Back to Journals » International Journal of Nanomedicine » Volume 16
Phase-Transformation Nanoparticle-Mediated Sonodynamic Therapy: An Effective Modality to Enhance Anti-Tumor Immune Response by Inducing Immunogenic Cell Death in Breast Cancer
Authors Si Y, Yue J, Liu Z, Li M, Du F, Wang X, Dai Z, Hu N, Ju J, Gao S, Wang X, Yuan P
Received 17 December 2020
Accepted for publication 17 February 2021
Published 5 March 2021 Volume 2021:16 Pages 1913—1926
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S297933
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Thomas Webster
Yiran Si,1 Jian Yue,2 Zhaoyang Liu,3 Mo Li,3 Feng Du,4 Xue Wang,2 Zhong Dai,5 Nanlin Hu,1 Jie Ju,1 Songlin Gao,1 Xiaobing Wang,3 Peng Yuan2
1Department of Medical Oncology, National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100021, People’s Republic of China; 2Department of VIP Medical Services, National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100021, People’s Republic of China; 3State Key Laboratory of Molecular Oncology, National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100021, People’s Republic of China; 4China Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and Translational Research (Ministry of Education/Beijing), The VIPII Gastrointestinal Cancer Division of Medical Department, Peking University Cancer Hospital and Institute, Beijing, 100142, People’s Republic of China; 5Department of Medical Oncology, Cancer Hospital of Huanxing Chaoyang District, Beijing, 100005, People’s Republic of China
Correspondence: Peng Yuan
Department of VIP Medical Services, National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, #17 Pan Jia Yuan Nan Li, Chao Yang District, Beijing, 100021, People’s Republic of China
Tel +86 10-87787245
Email [email protected]
Xiaobing Wang
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Oncology, National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, #17 Pan Jia Yuan Nan Li, Chao Yang District, Beijing, 100021, People’s Republic of China
Tel +86 10-87788430
Email [email protected]
Purpose: Immunologically quiescent of breast cancer cells has been recognized as the key impediment for the breast cancer immunotherapy. In this study, we aimed to investigate the role of nanoparticle-mediated sonodynamic therapy (SDT) in promoting anti-tumor immune of breast cancer cells and its potential immune mechanisms.
Materials and Methods: The phase-transformation nanoparticles (LIP-PFH nanoparticles) were in-house prepared and its physiochemical characters were detected. The CCK-8 assay, apoptosis analysis and Balb/c tumor model establishment were used to explore the anti-tumor effect of LIP-PFH nanoparticles triggered by low-intensity focused ultrasound (LIFU) both in vitro and in vivo. Flow cytometry and immunohistochemistry of CD4+T, CD8+T, CD8+PD-1+T in blood, spleen and tumor tissue were performed to represent the change of immune response. Detection of immunogenic cell death (ICD) markers was examined to study the potential mechanisms.
Results: LIP-PFH nanoparticles triggered by LIFU could inhibit the proliferation and promote the apoptosis of 4T1 cells both in vitro and in vivo. CD4+T and CD8+T cell subsets were significantly increased in blood, spleen and tumor tissue, meanwhile CD8+PD-1+T cells were reduced, indicating enhancement of anti-tumor immune response of breast cancer cells in the nanoparticle-mediated SDT group. Detection of ICD markers (ATP, high-mobility group box B1, and calreticulin) and flow cytometric analysis of dendritic cell (DC) maturity further showed that the nanoparticle-mediated SDT can promote DC maturation to increase the proportion of cytotoxic T cells by inducing ICD of breast cancer cells.
Conclusion: The therapy of nanoparticles-mediated SDT can effectively enhance anti-tumor immune response of breast cancer.
Keywords: breast cancer, immune response, phase-transformation nanoparticles, immunogenic cell death, DC maturation
Introduction
Breast cancer is a malignant tumor and the most common cancer in women.1 Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) has the worst prognosis among breast cancers because of its aggressiveness and degree of malignancy.2,3 Once recurrence and metastasis of TNBC develop after surgery, the median survival time is only approximately 9 months.4 At present, chemotherapy is still the main treatment for TNBC. Unfortunately, the prognosis for patients with TNBC is unsatisfactory due to the inevitable drug resistance. In recent years, immunotherapy has shown potential therapeutic effects on TNBC. However, only a few patients benefited from immunotherapy,5,6 which is affected by factors such as tumor immunogenicity and the immune microenvironment. Therefore, exploring new treatment methods to improve the immune response of breast cancer cells is the key to improving the effect of breast cancer immunotherapy.
Sonodynamic therapy (SDT) focused on the ultrasound energy on located tumor tissue, which was considered to be a safer and more acceptable therapy for patients compared to radiotherapy and chemotherapy.7,8 It has also been proved that SDT can accurately kill the cancer cells with minimal damages to neighboring normal tissues.9 Low-intensity focused ultrasound (LIFU) was used to activate sonosensitizer to cause the damage and even the death of tumor cells which was widely used in SDT.10,11 In recent years, nanoparticles have become the best candidate sonosensitizer due to physicochemical stability, tunable pore size and biosafety of nanomaterials.12,13 According to previous researches, nanoparticle-mediated SDT showed potential tumor suppression value in pancreatic cancer, colon cancer and brain tumor.14–16 The anti-tumor effect may be related to the phase-transformation of the nanoparticles induced by LIFU, causing cell damage in situ.17 However, there were few researches to explore the anti-tumor effect of phase-transformation nanoparticle-mediated SDT in breast cancer, and it is unknown whether the mechanism of the killing effect was related to immune activation.
In this study, we prepared phase-transformation perfluorocarbon nanoparticles (LIP-PFH nanoparticles). We aimed to explore the inhibitory effect of LIP-PFH nanoparticle-mediated SDT (LIP-PFH+LIFU) on breast cancer cells and the potentially activated immune response.
Materials and Methods
Cell Lines and Animals
Murine breast cancer 4T1 cells were provided by the Key Laboratory of Cellular and Molecular Biology of Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. These cells were tested by a professional organization (Microread Genetics Co., Ltd. Beijing, China) before use to confirm the source and quality. The cells were cultured in RPMI 1640 medium (Gibco, NY, USA) containing 5% fetal bovine serum, 1% streptomycin and 1% penicillin at 37°C under 5%CO2. Female Balb/c mice, 6–8 weeks old, were provided by Huafukang Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). The animal experiments were approved by the Laboratory Animal Ethics Committee of the Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and complied with the ethics standards formulated by the Animal Ethics Committee. The ethics registration number was NCC2019A196.
Synthesis and Characterization of LIP-PFH Nanoparticles
Phosphatidylcholine (DPPC), phosphatidylethanolamine (DSPC), phosphatidylethanolamine-polyethylene glycol 2000 (DSPE-PEG2000) and cholesterol (Avanti Polar Lipids Co., Ltd., US) were prepared as described in previous publications at a total mass ratio of 10:4:3:3 dissolved in 5mL of chloroform18,19 (Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., China), placed in a beaker and stirred until the solution was clear. The solution was transferred to a 50mL round bottom flask and evaporated in a fume hood overnight to form a uniform lipid film. PBS (2mL) was added to the ultrasonic bath to completely dissolve the film. Under ice bath conditions, the sample was emulsified with an ultrasonic breaker (Sonics, US; 160W, open 5s, stop 3s, a total of 90s) and 200μL of perfluorohexane (PFH) was added (BaiLingWei Technology Co., Ltd., China). After the emulsion was formed, the mixture was centrifuged and washed with PBS three times to obtain lipid PFH (LIP-PFH) nanoparticles, which appeared as a milky white liquid and could be stored at 4°C for further experiments. The morphology of LIP-PFH nanoparticles was characterized by optical microscopy (OM, Olympus, Japan) and transmission electron microscope (TEM, JEOL Co., Ltd., Japan). The distribution of particle size and zeta potential were detected by a nanoparticle analyzer (Zetasizer Nano ZS, Malvern Instruments, Malvern, UK).
Fluorescence Staining and Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope (CLSM)
For analysis of the intracellular uptake of LIP-PFH nanoparticles by 4T1 cells, at 24h, 16h, 8h, 4h, 2h and 0.5h before CLSM photography, 4T1 cells were cultured after mixing LIP-PFH nanoparticles marked by DiI (Beyotime Biotechnology Co., Ltd., China) with the medium. At 0h, dishes at different time points were removed. After the sample were washed with PBS, Hoechst 33342 live cell nuclear stain (Beyotime Biotechnology Co., Ltd., China) was added to the medium at 10μL/mL, incubated at 37°C and 5%CO2 for 10min, washed and photographed by CLSM. The quantitative intracellular uptake of LIP-PFH nanoparticles by 4T1 cells at different times was analyzed by flow cytometry. Then, LIFU (Sonovitro@FUAuto Ultrasound system, Sx Ultrasonic Co., Ltd., China) was used to stimulate the LIP-PFH nanoparticles, which accumulated in 4T1 cells at 1W/m2 for 1min, for 2min and for 3min according to the Sonovitro ultrasound operation handbook. The bubbles were observed after the LIP-PFH nanoparticles underwent a liquid-gas phase-transformation under an OM. Similarly, we used CLSM to capture the ultrasound condition of the 4T1 cells under LIFU stimulation after taking up LIP-PFH nanoparticles.
Cell Proliferation Analysis
Cell proliferation was evaluated by the CCK-8 assay (Dojindo Molecular Technologies, Inc., Japan). First, 4T1 cells (1 × 104 cells per well, 100μL) were seeded in 96-well plates. After 24h of incubation, the cells were divided into four groups. Group I was the control group; Group II was treated with LIP-PFH nanoparticles alone, in which LIP-PFH nanoparticles were mixed with the same number of cells and the medium; Group III was treated with LIFU alone (1W/m2, 2min); Group IV was treated with LIP-PFH nanoparticles combined with LIFU. According to the manufacturer’s instructions, a CCK-8 assay was conducted using a 450nm microplate reader (Thermo Fisher, US) to detect the OD value of the samples, and the relative cell proliferation rate was calculated.
Flow Cytometry
Cell apoptosis and the cell cycle were evaluated by the Annexin V and FITC apoptosis detection kit and cell cycle assay kit (Dojindo Molecular Technologies, Inc., Japan). First, 4T1 cells (5 × 104 cells per well, 500μL) were seeded in 24-well plates. After 24h of incubation, the cells were divided into four groups as described above to receive the corresponding intervention. After 24h of culture, the cells were collected to analyze cellular apoptosis and the percentages of the cells in the G1, S, and G2 phases by flow cytometry. To detect immune cells in the peripheral blood and spleen of mice, we collected 100μL of blood in a heparin anticoagulation tube (50μL for CD4+T/CD8+T cells, 50μL for CD8+PD-1+T cells) from the posterior orbital venous plexus before treatment (d7), during treatment (d14, d21) and after treatment (d28). Fifty microliters of whole blood were lysed with 2mL of red blood cell lysate for 5min and centrifuged at 1000r/min for 5min. The supernatant was discarded. Then, the samples were washed 3 times with PBS+1%FBS and stained with anti-CD3, anti-CD4, anti-CD45, anti-CD8 or anti-CD279 (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA) in the dark for 20min. PBS+1%FBS was added to wash the samples, and the analyses of CD4+T, CD8+T and CD8+PD-1+T cell subsets in peripheral blood were conducted by flow cytometry. After treatment (d28), the spleens of the mice were removed. We cleaned the adipose tissue, fully ground and lysed it with erythrocyte lysis buffer, and then stained it with appropriate antibodies (anti-CD45, anti-CD80, anti-CD86, anti-CD11c, anti-MHC Class II, anti-F4/80, anti-CD11b, anti-CD206, anti-CD16/32, anti-CD25, anti-Foxp3, BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA) to test the dendritic cells (DCs), macrophages and Tregs in the spleen. All flow cytometric results are analyzed using FlowJo 10.0 software.
Detection of Danger-Associated Molecular Patterns (DAMPs)
Cell supernatants were harvested at 3h, 6h, 12h, and 24h after the corresponding intervention in the above experiments in vitro. The ATP concentration was quantified by the luciferin/luciferase-based ATP assay kit (Beyotime Biotechnology Co., Ltd., China). Bioluminescence was assessed by a multifunctional microplate reader (Tecan, Austria). The high-mobility group box B1 (HMGB1) level in the supernatant was determined by an HMGB1 ELISA Kit (Shino-Test Corporation, Japan). For calreticulin (CRT) detection, 1×106 cells were harvested at 24h after the corresponding intervention and resuspended in 100μL of staining buffer (eBioscience, CA, USA). Prepared cells were incubated for 30min with anti-CRT (Alexa Fluor® 647) antibodies at 4°C in the dark. The samples were then washed and incubated with the viability detection/exclusion dye 7-aminoactinomycin D (7AAD) (Abcam, UK). Then, 7AAD-negative cells (dying cells) were gated, and membrane CRT rather than total CRT was detected. The mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) of CRT was calculated using FlowJo 10.0 software.
Tumor Model Establishment
For establishment of a tumor stock, 1 × 106 4T1 cells were injected into the flanks of Balb/c mice. After the tumor reached 20mm, the samples were used as a stock for tumor transplantation via surgery. The mice were sacrificed, and the tumors were harvested. Subsequently, the tumor tissue was cut into pieces of approximately 2mm3 and inoculated into the right flank of the mice. Three days after the establishment of the tumor model, the tumor size was 4–5mm, and the experimental mice were used for the following study. All 24 experimental mice were randomly divided into four groups as follows: Group 1 (PBS): 100μL of PBS was injected intraperitoneally; Group 2 (LIFU): LIFU was used to locally stimulate the tumor (1w/m2, 2min); Group 3 (nab-paclitaxel, nab-P): 10mg/kg of nab-P dissolved in 0.9% saline (100μL) was used for tail vein injection; Group 4 (LIP-PFH+LIFU): Multipoint injection of 100μL of LIP-PFH nanoparticles (containing approximately 106 nanoparticles) directly on the tumor tissues was performed. After 24h, stimulation with local LIFU was performed (1w/m2, 2min). All the above treatments were performed every 3 days. The tumor volumes were subsequently measured every 3 days and calculated (volume=R × r2/2, R represents the longest diameter and r represents the shortest diameter). After 3 weeks of treatment, the mice were killed. We collected tumors, important organs of mice and the tumor weight of each group was recorded.
Cytokine Measurement
Serum was isolated from the blood samples according to the schedule of flow cytometry (d7, d14, d21, d28), and the serum cytokine levels were analyzed using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs). The level of IFN-γ was measured using a mouse IFN-γ ELISA kit (Neobioscience Corp, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
IHC was performed using an indirect peroxidase method. Paraffin-embedded sections of tumor tissues on slides were fully dewaxed in xylene and rehydrated thoroughly in a decreasing graded series of ethanol concentrations. Endogenous peroxidase was quenched with 3% hydrogen peroxide, and the sections were blocked with 10% goat serum (ZSGB-Bio; Beijing, China) to reduce nonspecific antibody binding. All tissues were incubated overnight with primary antibody at 4°C. Antibodies against CD4, CD8, PD-1, CD31, CRT and HMGB1 were obtained from Abcam (Shanghai, China). For detection, the slides were returned to room temperature and incubated with horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG (1:200, Proteintech, Wuhan, China). Diaminobenzidine (DAB, ZSGB-Bio, Beijing, China) was used as the chromogenic substrate. The slides were counterstained with hematoxylin and mounted in resin. Images were acquired through an Aperio pathology scanner, and the stained IOD value was calculated using ImageJ software.
Statistical Analysis
All experiments were carried out in triplicate, and the mean value of triplicate experiments was used for statistical analysis. All data obtained are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). Statistical analysis was performed by two-sided Student’s t-test for two groups and one-way analysis of variance for multiple groups. Prism 7.0 software (GraphPad Prism software V7.01, San Diego, CA, USA) was used for statistical analysis. A significant level of results was reported when the p value was <0.05.
Results
Physicochemical Characteristics of the LIP-PFH Nanoparticles and Cellular Uptake by 4T1 Cells
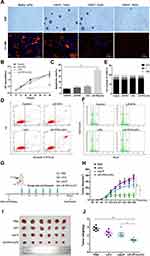
The LIP-PFH nanoparticles were composed of outer lipid and inner core PFH, which is a safe and nontoxic phase-transformation material20 (Figure 1). The prepared LIP-PFH nanoparticles appeared as a milky white suspension to the naked eye (Figure 2A). The nanoparticles were presented under OM and TEM (Figure 2B and C). The average particle size of the nanoparticles was 169.2±31.5 nm, and the average zeta potential was 8.2±3.6 mV (Figure 2D and E).
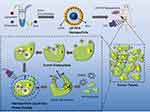 |
Figure 1 Design of LIP-PFH nanoparticles and schematic illustration of phase-transition of LIP-PFH nanoparticles triggered by LIFU leading to cell damage in situ. |
To explore the peak time of cellular uptake of the LIP-PFH nanoparticles by 4T1 cells, we used CLSM to continuously monitor multiple time points. After cocultivation of 4T1 cells with the LIP-PFH nanoparticles in medium for 8 h, the orange fluorescence of the LIP-PFH nanoparticles entering the cells was observed. Over time, the fluorescence increased and became more pronounced. After 24h, satisfactory accumulation in the cells was reached (Figure 3A). Additionally, the quantitative intracellular uptake of LIP-PFH nanoparticles at different times was analyzed with flow cytometry shown in Figure 3B.
 |
Figure 3 Cellular uptake of LIP-PFH nanoparticles by 4T1 cells at continuously multiple time points. (A) Images of CLSM; (B) quantitative analysis of flow analysis. |
Anti-Tumor Effect of LIP-PFH Nanoparticles Triggered by LIFU Both in vitro and in vivo
To confirm that LIFU triggered phase-transformation of the LIP-PFH nanoparticles and to evaluate the appropriate ultrasound conditions, we exposed the 4T1 cells aggregated with the LIP-PFH nanoparticles to LIFU stimulation at 1W/m2 for 1min, 2min and 3min. The results showed that with 1W/m2 for 2min, the nanoparticles with orange fluorescence that accumulated in the cells were released due to cell rupture and no longer showed strong orange fluorescence. The blue fluorescence of the nucleus also gradually decreased, indicating nuclear fragmentation (Figure 4A). Therefore, 1W/m2 for 2min was determined to be a suitable condition for LIFU to act on 4T1 cells. We designed cell proliferation, apoptosis and cell cycle experiments to verify the effect of the LIFU-triggered LIP-PFH nanoparticle on cell damage in situ. The CCK-8 results showed inhibited proliferation of 4T1 cells (Figure 4B) and significantly promoted cell apoptosis in the LIP-PFH+LIFU group (Figure 4C and D). However, in the cell cycle experiment, no significant differences in the cell cycle distribution of each group were found (Figure 4E and F).
Before starting the experiment in vivo, we firstly clarified the bio-compatibility and bio-safety of LIP-PFH nanoparticles. The hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of major organs of mice with LIP-PFH nanoparticles showed no histological changes compared with saline controls, which demonstrated that no physiological toxicity inherently existed in the LIP-PFH nanoparticles in vivo (Supplementary Figure S1). Next, according to the flow chart in Figure 4G, we established a tumor model and randomly divided the mouse into four groups for intervention. After 3 weeks of treatment, the tumor volume in the LIP-PFH+LIFU group was significantly smaller than that in the control (PBS) group (Figure 4H) and was also obviously different from that in the nab-P group. The tumors were harvested after the mice were sacrificed (Figure 4I). The tumor weight in the LIP-PFH+LIFU group was smaller than that in the control group and the nab-P group (Figure 4J). Furthermore, we also collected important organs including liver, lung and kidney. The H&E staining of these organs showed that distant metastases occurred on lung, not on liver and kidney and the lung metastases in the LIP-PFH+LIFU group were significantly better than that of the other groups (Supplementary Figure S2).
A Changed Immune Response of T-Cells After the LIP-PFH Nanoparticles Triggered by LIFU
To probe whether the LIP-PFH nanoparticles combined with LIFU could activate the immune response, we dynamically monitored the CD4+T, CD8+T and CD8+PD-1+T cell subsets in the peripheral blood of the mice. The LIP-PFH nanoparticles triggered by LIFU significantly increased the CD4+T and CD8+T cells in the peripheral blood compared with those in the control group and the nab-P group (Figure 5A and B) and CD8+PD-1+T cells were reduced in the LIP-PFH+LIFU group (Figure 5C). In addition, we synchronously monitored the IFN-γ released by peripheral blood (Figure 5D). We also analyzed the subsets of T cells in the spleen. The results showed that the expression trend in the spleen was the same as that in the peripheral blood. The CD4+T and CD8+T cells in the LIP-PFH+LIFU group were obviously higher than those in the control group and the nab-P group (Figure 5E and F), while the CD8+PD-1+T cells decreased (Figure 5G). We also preliminarily explored the expression of Tregs and macrophages in spleen. The results showed that the Tregs in the LIP-PFH+LIFU group were significantly lower than those in the control group and the nab-P group (Supplementary Figure S3A and B) and the M2-type macrophages in the LIP-PFH+LIFU group were also reduced than those in the other groups (Supplementary Figure S3C-G). The staining of CD31 in tumor tissues showed that the blood vessel density of the LIP-PFH+LIFU group was significantly decreased (Supplementary Figure S3H and I).
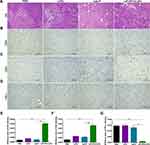
The H&E staining of the tumor tissue showed large areas of cell necrosis, nuclear fragmentation or lysis in the LIP-PFH+LIFU group (Figure 6A, black arrow) accompanied by high levels of lymphocyte infiltration (Figure 6A, red arrow). The tumor tissue of the LIP-PFH+LIFU group showed strong infiltration of CD4+T and CD8+T cells (Figure 6B, C, E and F), and reduced PD-1 expression on tumor-infiltrating T cells (Figure 6D and G). Based on the above results, LIP-PFH nanoparticle-mediated SDT effectively increased the proportion of lymphocytes infiltrating in the tumor microenvironment.
The LIP-PFH Nanoparticles Triggered by LIFU Enhanced the Immune Response by Inducing Immunogenic Cell Death (ICD) in 4T1 Cells to Promote DC Maturation
Dying cells release “danger signals” which alert the immune system to initiate immune responses. We investigated the mode of cell death induced by the LIFU-triggered LIP-PFH nanoparticle phase-transformation, which causes cell damage. We detected CRT exposure on dying cells and the release of ATP and HMGB1, which are validated DAMPs. LIFU combined with the LIP-PFH nanoparticles induced significant CRT exposure on the surface of dying cells after 24h (Figure 7A). Additionally, the release of ATP (Figure 7B) and HMGB1 (Figure 7C) peaked at 6 and 3h, respectively. The expression of CRT and HMGB1 on the cell membrane and in the extracellular space in the tumor tissue was also higher in the LIP-PFH+LIFU group than in the other groups (Figure 7D and E). These findings suggested that LIP-PFH nanoparticles-mediated SDT could effectively induce ICD to release endogenous entities in 4T1 breast cancer cells.
Next, we further explored how ICD can increase T cell expression. Some studies have shown that ICD had potential stimulatory effect on DC maturation.21 Our results found that the surface markers of mature DCs, such as CD80, MHCII and CD86, were improved in the LIP-PFH+LIFU group (Figure 7F–K). In addition, ICD also stimulated the release of IFN-γ (Figure 7L). DC maturation can further induce antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses and IFN-γ release has been confirmed in previous studies.22,23 Therefore, our research results finally confirmed that LIP-PFH nanoparticles-mediated SDT can promote DC maturation by inducing the ICD of tumor cells to release endogenous signaling molecules, thereby increasing the expression of CTL and stimulating IFN-γ release, which significantly improved the anti-tumor immune response of breast cancer cells. (Figure 8)
 |
Figure 8 Schematic diagram of the mechanism of the LIP-PFH nanoparticles triggered by LIFU to enhance anti-tumor immune. |
Discussion
Exploring new treatment methods is an effective way to improve the cure rate of breast cancer and improve patient survival. In recent years, immunotherapy for melanoma, renal cell carcinoma and lung cancer has developed rapidly, but progress in the treatment of breast cancer has been very limited.24,25 Only the IMpassion130 study has obtained promising results in advanced TNBC.26 The main reason is that breast cancer itself was a tumor with low immunogenicity and lacks effective immune responses to immunotherapy. Although a previous study found that TNBC had relatively strong immunogenicity, it was still a “cold tumor” compared with melanoma or lung cancer, with few tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), inhibitory tumor microenvironment and low expression of immune markers.27,28 It is usually impossible to obtain an effective antitumor immune response through single-agent immunotherapy. Therefore, identification of new treatment techniques to transform “cold tumors” into “hot tumors” is a new direction to improve the effect of immunotherapy in breast cancer.
Induction of ICD of cells is an effective way to achieve the above objectives, which can overcome the problems of poor tumor immunogenicity, low antigen sensitivity and enhance antitumor immunity.29 When ICD occurs in tumor cells, the following changes are observed: intracellular CRT is exposed on the cell membrane, ATP is secreted, and HMGB1 is released. Previous studies have shown that the release of ATP can recruit and activate antigen-presenting cells (APCs) represented by DCs. CRT on the cell membrane can send out “eat me” signals and increase the phagocytosis of tumor cells by APCs, and HMGB1 can promote the antigen extraction presented to T cells, which effectively activates the cytotoxic function of CD8+T cells and also promotes the release of IL-2, IFN-γ and other cytokines, reversing the tumor-suppressive immune microenvironment.30,31 Current drugs or treatments that induce ICD include some special chemotherapy drugs (such as doxorubicin, oxaliplatin, etc.) or physical stimulation such as radiotherapy. This study is the first to prove that LIP-PFH nanoparticles-mediated SDT can increase the expression of CD4+T and CD8+T cells by inducing ICD in breast cancer cells. In addition, this modality can reduce the expression of PD-1 on CD8+T cells. The combination of PD-1 on the surface of T cells and PD-L1 on the surface of tumor cells leads to immune escape of tumor cells,32 and a large number of CD8+T cells with low PD-1 expression can effectively alter immune-suppression and have the potential to transform effector T cells into cytotoxic T cells to present anti-tumor immunity.33,34 Moreover, LIP-PFH nanoparticle is a safe and nontoxic phase- transformation material which has been demonstrated in our previous study and other published researches.18–20 In our experiment, the mouse in the LIP-PFH+LIFU group were in good local and systemic condition, without obvious side effects after treatment.
The LIP-PFH nanoparticles triggered by LIFU also exerted potential regulatory effects on some inhibitory immune cells in the tumor microenvironment. Tregs can reduce the antitumor activity of CD4+T cells, which is closely related to the poor prognosis of tumors.35 The results of this study also confirmed the effect of this method on reducing the proportion of Tregs. Furthermore, M2-type macrophages promote tumor cell metastasis and angiogenesis and are classic immunosuppressive cells.36,37 In this study, the expression of M2-type macrophages and the blood vessel density of tumor tissue in the LIP-PFH+LIFU group were significantly reduced than those in the other groups. Therefore, whether the LIP-PFH nanoparticles-mediated SDT also had regulatory effects on immunosuppressive cells such as Tregs and tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) should be further investigated. Although our research has shown that LIP-PFH nanoparticle-mediated SDT can effectively enhance the immunogenicity of breast cancer cells, the follow-up exploration of LIP-PFH+LIFU combined with immunotherapy is urgently required. Moreover, several studies have demonstrated that the combination of phase-transformation nanoparticles and photothermal-chemotherapy has the ability to inhibit distant metastasis.38,39 In our study, LIP-PFH nanoparticles-mediated SDT also presented potential inhibitory effect on lung metastasis. However, more in-depth scientific experiments are needed to confirm that.
Conclusion
This study explored that the LIP-PFH phase-transformation nanoparticles-mediated SDT can increase anti-tumor immune response of breast cancer cells. The results of this study provide great potential for nanomedicine apply for enhancing the effectiveness of breast cancer immunotherapy and bring hope for the combination of nanoparticle-mediated SDT and immunotherapy to transform breast cancer from ‘cold tumors’ into ‘hot tumors’, which will have good application prospects in future.
Ethics Statement
The studies involving animals were reviewed and approved by the Laboratory Animal Ethics Committee of the Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, and complied with the ethics standards formulated by the Animal Ethics Committee. The ethics registration number was NCC2019A196.
Acknowledgments
We thank Sxultrasonic Co. Ltd for providing Sonovitro@FUAuto Ultrasound System (FUAuto-IG) in our experiment.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to data analysis, drafting and revising the article, gave final approval of the version to be published, and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC0115204), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81672634), CSCO Pilot Oncology Research Fund (Y-2019AZMS-0377), Capital Health Development Research Project (2018-2-4023), and Non-profit Central Research Institute Fund of Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Clinical and Translational Medicine Research (12019XK320071).
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136(5):E359–E386. doi:10.1002/ijc.29210
2. Ahn SK, Hwang JW. Global trends in immunotherapy research on breast cancer over the past 10 years. J Oncol. 2020;2020:4708394.
3. Liverani C, De Vita A, Minardi S, et al. A biomimetic 3D model of hypoxia-driven cancer progression. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):12263.
4. Fu WF, Chen QX, Wang XX, Zhang J, Song CG. The survival outcomes of t1an0m0 triple-negative breast cancer with adjuvant chemotherapy. Front Oncol. 2020;10:1753.
5. Bai X, Ni J, Beretov J, Graham P, Li Y. Triple-negative breast cancer therapeutic resistance: where is the Achilles’ heel? Cancer Lett. 2021;497:100–111.
6. Di Cosimo S. Advancing immunotherapy for early-stage triple-negative breast cancer. Lancet. 2020;396(10257):1046–1048.
7. Xu M, Zhou L, Zheng L, et al. Sonodynamic therapy-derived multimodal synergistic cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2021;497:229–242.
8. Bilmin K, Kujawska T, Grieb P. Sonodynamic therapy for gliomas. perspectives and prospects of selective sonosensitization of glioma cells. Cells. 2019;8:11.
9. Xie L, Feng X, Huang M, Zhang K, Liu Q. Sonodynamic therapy combined to 2-deoxyglucose potentiate cell metastasis inhibition of breast cancer. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2019;45(11):2984–2992.
10. Kuroki M, Hachimine K, Abe H, et al. Sonodynamic therapy of cancer using novel sonosensitizers.. Anticancer Res. 2007;27(6A):3673–3677.
11. Lafond M, Yoshizawa S, Umemura SI. Sonodynamic Therapy: advances and Challenges in Clinical Translation. J Ultrasound Med. 2019;38(3):567–580.
12. Prada F, Sheybani N, Franzini A, et al. Fluorescein-mediated sonodynamic therapy in a rat glioma model. J Neurooncol. 2020;148(3):445–454.
13. Wan GY, Liu Y, Chen BW, Liu YY, Wang YS, Zhang N. Recent advances of sonodynamic therapy in cancer treatment. Cancer Biol Med. 2016;13(3):325–338.
14. Yang C, Tan Y, Qi H, et al. Boosting of the enhanced permeability and retention effect with nanocapsules improves the therapeutic effects of cetuximab. Cancer Biol Med. 2020;17(2):433–443.
15. Yang W, Xu H, Liu Q, et al. 5-Aminolevulinic acid hydrochloride loaded microbubbles-mediated sonodynamic therapy in pancreatic cancer cells. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2020;48(1):1178–1188.
16. Liang S, Deng X, Chang Y, et al. Intelligent Hollow Pt-CuS Janus Architecture for synergistic catalysis-enhanced sonodynamic and photothermal cancer therapy. Nano Lett. 2019;19(6):4134–4145.
17. Aftab S, Shah A, Nadhman A, et al. Nanomedicine: an effective tool in cancer therapy. Int J Pharm. 2018;540(1–2):132–149.
18. Yu M, Xu X, Cai Y, Zou L, Shuai X. Perfluorohexane-cored nanodroplets for stimulations-responsive ultrasonography and O2-potentiated photodynamic therapy. Biomaterials. 2018;175:61–71.
19. Li M, Luo H, Zhang W, et al. Phase-shift, targeted nanoparticles for ultrasound molecular imaging by low intensity focused ultrasound irradiation. Int J Nanomed. 2018;13:3907–3920.
20. Su YL, Fang JH, Liao CY, Lin CT, Li YT, Hu SH. Targeted mesoporous iron oxide nanoparticles-encapsulated perfluorohexane and a hydrophobic drug for deep tumor penetration and therapy. Theranostics. 2015;5(11):1233–1248.
21. Wang X, Wang N, Yang Y, et al. Polydopamine nanoparticles carrying tumor cell lysate as a potential vaccine for colorectal cancer immunotherapy. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(7):3062–3075.
22. Alexia C, Cren M, Louis-Plence P, et al. Polyoxidonium((R)) activates cytotoxic lymphocyte responses through dendritic cell maturation: clinical effects in breast cancer. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2693.
23. Salmaninejad A, Zamani MR, Pourvahedi M, Golchehre Z, Hosseini Bereshneh A, Rezaei N. Cancer/Testis Antigens: expression, Regulation, Tumor Invasion, and Use in Immunotherapy of Cancers. Immunol Invest. 2016;45(7):619–640.
24. Emens LA. Breast Cancer Immunotherapy: facts and Hopes. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24(3):511–520.
25. Disis ML, Stanton SE. Immunotherapy in breast cancer: an introduction. Breast. 2018;37:196–199.
26. Schmid P, Adams S, Rugo HS, et al. Atezolizumab and nab-paclitaxel in advanced triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(22):2108–2121.
27. Marra A, Viale G, Curigliano G. Recent advances in triple negative breast cancer: the immunotherapy era. BMC Med. 2019;17(1):90.
28. Kwa MJ, Adams S. Checkpoint inhibitors in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC): where to go from here. Cancer. 2018;124(10):2086–2103.
29. Lu J, Liu X, Liao YP, et al. Nano-enabled pancreas cancer immunotherapy using immunogenic cell death and reversing immunosuppression. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):1811.
30. Duan X, Chan C, Lin W. Nanoparticle-Mediated immunogenic cell death enables and potentiates cancer immunotherapy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019;58(3):670–680.
31. Galluzzi L, Buque A, Kepp O, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G. Immunogenic cell death in cancer and infectious disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017;17(2):97–111.
32. Ai L, Xu A, Xu J. Roles of PD-1/PD-L1 pathway: signaling, cancer, and beyond. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1248:33–59.
33. Choi H, Deng J, Li S, et al. Pulsatile MEK inhibition improves anti-tumor immunity and T cell function in murine kras mutant lung cancer. Cell Rep. 2019;27(3):806–819 e805.
34. Verma V, Jafarzadeh N, Boi S, et al. MEK inhibition reprograms CD8(+) T lymphocytes into memory stem cells with potent antitumor effects. Nat Immunol. 2020;22:53.
35. Saleh R, Elkord E. Treg-mediated acquired resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors. Cancer Lett. 2019;457:168–179.
36. Linde N, Casanova-Acebes M, Sosa MS, et al. Macrophages orchestrate breast cancer early dissemination and metastasis. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):21.
37. Kitamura T, Qian BZ, Soong D, et al. CCL2-induced chemokine cascade promotes breast cancer metastasis by enhancing retention of metastasis-associated macrophages. J Exp Med. 2015;212(7):1043–1059.
38. Mou C, Yang Y, Bai Y, Yuan P, Wang Y, Zhang L. Hyaluronic acid and polydopamine functionalized phase change nanoparticles for ultrasound imaging-guided photothermal-chemotherapy. J Mater Chem B. 2019;7(8):1246–1257.
39. Yang Q, Li P, Ran H, et al. Polypyrrole-coated phase-change liquid perfluorocarbon nanoparticles for the visualized photothermal-chemotherapy of breast cancer. Acta Biomater. 2019;90:337–349.
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.