reference values of the tumor markers, the patients were divided into normal CYFRA 21–1 (CYFRA 21–1 ≤3.3 µg/L, n=233) and high CYFRA 21–1 (CYFRA 21–1 >3.3 µg/L, n=84) groups; normal SCC (SCC≤1.5 µg/L, n=267) and high SCC (SCC >1.5 µg/L, n=50) groups. Based on the ROC curves for predicting 5-year OS, the best cut-off values of the fibrinogen, NLR, PLR, and TMI were determined to be 3.42, 1.88, 119.5, and 0.53, respectively (Supplementary Figure S1). Using these cut-off values, the patients were subdivided into two groups: a low-fibrinogen group (fibrinogen ≤ 3.42, n=129) and high fibrinogen group (fibrinogen >3.42, n=188); low-NLR group (NLR ≤ 1.88, n=131) and high NLR group (NLR >1.88, n=186); low-PLR group (PLR ≤ 119.5, n=158) and high PLR group (PLR >119.5, n=159); low-TMI group (TMI ≤ 0.53, n=158) and high TMI group (TMI >0.53, n=159).
The Association Between TMI Alone and Clinicopathological Variables
The correlations between TMI and clinicopathological variables are shown in Table 1. Compared to the low-TMI group, the high-TMI group was associated with larger tumor size (P =0.008), higher NLR level (P=0.027), higher CYFRA 21–1 level (P <0.001), higher SCC level (P<0.001), higher pT status (P=0.008), and higher pN status (P=0.024).
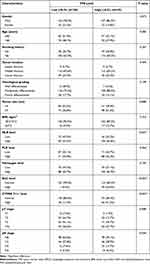 |
Table 1 The Associations Between the TMI Level and the Clinicopathological Variables in 317 Patients with ESCC |
The Prognostic Value of TMI
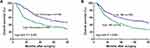
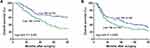
The one, three, and five- year OS rates for all patients were 82.3%, 53.3%, and 40.6%, respectively. The five-year OS rate of patients in the high fibrinogen group was significantly worse than that in the low fibrinogen group (33.5% vs 51.0%, log-rank, p <0.001, Figure 1A). Similarly, the five-year OS rate of patients in the high TMI group was significantly worse than that in the low TMI group (30.8% vs 50.4%, log-rank, p <0.001, Figure 1B). When the OS rate was evaluated after adjusting for the fibrinogen level, a significant difference was found between the high- and low-TMI groups in the low-fibrinogen patients (36.2% vs 63.3%, log-rank, p < 0.001, Figure 2A), however, there was no significant difference between the two groups in the high-fibrinogen patients (27.6% vs 40.2%, log-rank p=0.063, Figure 2B).
The Association Between F-TMI and Clinicopathological Variables
According to the grading system of the F-TMI score, 70 (22.1%) patients had an F-TMI score of 0, 147 (46.4%) patients had an F-TMI score of 1, and 100 (31.5%) patients had an F-TMI score of 2. We further assessed the association between F-TMI score and clinicopathological factors. The F-TMI score was significantly correlated with age (p=0.020), tumor size (p <0.001), NLR level (p=0.001), PLR level (p=0.005), pT status (p<0.001), and pN status (p=0.031), but was not significantly correlated with gender, smoking history, tumor location, histological grading, and BMI (p >0.05, Table 2).
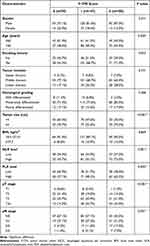 |
Table 2 Associations Between the F-TMI Score and Clinicopathological Variables in 317 Patients with ESCC |
Univariate and Multivariate Analyses
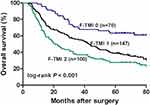
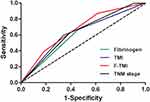
With regards to the prognosis, the five-year OS rates for patients with F-TMI scores of 2, 1, and 0 were 27.6%, 38.7%, and 63.3%, respectively (log-rank, p < 0.001). Therefore, patient prognosis could be stratified with the F-TMI score. The χ2 value of the F-TMI score was larger than that of TMI (27.7 vs 15.8), which indicated that the F-TMI system outperformed the TMI system in predicting OS (Figure 3).
Univariate analysis revealed that age, smoking history, tumor size, BMI, NLR, PLR, pT status, pN status, and F-TMI were significantly related to patient prognosis. All significant prognostic factors tested with univariate analysis were further evaluated using Cox multivariate analysis. The results demonstrated that tumor size (HR 1.412, 95% CI 1.035~1.927, P = 0.030), BMI (HR 1.555, 95% CI 1.009~2.396, P = 0.045), pT status (HR 1.217, 95% CI 1.012~1.463, P = 0.037), pN status (HR 1.281, 95% CI 1.098~1.495, P = 0.002) and F-TMI (HR 1.297, 95% CI 1.046~1.609, P = 0.018) were independently associated with the ESCC patients’ survival (Table 3).
 |
Table 3 Univariate and Multivariate Analyses of Clinical and Pathological Variables for Overall Survival in Patients with ESCC |
ROC Analysis
We further compared the predictive abilities of the fibrinogen, TMI, F-TMI, and TNM staging systems by ROC analyses for prognosis prediction. The AUCs for fibrinogen, TMI, and F-TMI were 0.604 (95% CI = 0.538~0.669), 0.627 (95% CI = 0.564~0.691) and 0.668 (95% CI = 0.606~0.731) for all patients. Furthermore, the prediction ability of the conventional AJCC TNM staging system was 0.633 (95% CI = 0.568~0.697). Comparison of ROC curves showed that the F-TMI system was the most accurate prognostic indicator among these indicators for predicting survival and could be used as an alternative prognostic staging tool for ESCC patients (Figure 4).
Discussion
Esophageal cancer remains one of the major causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide. Despite great advancements in early detection, surgical techniques, and multidisciplinary treatment in recent years, patients’ long-term survival is far from satisfactory.16
Many tumor-related variables based on blood tests have been reported to predict the prognosis of patients with esophageal cancer, including tumor markers, hypercoagulability, nutritional status, and immune inflammatory and histological biomarkers.17–19 However, there are substantial differences in survival between patients at the same tumor stage. Therefore, it is important and urgent to determine valuable biomarkers for identifying patients who are at risk and have poor prognosis.
It is well known that elevated CYFRA 21–1 and SCC-Ag are important tumor markers associated with tumor progression and adverse prognosis in patients with ESCC.20,21 However, the clinical use of only a single tumor marker for prognostic evaluation might be difficult because of the lack of high sensitivity.22 Nakamura et al23 reported that the sensitivity rates of SCC and CYFRA 21–1 in ESCC were only 28.6% and 33.9%, respectively. Results from our previous study revealed that high levels of CYFRA 21–1 and SCC-Ag was indicative of advanced disease and poor prognosis in patients with ESCC. However, neither of these two markers were observed as independent prognostic factors by multivariate analysis. Muley et al5 first introduced a novel TMI based on CYFRA 21–1 and CEA and proved it an independent prognostic factor for stage I NSCLC. Subsequently, the TMI based on CEA and KL-6 levels was raised by Tomita et al and was confirmed to be a useful variable to predict the prognosis of NSCLC patients.24 A similar TMI variable based on preoperative CYFRA 21–1 and SCC was proposed in the present work. Our study indicated that high TMI levels were significantly associated with progression and worse survival of ESCC patients, which was consistent with our previous study.14
The tumor-mediated activation of the coagulation system and systematic inflammatory response serve important functions in tumor progression, angiogenesis promotion, metastasis, and poor prognosis in several types of malignancies, including esophageal cancer.10,25 Previous studies have reported that elevated concentrations of plasma fibrinogen, which is synthesized in the liver and transformed into fibrin by activated thrombin, are characteristic of patients with cancer.26,27 Additionally, it was found that fibrinogen synthesis is significantly upregulated during inflammation.28 In the past two decades, a growing number of studies have focused on identifying the prognostic role of fibrinogen in esophageal cancer patients treated with different modalities. Still, the results remain inconclusive.10,12 In the present study, we found that elevated plasma fibrinogen levels were associated with tumor progression and poor prognosis in patients with ESCC, consistent with most findings from previous studies.
Currently, the mechanisms underlying the effect of plasma fibrinogen on the prognosis of esophageal cancer remain unknown. A previous study reported that interleukin-6 produced by cancer cells could stimulate the secretion of fibrinogen in patients with lung cancer.29 Also, fibrinogen synthesized by cancer cells eventually promotes angiogenesis and tumor cell growth by binding with some growth factors such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2).30,31 Palumbo et al32 reported that fibrinogen is favorable for the tumor stroma formation and adhesion of circulating tumor cells in the vasculature, thus increasing the probability of embolic tumor metastasis. In an in vitro study, Shu et al33 found that plasma fibrinogen at a high concentration induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), thereby increasing the migration, invasion, and metastatic capacity of co-cultured gallbladder cells. Recently, fibrinogen has been reported to promote cancer cell motility by inducing EMT and increasing the levels of p-PTEN, p-AKT, and p-mTOR in esophageal cancer cells.34 However, this explanation needs to be verified by further experiments.
In previous studies, the combined prognostic value of fibrinogen with inflammatory factors such as F-NLR, FA, and FAR have been discussed in ESCC.35,36 However, the fibrinogen and TMI have not been simultaneously assessed as markers of tumor progression and prognosis in patients with ESCC. The present study showed that combined F-TMI was closely associated with some tumor-related progression indicators, such as tumor size, depth of tumor invasion, lymph node metastasis, and systemic inflammatory response index. Furthermore, F-TMI was significantly associated with OS. Based on the F-TMI proposed in the current study, patients with ESCC can be divided into three distinct risk groups.
In our study, multivariate survival analysis demonstrated that F-TMI was an independent prognostic variable. We further evaluated if the combined F-TMI could improve the prognostic value compared to either parameter alone through ROC analysis. Accordingly, our results demonstrated that the F-TMI could increase the prognostic accuracy and compensate for the limitations imposed by using each marker individually.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to investigate the notable roles of combined F-TMI for assessing progression and prognosis in patients with ESCC. However, some limitations that must be addressed. First, this study was a retrospective and single-institution design, which might have led to several forms of bias. Second, only 5 years’ OS was included in our study, and we did not obtain complete recurrence data. Therefore, our study does not comprehensively reflect the survival of the patients. Third, the treatment modalities and chemotherapy regimens of patients after surgical resection might lead to heterogeneous outcomes in patients, which might have influenced the results. Fourth, some variables that may influence the prognosis were not included in the survival analysis because of incomplete information, such as lymphovascular emboli or perineural invasion. Finally, although this new scoring method distinguished the prognostic value of different biomarkers and improved prognostic accuracy, this scoring method’s validity still requires further verification. Therefore, further prospective multicenter studies with a larger sample size are required to validate our findings.
In summary, the present study showed that tumor marker index based on preoperative SCC and CYFRA 21–1 level is a novel factor in the evaluation of aggressive tumor biology and prognosis of ESCC patients. Additionally, with F-TMI, the combination of plasma fibrinogen and TMI showed superior predictive accuracy of five-year OS compared with either variable alone. We hypothesize that F-TMI could be an inexpensive, reliable, economical, and practical biomarker to determine tumor progression and prognosis in patients with ESCC in clinical practice.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81772619, 82002551), Clinical Trial Project of Tianjin Medical University (2017kylc006) and Bethune Charitable Foundation (HZB-20190528-18).
Disclosure
All authors state that they have no conflict of interest.
References
1. Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–132. doi:10.3322/caac.21338
2. Lam AK. Introduction: esophageal squamous cell carcinoma-current status and future advances. Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2129:1–6. doi:10.1007/978-1-0716-0377-2_1
3. Ikeguchi M, Kouno Y, Kihara K, et al. Evaluation of prognostic markers for patients with curatively resected thoracic esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. Mol Clin Oncol. 2016;5:767–772. doi:10.3892/mco.2016.1073
4. Yang Y, Huang X, Zhou L, et al. Clinical use of tumor biomarkers in prediction for prognosis and chemotherapeutic effect in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2019;19:526. doi:10.1186/s12885-019-5755-5
5. Muley T, Dienemann H, Ebert W. CYFRA 21-1 and CEA are independent prognostic factors in 153 operated stage I NSCLC patients. Anticancer Res. 2004;24:1953–1956.
6. Tomita M, Shimizu T, Ayabe T, Yonei A, Onitsuka T. Prognostic significance of tumour marker index based on preoperative CEA and CYFRA 21-1 in non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 2010;30:3099–3102.
7. Murray JC. Coagulation and cancer. Br J Cancer. 1991;64:422–424. doi:10.1038/bjc.1991.325
8. Weisel JW. Fibrinogen and fibrin. Adv Protein Chem. 2005;70:247–299. doi:10.1016/S0065-3233(05)70008-5
9. Ji R, Ren Q, Bai S, Wang Y, Zhou Y. Prognostic significance of pretreatment plasma fibrinogen in patients with hepatocellular and pancreatic carcinomas: a meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97:e10824. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000010824
10. Lin Y, Liu Z, Qiu Y, et al. Clinical significance of plasma D-dimer and fibrinogen in digestive cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2018;44:1494–1503. doi:10.1016/j.ejso.2018.07.052
11. Zhang K, Xu Y, Tan S, Wang X, Du M, Liu L. The association between plasma fibrinogen levels and lung cancer: a meta-analysis. J Thorac Dis. 2019;11:4492–4500. doi:10.21037/jtd.2019.11.13
12. Lv GY, Yu Y, An L, Sun XD, Sun DW. Preoperative plasma fibrinogen is associated with poor prognosis in esophageal carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Clin Transl Oncol. 2018;20:853–861. doi:10.1007/s12094-017-1794-z
13. Edge SB, Compton CC. The American Joint Committee on Cancer: the 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:1471–1474. doi:10.1245/s10434-010-0985-4
14. Qiao Y, Chen C, Yue J, Yu Z. Tumor marker index based on preoperative SCC and CYFRA 21-1 is a significant prognostic factor for patients with resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 2019;25:243–250. doi:10.3233/CBM-190058
15. Duan XF, Tang P, Shang XB, Jiang HJ, Zhao Q, Yu ZT. High body mass index worsens survival in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma after esophagectomy. Dig Surg. 2017;34:319–327. doi:10.1159/000453044
16. Ajani JA, D’Amico TA, Bentrem DJ, et al. Esophageal and esophagogastric junction cancers, version 2.2019, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2019;17:855–883. doi:10.6004/jnccn.2019.0033
17. Goto M, Liu M. Chemokines and their receptors as biomarkers in esophageal cancer. Esophagus. 2020;17:113–121. doi:10.1007/s10388-019-00706-8
18. Shoji F, Miura N, Matsubara T, et al. Prognostic significance of immune-nutritional parameters for surgically resected elderly lung cancer patients: a multicentre retrospective study. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2018;26:389–394. doi:10.1093/icvts/ivx337
19. Zhang H, Tang P, Miao X, et al. Does tumor size improve the accuracy of prognostic prediction in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma after surgical resection. Oncotarget. 2016;7:66623–66634. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.11286
20. Kanda M, Koike M, Shimizu D, et al. Optimized cutoff value of serum squamous cell carcinoma antigen concentration accurately predicts recurrence after curative resection of squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Ann Surg Oncol. 2020;27:1233–1240. doi:10.1245/s10434-019-07977-6
21. Kunizaki M, Hamasaki K, Wakata K, et al. Clinical value of serum p53 antibody in the diagnosis and prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2018;38:1807–1813. doi:10.21873/anticanres.12419
22. Jia K, Li W, Wang F, et al. Novel circulating peptide biomarkers for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma revealed by a magnetic bead-based MALDI-TOFMS assay. Oncotarget. 2016;7:23569–23580. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.8123
23. Nakamura T, Ide H, Eguchi R, Hayashi K, Takasaki K, Watanabe S. CYFRA 21-1 as a tumor marker for squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Dis Esophagus. 2017;11:35–39. doi:10.1093/dote/11.1.35
24. Tomita M, Ayabe T, Chosa E, Nose N, Nakamura K. Prognostic significance of a tumor marker index based on preoperative serum carcinoembryonic antigen and krebs von den lungen-6 levels in non-small cell lung cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2017;18:287–291. doi:10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.1.287
25. Zhang H, Shang X, Ren P, et al. The predictive value of a preoperative systemic immune-inflammation index and prognostic nutritional index in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:1794–1802. doi:10.1002/jcp.27052
26. Asanuma K, Matsumine A, Nakamura T, et al. Impact of plasma fibrinogen levels in benign and malignant soft tissue tumors. Cancer Biomark. 2016;16:453–458. doi:10.3233/CBM-160584
27. Luo Y, Kim HS, Kim M, Lee M, Song YS. Elevated plasma fibrinogen levels and prognosis of epithelial ovarian cancer: a cohort study and meta-analysis. J Gynecol Oncol. 2017;28:e36. doi:10.3802/jgo.2017.28.e36
28. Pieters M, Wolberg AS. Fibrinogen and fibrin: an illustrated review. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2019;3:161–172. doi:10.1002/rth2.12191
29. Yamaguchi T, Yamamoto Y, Yokota S, Nakagawa M, Ito M, Ogura T. Involvement of interleukin-6 in the elevation of plasma fibrinogen levels in lung cancer patients. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1998;28:740–744. doi:10.1093/jjco/28.12.740
30. Sahni A, Simpson-Haidaris PJ, Sahni SK, Vaday GG, Francis CW. Fibrinogen synthesized by cancer cells augments the proliferative effect of fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2). J Thromb Haemost. 2008;6:176–183. doi:10.1111/j.1538-7836.2007.02808.x
31. Verheul HM, van Erp K, Homs MY, et al. The relationship of vascular endothelial growth factor and coagulation factor (fibrin and fibrinogen) expression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Urology. 2010;75:608–614. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2009.05.075
32. Palumbo JS, Kombrinck KW, Drew AF, et al. Fibrinogen is an important determinant of the metastatic potential of circulating tumor cells. Blood. 2000;96:3302–3309. doi:10.1182/blood.V96.10.3302
33. Shu YJ, Weng H, Bao RF, et al. Clinical and prognostic significance of preoperative plasma hyperfibrinogenemia in gallbladder cancer patients following surgical resection: a retrospective and in vitro study. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:566. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-14-566
34. Zhang F, Wang Y, Sun P, et al. Fibrinogen promotes malignant biological tumor behavior involving epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the p-AKT/p-mTOR pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2017;143:2413–2424. doi:10.1007/s00432-017-2493-4
35. Kijima T, Arigami T, Uchikado Y, et al. Combined fibrinogen and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic marker of advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2017;108:193–199. doi:10.1111/cas.13127
36. Zhang Y, Xiao G. Prognostic significance of the ratio of fibrinogen and albumin in human malignancies: a meta-analysis. Cancer Manag Res. 2019;11:3381–3393. doi:10.2147/CMAR.S198419
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.