Back to Journals » Drug Design, Development and Therapy » Volume 17
Neuroprotective Effects of Melatonin and Celecoxib against Ethanol-Induced Neurodegeneration: A Computational and Pharmacological Approach [Corrigendum]
Al Kury LT, Zeb A, Abidin ZU, et al. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019;13:2715–2727.
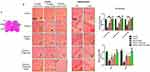
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 4B on page 2723. The image for Ethanol+celecoxib+mela (Piriform-PIR) was used mistakenly leading to a duplication with the Control (Piriform-PIR) images. A new image for Ethanol+celecoxib+mela (Piriform-PIR) was found from the original data and used as a replacement. The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the quality and scientific conclusions of the article.
The correct Figure 4 is as follows.
 © 2023 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2023 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.