Back to Journals » Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity » Volume 12
Genetic variants linked to T2DM risk in Kurdish populations
Authors Golsheh S, Keshavarzi F
Received 29 September 2018
Accepted for publication 5 March 2019
Published 5 April 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 431—437
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S189170
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Konstantinos Tziomalos
This paper has been retracted
Shadi Golsheh,1 Fatemeh Keshavarzi2
1Department of Biology, Kurdistan Science and Research Branch, Islamic Azad University, Sanandaj, Iran; 2Department of Biology, Sanandaj Branch, Islamic Azad University, Sanandaj, Iran
Background: The polymorphisms of the C–C chemokine receptor type 5 (CCR5) and the insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1) have been studied as candidates for the susceptibility to develop type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). CCR5 is a chemokine receptor, and the polymorphisms in the promoter region of this receptor are being studied as candidates for the susceptibility to develop T2DM. Also, IRS1 is a critical factor in the signaling pathway for insulin, and mutations in this gene have been reported, which contribute to the ability to develop T2DM. The aim of the current study was to determine the relationship between CCR5 (59029A/G) and IRS1 (rs10498210) polymorphisms with T2DM in Sanandajian patients.
Methods: Genomic DNA was isolated from 200 healthy individuals and 220 Kurdish T2DM patients by salt extraction method and the polymorphisms were examined by restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) method and then the results were analyzed using Chi-square test.
Results: The frequency of AA genotype in 220 Kurdish patients for both genes CCR5 (OR=1.9, P=0.02) and IRS1 (OR [95% CI]=2.62, P=0.02) were significantly more than controls. There was no significant association between AG or GG genotypes in with T2DM.
Conclusion: The presence of AA homozygote alleles in both loci of IRS1 (rs10498210) and CCR5 (59029A/G) genes increased the risk of T2DM.
Keywords: IRS1 (rs10498210), CCR5 (59029A/G), type 2 diabetes, Kurdish patients
Introduction
Diabetes or diabetes mellitus is referred to as a heterogeneous group of metabolic disorders characterized by chronic hyperglycemia and carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism disorders that result from a defect in the secretion of insulin, or impairment in its function, or both. Types of diabetes mellitus include type 1, type 2 diabetes and other kind of diabetes, but the two most common types of diabetes mellitus are type 1 and type 2, which are different in several aspects.1,2 Type 1 diabetes has been identified with autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells (insulin secreting cells) and accounts for about 5% of all diabetic people, while type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a predominant disorder characterized by insulin resistance or a relative decline in insulin production, and accounts for about 90% of all types of diabetes mellitus.3 Important factors that predispose a person to T2DM are multifactorial, including genetic factors and environments. However, its inheritance has certainly not been proven, but it is believed that first-degree relatives of diabetic patients have a higher chance to develop the disease. In this regard, recognizing gen polymorphisms of this disease seems to be necessary.4
Multiple genes have been studied in the pathogenesis of T2DM. One of these genes associated with T2DM is the IRS1 gene (accession number. 147545).5–8 Another gene associated with T2DM is the CCR5 gene (accession number. 601373).9–11
Insulin initiates a wide range of growth and metabolic effects by binding to its receptor and activating the property of tyrosine kinase. These events cause phosphorylation of tyrosine kinase residues at the level of anchored proteins, which include insulin receptor substrate proteins (IRS).12 The phosphorylated IRS proteins are used as multi-position anchored proteins for different molecules that have homologous domains (SH2) or Src. The activity of these second SH proteins triggers the signaling cascade and results in the activity of several downstream filters that ultimately transmits the insulin message to the cellular vector pathways, thereby regulating cell differentiation, growth, survival and metabolism. In different studies, the frequency of IRS1 polymorphisms in type 2 diabetic patients was more than control group.13–15 The IRS1 is a cytoplasmic substrate for insulin and also is a receptor for IGF-1, which plays a vital role in signaling. In recent studies, various roles in IRS1 have been discovered, especially in patients with non-insulin diabetes mellitus. The IRS1 gene polymorphisms were identified in 1993.16,17
Chemokines are a large family of low molecular weight secretion proteins that play fundamental roles in physiological and pathophysiological processes such as angiogenesis, inflammation, atherosclerosis and autoimmune or allergic or infectious diseases.18,19 Their initial function is to regulate the migration of leukocytes at the concentration gradient, but they also play a role in the activation of the cells producing and secreting inflammatory mediators. These chemokines do their function by connecting to their G-protein receptors.19 Excessive nutrition that has high levels of glucose and fatty acids can put stress on the pancreatic islets and insulin-sensitive tissues such as fat and liver and muscle, leading to the production and release of topical cytokines and inflammatory chemokines.20 Among these inflammatory chemokines, MCP-1, MIP-1α, MIP-1β, RANTES (Regulated upon Activation, Normal T-cell Expressed, and Secreted) and MCP-2 are mentioned. These chemokines interact with their receptors, triggering monocytes, as well as increasing the number of macrophages in the inflammation position. Chemokine receptors that can be mentioned include CCR2 (CC chemokine receptor type 2), chemokine receptor MCP-1, and also chemokine receptors CCR5, MIP-1α, MIP-1β, RANTES and MCP-2.21
The CCR5 gene is located at 3q21.3 position on the chromosome. The CCR5 (59029A/G) polymorphism has been reported in the promoter region of the CCR5 receptor gene.22 Studies indicated that the CCR5 (59029A/-) genotype results in increased expression of this receptor by peripheral blood mononuclear cells of individuals with this genotype, and therefore it is probably the genotype regulating the expression of the CCR5 gene.9,20
In this regard, the relationship between the IRS1 (rs10498210) polymorphisms and CCR5 (59029A/G) and the risk of T2DM have not been clearly and precisely indicated. Therefore, this study was conducted with the aim of investigating this relationship.
Methods
Ethical statements
The study was ethically approved by the regional Ethics Committee of Sanandaj Branch, Islamic Azad University, and the study was conducted in accordance with the provisions of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Samples
This research is a case-control study. During this study, the peripheral blood samples of 220 T2DM patients (fasting blood glucose higher than 150 mg/dL in two times) and non-200 diabetic subjects as control (fasting blood glucose less than 100 mg/dL in two times and gender- and ethnic-matched with the patients). Patients were selected randomly among individuals who referred to the Kurdistan Diabetes Centers in Kurdistan of Iran. Patients were selected in such a way that their diabetes was controlled (measured by HbAlc by the diabetes center). Inclusion criteria were diagnosed according to the American Diabetes Association diagnostic criteria (the blood glucose level of >250 mg/dL or severe hyperglycemia). Written consent was received from the individuals and they were informed that sampling was for research purposes only.
DNA extraction
Extraction of DNA from the blood samples was performed by salt extraction method and DNA extraction was determined on agarose gel 1%. The isolated DNA was placed in separate microtubes and stored at −20°C until PCR was performed.
Molecular analysis
Determination of genotype was carried out by PCR-RFLP method and the primers (Table 1) were used for replication of pieces. For the CCR5 (59029A/G) polymorphism, the primers were taken from other articles but for IRS1 (rs10498210) polymorphism was designed.
 | Table 1 The sequences of primers used in the study for IRS1 (rs10498210) and CCR5 (59029A/G) |
PCR was performed in final volume of 20 μl using Sinagene PCR kit. The PCR cycles of the desired gene are presented in Table 2 separately. To ensure the correct replication of the desired piece, the PCR products were loaded on agarose gel 1.8%. and its quality was determined.
 | Table 2 PCR proliferation conditions |
In order to cut the desired region in the CCR5 gene, the SduI enzyme was selected, which is detected as GGGCAC, and consequently, in the presence of the allele G in polymorphic position, enzyme cut the piece and in the presence of the allele A, the piece does not cut. The piece produced by PCR for the CCR5 gene is a 258 bp base pair piece, and if the piece is cut, two pieces of 131 and 127 bases are created. To cut the desired region in the IRS1 gene, the MaeII enzyme was selected, which is detected as ACGT. The PCR-proliferated piece is 371 bp. In the presence of the allele G in the polymorphic position, the enzyme has cut position, which results in two pieces of 229 and 142 bp, and in the presence of the allele A at the polymorphic position, the 371 bp piece is not broken, and totally one piece will remain. Then the digested products were loaded on 3% agarose gel and their genotypes were determined. Achieved frequencies significance between type 2 and control subjects were statistically analyzed using software popgene1.32 and by SPSS v20 and at significant level (p<0.05).
Results
This case-control study was performed on 420 unrelated individuals, including 220 patients with type 2 diabetic and 200 healthy controls. The allele frequencies of genotypes for all two SNPs were shown in Table 3. In the population studied, the frequency AA, AG and GG genotypes of the CCR5 gene were 120 (54.54), 84 (38.18) and 16 (7.27), respectively, among the patients and 81 (40.5), 70 (35) and 49 (24.5), respectively, in the control subjects. Also, in the IRS1 gene it was as follows: among the 220 patients, the frequency of AG, AG and GG was 150 (68.18), 52 (23.63) and 20 (9.09), respectively, and also, among the 200 control subjects, the frequency of GG, AG and AA were 176 (88), 20 (10) and 4 (2), respectively. In patients, the allelic frequency of AA in both genes CCR5 (OR (95% CI)=1.9 P=0.02) and IRS1 (OR (95% CI)=2.62 P=0.02) were significantly more than controls. There was no significant association between AG or GG genotypes in with T2DM (Table 3).
 | Table 3 Distribution of alleles and genotypes of CCR5 (59029A/G) and IRS1 (rs10498210) genes among T2DM patients and healthy controls |
Figure 1 shows the image of the agarose gel 3% for CCR5 (59029A/G) polymorphism and also shows how to determine its genotype in ladder and size pieces as described above.
 | Figure 1 Genotype detection (59029A/G) CCR5. |
Figure 2 shows the image of the agarose gel 3% for IRS1 (rs10498210) polymorphism and also shows how to determine its genotype in ladder and size pieces as described in "Molecular analysis" section.
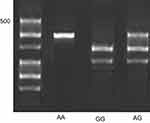 | Figure 2 Genotype detection (rs10498210) IRS1. |
In this study, Hardy Weinberg equilibrium and heterozygosity were also studied for populations. The Hardy Weinberg equilibrium points to the fact that the genetic and genotype frequency is constant from generation to generation. The probability level in both type 2 diabetic and control subjects was greater than 0.05 for IRS1 and CCR5 genes, indicating a Hardy Weinberg equilibrium in these populations (Table 3).
Heterozygosity for a gene position is defined as a frequency of heterozygote people for that position relative to the total population. For a gene position, if the heterozygosity is greater than 0.1, it is polymorphic and if it is more than 0.7, it is extremely polymorphic. Based on the results of this study, it was found that the difference between observed and expected heterozygosity for both studied polymorphisms was less than 0.1, so that the gene positions in this study are not polymorphic. In the next step, the mean of patient’s clinical data which were collected from their files in Diabetes Center of Kurdistan was analyzed. The results of clinical data analysis are presented in Tables 4 and 5.
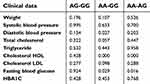 | Table 4 Comparison of type 2 diabetic patients' clinical data among different genotypes of polymorphism IRS1 (rs10498210) |
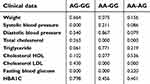 | Table 5 Comparison of type 2 diabetic patients' clinical data among different genotypes of polymorphism CCR5 (59029A/G) |
Discussion
This case-control study was performed on patients and healthy control from Iranian Kurdistan. The frequencies of genotypes and alleles for all two SNPs are shown in Table 3. Results show that among patients and control subjects the allelic frequency AA, AG and GG genotypes of the CCR5 gene were 120 (54.54), 84 (38.18) and 16 (7.27), and 81 (40.5), 70 (35) and 49 (24.5), respectively. Also, in the IRS1 gene it was as follows: among the 220 patients, the allelic frequency of AG, AG and GG was 150 (68.18), 52 (23.63) and 20 (9.09), respectively, and also, among the 200 control subjects, the frequency of GG, AG and AA was 176 (88), 20 (10) and 4 (2), respectively. The frequency of AA genotype in patients in both genes CCR5 (OR (95% CI)=1.9 P=0.02) and IRS1 (OR (95% CI)=2.62 P=0.02) was significantly more than controls. There was no significant association between AG or GG genotypes with T2DM (Table 3). Also, weight, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, total cholesterol, triglyceride, cholesterol HDL, cholesterol LDL, fasting blood glucose and HBA1C were significantly higher in the patients' group when compared to the control group (Tables 4 and 5).
McDermott et al., who found for the first time the A/G polymorphism in the 59029 base pair in the promoter region of this gene, reported that both alleles of this polymorphism are common in societies, and the allelic frequency of 59029A, depending on the ethnic population, varies between 43% and 68%. Differences in the frequency of allelic A in different communities can be due to genetic differences between populations.22,23
According to the results, it is possible that the CCR5 genotype (AA 59029) plays an important role in the pathogenesis of T2DM. Studies indicated that the CCR5 (59029A/-) genotype results in increased expression of CCR5 by peripheral blood mononuclear cells of individuals with this genotype. In a study by Dytfeld et al., the expression of CCR5 receptor expression was measured on the peripheral blood mononuclear cells of type 2 diabetics, and it was determined that the expression of CCR5 receptor on the cell surface in type 2 diabetic patients is also increasing, and high expression of this receptor can be considered as an indicator of atherosclerosis in diabetic people.24
Given the evidence of T2DM which was recently provided and type 2 diabetes introduced as an inflammatory disease, it can be expected that high expression of this receptor (CCR5) on the level of single-cellular cells of the blood increases inflammatory responses and increases the risk of T2DM. However, in order to confirm with certainty the existence of such a connection, further studies in a wider population are needed.
Regarding the role of IRS1 gene in the pathway of insulin signaling and the negative effect of rs10498210 polymorphism on the performance of this protein, it can be expected that this polymorphism is present in the etiology of T2DM. Recent studies have indicated that IRS1 plays an important role in regulating insulin secretion in beta cells of the pancreas. It has been shown that glucose-stimulated insulin secretion may be triggered by the autocrine activation of insulin signaling pathway, including insulin receptor phosphorylation, tyrosine phosphorylation in IRS1 and the activation of PI3-Kinase.
Putting together these data leads to the hypothesis that a single molecular impairment in the pathway of insulin signaling, including an incomplete interaction between PI3-Kinase and IRS1, may lead to insulin resistance, as well as insulin secretion defect.
So far, there has been a weak link between this polymorphism and T2DM, especially in obese people, but few studies have reported the association between this polymorphism and diabetes. In general, a variety of allele A in IRS1 frequencies have been reported in many studies, and controversial reports have revealed the association of this polymorphism with type 2 diabetes.25 Finally, according to the results of this study, it can be concluded that the probability of positive effect of allele A on studied polymorphisms IRS1 (rs10498210) and CCR5 (59029A/G) increase the risk of T2DM. Also, clinical data from diabetic patients suggest that the allele A from both studied polymorphisms plays a positive role in increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetic patients. However, to be sure about the impact of these polymorphisms on T2DM, it is necessary to study a larger population. It is also possible to compare the clinical data of patients with healthy subjects and examine the effect of these two polymorphisms on the clinical data of these two groups and more effectively to study the role of these polymorphisms in increasing the risk of disease cardiovascular disease. The two studied genes in current study are associated with insulin resistance based on two different mechanisms. IRS1 plays a role in the insulin signaling pathway in its target tissues and CCR5 plays a role in the inflammation pathway in fatty tissues and beta cells in the pancreas. By simultaneous examination of these two genes and the effect of their different variants together, in type 2 diabetic patients, greater recognition of the importance of each of these pathways in the pathogenesis of T2DM can be obtained.
Conclusion
The presence of AA homozygote alleles in both loci of IRS1 (rs10498210) and CCR5 (59029A/G) genes increased the risk of T2DM. There was no significant association between AG or GG genotypes in with T2DM.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank the volunteers who contributed samples for this study.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Bhattacharya S, Dey D, Roy SS. Molecular mechanism of insulin resistance. J Biosci. 2007;32(2):405–413.
2. Meshkani R, Taghikhani M, Mosapour A, et al. 1484insG polymorphism of the PTPN1 gene is associated with insulin resistance in an Iranian population. Arch Med Res. 2007;38(5):556–562. doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2007.01.010
3. Meshkani R, Taghikhani M, Al-Kateb H, et al. Polymorphisms within the protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTPN1) gene promoter: functional characterization and association with type 2 diabetes and related metabolic traits. Clin Chem. 2007;53(9):1585–1592. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2007.088146
4. Häring HU, Merker L, Seewaldt-Becker E, et al. Empagliflozin as add-on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Care. 2014;37(6):1650–1659. doi:10.2337/dc13-2105
5. Brunetti A, Chiefari E, Foti D. Recent advances in the molecular genetics of type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes. 2014;5(2):128–140. doi:10.4239/wjd.v5.i2.128
6. Brender JR, Krishnamoorthy J, Messina GM, et al. Zinc stabilization of prefibrillar oligomers of human islet amyloid polypeptide. Chem Commun (Camb). 2013;49:3339–3341. doi:10.1039/c3cc40383a
7. Alharbi KK, Khan IA, Munshi A, Alharbi FK, Al-Sheikh Y, Alnbaheen MS. Association of the genetic variants of insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1) with type 2 diabetes mellitus in a Saudi population. Endocrine. 2014;47(2):472–477. doi:10.1007/s12020-014-0177-2
8. Alharbi KK, Khan IA, Abotalib Z, Al-Hakeem MM. Insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS1) Gly927Arg: correlation with gestational diabetes mellitus in Saudi women. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:146–495. doi:10.1155/2014/146495
9. Mokubo A, Tanaka Y, Nakajima K, et al. Chemotactic cytokine receptor 5 (CCR5) gene promoter polymorphism (59029A/G) is associated with diabetic nephropathy in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: a 10-year longitudinal study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2006;73(1):89–94. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2005.12.006
10. Balistreri CR, Caruso C, Grimaldi MP, et al. Ccr5 receptor. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1100(1):162–172. doi:10.1196/annals.1395.014
11. Muntinghe FL, Gross S, Bakker SJ, et al. CCR5Δ32 genotype is associated with outcome in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2009;86(2):140–145. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2009.08.013
12. White MF. The insulin signalling system and the IRS proteins. Diabetologia. 1997;40(2):S2–S17.
13. Huri HZ, Makmor-Bakry M, Hashim R, Mustafa N, Wan Ngah WZ. Optimisation of glycaemic control during episodes of severe/acute hyperglycaemia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Clin Pharm. 2012;34(6):863–870. doi:10.1007/s11096-012-9682-7
14. Richter EA, Exercise HM. GLUT4, and skeletal muscle glucose uptake. Physiol Rev. 2013;93:993–1017. doi:10.1152/physrev.00038.2012
15. Chang YJ, Pownall S, Jensen TE, et al. The Rho-guanine nucleotide exchange factor PDZ-RhoGEF governs susceptibility to diet-induced obesity and type 2 diabetes. eLife. 2015;4:e06011. doi:10.7554/eLife.06416
16. Audouze K, Brunak S, Grandjean P. A computational approach to chemical etiologies of diabetes. Sci Rep. 2013;3:2712. doi:10.1038/srep02712
17. Ullrich S. IGF-1 and Insulin-Receptor Signalling in Insulin-Secreting Cells: From Function to Survival. Islets of Langerhans. Islets of langerhans: Springer; 2015:659–685.
18. Herder C, Haastert B, Müller-Scholze S, et al. Association of systemic chemokine concentrations with impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes: results from the Cooperative Health Research in the Region of Augsburg Survey S4 (KORA S4). Diabetes. 2005;54(suppl 2):S11–S17.
19. Baggiolini M. Chemokines in pathology and medicine. J Intern Med. 2001;250(2):91–104.
20. Ahluwalia TS, Khullar M, Ahuja \ M, et al. Common variants of inflammatory cytokine genes are associated with risk of nephropathy in type 2 diabetes among Asian Indians. PLoS One. 2009;4(4):e5168. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0005168
21. Abbas A, Lichtman A, Pillai S. Cellular and Molecular Immunology: With Student Consult Online Access. Islets of langerhans: Elsevier Health Sciences; 2014.
22. McDermott DH, Zimmerman PA, Guignard F, et al. CCR5 promoter polymorphism and HIV-1 disease progression. Lancet. 1998;352(9131):866–870. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(98)04158-0
23. Passam AM, Zafiropoulos A, Miyakis S, et al. CCR2-64I and CXCL12 3′ A alleles confer a favorable prognosis to AIDS patients undergoing HAART therapy. J Clin Virol. 2005;34(4):302–309. doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2004.05.021
24. Dytfeld J, Bogdański P, Pupek-Musialik D, Jagodziński P, Bryl W, Kujawa A. Expression of chemokine receptor CCR5 in patients with type 2 diabetes. olskie Towarzystwo Lekarskie. 2006;20(116):195–198.
25. Yousef AA, Eg B, Abd Allah W, et al. IRS1 genetic polymorphism (r.2963G>A) in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients associated with insulin resistance. Appl Clin Genet. 2018;11:99–106.
 © 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
