Back to Journals » Journal of Inflammation Research » Volume 14
Potential Biomarkers for Diagnosing Major Depressive Disorder Patients with Suicidal Ideation
Authors Bai S , Fang L, Xie J, Bai H, Wang W, Chen J
Received 18 December 2020
Accepted for publication 3 February 2021
Published 22 February 2021 Volume 2021:14 Pages 495—503
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JIR.S297930
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Professor Ning Quan
Shunjie Bai,1 Liang Fang,2,3 Jing Xie,4 Huili Bai,1 Wei Wang,5 Jian-jun Chen6
1Department of Laboratory Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, People’s Republic of China; 2Department of Neurology, Yongchuan Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, People’s Republic of China; 3Chongqing Key Laboratory of Cerebral Vascular Disease Research, Yongchuan Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, People’s Republic of China; 4Department of Endocrinology and Nephrology, The Fourth People’s Hospital of Chongqing, Chongqing, People’s Republic of China; 5Department of Neurology, The Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang, People’s Republic of China; 6Institute of Life Sciences, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, People’s Republic of China
Correspondence: Jian-jun Chen, Email [email protected]
Background: Major depressive disorder (MDD) and suicide are two major health problems, but there are still no objective methods to diagnose MDD or suicidal ideation (SI). This study was conducted to identify potential biomarkers for diagnosing MDD patients with SI.
Methods: First-episode drug-naïve MDD patients with SI and demographics-matched healthy controls (HCs) were recruited. First-episode drug-naïve MDD patients without SI were also included. The serum lipids, C-reactive protein (CRP), transferring (TRSF), homocysteine (HCY) and alpha 1-antitrypsin (AAT) in serum were detected. The univariate and multivariate statistical analyses were used to identify and validate the potential biomarkers.
Results: The 86 HCs, 53 MDD patients with SI and 20 MDD patients without SI were included in this study. Four potential biomarkers were identified: AAT, TRSF, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDLC), and apolipoprotein A1 (APOA1). After one month treatment, the levels of AAT and APOA1 were significantly improved. The panel consisting of these potential biomarkers had an excellent diagnostic performance, yielding an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.994 and 0.990 in the training and testing set, respectively. Moreover, this panel could effectively distinguish MDD patients with SI from MDD patients without SI (AUC=0.928).
Conclusion: These results showed that these potential biomarkers could facilitate the development of an objective method for diagnosing MDD patients with SI, and the decreased AAT levels in MDD patients might lead to the appearance of SI by resulting in the elevated inflammation.
Keywords: major depressive disorder, suicidal ideation, biomarkers
Introduction
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a common neuropsychological disease with a persistent feeling of sadness and a loss of interest in activities. As the leading cause of disability globally, it is estimated to affect about 6% of adults aged 18 or older each year.1 Nowadays, the pathogenesis of MDD is still unknown, although many theories have been developed to reveal the underline biological mechanisms of this disease.2–4 What is worse, MDD can significantly increase the risk of suicide if it was not timely and effectively treated. Both MDD and suicide are major health hazards, which bring big economic burden to individual and society.
The strong association between MDD and suicide has been proved by many studies.5,6 The risk of suicide in MDD population is estimated at about 4%, and over 50% of suicidal people meet the criteria of MDD.7 Hawton et al reported that depression severity was a key suicide risk factor.8 Moreover, Gijzen et al viewed suicidal ideation (SI) as a symptom of adolescent depression, and found that loneliness, one of the most central symptoms in the depression network, was the most contributing factor of SI.9 However, at present, no objective methods are available to predict MDD, SI or MDD patients with SI. Thus, it is urgently needed to develop an objective method for diagnosing MDD patients with SI.
Currently, the diagnosis of MDD patients with SI relies on self-reported measures, such as questionnaires and interviews, rather than objective laboratory tests. But individuals with MDD and/or SI are highly likely to hide their true thoughts, resulting in a considerable error rate. To solve this problem, many works have been done to identify potential biomarkers for MDD patients with SI.10–13 Our previous study found that the extrinsic coagulation pathway might be a biomarker for suicidal behavior in MDD.11 Some researchers proposed that the neural representations or health records could be used to build the depression and suicide risk prediction models.12,13 Just et al used the machine-learning algorithms to separate suicidal ideators from controls with an accuracy of 91%, based on their altered neural signatures.12 Other researchers reported that health records could also be used to predict the risk of depression and suicide.13 However, up to now, no biomarkers for diagnosing MDD patients with SI have been widely accepted.
The alpha 1-antitrypsin (AAT) has anti-inflammatory effects, and there is a close relationship between inflammation and depression/suicide.14 Our previous study found that the level of AAT was decreased in the blood of MDD patients.15 In another study, we found that the peripheral metabolic abnormalities of lipids might increase the risk of suicidal behavior in MDD patients.16 Maes et al reported that high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDLC) held the promise to be a biomarker for depressed men with suicidal behavior.17 Meanwhile, apolipoprotein A1 (APOA1) was found to be decreased in post-stroke depression patients compared to healthy controls (HCs).18 In addition, previous study found the close relationship between transferrin (TRSF) and MDD/suicide.19 Therefore, to identify novel potential biomarkers for diagnosing MDD patients with SI, in this study, we analyzed the differences of these molecules in serum between MDD patients with SI and HCs.
Patients and Methods
MDD Patients and HCs Enrolment
This study was approved by the Ethical Committee of Chongqing Medical University (Approved No. 20,200,320), and conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Three cohorts were recruited: i) 86 HCs were recruited from the Medical Examination Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University; ii) 53 first-episode drug-naïve MDD patients with SI and iii) 20 first-episode drug-naïve MDD patients without SI were recruited from the Department of Psychiatry, the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University. We collected relevant data from the included subjects: i) Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HDRS) and Beck Scale for Suicide Ideation-Chinese Version (BSI-CV); ii) questionnaires about the history of MDD or SI; iii) peripheral blood samples. Informed written consent was obtained from all the included subjects. The detailed information of the included subjects is displayed in Table 1.
 |
Table 1 Baseline Data of MDD Patients and Healthy Controls |
Two experienced psychiatrists conducted the MDD diagnosis using DSM-IV-TR criteria, and depression severity was assessed using HDRS. Only the first-episode drug-naïve MDD patients with HDRS score ≥17 were enrolled. The definition of SI in this study was: have passive wish for death or active non-specific ideation, but never attempt suicide. BSI-CV was used to assess the suicidal ideation severity. MDD patients meeting the definition of SI and with BSI-CV score >10 were assigned into the MDD patients with SI group, and MDD patients not meeting the definition of SI and with BSI-CV score <10 were assigned into the MDD patients without SI group. HCs had no previous lifetime history of DSM-IV Axis I/II, SI, suicide attempts or behaviors, neurological, or systemic medical illness.
MDD patients with other mental disorders (not include anxiety disorder), other pathological organic diseases (eg, cardio and metabolic diseases, inflammatory-related diseases), alcohol abuse, receiving antidepressant therapy or illicit drug use were excluded. Meanwhile, the previous suicide attempts and suicide behavior were screened during psychiatric evaluation, and MDD patients with previous suicide attempts or suicide behavior were also excluded. It was essential to use the independent samples to validate the identified biomarkers, thus the included MDD patients with SI and HCs were randomly assigned into two sets: training set (35 MDD patients with SI and 57 HCs) and testing set (18 MDD patients with SI and 29 HCs). Meanwhile, the 20 MDD patients without SI were viewed as blind set to further assess the diagnostic performance of the identified biomarkers.
Samples Collection
After overnight fasting, morning blood samples were immediately collected after the psychiatric evaluation. Blood samples were collected through venipuncture from the included subjects. After centrifugation at 1500 rpm for 10 minutes at room temperature, the serum was obtained and stored at −80°C until later analysis. After blood samples collection, a range of different treatments as part of regular standard of care was provided to the included MDD patients. The treatment method was antidepressants plus family psychoeducation. The patients and their families were told not to change the treatment method in one month. Finally, only 20 of the included MDD patients with SI were willing to receive this treatment method and successfully provided blood samples after one-month treatment. The rest of included MDD patients refused to receive this treatment method or failed to provide blood samples after one-month treatment.
Biochemical Indicators Detecting
The following biochemical indicators were detected in this study: total Cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), HDLC, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDLC), APOA1, apolipoprotein B (APOB), lipoprotein a (LPA), hypersensitive C-reactive protein (CRP), TRSF, homocysteine (HCY), and AAT. The commercially available enzymatic colorimetric assays (TC, TG, HDLC, LDLC, APOA1, APOB, LPA, CRP, and TRSF were purchased from Roche Diagnostics, Switzerland; HCY were purchased from Jiuqiang, Beijing; AAT were purchased from DIALAB diagnostic, Austria) and an automated analyzer system (Cobas 8000 modular device Roche Diagnostics, Switzerland) were used.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were carried out using R studio (version 3.5.2), SPSS version 18 (SPSS, Chicago, IL, US) and SIMCA-P14.0. The Student’s t-test, chi-square test, one-way analysis of variance, Pearson correlation analysis or paired t-test was used when appropriate. The orthogonal partial least-squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) was used to find the biochemical indicators with variable importance in projection (VIP)>1.0. The Random Forest was then used to obtain a simplified biomarker panel from these biochemical indicators with VIP>1.0. Finally, the diagnostic performance of the identified biomarker panel was assessed using the receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis.20,21 A p-value <0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
Results
OPLS-DA Model Built
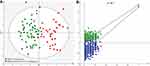
To ensure that the identified potential biomarkers were not influenced by antidepressants, the first-episode drug-naïve MDD patients with SI were chosen. The OPLS-DA model built with training set showed that the MDD patients with SI were obviously separated from HCs with no overlap (R2Y cum=0.74, Q2=5 0.70, Figure 1A). The positive values of R2Y and Q2 demonstrated that there was a robust difference among those detected biochemical indicators between MDD patients with SI and HCs. Moreover, the results of 399-permutation test showed that the original R2Y and Q2 values were higher than their corresponding permutated values (Figure 1B), further suggesting the valid of built OPLS-DA model.
OPLS-DA Model Validation
To independently assess the diagnostic performance of the built model, we used the testing set to test it. The T-predicted scatter plot from the built OPLS-DA model showed that 26 of the 29 HCs from the testing set and all MDD patients with SI from the testing set were correctly predicted (Figure 2A). Meanwhile, to determine whether the built OPLA-DA model was relatively specific to MDD patients with SI versus MDD patients without SI, we recruited 20 MDD patients without SI as a blind set to further test it. The results showed that only 4 of 20 MDD patients without SI were wrongly diagnosed as MDD patients with SI (Figure 2B).
Identification of Differential Biochemical Indicators
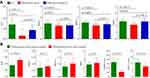
The corresponding OPLS-DA loading plot was analyzed to systematically identify the differential biochemical indicators responsible for the discrimination between MDD patients with SI and HCs. After adjusting for age, body mass index (BMI), sex, education, HDRS score and BSI-CV score, four biochemical indicators with VIP>1.0 were identified: AAT (VIP=1.69), HDLC (VIP=1.31), APOA1 (VIP=1.47) and TRSF (VIP=1.27). As compared to HCs, MDD patients with SI were characterized by lower levels of AAT, HDLC, APOA1 and TRSF. The univariate statistical analysis was then used to validate the differences identified by multivariate statistical analysis; all of these biochemical indicators with VIP>1.0 remained significantly changed (Figure 3A). Meanwhile, we found that compared to MDD patients without SI, AAT (p=0.0015) and TRSF (p=2.49E-5) were significantly lower in MDD patients with SI. After one-month treatment, the results of paired t-test showed that all of these differential biochemical indicators were increased, but only the increases of AAT (p=7.86E-7) and APOA1 (p=0.011) were significant. Meanwhile, the HDRS score and BSI-CV score were significantly decreased after one-month treatment (Figure 3B). The 15 of 20 MDD patients receiving treatment met the response criteria (at least 50% reduction in HDRS score after treatment), and there were no significant differences in those four biomarkers between responders and non-responders. Limited by the small samples (15 responders vs 5 non-responders), these results were needed further validation.
Identification and Validation of Biomarker Panel
The Random Forest was used to obtain a biomarker panel consisting of these identified differential biochemical indicators. In the training set, the biomarker panel could effectively distinguish MDD patients with SI from HCs with an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.994 (95% confidence interval (CI) = 0.984–1.000) (Figure 4). Secondly, the biomarker panel was used to independently classify the samples from the testing set. The ROC analysis yielded an AUC of 0.990 (95% CI = 0.969–1.000) in separating MDD patients with SI from HCs (Figure 4). Finally, a blind set (20 MDD patients without SI) was used to further assess the diagnostic performance of this panel in discriminating MDD patients with SI from MDD patients without SI, and the ROC analysis yielded an AUC of 0.928 (95% CI= 0.846–1.000) (Figure 4).
Correlation Analysis in MDD Patients with SI
Correlation analyses between age, BMI, education, HDRS score, BSI-CV score and the detected biochemical indicators were conducted. The results showed that the age was significantly positively correlated with TC (r=0.34, p=0.014) and APOB (r=0.42, p=0.002), and significantly negatively correlated with TRSF (r=−0.39, p=0.005). The education was significantly negatively correlated with LPA (r=−0.31, p=0.026). We also found that there was a significantly positive correlation between HDRS score and BSI-CV score (r=0.33, p=0.014); the HDRS score was also significantly positively correlated with TC (r=0.33, p=0.014), and significantly negatively correlated with AAT (r=−0.42, p=0.002). The BSI-CV was significantly negatively correlated with AAT (r=−0.32, p=0.020).
Discussion
MDD can significantly increase the risk of suicide for individuals. Currently, the bottleneck in clinical diagnosis of MDD patients with SI is the lack of biomarkers to support objective laboratory-based testing. Here, four potential biomarkers (AAT, HDLC, APOA1 and TRSF) were identified. The panel consisting of AAT, HDLC, APOA1 and TRSF was identified as an effective diagnostic tool, yielding an AUC of 0.994 and 0.990 in the training and testing set, respectively. Moreover, this panel could effectively separate MDD patients with SI from MDD patients without SI (AUC=0.928). These results suggested that these potential biomarkers could aid in the development of objective methods for diagnosing MDD patients with SI.
Generally speaking, biomarkers from brain are the best, because the brain is the target organ in psychiatric disorders.22 Nagy et al have done a wonderful work to study the brain-based biomarkers for MDD.23 Considering the close relationship between brain and peripheral blood, biomarker identified from peripheral blood will be a practical alternative. Some studies have found the meaningful correlations between brain and blood.24,25 Our and others work have identified some potential biomarkers for MDD or suicide from the blood.11,26–28 Therefore, our identified highly accurate biomarkers from the blood might be an alternative solution for diagnosing MDD patients with SI.
AAT could inhibit the release of many pro-inflammatory factors, such as interleukin-6 (IL-6) and CRP. O’Donovan et al reported that SI was associated with elevated inflammation (IL-6 and CRP) in MDD patients.14 Here, we found the increased CRP and significantly decreased AAT in MDD patients with SI. Meanwhile, the decreased AAT in the blood of MDD patients was also found in our previous study.15 Beiko et al reported that individuals with AAT deficiency were more likely to experience anxiety and depression.29 Many studies have reported that inflammation had a close relationship with depression and suicide.14,30,31 Furthermore, the AAT was significantly negatively correlated with BSI-CV score. Taken together, we deduced that the decreased AAT levels in MDD patients might result in the elevated inflammation, and eventually led to the appearance of SI.
Previous study reported that the serum HDLC might be a potential biomarker for depressed men with suicidal behavior, and the lower HDLC was probably induced by the immune/inflammatory response.17 In this study, the significantly decreased HDLC level was also identified as a potential biomarker for MDD patients with SI. Meanwhile, our previous study found that the plasma APOA1 level and CRP level was decreased and increased, respectively, in post-stroke depression patients compared to HCs.18 The similar results were also observed here in MDD patients with SI. In addition, researchers reported that there was a relationship between TRSF and MDD/suicide,19 and TRSF might have a role in inflammation mechanism.32,33 Here, the significantly decreased TRSF level was found in MDD patients with SI. The abovementioned findings suggested that inflammatory response might be essential in the occurrence of SI in MDD patients.
Nowadays, there are no objective indicators to tell clinicians whether or not their antidepressant methods in use are effective for patients.34 Therefore, many MDD patients are defined as having treatment-resistant depression (TRD) after a period of ineffective treatment.35,36 In this study, we found that, after one-month treatment, the HDRS score and BSI-CV score in those 20 MDD patients with SI were significantly decreased, and the level of AAT was significantly increased. Meanwhile, the AAT was found to be significantly negatively correlated with both HDRS score and BSI-CV score. Our results suggested that AAT might be a potential predictor of antidepressant treatment outcome in MDD with SI.
Our previous studies reported that there were age-specific differential changes on gut microbiota composition and urinary metabolites in MDD patients.4,37 Meanwhile, we also found that there were sex differences in gut microbiota composition in MDD patients.38 Thus, to avoid the influences of clinical characteristics on our results, the identified potential biomarker panel here was adjusted for age, body mass index (BMI), sex, education, HDRS score and BSI-CV score. However, future studies should recruit large patient samples to explore the possibility of the combination of clinical characteristics and this biomarker panel, which might aid in making a more personalized treatment method for MDD patients with SI.
MDD and anxiety disorder are two mental disorders with similar core components. In mental health, one of the more common comorbidities is that of MDD and anxiety disorder. Previous studies reported that the anxiety symptoms are frequently found to coexist with depression symptoms.39,40 An epidemiologic study found that in patients with lifetime MDD, 59% of patients experienced at least one lifetime anxiety disorder.41 Therefore, considering the high prevalence of comorbid anxiety disorder and MDD, we did not exclude the MDD patients with anxiety disorder in this study, which might enhance the generalizability of our conclusion. However, clinicians should still cautiously assess the anxiety disorder of MDD patients when using this biomarker panel to diagnose SI in a broader MDD population.
Limitations should be mentioned here. Firstly, the number of included MDD patients with SI is small; then our results are still needed future studies to validate and support. Secondly, although the panel could effectively separate MDD patients with SI from MDD patients without SI, it is unknown whether it could effectively separate MDD patients with SI from other psychiatric disorders, such as BD and schizophrenia. Thirdly, all the included subjects are recruited from the same site, which might limit the general applicability of our conclusion. Fourthly, only 20 MDD patients with SI received antidepressant therapy and provided blood samples again after one month, then the changes of these potential biomarkers after treatment are needed future studies to validate and support. Fifthly, considering the higher rates of substance use and comorbidities associated with suicide risk, future studies are needed to find out whether or not our results are appropriate for MDD patients with substance use and comorbidities associated with suicide risk. Finally, only blood samples are used here, samples from central nervous system should be further explored to make sure that our identified biomarkers are physiologically relevant to disease pathogenesis.
In conclusion, a panel consisting of AAT, HDLC, APOA1 and TRSF was identified here, which could effectively diagnose MDD patients with SI from HCs and MDD patients without SI. These highly accurate biomarkers might be helpful for future developing an objective method for MDD patients with SI and provide an insight to our understanding of MDD with suicide. However, our results are still needed to be replicated in sufficiently large groups. If replicated, the combination of clinical characteristics and our results might aid in making a more personalized treatment method for MDD patients with SI.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation Project of China (81901398, 81701360), the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing, China (Grant No. cstc2019jcyj-msxmX0025), and the Chongqing Yuzhong District Science & Technology Commission (20190115).
Disclosure
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
1. Bromet E, Andrade LH, Hwang I, et al. Cross-national epidemiology of DSM-IV major depressive episode. BMC Med. 2011;9(1):90. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-9-90
2. Wu M, Tian T, Mao Q, et al. Associations between disordered gut microbiota and changes of neurotransmitters and short-chain fatty acids in depressed mice. Transl Psychiatry. 2020;10(1):350. doi:10.1038/s41398-020-01038-3
3. Guilloux JP, Douillard-Guilloux G, Kota R, et al. Molecular evidence for BDNF- and GABA-related dysfunctions in the amygdala of female subjects with major depression. Mol Psychiatry. 2012;17(11):1130–1142. doi:10.1038/mp.2011.113
4. Chen JJ, He S, Fang L, et al. Age-specific differential changes on gut microbiota composition in patients with major depressive disorder. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(3):2764–2776. doi:10.18632/aging.102775
5. Dumais A, Lesage AD, Alda M, et al. Risk factors for suicide completion in major depression: a case-control study of impulsive and aggressive behaviors in men. Am J Psychiatry. 2005;162(11):2116–2124. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.162.11.2116
6. Qiao D, Zhang A, Sun N, et al. Altered static and dynamic functional connectivity of habenula associated with suicidal ideation in first-episode, drug-naïve patients with major depressive disorder. Front Psychiatry. 2020;11:608197. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2020.608197
7. Hawton K, van Heeringen K. Suicide. Lancet. 2009;373(9672):1372–1381. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60372-X
8. Hawton K. Risk factors for suicide in individuals with depression: a systematic review. J Affect Disord. 2013;147(1–3):17–28.
9. Gijzen MWM, Rasing SPA, Creemers DHM, Smit F, Engels RCME, De Beurs D. Suicide ideation as a symptom of adolescent depression. A network analysis. J Affect Disord. 2021;278:68–77. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2020.09.029
10. Bhak Y, Jeong HO, Cho YS, et al. Depression and suicide risk prediction models using blood-derived multi-omics data. Transl Psychiatry. 2019;9(1):262. doi:10.1038/s41398-019-0595-2
11. Yang Y, Chen J, Liu C, et al. The extrinsic coagulation pathway: a biomarker for suicidal behavior in major depressive disorder. Sci Rep. 2016;6(1):32882. doi:10.1038/srep32882
12. Just MA, Pan L, Cherkassky VL, et al. Machine learning of neural representations of suicide and emotion concepts identifies suicidal youth. Nat Hum Behav. 2017;1(12):911–919. doi:10.1038/s41562-017-0234-y
13. Walsh CG, Ribeiro JD, Franklin JC. Predicting risk of suicide attempts over time through machine learning. Clin Psychol Sci. 2017;5(3):457–469. doi:10.1177/2167702617691560
14. O’Donovan A, Rush G, Hoatam G, et al. Suicidal ideation is associated with elevated inflammation in patients with major depressive disorder. Depress Anxiety. 2013;30(4):307–314. doi:10.1002/da.22087
15. Gui SW, Liu YY, Zhong XG, et al. Plasma disturbance of phospholipid metabolism in major depressive disorder by integration of proteomics and metabolomics. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2018;14:1451–1461. doi:10.2147/NDT.S164134
16. Zheng P, Gao HC, Qi ZG, et al. Peripheral metabolic abnormalities of lipids and amino acids implicated in increased risk of suicidal behavior in major depressive disorder. Metabolomics. 2013;9(3):688–696. doi:10.1007/s11306-012-0474-9
17. Maes M, Smith R, Christophe A, et al. Lower serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) in major depression and in depressed men with serious suicidal attempts: relationship with immune-inflammatory markers. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1997;95(3):212–221. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0447.1997.tb09622.x
18. Zhan Y, Yang YT, You HM, et al. Plasma-based proteomics reveals lipid metabolic and immunoregulatory dysregulation in post-stroke depression. Eur Psychiatry. 2014;29(5):307–315. doi:10.1016/j.eurpsy.2014.03.004
19. Dean B, Tsatsanis A, Lam LQ, Scarr E, Duce JA. Changes in cortical protein markers of iron transport with gender, major depressive disorder and suicide. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2020;21(2):119–126. doi:10.1080/15622975.2018.1555377
20. He S, Mao X, Lei H, et al. Peripheral blood inflammatory-immune cells as a predictor of infertility in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Inflamm Res. 2020;13:441–450. doi:10.2147/JIR.S260770
21. Huang Q, Cao Y, Wang S, Zhu R. Creation of a novel inflammation-based score for operable colorectal cancer patients. J Inflamm Res. 2020;13:659–671. doi:10.2147/JIR.S271541
22. Rego T, Velakoulis D. Brain imaging in psychiatric disorders: target or screen? BJPsych Open. 2019;5(1):e4. doi:10.1192/bjo.2018.79
23. Nagy C, Suderman M, Yang J, et al. Astrocytic abnormalities and global DNA methylation patterns in depression and suicide. Mol Psychiatry. 2015;20(3):320–328. doi:10.1038/mp.2014.21
24. Witt SH, Sommer WH, Hansson AC, Sticht C, Rietschel M, Witt CC. Comparison of gene expression profiles in the blood, hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of rats. In Silico Pharmacol. 2013;1(1):15. doi:10.1186/2193-9616-1-15
25. Walton E, Hass J, Liu J, et al. Correspondence of DNA methylation between blood and brain tissue and its application to schizophrenia research. Schizophr Bull. 2016;42(2):406–414. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbv074
26. Le-niculescu H, Levey DF, Ayalew M, et al. Discovery and validation of blood biomarkers for suicidality. Mol Psychiatry. 2013;18(12):1249–1264. doi:10.1038/mp.2013.95
27. Spijker S, Van Zanten JS, De Jong S, et al. Stimulated gene expression profiles as a blood marker of major depressive disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2010;68(2):179–186. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.03.017
28. Zhang HP, Liu XL, Chen JJ, et al. Circulating microRNA 134 sheds light on the diagnosis of major depressive disorder. Transl Psychiatry. 2020;10(1):95. doi:10.1038/s41398-020-0773-2
29. Beiko T, Strange C. Anxiety and depression in patients with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency: current insights and impact on quality of life. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2019;15:959–964. doi:10.2147/TCRM.S175369
30. Leonard BE. Inflammation and depression: a causal or coincidental link to the pathophysiology? Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2018;30(1):1–16. doi:10.1017/neu.2016.69
31. Bergmans RS, Kelly KM, Mezuk B. Inflammation as a unique marker of suicide ideation distinct from depression syndrome among U.S. adults. J Affect Disord. 2019;245:1052–1060. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2018.11.046
32. Wang C, Wang X, Song G, et al. A high-fructose diet in rats induces systemic iron deficiency and hepatic iron overload by an inflammation mechanism. J Food Biochem. 2021;45(1):e13578. doi:10.1111/jfbc.13578
33. Wu C, Li H, Zhang P, et al. Lymphatic flow: a potential target in sepsis-associated acute lung injury. J Inflamm Res. 2020;13:961–968. doi:10.2147/JIR.S284090
34. Perlman K, Benrimoh D, Israel S. A systematic meta-review of predictors of antidepressant treatment outcome in major depressive disorder. J Affect Disord. 2019;243:503–515. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2018.09.067
35. Li QS, Tian C, Hinds D. Genome-wide association studies of antidepressant class response and treatment-resistant depression. Transl Psychiatry. 2020;10(1):360. doi:10.1038/s41398-020-01035-6
36. Thai M, Başgöze Z, Klimes-Dougan B, et al. Neural and behavioral correlates of clinical improvement to ketamine in adolescents with treatment resistant depression. Front Psychiatry. 2020;11:820. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00820
37. Chen JJ, Xie J, Li WW. Age-specific urinary metabolite signatures and functions in patients with major depressive disorder. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(17):6626–6637. doi:10.18632/aging.102133
38. Chen JJ, Zheng P, Liu YY, et al. Sex differences in gut microbiota in patients with major depressive disorder. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2018;14:647–655. doi:10.2147/NDT.S159322
39. Coplan JD, Aaronson CJ, Panthangi V, Kim Y. Treating comorbid anxiety and depression: psychosocial and pharmacological approaches. World J Psychiatry. 2015;5(4):366–378. doi:10.5498/wjp.v5.i4.366
40. Endedijk HM, Nelemans SA, Schür RR, et al. The role of stress and mineralocorticoid receptor haplotypes in the development of symptoms of depression and anxiety during adolescence. Front Psychiatry. 2020;11:367. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00367
41. Kessler RC, Merikangas KR, Wang PS. Prevalence, comorbidity, and service utilization for mood disorders in the United States at the beginning of the twenty-first century. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2007;3(1):137–158. doi:10.1146/annurev.clinpsy.3.022806.091444
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.