Back to Journals » Drug Design, Development and Therapy » Volume 11
Paclitaxel-loaded star-shaped copolymer nanoparticles for enhanced malignant melanoma chemotherapy against multidrug resistance
Authors Su Y, Hu J, Huang Z, Huang Y, Peng B, Xie N, Liu H
Received 10 November 2016
Accepted for publication 16 January 2017
Published 6 March 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 659—668
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S127328
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Georgios Panos
Yongsheng Su,1 Jian Hu,1 Zhibin Huang,1 Yubin Huang,1 Bingsheng Peng,1 Ni Xie,2 Hui Liu1
1Department of Burn and Plastic Surgery, The People’s Hospital of Baoan Shenzhen Affiliated to Southern Medical University, 2Core Laboratory, Shenzhen Second People’s Hospital, First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, People’s Republic of China
Abstract: Malignant melanoma (MM) is the most dangerous type of skin cancer with annually increasing incidence and death rates. However, chemotherapy for MM is restricted by low topical drug concentration and multidrug resistance. In order to surmount the limitation and to enhance the therapeutic effect on MM, a new nanoformulation of paclitaxel (PTX)-loaded cholic acid (CA)-functionalized star-shaped poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA)-d-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS) nanoparticles (NPs) (shortly PTX-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs) was fabricated by a modified method of nanoprecipitation. The particle size, zeta potential, morphology, drug release profile, drug encapsulation efficiency, and loading content of PTX-loaded NPs were detected. As shown by confocal laser scanning, NPs loaded with coumarin-6 were internalized by human melanoma cell line A875. The cellular uptake efficiency of CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs was higher than those of PLGA NPs and PLGA-TPGS NPs. The antitumor effects of PTX-loaded NPs were evaluated by the MTT assay in vitro and by a xenograft tumor model in vivo, demonstrating that star-shaped PTX-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs were significantly superior to commercial PTX formulation Taxol®. Such drug delivery nanocarriers are potentially applicable to the improvement of clinical MM therapy.
Keywords: malignant melanoma, paclitaxel, nanoparticles, enhanced therapeutic effects, drug delivery
Introduction
Malignant melanoma (MM), which develops in pigment cells (eg, melanocytes), mainly occurs in the skin and is prone to blood metastasis and mortality. Moreover, the incidence and death rates of MM are increasing annually, and thereby, MM has become an obvious public health threat. Recently, MM has mainly been treated by surgical resection, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and immunotherapy. However, in case of metastasis, surgical resection leads to unsatisfactory therapeutic effects, even if various chemotherapeutic agents are used concomitantly. Thus, it is of great significance to boost the clinical efficacy of chemotherapy on MM. Paclitaxel (PTX) has well-documented significant effects on MM treatment.1,2 As a highly effective anticancer drug, it can stabilize microtubules, block cancer cell cycle in the G2/M phase, and finally induce apoptosis.3 However, PTX has an extremely hydrophobic structure that limits its aqueous solubility (<0.4 μg/mL) and significantly reduces its bioavailability. This drawback can be circumvented by dissolving PTX in a Cremophor-EL®/ethanol (polyoxyethylene castor oil and ethanol) (1/1, v/v) mixture commercially named Taxol®. Nevertheless, Polyoxyethylene castor oil causes severe side reactions (hypersensitivity, cardiotoxicity, peripheral neuropathy, etc.).4 In order to reduce adverse events, researchers have endeavored to replace Polyoxyethylene castor oil for delivering PTX.
In recent years, nanomedicine in the form of particulate carriers (eg, nanoparticles [NPs], micelles, liposomes, nanoemulsions) offers bright promise for the delivery of anticancer drugs,5–8 by which drugs can be synthesized and administered in different ways. Several nanosized delivery systems, such as polymeric NPs and lipid nanocapsules, have shown enhanced bioavailability of PTX after injection. It is quite convincing that cancer nanotechnology significantly contributes to enhancing the bioavailability of chemotherapeutic drugs.9 Furthermore, the nanosized delivery systems used as drug carriers allow sustained release, have high encapsulation efficiency (EE), and accumulate preferentially at tumor sites owing to the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect.10,11 Kretzer et al reported that lipid nanoemulsions which bind to low-density lipoprotein receptors could be used as carriers of PTX, and they decreased toxicity and increased the antitumor efficacy of PTX.12 Battogtokh and Ko reported the PTX-loaded polymeric NPs showed sustained release and high cytotoxic efficacy comparable to that of free PTX on B16F10 melanoma cell lines, suggesting the PTX nanocarriers are potentially applicable to the treatment of melanoma.13
Currently, biodegradable drug-loaded polymeric NPs have been spotlighted due to passive and active drug-targeted therapeutic effects after intravenous administration into human body.14,15 Branched copolymers, such as star-shaped copolymers, hyper-branched copolymers, and dendrimers, have been highlighted owing to excellent mechanical and rheological properties.16,17 Star-shaped block copolymer is a branched polymer, the branches of which all extend to form a core.18 The drug carriers based on star-shaped polymers have smaller hydrodynamic radii as well as high EEs and loading contents (LCs) than those of the linear polymers with similar molecular weights.19,20
In this study, cholic acid (CA)-functionalized poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA)-D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS) (shortly CA-PLGA-TPGS), a star-shaped copolymer, was employed to prepare drug carriers applicable to biomedicine. PLGA is one of the most widely accessed biodegradable polymers that have been applied to the biomedical field.21,22 As a water-soluble vitamin E derivative and also an excellent emulsifier, TPGS is prepared by esterifying vitamin E succinate with polyethylene glycol 1000. It is an excipient that overcomes multidrug resistance and a P-glycoprotein (P-gp) inhibitor that augments the oral bioavailability and cytotoxicity of anticancer drugs.23–25 CA, which is the main bile acid in human body, was selected as the poly-hydroxy initiator due to good biocompatibility.26 PLGA, TPGS, and CA have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration and used in pharmaceutical products.9,27
Although NPs prepared from PLGA and TPGS-PLGA have been widely researched as drug delivery vehicles, linear copolymers were used in most cases. In this study, to fabricate a versatile drug carrier with satisfactory drug EE and LC for MM therapy, CA-PLGA-TPGS was selected as the vehicle for chemotherapeutic drug PTX. Drug-loaded NPs were prepared and characterized, and their in vivo and in vitro antitumor effects were evaluated. Commercial PTX formulation Taxol, PLGA, and PTX-loaded linear copolymer PLGA-TPGS NPs were selected for comparison.28,29
Materials and methods
Materials
TPGS, MTT, and coumarin-6 (C6) were bought from Sigma-Aldrich (St Louis, MO, USA). PTX powders with about 98% purity (HPLC grade) were obtained from Shanghai Jinhe Bio-Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, People’s Republic of China). Star-shaped copolymer CA-PLGA-TPGS and linear copolymer PLGA-TPGS were kindly supplied by Graduate School at Shenzhen, Tsinghua University (People’s Republic of China). PLGA (Mn ≈20,000, lactic acid [LA]:glycolic acid [GA] =75:25) was provided by Jinan Daigang Biomaterial Co., Ltd. (Jinan, People’s Republic of China). Besides HPLC-grade chromatographic solvents, all the other chemicals were of the commercially available highest grade. Distilled deionized water was utilized throughout this study. Human melanoma cell line A875 was purchased from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA).
Preparation of PTX-loaded NPs
PTX-loaded NPs were fabricated by a modified method of nanoprecipitation as described by Zeng et al.9,30 In brief, 20 mg PTX and 200 mg copolymer CA-PLGA-TPGS, PLGA-TPGS, and PLGA were dissolved by vortexing and sonication in 16 mL of acetone, respectively. Under stirring, the resulting mixture was added dropwise into a 200 mL aqueous solution containing 0.03% TPGS. Then, the suspension was stirred uncovered overnight to completely remove acetone, centrifuged for 15 min at 20,000 rpm, and washed three times to eliminate the unencapsulated anticancer drug PTX and the emulsifier TPGS. In the end, the dispersed solution was freeze-dried for 48 h prior to use. By a similar method, fluorescent molecule C6-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS, PLGA, and PLGA-TPGS NPs were prepared, for which C6 instead of PTX was used. Before use, the freeze-dried NPs were redispersed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS).
Characterizations of PTX-loaded NPs
Zeta potential, particle size, and morphology
Zeta potential and particle size were detected by Malvern Mastersizer 2000 (Zetasizer Nano ZS90; Malvern Instruments Ltd., Malvern, UK). Freshly prepared NPs were diluted appropriately before measurements that were performed at room temperature after 10 min of equilibration. The average of three independent measurements was recorded. Surface morphology was observed by field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM; JEOL JSM-6301F; JEOL, Tokyo, Japan). For sample preparation, the particles were fixed with a double-sided sticky tape on a stub and thereafter coated by a platinum layer for 60 s using JFC-1300 automatic fine platinum coater (JEOL).
Drug LC and EE
Under vigorous vortexing, PTX-loaded NPs (5 mg) were dissolved in 1 mL of dichloromethane.31 The solution was then transferred to a 5 mL mobile phase comprising deionized water and acetonitrile (50:50, v:v). Dichloromethane was evaporated by introducing a nitrogen stream for about 15 min, yielding a clear solution for subsequent high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) (LC 1200; Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). HPLC was conducted with a reverse-phase C18 column (150×4.6 mm, 5 μm, C18; Agilent Technologies) at 35°C, using mobile phase at the flow rate of 1 mL/min. With a UV detector, the effluent was determined at λmax of 227 nm. Drug LC was defined as the percentage of the weight of incorporated PTX to that of NPs, and EE was defined as the percentage of PTX weight in NPs to its initial feeding amount. The measurements were performed in triplicate.
Drug release profiles in vitro
In vitro drug release from PTX-loaded NPs was tested as described by Wang et al.32 Briefly, PTX-loaded NP powders (5 mg) were suspended in 1 mL of PBS containing 0.1% Tween 80 (release buffer) and then transferred to a dialysis membrane bag (molecular weight cut-off =3,500 Da; Spectra Por®; Spectrum Laboratories, Inc., Rancho Dominguez, CA, USA). Tween 80 was utilized to raise the solubility of PTX in this buffer and to prevent its binding to the tube wall. Then, the bag was immersed into a centrifuge tube containing 15 mL of release buffer. The tube was thereafter placed in an orbital shaker water bath and shaken at 37°C and 120 rpm, and the entire release buffer was collected and refreshed at indicated time intervals. Released PTX was quantified by HPLC with the method already mentioned. The relationship between cumulative PTX release from drug-loaded NPs and time was determined.
Cell culture
In a humidified 5% CO2 atmosphere, A875 cells were cultured at 37°C in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM) supplemented with 1% penicillin/streptomycin and 10% fetal bovine serum.
Cellular uptake of C6-loaded NPs
As a model fluorescent molecule, C6 can be encapsulated in the prepared NPs and then internalized by A875 cells. The cells were incubated with 100 μg/mL C6-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs for 2 h at 37°C, washed three times with cold PBS, and fixed for 20 min in methanol. Afterwards, they were stained for 30 min with propidium iodide (PI), washed with PBS twice, and finally observed using confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM; LSM 410; Carl Zeiss AG, Oberkochen, Germany) equipped with an imaging software. The cell images were captured by a differential interference contrast channel, and the images of C6-loaded NPs and PI-stained nuclei were recorded with the following channels: fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) channel (C6) excited at 485 nm and PI channel excited at 530 nm.33 For quantitative analysis, A875 cells were seeded in 96-well plates at the density of 1×104 cells/well and incubated overnight, and then 50, 100, and 200 μg/mL C6-loaded NPs were added, respectively, and equilibrated for 1 h with Hank’s buffered salt solution at 37°C. After 2 h of incubation, the culture medium was discarded, and the wells were washed by 50 μL of cold PBS solution three times. The cells were thereafter lysed by adding 50 μL of 0.2 N sodium hydroxide containing 0.5% Triton X-100 into each well.
In vitro cytotoxicity assay of PTX-loaded NPs
A875 cells were inoculated at the density of 5×103 cells/well in 96-well plates and incubated in 100 μL of medium overnight. Then, they were incubated with the suspension of PTX-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs, that of PLGA-TPGS NPs, or polyoxyethylene castor oil and ethanol at equivalent PTX concentrations of 0.25–25 μg/mL for 24 and 48 h, respectively. PTX-free CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs with the same NPs dose were also tested. The formulations were replaced by 5 mg/mL MTT-containing DMEM at indicated time intervals. After incubation of the cells for 4 h, MTT was aspirated off, and formazan crystals were dissolved by adding dimethyl sulfoxide. The absorbance was detected by a microplate reader at 570 nm. The absorbance was calibrated to zero by using untreated cells with 100% viability as control and the cells without MTT addition as blank. IC50, the drug concentration that inhibits the growth of 50% cells, was calculated. This value was assessed through curve-fitting of the cell viability data and comparing them with those of control.34
In vivo antitumor efficacy of PTX-loaded NPs
Female nude mice (BALB/c-nu, 15–20 g, 6 weeks old) were bought from Guangdong Medical Laboratory Animal Center (People’s Republic of China). The protocols for animal assays were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Southern Medical University. Guidelines of the institutional animal ethics committee were followed for in vivo experiments. Each mouse was subcutaneously injected with 100 μL of medium containing about 2×106 A875 cells into the back. The subcutaneous tumor growth after inoculation of A875 cells was frequently observed. Tumor length and width were measured with a vernier caliper, and the three-dimensional volume of an ellipsoid tumor tissue (V) was calculated according to the formula 4π/3× (length/2) × (width/2)2.35,36 Treatment was initiated when the volume reached approximately 100 mm3 (referred to as the 0th day). The tumor-bearing mice were divided into three groups randomly (n=6) and subjected to tail intravenous injection with saline (control) or PTX-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs and polyoxyethylene castor oil and ethanol in PBS at the dose of 10 mg PTX/kg on the 0th, 4th, and 8th days, respectively. The tumor size and body weight of each mouse were measured every 2 days. Twelve days after treatment, they were sacrificed by cervical decapitation. The antitumor activity was evaluated by measuring the terminal tumor weight.
Statistical analysis
Unless stated otherwise, all the experiments were performed at least three times. The experimental data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance followed by Bonferroni test with Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) 16.0 software. *P<0.05 was considered as statistically significant and **P<0.01 as extremely statistically significant.
Results and discussion
Characterization of star-shaped copolymer
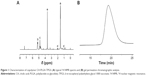
The structure of prepared copolymer CA-PLGA-TPGS was detected by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR; Bruker AMX 500) and CDCl3 used as a solvent. The molecular weight and molecular weight distribution were confirmed by gel permeation chromatography (GPC; Waters Corp., Milford, MA, USA). As shown by 1H NMR in Figure 1A, five peak signals can be observed: a (δ =1.62 ppm, LA repeating unit: –CHCH3), b (δ =5.21 ppm, LA repeating unit: –CH CH3), c (δ =4.82 ppm, GA repeating unit: –CH2–), d (δ =0.50–2.40 ppm, CA moiety: –CH2– and –CH–), and e (δ =3.65 ppm, TPGS repeating unit: –CH2CH2O–). The evidence indicated that the copolymer CA-PLGA-TPGS with a well-defined structure was synthesized successfully. The GPC analysis of CA-PLGA-TPGS is presented in Figure 1B, from which it could be further confirmed that the copolymer CA-PLGA-TPGS was prepared successfully. Figure 1B showed that the peak for CA-PLGA-TPGS appeared at 19.3 min. Moreover, the polydispersity index (PDI) of the copolymers was 1.27, which is rather narrow.
Characterizations of NPs
Particle size, zeta potential, morphology, and drug LC and EE
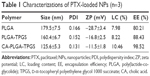
The particle sizes and size distribution of PTX-loaded NPs were detected by dynamic light scattering (DLS), and the results are listed in Table 1. The surface properties and particle sizes of NPs play a crucial role in drug release and cellular uptake together with biodistribution and pharmacokinetics in vivo.37,38 The average hydrodynamic sizes of PTX-loaded NPs ranged from 125.6 to 179.5 nm in diameter, and so they can easily accumulate in the tumor vasculature due to the EPR effect.9,39,40 CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs had a much smaller size than those of PLGA and PLGA-TPGS NPs, which can be ascribed to the constrained, star-shaped copolymer geometry. Moreover, all the PTX-loaded NPs had narrow size distributions (PDI <0.2), which is beneficial to clinical nanomedical applications. The size distributions of PTX-loaded PLGA-TPGS, CA-PLGA-TPGS, and PLGA NPs detected by DLS are shown in Figure 2A. The in vivo stability of NPs through electrostatic repulsion is also reflected by zeta potential. PTX-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS, PLGA-TPGS, and PLGA NPs had the zeta potentials of −11.5±1.8, −16.8±2.5, and −28.7±3.4 mV, respectively. With ionized carboxyl groups from polyglycolic acid and polylactic acid segments, all the NPs had negative surface charges.41 Furthermore, the zeta potentials of PTX-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS and PLGA-TPGS NPs were decreased by TPGS segment compared with that of PLGA NPs.30
The morphology of all NPs was then observed by FESEM. As exhibited in Figure 2B, PTX-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs had near-spherical shapes and the mean size of around 90 nm that is obviously smaller than that detected by DLS. Probably, dry NPs were vulnerable to shrinkage and collapse.42
The drug LC and EE of CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs exceeded those of PLGA and PLGA-TPGS NPs because of the stronger binding between the star-shaped core PLGA and the hydrophobic drug PTX. Besides, the drug LC and EE of CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs were 10.46% and nearly 100%, respectively, meeting the requirements of nanomedical and clinical applications.
Stability of PTX-loaded NPs
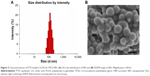
During nanoformulation storage, drug-loaded NPs are prone to aggregation because the absolute value of zeta potential decreases. Therefore, their size distribution becomes nonuniform, and only the fresh NPs are suitable for therapy. In this study, to investigate the stability of PTX-loaded NPs (stored at 4°C), their mean size, size distribution, and zeta potential were measured every 10 days until the 90th day after preparation. During 3 months of storage, the size or zeta potential of PTX-loaded NPs hardly changed at 4°C (Figure 3), indicating that all these NPs were fairly stable.
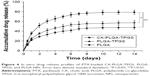
Drug release profiles in vitro
Figure 4 presents the accumulative drug release profiles of PTX-loaded NPs in vitro in pH 7.4 PBS containing 0.1% (w/v) Tween 80 in the first 14 days. After initial burst releases, all NPs exhibited continuous, steady release patterns. In the initial 2 days, 51.72%, 35.19%, and 28.67% of PTX were released, respectively, from drug-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs, PLGA-TPGS NPs, and PLGA NPs. After 2 weeks, their accumulative drug releases were 78.69%, 57.14%, and 47.53%, respectively. Following typical biphasic release patterns, the NPs released PTX rapidly in the initial 2 days because this drug was only beneath the periphery or entrapped poorly. Subsequently, PTX was sustainably released mainly through diffusion from the rigid core.9 Accumulative PTX releases in the 14 days followed a descending order of CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs > PLGA-TPGS NPs > PLGA NPs, suggesting that CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs released PTX faster than PLGA-TPGS NPs did, although they had similar molecular weights. CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs released drug most rapidly because of the highest LC, the smallest particle size, and the hydrophilicity of TPGS outer shell. PTX release from polymeric NPs with higher density and drug LC was promoted because this was a diffusion process in vitro. At the same time, the release decelerated owing to the reduced drug density inside the inner shell. With a higher hydrophilicity, the TPGS outer shell facilitated the penetration of release medium into the cores of NPs and thus led to matrix swelling. Similar to the results of Baimark43 and Zhu et al,44 the drug release concentrations of star-shaped copolymer CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs were better kept at therapeutic levels than those of other NPs in the same periods.
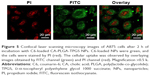
Cellular uptake of C6-loaded NPs
Usually, drug-loaded NPs exert therapeutic effects on cancer cells depending on internalization and sustained retention.45 In vitro investigation provides indirect evidence for verifying the advantages of nanoformulation in comparison with free anticancer drug, although it is different from in vivo bioprocess. In this study, cellular NPs uptake was observed by replacing PTX with C6 in the nanocarriers.46 To this end, A875 cells were incubated with NPs loaded with C6. Figure 5 presents their CLSM images after incubation with the suspension of C6-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs in DMEM for 2 h (NPs concentration: 100 μg/mL). The images were captured from PI channel (red), FITC channel (green), or the overlay of them. Given that green C6-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs were located closely surrounding the red cell nuclei (stained by PI), these NPs were considered to have been internalized effectively into A875 cells.
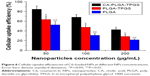
The cellular uptake efficiencies of C6-loaded NPs were further quantified (Figure 6), which reduced with rising concentration of incubated NPs from 50 to 200 μg/mL. Such efficiencies of CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs were 1.33-, 1.43-, and 1.50-fold those of PLGA-TPGS NPs after incubation with 50, 100, and 200 μg/mL NPs, respectively, which can be ascribed to the higher cell adherence and smaller size. The cellular uptake efficiencies of PLGA-TPGS and CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs surpassed that of PLGA NPs owing to the smaller hydrodynamic sizes of the former two and the TPGS segment. TPGS overcame the multidrug resistance of A875 cells by suppressing P-gp, which may decrease the excretion of fluorescence molecule C6. Taken together, with higher cellular uptake efficiency and smaller hydrodynamic size, CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs can feasibly be applied in cancer therapy as drug carriers.
In vitro cytotoxicity of PTX-loaded NPs
A875 cells were employed to study the cytotoxicity of PTX-loaded NPs in vitro and to demonstrate whether PTX encapsulated into these NPs was maintained bioactive. Based on the achievable plasma PTX levels in human body, the cells were treated by suspensions of PTX-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS, PLGA-TPGS, and PLGA NPs or polyoxyethylene castor oil and ethanol for 24 and 48 h at equivalent PTX concentrations of 0.25, 2.5, and 25 μg/mL, respectively.32,47 PTX-free CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs with the same NPs dose were used as well. The percentage of viable cells was detected by the MTT assay (Figure 7). First, CA-PLGA-TPGS seemed nontoxic to and biocompatible with cells and tissues because all the PTX-free CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs at different concentrations did not show significant cytotoxicity. Second, with increasing incubation time and drug dose, the cytotoxicities of all the four formulations were augmented. Third, PTX-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs had the most evident in vitro cytotoxicity. After incubation for 24 h at the drug concentration of 2.5 μg/mL, the cell viability was 64.78% for CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs, 67.53% for PLGA-TPGS NPs, 68.38% for PLGA NPs, and 69.78% for polyoxyethylene castor oil and ethanol. However, after incubation for 48 h, the cytotoxicity of PTX-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs was 23.62% higher than that of polyoxyethylene castor oil and ethanol. With prolonged incubation, the therapeutic effects of PTX-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs were boosted compared with those of other drug-loaded NPs and polyoxyethylene castor oil and ethanol because of faster drug release and higher cellular uptake. Moreover, CA-PLGA-TPGS had more TPGS which was also cytotoxic and thus able to cooperate with chemotherapeutic drug PTX.23,48
The cytotoxicities of the four PTX formulations against A875 cells were further quantified based on IC50 values. IC50 values of A875 cells treated with PTX-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS, PLGA-TPGS, and PLGA NPs and polyoxyethylene castor oil and ethanol for 24 and 48 h are summarized in Table 2. The IC50 values of polyoxyethylene castor oil and ethanol and PTX-loaded nanocarriers were similar after incubation for 24 h. Nevertheless, the IC50 values of PTX-loaded nanocarriers after 48 h, especially that of PTX-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs, were obviously lower than that of polyoxyethylene castor oil and ethanol, demonstrating that these nanocarriers were much more cytotoxic against A875 cells because of continuous drug release. Moreover, the therapeutic effects of PTX-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs were superior to those of PLGA and PLGA-TPGS NPs, although the copolymer vehicles had similar molecular weights.
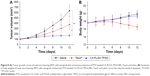
In vivo antitumor efficacy
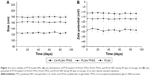
Based on the satisfactory cytotoxicity against A875 cells in vitro, CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs may be an eligible vehicle for MM treatment. In the present study, the antitumor effects of PTX-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs were also assessed in A875 cells-bearing nude mice. Figure 8A presents the 12-day tumor growth of mice injected with PTX-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs, polyoxyethylene castor oil and ethanol, and saline (control). Every 4 days, the mice were subjected to tail intravenous injection with PTX-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs and polyoxyethylene castor oil and ethanol for four consecutive cycles. Every 2 days, the tumor volume and body weight were recorded until the 12th day. As shown in Figure 8A, polyoxyethylene castor oil and ethanol and PTX-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs sharply slowed down the growth of tumors in mice compared with saline. Furthermore, the PTX-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs group had slower tumor growth than those of the other two groups. In short, PTX was effectively released from PTX-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs, with its bioactivity well retained. This is of great significance to clinical MM therapy.
In the development of novel drug delivery systems, it is imperative to reduce the adverse events of drug-loaded NPs. The systemic adverse effects on animals can be evaluated by measuring body weight changes. Figure 8B presents changes in the body weights of all nude mice. The polyoxyethylene castor oil and ethanol group significantly lost weight, whereas the mice injected with PTX-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs gained weight. Throughout the experiment, the mice treated by PTX-loaded NPs remained vigorous and healthy, but those treated by polyoxyethylene castor oil and ethanol exhibited weakened vitality, one of which even died. Hence, the mice injected with PTX-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs were less susceptible to side effects than the polyoxyethylene castor oil and ethanol-treated mice, which is consistent with the results of Zhao et al.31
Conclusion
PTX-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs for MM treatment were fabricated by a slightly modified method of nanoprecipitation. Their hydrodynamic size was measured by DLS as 125.6±5.3 nm, which was smaller than those of PLGA and PLGA-TPGS NPs. CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs exhibited higher drug LC and EE than those of PLGA and PLGA-TPGS NPs, with much faster drug release. In vitro cellular uptake study indicated that the NPs were internalized by A875 cells and that the cellular uptake efficiency of CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs was maximum. PTX-loaded CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs exerted markedly better antitumor effects in vitro and in vivo than those of polyoxyethylene castor oil and ethanol. In summary, PTX-loaded star-shaped CA-PLGA-TPGS NPs are promising vehicles for MM chemotherapy.
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong (2016A030313029), Scientific Plan Program of Guangdong (2014A020212038), Innovation Program of Shenzhen (JCYJ20150330102720122), and International Cooperation Foundation of Shenzhen (GJHZ20160301163138685).
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Zhang W, Shi Y, Chen Y, Hao J, Sha X, Fang X. The potential of Pluronic polymeric micelles encapsulated with paclitaxel for the treatment of melanoma using subcutaneous and pulmonary metastatic mice models. Biomaterials. 2011;32(25):5934–5944. | ||
Kundranda MN, Niu J. Albumin-bound paclitaxel in solid tumors: clinical development and future directions. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015;9:3767–3777. | ||
Ruttala HB, Ko YT. Liposomal co-delivery of curcumin and albumin/paclitaxel nanoparticle for enhanced synergistic antitumor efficacy. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015;128:419–426. | ||
Xiong W, Peng L, Chen H, Li Q. Surface modification of MPEG-b-PCL-based nanoparticles via oxidative self-polymerization of dopamine for malignant melanoma therapy. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015;10:2985–2996. | ||
Kannan V, Balabathula P, Thoma LA, Wood GC. Effect of sucrose as a lyoprotectant on the integrity of paclitaxel-loaded liposomes during lyophilization. J Liposome Res. 2015;25(4):270–278. | ||
Zhu H, Chen H, Zeng X, et al. Co-delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs with vitamin E TPGS by porous PLGA nanoparticles for enhanced chemotherapy against multi-drug resistance. Biomaterials. 2014;35(7):2391–2400. | ||
Balata GF, Essa EA, Shamardl HA, Zaidan SH, Abourehab MA. Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems as a tool to improve solubility and bioavailability of resveratrol. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016;10:117–128. | ||
Su Y, Liu H, Wang J, Lin B, Miao Y, Hu Z. Antimicrobial peptide lysozyme has the potential to promote mouse hair follicle growth in vitro. Acta Histochem. 2015;117(8):798–802. | ||
Zeng X, Tao W, Mei L, Huang L, Tan C, Feng SS. Cholic acid-functionalized nanoparticles of star-shaped PLGA-vitamin E TPGS copolymer for docetaxel delivery to cervical cancer. Biomaterials. 2013;34(25):6058–6067. | ||
Chang D, Gao Y, Wang L, et al. Polydopamine-based surface modification of mesoporous silica nanoparticles as pH-sensitive drug delivery vehicles for cancer therapy. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2016;463:279–287. | ||
Barba AA, Dalmoro A, d’Amore M, Vascello C, Lamberti G. Biocompatible nano-micro-particles by solvent evaporation from multiple emulsions technique. J Mater Sci. 2014;49(14):5160–5170. | ||
Kretzer IF, Maria DA, Guido MC, Contente TC, Maranhão RC. Simvastatin increases the antineoplastic actions of paclitaxel carried in lipid nanoemulsions in melanoma-bearing mice. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016;11:885–904. | ||
Battogtokh G, Ko YT. Self-assembled polymeric nanoparticle of PEGylated chitosan-ceramide conjugate for systemic delivery of paclitaxel. J Drug Target. 2014;22(9):813–821. | ||
Herranz-Blanco B, Shahbazi MA, Correia AR, et al. Targeted cancer therapy: pH-switch nanoprecipitation of polymeric nanoparticles for multimodal cancer targeting and intracellular triggered delivery of doxorubicin (Adv. Healthcare Mater. 15/2016). Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(15):1834. | ||
Razavi M, Nyamathulla S, Karimian H, Noordin MI. Novel swellable polymer of orchidaceae family for gastroretentive drug delivery of famotidine. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014;8:1315–1329. | ||
Totani M, Ando T, Terada K, et al. Utilization of star-shaped polymer architecture in the creation of high-density polymer brush coatings for the prevention of platelet and bacteria adhesion. Biomater Sci. 2014;2(9):1172–1185. | ||
Zeng X, Tao W, Mei L, Feng SS. Docetaxel-loaded nanoparticles of dendrimer-like amphiphilic copolymer for cancer therapy. J Control Release. 2015;213:e119. | ||
Cuong NV, Hsieh MF, Chen YT, Liau I. Doxorubicin-loaded nanosized micelles of a star-shaped poly(ε-caprolactone)-polyphosphoester block co-polymer for treatment of human breast cancer. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2011;22(11):1409–1426. | ||
Ma D, Liu ZH, Zheng QQ, et al. Star-shaped polymer consisting of a porphyrin core and poly(L-lysine) dendron arms: synthesis, drug delivery, and in vitro chemo/photodynamic therapy. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2013;34(6):548–552. | ||
Tao W, Zeng X, Zhang J, et al. Synthesis of cholic acid-core poly(ε-caprolactone-ran-lactide)-b-poly(ethylene glycol) 1000 random copolymer as a chemotherapeutic nanocarrier for liver cancer treatment. Biomater Sci. 2014;2(9):1262–1274. | ||
Byeon HJ, Kim I, Choi JS, Lee ES, Shin BS, Youn YS. PEGylated apoptotic protein-loaded PLGA microspheres for cancer therapy. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015;10:739–748. | ||
Gao N, Chen Z, Xiao X, et al. Surface modification of paclitaxel-loaded tri-block copolymer PLGA-b-PEG-b-PLGA nanoparticles with protamine for liver cancer therapy. J Nanopart Res. 2015;17(8):347. | ||
Assanhou AG, Li W, Zhang L, et al. Reversal of multidrug resistance by co-delivery of paclitaxel and lonidamine using a TPGS and hyaluronic acid dual-functionalized liposome for cancer treatment. Biomaterials. 2015;73:284–295. | ||
Su YS, Miao Y, Jiang JD, Liu H, Hu J, Hu ZQ. A simple and rapid model for hair-follicle regeneration in the nude mouse. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015;40(6):653–658. | ||
Zhu D, Tao W, Zhang H, et al. Docetaxel (DTX)-loaded polydopamine-modified TPGS-PLA nanoparticles as a targeted drug delivery system for the treatment of liver cancer. Acta Biomater. 2016;30:144–154. | ||
Janvier F, Zhu JX, Armstrong J, Meiselman HJ, Cloutier G. Effects of amphiphilic star-shaped poly(ethylene glycol) polymers with a cholic acid core on human red blood cell aggregation. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2013;18:100–107. | ||
Wu Y, Wang Z, Liu G, et al. Novel simvastatin-loaded nanoparticles based on cholic acid-core star-shaped PLGA for breast cancer treatment. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2015;11(7):1247–1260. | ||
Retsas S, Mohith A, Mackenzie H. Taxol and vinorelbine: a new active combination for disseminated malignant melanoma. Anticancer Drugs. 1996;7(2):161–165. | ||
Nakahara T, Tamaki Y, Tominaga N, et al. Novel amelanotic and melanotic cell lines NM78-AM and NM78-MM derived from a human oral malignant melanoma. Human Cell. 2010;23(1):15–25. | ||
Zeng X, Tao W, Wang Z, et al. Docetaxel-loaded nanoparticles of dendritic amphiphilic block copolymer H40-PLA-b-TPGS for cancer treatment. Part Part Syst Char. 2015;32(1):112–122. | ||
Zhao T, Chen H, Dong Y, et al. Paclitaxel-loaded poly(glycolide-co-ε-caprolactone)-b-D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 2000 succinate nanoparticles for lung cancer therapy. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:1947–1957. | ||
Wang T, Zhu D, Liu G, et al. DTX-loaded star-shaped TAPP-PLA-b-TPGS nanoparticles for cancer chemical and photodynamic combination therapy. RSC Adv. 2015;5:50617–50627. | ||
Huang L, Chen H, Zheng Y, et al. Nanoformulation of D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate-b-poly(ε-caprolactone-ran-glycolide) diblock copolymer for breast cancer therapy. Integr Biol (Camb). 2011;3(10):993–1002. | ||
Zhang J, Tao W, Chen Y, et al. Doxorubicin-loaded star-shaped copolymer PLGA-vitamin E TPGS nanoparticles for lung cancer therapy. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2015;26(4):165. | ||
Cao W, Zeng X, Liu G, et al. Porphine functionalized nanoparticles of star-shaped poly(ε-caprolactone)-b-D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate biodegradable copolymer for chemophotodynamic therapy on cervical cancer. Acta Biomater. 2015;26:145–158. | ||
Tao W, Zeng X, Wu J, et al. Polydopamine-based surface modification of novel nanoparticle-aptamer bioconjugates for in vivo breast cancer targeting and enhanced therapeutic effects. Theranostics. 2016;6(4):470–484. | ||
Zhang J, Zhao C, Liu Y, Cao L, Wu Y, Huang Q. Size-dependent effect of prochloraz-loaded mPEG-PLGA micro- and nanoparticles. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2016;16(6):6231–6237. | ||
Wang H, Jia Y, Hu W, Jiang H, Zhang J, Zhang L. Effect of preparation conditions on the size and encapsulation properties of mPEG-PLGA nanoparticles simultaneously loaded with vincristine sulfate and curcumin. Pharm Dev Technol. 2013;18(3):694–700. | ||
Ngoune R, Peters A, von Elverfeldt D, Winkler K, Pütz G. Accumulating nanoparticles by EPR: a route of no return. J Control Release. 2016;238:58–70. | ||
Acharya S, Sahoo SK. PLGA nanoparticles containing various anticancer agents and tumour delivery by EPR effect. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011;63(3):170–183. | ||
Guan Q, Sun S, Li X, et al. Preparation, in vitro and in vivo evaluation of mPEG-PLGA nanoparticles co-loaded with syringopicroside and hydroxytyrosol. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2016;27(2):24. | ||
Lian D, Chen Y, Xu G, et al. Delivery of siRNA targeting HIF-1α loaded chitosan modified D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate-b-poly(ε-caprolactone-ran-glycolide) nanoparticles into nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell to improve the therapeutic efficacy of cisplatin. RSC Adv. 2016;6(44):37740–37749. | ||
Baimark Y. Preparation of surfactant-free linear and star-shaped poly (L-lactide)-b-methoxy polyethylene glycol nanoparticles for drug delivery. J Appl Sci. 2012;12(3):263–270. | ||
Zhu Z, Li Y, Li X, et al. Paclitaxel-loaded poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone)-b-poly(epsilon-caprolactone) nanoparticles: preparation and antitumor activity in vivo. J Control Release. 2010;142(3):438–446. | ||
Loureiro JA, Gomes B, Fricker G, Coelho MA, Rocha S, Pereira MC. Cellular uptake of PLGA nanoparticles targeted with anti-amyloid and anti-transferrin receptor antibodies for Alzheimer’s disease treatment. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016;145:8–13. | ||
Korang-Yeboah M, Gorantla Y, Paulos SA, Sharma P, Chaudhary J, Palaniappan R. Polycaprolactone/maltodextrin nanocarrier for intracellular drug delivery: formulation, uptake mechanism, internalization kinetics, and subcellular localization. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015;10:4763–4781. | ||
Muthu MS, Kutty RV, Luo Z, Xie J, Feng SS. Theranostic vitamin E TPGS micelles of transferrin conjugation for targeted co-delivery of docetaxel and ultra bright gold nanoclusters. Biomaterials. 2015;39:234–248. | ||
Ishak RA, Osman R. Lecithin/TPGS-based spray-dried self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems: in vitro pulmonary deposition and cytotoxicity. Int J Pharm. 2015;485(1–2):249–260. |
 © 2017 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2017 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.