Back to Journals » Drug Design, Development and Therapy » Volume 11
Intracellular trafficking of new anticancer therapeutics: antibody–drug conjugates
Authors Kalim M, Chen J, Wang S, Lin C, Ullah S, Liang K, Ding Q, Chen S , Zhan JB
Received 24 February 2017
Accepted for publication 31 May 2017
Published 2 August 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 2265—2276
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S135571
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Manfred Ogris
Muhammad Kalim,1 Jie Chen,1 Shenghao Wang,1 Caiyao Lin,1 Saif Ullah,1 Keying Liang,1 Qian Ding,1 Shuqing Chen,2 Jinbiao Zhan1
1Department of Biochemistry and Genetics, School of Medicine, 2Department of Pharmaceutical Analysis, College of Pharmaceutical Science, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, People’s Republic of China
Abstract: Antibody–drug conjugate (ADC) is a milestone in targeted cancer therapy that comprises of monoclonal antibodies chemically linked to cytotoxic drugs. Internalization of ADC takes place via clathrin-mediated endocytosis, caveolae-mediated endocytosis, and pinocytosis. Conjugation strategies, endocytosis and intracellular trafficking optimization, linkers, and drugs chemistry present a great challenge for researchers to eradicate tumor cells successfully. This inventiveness of endocytosis and intracellular trafficking has given considerable momentum recently to develop specific antibodies and ADCs to treat cancer cells. It is significantly advantageous to emphasize the endocytosis and intracellular trafficking pathways efficiently and to design potent engineered conjugates and biological entities to boost efficient therapies enormously for cancer treatment. Current studies illustrate endocytosis and intracellular trafficking of ADC, protein, and linker strategies in unloading and also concisely evaluate practically applicable ADCs.
Keywords: antibody–drug conjugate, antibody, endocytosis, intracellular trafficking, clathrin
Introduction
Antibody–drug conjugate (ADC) is a milestone novel class of therapeutic agents in targeted cancer therapy. ADCs combine the antigenic specificity of an antibody with the assistance of potent tumorigenic effects of cytotoxic compounds. Traditionally, chemotherapeutic procedures have for quite some time been in practice to help distinctive tumors treatment. However, targeted cancer therapy gained major interest in anticancer therapeutics that convey highly cytotoxic drugs directly to a tumor site. This approach of antibody-mediated drug delivery elevates maximum tolerance and has gained a considerable momentum in cancer therapy with the recent approval of two ADCs by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), Kadcyla and Adcetris, along with >40 conjugates in clinical trials.1 Kadcyla, comprised of monoclonal antibody (mAb), Herceptin, conjugated by means of lysine residue to DM1 that hinders cell division.2 Adcetris comprised the cAC10, a human–mouse chimeric antibody, through monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE), a cysteine residue that inhibits tubulin polymerization.3 These conjugates provide a unique opening of studying the mechanism of ADC action with tumor biology and cancer indication in drug development.
Cells constantly internalize extracellular molecules to lumen and degrade through complex enzymatic pathways. This inventiveness of endocytosis and intracellular trafficking has given considerable momentum recently to develop specific antibodies and ADCs to treat cancer cells. It is profitable to accentuate endocytosis and intracellular trafficking pathways successfully for ADC design. This evolving approach of targeted therapy was because of the Ehrlich concept of “magic bullet”.4,5 Further maturity of hybridoma technology by Kohler and Milstein6 in 1975 and recent advancements in antibody engineering, significantly enlighten the field of ADCs production.
Designing of ADC occurs in such a way that mimics toxicity of drugs and augments the antitumor activity of potent payloads, by inhibiting tubulin (eg, auristatin, maytansinoids), double-stranded DNA break, or minor groove binder/alkylators of DNA (eg, ducomycin)7,8 as shown in Table 1. These drugs are mostly derived from the natural source that triggers cell cycle arrest followed by apoptosis. Naito et al9 reported morphological changes before cell arrest at a G2/M phase in CD33-positive acute myeloid cells by using calicheamicin-676 drug. Despite numerous reports on drugs cytotoxicity, the intracellular trafficking studies of ADCs are still unclear. Current studies summarize knowledge of endocytosis and trafficking mechanism of ADCs with the current approach of their action.
  | Table 1 Different compounds and their targets used in ADCs optimization |
Endocytosis and trafficking of ADC
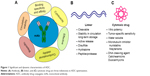
ADC comprised of an mAb, linker, and cytotoxic payloads. The antibody counterpart binds specifically with target antigen on the tumor cell surface. Different features of antibody enhance optimization of ADC as summarized in Figure 1. Physical and chemical properties of these conjugates are briefly studied in literature but degradation and intracellular trafficking properties of ADC are relatively unknown.10 Successful optimization and development of ADC largely depend on its building units, tumor biology, antigen presentation, binding site chemistry, linker stability and its types, payload potency of loading drug, and drug–antibody ratio (DAR).11–13 Ideally, ADC must have selectivity, effective lytic nature, and ability to release its guided drug in active form to deliver optimum potency in killing cancerous cells. Antigen expression level is a key and dynamic parameter for initiation of putative results, as it will determine how much ADC will bind to the cancerous cell and internalize. Low expression level limits the binding and inadequate endocytosis, thereby restricting efficient delivery of ADC-loaded drug.14
Endocytosis can be manifested by different internalization routes such as clathrin-mediated, caveolae-mediated, and clathrin–caveolin-independent endocytosis15 (Figure 2), but much work has been focused on clathrin-mediated endocytosis (CME). The first two are receptor-mediated endocytosis, while the latter one is receptor-independent endocytosis. High binding interaction of antigen–antibody results in accumulation of more ADCs on the membrane surface. It is hard to distinguish among these pathways as some molecules are not restricted to a single pathway. CME was reported as the central route adopted by various ADCs. Trafficking of ADCs occurs with the aid of adaptor protein (AP2), dynamin, epsin, and phosphatidylinositol (4,5) bi-phosphate (PIP2).16
Precise ligands accomplished binding activity of antigen and antibody on tumor surface more actively. These ligands include protein molecules, small molecular receptors, antibodies, peptides and proteins, and carbohydrates.17–19 The most prominent among these are target-specific mAb fragments,20 transferrin,21 peptides,22 and folate.23 Endocytosis of tiny, unionized hydrophobic molecules occurs passively, while large, charged polar, or conjugated molecules are carried inside in the form of complex coordinated pathways by utilization of energy-rich sources.24–26 The most prominent recruitment pathway reported for transportation is clathrin-mediated by the formation of clathrin-coated vesicles (CCVs) or membrane invagination coats that cover 2% total area.27,28 The other less prominent pathways including caveolin-mediated,29 clathrin–caveolin-independent,30 and cholesterol/macropinocytosis-mediated are also reported in literature.31 Mayor et al also reported that other small caveolae vesicles contain lipid microdomain involved in different transduction events with lack of clathrin protein function.32
After passing membrane barriers, conjugate marched toward endosomes and emptied there with indication of prominent markers, ie, Rab 5, Rab 7 and Rab 11.33,34 Early endosome becomes late endosome by losing protein which plays the vital role in recycling. The decrease in pH occurs by utilization of proton pump.35 Late endosome fuses with lysosome resulting in pH decrease. ADCs’ degradation occurs due to acidic environment and enzymatic activities of lysosome.36,37
Recycling of membrane proteins and lipid occurs through the complex process by utilization of Rab proteins/GTPases to regulate mechanism of endocytosis and proteins balance at the membrane surface.33,34,38 CME and caveolin-mediated endocytosis utilized Rab 11 protein to recycle back ADC.34 Nexinprotein performs this recycling activity from the endosome toward the membrane surface.33,39 Time optimization of recurring changes after 1 hour of endocytosis. The ADC-carrying payload reaches the lysosome and releases the drug due to a breakage of a linker. The free payloads reach the targeted area resulting in a disruption of tubules or cell cycle arrest, which ultimately results in apoptosis of the cancer cell as shown in Figure 3.
Protein machinery in endocytosis
ADCs travel inside the cell via the bucket of clathrin-coated pits, become uncoated by the Hsp70 protein complex, and fuse with early endosomes to acquire the endosomal–lysosomal trafficking.39 ATP-dependent proton pump exists in endosome and lysosome and changes the pH of early endosomes (6.0–6.2), late endosomes (5.5), and lysosomes (4.5–5.0).40 The acidification results in dissociation of ligands, such as insulin, epidermal growth factor (EGF), and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) from receptors in early endosomes, and vacant receptors get into surface membrane via recycling compartment of narrow tubules. Several kinds of literature reported an alternative set of protein machinery that led to the formation of the same morphological structures as in the case of endocytic tubes and caveolae.41 A progress report conducted by Sabharanjak et al42 in Satyajit Mayor (National Center for Bio Science, Bangalore) characterized clathrin-, dynamin-, and caveolae-independent internalization pathways for transportation of glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored proteins and an addition of early endosomal compartments (GEEC) as an intermediate protein. Chadda et al43 also reported that cholesterol-dependent recruitment and active Cdc42 stabilization on the plasma surface membrane initiate the pinocytic pathway that led localized actin polymerization. Cdc42 is controlled by Arf1, such as ARH-GAP10 and small GTPases, to regulate endocytosis. It was also reported that CME required adaptor proteins such as AP2, EPS-15, and clathrin triskelion for the formation of clathrin-coated pits at the membrane surface.44,45 Several pathways share the same requirements for dynamin and Arf6 (ADP-ribosylation factor). Donaldson46 also reported multiple roles of Arf6 in structure, signals, and membrane trafficking of a cell. Caveolae are generated by addition of a primary protein, caveolin, which is a specialized form of lipid rafts.47 Caveolae become caveosome, a caveolin-enriched organelle, processed further by the endosome. Dynamin, protein kinase C, and Src kinases regulate the activation further.48 Clathrin- and caveolin-independent endocytosis is mediated by different protein machineries such as dynamin,49 CDC42, ARF150 and ARF6,51 tyrosine kinases,52 RacGTPases, and USP6NL.53 These studies show a broad framework of internalization kinetics and its impact on provision of ADC to entire tumor mass.16
Linker strategy and drug release
Endocytosis and trafficking of ADCs by tumor cells are typically sorted by endosomal/lysosomal pathways. Many studies reported the active release of drugs in lysosome either by cleavage of the linker or by antibody backbone degradation. This release of drugs largely depends on linker design and its chemistry. Generally, linkers must have high stability in circulation and the ability to release a drug in the targeted regions of tumor cells. Currently four different types of linkers in use are broadly divided into cleavable and non-cleavable linkers.54 Acid-labile hydrazine linkers, peptide linkers, and disulfide linkers are included in cleavable linkers. Acid-labile hydrazine linkers are cleaved in the lysosome compartment as a result of low pH. Unfortunately, acid labile hydrazine linkers have established off-target release in clinical examination.55,56 Peptide linkers conceivably selective for cleavage in lysosome by activity of cathepsin B.57 Unlike the hydrazine linker, peptide linkers show high serum stability and improved antitumor effects of ADC. Phe-Lys and Val-Cit are physiological stable peptide linkers but hydrolyze rapidly in the presence of enzymes.58 The longer half-life of peptide linkers was recorded as compared to other cleavable linkers.59 Disulfide linkers also raise questions of non-specific cytotoxicity and instability and off-target release of drugs.
Recent advancement in linker technology has been covered by non-cleavable linkers. The chemical bond of non-cleavable linkers is highly stable in circulation and inside the cell. The release of an active potent drug inside a tumor cell is realized by degradation of antibodies in the lysosome.57 More importantly, the recently approved ADC, trastuzumab-DM1 (Kadcycla), also utilized non-cleavable linkers to treat metastatic breast cancer. More effective studies were also reported in vivo analysis by using non-cleavable linkers compared to their disulfide counterpart.60,61
The linker is one of the most vital components of ADCs that anchor cytotoxic drugs to an antibody. It must be stable in circulation and potent in effective drug release inside the cell to acquire maximal therapeutic windows.62 Once internalization was confirmed, it should be cleavable by enzymatic action or acidic change in lysosomes. Four different types of linkers were reported including disulfide and peptide base and acid cleavable and non-cleavable linkers. Three common strategies have been reported for a release of efficient drugs, ie, pH sensitivity, protease sensitivity, and glutathione sensitivity. The protease of lysosome recognizes a specific peptide sequence in the linker.58 Lower pH of the endosome (5.0–6.0) and lysosome (4.8), as compared to cytosolic pH (7.4), elicits hydrolysis of a linker acid-labile group as in hydrazone. The third strategy of drug release exploits the higher ratio of intracellular glutathione as compared to plasma.16
Early development of ADC was conducted by utilization of the hydrazine linker, but a major downfall in its productivity, it undergoes spontaneous cleavage compared to disulfide and peptide linkers, was reported.63 These linkers are enzymatic in hydrolysis and can be selected for preferential expression, minimizing the spontaneous release of drugs in circulation.56,64 Peptide linkers exhibit improved antitumor activity and stability, demonstrating bystander cytotoxicity.65 Cytotoxic drugs endure modification by disulfide reduction to methylation and have access to neighboring cells, resulting in lyses.66 This mechanism is very fruitful to eradicate the tumor cells that do not express the targeted antigen within the tumor cell.67,68
Efficacy of antibody and linker technology can be elevated by making changes in binding sites to confer consistency of ADC.69,70 Lyon et al71 introduce a novel concept of maleimide linkers that catalyze their own thiosuccinimide ring hydrolysis, prevent drug loss, and develop a high stable ADC. King et al also reported a novel series of branched hydrazone linkers and made immune conjugates of mAbs BR96 and doxorubicin that were stable at pH 7. These conjugates release DOX molecules at lysosomal pH. They concluded a possible outcome of using a reduced amount of mAb load via branched methodology to acquire desired cytotoxic activity.72 Recently, specificity of HER2 antibodies and enhanced activity of doxorubicin-labeled liposomes against cancer were also reported by our research group.73 However, poor circulation stability of hydrazine linker was also recorded as in the case of gemtuzumab ozogamicin (GO), resulting in low clinical efficacy and safety.74
On the other hand, premature release in circulation is being prevented by utilizing non-cleavable linkers.56 Non-cleavable linkers result in enzymatic degradation of ADC in lysosome and accurate release of drug with their conjugated amino acid lysine or cysteine.67 Active research by chemists to develop new linkers and discover novel potent effector molecules that suit ADC is currently being investigated.
Co-localization of ADC
Properties of cell surface proteins targeted by ADCs have not been fully exploited, of which the rate of internalization and the route of intracellular trafficking are of particular importance. Targeted delivery of anticancer drugs to tumor cells using mAb against cell surface receptors is an emerging therapeutic strategy. The rate of internalization was compared between ADCs with their antibodies, and similar effects were found as in the case of anti-CD30 (cAC10) and the antimitotic agent, auristatin.75 Similarly, it was also reported that conjugate of anti-MUC-1 in breast and ovarian cancer xenografts, with DNA minor groove binder, calicheamicin, have the same endocytosis rate.76 In contrast, some auristatin conjugates efficiently internalized as compared to their antibody moieties. Ingle et al reported the efficiency of both CD19 and CD21, B cell surface receptors, and found that even at higher expressions of CD21 receptors, the ADC is unable to internalize. But the absence of CD21 results in efficient endocytosis of anti-CD19 ADC molecules. These receptor molecules develop a complex on B cell surfaces that mimics internalization of CD19 by CD21.77 Similarly, selective binding of antibodies contributes enormously in elevated endocytosis and potent toxicity of ADC. It was also recorded that there are no set parameters with optimal binding/internalization affinity, and maximum correlation of ADC and antibodies as strong binding results in faster internalization and efficient ADC trafficking.55 These reports attract consideration extensively to acknowledge molecular mechanism of receptor mediated endocytosis and particular cell target properties while designing ADC.
Law et al reported two different co-localization studies of anti-CD70 antibody and anti-CD20 with the anti-tubulin auristatin conjugate. Anti-CD70 conjugate followed CME and trafficked to the lysosome for payload release. The released payload, by the enzymatic activity of lysosomes, results in microtubule channels disruption and G2/M cell cycle arrest in metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC).78 Anti-CD20 antibody and auristatin conjugate was carried by both CME and caveolin together. They used two anti-CD20 conjugates, rituximab-vcMMAE and 1F5-vcMMAE, to selectively target B-lymphoma cell lines, trafficked to a cell. The enzymatic activity of lysosome results in linker destruction, releasing the payload and eventually caused G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis.79 One pre-clinical study was conducted previously by our research group by targeting CD20-positive B lymphoid malignancies, using ofatumumab auristatin conjugate ofatumumab-valine citrullin-monomethyl auristatin (OFA-vcMMAE), resulting in complete inhibition of CD20-positive cells and exhibited enhanced activity as compared to unconjugated OFA.80 Recently, Pan et al recorded conjugation of TRAIL (Tumor-Inducing Factor-Related Apoptosis Inducing Ligands) with MMAE for efficient drug delivery to tumor cell.81
Co-localization of auristatin and anti-melanotransferrin conjugate was also reported in melanoma-sensitive cell lines (SK-MEL5 and A2058) and -resistant cell lines (L49-vcMMAE).82 In sensitive cell lines, conjugate followed CME pathways for its endocytosis, while resistant cell lines utilized caveolin-II of caveolae to colonize the conjugate. One study revealed that inhibition of anti-CD30–trastuzumab conjugate occurs by clathrin inhibitor and internalized by caveolae-mediated endocytosis to cell.75 Acidic environment of endosome–lysosome slows down the trafficking of anti-CD30, and its trastuzumab conjugate was also reported.75,83 Higher concentration of ADCs in surrounding medium facilitates its endocytosis silently through the membrane surface as was reported in GO that non-specifically inhibits the CD33-negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells, while the lower concentration of GO in surrounding medium results in triggering of CME pathway to take ADCs into CD33-positive malignant cells.84 The pinocytosis neither induces S-G2/M cell arrest nor apoptosis but results from necrotic lyses.85 However, the exact and precise quantification of ADC is still a topic of debate. These reports reveal different routes of ADC induction to the cell from surroundings and its trafficking to the targeted region of a cancer cell.
ADCs in clinical use and their mechanism studies
More than 100 different ADCs are in different stages of clinical evaluation, majority carrying microtubule disrupting loads (maytansinoids/auristatins). Subsequent paragraphs describe detailed assessment of different ADCs and their intracellular trafficking. Only three ADCs obtained approval by FDA. Two of them employ effective tubulin-disrupting agents, either MMAE or maytansine derivatives (DM1), and the other one utilizes calicheamicin DNA strand-breaking agent as shown in Table 2. The trafficking studies of these drugs are still unknown. One quantitative model study is available in current literature that describes cellular processing, trafficking mechanism, internalization rate, proteolytic degradation, and binding mechanism of trastuzumab–maytansinoid conjugate.86
GO (Mylotarg)
GO was the first ADC that gained marketing approval from FDA in 2000. GO (Mylotarg) made conjugation with CD33-positive cells by anti-CD30 counterpart and released its payload calicheamicin compound to cell lumen due to breakage of hydrazone linker. GO was subsequently withdrawn from the market in 2010 due to its toxicity and insufficient clinical results.74 This conjugate got access to the cell through antigen-independent manner and was internalized from surrounding medium by pinocytosis and destroyed cells by necrotic lyses.85 CME was also reported of GO, resulting in S-G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of CD33+ acute myeloid leukemia cell.84
Prostate specific membrane antigen conjugate valine citrullin-monomethyl auristatin (PSMA-vcMMAE)
Prostate specific membrane antigen conjugate valine citrullin-monomethyl auristatin (PSMA-vcMMAE) is composed of fully human anti-PSMA mAb, conjugated with MMAE through cleavable valine–citrulline linker.87 PSMA-vcMMAE is the second evaluated ADC in clinical studies, while the first one, MLN2704, was restricted in 2008 due to less efficacy and limited peripheral neuro-therapy.88 Internalization of this conjugate takes place through antigen-mediated pathways and trafficking to lysosome. Releases of MMAE synthetic dolastatin 10 analogs have taken place by cathepsin action in lysosome that results from inhibition of tubulin polymerization in prostatic cancer cells.87 Gao et al reported Yajie prostate specific membrane antigen (YPSMA)-1-modified micelles that exhibited a rapid release behavior at endosomal/lysosomal pH. They introduced for the first time that both lysosome and endosomal escape exist for pH-sensitive micelles. The modified micelles enhance the cytotoxicity of the drug due to increase uptake of PSMA-positive prostate cancer cells. One possible approach of pH sensitivity to deliver drugs efficiently to PSMA-positive cells was also investigated.89
Inotuzumab ozogamicin (CMC-544)
CMC-544 is a second NAc-γ calicheamicin–conjugate that links via hydrazone linker and targets CD22 on B-cell malignancies. This ADC was found highly constant, effective, dynamic, and precise both in vitro and in vivo. Phase III trials are being reported in various clinical trials as in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), but due to lack of improvement and constancy in overall cell, it is withdrawn from this trial in CD22-positive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.90,91
Brenduximab vedotin (Adcetris, SGN-35)
Adcetris is a conjugate of synthetic anti-tubulin agent MMAE (dolstatin-10) and chimeric CD30 antibody (cAC10) linked by valine–citrulline dipeptide linker.92 It ties with CD30-positive cells and internalizes though CME, trafficked to the lysosome where discharge its conveying payload. MMAE binds with tubulin and inhibits its polymerization through G2/M phase arrest in CD30 lymphoma cells.75 Monotherapy of unconjugated anti-CD30 antibody (cAC10) and drug conjugate MMAE–brenduximab vedotin was investigated separately to examine the response rate. Insufficient 8% response rate was recorded by using single antibody treatment, while complete eradication response was calculated by using ADC, prompted sharp approval by FDA in 2011.93,94
Ado-trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1)
T-DM1 comprised trastuzumab antibody conjugated with maytansinoid by means of lysine by utilizing non-cleavable thioether linker, demonstrating promising viability against HER2-positive metastatic cancer.95 T-DM1 is internalized through receptor-mediated endocytosis and trafficked to lysosome to release its carrying drug. This intracellular release of maytansinoid prevents microtubule assembly and polymerization and disrupts HER3/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and Fcγ receptor-mediated engagement of effector immune cells directed to mitotic arrest, apoptosis, and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity.96,97 Pre-clinical studies of T-DM1 demonstrate potent anti-proliferative activity both in vitro and in vivo as compared to trastuzumab alone. More interestingly, it was found effective against trastuzumab-resistant cells and also xenografts models.95 Other studies indicate that T-DM1 also potentiates antibodies activity (such as pertuzumab and B20-4.1), chemotherapeutic agents (such as carboplatin and 5-fluorouracil), and kinase inhibitor molecules (such as laptinib and PI3 kinase inhibitor) against HER-2 tumor cells.98 These data led to Ado-trastuzumab emtansine being approved in 2013 by FDA to treat HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer patients.99
Indatuximab ravtansine (BT062)
Indatuximab ravtansine (Biotest AG Dreieich, Germany) is composed of anti-CD138 mAb (nBT062) conjugated through disulfide linker with maytansinoid DM4 toxin. CD138 was highly expressed in solid tumor and specifically on multiple myeloma cells. Internalization of indatuximab ravtansine occurs and processed further to release DM4 by the proteolytic activity of lysosome. DM4 inhibits tubulin polymerization and subsequently cell cycle arrest and tumor death.95,96
Maytansinoid conjugates
This conjugate includes different ADCs such as IMGN388,100 SAR3419,101 BIIB015,102 and nBT062103 that utilized maytansinoid disulfide cleavable linker. These conjugates are internalized through receptor-mediated endocytosis and trafficked to lysosome to release their active drugs. The maytansinoid conjugate binds to tubulin, disrupts the microtubule, and led to inhibition of cell division and ultimately result in cell death.104 The clinical trials of BIIB015 in 2010 and IMGN 388 in 2011 were prematurely stopped in Phase I studies due to their limited scope and insufficient efficacy as shown in Table 2.
Lorvotuzumab mertansine
Lorvotuzumab mertansine (BB-10901, hu N901-DM1, or IMGN901), a humanized version of the N901 antibody linked via a disulfide linker to DM1, targeting CD56 in most small cell lung cancers (SCLCs) was reported by Whiteman et al105 in detail. They also presented the potent activity of lorvotuzumab mertansine in the combination of different agents to activate different killing pathways or sensitization of one agent killing by other. DM1, synthetic derivative of maytansinioid,106 is a potent anti-microtubule cytotoxic agent that binds to tubulin at a vinca alkaloid binding site that leads to inhibition of tubule assembly and proliferation, resulting in cell death.107
Glembatumumab vedotin (CDX-011)
CDX-011 comprised of human IgG2 anti-gpNMB antibody – osteoactivin – and MMAE linked via cleavable valine–citrulline protease sensitive linker. Phase I/II study of this ADC was undertaken.108,109 Vaklavas and Forero reported multiple steps that involved from endocytosis/trafficking to final release of this drug. Drug acquired access to a cell through receptor-mediated endocytosis followed by lysosomal degradation of proteases, targeting mitotic spindles in metastatic breast cancer cells.110 At present, CDX-011 is in the premature stage in the clinical evaluation of melanoma and breast cancer.
Conclusion and future prospects
Antibody-based cancer treatment has been intensively studied and is well known that it has direct or indirect effects on a cancer cell. The potency is shown by these conjugates and different action performed by signal inhibition, limiting proliferation, apoptosis induction, cytotoxic drugs or radiation delivery, induction, and activation of immune cells and cytotoxicity, cell inhibition, or payload delivering to targeted area.111 Recent approval of Adcetris and Kadcyla realized the potential benefits of ADCs. Our current review attempts to describe the developmental progress of ADC optimization, evaluation of extensive and better knowledge-related endocytosis, intracellular trafficking, and targeted action on tumor cells. Endocytosis and trafficking of ADCs performed the most critical role in affecting the target cells. Past investigations conclude that ADCs recognize their particular focuses on the cell surface, tie with the antigen, and intervene endocytosis that tile exceptional knowledge in ADCs viability. Protein machinery, lysosomal lumen nature, and linker procedure hold an imperative part in drug discharge that transported ADC to its focused area. Biologists are struggling to concentrate on the cell surface antigen, for specific attachment and further intracellular trafficking of ADCs. Recent studies indicate that an engineered antibody can be utilized to exploit the endocytosis pathway that gives a substantial inclination for future studies and better design of ADC. The experimental analysis provides knowledge of the intracellular process in greater aspects, dissolves recent divergences, and enhances our ability to select novel and efficient targets for antibody attachment and internalization of ADC. Additional fundamental research studies of tumor cell toxicity, target receptor modification, and cascade signaling analysis of receptor modulation by antibodies are needed to enrich the field of cancer immunotherapy and design better treatments for tumor therapy.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (grant no 81430081) and Special Program from the Department of Science and Technology, Zhejiang Province (grant no 009C13041), People’s Republic of China.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Polakis P. Antibody drug conjugates for cancer therapy. Pharmacol Rev. 2016;68(1):3–19. | ||
Kim MT, Chen Y, Marhoul J, Jacobson F. Statistical modeling of the drug load distribution on trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcyla), a lysine-linked antibody drug conjugate. Bioconjug Chem. 2014;25(7):1223–1232. | ||
Katz J, Janik JE, Younes A. Brentuximab vedotin (SGN-35). Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(20):6428–6436. | ||
Bechhold H, Ehrlich P. Connections between chemical constitution and desinfection effect. Article on the study of “inner antisepsis”. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1906;47(2/3):173–199. | ||
Ehrlich P. Address in pathology, on chemiotherapy: delivered before the Seventeenth International Congress of Medicine. Br Med J. 1913; 2(2746):353–359. | ||
Kohler G, Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity (Reprinted from Nature, vol 256, 1975). J Immunol. 2005;174(5):2453–2455. | ||
Jordan MA, Wilson L. Microtubules as a target for anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4(4):253–265. | ||
Perego P, Corna E, De Cesare M, et al. Role of apoptosis and apoptosis-related genes in cellular response and antitumor efficacy of anthracyclines. Curr Med Chem. 2001;8(1):31–37. | ||
Naito K, Takeshita A, Shigeno K, et al. Calicheamicin-conjugated humanized anti-CD33 monoclonal antibody (gemtuzumab ozogamicin, CMA-676) shows cytocidal effect on CD33-positive leukemia cell lines, but is inactive on P-glycoprotein-expressing sublines. Leukemia. 2000;14(8):1436–1443. | ||
Ross PL, Wolfe JL. Physical and chemical stability of antibody drug conjugates: current status. J Pharm Sci. 2016;105(2):391–397. | ||
McCombs JR, Owen SC. Antibody drug conjugates: design and selection of linker, payload and conjugation chemistry. AAPS J. 2015; 17(2):339–351. | ||
Thomas A, Teicher BA, Hassan RT. Antibody-drug conjugates for cancer therapy. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(6):E254–E262. | ||
Sievers EL, Senter PD. Antibody-drug conjugates in cancer therapy. Annu Rev Med. 2013;64:15–29. | ||
Bander NH. Antibody-drug conjugate target selection: critical factors. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1045:29–40. | ||
Conner SD, Schmid SL. Regulated portals of entry into the cell. Nature. 2003;422(6927):37–44. | ||
Ritchie M, Tchistiakova L, Scott N. Implications of receptor-mediated endocytosis and intracellular trafficking dynamics in the development of antibody drug conjugates. MAbs. 2013;5(1):13–21. | ||
Li Y, Wang J, Wientjes MG, Au JLS. Delivery of nanomedicines to extracellular and intracellular compartments of a solid tumor. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012;64(1):29–39. | ||
Wang J, Lu Z, Wientjes MG, Au JLS. Delivery of siRNA therapeutics: Barriers and Carriers. AAPS J. 2010;12(4):492–503. | ||
Wang J, Lu Z, Gao Y, Wientjes MG, Au JLS. Improving delivery and efficacy of nanomedicines in solid tumors: role of tumor priming. Nanomedicine. 2011;6(9):1605–1620. | ||
Matsudaira H, Asakura T, Aoki K, et al. Target chemotherapy of anti-CD147 antibody-labeled liposome encapsulated GSH-DXR conjugate on CD147 highly expressed carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 2010;36(1):77–83. | ||
Hatakeyama H, Akita H, Maruyama K, Suhara T, Harashima H. Factors governing the in vivo tissue uptake of transferrin-coupled polyethylene glycol liposomes in vivo. Int J Pharm. 2004;281(1–2):25–33. | ||
Mamot C, Drummond DC, Greiser U, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-targeted immunoliposomes mediate specific and efficient drug delivery to EGFR- and EGFRvIII-overexpressing tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2003;63(12):3154–3161. | ||
Xiang G, Wu J, Lu Y, Liu Z, Lee RJ. Synthesis and evaluation of a novel ligand for folate-mediated targeting liposomes. Int J Pharm. 2008; 356(1–2):29–36. | ||
Khalil IA, Kogure K, Akita H, Harashima H. Uptake pathways and subsequent intracellular trafficking in nonviral gene delivery. Pharmacol Rev. 2006;58(1):32–45. | ||
Huotari J, Helenius A. Endosome maturation. Embo J. 2011;30(17):3481–3500. | ||
Mathivanan S, Ji H, Simpson RJ. Exosomes: extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. J Proteomics. 2010;73(10):1907–1920. | ||
Robinson MS. Forty years of clathrin-coated vesicles. Traffic. 2015;16(12):1210–1238. | ||
Bitsikas V, Correa IR Jr, Nichols BJ. Clathrin-independent pathways do not contribute significantly to endocytic flux. Elife. 2014;3:e03970. | ||
Parton RG. Caveolae meet endosomes: a stable relationship? Dev Cell. 2004;7(4):458–460. | ||
Doherty GJ, McMahon HT. Mechanisms of endocytosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 2009;78:857–902. | ||
Mercer J, Helenius A. Virus entry by macropinocytosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11(5):510–520. | ||
Mayor S, Parton RG, Donaldson JG. Clathrin-independent pathways of endocytosis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014;6(6):a016758. | ||
Scita G, Di Fiore PP. The endocytic matrix. Nature. 2010;463(7280):464–473. | ||
Zhang J, Zhang X, Liu G, et al. Intracellular trafficking network of protein nanocapsules: endocytosis, exocytosis and autophagy. Theranostics. 2016;6(12):2099–2113. | ||
Anitei M, Hoflack B. Bridging membrane and cytoskeleton dynamics in the secretory and endocytic pathways. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;14(1): 11–19. | ||
Rusten TE, Vaccari T, Stenmark H. Shaping development with ESCRTs. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;14(1):38–45. | ||
Coppola S, Cardarelli F, Pozzi D, et al. The role of cytoskeleton networks on lipid-mediated delivery of DNA. Ther Deliv. 2013;4(2):191–202. | ||
Grant BD, Donaldson JG. Pathways and mechanisms of endocytic recycling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10(9):597–608. | ||
Mukherjee S, Ghosh RN, Maxfield FR. Endocytosis. Physiol Rev. 1997;77(3):759–803. | ||
Weisz OA. Acidification and protein traffic. Int Rev Cytol. 2003;226:259–319. | ||
Frick M, Bright NA, Riento K, Bray A, Merrified C, Nichols BJ. Coassembly of flotillins induces formation of membrane microdomains, membrane curvature, and vesicle budding. Current Biol. 2007;17(13):1151–1156. | ||
Sabharanjak S, Sharma P, Parton RG, Mayor S. GPI-anchored proteins are delivered to recycling endosomes via a distinct cdc42-regulated, clathrin-independent pinocytic pathway. Dev Cell. 2002;2(4):411–423. | ||
Chadda R, Howes MT, Plowman SJ, Hancock JF, Parton RG, Mayor S. Cholesterol-sensitive Cdc42 activation regulates actin polymerization for endocytosis via the GEEC pathway. Traffic. 2007;8(6):702–717. | ||
Schmid EM, McMahon HT. Integrating molecular and network biology to decode endocytosis. Nature. 2007;448(7156):883–888. | ||
Brodsky FM, Chen CY, Knuehl C, Towler MC, Wakeham DE. Biological basket weaving: formation and function of clathrin-coated vesicles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2001;17:517–568. | ||
Donaldson JG. Multiple roles for Arf6: sorting, structuring, and signaling at the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(43):41573–41576. | ||
Parton RG, Simons K. The multiple faces of caveolae. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8(3):185–194. | ||
Pelkmans L, Burli T, Zerial M, Helenius A. Caveolin-stabilized membrane domains as multifunctional transport and sorting devices in endocytic membrane traffic. Cell. 2004;118(6):767–780. | ||
Llorente A, Rapak A, Schmid SL, van Deurs B, Sandvig K. Expression of mutant dynamin inhibits toxicity and transport of endocytosed ricin to the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1998;140(3):553–563. | ||
Kumari S, Mayor S. ARF1 is directly involved in dynamin-independent endocytosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10(1):30–41. | ||
Hanai A, Ohgi M, Yagi C, Ueda T, Shin HW, Nakayama K. Class I Arfs (Arf1 and Arf3) and Arf6 are localized to the Flemming body and play important roles in cytokinesis. J Biochem. 2016;159(2):201–208. | ||
Orth JD, Krueger EW, Weller SG, McNiven MA. A novel endocytic mechanism of epidermal growth factor receptor sequestration and internalization. Cancer Res. 2006;66(7):3603–3610. | ||
Lanzetti L, Palamidessi A, Areces L, Scita G, Di Fiore PP. Rab5 is a signalling GTPase involved in actin remodelling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Nature. 2004;429(6989):309–314. | ||
Casi G, Neri D. Antibody-drug conjugates: basic concepts, examples and future perspectives. J Control Release. 2012;161(2):422–428. | ||
Carter PJ, Senter PD. Antibody-drug conjugates for cancer therapy. Cancer J. 2008;14(3):154–169. | ||
Ducry L, Stump B. Antibody-drug conjugates: linking cytotoxic payloads to monoclonal antibodies. Bioconjug Chem. 2010;21(1):5–13. | ||
Doronina SO, Mendelsohn BA, Bovee TD, et al. Enhanced activity of monomethyl auristatin F through monoclonal antibody delivery: effects of linker technology on efficacy and toxicity. Bioconjug Chem. 2006;17(1):114–124. | ||
Dubowchik GM, Firestone RA, Padilla L, et al. Cathepsin B-labile dipeptide linkers for lysosomal release of doxorubicin from internalizing immunoconjugates: model studies of enzymatic drug release and antigen-specific in vitro anticancer activity. Bioconjug Chem. 2002;13(4):855–869. | ||
Sanderson RJ, Hering MA, James SF, et al. In vivo drug-linker stability of an anti-CD30 dipeptide-linked auristatin immunoconjugate. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(2):843–852. | ||
Phillips GDL, Li G, Dugger DL, et al. Targeting HER2-positive breast cancer with trastuzumab-DM1, an antibody-cytotoxic drug conjugate. Cancer Res. 2008;68(22):9280–9290. | ||
Feld J, Barta SK, Schinke C, Braunschweig I, Zhou Y, Verma AK. Linked-in: design and efficacy of antibody drug conjugates in oncology. Oncotarget. 2013;4(3):397–412. | ||
Nolting B. Linker technologies for antibody drug conjugates. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1045:71–100. | ||
Gerber H-P, Senter PD, Grewal IS. Antibody drug-conjugates targeting the tumor vasculature current and future developments. MAbs. 2009;1(3):247–253. | ||
Polakis P. Arming antibodies for cancer therapy. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2005;5(4):382–387. | ||
Kovtun YV, Audette CA, Ye YM, et al. Antibody-drug conjugates designed to eradicate tumors with homogeneous and heterogeneous expression of the target antigen. Cancer Res. 2006;66(6):3214–3221. | ||
Chari RVJ. Targeted cancer therapy: conferring specificity to cytotoxic drugs. Acc Chem Res. 2008;41(1):98–107. | ||
Erickson HK, Widdison WC, Mayo MF, et al. Tumor delivery and in vivo processing of disulfide-linked and thioether-linked antibody-maytansinoid conjugates. Bioconjug Chem. 2010;21(1):84–92. | ||
Okeley NM, Miyamoto JB, Zhang X, et al. Intracellular activation of SGN-35, a potent anti-CD30 antibody-drug conjugate. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16(3):888–897. | ||
Shen B-Q, Bumbaca D, Saad O, et al. Catabolic fate and pharmacokinetic characterization of trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1): an emphasis on preclinical and clinical catabolism. Curr Drug Metab. 2012; 13(7):901–910. | ||
Kung Sutherland MS, Walter RB, Jeffrey SC, et al. SGN-CD33A: a novel CD33-targeting antibody-drug conjugate using a pyrrolobenzodiazepine dimer is active in models of drug-resistant AML. Blood. 2013;122(8):1455–1463. | ||
Lyon RP, Setter JR, Bovee TD, et al. Self-stabilizing ADCs: antibody-drug conjugates prepared with maleimido drug-linkers that catalyze their own thiosuccinimide ring hydrolysis. Cancer Res. 2013;73(8): (Suppl 1). | ||
King HD, Yurgaitis D, Willner D, et al. Monoclonal antibody conjugates of doxorubicin prepared with branched linkers: a novel method for increasing the potency of doxorubicin immunoconjugates. Bioconjug Chem. 1999;10(2):279–288. | ||
Li Q, Tang Q, Zhang P, et al. Human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 antibodies enhance the specificity and anticancer activity of light-sensitive doxorubicin-labeled liposomes. Biomaterials. 2015;57:1–11. | ||
Rowe JM, Lowenberg B. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin in acute myeloid leukemia: a remarkable saga about an active drug. Blood. 2013;121(24):4838–4841. | ||
Sutherland MSK, Sanderson RJ, Gordon KA, et al. Lysosomal trafficking and cysteine protease metabolism confer target-specific cytotoxicity by peptide-linked anti-CD30-auristatin conjugates. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(15):10540–10547. | ||
Hamann PR, Hinman LM, Beyer CF, et al. A calicheamicin conjugate with a fully humanized anti-MUC1 antibody shows potent antitumor effects in breast and ovarian tumor xenografts. Bioconjug Chem. 2005;16(2):354–360. | ||
Ingle GS, Chan P, Elliott JM, et al. High CD21 expression inhibits internalization of anti-CD19 antibodies and cytotoxicity of an anti-CD19-drug conjugate. Br J Haematol. 2008;140(1):46–58. | ||
Law CL, Gordon KA, Toki BE, et al. Lymphocyte activation antigen CD70 expressed by renal cell carcinoma is a potential therapeutic target for anti-CD70 antibody-drug conjugates. Cancer Res. 2006;66(4):2328–2337. | ||
Law CL, Cerveny CG, Gordon KA, et al. Efficient elimination of B-lineage lymphomas by anti-CD20-auristatin conjugates. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(23):7842–7851. | ||
Li ZH, Zhang Q, Wang HB, et al. Preclinical studies of targeted therapies for CD20-positive B lymphoid malignancies by Ofatumumab conjugated with auristatin. Invest New Drugs. 2014;32(1):75–86. | ||
Pan L-Q, Wang H-B, Xie Z-M, et al. Novel conjugation of tumor-necrosis-factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) with monomethyl auristatin E for efficient antitumor drug delivery. Adv Mater Deerfield. 2013;25(34):4718–4722. | ||
Smith LM, Nesterova A, Alley SC, Torgov MY, Carter PJ. Potent cytotoxicity of an auristatin-containing antibody-drug conjugate targeting melanoma cells expressing melanotransferrin/p97. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006;5(6):1474–1482. | ||
Austin CD, Wen XH, Gazzard L, Nelson C, Scheller RH, Scales SJ. Oxidizing potential of endosomes and lysosomes limits intracellular cleavage of disulfide-based antibody-drug conjugates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(50):17987–17992. | ||
Walter RB, Raden BW, Kamikura DM, Cooper JA, Bernstein ID. Influence of CD33 expression levels and ITIM-dependent internalization on gemtuzumab ozogamicin-induced cytotoxicity. Blood. 2005;105(3):1295–1302. | ||
Jedema I, Barge RMY, van der Velden VHJ, et al. Internalization and cell cycle-dependent killing of leukemic cells by gemtuzumab ozogamicin: rationale for efficacy in CD33-negative malignancies with endocytic capacity. Leukemia. 2004;18(2):316–325. | ||
Maass KF, Kulkarni C, Betts AM, Wittrup KD. Determination of cellular processing rates for a trastuzumab-maytansinoid antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) highlights key parameters for ADC design. AAPS J. 2016;18(3):635–646. | ||
Wang X, Ma D, Olson WC, Heston WDW. In vitro and in vivo responses of advanced prostate tumors to PSMA ADC, an auristatin-conjugated antibody to prostate-specific membrane antigen. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011;10(9):1728–1739. | ||
Galsky MD, Eisenberger M, Moore-Cooper S, et al. Phase I trial of the prostate-specific membrane antigen directed immunoconjugate MLN2704 in patients with progressive metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(13):2147–2154. | ||
Gao Y, Li Y, Li Y, et al. PSMA-mediated endosome escape-accelerating polymeric micelles for targeted therapy of prostate cancer and the real time tracing of their intracellular trafficking. Nanoscale. 2015; 7(2):597–612. | ||
Advani A, Coiffier B, Czuczman MS, et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics, and preliminary clinical activity of inotuzumab ozogamicin, a novel immunoconjugate for the treatment of B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: results of a phase I study. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(12):2085–2093. | ||
Kantarjian H, Thomas D, Jorgensen J, et al. Inotuzumab ozogamicin, an anti-CD22-calecheamicin conjugate, for refractory and relapsed acute lymphocytic leukaemia: a phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13(4):403–411. | ||
Francisco JA, Cerveny CG, Meyer DL, et al. cAC10-vcMMAE, an anti-CD30-monomethyl auristatin E conjugate with potent and selective antitumor activity. Blood. 2003;102(4):1458–1465. | ||
Younes A, Bartlett NL, Leonard JP, et al. Brentuximab vedotin (SGN-35) for relapsed CD30-positive lymphomas. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(19):1812–1821. | ||
Younes A, Gopal AK, Smith SE, et al. Results of a pivotal phase II study of brentuximab vedotin for patients with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(18):2183–2189. | ||
Lewis Phillips GD, Li G, Dugger DL, et al. Targeting HER2-positive breast cancer with trastuzumab-DM1, an antibody-cytotoxic drug conjugate. Cancer Res. 2008;68(22):9280–9290. | ||
Barok M, Joensuu H, Isola J. Trastuzumab emtansine: mechanisms of action and drug resistance. Breast Cancer Res. 2014;16(2):209. | ||
LoRusso PM, Weiss D, Guardino E, Girish S, Sliwkowski MX. Trastuzumab emtansine: a unique antibody-drug conjugate in development for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(20):6437–6447. | ||
Phillips GDL, Fields CT, Crocker L, et al. Potent anti-tumor activity of trastuzumab-DM1 antibody-drug conjugate in combination with cytotoxic chemotherapeutic agents, antibodies or small molecule kinase inhibitors. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res Annu Meet. 2008;49:502. | ||
Chari RVJ, Miller ML, Widdison WC. Antibody-drug conjugates: an emerging concept in cancer therapy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2014; 53(15):3796–3827. | ||
Vater CA, Manning C, Millar H, et al. Anti-tumor efficacy of the integrin-targeted immunoconjugate IMGN388 in preclinical models. EJC Suppl. 2008;6(12):167–168. | ||
Blanc V, Bousseau A, Caron A, Carrez C, Lutz RJ, Lambert JM. SAR3419: an anti-CD19-maytansinoid immunoconjugate for the treatment of B-cell malignancies. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(20):6448–6458. | ||
Kelly RK, Olson DL, Sun Y, et al. An antibody-cytotoxic conjugate, BIIB015, is a new targeted therapy for Cripto positive tumours. Eur J Cancer. 2011;47(11):1736–1746. | ||
Ikeda H, Hideshima T, Fulciniti M, et al. The monoclonal antibody nBT062 conjugated to cytotoxic maytansinoids has selective cytotoxicity against CD138-positive multiple myeloma cells in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(12):4028–4037. | ||
Erickson HK, Park PU, Widdison WC, et al. Antibody-maytansinoid conjugates are activated in targeted cancer cells by lysosomal degradation and linker-dependent intracellular processing. Cancer Res. 2006; 66(8):4426–4433. | ||
Whiteman KR, Johnson HA, Mayo MF, et al. Lorvotuzumab mertansine, a CD56-targeting antibody-drug conjugate with potent antitumor activity against small cell lung cancer in human xenograft models. MAbs. 2014;6(2):556–566. | ||
Berdeja JG. Lorvotuzumab mertansine: antibody-drug-conjugate for CD56(+) multiple myeloma. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2014;19:163–170. | ||
Lutz RJ, Whiteman KR. Antibody-maytansinoid conjugates for the treatment of myeloma. MAbs. 2009;1(6):548–551. | ||
Keir CH, Vahdat LT. The use of an antibody drug conjugate, glembatumumab vedotin (CDX-011), for the treatment of breast cancer. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12(2):259–263. | ||
Naumovski L, Junutula JR. Glembatumumab vedotin, a conjugate of an anti-glycoprotein non-metastatic melanoma protein B mAb and monomethyl auristatin E for the treatment of melanoma and breast cancer. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2010;12(2):248–257. | ||
Vaklavas C, Forero A. Management of metastatic breast cancer with second-generation antibody-drug conjugates: focus on glembatumumab vedotin (CDX-011, CR011-vcMMAE). BioDrugs. 2014;28(3):253–263. | ||
Scott AM, Allison JP, Wolchok JD. Monoclonal antibodies in cancer therapy. Cancer Immun. 2012;12:14. | ||
Lambert JM. Antibody-maytansinoid conjugates: a new strategy for the treatment of cancer. Drugs Future. 2010;35(6):471–480. | ||
Ikemoto N, Kumar RA, Ling TT, Ellestad GA, Danishefsky SJ, Patel DJ. Calicheamicin-DNA complexes – warhead alignment and saccharide recognition of the minor-groove. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92(23):10506–10510. | ||
Boger DL, Johnson DS. CC-1065 and the duocarmycins – unraveling the keys to a new class of naturally derived DNA alkylating-agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92(9):3642–3649. | ||
Abal M, Andreu JM, Barasoain I. Taxanes: microtubule and centrosome targets, and cell cycle dependent mechanisms of action. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2003;3(3):193–203. | ||
Minotti G, Menna P, Salvatorelli E, Cairo G, Gianni L. Anthracyclines: molecular advances and pharmacologic developments in antitumor activity and cardiotoxicity. Pharmacol Rev. 2004;56(2):185–229. | ||
Monneret C. Recent developments in the field of antitumour anthracyclines. Eur J Med Chem. 2001;36(6):483–493. | ||
Dornan D, Bennett F, Chen Y, et al. Therapeutic potential of an anti-CD79b antibody-drug conjugate, anti-CD79b-vc-MMAE, for the treatment of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 2009;114(13):2721–2729. | ||
Li D, Poon KA, Yu S-F, et al. DCDT2980S, an anti-CD22-monomethyl auristatin E antibody-drug conjugate, is a potential treatment for non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013;12(7):1255–1265. | ||
Mayo MF, Leung AP, Wang L, et al. In vivo stability in mice of SAR566658 (huDS6-DM4), an immunoconjugate targeting solid tumours. EJC Suppl. 2008;6(12):169. | ||
Petrul HM, Schatz CA, Kopitz CC, et al. Therapeutic mechanism and efficacy of the antibody-drug conjugate BAY 79-4620 targeting human carbonic anhydrase 9. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012;11(2):340–349. | ||
Bendell J, Blumenschein G, Zinner R, et al. First-in-human phase I dose escalation study of a novel anti-mesothelin antibody drug conjugate (ADC), BAY 94-9343, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Res. 2013;73(8): (Suppl 1). | ||
Thompson JA, Forero-Torres A, Heath EI, et al. The effect of SGN-75, a novel antibody-drug conjugate (ADC), in treatment of patients with renal cell carcinoma (RCC) or non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL): a phase I study. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(15): (Suppl S). | ||
Oflazoglu E, Stone IJ, Gordon K, et al. Potent anticarcinoma activity of the humanized anti-CD70 antibody h1F6 conjugated to the tubulin inhibitor auristatin via an uncleavable linker. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(19):6171–6180. | ||
Govindan SV, Cardillo TM, Moon S-J, Hansen HJ, Goldenberg DM. CEACAM5-targeted therapy of human colonic and pancreatic cancer xenografts with potent labetuzumab-SN-38 immunoconjugates. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(19):6052–6061. | ||
Thevanayagam L, Bell A, Chakraborty I, et al. Novel detection of DNA-alkylated adducts of antibody-drug conjugates with potentially unique preclinical and biomarker applications. Bioanalysis. 2013;5(9):1073–1081. | ||
Kurkjian C, LoRusso P, Sankhala KK, et al. A phase I, first-in-human study to evaluate the safety, pharmacokinetics (PK), and pharmacodynamics (PD) of IMGN853 in patients (Pts) with epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) and other FOLR1-positive solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(15): (Suppl S). | ||
Setiady YY, Park PU, Ponte JF, et al. Development of a novel antibody-maytansinoid conjugate, IMGN289, for the treatment of EGFR-expressing solid tumors. Cancer Res. 2013;73(8): (Suppl 1). | ||
Adair JR, Howard PW, Hartley JA, Williams DG, Chester KA. Antibody-drug conjugates – a perfect synergy. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12(9):1191–1206. | ||
Beckwith KA, Frissora FW, Stefanovski MR, et al. The CD37-targeted antibody-drug conjugate IMGN529 is highly active against human CLL and in a novel CD37 transgenic murine leukemia model. Leukemia. 2014;28(7):1501–1510. | ||
Gudas JM, An Z, Morrison RK, et al. ASG-5ME is a novel antibody drug conjugate (ADC) for treating prostate cancers. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res Annu Meet. 2010;51:1066. |
 © 2017 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2017 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.