Back to Journals » International Journal of Nanomedicine » Volume 16
Application of Radiosensitizers in Cancer Radiotherapy
Authors Gong L, Zhang Y, Liu C, Zhang M , Han S
Received 18 November 2020
Accepted for publication 19 January 2021
Published 12 February 2021 Volume 2021:16 Pages 1083—1102
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S290438
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Liuyun Gong, 1 Yujie Zhang, 2, 3 Chengcheng Liu, 2 Mingzhen Zhang, 2, 3 Suxia Han 1
1Department of Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, Shaanxi, 710061, People’s Republic of China; 2School of Basic Medical Sciences, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, Shaanxi, 710061, People’s Republic of China; 3Key Laboratory of Environment and Genes Related to Diseases, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Ministry of Education, Xi’an, Shaanxi, 710061, People’s Republic of China
Correspondence: Mingzhen Zhang; Suxia Han Email [email protected]; [email protected]
Abstract: Radiotherapy (RT) is a cancer treatment that uses high doses of radiation to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. Although great success has been achieved on radiotherapy, there is still an intractable challenge to enhance radiation damage to tumor tissue and reduce side effects to healthy tissue. Radiosensitizers are chemicals or pharmaceutical agents that can enhance the killing effect on tumor cells by accelerating DNA damage and producing free radicals indirectly. In most cases, radiosensitizers have less effect on normal tissues. In recent years, several strategies have been exploited to develop radiosensitizers that are highly effective and have low toxicity. In this review, we first summarized the applications of radiosensitizers including small molecules, macromolecules, and nanomaterials, especially those that have been used in clinical trials. Second, the development states of radiosensitizers and the possible mechanisms to improve radiosensitizers sensibility are reviewed. Third, the challenges and prospects for clinical translation of radiosensitizers in oncotherapy are presented.
Keywords: radiosensitizers, cancer radiotherapy, therapeutics, nanomedicine, mechanism
Corrigendum for this paper has been published
Introduction
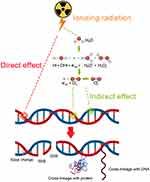
Cancer remains one of the greatest challenges to human health. World Health Organization (WHO) reported that about 8.8 million deaths worldwide were due to cancer in 2015, and the deaths are expected to break through 13 million in 2030 according to the report by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). To reduce the deaths from cancer, several strategies have been developed in recent years to improve cancer therapy including surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, hormone therapy, stem cell transplant and precision medicine.1 Among them, radiotherapy (RT) is considered as one important and effective modality to kill or control tumors since Marie Curie, the Nobel Prize winner, discovered radioactivity.2 Typically, RT is a treatment modality to cancer cells by using high-energy photon radiation such as X-rays, gamma (γ)-rays, and others. RT can take effect via direct and indirect mechanisms to destroy cancer cells and tumor tissue (Figure 1).
In the direct action, radiation directly induces single-strand breaks (SSB) and double-strand breaks (DSB) in DNA, resulting in the termination of cell division and proliferation, or even cell necrosis and apoptosis. In the case of indirect action, radiation induces the generation of ROS, which can induce cellular stress in, and injure biomolecules, and and ultimately alter cellular signaling pathways. Clinical studies have shown that more than half (about 70%) of patients need to receive RT, and in some cases RT is the only kind of cancer treatment.3 Therefore, there is a great need to develop approaches to improve radiosensitivity.
Innovative technologies can provide alternative strategies to improve RT efficiency. For example, image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) is the use of imaging during radiation therapy to improve the precision and accuracy of treatment delivery. IGRT can be used to treat tumors in areas of the body that move, such as the lungs. RT machines are equipped with imaging technology to allow your doctor to image the tumor before and during treatment. By comparing these images to the reference images taken during simulation, the patient’s position and/or the radiation beams may be adjusted to more precisely target the radiation dose to the tumor. To help align and target the radiation equipment, some IGRT procedures may use fiducial markers, ultrasound, MRI, X-ray images of bone structure, CT scan, 3D body surface mapping, electromagnetic transponders or colored ink tattoos on the skin.4 Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) is an advanced mode of high-precision RT that uses computer-controlled linear accelerators to deliver precise radiation doses to a malignant tumor or specific areas within the tumor.5 Although the abovementioned innovative technologies greatly improve the therapeutic effect, there are still obstacles such as cancer stem cells and tumor heterogeneity making it difficult to use RT alone to cure tumors. Radiosensitizers with the ability to increase the radiosensitivity of tumor tissue and pharmacologically decrease normal tissue toxicity are expected to be an efficient way to improve RT.6
Radiosensitizers are compounds that, when combined with radiation, achieve greater tumor inactivation than would have been expected from the additive effect of each modality. G E Adams, a pioneer in the field of RT, classified radiosensitizers into five categories: (1) suppression of intracellular thiols or other endogenous radioprotective substances; (2) formation of cytotoxic substances by radiolysis of the radiosensitizer; (3) inhibitors of repair of biomolecules; (4) thymine analogs that can incorporate into DNA; and (5) oxygen mimics that have electrophilic activity.7,8 This classification was based on the mechanism of DNA damage and repair and indicated the direction for radiosensitizers at the early stage. However, with the continuous technological innovation, more and more materials and drugs with radiotherapy sensitization have been defined as radiosensitizers. In addition, some in-depth mechanisms for radiosensitization have also been discovered.9,10 According to the latest research, radiosensitizers can be classified into three categories based on their structures: small molecules (Figure 2), macromolecules (Table 1), and nanomaterials (Table 2).11 In the following part, the applications, the main role, and influencing factors of these three types of radiosensitizers are first summarized, especially those have currently entered clinical trials. Second, the development status and the mechanism of action of the radiosensitizer are also summarized. Third, the future development and application of the radiosensitizer was presented.
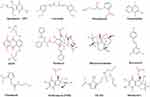 |
Figure 2 Molecular structures of some representative small-molecule radiosensitizers discussed in this paper. |
 |
Table 1 Some Macromolecule Radiosensitizers Discussed in This Paper |
 |
Table 2 The List of Nanomaterials Used for Radiosensitization |
Small Molecules
Oxygen
Hypoxia in tumor microenvironment is one of the major limitations to radiotherapy. Tumor cells in the hypoxic microenvironment are much more resistant to radiation than in the normal oxygen microenvironment.12–14 Oxygen enhancement ratio (OER) or oxygen enhancement effect in radiobiology refers to the enhancement of the therapeutic or detrimental effect of ionizing radiation due to the presence of oxygen. This so-called oxygen effect is most notable when cells are exposed to an ionizing radiation dose.15,16 Oxygen, a potent radiosensitizer, promotes free radical formation through its unique electronic configuration. As the most electrophilic cellular molecule, oxygen is easily reduced by electrons formed from the incident radiation. After oxygenated tumor irradiation, energy transfer results in the radiolysis of water with the initial formation of an ion radical that then forms the highly reactive hydroxyl radical after reaction with another water molecule. Oxygen leads to the formation of peroxide after reaction with the hydroxyl radical. Then, the peroxide results in permanent cellular and DNA damage.13
Accompanied with solid tumor growth, the surrounding vasculatures are not in sufficient quantities to supply oxygen to the new cells, the cancer cell mass becomes heterogeneous gradually, and necrosis occurs following ischemia. Normally, cancer cells undergo apoptosis through the p53 pathway, while those heterogeneous cells adapt to the hypoxic environment efficiently by activation of additional signaling pathways, especially the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) pathway.17–19 Studies showed that HIF-1α was associated with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling pathway, glucose transport, and glycolysis pathway, which could help the tumor to build vasculature.19–21 Under hypoxia, the cancer cells are more aggressive and resisted radiotherapy significantly. Thus, hypoxia often occurs in most solid tumors and leads to radioresistance both through increasing free radical scavenging and changing patterns of gene expression.22,23
More and more research has been devoted to overcoming hypoxia problems, from using high-pressure oxygen tanks and blood substitutes that carried oxygen, to using intricate, accurate approaches that proportionated differences in partial pressure of oxygen (PO2) between tumors and healthy tissue.24,25 Hyperbaric oxygen is the most direct method to ameliorate hypoxia in tumor cells, while this method is inconvenient and may increase complications sometimes.26,27 A new radiosensitizer, Kochi oxydol-radiation therapy for unresectable carcinomas (KORTUC), is being evaluated by a Phase I/II clinical trial (NCT02757651) for the treatment of malignant tumors that contain numerous hypoxic cancer cells and/or large quantities of antioxidative enzymes.28
Oxygen Mimics
Oxygen mimetics, using the chemical properties of molecular oxygen as a template, have higher electron affinity and better diffusion properties to anoxic tissue than oxygen. As oxygen mimetics can theoretically substitute for oxygen in “fixing” radiation-induced damage of DNA, making it nonrepairable and hence lethal. Therefore, oxygen mimetics are considered as “true radiosensitizers”. The most representative oxygen mimetics are nitro-containing compounds and nitric oxide (NO).13
The prototype of electron-affinity radiosensitizers is nitrobenzene, and then researchers focus on nitroimidazole and its derivatives.29–31 Nitroimidazoles, which undergo enzymatic and radiation-induced redox reactions. These agents are intrinsic inactive, their effect becomes evident only in the presence of ionizing radiation to “fix” or stabilize DNA radical lesions in oxygen-deficient cells.32 Misonidazole, a 2-nitroimidazole, is one of the earliest developed nitroimidazoles. In preclinical studies, misonidazole showed better radiosensitizing effect than 5-nitro imidazole or metronidazole (Flagyl®) in the majority of solid murine tumors.33–35 However, the results were unsatisfactory in clinical trials, since severe neurotoxicity was caused by misonidazole.36–39 Metronidazole, a 5-substituted nitroimidazole, which has less electron-affinic was proven as an inferior radiosensitizer.40,41 In conclusion, because of the dose-limiting toxicity at clinically tolerable doses, misonidazole and metronidazole are not the ideal candidates in radiotherapy.42
In view of the issues discussed above, further efforts have been made to improve the pharmacokinetic properties of nitroimidazoles. Second-generation nitroimidazole radiosensitizers, such as etanidazole or nimorazole, are designed to increase the hydrophilicity of the reagents and thereby reduce neurotoxicity. For example, etanidazole has better hydrophilicity than misonidazole because its side chain is modified by hydroxyl.43 Although etanidazole presents lower preclinical toxicity and higher efficacy, it shows no obvious benefit for head and neck cancer patients in randomized studies.44 Nimorazole, a 5-nitroimidazole, is recommended for the treatment of head and neck cancers in Denmark since its beneficial effects in several clinical trials. Moreover, it has been further explored in an EORTC international trial.45–51 Notably, the DAHANCA 28 trial demonstrated that hyperfractionated, accelerated radiotherapy with concomitant cisplatin and nimorazole (HART-CN) for patients was feasible and yielded favorable tumor control.52 Other nitro compounds have also been exploited for hypoxia radiosensitization. Dinitroazetidine, RRx-001, has been evidenced as an effective radiosensitizer with low toxicity and is now being evaluated in the NCT02871843 clinic trial.53
Nitrogen oxides, in particular, NO, act as radiosensitizers through many direct and indirect mechanisms. Similar to the oxidative stress induced by oxygen, NO can “fix” or stabilize radiation-induced DNA damage through nitrosative stress pathways.54 Oxidative and nitrosative stress pathways involve the generation of reactive species. For example, nitrous acid, peroxynitrite (ONOO–), and nitric acid produce cytotoxic effects through mechanisms including DNA cross-linking, protein nitrosylation, glutathione depletion, and inhibition of mitochondrial respiration.55–58 As an uncharged free radical, NO can diffuse across cell membranes freely and bind to soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) to induce cyclic GMP production, thereby regulating vascular physiology.59–61 Researchers have reported that 5-nitroimidazoles and sanazole can release NO.62,63
A phase I study of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients suggested that NO donation increased tumor perfusion and, therefore, promoted tumor growth.64 However, a phase II study of prostate cancer patients claimed that low-dose NO had no direct cytotoxic effect, but could decrease hypoxia through improving blood flow in tumor tissue.65 Some anticancer drugs approved by US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), such as bevacizumab, sorafenib, and etaracizumab played their roles by blocking the VEGF pathway to some extent.66 VEGF is overexpressed in anoxia environment, which leads to endothelial cell proliferation and neovascularization. In angiogenesis, there is a positive and negative feedback regulation relationship between VEGF and NO, which maintains vascular homeostasis precisely.67 In addition, Liebmann et al proved that pretreatment with NO improved the survival of mice after irradiation.68
Active Compounds from Chinese Herbs
In recent years, more and more researchers reported that active compounds from Chinese herbs such as curcumin,69–71 resveratrol,72–74 dihydroartemisinin75–77 and paclitaxel,78–80 could enhance tumor radiotherapy sensitivity (Figure 2). Curcumin is a polyphenolic active compound extracted from turmeric. Curcumin exerts anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting the transcription factor NF-κB, which is involved in both tumorigenesis and radioresistance.81 In a preclinical study, Chendil et al reported that when treated with RT and curcumin together, the human prostate cancer cell line, PC3 presented threefold fewer surviving and the mechanism was supposed to have a relationship with NF-κB.82 In addition, nanocurcumin as a radiosensitizer is being evaluated by a Phase II clinical trial (NCT02724618). Other relevant research on mutant p53 Ewing’s sarcoma cells proved that radiosensitivity of curcumin was associated with other p53-response genes.83
Resveratrol is an active compound extracted from grapes, knotweed, peanuts, mulberry and other plants. Tan et al proved that resveratrol enhanced the radiosensitivity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by downregulating E2F1.73 Liao et al found that resveratrol enhanced radiosensitivity in human NSCLC NCI-H838 cells by inhibiting NF-κB activation.84 Dihydroartemisinin is a derivative of artemisinin, which can shorten the G2/M phase, while increases the G0/G1 and S phase, thereby reducing the radiation resistance.85 Although the relevant clinical research has not yet been carried out, researchers have demonstrated that resveratrol86–89 and dihydroartemisinin90–92 possessed radiosensitization on cancer cells in vitro.
Paclitaxel is widely known as a very good natural anticancer drug.93,94 As a new type of antimicrotubule drug, paclitaxel can inhibit the microtubule networks formation and prevent the tumor cells proliferation to achieve radiosensitization.95 Results showed that paclitaxel could obviously enhance the radiosensitivity of inoperable patients with locally advanced esophageal cancer and improve the prognosis of patients with acceptable therapeutic effect.96 A three-arm randomized Phase III trial (NCT02459457)—comparison of paclitaxel-based three regimens concurrent with radiotherapy for patients with local advanced esophageal cancer and a Phase III study (NCT01591135) of comparing paclitaxel plus 5-fluorouracil vs cisplatin plus 5-fluorouracil in chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced esophageal carcinoma are underevaluated.
Hypoxia-specific Cytotoxins
Some bioreductive agents, such as aromatic N-oxides, transition metal complexes, quinones, aliphatic N-oxides and nitro compounds, have radiosensitization effects by virtue of their preferential cytotoxicity toward hypoxic cells.11 Tirapazamine (TPZ), a hypoxia-selective radiosensitizer, has shown promising results in clinical trials.97,98 Under hypoxic environments, TPZ can be reduced by reductase in cells to a metabolite that produces free radical and then leads to SSB, DSB, and base damage on DNA.99 A Phase I clinical trial of TPZ with cisplatin and radiotherapy in small cell lung cancer showed prolonged survival of patients.100 A Phase II study of TPZ with chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced head and neck cancer reported improvements in failure-free survival and response of patients.101 However, further phase III trials of TPZ with chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced head and neck cancer concluded that there was no obvious improvement in patient survival.102 In addition, SN30000 (previously known as CEN-209), an analog of TPZ, with more favorable diffusion property that provides greater toxicity in hypoxic cancer cells than TPZ, is currently under development by the Drug Development Office of Cancer Research UK.103
AQ4N, a representative to aliphatic N-oxide, can be reduced to AQ4 by cytochrome P450 isoenzymes or nitric oxide synthase 2A.104 In vivo experiments showed that combined utilization of AQ4N with radiotherapy resulted in increased antitumor efficacy, as well as negligible toxicity to normal tissue compared with radiation alone.105 Positive results were also evidenced in Phase I clinical trials.106 A Phase I clinical trial in glioblastoma and head and neck tumor patients proved that AQ4N could be specifically activated in hypoxic regions of solid tumors.107 Unfortunately, a Phase II clinical trial of AQ4N with radiotherapy and temozolomide in glioblastoma began in 2006, was in a pending status (NCT00394628).
TH-302 (evofosafamide), a similar compound that can be reduced to bromo-isophosphoramide mustard in hypoxic conditions, has radiosensitization activity, especially in hypoxic cells.108,109 In preclinical models of rhabdomyosarcoma (skeletal muscle) and NSCLC, TH-302 combined with radiotherapy treatment resulted in significant tumor growth delay.110 In addition, in a study in patient-derived xenograft models of pancreatic cancer, combination treatment of TH-302 and radiotherapy was more efficient than either treatment alone.111 TH-302 can specifically target the hypoxic tumor cells and induce DNA damage simultaneously in adjacent tumor tissue of the hypoxic zone, and thus holds potential radiosensitization effects in solid tumor treatment.112 However, on the database of US National Institutes of Health clinical trials, only one of the 26 trials listed proposed combination treatment of TH-302 with radiotherapy (NCT02598687), and it was withdrawn because two phase III trials did not meet their primary endpoint.113
Mitomycin C, a quinone-based anticancer therapeutic, can be activated via DNA cross-linking. In preclinical study, mitomycin C showed only slight toxicity in hypoxic cells, which promotes the development of other hypoxia-sensitive quinones selection.114 Among them, porfiromycin (POR) and apaziquone (EO9) are bioreductive prodrugs, represent the leading candidates.104 Preclinical studies concluded that POR held higher hypoxic selectivity than mitomycin C.115 Although preclinical trials proved POR had acceptable toxicity, the following Phase 3 trial demonstrated that POR had a poorer therapeutic effect than mitomycin C.116 Preclinical studies indicated that EO9 had greater antitumor property than mitomycin C, indicating EO9 can be a ideal radiosensitizer.117
Other Chemical Radiosensitizers
Other types of chemical radiosensitizers have also seen some progress and some of them are in preclinical evaluations. For example, chemicals that influence cell signaling, suppress radioprotective substances, pseudosubstrates and targeted delivery systems are exploited. With the development of research on radioresistance mechanism, it has been found that multiple signal pathways are related to radioresistance, providing more targets for radiosensitization, such as PI3K–Akt–mTOR,118 Wnt,119 MAPK,120 MDM2121 and c-MET–PI3K–Akt.122 For example, BKM120, the oral PI3K inhibitor, can inhibit the activity of PI3K/Akt by targeting the PI3K-Akt pathway, thereby increasing cell apoptosis and inhibiting DNA double-strand break repair in liver cancer cells.123 BEZ235, a dual PI3K–mTOR inhibitor, can improve the radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer cells.124 AMG 232, a picomolar affinity piperidinone inhibitor of MDM2, can suppress tumor growth on a mouse model.121
Suppression of radioprotective substances, such as glutathione (GSH), is another strategy of radiosensitization. Inhibition of GSH can prevent DNA damage repair and lead to increased damage in tumor cells, which improves the efficacy of radiotherapy in turn.125 In addition, pseudosubstrates lead cells undergoing DNA synthesis unable to distinguish thymidine and its halogenated analogs efficiently. It is a new area of clinical research to use halogenated pyrimidine analogs, like bromodeoxyuridine (BrdUrd) and iododeoxyuridine (IdUrd), as potential clinical radiosensitizers.126 One study demonstrated that electron affinities of 5-halogenated deoxyuridine led to enough ability to bind a radiation-produced secondary electron, thereby increasing the sensitivity of radiotherapy.127
In addition, research on new indications for existing drugs provides a new paradigm for the development of radiosensitizers. For instance, papaverine, an ergot alkaloid first isolated from Papaver somniferum in 1848, has been used for treatment of vasospasm, cerebral thrombosis, pulmonary embolism and erectile dysfunction.128 Denko et al identified papaverine as an inhibitor of mitochondrial complex I and proved that papaverine could increase oxygenation and enhance radiation response.128 A phase I trial (NCT03824327) study on papaverine and stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for NSCLC or lung metastases is under evaluation. In summary, small-molecule chemicals as radiosensitizers initiated in the past five years under clinical trials are summarized in Table 3.
 |
Table 3 Registered Ongoing Clinical Trials (https://Clinicaltrials.gov/) of Small-molecule Chemical Radiosensitizers |
Macromolecules
Proteins and Peptides
Proteins and peptides, such as antibodies and short peptides, have high affinity with antigens and receptors overexpressed on the surface of tumor cells, making them usable as radiosensitizers.129 For instance, HER3-ADC, a maytansine-based antibody-drug conjugate targeting HER3, which induces cell arrest in the G2/M phase to inhibit DNA damage repair and thereby improves radiosensitivity of HER3-positive pancreatic cancer cells.130 SYM004, a epidermal growth factor receptor targeting antibody, can inhibit DNA double strand breaks repair and induces apoptosis via downregulating MAPK signaling, and thereby improves radiosensitivity in tumor cells.120 Cetuximab and nimotuzumab, binding the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), can increase radiation-induced apoptosis and DNA damage, and thereby improve the radiosensitivity of human epidermal-like A431 cells.131 The hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)/Met signaling pathway which mediates DNA double-strand break repair is upregulated in the majority of cancers. AMG102, a monoclonal antibody against HGF, can inhibit DNA damage repair and increase radiosensitivity of glioblastoma multiforme.132 In addition, proteins and peptides in serum, such as C-reactive peptide,133 HSP134 and paraoxonase-2135 contribute to radioresistance and can be used as radiotherapy targets. ECI301, a mutant derivative of macrophage inhibitory protein-1a, can be assisted by HSP-70 and HMGB1, thereby enhancing the effect of radiotherapy.134 Other proteins, like DNAzyme (DZ1)136 and NKTR-214,137 can also improve the effect of radiotherapy.
miRNAs
MicroRNAs (miRNAs), which encode by endogenous genes are noncoding single-stranded RNA molecules containing about 22 nucleotides. Studies have shown that some specific miRNAs can be used to improve radiotherapy efficacy138,139 and some miRNAs can be used as radiotherapy sensitization targets.140 For example, miR-621 targets SETDB1 in hepatocellular carcinoma can be used as a tumor radiosensitizer directly.141 miR-205 targets zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1) and the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme Ubc13 to enhance the radiosensitivity of breast cancer cells.142 miR-144-5p targets ATF2 to enhance radiosensitivity of NSCLC.143 miR-146a-5p enhances radiosensitivity in hepatocellular carcinoma through activation of DNA repair pathway.144 miR-150 modulates AKT pathway in NK/T cell lymphoma to enhance radiosensitivity.145 miR-99a targets mTOR pathway to enhance the radiosensitivity of NSCLC.146 miR-139-5p modulates radiotherapy resistance in breast cancer by repressing multiple gene networks of DNA repair and ROS defense.147 Transcriptional activation of miR-320a induces cancer cell apoptosis under ionizing radiation conditions.148 However, inhibition of miR-21-5p promotes the radiation sensitivity of NSCLC.149 Inhibition of miR-630 enhances radiotherapy resistance in human glioma by directly targeting CDC14A.150 Furthermore, a clinical study included 55 atypical meningioma patients found in seven upregulated miRNAs (miR-4286, miR-4695-5p, miR-6732-5p, miR-6855-5p, miR-7977, miR-6765-3p, miR-6787-5p) and seven downregulated miRNAs (miR-1275, miR-30c-1-3p, miR-4449, miR-4539, miR-4684-3p, miR-6129, miR-6891-5p) in patients. Those miRNAs may induce radioresistant and radiosensitive, respectively.
siRNAs
siRNA, known as short interfering RNA or silencing RNA, is a class of double-stranded RNA, noncoding RNA molecules, typically 20–27 base pairs in length, similar to miRNA, and operating within the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway.151 HuR is a protein related to radiotherapy resistance, knockdown of HuR by siRNA resulting DNA damage and enhanced radiosensitivity.152 S100A4, a member of the S100 family of transcription factors, modulates various activities of malignant tumor cells through different mechanisms. A short siRNA against S100A4 enhances the radiosensitivity of human A549 cells.153 NBS1 plays an important role in the radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks reparation, siRNA targets NBS1 can increase radiation sensitivity of cancer cells.154 Survivin, a member of the inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) protein family, is overexpressed in most cancers resulting in aggressive behavior of tumor and therapy resistance. Downregulation of survivin by siRNA can enhance radiosensitivity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.155 Therefore, numerous siRNAs can be used as radiosensitizers by silencing genes related to radioresistance.
Oligonucleotides
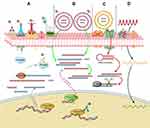
Similar to siRNAs, oligonucleotides also play important roles in gene expression regulation. Since they are easy to design and synthesize, antisense oligonucleotides have great potential to develop as radiosensitizers.11 Telomerase expresses in many kinds of tumors (>85%), while the expression of telomerase is restricted in normal tissues. A study indicated that expression of telomerase could be inhibited by radiolabeled oligonucleotides, which targeted the RNA subunit of telomerase, thereby inducing DNA damage in telomerase-positive tumor cells.156 In addition, the phosphorothioate-modified antisense oligonucleotides (PS-ASODN) against human telomerase reverse transcriptase were reported to promote radiotherapy effect in liver cancer.157 Furthermore, Park et al reported that inhibition of cyclic AMP response element-directed transcription using decoy oligonucleotides enhanced tumor-specific radiosensitivity.158 Yu et al demonstrated that antisense oligonucleotides targeted human telomerase RNA (hTR ASODN) could improve the radiosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells.159 The radiosensitization mechanism of macromolecules was summarized in Figure 3.
Nanomaterials
Noble Metal nanomaterials
The X-ray absorption coefficient (μ) represents the relationship between the X-ray absorption phenomenon (E) and atomic number (Z), μ=ρZ4/(AE3), where ρ is the density and A is the atomic mass of the element.160 Therefore, the change of atomic number (Z) causes a significant change of X-ray absorption coefficient (μ). Noble metal nanomaterials, such as gold (Au, Z=79), silver (Ag, Z=47) and platinum (Pt, Z=78) can effectively absorb X-ray energy and interact with radiation in tumor cells, and then emit photoelectrons, auger electrons, compton electrons and other secondary electrons. These secondary electrons not only interact with DNA directly, but also react with water to increase the production of ROS and further increase the sensitivity of tumor cells to radiation. This process is a physical sensitization mechanism.161 Furthermore, functionalized noble metal nanomaterials promote the generation of ROS, transfer the cell cycle into a radiosensitive state, and inhibit p53 signaling pathway to induce cell autophagy and lysozyme body function disorder, thereby increasing radiotherapy sensitivity. This process is a biochemical sensitization mechanism.162,163
Gold nanoparticles with good chemical stability, easy preparation, controllable size and shape, easy surface functionalization, high biocompatibility, and low toxicity have proven satisfactory radiosensitizing effects in various tumors.164–167 Silver nanoparticles and platinum nanoparticles are also commonly used in biomedicine.168,169 Research found that silver nanoparticles combined with radiotherapy could enhance the radiosensitivity of human glioma cells in vitro and extended the survival time of glioma mice.170,171 Liu et al demonstrated that silver nanoparticles could induce apoptosis of cancer cells through G2/M phase arrest after radiation, and they suggested that silver nanoparticles could be used as a nanoradiosensitizer for hypoxic glioma radiotherapy.172 Recently, Fathy reported that thymoquinone-capping silver nanoparticles represented a promising engineered nanoformulation for enhancing cancer radiosensitivity.173 Li et al demonstrated that platinum nanoparticles could enhance radiosensitivity through increasing DNA damage, ROS stress, and cell cycle arrest.163 They also proved that platinum nanoparticles could convert endogenic H2O2 to O2 in cancer cells, thus significantly improving radiosensitivity without apparent toxicity to animals in vivo.163
Heavy Metal Nanomaterials
Similar to noble metal nanomaterials, gadolinium (Gd, Z=64), hafnium (Hf, Z=72), tantalum (Ta, Z=73), tungsten (W, Z=74), and bismuth (Bi, Z=83) are also metal elements with large atomic coefficients and have a great X-ray attenuation capability.174–176 Based on this, numerous studies have focused on these heavy metal nanomaterials to investigate their radiotherapy sensitization. However, they usually cause damage to healthy tissues with direct contact.177 Therefore, their stable forms such as oxides, sulfides, and selenides are explored as the radiosensitizers.178–180
Gadolinium-based nanoparticles are usually known as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents. It should be noted that researchers discovered a family of gadolinium-based nanoparticles called AGuIX for combined MRI and radiosensitization.181 Results showed that AGuIX could interact with X-rays and γ-rays at a certain concentration. After internalization through the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect, AGuIX could be resident in the tumor for a long time before being cleared by the kidneys.182 Preclinical animal experiments proved that AGuIX held obvious radiosensitization effects in several tumor models without obvious toxicity.183 A Phase I clinical trial (NCT03308604) to evaluate the optimal dose of AGuIX combined with chemoradiation in patients with locally advanced cervical cancer; a Phase II clinical trial (NCT03818386) using AGuIX gadolinium-chelated polysiloxane based nanoparticles and whole brain radiotherapy in patients with multiple brain metastases; and a single-arm phase II trial (NCT04094077) aiming to evaluate the efficacy of AGuIX during fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy of brain metastasis are being evaluated.
Hafnium, in the same family as titanium and zirconium, is chemical inertness. The oxidation state of hafnium, hafnium dioxide (HfO₂), was usually used in radioactive protective coatings, biosensors, and X-ray contrast agents.184,185 Jayaraman et al demonstrated that HfO2 nanoparticles had excellent biocompatibility.185 Researchers from France discovered that HfO₂ can be used as a radiosensitizer with low cytotoxicity.186 A Phase I trial (NCT03589339) combining hafnium oxide nanoparticles (NBTXR3) with anti-PD-1 therapy in microsatellite instability-high solid malignant tumour and a Phase I–II clinical trial (NCT02805894) of NBTXR3 in prostate adenocarcinoma are under evaluation.
Tantalum is a nontoxic, biologically inert element with good biocompatibility.187 Studies found that TaOx and Ta2O5 could be used as CT imaging contrast agents.188–190 Brown et al found Ta2O5 nanoparticles showed a radiasentizition effect on radioresistant glioma cells.191 Song et al showed hollow shell tantalum oxide (HTaOx) had a large X-ray attenuation capability and could enhance radiation therapy effects by Compton scattering and Auger effect.192 In addition, TaOx can be used as functional group carrier to load drugs, thereby improving tumor hypoxic environment. For example, HTaOx loaded with catalase, which reacted with H2O2 in the tumor microenvironment, then improved the oxygen content and overcame the radiotherapy tolerance of hypoxic tumor cells, thereby improving the radiotherapy effect.193
Tungsten and bismuth also have significative applications in medicine.194,195 Hossain et al concluded that bismuth nanoparticles had stronger radiosensitizing effect than gold and platinum nanoparticles at the same physical and chemical conditions.196 Yu et al found that the ultra-small semi-metallic Bi nanoparticles with LyP-1 peptide modified at 3.6 nm showed obvious radiosensitization effect.197 Recently, a large number of studies shown that some nanomaterials of tungsten and bismuth had excellent photothermal absorption conversion performance and strong X-ray absorption capacity, therefore they can be used for tumor radiosensitization as well as synergistic therapy of hyperthermia and radiotherapy.198–201
In addition, research about several high Z metal elements combined together to further improve the radiosensitization effect were also explored. For example, SiBiGdNP chelated Bi and Gd in organosilane to improve the sensitivity of radiotherapy.202 GdW10O36 contained both W and Gd to expect they had better radiotherapy sensitization effect.203
Ferrite Nanomaterials
Ferrite-based nanomaterials can catalyze the generation of free radicals through Fenton’s reaction (1) and Haber–Weiss reaction (2) to enhance the effect of radiosensitization.204
Fe2+ + H2O2 → Fe3+ + OH + OH−
Fe3+ + H2O2 → Fe2+ + OOH + H+ (1)
Fe3+ + O2 − → Fe2+ + O2
Fe2+ + H2O2 → Fe3+ + OH− + OH (2)
Studies proved that Fe3O4 had a dose-enhancing effect for radiotherapy, especially superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles (SPIONS) possessing MRI imaging property had good application prospects in image-guided tumor radiotherapy.205
The composition of the spinel structure ferrite is usually stated as MFe2O4, where M=Fe, Zn, Co, Mn, Ni.206 Among them, ZnFe2O4, MnFe2O4, CoFe2O4 nanoparticles were widely investigated.207 For example, Meidanchi et al confirmed that ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles interacted with γ-rays to produce photoelectric effect resulting in a higher release level of electron in radioresistant cells.208 Studies also indicated that ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles could be used as radiosensitizers.208,209 Salunkhe et al demonstrated that MnFe2O4 and CoFe2O4 nanoparticles could improve the therapeutic efficacy of cancer through multimodal image-guided combination therapy.210
Semiconductor Nanomaterials
Semiconductor quantum dots have unique properties, such as quantum dimension effect, surface effect, and quantum confinement effect, making them great candidates in biomedicine applications.211 Until now, numerous studies focused on using semiconductor quantum dots as photosensitizers and radiosensitizers for tumor treatment have been reported.212–214 When the electronic energy levels are in the range of 1–5 eV, the semiconductor nanomaterials can absorb the photon energy and perform as photosensitizers, showing photocatalytic properties. When the electronic energy levels are at keV and MeV (X-rays and γ-rays), semiconductor nanomaterials can enhance absorption of high-energy photons acting as radiosensitizers and causing damage to cancer cells.212 Nakayama et al synthesized a semiconductor nanomaterial PAA-TiOx to generate hydroxyl radicals under the irradiation of X-rays, which increased DNA damage and inhibited tumor growth significantly.215 Morita et al clarified the radiosensitization mechanism of PAA-TiOx nanoparticles by releasing H2O2 to relieve hypoxia in tumor cells.216 TiO2 nanotubes have been reported to enhance the radiosensitization effect through regulating G2/M cycle arrest and reducing DNA repair of tumor cells.177 The mechanism of radiosensitization of metal-based nanomaterials is shown in Figure 4.
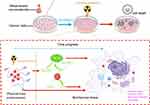 |
Figure 4 Radiosensitization mechanism of metal-based nanomaterials. The process contains physical and biochemical sensitization mechanism. |
Nonmetallic Nanomaterials
Many nonmetallic nanomaterials also possess the function of radiosensitization.217 For example, C60, fullerene, has potent anticancer activities, however, the potential toxicity to normal tissues limits its further use. Therefore, nanocrystals of C60 (Nano-C60) with negligible toxicity to normal cells have been developed as a radiosensitizer.218 In addition, nanodiamonds and carbon nanotubes can reduce radioresistance of tumor cells by promoting ROS generation, destroying DNA double-strands, and regulating the cell cycle.219,220 Selenium (Se) nanoparticles not only work as chemotherapeutic drugs, but also improve the antitumor effect of X-rays by activating ROS to induce DNA damage in cancer cells.221
Nanostructured Chemicals and Drug Delivery Systems
Nano-based delivery systems are efficient approaches for drug targeted transportation, which can deliver radiosensitizers, such as chemicals, oxygen carriers, siRNAs and catalases to the tumor sites and have attracted wide interest of researchers recently.222 More importantly, nanobased delivery systems can precisely deliver radioactive particles like223 Ac (releasing a-particles), 131I, and 125I to tumor sites.223 With the development of nanotechnology, nanobased delivery systems have great potential for radiosensitizer delivery.
However, there is still a challenge to achieve clinical translation of nanobased delivery systems, factors like physicochemical properties of the nanoformulations, radiation sources, and indications block their clinical translation.223 In addition, long circulation lifetime of nanodelivery systems may increase the risk of long-term toxicity.224 Another critical factor is stability in body fluid of nanodelivery systems. Because the aggregation of nanoparticles in body fluid will influence the pharmacokinetics and the cellular response and generate serious side effects such as blocking the blood vessels.222 Therefore, attention should be paid to these factors when designing the nanodelivery systems. Size is also an important factor, small size and high Z nanoparticles often hold better radiosensitizing effect than larger-size ones.223 In particular, the small size nanoparticles with positive charge can bind to negative charged DNA and can be eliminated by renal clearance conveniently. In addition, functional modification of nanostructures using biocompatible materials can improve their stability and targeting.225
Conclusions and Prospects
Radiosensitizers have been developed for decades from the earliest “free radical damage and fixation” strategies to gene regulation, from chemicals to biological macromolecules and nanomaterials. Although each radiosensitizer has dialectical advantages and limitations, the mechanisms of sensitization are similar. The main mechanisms include: (I) inhibiting radiation-induced repair of DNA damage, increasing the degree of DNA damage; (II) disturbing the cell cycle and organelle function to improve cytotoxicity; and (III) inhibiting the expression of radiation resistance genes or promoting the expression of radiation sensitive genes.
Although small molecules, macromolecules, and nanomaterial radiosensitizers are being developed, and some nanoradiosensitizers have been used for clinical research (Table 4), the result still cannot meet clinical translation needs. Therefore, there is an urgent need to find new targets of radiotherapy and new mechanisms of sensitization, and after that to develop more effective radiosensitizing drugs. First of all, multitarget radiosensitizers often have more obvious efficacy than single target, researchers can focus on screening multitarget radiosensitizers or drug combinations. New approaches, in particular, nanotechnology based as radiosensitizers have shown promise. Nanomaterials with low cytotoxicity, good biocompatibility, and ease of functionalization need to be explored. In addition, other technologies, such as molecular structure analysis, molecular cloning technology, and bioinformatics analysis can accelerate the development of new radiosensitizers. Moreover, development of new drug delivery systems can also improve radiosensitization efficacy. Finally, the application of artificial intelligence and machine learning in new drug discovery and clinical trials, may guide development of new radiosensitizers and optimization of existing radiosensitizers.
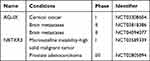 |
Table 4 Clinical Translation of Some Nanoradiosensitizers |
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by Innovation Capacity Support Plan of Shaanxi Province (2018TD-002), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82000523), the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi province (Grant No. 2020JQ-087, 2020JQ-095), the “Young Talent Support Plan” of Xi’an Jiaotong University (YX6J001), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (xzy012019070).
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Krzyszczyk P, Acevedo A, Davidoff EJ, et al. The growing role of precision and personalized medicine for cancer treatment. Technology (Singap World Sci). 2018;6(3–4):79–100. doi:10.1142/S2339547818300020
2. Kułakowski A. The contribution of Marie Skłodowska-Curie to the development of modern oncology. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011;400(6):1583–1586. doi:10.1007/s00216-011-4712-1
3. Martin OA, Martin RF. Cancer radiotherapy: understanding the price of tumor eradication. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:261. doi:10.3389/fcell.2020.00261
4. Franzone P, Fiorentino A, Barra S, et al. Image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT): practical recommendations of Italian Association of Radiation Oncology (AIRO). Radiol Med. 2016;121(12):958–965. doi:10.1007/s11547-016-0674-x
5. Ge Y, Wu QJ. Knowledge-based planning for intensity-modulated radiation therapy: a review of data-driven approaches. Med Phys. 2019;46(6):2760–2775. doi:10.1002/mp.13526
6. Farhood B, Goradel NH, Mortezaee K, et al. Melatonin as an adjuvant in radiotherapy for radioprotection and radiosensitization. Clin Transl Oncol. 2019;21(3):268–279. doi:10.1007/s12094-018-1934-0
7. Fowler JF, Adams GE, Denekamp J. Radiosensitizers of hypoxic cells in solid tumors. Cancer Treat Rev. 1976;3(4):227–256. doi:10.1016/s0305-7372(76)80012-6
8. Adams GE. Chemical radiosensitization of hypoxic cells. Br Med Bull. 1973;29(1):48–53. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070956
9. Wen P, Xia J, Cao X, et al. dbCRSR: a manually curated database for regulation of cancer radiosensitivity. Database (Oxford). 2018;2018. doi:10.1093/database/bay049
10. Garibaldi C, Jereczek-Fossa BA, Marvaso G, et al. Recent advances in radiation oncology. Ecancermedicalscience. 2017;11:785. doi:10.3332/ecancer.2017.785
11. Wang H, Mu X, He H, Zhang XD. Cancer radiosensitizers. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2018;39(1):24–48. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2017.11.003
12. Hirayama R. Mechanism of oxygen effect for photon andheavy-ion beams. Japanese Journal of Medical Physics. 2014;34(2):65–69.
13. Oronsky BT, Knox SJ, Scicinski J. Six degrees of separation: the oxygen effect in the development of radiosensitizers. Transl Oncol. 2011;4(4):189–198. doi:10.1593/tlo.11166
14. Harrison LB, Chadha M, Hill RJ, Hu K, Shasha D. Impact of tumor hypoxia and anemia on radiation therapy outcomes. Oncologist. 2002;7(6):492–508. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.7-6-492
15. Zheng L, Kelly CJ, Colgan SP. Physiologic hypoxia and oxygen homeostasis in the healthy intestine. A review in the theme: cellular responses to hypoxia. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2015;309(6):C350–C360. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00191.2015
16. Richardson RB, Harper ME. Mitochondrial stress controls the radiosensitivity of the oxygen effect: implications for radiotherapy. Oncotarget. 2016;7(16):21469–21483. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.7412
17. Bel Aiba RS, Dimova EY, Görlach A, Kietzmann T. The role of hypoxia inducible factor-1 in cell metabolism–a possible target in cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2006;10(4):583–599. doi:10.1517/14728222.10.4.583
18. Zhu H, Zhang S. Hypoxia inducible factor-1α/vascular endothelial growth factor signaling activation correlates with response to radiotherapy and its inhibition reduces hypoxia-induced angiogenesis in lung cancer. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(9):7707–7718. doi:10.1002/jcb.27120
19. Verdegem D, Moens S, Stapor P, Carmeliet P. Endothelial cell metabolism: parallels and divergences with cancer cell metabolism. Cancer Metabol. 2014;2(1):19. doi:10.1186/2049-3002-2-19
20. Boyle RG, Travers S. Hypoxia: targeting the tumour. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2006;6(4):281–286. doi:10.2174/187152006777698169
21. Maxwell PH. The HIF pathway in cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2005;16(4–5):523–530. doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2005.03.001
22. Al Tameemi W, Dale TP, Al-Jumaily RMK, Forsyth NR. Hypoxia-modified cancer cell metabolism. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019;7:4. doi:10.3389/fcell.2019.00004
23. Pettersen EO, Ebbesen P, Gieling RG, et al. Targeting tumour hypoxia to prevent cancer metastasis. From biology, biosensing and technology to drug development: the METOXIA consortium. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2015;30(5):689–721. doi:10.3109/14756366.2014.966704
24. Cabrales P, Intaglietta M. Blood substitutes: evolution from noncarrying to oxygen- and gas-carrying fluids. ASAIO J. 2013;59(4):337–354. doi:10.1097/MAT.0b013e318291fbaa
25. Hardavella G, Karampinis I, Frille A, Sreter K, Rousalova I. Oxygen devices and delivery systems. Breathe (Sheffield, England). 2019;15(3):e108–e116. doi:10.1183/20734735.0204-2019
26. Choudhury R. Hypoxia and hyperbaric oxygen therapy: a review. Int J Gen Med. 2018;11:431–442. doi:10.2147/ijgm.S172460
27. Stępień K, Ostrowski RP, Matyja E. Hyperbaric oxygen as an adjunctive therapy in treatment of malignancies, including brain tumours. Med Oncol (Northwood, London, England). 2016;33(9):101. doi:10.1007/s12032-016-0814-0
28. Ogawa Y, Kubota K, Ue H, et al. Phase I study of a new radiosensitizer containing hydrogen peroxide and sodium hyaluronate for topical tumor injection: a new enzyme-targeting radiosensitization treatment, Kochi oxydol-radiation therapy for unresectable carcinomas, type II (KORTUC II). Int J Oncol. 2009;34:609–618. doi:10.3892/ijo_00000186
29. Chapman JD, Webb RG, Borsa J. Radiosensitization of mammalian cells by p-nitroacetophenone. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1971;19(6):561–573. doi:10.1080/09553007114550741
30. Adams GE, Asquith JC, Dewey DL, Foster JL, Michael BD, Willson RL. Electron affinic sensitization. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1971;19(6):575–585. doi:10.1080/09553007114550751
31. Higgins GS, O’Cathail SM, Muschel RJ, McKenna WG. Drug radiotherapy combinations: review of previous failures and reasons for future optimism. Cancer Treat Rev. 2015;41(2):105–113. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2014.12.012
32. Spisz P, Zdrowowicz M, Makurat S, et al. Why does the type of halogen atom matter for the radiosensitizing properties of 5-halogen substituted 4-thio-2’-deoxyuridines? Molecules. 2019;24(15):2819. doi:10.3390/molecules24152819
33. Brown JM. Selective radiosensitization of the hypoxic cells of mouse tumors with the nitroimidazoles metronidazole and Ro 7-0582. Radiat Res. 1975;64(3):633–647. doi:10.2307/3574253
34. Dische S, Saunders MI, Lee ME, Adams GE, Flockhart IR. Clinical testing of the radiosensitizer Ro 07-0582: experience with multiple doses. Br J Cancer. 1977;35(5):567–579. doi:10.1038/bjc.1977.90
35. Brown JM. Clinical trials of radiosensitizers: what should we expect? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1984;10(3):425–429. doi:10.1016/0360-3016(84)90063-4
36. Dische S, Saunders MI, Flockhart IR, Lee ME, Anderson P. Misonidazole-a drug for trial in radiotherapy and oncology. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1979;5(6):851–860. doi:10.1016/0360-3016(79)90070-1
37. Barker HE, Paget JTE, Khan AA, Harrington KJ. The tumour microenvironment after radiotherapy: mechanisms of resistance and recurrence. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015;15(7):409–425. doi:10.1038/nrc3958
38. Overgaard J, Hansen HS, Andersen AP, et al. Misonidazole combined with split-course radiotherapy in the treatment of invasive carcinoma of larynx and pharynx: report from the DAHANCA 2 study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1989;16(4):1065–1068. doi:10.1016/0360-3016(89)90917-6
39. Urtasun RC, Chapman JD, Feldstein ML, et al. Peripheral neuropathy related to misonidazole: incidence and pathology. Br J Cancer Suppl. 1978;3:271–275.
40. Wardman P. Nitroimidazoles as hypoxic cell radiosensitizers and hypoxia probes: misonidazole, myths and mistakes. Br J Radiol. 2019;92(1093):20170915. doi:10.1259/bjr.20170915
41. Bonnet M, Hong CR, Wong WW, et al. Next-generation hypoxic cell radiosensitizers: nitroimidazole alkylsulfonamides. J Med Chem. 2018;61(3):1241–1254. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01678
42. Rosenberg A, Knox S. Radiation sensitization with redox modulators: a promising approach. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;64(2):343–354. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.10.013
43. Coleman CN, Wasserman TH, Urtasun RC, et al. Final report of the phase I trial of the hypoxic cell radiosensitizer SR 2508 (etanidazole) radiation therapy oncology group 83-03. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1990;18(2):389–393. doi:10.1016/0360-3016(90)90105-s
44. Brown JM, Wilson WR. Exploiting tumour hypoxia in cancer treatment. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4(6):437–447. doi:10.1038/nrc1367
45. Overgaard J, Hansen HS, Overgaard M, et al. A randomized double-blind phase III study of nimorazole as a hypoxic radiosensitizer of primary radiotherapy in supraglottic larynx and pharynx carcinoma. Radiother Oncol. 1998;46(2):135–146. doi:10.1016/s0167-8140(97)00220-x
46. Overgaard J, Eriksen JG, Nordsmark M, Alsner J, Horsman MR. Plasma osteopontin, hypoxia, and response to the hypoxia sensitiser nimorazole in radiotherapy of head and neck cancer: results from the DAHANCA 5 randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2005;6(10):757–764. doi:10.1016/s1470-2045(05)70292-8
47. Metwally MA, Frederiksen KD, Overgaard J. Compliance and toxicity of the hypoxic radiosensitizer nimorazole in the treatment of patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Acta Oncologica (Stockholm, Sweden). 2014;53(5):654–661. doi:10.3109/0284186x.2013.864050
48. Bentzen J, Toustrup K, Eriksen JG, Primdahl H, Andersen LJ, Overgaard J. Locally advanced head and neck cancer treated with accelerated radiotherapy, the hypoxic modifier nimorazole and weekly cisplatin. Results from the DAHANCA 18 phase II study. Acta Oncologica (Stockholm, Sweden). 2015;54(7):1001–1007. doi:10.3109/0284186x.2014.992547
49. Saksø M, Andersen E, Bentzen J, et al. A prospective, multicenter DAHANCA study of hyperfractionated, accelerated radiotherapy for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Acta Oncologica (Stockholm, Sweden). 2019;58(10):1495–1501. doi:10.1080/0284186x.2019.1658897
50. Thomson D, Yang H, Baines H, et al. NIMRAD - a phase III trial to investigate the use of nimorazole hypoxia modification with intensity-modulated radiotherapy in head and neck cancer. Clin Oncol (Royal College of Radiologists (Great Britain)). 2014;26(6):344–347. doi:10.1016/j.clon.2014.03.003
51. Toustrup K, Sørensen BS, Lassen P, Wiuf C, Alsner J, Overgaard J. Gene expression classifier predicts for hypoxic modification of radiotherapy with nimorazole in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Radiother Oncol. 2012;102(1):122–129. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2011.09.010
52. Saksø M, Jensen K, Andersen M, Hansen CR, Eriksen JG, Overgaard J. DAHANCA 28: a phase I/II feasibility study of hyperfractionated, accelerated radiotherapy with concomitant cisplatin and nimorazole (HART-CN) for patients with locally advanced, HPV/p16-negative squamous cell carcinoma of the oropharynx, hypopharynx, larynx and oral cavity. Radiother Oncol. 2020;148:65–72. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2020.03.025
53. Oronsky B, Scicinski J, Ning S, et al. RRx-001, a novel dinitroazetidine radiosensitizer. Invest New Drugs. 2016;34(3):371–377. doi:10.1007/s10637-016-0326-y
54. Oronsky BT, Knox SJ, Scicinski JJ. Is Nitric oxide (NO) the last word in radiosensitization? A review. Transl Oncol. 2012;5(2):66–71. doi:10.1593/tlo.11307
55. Edfeldt NB, Harwood EA, Sigurdsson ST, Hopkins PB, Reid BR. Solution structure of a nitrous acid induced DNA interstrand cross-link. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32(9):2785–2794. doi:10.1093/nar/gkh606
56. Bonavida B, Khineche S, Huerta-Yepez S, Garbán H. Therapeutic potential of nitric oxide in cancer. Drug Resist Updat. 2006;9(3):157–173. doi:10.1016/j.drup.2006.05.003
57. Nelson EJ, Connolly J, McArthur P. Nitric oxide and s-nitrosylation: excitotoxic and cell signaling mechanism. Biol Cell. 2003;95(1):3–8. doi:10.1016/s0248-4900(03)00004-2
58. Meffert MK, Premack BA, Schulman H. Nitric oxide stimulates Ca(2+)-independent synaptic vesicle release. Neuron. 1994;12(6):1235–1244. doi:10.1016/0896-6273(94)90440-5
59. Tsai EJ, Kass DA. Cyclic GMP signaling in cardiovascular pathophysiology and therapeutics. Pharmacol Ther. 2009;122(3):216–238. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2009.02.009
60. Lundberg JO, Gladwin MT, Weitzberg E. Strategies to increase nitric oxide signalling in cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015;14(9):623–641. doi:10.1038/nrd4623
61. Rogers N, Seeger F, Garcin E, Roberts D, Isenberg J. Regulation of soluble guanylate cyclase by matricellular thrombospondins: implications for blood flow. Review. 2014;5(134). doi:10.3389/fphys.2014.00134
62. Kondakova IV, Tcheredova VV, Zagrebelnaya GV, Cherdyntseva NV, Kagiya TV, Choinzonov EL. Production of nitric oxide by hypoxic radiosensitizer sanazole. Exp Oncol. 2004;26(4):329–333.
63. Girard M, Clairmont F, Maneckjee A, Mousseau N, Dawson B, Whitehouse L. 5-Nitroimidazoles. II: unexpected reactivity of ronidazole and dimetridazole with thiols. Can J Chem. 2011;71:1349–1352. doi:10.1139/v93-174
64. Ng QS, Goh V, Milner J, et al. Effect of nitric-oxide synthesis on tumour blood volume and vascular activity: a phase I study. Lancet Oncol. 2007;8(2):111–118. doi:10.1016/s1470-2045(07)70001-3
65. Siemens DR, Heaton JP, Adams MA, Kawakami J, Graham CH. Phase II study of nitric oxide donor for men with increasing prostate-specific antigen level after surgery or radiotherapy for prostate cancer. Urology. 2009;74(4):878–883. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2009.03.004
66. Libert N, Tourtier JP, Védrine L, Chargari C, Riou B. Inhibitors of angiogenesis: new hopes for oncologists, new challenges for anesthesiologists. Anesthesiology. 2010;113(3):704–712. doi:10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181ed098d
67. Pandey AK, Singhi EK, Arroyo JP, et al. Mechanisms of VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) inhibitor-associated hypertension and vascular disease. Hypertension (Dallas, Tex: 1979). 2018;71:e1–e8. doi:10.1161/hypertensionaha.117.10271
68. Liebmann J, DeLuca AM, Coffin D, et al. In vivo radiation protection by nitric oxide modulation. Cancer Res. 1994;54(13):3365–3368.
69. Schwarz K, Dobiasch S, Nguyen L, Schilling D, Combs SE. Modification of radiosensitivity by curcumin in human pancreatic cancer cell lines. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):3815. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-60765-1
70. Verma V. Relationship and interactions of curcumin with radiation therapy. World J Clin Oncol. 2016;7(3):275–283. doi:10.5306/wjco.v7.i3.275
71. Li G, Wang Z, Chong T, Yang J, Li H, Chen H. Curcumin enhances the radiosensitivity of renal cancer cells by suppressing NF-κB signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;94:974–981. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.07.148
72. da Costa Araldi IC, Bordin FPR, Cadoná FC, et al. The in vitro radiosensitizer potential of resveratrol on MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Chem Biol Interact. 2018;282:85–92. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2018.01.013
73. Tan Y, Wei X, Zhang W, et al. Resveratrol enhances the radiosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by downregulating E2F1. Oncol Rep. 2017;37(3):1833–1841. doi:10.3892/or.2017.5413
74. Mikami S, Ota I, Masui T, et al. Resveratrol‑induced REG III expression enhances chemo‑ and radiosensitivity in head and neck cancer in xenograft mice. Oncol Rep. 2019;42(1):436–442. doi:10.3892/or.2019.7137
75. Kim SJ, Kim MS, Lee JW, et al. Dihydroartemisinin enhances radiosensitivity of human glioma cells in vitro. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2006;132(2):129–135. doi:10.1007/s00432-005-0052-x
76. Li Y, Sui H, Jiang C, et al. Dihydroartemisinin increases the sensitivity of photodynamic therapy via NF-κB/HIF-1α/VEGF pathway in esophageal cancer cell in vitro and in vivo. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48:2035–2045. doi:10.1159/000492541
77. Zhang L, Cheng LQ, Zhou Z, Lv LL, Liu GX. Effects of dihydroartemisinin on radiosensitivity of Raji cells. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2017;33:385–390. doi:10.12047/j.cjap.5565.2017.093
78. Momtazi-Borojeni AA, Mosafer J, Nikfar B, et al. Curcumin in advancing treatment for gynecological cancers with developed drug- and radiotherapy-associated resistance. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2019;176:107–129. doi:10.1007/112_2018_11
79. Chen Y, Zhu Z, Zhao W, et al. A randomized phase 3 trial comparing paclitaxel plus 5-fluorouracil versus cisplatin plus 5-fluorouracil in Chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced esophageal carcinoma-the ESO-shanghai 1 trial protocol. Radiat Oncol (London, England). 2018;13(1):33. doi:10.1186/s13014-018-0979-0
80. Ren W, Sha H, Yan J, et al. Enhancement of radiotherapeutic efficacy for esophageal cancer by paclitaxel-loaded red blood cell membrane nanoparticles modified by the recombinant protein anti-EGFR-iRGD. J Biomater Appl. 2018;33(5):707–724. doi:10.1177/0885328218809019
81. Aggarwal BB. Nuclear factor-kappaB: the enemy within. Cancer Cell. 2004;6(3):203–208. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2004.09.003
82. Chendil D, Ranga RS, Meigooni D, Sathishkumar S, Ahmed MM. Curcumin confers radiosensitizing effect in prostate cancer cell line PC-3. Oncogene. 2004;23(8):1599–1607. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207284
83. Veeraraghavan J, Natarajan M, Herman TS, Aravindan N. Curcumin-altered p53-response genes regulate radiosensitivity in p53-mutant ewing’s sarcoma cells. Anticancer Res. 2010;30(10):4007–4015.
84. Liao HF, Kuo CD, Yang YC, et al. Resveratrol enhances radiosensitivity of human non-small cell lung cancer NCI-H838 cells accompanied by inhibition of nuclear factor-kappa B activation. J Radiat Res. 2005;46(4):387–393. doi:10.1269/jrr.46.387
85. Aung TN, Qu Z, Kortschak RD, Adelson DL. Understanding the effectiveness of natural compound mixtures in cancer through Their molecular mode of action. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18:656. doi:10.3390/ijms18030656
86. Tak JK, Lee JH, Park JW. Resveratrol and piperine enhance radiosensitivity of tumor cells. BMB Rep. 2012;45(4):242–246. doi:10.5483/bmbrep.2012.45.4.242
87. Quan F, Zhao Q, Shao Y, Li H, Zhao R. Resveratrol enhances radiosensitivityof human hypopharyngeal carcinoma cell line in nudemice. Journal of Southern Medical University. 2014;34(11):1646–1649.Chinese.
88. Shao Y, Quan F, Li HH, Yao XB, Zhao Q, Zhao RM. The radiosensitizing effect of resveratrol on hopypharyngeal carcinoma cell line FADU and its effect on the cell cycle. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2015;35:699–703.
89. Fang Y, DeMarco VG, Nicholl MB. Resveratrol enhances radiation sensitivity in prostate cancer by inhibiting cell proliferation and promoting cell senescence and apoptosis. Cancer Sci. 2012;103(6):1090–1098. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2012.02272.x
90. Luo J, Chen X, Chen G, et al. Dihydroartemisinin induces radiosensitivity in cervical cancer cells by modulating cell cycle progression. Saudi Med J. 2013;34(3):254–260.
91. Zuo ZJ, Wang ST, Jiang LX, et al. Effect of dihydroartemisinin combined irradiation on the apoptosis of human lung cancer GLC-82 cells and its mechanism study. Chin J Integr Med. 2014;34(10):1220–1224.
92. Zhang ZS, Wang J, Shen YB, et al. Dihydroartemisinin increases temozolomide efficacy in glioma cells by inducing autophagy. Oncol Lett. 2015;10(1):379–383. doi:10.3892/ol.2015.3183
93. Barbuti A, Chen Z-S. Paclitaxel through the ages of anticancer therapy: exploring its role in chemoresistance and radiation therapy. Cancers. 2015;7:2360–2371. doi:10.3390/cancers7040897
94. von Eiff D, Bozorgmehr F, Chung I, et al. Paclitaxel for treatment of advanced small cell lung cancer (SCLC): a retrospective study of 185 patients. J Thorac Dis. 2020;12(3):782–793. doi:10.21037/jtd.2019.12.74
95. Mukhtar E, Adhami VM, Mukhtar H. Targeting microtubules by natural agents for cancer therapy. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014;13(2):275–284. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.Mct-13-0791
96. Xia Y, Li YH, Chen Y, et al. A phase II trial of concurrent chemoradiotherapy with weekly paclitaxel and carboplatin in advanced oesophageal carcinoma. Int J Clin Oncol. 2018;23(3):458–465. doi:10.1007/s10147-018-1240-4
97. Cowen RL, Williams KJ, Chinje EC, et al. Hypoxia targeted gene therapy to increase the efficacy of tirapazamine as an adjuvant to radiotherapy: reversing tumor radioresistance and effecting cure. Cancer Res. 2004;64(4):1396–1402. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-03-2698
98. Marcu L, Olver I. Tirapazamine: from bench to clinical trials. Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2006;1(1):71–79. doi:10.2174/157488406775268192
99. Delahoussaye YM, Hay MP, Pruijn FB, Denny WA, Brown JM. Improved potency of the hypoxic cytotoxin tirapazamine by DNA-targeting. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003;65(11):1807–1815. doi:10.1016/s0006-2952(03)00199-0
100. Le QT, McCoy J, Williamson S, et al. Phase I study of tirapazamine plus cisplatin/etoposide and concurrent thoracic radiotherapy in limited-stage small cell lung cancer (S0004): a Southwest Oncology Group study. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(16):5418–5424. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-04-0436
101. Rischin D, Peters L, Fisher R, et al. Tirapazamine, cisplatin, and radiation versus fluorouracil, cisplatin, and radiation in patients with locally advanced head and neck cancer: a randomized phase II trial of the Trans-Tasman Radiation Oncology Group (TROG 98.02). J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:79–87. doi:10.1200/jco.2005.01.072
102. Rischin D, Peters LJ, O’Sullivan B, et al. Tirapazamine, cisplatin, and radiation versus cisplatin and radiation for advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (TROG 02.02, HeadSTART): a phase III trial of the Trans-Tasman Radiation Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(18):2989–2995. doi:10.1200/jco.2009.27.4449
103. Wang J, Guise C, Dachs G, et al. Identification of one-electron reductases that activate both the hypoxia prodrug SN30000 and diagnostic probe EF5. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014;91(4):436–446. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2014.08.003
104. Mistry IN, Thomas M, Calder EDD, Conway SJ, Hammond EM. Clinical advances of hypoxia-activated prodrugs in combination with radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017;98(5):1183–1196. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.03.024
105. Patterson LH, McKeown SR, Ruparelia K, et al. Enhancement of chemotherapy and radiotherapy of murine tumours by AQ4N, a bioreductively activated anti-tumour agent. Br J Cancer. 2000;82(12):1984–1990. doi:10.1054/bjoc.2000.1163
106. Steward WP, Middleton M, Benghiat A, et al. The use of pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic end points to determine the dose of AQ4N, a novel hypoxic cell cytotoxin, given with fractionated radiotherapy in a phase I study. Ann Oncol. 2007;18(6):1098–1103. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdm120
107. Albertella MR, Loadman PM, Jones PH, et al. Hypoxia-selective targeting by the bioreductive prodrug AQ4N in patients with solid tumors: results of a phase I study. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(4):1096–1104. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-07-4020
108. Hong CR, Dickson BD, Jaiswal JK, et al. Cellular pharmacology of evofosfamide (TH-302): a critical re-evaluation of its bystander effects. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018;156:265–280. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2018.08.027
109. Takakusagi Y, Kishimoto S, Naz S, et al. Radiotherapy synergizes with the hypoxia-activated prodrug evofosfamide: in vitro and in vivo studies. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018;28:131–140. doi:10.1089/ars.2017.7106
110. Peeters SG, Zegers CM, Biemans R, et al. TH-302 in combination with radiotherapy enhances the therapeutic outcome and is associated with pretreatment [18F]HX4 hypoxia PET imaging. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21:2984–2992. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-15-0018
111. Lohse I, Rasowski J, Cao P, et al. Targeting hypoxic microenvironment of pancreatic xenografts with the hypoxia-activated prodrug TH-302. Oncotarget. 2016;7(23):33571–33580. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.9654
112. Wang Z, Dabrosin C, Yin X, et al. Broad targeting of angiogenesis for cancer prevention and therapy. Semin Cancer Biol. 2015;35:S224–s243. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.01.001
113. Larue RT, Van De Voorde L, Berbée M, et al. A Phase 1 ‘window-of-opportunity’ trial testing evofosfamide (TH-302), a tumour-selective hypoxia-activated cytotoxic prodrug, with preoperative chemoradiotherapy in oesophageal adenocarcinoma patients. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:644. doi:10.1186/s12885-016-2709-z
114. Wang Y, Gray JP, Mishin V, Heck DE, Laskin DL, Laskin JD. Distinct roles of cytochrome P450 reductase in mitomycin C redox cycling and cytotoxicity. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010;9(6):1852–1863. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.Mct-09-1098
115. Rockwell S, Keyes SR, Sartorelli AC. Preclinical studies of porfiromycin as an adjunct to radiotherapy. Radiat Res. 1988;116(1):100–113. doi:10.2307/3577481
116. Haffty BG, Wilson LD, Son YH, et al. Concurrent chemo-radiotherapy with mitomycin C compared with porfiromycin in squamous cell cancer of the head and neck: final results of a randomized clinical trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;61(1):119–128. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.07.730
117. Burd R, Lavorgna SN, Lenaz L, et al. Radiosensitization of hypoxic tumors by the bioreductive agent apaziquone (EO9, EOquin (TM)). Clin Cancer Res. 2005;9008S–9008S.
118. Wang Z, Ding Y, Geng G, Zhu N. Analysis of energy efficiency retrofit schemes for heating, ventilating and air-conditioning systems in existing office buildings based on the modified bin method. Energy Convers Manage. 2014;77:233–242. doi:10.1016/j.enconman.2013.09.037
119. Suwala AK, Kahlert UD, Maciaczyk J. Abstract 2515: pharmacological WNT-inhibition acts synergistically with chemo- and radiotherapy by overcoming treatment-resistance in glioma stem cells. Cancer Res. 2016;76(14Supplement):2515. doi:10.1158/1538-7445
120. Saker J, Huang S, Park L, Pedersen M, Kragh M, Harari P. Abstract 1027: EGFR targeting antibody SYM004 causes radiosensitization in tumor cells expressing wild-type K-Ras via modulation of MAPK signaling. Cancer Res. 2013;73(8Supplement):1027. doi:10.1158/1538-7445
121. Prabakaran PJ, Javaid AM, Swick AD, et al. Radiosensitization of adenoid cystic carcinoma with MDM2 inhibition. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23(20):6044–6053. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-17-0969
122. Zhuang HM, Miao XL, Zhao ZQ, Zhang L. Application of nano calcium phosphate biomaterials and bone tissue engineering on in exercise-induced injury. Adv Mater Res. 2014;951:109–112. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.951.109
123. Liu WL, Gao M, Tzen KY, et al. Targeting phosphatidylinositide3-Kinase/Akt pathway by BKM120 for radiosensitization in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2014;5(11):3662–3672. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.1978
124. Chen Y-H, Wei M-F, Wang C-W, et al. Dual phosphoinositide 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor is an effective radiosensitizer for colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 2015;357(2):582–590. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2014.12.015
125. Jayakumar S, Patwardhan RS, Pal D, Sharma D, Sandur SK. Dimethoxycurcumin, a metabolically stable analogue of curcumin enhances the radiosensitivity of cancer cells: possible involvement of ROS and thioredoxin reductase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;478(1):446–454. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.06.144
126. Kinsella TJ, Dobson PP, Mitchell JB, Fornace AJ. Enhancement of X ray induced DNA damage by pre-treatment with halogenated pyrimidine analogs. Int J Radiat Oncol. 1987;13(5):733–739. doi:10.1016/0360-3016(87)90292-6
127. Wang S, Zhao P, Zhang C, Bu Y. Mechanisms responsible for high energy radiation induced damage to single-stranded DNA modified by radiosensitizing 5-halogenated deoxyuridines. J Phys Chem B. 2016;120:2649–2657. doi:10.1021/acs.jpcb.5b11432
128. Benej M, Hong X, Vibhute S, et al. Papaverine and its derivatives radiosensitize solid tumors by inhibiting mitochondrial metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2018;115(42):10756–10761. doi:10.1073/pnas.1808945115
129. Lhuillier C, Rudqvist N-P, Elemento O, Formenti SC, Demaria S. Radiation therapy and anti-tumor immunity: exposing immunogenic mutations to the immune system. Genome Med. 2019;11(1):40. doi:10.1186/s13073-019-0653-7
130. Bourillon L, Bourgier C, Gaborit N, et al. An auristatin-based antibody-drug conjugate targeting HER3 enhances the radiation response in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer. 2019;145(7):1838–1851. doi:10.1002/ijc.32273
131. González JE, Barquinero JF, Lee M, García O, Casaco A. Radiosensitization induced by the anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibodies cetuximab and nimotuzumab in A431 cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 2012;13(2):71–76. doi:10.4161/cbt.13.2.18439
132. Buchanan IM, Scott T, Tandle AT, et al. Radiosensitization of glioma cells by modulation of Met signalling with the hepatocyte growth factor neutralizing antibody, AMG102. J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15(9):1999–2006. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01122.x
133. Nieder C, Mannsåker B, Dalhaug A, Pawinski A, Haukland E. Palliative radiotherapy in cancer patients with increased serum c-reactive protein level. Article. In Vivo (Brooklyn). 2016;30(5):581–586.
134. Kanegasaki S, Matsushima K, Shiraishi K, Nakagawa K, Tsuchiya T. Macrophage inflammatory protein derivative ECI301 enhances the alarmin-associated abscopal benefits of tumor radiotherapy. Cancer Res. 2014;74:5070–5078. doi:10.1158/0008-5472
135. Krüger M, Amort J, Wilgenbus P, et al. The anti-apoptotic PON2 protein is Wnt-catenin-regulated and correlates with radiotherapy resistance in OSCC patients. Oncotarget. 2016;7(32).
136. Cao Y, Yang L, Jiang W, et al. Therapeutic evaluation of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein-1 targeted DNAzyme for treating of nasopharyngeal carcinomas. Mol Ther. 2014;22(2):371–377. doi:10.1038/mt.2013.257
137. Walker JM, Rolig AS, Charych DH, et al. NKTR-214 immunotherapy synergizes with radiotherapy to stimulate systemic CD8+ T cell responses capable of curing multi-focal cancer. Immunother Cancer. 2020;8(1). doi:10.1136/jitc-2019-000464
138. Gandellini P, Rancati T, Valdagni R, Zaffaroni N. miRNAs in tumor radiation response: bystanders or participants? Trends Mol Med. 2014;20(9):529–539. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2014.07.004
139. de Jong MC, Ten Hoeve JJ, Grénman R, et al. Pretreatment microRNA expression impacting on epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition predicts intrinsic radiosensitivity in head and neck cancer cell lines and patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21:5630–5638. doi:10.1158/1078-0432
140. Huang A, Ono Y. Estimation of wrist flexion angle from muscle thickness changes measured by a flexible ultrasonic sensor. IEEE. 2016;188–191.
141. Shao Y, Song X, Jiang W, et al. MicroRNA-621 acts as a tumor radiosensitizer by directly targeting SETDB1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Ther. 2019;27(2):355–364. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.11.005
142. Zhang P, Wang L, Rodriguez-Aguayo C, et al. miR-205 acts as a tumour radiosensitizer by targeting ZEB1 and Ubc13. Nat Commun. 2014;5:5671. doi:10.1038/ncomms6671
143. Song L, Peng L, Hua S, et al. miR-144-5p enhances the radiosensitivity of non-small-cell lung cancer cells via targeting ATF2. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:5109497. doi:10.1155/2018/5109497
144. Luo J, Si ZZ, Li T, et al. MicroRNA-146a-5p enhances radiosensitivity in hepatocellular carcinoma through replication protein A3-induced activation of the DNA repair pathway. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019;316(3):C299–c311. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00189.2018
145. Wu SJ, Chen J, Wu B, Wang YJ, Guo KY. MicroRNA-150 enhances radiosensitivity by inhibiting the AKT pathway in NK/T cell lymphoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018;37(1):18. doi:10.1186/s13046-017-0639-5
146. Yin H, Ma J, Chen L, et al. MiR-99a enhances the radiation sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting mTOR. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46(2):471–481. doi:10.1159/000488615
147. Pajic M, Froio D, Daly S, et al. miR-139-5p Modulates radiotherapy resistance in breast cancer by repressing multiple gene networks of DNA repair and ROS defense. Cancer Res. 2018;78(2):501–515. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.Can-16-3105
148. Hu Z, Tie Y, Lv G, Zhu J, Fu H, Zheng X. Transcriptional activation of miR-320a by ATF2, ELK1 and YY1 induces cancer cell apoptosis under ionizing radiation conditions. Int J Oncol. 2018;53(4):1691–1702. doi:10.3892/ijo.2018.4497
149. Song Y, Zuo Y, Qian XL, et al. Inhibition of microRNA-21-5p promotes the radiation sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer through HMSH2. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(3):1258–1272. doi:10.1159/000481839
150. Zhang L, Wang C, Xue Z-X. Inhibition of miR-630 enhances the cell resistance to radiation by directly targeting CDC14A in human glioma. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(3):1255–1265.
151. Gu J, Li Y, Zeng J, et al. Knockdown of HIF-1α by siRNA-expressing plasmid delivered by attenuated Salmonella enhances the antitumor effects of cisplatin on prostate cancer. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):7546. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-07973-4
152. Mehta M, Basalingappa K, Griffith JN, et al. HuR silencing elicits oxidative stress and DNA damage and sensitizes human triple-negative breast cancer cells to radiotherapy. Oncotarget. 2016;7(40):64820–64835. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.11706
153. Qi R, Qiao T, Zhuang X. Small interfering RNA targeting S100A4 sensitizes non-small-cell lung cancer cells (A549) to radiation treatment. Onco Targets Ther. 2016;9:3753–3762. doi:10.2147/ott.S106557
154. Ohnishi K, Scuric Z, Schiestl RH, Okamoto N, Takahashi A, Ohnishi T. siRNA targeting NBS1 or XIAP increases radiation sensitivity of human cancer cells independent of TP53 status. Radiat Res. 2006;166(3):454–462. doi:10.1667/rr3606.1
155. Khan Z, Khan AA, Prasad GBKS, Khan N, Tiwari RP, Bisen PS. Growth inhibition and chemo-radiosensitization of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) by survivin-siRNA lentivirus. Radiother Oncol. 2016;118(2):359–368. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2015.12.007
156. Jackson MR, Bavelaar BM, Waghorn PA, et al. Radiolabeled oligonucleotides targeting the RNA subunit of telomerase inhibit telomerase and induce DNA damage in telomerase-positive cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2019;79(18):4627–4637. doi:10.1158/0008-5472
157. Cao F, Ju X, Chen D, et al. Phosphorothioate‑modified antisense oligonucleotides against human telomerase reverse transcriptase sensitize cancer cells to radiotherapy. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(2):2089–2094. doi:10.3892/mmr.2017.6778
158. Park SI, Park SJ, Lee J, et al. Inhibition of cyclic AMP response element-directed transcription by decoy oligonucleotides enhances tumor-specific radiosensitivity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;469(3):363–369. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.11.122
159. Yu C, Yu Y, Xu Z, et al. Antisense oligonucleotides targeting human telomerase mRNA increases the radiosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11(4):2825–2830. doi:10.3892/mmr.2014.3105
160. Hernández-Rivera M, Kumar I, Cho SY, et al. High-performance hybrid bismuth–carbon nanotube based contrast agent for X-ray CT imaging. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9:5709–5716. doi:10.1021/acsami.6b12768
161. Haume K, Rosa S, Grellet S, et al. Gold nanoparticles for cancer radiotherapy: a review. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2016;7(1):8. doi:10.1186/s12645-016-0021-x
162. Ma N, Liu P, He N, Gu N, Wu F-G, Chen Z. Action of gold nanospikes-based nanoradiosensitizers: cellular internalization, radiotherapy, and autophagy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9:31526–31542. doi:10.1021/acsami.7b09599
163. Li Y, Yun K-H, Lee H, Goh S-H, Suh Y-G, Choi Y. Porous platinum nanoparticles as a high-Z and oxygen generating nanozyme for enhanced radiotherapy in vivo. Biomaterials. 2019;197:12–19. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.01.004
164. Yang X, Yang M, Pang B, Vara M, Xia Y. Gold nanomaterials at work in biomedicine. Chem Rev. 2015;115(19):10410–10488. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00193
165. Cui L, Her S, Borst GR, Bristow RG, Jaffray DA, Allen C. Radiosensitization by gold nanoparticles: will they ever make it to the clinic? Radiother Oncol. 2017;124(3):344–356. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2017.07.007
166. Zhang XD, Luo Z, Chen J, et al. Ultrasmall glutathione-protected gold nanoclusters as next generation radiotherapy sensitizers with high tumor uptake and high renal clearance. Sci Rep. 2015;5:8669. doi:10.1038/srep08669
167. Luo D, Wang X, Zeng S, Ramamurthy G, Burda C, Basilion JP. Prostate-specific membrane antigen targeted gold nanoparticles for prostate cancer radiotherapy: does size matter for targeted particles? Chem Sci. 2019;10(35):8119–8128. doi:10.1039/c9sc02290b
168. Mathur P, Jha S, Ramteke S, Jain NK. Pharmaceutical aspects of silver nanoparticles. Artif Cells, Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(sup1):115–126. doi:10.1080/21691401.2017.1414825
169. Li S, Porcel E, Remita H, et al. Platinum nanoparticles: an exquisite tool to overcome radioresistance. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2017;8(1):4. doi:10.1186/s12645-017-0028-y
170. Pinel S, Thomas N, Boura C, Barberi-Heyob M. Approaches to physical stimulation of metallic nanoparticles for glioblastoma treatment. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019;138:344–357. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2018.10.013
171. Zhao J, Liu P, Ma J, et al. Enhancement of radiosensitization by silver nanoparticles functionalized with polyethylene glycol and aptamer as1411 for glioma irradiation therapy. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:9483–9496. doi:10.2147/IJN.S224160
172. Liu Z, Tan H, Zhang X, et al. Enhancement of radiotherapy efficacy by silver nanoparticles in hypoxic glioma cells. Artif Cells, Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(sup3):S922–s930. doi:10.1080/21691401.2018.1518912
173. Fathy MM. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using thymoquinone and evaluation of their radio-sensitizing activity. BioNanoScience. 2020;10(1):260–266. doi:10.1007/s12668-019-00702-3
174. Rajaee A, Wang S, Zhao L, et al. Multifunction bismuth gadolinium oxide nanoparticles as radiosensitizer in radiation therapy and imaging. Phys Med Biol. 2019;64(19):195007. doi:10.1088/1361-6560/ab2154
175. Fält T, Söderberg M, Wassélius J, Leander P. Material decomposition in dual-energy computed tomography separates high-Z elements from iodine, identifying potential contrast media tailored for dual contrast medium examinations. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2015;39(6):975–980. doi:10.1097/rct.0000000000000298
176. Chen X, Song J, Chen X, Yang H. X-ray-activated nanosystems for theranostic applications. Chem Soc Rev. 2019;48(11):3073–3101. doi:10.1039/c8cs00921j
177. Liu Y, Zhang P, Li F, et al. Metal-based nano enhancers for future radiotherapy: radiosensitizing and synergistic effects on tumor cells. Theranostics. 2018;8(7):1824–1849. doi:10.7150/thno.22172
178. Mardare AI, Mardare CC, Kollender JP, Huber S, Hassel AW. Basic properties mapping of anodic oxides in the hafnium-niobium-tantalum ternary system. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2018;19(1):554–568. doi:10.1080/14686996.2018.1498703
179. Taupin F, Flaender M, Delorme R, et al. Gadolinium nanoparticles and contrast agent as radiation sensitizers. Phys Med Biol. 2015;60(11):4449–4464. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/60/11/4449
180. Shahbazi M-A, Faghfouri L, Ferreira MPA, et al. The versatile biomedical applications of bismuth-based nanoparticles and composites: therapeutic, diagnostic, biosensing, and regenerative properties. Chem Soc Rev. 2020;49(4):1253–1321. doi:10.1039/C9CS00283A
181. Le Duc G, Roux S, Paruta-Tuarez A, et al. Advantages of gadolinium based ultrasmall nanoparticles vs molecular gadolinium chelates for radiotherapy guided by MRI for glioma treatment. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2014;5(1):4. doi:10.1186/s12645-014-0004-8
182. Hu P, Fu Z, Liu G, et al. Gadolinium-based nanoparticles for theranostic MRI-guided radiosensitization in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019;7:368. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2019.00368
183. Detappe A, Lux F, Tillement O. Pushing radiation therapy limitations with theranostic nanoparticles. Nanomedicine (London, England). 2016;11(9):997–999. doi:10.2217/nnm.16.38
184. McGinnity TL, Dominguez O, Curtis TE, Nallathamby PD, Hoffman AJ, Roeder RK. Hafnia (HfO2) nanoparticles as an X-ray contrast agent and mid-infrared biosensor. Nanoscale. 2016;8(28):13627–13637. doi:10.1039/C6NR03217F
185. Jayaraman V, Bhavesh G, Chinnathambi S, Ganesan S, Aruna P. Synthesis and characterization of hafnium oxide nanoparticles for bio-safety. Mater Express. 2014. doi:10.1166/mex.2014.1190
186. Bonvalot S, Le Pechoux C, De Baere T, et al. First-in-human study testing a new radioenhancer using nanoparticles (NBTXR3) activated by radiation therapy in patients with locally advanced soft tissue sarcomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;23:908–917. doi:10.1158/1078-0432
187. Prasad K, Bazaka O, Chua M, et al. Metallic biomaterials: current challenges and opportunities. Materials (Basel). 2017;10(8):884. doi:10.3390/ma10080884
188. Jin Y, Ma X, Zhang S, et al. A tantalum oxide-based core/shell nanoparticle for triple-modality image-guided chemo-thermal synergetic therapy of esophageal carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2017;397:61–71. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2017.03.030
189. Rathnayake S, Mongan J, Torres AS, et al. In vivo comparison of tantalum, tungsten, and bismuth enteric contrast agents to complement intravenous iodine for double-contrast dual-energy CT of the bowel. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2016;11(4):254–261. doi:10.1002/cmmi.1687
190. Lu Y-C, Yang C-X, Yan X-P. Radiopaque tantalum oxide coated persistent luminescent nanoparticles as multimodal probes for in vivo near-infrared luminescence and computed tomography bioimaging. Nanoscale. 2015;7(42):17929–17937. doi:10.1039/C5NR05623C
191. Brown R, Tehei M, Oktaria S, et al. High-Z nanostructured ceramics in radiotherapy: first evidence of ta2O5-induced dose enhancement on radioresistant cancer cells in an MV photon field. Part Part Syst Charact. 2014;31(4):500–505. doi:10.1002/ppsc.201300276
192. Song G, Chao Y, Chen Y, et al. All-in-one theranostic nanoplatform based on hollow TaOx for chelator-free labeling imaging, drug delivery, and synergistically enhanced radiotherapy. Adv Funct Mater. 2016;26(45):8243–8254. doi:10.1002/adfm.201603845
193. Song G, Chen Y, Liang C, et al. Catalase-loaded TaOx nanoshells as bio-nanoreactors combining high-Z element and enzyme delivery for enhancing radiotherapy. Adv Mater. 2016;28(33):7143–7148. doi:10.1002/adma.201602111
194. Bulatov A, Moskvin L, Rodinkov O, Ermakov S. Department of analytical chemistry of saint petersburg state university celebrates one hundred and fifty years anniversary: international year of the periodic table of chemical elements. Talanta. 2020;206:119759. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2019.03.081
195. Chellan P, Sadler PJ. The elements of life and medicines. Philos Trans a Math Phys Eng Sci. 2015;373(2037). doi:10.1098/rsta.2014.0182
196. Hossain M, Su M. Nanoparticle location and material-dependent dose enhancement in X-ray radiation therapy. J Phys Chem C. 2012;116(43):23047–23052. doi:10.1021/jp306543q
197. Yu X, Li A, Zhao C, Yang K, Chen X, Li W. Ultrasmall semimetal nanoparticles of bismuth for dual-modal computed tomography/photoacoustic imaging and synergistic thermoradiotherapy. ACS Nano. 2017;11(4):3990–4001. doi:10.1021/acsnano.7b00476
198. Qiu J, Xiao Q, Zheng X, et al. Single W18O49 nanowires: a multifunctional nanoplatform for computed tomography imaging and photothermal/photodynamic/radiation synergistic cancer therapy. Nano Res. 2015;8(11):3580–3590. doi:10.1007/s12274-015-0858-z
199. Gong L, Yan L, Zhou R, Xie J, Wu W, Gu Z. Two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenide nanomaterials for combination cancer therapy. J Mater Chem B. 2017;5(10):1873–1895. doi:10.1039/C7TB00195A
200. Cheng X, Yong Y, Dai Y, et al. Enhanced radiotherapy using bismuth sulfide nanoagents combined with photo-thermal treatment. Theranostics. 2017;7(17):4087–4098. doi:10.7150/thno.20548
201. Feng L, Yang D, Gai S, et al. Single bismuth tungstate nanosheets for simultaneous chemo-, photothermal, and photodynamic therapies mediated by near-infrared light. Chem Eng J. 2018;351:1147–1158. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2018.06.170
202. Detappe A, Thomas E, Tibbitt MW, et al. Ultrasmall silica-based bismuth gadolinium nanoparticles for dual magnetic resonance–computed tomography image guided radiation therapy. Nano Lett. 2017;17(3):1733–1740. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b05055
203. Yong Y, Zhou L, Zhang S, et al. Gadolinium polytungstate nanoclusters: a new theranostic with ultrasmall size and versatile properties for dual-modal MR/CT imaging and photothermal therapy/radiotherapy of cancer. NPG Asia Mater. 2016;8(5):e273–e273. doi:10.1038/am.2016.63
204. Ma P, Xiao H, Yu C, et al. Enhanced cisplatin chemotherapy by iron oxide nanocarrier-mediated generation of highly toxic reactive oxygen species. Nano Lett. 2017;17(2):928–937. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b04269
205. Vallabani NVS, Singh S. Recent advances and future prospects of iron oxide nanoparticles in biomedicine and diagnostics. 3 Biotech. 2018;8(6):279. doi:10.1007/s13205-018-1286-z
206. Tang GD, Li ZZ, Ma L, et al. Three models of magnetic ordering in typical magnetic materials. Phys Rep. 2018;758:1–56. doi:10.1016/j.physrep.2018.06.009
207. Nica V, Caro C, Páez-Muñoz JM, Leal MP, Garcia-Martin ML. Bi-magnetic core-shell CoFe(2)O(4)@MnFe(2)O(4) nanoparticles for in vivo theranostics. Nanomaterials (Basel, Switzerland). 2020;10(5). doi:10.3390/nano10050907
208. Meidanchi A, Akhavan O, Khoei S, Shokri A, Hajikarimi Z, Khansari N. ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles as radiosensitizers in radiotherapy of human prostate cancer cells. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015;46:394–399. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2014.10.062
209. Hidayatullah M, Nurhasanah I, Budi WS. ZnFe2O4nanoparticles for potential application in radiosensitization. J Phys Conf Ser. 2016;694:012028. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/694/1/012028
210. Salunkhe A, Khot V, Patil SI, et al. Magneto-chemotherapy with high-magnetic-moment iron oxide nanoparticles for cancer theranostics. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2020;3(4):2305–2313. doi:10.1021/acsabm.0c00077
211. Shao L, Gao Y, Yan F. Semiconductor quantum dots for biomedicial applications. Sensors (Basel). 2011;11(12):11736–11751. doi:10.3390/s111211736
212. Juzenas P, Chen W, Sun Y-P, et al. Quantum dots and nanoparticles for photodynamic and radiation therapies of cancer. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008;60(15):1600–1614. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2008.08.004
213. Cline B, Delahunty I, Xie J. Nanoparticles to mediate X-ray-induced photodynamic therapy and Cherenkov radiation photodynamic therapy. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2019;11(2):e1541. doi:10.1002/wnan.1541
214. Yang W, Read PW, Mi J, et al. Semiconductor nanoparticles as energy mediators for photosensitizer-enhanced radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;72(3):633–635. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.06.1916
215. Nakayama M, Sasaki R, Ogino C, et al. Titanium peroxide nanoparticles enhanced cytotoxic effects of X-ray irradiation against pancreatic cancer model through reactive oxygen species generation in vitro and in vivo. Radiat Oncol. 2016;11(1):91. doi:10.1186/s13014-016-0666-y
216. Morita K, Miyazaki S, Numako C, et al. Characterization of titanium dioxide nanoparticles modified with polyacrylic acid and H2O2 for use as a novel radiosensitizer. Free Radic Res. 2016;50(12):1319–1328. doi:10.1080/10715762.2016.1241879
217. Jin J, Zhao Q. Engineering nanoparticles to reprogram radiotherapy and immunotherapy: recent advances and future challenges. J Nanobiotechnology. 2020;18(1):75. doi:10.1186/s12951-020-00629-y
218. Sun H, Wang X, Zhai S. The rational design and biological mechanisms of nanoradiosensitizers. Nanomaterials (Basel, Switzerland). 2020;10(3):504. doi:10.3390/nano10030504
219. Martel A. Recent progress in biomedical applications of nanodiamonds. Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2018;8:11–24. doi:10.5923/j.nn.20180801.03
220. Jia Y, Weng Z, Wang C, et al. Increased chemosensitivity and radiosensitivity of human breast cancer cell lines treated with novel functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes. Oncol Lett. 2017;13(1):206–214. doi:10.3892/ol.2016.5402
221. Chan L, He L, Zhou B, et al. Cancer-targeted selenium nanoparticles sensitize cancer cells to continuous γ radiation to achieve synergetic chemo-radiotherapy. Chem Asian J. 2017;12(23):3053–3060. doi:10.1002/asia.201701227
222. Bromma K, Cicon L, Beckham W, Chithrani DB. Gold nanoparticle mediated radiation response among key cell components of the tumour microenvironment for the advancement of cancer nanotechnology. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):12096. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-68994-0
223. Patra JK, Das G, Fraceto LF, et al. Nano based drug delivery systems: recent developments and future prospects. J Nanobiotechnology. 2018;16(1):71. doi:10.1186/s12951-018-0392-8
224. Chenthamara D, Subramaniam S, Ramakrishnan SG, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of nanoparticles and routes of administration. Biomater Res. 2019;23(1):20. doi:10.1186/s40824-019-0166-x
225. Blanco E, Shen H, Ferrari M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat Biotechnol. 2015;33(9):941–951. doi:10.1038/nbt.3330
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.