Back to Journals » International Journal of Nanomedicine » Volume 15
Characterization and Anti-Cancerous Effect of Putranjiva roxburghii Seed Extract Mediated Silver Nanoparticles on Human Colon (HCT-116), Pancreatic (PANC-1) and Breast (MDA-MB 231) Cancer Cell Lines: A Comparative Study
Authors Balkrishna A, Sharma VK, Das SK , Mishra N, Bisht L, Joshi A, Sharma N
Received 7 September 2019
Accepted for publication 3 December 2019
Published 24 January 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 573—585
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S230244
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Anderson Oliveira Lobo
Acharya Balkrishna, 1, 2 Vinay Kumar Sharma, 1, 2 Subrata K Das, 1 Nayan Mishra, 1 Laxmi Bisht, 1 Alpana Joshi, 1 Niti Sharma 1
1Drug Discovery and Development Division, Patanjali Research Foundation Trust, Haridwar, Uttarakhand 249405, India; 2University of Patanjali, Haridwar, Uttarakhand 249405, India
Correspondence: Niti Sharma Tel +91-1334-242418
Email [email protected]
Vinay Kumar Sharma Email [email protected]
Introduction: A comparative study of Putranjiva roxburghii Wall. seed extract and developed silver nanoparticles (PJSNPs) for improving bioavailability that enhance their anti-cancer activity against HCT-116 (colon carcinoma), PANC-1 (pancreatic carcinoma), MDA-MB 231 (breast carcinoma) cell lines was performed.
Materials and Methods: The green synthesis of PJSNPs (Putranjiva silver nanoparticles) was performed using PJ (Putranjiva) extract, and characterization of synthesized nanoparticles was accomplished through UV-Vis spectrum, X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (TEM-EDAX), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and Raman spectroscopy.
Results: The results revealed that PJSNPs are homogeneous, spherical in shape, ∼ 8± 2 nm in size, and negatively charged with a zeta potential of about − 26.71 mV. The cytotoxicity pattern observed was AgNO 3 > PJSNPs > PJ extract. The morphological changes of the cells were observed by flow cytometry and also by the DNA ladder pattern on gel electrophoresis, which indicated that the process of cell death occurred via the apoptosis mechanism and PJSNPs were exerting late-stage apoptosis in all the tested cell lines. The small size and negative value of zeta potential could be the factors responsible for greater bioavailability and thus increased uptake by the tumor cells.
Conclusion: The MTT assay and morphological changes observed by various methods indicate that the novel PJSNPs are a better anticancer agent than PJ extract. All the above properties make biologically synthesized PJSNPs an important target in the field of anti-cancer drug discovery.
Keywords: green synthesis, Putranjiva, silver nanoparticles, anti-cancer, apoptosis
Background
Nanotechnology has gained tremendous popularity in recent years and has become a vital part of the drug discovery and development particularly, the drug delivery system. Due to their distinctive properties, metal nanoparticles have proved their worth in electronics, photonics, as well as biomedicine.1–3 Amongst all the metals used, silver is the most desirable one as pure silver has the maximum electrical and thermal conductivity and minimum contact resistance.4 Silver nanoparticles are being used in industries5 and also have shown to improve antimicrobial and anti-cancer activity besides having a significant role in the drug delivery system.6,7
Various chemical8–10 and physical11–13 methods have been used for the synthesis of nanoparticles. However, these methods are losing reputation due to low yield, high energy supplies and generation of toxic by-products.14 The concept of green synthesis has evolved to overcome the above limitations for the synthesis of nanoparticles as it is cost-effective, bio-compatible and eco-friendly in nature. Various green methods such as using the microwave, electrochemical reduction, sonochemical preparation, or supercritical technology15–17 have been deployed for the synthesis of SNPs. Other than that, the use of micro- or marine organisms and plant extracts for the synthesis of SNPs are well accepted due to their biocompatibility or biomimetic approach.18,19
Moreover, the plant extracts not only act as reducing agents but also stabilize the preparation of nanoparticles.20,21 They are rich in biomolecules that act as bio-reductants for the formation of metallic nanoparticles in the solution resulting in color change of the solution due to the surface plasmon resonance phenomenon.22
In the present study, a facile green method for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles (SNPs) using silver nitrate solution and Putranjiva roxburghii Wall. extract as the reducing agent has been reported.
Putranjiva roxburghii Wall. (Family Putranjivaceae) is an evergreen tree found growing in wild as well as cultivated in the Indian subcontinent. It is regarded as one of the best herbs for rejuvenation and restoration of the female reproductive system in the Indian traditional system of medicine. Apart from having analgesic, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory activities23,24 it is also used for treating azoospermia,25 elephantiasis, eye infection, habitual abortion, sterility, constipation, cough, cold and fever.26,27 In spite of tremendous ethnobiological importance, its anti-cancer properties have not been fully explored yet and also there is no report on green synthesis of AgNPs (Silver nanoparticles) from Putranjiva roxburghii Wall. seed extract till now; hence, in the present article, we have prepared a novel nano-composite named ‘Putranjiva roxburghii Wall. seed extract mediated SNPs’ (abbreviated as PJSNPs) to target tumor cells for the development of new anti-cancer agents, and characterized them using UV-Vis absorption spectrum, X-ray Diffraction (XRD), Transmission Electron Microscopy Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (TEM-EDAX), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM), Zeta potential and Raman spectroscopy. Additionally, the cytotoxic properties of PJSNPs and their anti-cancerous effects were investigated against HCT-116 (colon carcinoma), PANC-1 (pancreatic carcinoma), MDA-MB 231 (breast carcinoma) cell lines.
Materials and Methods
Materials
The seeds of Putranjiva roxburghii Wall. were a generous gift by Patanjali Ayurveda Ltd., Haridwar, India. The specimen was deposited at PHD, Patanjali Yogpeeth, Haridwar (Voucher no. PRIA/06/05/2017/002). The solvents, chemicals and kits were purchased from Merck, Sigma-Aldrich, and Invitrogen. The cell lines HCT-116 (colon carcinoma), PANC-1 (pancreatic carcinoma), MDA-MB 231 (breast carcinoma) were purchased from NCCS, Pune, India. The microorganism for antimicrobial study were procured from NCL, Pune, India. The blinded blood sample of a healthy volunteer was taken after obtaining his written consent by a registered clinician at Pathology lab, Patanjali Ayurvedic Hospital, Haridwar, India and was generously gifted to us. The study was approved by the Bioethical Committee for Scientific Research at the Patanjali Ayurvedic Hospital, Haridwar, India.
Preparation of Extract
About 10 g of seeds were milled into a fine powder and boiled for 2 hrs in 100 mL of deionized water. The extract was filtered to remove the particulate matter to get the clear solutions which were then refrigerated (4°C) for further experiments. At each and every step of the experiment, sterility conditions were maintained for the accuracy of the results.
Synthesis of PJSNPs
During the initial optimization procedure, different concentrations of silver nitrate solutions (1–10 mM) were prepared and treated with different amount of the seed extract (1–5 mL). The mixture was heated at 80°C for 1 hr. The best results were obtained with 1 mM AgNO3 and 5 mL extract. So we proceeded with the best conditions for further experiments.28
On reduction of Ag+ to Ago in AgNO3 solution, through the Putranjiva seed extract, the color of the solution changes. The formation of SNPs (Silver Nano Particles) was furthermore confirmed by spectrophotometric investigation (Absorbance scan 200–800 nm). The precipitate was collected by filtration, washed with deionized water several times, and finally dried in air at 60°C for 6 hrs.
Characterization of Nanoparticles
The prepared silver nanoparticles were analyzed and characterized using UV-Vis spectrophotometer (Shimadzu UV-1800), crystalline metallic silver was examined by X-ray diffractometer (Bruker D8), AFM (Shimadzu SPM9500J2), TEM (TEM-TECNAI-20-G2), FTIR (Cary 630), Raman spectrometer (Nuspec 2.0), Zeta-Sizer (Anton Paar MCP 300), and EDAX (JEOL, JSM-2100F).
Cell Lines & Culture Conditions
The human cancer cell lines, namely, HCT-116 (colon carcinoma), PANC-1 (pancreatic carcinoma) and MDA-MB 231 (breast carcinoma) were cultured in DMEM medium supplemented with 10% FBS (Invitrogen) and 1% antibiotic (Invitrogen) and grown overnight at 37ºC in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2.
Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell (PBMC) Preparation and Cell Culture
The PBMCs were isolated from 5 mL of whole blood consisting of anti-coagulant EDTA (Sigma, MO, USA) from a healthy adult donor on a Ficoll-Hypaque (Hornby, Ontario, Canada) density gradient according to the method described earlier.29 The cells were cultured within T25 culture flask (Corning Incorporated, NY, USA) for overnight in the supplemented RPMI (Sigma, MO, USA) with fetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 U/mL penicillin, 100 µg/mL streptomycin (Sigma, MO, USA) and 2 mM L-glutamine (Gibco, NY, USA) at 37°C for 24 h before any treatments. Before performing the experiment, the medium was discarded and the separated cells were washed and counted.
Cytotoxicity Assay
The MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) assay is a colorimetric assay for determining cell viability. The NAD(P)H oxidoreductase enzymes may possibly reveal the number of viable cells as these enzymes can reduce the tetrazolium dye MTT to purple insoluble formazan. Cytotoxicity evaluation of AgNO3, PJ & PJSNPs was performed in cancer cells (HCT-116, PANC-1 and MDA-MB 231) using MTT assay as described by Mosmann.30 The cytotoxic effect of AgNO3 & PJSNPs was also evaluated in PBMC cells. The cells were harvested and seeded at a density of 1×105 cells/mL in a 96-well plate and were incubated for 24 h in an incubator (37°C, 5% CO2). A series of dilution (10 to 0.0097 mg/mL) of nanoparticles in the medium was added to the cells. After 24 h of incubation, 12 mM MTT stock solution was added to each well and was further incubated at 37°C for 4 hrs. Formazan crystals formed after 4 hrs in each well were dissolved in 100 μL of SDS-HCl solution and kept for incubation in a humidified chamber at 37°C for 4 hrs. The plate was read on a multi-mode plate reader (EnVision, Perkin Elmer) at 570 nm.
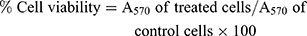
Cell Apoptosis Assay
The number of apoptotic cells induced by PJSNPs with different concentrations was measured by flow cytometry using Annexin V-FITC-PI kit (Sigma-Aldrich, Germany). The Annexin V-PI assay evaluates phosphatidylserine translocation from the inner to the outer layer of the plasma membrane which is an event typically associated with apoptosis. HCT-116, PANC-1 and MDA-MB 231 cells (2×105 per well) were seeded into 6-well plates and treated with IC50 concentrations of PJSNPs. Both control and treated cells were incubated for 24 hrs in an incubator (37°C, 5% CO2). Following the incubation, the cells were washed twice with PBS. Later, the cells (1 × 106 cells/mL) were resuspended in 1X binding buffer. Subsequently, 5 µL each of AnnexinV-FITC and propidium iodide were added to control and treated cell lines. The tubes were incubated at room temperature for exactly 15 min and protected from light. Finally, the cells were analyzed by flow cytometry (FC500, Beckman-Coulter, Hialeah, FL, USA). The controls used to set up compensation and quadrants were unstained cells, cell stained with FITC and Annexin V and cell stained with PI. Flow cytometric analysis was performed using Partec FloMax software.
DNA Fragmentation Assay
The suspension of HCT-116, MDA-MB 231, PANC-1 (106 cells/mL) were seeded in 6-well microplates and treated with IC50 concentration of PJSNPs. The DNA extraction was done using a salting-out method. Extracted DNA was run on a 1% agarose gel for 20 min by applying 100 V, which was then stained with ethidium bromide, and the bands were detected using an ultraviolet transilluminator.
Statistical Analysis
The results are presented as mean ± standard deviation of three experiments. Analysis of the dose–response curve was done using the Software GraphPad Prism 7. IC50 values were determined by plotting triplicate data points over a concentration range and calculating values using regression analysis of Prism software using a 95% confidence level.
Results and Discussion
Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles
UV-Vis Spectra Analysis
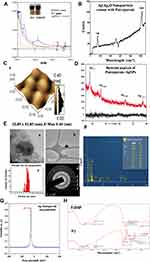
The synthesis of the SNPs in aqueous solution was monitored by recording the absorption spectra at a wavelength range of 200–800 nm (Figure 1A). As the plant extract was mixed with AgNO3, the color of the reaction mixture changed from brown to reddish brown (Figure 1A inset) due to excitation of surface plasmon resonance (SPR) vibration of silver nanoparticles,22 while no color change was observed in the absence of plant extract in AgNO3. The complete color change took after about 30 mins; thereafter, no further color of the reaction mixture changed, indicating that the silver salt present in the reaction mixture has been reduced completely. Nanoparticles absorb light at a different wavelength and get excited due to charge density at the interface between conductor and insulator, the mechanism known as surface plasmon resonance. The absorbance peak between 400 and 450 nm by UV-Vis analysis is the characteristic of SNPs31 and the results obtained are in complete correlation with the earlier studies.21,32 The change in color and λmax with a prominent peak around 420 nm correspond to SNPs formation. SPR peak located between 410 and 450 nm has been observed for SNPs and might be attributed to spherical nanoparticles.31,33,34
Raman Spectroscopic Analysis
Raman spectroscopy (Deitanu Rock Hound Nuspec 2.0) can be used to study chemical identification, characterization of molecular structures, effects of bonding, environment and the stress of the compounds. The Putranjiva roxburghii Wall. capped silver nanoparticles are fine black powder, highly photosensitive towards a wide range of light wavelength similar to the majority of silver compounds.
The most representative Ag2O spectrum shows a very intense band with a peak at 146 cm−1 attributing to Ag lattice vibrational modes, ie, phonons (Figure 1B). The range 200–580 cm−1 is characterized by a broadband in which it is possible to define Raman shifts at 288 and 537 cm−1. The bands at 537 cm−1 can be ascribed to the n(Ag–O) vibrations for sub-surface species and n(O–O) mode for adsorbed molecular oxygen. The peak observed at 1030 cm−1 is probably due to chemosorbed atomic/molecular oxygen species.35 Although sub-surface species might promote adsorption of molecular oxygen, it could also be a probable consequence of surface restructuring in silver nanoparticles.36
Atomic Force Microscopy
The surface topology of the PJSNPs was studied by atomic force microscopy analysis (Figure 1C). This method is used as a primary method to monitor SNPs dissolution and agglomeration pattern. The biologically synthesized silver nanoparticle size was measured using line profile determination of individual particles in the range of 32.85 x 32.85 nm.37 The silver nanoparticles were imaged by AFM to understand the accurate configuration and to confirm that the silver nanoparticles were more or less homogeneous in size and shape. The topography of AFM micrograph clearly indicates that PJSNPs possess spherical shape with ~8 ±2 nm size measured using line profile determination of individual spherical-shaped particles.
X-Ray Diffraction Analysis
The XRD spectrum was recorded to confirm the crystalline structure of synthesized AgNP. The crystallographic structure of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles (Table 1; Figure 1D) depicted four distinct peaks at 37.96°, 45.95°, 64.36° and 77.10° which were the corresponding values of (1 1 1), (2 0 0), (2 2 0) and (311) lattice planes of the face-centered cubic (FCC) silver, closely matching with the reported reference values.38 All diffraction peaks could be well indexed with the cubic structure of silver (Ag) [JCPDS No. 087–0720]. The absence of any other chemical phase indicated the purity and crystallinity of the synthesized PJSNPs. A systematic increase in the broadening of the diffraction peaks with increasing 2θ indicated a concomitant reduction in particle size. The obtained diffraction spectrum strongly suggested the presence of silver nanoparticles in accordance with AFM and Raman spectrum analysis. The 2θ positions of lattice planes were slightly shifted towards the lower angle because of strain generation in silver nano-crystals due to the presence of Putranjiva roxburghii Wall. The resulting PJSNPs are highly uniform in phase & composition. The crystalline phase purity was confirmed by Rietveld refinement of XRD and the uniformity in composition was deduced from the Vegard’s law because the occupancy refinement of PJSNPs cannot give a satisfactory measurement of the stoichiometry. The obtained results were consistent with the sizes of SNPs obtained from TEM analysis.
 |
Table 1 A Summary of Observed d-Spacings, hkl and Lattice Constant for the Biologically Synthesized PJSNPs |
Apart from the characteristic peaks FCC Ag, the diffractogram also showed small hump-like peaks at 44.05° and 54.61° which may be due to the crystallization of the bio-organic phase on the surface of the SNPs. In the Rietveld analysis, the d-value at 44.05° and 54.61° were also under consideration limit but not matched with the SNPs lattice plane. Some other studies reported similar results with various additional peaks39,40 and bio-organic compound/protein (s) might be responsible for such pattern. The authors have suggested that magnesium ions present in the chlorophyll might act as strong X-ray scattering centers in the bio-organic crystalline phase.41
Transmission Electron Microscopy and EDAX
The Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) provided further insight into the morphology and size details of the synthesized SNPs. Transmission electron micrograph reveals that PJSNPs are spherical, as can be observed in Figure 1E, HTEM micrograph (Figure 1E-a and b) and particle size distribution histogram (Figure 1E-c) correspond to silver nanoparticles formed after 24 h of reaction. PJSNPs sizes are ~8 ±2 nm. A typical selected area diffraction pattern is shown in the inset of (Figure 1E-d). Main Diffraction rings can be indexed as (111), (200), (220) and (311) reflections (indicated by numbers 1, 2, 3 and 4, respectively), corresponding to a face-centered cubic (FCC) crystalline structure of PJSNPs. In Figure (1E-a), few particles appeared with contrast difference, while the inorganic core Ag nanoparticles can be seen as darker contrast and polymer shell can be seen as lighter contrast.42 The results are being in good agreement with XRD data. The SAED pattern of nanoparticles sample has also been shown in Figure (1E-d), which revealed a characteristic circular diffraction pattern corresponding to (111), (200), (220) and (311) planes of the face-centered cubic silver nanoparticles.
EDAX analysis shows the presence of eight elements (Ag, C, Cl, S, O, Au, P and Cr) in the PJSNPs powder (Figure 1F), where the silver (60.2 weight%) is present as major element followed by carbon (25.4 weight%), chlorine (5.9 weight%), sulfur (2.6 weight%), oxygen (2.5 weight%) and gold (1.7 weight%). However, some other unidentified peaks were also seen (contributing 1.7 weight%). Thus, this study indicates that pure crystalline nature is solely composed of silver. Similar studies exhibiting weak signals from Cl in synthesized SNPs colloid have also been reported which may be due to the presence of impurities in bacterial supernatant.43
As TEM coupled Oxford EDAX, microprobe analysis is a quantitative analysis of several spots was carried out, and finally, an average value of elements is considered. TEM and EDAX studies revealed the spherical nature of particles synthesized from silver metal.
Zeta Potential
Zeta potential experiments were carried out to investigate the electrostatic stability of the synthesized PJSNPs. The magnitude of the zeta potential is a measure of electrostatic repulsion between adjoining and similarly charged particles in a dispersion. Molecules or colloids with high zeta potential values are electrostatically stable in comparison to colloids with low zeta potential as in the later case attractive forces are greater than the repulsive forces resulting in coagulation.44 In the present study, PJSNPs owned a zeta potential of −26.71 mV (Figure 1G) which suggests that the surface of the nanoparticles is negatively charged and dispersed in the medium. The negative value confirms the repulsion between the particles and proves that they are very stable. Also, the negatively charged particles are less cytotoxic compared to positively charged and the later ones are rapidly cleared from the bloodstream.45
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
The FTIR measurement was studied to identify the possible biomolecules responsible as capping and reducing agent for the SNPs synthesized by the extract (Figure 1H). The intense broadbands at 3600 and 3200 cm−1 are probably due to the O–H and C–H stretching modes, respectively. The PJSNPs did not show any band at 1744 cm−1, whereas the prominent band of the same frequency was observed in the PJ extract, indicating that the SNPs are stabilized through the C=O bond. Carbonyl groups of the amino acid residues and peptides of proteins have a strong affinity for metal binding, signifying the importance of protein as an encapsulating agent.46 Similarly, the absence of a peak at 1461 cm−1 (C=C group) in PJSNPs is probably due to the reduction of AgNO3 to Ag.47 Comparison of the FTIR spectra of PJSNPs with PJ extract discloses the occurrence of functional groups such as amines, carboxylic acids, aldehydes and alcohols which are most likely to be accountable for reducing and capping the silver ions.48
Anticancer Potential of PJ Extract and PJSNPs
Brine Shrimp Lethality Assay
It is an important tool for the preliminary cytotoxicity screening of plant extracts based on the ability to kill laboratory-cultured brine shrimp. Criteria of toxicity followed were LC50 values >1000 μg/mL (non-toxic), 500 to 1000 μg/mL (weak toxicity) and <500 μg/mL (toxic).49,50
In the present study, four different concentrations (2, 20, 200 and 2000 µg/mL) of PJ extract, as well as PJSNPs, were used to access their cytotoxicity using the brine shrimp lethality assay. LC50 values for PJ (2000 µg/mL) were three times higher than the PJSNPs (632.45 µg/mL). As already reported LC50 values > 1000 μg/mL are non-toxic; consequently, PJ is non-cytotoxic in nature; however, PJSNPs exhibited weak toxicity in the brine shrimp lethality assay. The toxicity of silver nanoparticles against brine shrimp has also been reported in the literature.51,52 Collectively, the cytotoxic effects of PJSNPs to brine shrimp can be associated with anti-cancer properties and could be developed further as an unconventional source of anti-cancer drugs. Therefore, we further studied the cytotoxic effect of the PJ extract and PJSNPs in the different cell lines using the MTT assay.
MTT Assay
The MTT reduction assay is used for the determination of the cytotoxic effect of a substance in the liver cells. The AgNO3, PJ extract and PJSNPs were tested against PANC-1, MDA-MB 231 and HCT-116 cell lines. The results (Table 2; Figure 2) show the cytotoxicity at different concentrations (10 to 0.0097 mg/mL) in a dose-dependent manner which is supported by a previous study in which silver nanoparticles have affected the cell viability in a dose-dependent manner in a variety of mammalian cell lines.53
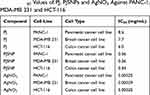 |
Table 2 IC50 Values of PJ, PJSNPs and AgNO3 Against PANC-1, MDA-MB 231 and HCT-116 |
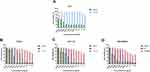
As compared to control, the percentage of cell growth inhibition was found to be very high with different concentrations of AgNO3 followed by PJSNPs and PJ. The cytotoxic effect of AgNO3 and PJSNPs were also tested in isolated PBMC cells where AgNO3 caused cytotoxicity (55% cell viability) even at the lowest concentration (0.0097 mg/mL) whereas PJSNPs showed no toxic effect of the same concentration (Figure 3). The IC50 values of PJ extract (8.6, 6.0 and 7.7 mg/mL) were higher compared to PJSNPs (0.36, 0.54 and 0.26 mg/mL) and AgNO3 (0.00025, 0.0025 and 0.0029 mg/mL) against PANC-1, HCT-116 and MDA-MB 231 cell lines after 24 hrs of incubation (Table 2). From the results, the cytotoxicity of AgNO3 > PJSNPs > PJ which signifies the importance of nanonization of AgNO3 to PJSNP as the former is showing toxicity in normal cells also at the lowest tested concentration. The reason for higher toxicity of PJSNPs may be due to the stimulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) activity leading to various cellular events like cytotoxicity, unregulated cell signaling, DNA damage, apoptosis, and cancer.54,55 In the previous studies, silver nanoparticles are reported to interfere with the electron-transport chain by activation of NADPH-related enzymes and depolarizing the mitochondrial membrane resulting in increased cellular levels of ROS.56–58 In another study when human glioblastoma and fibroblast cells were treated with silver nanoparticles, high levels of ROS-mediated cytotoxicity were observed due to disruption of the electron-transfer chain.59 However, in one of the studies, researchers reported a different mechanism which involves deactivation of enzymes by the formation of stable S-Ag bond with the thiol group of enzymes in the cell membrane; or denaturation of the DNA by breaking hydrogen bonds between nitrogen.22 Some of the studies claim that the smaller the size of silver nanoparticles, the stronger is the cytotoxicity,60,61 because the size has an effect on its uptake by the cells. We have also observed similar results in the present study that the small size (~8 ±2 nm) of PJSNPs may be the reason for better cellular activity of PJSNPs compared to PJ extract.
The cytotoxicity displayed by PJSNPs at lower concentrations might be linked to the phytoconstituents present in the plant extracts which are involved in AgNP formation.62 Moreover, the cytotoxic effects of biosynthesized AgNPs against breast cancer MCF-7 cell line,63 Hep-2 cancer cell line64 and HeLa cell lines65 also support our outcomes.
Apoptosis Induction
To find out if the mechanism of cell death is by apoptosis, the cancer cell lines were treated at IC50 concentration of PJSNPs. The results were evaluated by Annexin V-FITC/PI assay and DNA fragmentation assay.
- Annexin V-FITC/PI assay. Cell death induced by PJSNPs was investigated for apoptotic activity by monitoring Phosphatidylserine (PS) translocation using the Annexin V-FITC/PI assay. Early apoptosis is characterized by the translocation of PS from the inner layer of the plasma membrane to the outer surface.66 Apoptotic cells are reflected by the quantification of Annexin V-FITC binding to externalized PS. In flow cytometer analysis, Annexin V/Propidium iodide (AnnV/PI) staining is based on the ability of the protein Annexin V to bind to Phosphatidylserine (PS), which is externalized in the outer cell membrane leaflet upon induction of apoptosis. In viable cells, PS is located in the inner-membrane leaflet, but upon induction of apoptosis, it is translocated to the outer-membrane leaflet and becomes available for Annexin V binding. The addition of PI enabled viable (AnnV−/PI−), early apoptotic (AnnV+/PI−), late apoptotic (AnnV+/PI+), and necrotic (AnnV−/PI+) cells to be distinguished.67 The flow cytometry analysis of HCT-116, MDA-MB 231 and PANC-1 and cells showed that the cell population tended to shift from viable to apoptotic, on treatment with PJSNPs. After treatment with IC50 concentration of PJSNPs, the apoptotic cells were found higher in HCT-116 (71.5%), MDA-MB 231 (69.0%) and PANC-1 (76.8%) cells as compared to the respective control. In contrast, the more number of live cells was found in untreated HCT-116 (87.2%), MDA-MB 231 (73.3%) and PANC-1 (99.1%) cells (Figure 4). In addition, the percent of dead (necrotic) cells observed in treated cells were 8.38, 1.18 and 3.78 in HCT-116, MDA-MB 231 and PANC-1, respectively (Figure 4). These results demonstrate the ability of PJSNPs to exert apoptosis in all the tested cancer cell lines.
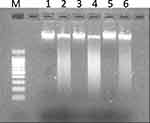
- DNA fragmentation assay. The DNA of HCT-116, PANC-1 and MDA-MB 231 cells treated with PJSNPs at IC50 concentration were extracted and loaded on the agarose gel. The results of DNA “laddering” pattern extracted from cells treated with PJSNPs are shown in Figure 5, (Supplementary Figure 1). The fragmentation pattern we observed was quite similar to that reported for cancer cell lines treated with silver nanoparticle.68 It appears that during DNA fragmentation the silver particles accumulated inside the nucleus may possibly influence the DNA and cell division69 by stimulating dose-dependent DNA damage, chromosomal aberrations, errors in chromosome segregation, sister chromatic exchanges and formation of micronuclei.59,70 Consequently, it can be speculated that the similar pathways are pursued by PJSNPs to induce DNA fragmentation.
Conclusion
Putranjiva roxburghii Wall. mediated silver nanoparticles (PJSNPs) were synthesized and characterized using various techniques. The silver nanoparticles were ~8± 2 nm spherical shaped, face-centered cubic having a negative charge. The small size and negative zeta potential could be the reasons that they are specifically taken up by the tumor cells. The biological studies indicated that aqueous extract of Putranjiva roxburghii Wall. seed was non-cytotoxic while the silver nanoparticles displayed weak cytotoxicity in the brine shrimp lethality assay. In MTT assay, PJSNPs displayed better cytotoxicity than PJ extract. However, AgNO3 is toxic to normal cell also at the lowest tested concentration whereas PJSNPs showed no toxic effect at the same concentration. This reflects the importance of nanonization of AgNO3 to PJSNP as the former is displaying toxic effect in normal cells also. In addition, the flow cytometric studies confirmed that the PJSNPs induced cell death via the apoptosis mechanism.
Thus, our findings propose the anticancer prospective of biosynthesized PJSNPs against human cancer cells and might play a significant role in the development of new and effective therapeutic agent for cancer treatment.
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to Patanjali Yogpeeth, Haridwar (India) for providing Putranjiva roxburghii Wall. seeds and to the Patanjali Ayurvedic Hospital, Haridwar (India) for providing blinded whole blood samples from healthy donors for the study. We also gratefully acknowledge UGC-DAE Consortium for Scientific Research, Indore (India) for providing the facilities for AFM, XRD and Raman, and the Indian Institute of Petroleum, Dehradun (India) for EDAX facility. The authors sincerely acknowledge Dr. L.N. Misra, Chief Research Advisor, Patanjali Research Foundation, Haridwar (India) for his suggestions and expert guidance in improving the quality of the paper.
Disclosure
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
1. Lu W, Lieber CM. Nanoelectronics from the bottom up. Nat Mater. 2007;6:841–850. doi:10.1038/nmat2028
2. Shen Y, Friend CS, Jiang Y, et al. Nanophotonics: interactions, materials and applications. J Phys Chem B. 2000;104:7577–7587. doi:10.1021/jp0016131
3. Karni TC, Langer R, Kohane DS. The smartest materials: the future of nanoelectronics in medicine. ACS Nano. 2012;6:6541–6545. doi:10.1021/nn302915s
4. Nordberg G, Gerhardsson L. Silver. In: HG S, Sigel H, Sigel A, editors. Handbook on Toxicity of Inorganic Compounds. New York: Marcel Dekker; 1988:619–624.
5. Stark WJ, Stoessel PR, Wohlleben W, Hafner A. Industrial applications of nanoparticles. Chem Soc Rev. 2015;44(16):5793–5805. doi:10.1039/C4CS00362D
6. Jain S, Mehata MS. Medicinal plant leaf extract and pure flavonoid mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their enhanced antibacterial property. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):15867. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-15724-8
7. Prow TW, Grice JE, Lin LL, et al. Nanoparticles and microparticles for skin drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011;63(6):470–491. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2011.01.012
8. Nair R, Varghese SH, Nair BG, Maekawa T, Yoshida Y, Kumar DS. Nanoparticulate material delivery to plants. Plant Sci. 2010;179(3):154–163. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2010.04.012
9. Bankura KP, Maity D, Mollick MM, et al. Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of dextran stabilized silver nanoparticles in aqueous medium. Carbohydr Polym. 2012;89(4):1159–1165. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.03.089
10. Kora AJ, Arunachalam J. Assessment of antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles on Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its mechanism of action. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011;27(5):1209–1216. doi:10.1007/s11274-010-0569-2
11. Abid JP, Wark AW, Brevet PF, Girault HH. Preparation of silver nanoparticles in solution from a silver salt by laser irradiation. Chem Comm. 2002;7:792–793. doi:10.1039/b200272h
12. Solano-Ruiz E, Sato Berrú R, Ocotlán-Flores J, Saniger JM. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles by sonochemical induced reduction application in SERS. J Nanopart Res. 2010;9:77–81. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/JNanoR.9.77
13. Maity D, Kanti Bain M, Bhowmick B, et al. In situ synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles using water soluble polymer. J Appl Polym Sci. 2011;122(4):2189–2196. doi:10.1002/app.34266
14. El-Rafie MH, El-Naggar ME, Ramadan MA, et al. Environmental synthesis of silver nanoparticles using hydroxypropyl starch and their characterization. Carbohydr Polym. 2011;86(2):630–635. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.04.088
15. Kalathil S, Lee J, Cho MH. Electrochemically active biofilm-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles in water. Green Chem. 2011;13:1482–1485. doi:10.1039/c1gc15309a
16. Zaarour M, El Roz M, Dong B, et al. Photochemical preparation of silver nanoparticles supported on zeolite crystals. Langmuir. 2014;30:6250–6256. doi:10.1021/la5006743
17. Kessler MT, Hentschel MK, Heinrichs C, Roitsch S, Prechtl MH. Fast track to nanomaterials: microwave assisted synthesis in ionic liquid media. RSC Adv. 2014;4:14149–14156. doi:10.1039/C3RA47801G
18. Adil SF, Assal ME, Khan M, Al-Warthan A, Siddiqui MRH, Liz-Marzán LM. Biogenic synthesis of metallic nanoparticles and prospects toward green chemistry. Dalton Trans. 2015;44:9709–9717. doi:10.1039/C4DT03222E
19. Otari S, Patil R, Waghmare S, Ghosh S, Pawar S. A novel microbial synthesis of catalytically active Ag–alginate biohydrogel and its antimicrobial activity. Dalton Trans. 2013;42:9966–9975. doi:10.1039/c3dt51093j
20. Ghaffari-Moghaddam M, Hadi-Dabanlou R, Khajeh M, et al. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using plant extracts. Kr J Chem Eng. 2014;31(4):548–557.
21. Shiv Shankar S, Rai A, Ahmad A, Sastry M. Rapid synthesis of Au, Ag, and bimetallic Au core–ag shell nanoparticles using neem (Azadirachta indica) leaf broth. Colloid Interf Sci. 2004;275(2):496–502. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2004.03.003
22. Ahmed S, Ahmad M, Swami BL, Ikram S. A review on plants extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications: a green expertise. J Adv Res. 2016;7(1):17–28. doi:10.1016/j.jare.2015.02.007
23. Reanmongkol W, Noppapan T, Subhadhirasakul S. Antinociceptive, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory activities of Putranjiva roxburghii Wall. Wall. leaf extract in experimental animals. J Nat Med. 2009;63:290–296. doi:10.1007/s11418-009-0336-6
24. Rajagopal PL, Kiron SS, Sreejith KR, Aneeshia S. Phytochemical, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory studies on the leaves of Putranjiva roxburghii. Am J Pharm Tech Res. 2014;4:429–435.
25. Sahni KC. The Book of Indian Tree.
26. Singh A, Dubey NK. An ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants in Sonebhadra District of Uttar, Pradesh, India with reference to their infection by foliar fungi. J Med Plants Res. 2013;6(14):2727–2746.
27. Maurya R, Dongarwar N. Studies on the medicinal uses of wild trees of Nagpur district. Int J Life Sci Pharma Res. 2012;2:21–25.
28. Khan MZH, Tareq FK, Hossen MA, Roki MNAM. Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Coriandrum sativum leaf extract. J Eng Sci Tech. 2018;13(1):158–166.
29. Molaae N, Mosayebi G, Pishdadian A, Ejtehadifar M, Ganji A. Evaluating the proliferation of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells using MTT assay. Int J Basic Sci Medi. 2017;2(1):25–28. doi:10.15171/ijbsm.2017.06
30. Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Method. 1983;65(1–2):55–63. doi:10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4
31. Raman RP, Parthiban S, Srinithya B, et al. Biogenic silver nanoparticles synthesis using the extract of the medicinal plant Clerodendron serratum and its in-vitro antiproliferative activity. Mat Lett. 2015;160:400–403. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2015.08.009
32. Prathna TC, Chandrasekaran N, Raichur AM, Mukherjee A. Biomimetic synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Citrus limon (lemon) aqueous extract and theoretical prediction of particle size. Colloids Surf B Biointerf. 2011;82:152–159. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2010.08.036
33. Zaheer Z. Silver nanoparticles to self-assembled films: green synthesis and characterization. Colloids Surf B Biointerf. 2012;90:48–52. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2011.09.037
34. Rahisuddin A. Extracellular synthesis of silver dimer nanoparticles using Callistemon viminalis (bottlebrush) extract and evaluation of their antibacterial activity. Spec Lett. 2016;49:268–275. doi:10.1080/00387010.2016.1140654
35. Martina I, Wiesinger R, Jembrih-Simbürger D, Scheiner M. Micro-raman characterisation of silver corrosion products: instrumental set up and reference database. E-Preserv Sci. 2012;9:1–8.
36. Liang H, Li Z, Wang W, et al. Highly surface-roughened “Flower-like” silver nanoparticles for extremely sensitive substrates of surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Adv Mater Tech. 2009;21(45):4614–4618. doi:10.1002/adma.v21:45
37. Chistensen L, Vivekanandhan S, Misra M, Mohanty AK. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Murraya koenigii (curry leaf): an investigation on the effect of broth concentration in reduction mechanism and particle size. Adv Mater Lett. 2011;2(6):429–434. doi:10.5185/amlett.2011.4256
38. Al-Harbi MS, El-Deeb BA, Mostafa N, Amer SA. Extracellular biosynthesis of SNPs by the bacterium Proteus mirabilis and its toxic effect on some aspects of animal physiology. Adv Nanoparticles. 2014;3(3):83. doi:10.4236/anp.2014.33012
39. Shaik MR, Khan M, Kuniyil M, et al. Plant-extract-assisted green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using origanum vulgare L. Extract and their microbicidal activities. Sustainability. 2018;10(4):913. doi:10.3390/su10040913
40. Tripathy A, Raichur AM, Chandrasekaran N, Prathna T, Mukherjee A. Process variables in biomimetic synthesis of silver nanoparticles by aqueous extract of Azadirachta indica (Neem) leaves. J Nanopart Res. 2010;12:237–246. doi:10.1007/s11051-009-9602-5
41. Shankar SS, Ahmad A, Sastry M. Geranium leaf assisted biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles. Biotechnol Prog. 2003;2003(19):1627–1631. doi:10.1021/bp034070w
42. Jang J, Lim B. Facile fabrication of inorganic‐polymer core–shell nanostructures by a one‐step vapor deposition polymerization. Angewandte Chemie. 2003;115(45):5758–5761. doi:10.1002/(ISSN)1521-3757
43. Vanaja M, Paulkumar K, Baburaja M, et al. Degradation of methylene blue using biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles. Bioinorg Chem Appl. 2014;2014.
44. Hanaor D, Michelazzi M, Leonelli C, Sorrell CC. The effects of carboxylic acids on the aqueous dispersion and electrophoretic deposition of ZrO2. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2012;32:235–244. doi:10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2011.08.015
45. Honary S, Zahir F. Effect of zeta potential on the properties of nano-drug delivery systems-a review (Part 2). Trop J Pharma Res. 2013;12:265–273.
46. Kushwaha H, Malik C. Assessment of antibacterial and antifungal activities of silver nanoparticles obtained from the callus extracts (stem and leaf) of Tridax procumbens. Ind J Biotechnol. 2014;13:114–120.
47. He Y, Du Z, Lv H, et al. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat. extract and their application in clinical ultrasound gel. Int J Nanomed. 2013;8:1809–1815.
48. Philip D. Mangifera indica leaf-assisted biosynthesis of well-dispersed silver nanoparticles. Spectrochim Acta a Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2011;78(1):327–331. doi:10.1016/j.saa.2010.10.015
49. Déciga-Campos M, Rivero-Cruz I, Arriaga-Alba M, et al. Acute toxicity and mutagenic activity of Mexican plants used in traditional medicine. J Ethnopharmacol. 2007;110:334–342. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2006.10.001
50. Bastos MLA, Lima M, Conserva LM, et al. Studies on the antimicrobial activity and brine shrimp toxicity of Zeyheria tuberculosa (Vell.) Bur. (Bignoniaceae) extracts and their main constituents. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2009;8:16–22. doi:10.1186/1476-0711-8-16
51. Kummara S, Patil MB, Uriah T. Synthesis, characterization, biocompatible and anti-cancer activity of green and chemically synthesized silver nanoparticles- A comparative study. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;84:10–21. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2016.09.003
52. Acharya B, Sharma N, Sharma VK, et al. Green synthesis, characterisation and biological studies of SNPs prepared using Shivlingi (Bryonia laciniosa) seed extract. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2017;12(3):371–375.
53. Sambale F, Wagner S, Stahl F, et al. Investigations of the toxic effect of silver nanoparticles on mammalian cell lines. J Nanomater. 2015;16(1):6.
54. Nel A, Xia T, Mädler L, Li N. Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science. 2006;311:622–627. doi:10.1126/science.1114397
55. Xia T, Kovochich M, Liong M, et al. Comparison of the mechanism of toxicity of zinc oxide and cerium oxide nanoparticles based on dissolution and oxidative stress properties. ACS Nano. 2008;2:2121–2134. doi:10.1021/nn800511k
56. Soenen SJ, Rivera-Gil P, Montenegro J-M, et al. Cellular toxicity of inorganic nanoparticles: common aspects and guidelines for improved nanotoxicity evaluation. Nano Today. 2011;6:446–465. doi:10.1016/j.nantod.2011.08.001
57. Smith KR, Klei LR, Barchowsky A. Arsenite stimulates plasma membrane NADPH oxidase in vascular endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2001;280:L442–L449. doi:10.1152/ajplung.2001.280.3.L442
58. Xia T, Kovochich M, Brant J, et al. Comparison of the abilities of ambient and manufactured nanoparticles to induce cellular toxicity according to an oxidative stress paradigm. Nano Lett. 2006;6:1794–1807. doi:10.1021/nl061025k
59. AshaRani P, Low Kah Mun G, Hande MP, Valiyaveettil S. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human cells. ACS Nano. 2008;3:279–290. doi:10.1021/nn800596w
60. He D, Bligh MW, Waite TD. Effects of aggregate structure on the dissolution kinetics of citrate-stabilized silver nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol. 2013;47:9148–9156. doi:10.1021/es400391a
61. Kittler S, Greulich C, Diendorf J, Köller M. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles increases during storage because of slow dissolution under release of silver ions. Chem Mater. 2010;22:4548–4554. doi:10.1021/cm100023p
62. Farah MA, Ali MA, Chen S-M, et al. Silver nanoparticles synthesized from adenium obesum leaf extract induced DNA damage, apoptosis and autophagy via generation of reactive oxygen species. Colloids Surf B Biointerf. 2016;141:158–169. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.01.027
63. Vivek R, Thangam R, Muthuchelian K, et al. Green biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from Annona squamosa leaf extract and its in vitro cytotoxic effect on MCF-7 cells. Process Biochem. 2012;47(12):2405–2410. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2012.09.025
64. Jacob SJP, Finub JS, Narayanan A. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using piper longum leaf extracts and its cytotoxic activity against Hep-2 cell line. Colloids Surf B Biointerf. 2012;91:212–214. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2011.11.001
65. Suman TY, Radhika Rajasree SR, Kanchana A, et al. Biosynthesis, characterization and cytotoxic effect of plant mediated silver nanoparticles using Morinda citrifolia root extract. Colloids Surf B Biointerf. 2013;106:74–78. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.01.037
66. Cury-Boaventura MF, Pompéia C, Curi R. Comparative toxicity of oleic acid and linoleic acid on Jurkat cells. Clin Nutr. 2004;23:721–732. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2003.12.004
67. Baskić D, Popović S, Ristić P, Arsenijević NN. Analysis of cycloheximide-induced apoptosis in human leukocytes: fluorescence microscopy using annexin V/propidium iodide versus acridin orange/ethidium bromide. Cell Biol Int. 2006;30(11):924–932. doi:10.1016/j.cellbi.2006.06.016
68. Kalishwaralal K, Banumathi E, Pandian SRK, et al. Silver nanoparticles inhibit VEGF induced cell proliferation and migration in bovine retinal endothelial cells. Colloids Surf B Biointerf. 2009;73:51–57. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2009.04.025
69. Wang J, Zhou G, Chen C, et al. Acute toxicity and bio distribution of different sized titanium dioxide particles in mice after oral administration. Toxicol Lett. 2007;168:176–185. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2006.12.001
70. Lu P-J, Ho I-C, Lee T-C. Induction of sister chromatid exchanges and micronuclei by titanium dioxide in Chinese hamster ovary-K1 cells. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 1998;414:15–20. doi:10.1016/S1383-5718(98)00034-5
 © 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.