Back to Journals » International Journal of Nanomedicine » Volume 14
Top-down fabrication-based nano/microparticles for molecular imaging and drug delivery
Authors Aryal S, Park H , Leary JF, Key J
Received 12 April 2019
Accepted for publication 25 June 2019
Published 19 August 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 6631—6644
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S212037
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Thomas Webster
Susmita Aryal,1,* Hyungkyu Park,1,* James F Leary,2 Jaehong Key1
1Department of Biomedical Engineering, Yonsei University, Wonju, Gangwon-do 26493, South Korea; 2Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN 47906, USA
Correspondence: Jaehong Key
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Yonsei University, 1 Yonseidae-gil Wonju, Gangwon-do 26493, South Korea
Tel +82 33 760 2857
Fax +82 33 760 2919
Email [email protected]
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Abstract: Recent breakthroughs in nanoparticle research have led to improved drug delivery and have overcome problems associated with normal drug delivery methods. Optimizing the design of nanoparticles in terms of controlled size, shape, and surface chemistry of nanoparticles can maximize the therapeutic efficacy. To maximize therapeutic effects, advanced formulation and fabrication methods have been developed. Biomedical applications of nanoparticles produced using the new fabrication techniques, including drug delivery and molecular imaging, have been widely explored. This review highlights the simple and versatile manufacturing techniques that can be used in the development of new types of nanoparticles that have strictly controlled physiochemical properties and their multifaceted advantages in drug delivery and molecular imaging.
Keywords: fabrication, lithography, cancer, advanced manufacturing method
Introduction
In the past 50 years, intensive research has been carried out in the fields of nanoscience and nanotechnology, which has led to great progress. New nano-drug delivery methods have led to new paradigms for health care. The special characteristics of nanoparticles, including their ease of accessibility and functionalization, biocompatibility, and stability, have made them valuable candidates for targeted therapy.1 These unique features allow encapsulation of toxic drugs and specific transport to the tumor site using either passive or active targeting methods.2 However, despite many new approaches in drug delivery using nanoparticles, only a few have actually led to tangible and significant results. Fabrication of nanoparticles with specific functional properties, including size, shape, and composition, is the key issue. This review provides an outline with respect to the current challenges and potential of fabricating nanoparticles for general purpose drug delivery and molecular imaging.
Various nanoparticle carrier designs have been developed and refined. But numerous hurdles still remain. In nanoparticle-based therapeutics, conventional synthesis of nanoparticles using techniques like emulsification produce polydispersed particles whose physicochemical characteristics, drug release profiles, degradation kinetics, and materials are troublesome to assess. Controlling these parameters is crucial for the effective application of the nanoparticles. Advances in design methodologies have succeeded in overcoming some of the limitations and have provided an exceptional approach in creating drug delivery particles with a rational design and highly ordered structure with numerous functional characteristics. Recent and ongoing studies related to design include top-down manufacturing approaches, such as soft lithography, micro-molding, and imprinting. Several groups have effectively used top-down microfabrication strategies and have generated drug delivery nanoparticles.3 In this review, we consider novel lithography-based fabrication approaches together with their remarkable applications in drug delivery and molecular imaging. Lithography can produce particles with a homogeneous size as well as unique designs. Non-spherical shapes have attracted increased attention in biomedical applications. Specifically, the penetration, pathway, and cellular uptake are determined by shape and shape-related factors, such as the aspect ratio and particle edge character.4,5
Lithography techniques in biomedical applications have the possibility to make well-defined nanoparticles and have become the alternative for the traditional method. A top-down method provides consistency in terms of particle size, shape, and geometry, and provides a monodisperse population with better yields, allowing the scale-up of manufacturing. Furthermore, this approach also improves encapsulation efficiency and drug stability.6
Nanoparticles in molecular imaging
Molecular imaging noninvasively provides a detailed picture that aids in the understanding of the biological behavior inside organisms.7 Molecular imaging is important in early disease detection, screening, diagnosis, therapy, and image-guided treatment of life-threatening diseases. However, current limitations of some molecular imaging techniques include poor target specificity, toxicity, expense, and low rate of tissue penetration.7,8 For these reasons, nanoparticles are emerging as a new class of molecular imaging agent because of their exclusive properties, which include small size, large surface area, improved in vivo pharmacokinetics, strong target binding via multiple ligands, and multimodal signaling capacity. In addition, nanoparticle-mediated molecular imaging has inherently low toxicity compared to conventional imaging agents. To expand the possibilities for nanoparticles in molecular imaging, selective targeting component(s) should be conjugated to the surface of the nanoparticles. This aids in achieving better image quality and also increases the applicability and functionality of imaging. The evolution of medical imaging from plain radiography to X-ray imaging, computer assisted tomography (CT), ultrasound (US) imaging, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and optical imaging holds enormous potential for improved health care.9
MRI
MRI is a non-invasive biomedical imaging technique that provides diverse anatomical, physiological, and molecular information from the interior of the organism. MRI is often preferred as it offers high tissue penetration depth and spatial resolution sufficient to visualize the entire human body. For example, superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles act as contrast agent in MRI due to their small size, which enables prolonged circulation, facilitates surface modification to favor internalization, low toxicity, and high relaxivity, which are important in MRI-mediated diagnosis. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles can be used to detect disease in macrophage-rich tissues. However, drawbacks of MRI include low sensitivity, which has limited the use of MRI. MRI can be improved by controlling physiochemical properties of the contrast agent.10 For example Culver et al.11 showed that gold nanostars incorporated with gadolinium are a promising contrast agent for MRI.
X-ray imaging and CT
CT is a leading imaging technology that provides three-dimensional anatomic imaging with high spatial resolution. Gold nanoparticles can be used as an X-ray contrast agent. Their relevant properties include high X-ray attenuation, lack of toxicity, colloidal stability, and targeted delivery.12 However, disadvantages of CT include high dose of ionizing radiation that is required and insufficient imaging sensitivity. Dual modality applications can be applied to overcome these limitations.
Optical imaging
Advantages of optical imaging include high sensitivity, low cost, and great potential for use with small animals. Quantum dots are a form of nanoparticles that are used extensively for optical imaging. However, optical imaging is hindered by the limited depth of penetration of light, which limits imaging deep within tissues, and the low spatial resolution compared to CT and MRI.
Every molecular imaging modality has specific advantages and disadvantages. A combination of imaging technologies is an important strategy to overcome the shortcomings of an individual imaging technology. The development of multimodal imaging nanoparticles has intensified in recent years. These probes contain two or more components that allow their detection by more than one imaging technology. No single methodology is adequate to provide all the fundamental data. The focal points of one method can be combined with the advantages of the other, while lessening the drawbacks of both at the same time. Nanotechnology can facilitate combinations of two or three imaging modalities like MR-optical, MR-positron emission tomography (PET), PET-CT, optical-PET, MR-CT, and MR-PET-optical.13 For example, PET imaging provides qualitative information about the disease with high sensitivity, with CT and MRI being important role in providing a resulting high resolution image that conveys anatomical information. Therefore, combinations of these imaging modalities can provide highly sensitive, high spatial resolution approaches that minimize the drawbacks of the individual techniques.14
Imaging by nanoparticles can be performed by single, double, or triple imaging modalities. Triple model imaging offers more unique and comprehensive information than either the single or dual modality. However, single modal imaging techniques are stable, target specific, less toxic, and biocompatible.
The goal of nanoparticle research is to control biological behavior and electromagnetic properties by controlling shape, size, and surface characteristics to make them suitable for imaging. The geometry of the nanoparticles influences their efficacy both in vitro and in vivo. According to Hwang et al.,15 unlike spheres, disks have a directional preference to an external magnetic field arising from their symmetrical shape. The authors opined that the unique shape is the key to improve their efficacy. Non-spherical particles outperform their spherical counterparts with several crucial advantages that include prolonged circulation and reduced macrophage uptake.
An ideal nanoparticle imaging agent for clinical use must have high sensitivity, sufficient resolution, low toxicity, and must be rapidly excreted and biodegradable.
Drug delivery with nanoparticles
The aim of nanoparticle-based drug delivery is enhanced delivery to reduce the toxicity of the free drug to the non-targeted organs, which can prevent drug degradation. Many types of nanoparticles have been developed for drug delivery, but only few have been approved and tested in clinical trials.16 Nanoparticles can be comprised of organic macromolecules, dendrimers, self-assemblies of smaller molecules, carbon nanotubes, and other components.17–20 Delivering therapeutic drugs to the target organ is the major obstacle. Protecting the drug from rapid degradation and clearance is also important.
Nanoparticles can help detect the location and extent of disease, and can provide information about the response to treatment. Design of nanoparticles that is characterized according to particle composition, size, shape, and surface properties define the therapeutic outcome. The size, shape, and surface chemistry of nanoparticles can greatly influence cellular uptake and treatment efficacy. Smaller nanoparticles are typically internalized more into cells than larger nanoparticles.21 For example, one study described particles with a diameter of 25 nm that were more efficaciously internalized into the cytoplasm of MCF-7 cells in contrast to 150 nm nanoparticles.22 Improved control of the size, structure, and biophysical properties of nanoparticles have led to tailored effects on molecular and cellular interactions.
Particle shape is another important parameter that regulates the in vivo performance of delivery vehicles. Uptake of nanoparticles is dependent on the particle shape, which involves factors like cell-particle interaction, strain energy required to wrap the membrane around the particles, and particle concentration at the cell membrane.23 Moreover, controlling the shape of nanoparticles can be used to target the nanoparticles to the desired cells and to avoid rapid clearance. The progression of advanced biomedical manufacturing techniques has raised the possibility of producing nanoparticles that are not spherical. Compared to spherical particles, non-spherical nanoparticles can be more readily internalized. For example, disk-shaped particles have higher binding capability compared to spherical particles in the interaction between the particles and cells.24 These non-spherical morphologies offer significant advantages concerning key pharmacokinetic parameters in vivo. In addition, several studies have clarified the relationship between biological responses and shape and size of nanoparticles. Size and shape can advantageously modulate immune activities like activation and suppression, and can help guide the particles toward the desired organ. For example, Lebre et al described that spherical, micron-sized hydroxyapatite particles evoke a weaker inflammatory response than smaller particles with a sharp edge, and noted that the size and shape of nanoparticles are profoundly pertinent physical attributes that influence the interaction between nanoparticles and living cells.25
Surface property also affects the interaction between nanomaterials and cells. This property is directly related with physical stability. Particles with neutral zeta potential tend to aggregate more rapidly. A stronger charge can increase the stability of the particles, which extends their shelf life. Strongly cationic nanoparticles interact more favorably with cell membranes, which will enhance their intracellular uptake. However, cationic particles are more toxic. This problem has spurred the use of different chemistries to modulate the surface of nanoparticles with the goal of improving their biomedical applications. Positively charged nanoparticles can be taken up by cells to a greater extent than anionic nanoparticles. For example, one study compared chitosan that was uncoated (positively charged) or coated with hyaluronic acid (negatively charged). The uptake of coated chitosan coated with hyaluronic acid was reduced and a relatively large amount of uncoated chitosan nanoparticles were rapidly taken up by the cells.26
Another important factor in the cellular uptake of nanoparticles is the elastic deformation of the particles. Key et al27 demonstrated the avid deposition of soft discoidal polymeric nanoconstructs (DPNs) in tumor tissue. Similarly, phagocytic cells engulfed more rigid particles than did soft particles. Rigid particles have low deformability, prolonged period of interaction, and pronounced internalization. In contrast, soft particles have high deformability, short interaction, and are poorly internalized. While rigid DPNs are internalized more avidly than soft DPNs, the latter show extended circulation time due to their deformability. It is also assumed that by mimicking the vascular behavior of blood cells, soft DPNs exhibit higher efficiency and better escape from macrophages. Thus, nanoparticle elasticity is also responsible for low macrophage uptake, extended longevity in the blood, and progressive accumulation within the tumor vascular bed (Figures 1 and 2).28,29
 |
Figure 1 Nanoparticle size, shape, and surface charge dictate biodistribution among the different organs including the lungs, liver, spleen and kidneys. Notes: (A) Spherical particles, including gold nanoparticles, liposomes, and polymeric micelles/nanoparticles can vary in size and differ in vivo fates. Particles >150 nm are entrapped within the liver and spleen while the small-sized nanoparticles are filtered out through the kidneys. (B) Different nanoparticle shapes exhibit unique flow characteristics that substantially alter circulating lifetimes, cell membrane interactions and macrophage uptake, which in turn affect biodistribution among the different organs. (C) Charge of nanoparticles influences opsonization, circulation times and interaction with macrophages. Positively charged particles are more prone to sequestration by macrophages in the lungs, liver, and spleen. Neutral and slightly negatively charged nanoparticles have longer circulation lifetimes and less accumulation in the aforementioned organs. Reprinted by permission from Springer Nature: Nature, Nature Biotechnology (https://www.nature.com/nbt/), Blanco E, Shen H, Ferrari M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat Biotechnol. 2015;33(9):941–951, Copyright © 2015.55 |
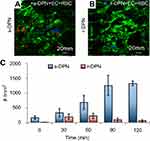 |
Figure 2 Intravital microscopy images showing soft (A) and rigid (B) discoidal polymeric nanoconstructs (DPNs) within the tortuous and abnormal tumor microvasculature, respectively. (C) Bar graph summarizing the level of DPN accumulation with the tumor microvasculature. Note: Reprinted with permission from Key J, Palange AL, Gentile F, et al. Soft discoidal polymeric nanoconstructs resist macrophage uptake and enhance vascular targeting in tumors. ACS Nano. 2015;9(12):11628–11641. Copyright © 2015 American Chemical Society.27 |
Nano sized, injectable drug carriers with modifiable surfaces and precise geometries have several advantageous properties, which include the ability to encapsulate a large amount of drug, protection from biodegradation, increased bioavailability, and drug release in a controlled manner. The overall goals are to achieve a conceptual design that produces nanoparticles that mimic biological cells, recognize disease-related cells, and provide on-demand systemic drug delivery, which all lessen side effects.
Despite various approaches in developing new nanoparticles for tumor cells, it is still difficult to produce homogeneously sized nanoparticles in high quality yield that can conveniently pass the leaky vasculature. For this reason, various researchers have been striving to improve the yield and generate homogeneously sized nanoparticles through traditional chemical syntheses. A new method to develop gold nanoparticles has produced dramatic improvements, with a gain in yield exceeding 85% as well as improved reproducibility.27 Table 1 summarizes the results from various nanoparticle-based methods.
 |
Table 1 Advanced nanofabrication technique for the synthesis of diverse nanoparticles and their advantages |
Experimental approaches for the design of nanoparticles
Advancements in the top-down development of fabrication of nanoparticles have created the possibility of developing nanoparticles with uniform sizes and shapes. Such fabrication methods provide the desired structure with the appropriate properties, which are difficult to obtain using bottom-up approaches, such as thermodynamically driven self-assembly. In this section, we focus on advancements in fabrication methods for shape-specific nanoparticle drug carriers and discuss their advantages and disadvantages.
Microfluidic devices can generate homogeneous nanoparticles with higher yield. Nanoparticle size is improved compared to those obtained from conventional methods. Microfluidic devices have been developed to synthesize particles with diameters ranging from nanometers to micrometers, using materials that include semiconductors, metals, and polymers. For example, in one study, a focused flow device was used to generate monodisperse polymeric particles.30 The monodisperse particles were synthesized with minimal variations in size (25 to 30 µm), with a prevalent diameter of 28 µm. In the same study, monodisperse microparticles were fabricated and the release kinetics of bupivacaine was compared with microparticles having the same size that had been generated by the conventional method. Monodisperse particles generated from the microfluidic device displayed higher yields and could encapsulate larger molecules. Furthermore, the monodispersed particles prepared by the microfluidic device released the drug more slowly than conventional polydispersed particles of a similar size. In addition, the initial burst release of drug from the monodispersed microfluidic particles was significantly less compared to conventional polydispersed particles (Figure 3).
 |
Figure 3 The left side shows (A) a schematic illustration of the procedure to fabricate monodisperse polymer microparticles and (B) optical microscopy image showing the orifice of the flow-focusing region generating droplets of dichloromethane (DCM) in water. The right-hand side shows (A, B) scanning electron microscopy images of monodisperse poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) microparticles with a diameter of approximately 28 μm. (C) Size distribution of the microparticles measured using a coulter counter.Note: Reprinted with permisson from Xu QB, Hashimoto M, Dang TT, et al. Preparation of monodisperse biodegradable polymer microparticles using a microfluidic flow-focusing device for controlled drug delivery. Small. 2009;5(13):1575–1581. Copyright © 2009 Wiley‐VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.30 |
Dong et al31 used micro-fabricated devices manufactured using thin-film deposition, photolithography, and etching utilizing computer-aided design software. Soft lithography was used to experiment with micro- and nano-scale patterns on the surface of photomasks to make a unique structure. Soft lithography can be used to emulsify polymeric tools and particles, since it is capable of better size control concerning structure and composition. It is also inexpensive and capable of high-throughput. Well-established techniques include replica molding, micro- and nano-transfer molding, and solvent-assisted micro-molding, among others. However, to overcome the synthesis problems with these methods remains challenging.
Other researchers introduced an injectable nanoparticle generator to overcome multiple biological barriers to cancer drug delivery.32 This technique can load various therapeutic agents like cancer drugs and can control the total dosage of loaded cancer agents through the linkage of conjugate molecules on the surface of nanoparticles. The nanoparticles developed by using the injectable nanoparticle generator successfully accumulated in tumors of mice. Nanoparticles made by an injectable nanoparticle generator can conjugate with molecular imaging probes and can be used therapeutically in tumor imaging and treatment (Figures 4 and 5).
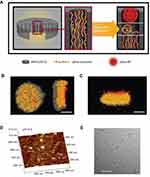 |
Figure 4 iNPG-pDox characterization and pDox (polymeric drug) assembly and release from iNPG (injectable nanoparticle generator).Notes: (A) Schematic diagram depicting iNPG-pDox composition, pDox prodrug encapsulation, and pDox nanoparticle assembly and release from nanopores. (B) Z-series confocal microscopy imaging of the iNPG-pDox particles, highlighting the presence of pDox (red) within the nanopores of the silicon carrier particle (gray). Scale bar, 1 µm. (C) Three dimensional reconstruction following sagittal cross-sectioning of the iNPG-pDox particles, depicting pDox (red) within the nanopores of the silicon carrier particle (gray), as well as the presence of pDox nanoparticles (red) released from the microparticles. Scale bar, 1 µm. (D) AFM analysis of size distribution of pDox nanoparticles released from iNPG-pDox at pH 7.4. (E) Cryogenic TEM of pDox nanoparticles released from iNPG-pDox at pH 7.4. Scale bar, 150 nm. Reprinted by permission from Springer Nature: Nature, Nature Biotechnology (https://www.nature.com/nbt/), Xu R, Zhang G, Mai J, et al. An injectable nanoparticle generator enhances delivery of cancer therapeutics. Nat Biotechnol. 2016;34(4):414–418, Copyright © 2016.32 |
 |
Figure 5 Inhibition of tumor growth and prolonged survival in mice bearing 4T1 tumor metastases to the liver and lung after treatment with iNPG-pDox.Note: Reprinted by permission from Springer Nature: Nature, Nature Biotechnology (https://www.nature.com/nbt/), Xu R, Zhang G, Mai J, et al. An injectable nanoparticle generator enhances delivery of cancer therapeutics. Nat Biotechnol. 2016;34(4):414–418, Copyright © 2016.32 |
The technique of photolithography is based on a top-down approach that manufactures a pattern on the polymer layer of the photomask. Photolithography can provide high resolution and can avoid contamination. Additionally, it uses near-infrared light, which can minimize side effects related to photodamage. These advantages of photolithography have prompted its use to investigate and observe deeper tissues and large-scale patterning. Although this novel technique has many advantages compared to other existing techniques, photolithography requires expensive facilities. Electrospray is a plausible microencapsulation method developed to overcome the limitations of bottom-up approaches like solvent extraction. This method is promising in the production of monodisperse particles ranging in size from sub-micrometers to micrometers by applying a high positive voltage between a needle and the ground.33,34 In one study, coaxial electrospray was used for multimodal imaging and image-guided therapy.35 Experimental and theoretical studies on coaxial electrospray of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microparticles have sought to overcome the limitations concerning poor encapsulation and loss of bioactivity during the nanofabrication.
Priyadarshana et al synthesized magnetite nanoparticles by destructuring natural high purity ore using a top-down approach in the presence of oleic acid. Various methods, including precipitation, thermal decomposition, and sol-gel techniques, have been reported for the synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles. Nanoparticles generated using the wet grinding approach have a narrower size distribution, smoother morphology, and less agglomeration, along with a brief grinding time.36
Merkel et al37 reported that top-down fabrication methods can easily control particle size and shape. The methods also permit an extensive examination of the versatility of Particle Replication In Non-wetting Templates (PRINT®). This method permits good resolution of particle size and shape, and can be easily scaled up at low cost (Figure 6).
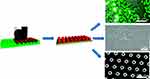 |
Figure 6 Scheme showing the imprint lithography method used to fabricate different shapes of nanoparticles.Note: Reprinted with permission from Merkel TJ, Herlihy KP, Nunes J, Orgel RM, Rolland JP, DeSimone JM. Scalable, shape-specific, top-down fabrication methods for the synthesis of engineered colloidal particles. Langmuir. 2010;26(16):13086–13096. Copyright © 2010 American Chemical Society.37 |
Doshi et al induced the formation of red blood cell (RBC)-like particles.38 Since RBCs can survive for approximately 120 days and circulate in the bloodstream, this biomaterial is a compelling candidate for drug delivery and therapy. Aryal et al showed that polymeric nanoparticles cloaked by RBC membrane displayed prolonged circulation and permitted sustained drug release.39 The authors used two different methods (physical encapsulation and chemical conjugation) to make nanoparticles loaded with doxorubicin. While encouraging, challenges remain. RBC-like particles are not natural, so that their elasticity and ability to contain oxygen are not similar to natural RBCs. Additionally, since the RBC-like particles are made with synthetic, rather than biological, components, these particles are considered artificial synthesized nanoparticles.
Merkel et al also showed that particles replicated through non-wetting templates can circulate longer than conventional microparticles and can vary in their biodistribution.40 These nanoparticles were fabricated by the PRINT technique to resemble RBCs that were resilient and round.
Lin et al reported a novel way to create patterns on a solid surface using bubble-pen lithography. Patterns can be applied to develop well designed nanoparticles.41 The size resolution limitations of lithography to make nanoparticles made it challenging to create a pattern using photon, electron or ion beams, and thus made it difficult to generate unique size-controlled and designed colloidal particles. However, the authors overcame these difficulties by using a single laser beam to generate a microbubble pattern on the substrate. Plasmon-enhanced photo-thermal effects have been applied to this technique to generate well designed and size-controlled nanoparticles with a diameter of approximately 200 nm. Usually, nanoparticles of approximately 100 nm can be delivered successfully to nuclei of living cells and particles less than 200 nm can penetrate the bilayer of erythrocytes.42 Particles of different sizes show various degrees of cellular uptake and responses after the surface modification of nanoparticles. The image presented in Figure 7 shows that well-controlled nanoparticles can be patterned on the surface.
 |
Figure 7 Schematic illustration of the pattern-writing process using an optically controlled microbubble on a plasmonic substrate.Note: Reprinted with permission from Lin LH, Peng XL, Mao ZM, et al. Bubble-Pen Lithography. Nano Lett. 2016;16(1):701–708. Copyright © 2016 American Chemical Society.41 |
Gratton et al demonstrated a series of particles having varying sizes and shapes, which were designed using a top-down lithographic fabrication method.43 These nanoparticles were made with polyethylene glycol to study the effects of the various sizes, shapes, and surface charges once the nanoparticles became distributed in cells. Cell-binding and interaction can be affected by the shape and size of nanoparticles. Thus, approaches to maintain an exact particle size and modify particle shape can be another way to improve cell uptake and interaction rate, which can be critical for the cellular uptake and penetration of nanoparticles. The uptake and penetration of nanoparticles by living cells is very complex. The process following internalization or passage across the cell membrane is not well-known. Doxil has been approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration. It has low cardiotoxicity compared to the original therapeutic agent, doxorubicin.43 However, the clinical data for doxil has not indicated compelling efficacy. This could be because of the low biodistribution of doxil in tumor cells and the inefficient intra-release profile of the drug from nanoparticles that are approximately 100 nm in size to tumor cells.44 Nanoparticles of various sizes and shapes were made to investigate basis of the interaction and subsequent events between nanoparticles and living cells. Figure 8 illustrates representative nanoparticles that were made. In this study, they also compared the interaction of particles with the cell membranes of living cells.43
 |
Figure 8 Micrographs of PRINT particles varying in both size and shape.Note: (A–C) Scanning electron micrograph of the cubic series of particles (diameters = 2 μm [A], 3 μm [B], and 5 μm [C]). (D–F) Fluorescence micrographs of the cubic series of particles (diameters = 2 μm [D], 3 μm [E], and 5 μm [F]). (G and H) Scanning electron micrographs of the cylindrical series of microparticles having the same height (1 μm), but varying diameters (diameters = 0.5 μm [G] and 1 μm [H]). (I–K) Scanning electron micrographs of the series of cylindrical nanoparticles (diameters = 200 nm, height = 200 nm [I]; diameter = 100 nm, height = 300 nm [J]; diameter = 150 nm, height = 450 nm [K]). Scale bars, A–F, 20 μm; G–K, 1 μm. Reprinted with permission from Gratton SE, Ropp PA, Pohlhaus PD, et al. The effect of particle design on cellular internalization pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105(33):11613–11618. Copyright © 2008 National Academy of Sciences.43 |
Synthesizing nanoparticles by physical and chemical processes is expensive and involves the use of toxic and otherwise hazardous chemicals that pose environmental, biological, and personnel risks. Ekta et al described the preparation of different silver nanoparticles by “green chemistry” using starch derived from boiled raw rice. The authors fabricated spherical, rod, hexagonal, and flower-shaped silver nanoparticles using green synthesis, with simple, cost-effective, and eco-friendly procedures that did not involve the use of hazardous agents and materials. Along with plant extracts, green synthesis is also used in unicellular organisms like bacteria and fungi.45
Hager et al proposed a new electron microscopy-based approach in which individual array methods were harnessed to develop single-stranded DNA structures on carbon “nano-islands”.46 This method is highly compatible with the detection of single molecules using fluorescence microscopy, and biophysical and cell biological approaches, where it allows mimicking of cell surfaces and enables the study of cell adhesion and signaling processes. A technique to array nanostructures on the surface can facilitate the creation of a unique microarray or a single nanomolecule that can be used therapeutically or for drug delivery. Biomolecules like DNA, RNA, and antibodies can avidly affiliate with cell membranes or can be internally localized where they trigger therapeutics effects while binding with each other. Conventional methods to develop unique structures and nanomolecules using such biomolecules are difficult. In living cells, the activities of biomolecules can be impeded by disintegration and discharge of toxic cations from the nanomaterial surface, which inhibit respiratory pathways, ATP generation, and other activities. This ultimately leads to death of the bacteria. Retaining bioactivity is crucial in conventional chemical synthesis procedures. Efforts to improve this limitation have included the development of new materials that contain biomolecules. In one approach, single-stranded DNA was immobilized by the electron beam of an electron microscope. Furthermore, multiple DNA strands could be mobilized on 100×100 nm islands and could be used to overlay DNA arrays or for other relevant applications (Figure 9).
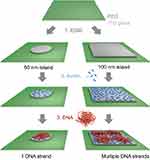 |
Figure 9 Scheme illustrating the generation of nanoarrays of individual DNA strands using 50 nm islands (left) and arrays with multiple DNA strands per 100×100 nm islands (right).Note: Reproduced from Hager R, Halilovic A, Burns JR, Schaffler F, Howorka S. Arrays of individual DNA molecules on nanopatterned substrates. Sci Rep. 2017;7:42075 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).46 |
Huanbutta et al described a novel approach to load therapeutic molecules into nanoparticles for colon-specific drug delivery.47 Nanoparticles containing the anti-inflammatory drug prednisolone were made by electrohydrodynamic atomization with various concentrations of Eudragit® S100 (EDS) concentrations and prednisolone/EDS weight ratios. Electrohydrodynamic atomization may prove useful in the simple manufacture of drug containing nanoparticles for the delivery of the payload. Bowerman et al demonstrated that a commercial anticancer drug can be loaded in nanoparticles using an imprint lithography based on PRINT.48 These rod-shaped poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)-docetaxel nanoparticles displayed increased circulation time and similar docetaxel exposure to the tumor compared to nanoparticles alone.
Ishida et al49 described a Langmuir-Blodgett technique that was used to fabricate two-dimensional arrays of 50 nm gold nanoparticles. The hydrophobic nanoparticles were about 50 nm in diameter and stable. The stability was maintained in the dry state, which allowed their subsequent re-dispersion in chloroform.
Zhan et al reported that non-lithographic, nanopatterning approaches fabricate nanoparticles of 100 nm or smaller in size on substrates having a large area.50 Current specialized lithography techniques are intricate and expensive compared to conventional fabrication. By combining the nanoimprinting method with an ultrathin alumina membrane, homogeneous nanoparticle patterns can be inexpensively made on large areas of substrates. The ultrathin alumina membrane does not require coating and heating of nanoparticles, and is more environmentally friendly and simple.
Inorganic nanoparticles are an attractive candidate in drug delivery. In particular, silica nanoparticles feature unique properties, such as tunable void volume, low density, large surface area, ease of surface modification, stability, and biocompatibility. Zhang et al fabricated hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles based on soft-or -hard-templating methods. The nanoparticles exhibited relatively high drug loading capacity and protein adsorption capacity, as well as controlled pH-responsive release behavior. Compared with conventional silica nanoparticles, the hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles with a large cavity and a permeable mesoporous shell had obvious advantages in mass diffusion and transportation, as well as in storage capacity. This fabrication method is desirable as it enables the preparation of high quality nanoparticles with a tunable particle size, high surface area, and controlled morphology. Currently, however, the manufacture of the desired quantity of mesoporous silica nanoparticles needed to scale-up to a commercial scale is challenging.51
Particle stretching is another technique of fabricating nano- and microparticles with different shapes. Spherical particles prepared by the bottom-up method can be used to produce anisotropic shapes. In this fabrication method, the shape varies with the physical properties of the particles, and with the film and the interaction between them. Champions et al produced more than 20 different shapes of nano- and microparticles using particle stretching methods. Spherical polystyrene particles were used as the starting material and polyvinyl alcohol as the aqueous phase. The prepared particles displayed the same polydispersity index as spherical particles before stretching. The particle yield was high, with 108 to 109 particles produced per stretching apparatus. The uniqueness of the particle stretching technique is the capacity to compare varied shaped particles molded from the same stock.52
The fabrication process is limited by high operating cost, low throughput, surfactants exposed to corrosive etchants, high energy radiation, relatively high temperature, and the wavelength used. These limitations have proven unfavorable to the use of conventional lithographic techniques for many researchers. These drawbacks motivated the exploration and development of a new nanofabrication technique. Recent nanofabrication techniques have created opportunities for fabrication on the nonplanar surface and over a large surface area. These techniques are also applicable to biological materials and to sensitive organic and organometallic materials. Moreover, they enable fabrication at low cost and offer high-throughput compared with conventional lithographic methods.53
Conclusions and outlooks
This review considered recent top-down nanofabrication strategies to achieve therapeutics and imaging performances that are superior to the current performance of nanoparticles. However, despite the tremendous development and acceptance of nanoparticles for clinical uses that include therapeutics and molecular imaging, nanomedicine faces a critical bottleneck in moving nanoparticles from the bench to the bedside. Major obstacles preventing the clinical translation of nanomedicine are the inability to increase specific target site accumulation, decrease off-target site accumulation, and lessen rapid clearance by immune cells. With the emergence of recent top-down nanofabrication techniques like lithography, monodispersed particles with controlled shape and size can be generated. They can be used to increase the accumulation of nanoparticles in tumor sites, with significantly enhanced binding with and uptake into target cells. Furthermore, with the advancement in microfluidic technologies to mimic organs, organ functions in the diseased tissues as nanoparticle interactions can be investigated to gather fundamental information with regard to drug delivery to predict in vivo performances. The top-down nanofabrication approach used to synthesize nanoparticles is proving to be an alternative tact to overcome the disadvantages and barriers of the bottom-up method. However, challenges such as scale-up of manufacture, stability of nanoparticles, and effective delivery remain to be overcome.
Abbreviation list
CT, computed tomography; DCM, dichloromethane; DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid; DPN, discoidal polymeric nanoconstructs; EDS, Eudragit® S100; iNPG, injectable nanoparticle generator; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; PET, positron emission tomography; PLGA, poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid); PRINT, particle replication in non-wetting templates; RBC, red blood cells; RNA, ribonucleic acid.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), No. 2018R1D1A1B07042339 and No. 2019K2A9A2A08000123.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. De Jong WH, Borm PJ. Drug delivery and nanoparticles:applications and hazards. Int J Nanomedicine. 2008;3(2):133–149. doi:10.2147/IJN.S596
2. Bazak R, Houri M, Achy SE, Hussein W, Refaat T. Passive targeting of nanoparticles to cancer: a comprehensive review of the literature. Mol Clin Oncol. 2014;2(6):904–908. doi:10.3892/mco.2014.356
3. Betancourt T, Brannon-Peppas L. Micro- and nanofabrication methods in nanotechnological medical and pharmaceutical devices. Int J Nanomedicine. 2006;1(4):483–495. doi:10.2147/nano.2006.1.4.483
4. Nishiyama N. Nanomedicine: nanocarriers shape up for long life. Nat Nanotechnol. 2007;2(4):203–204. doi:10.1038/nnano.2007.88
5. Champion JA, Katare YK, Mitragotri S. Particle shape: a new design parameter for micro- and nanoscale drug delivery carriers. J Control Release. 2007;121(1–2):3–9. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2007.03.022
6. Glangchai LC, Caldorera-Moore M, Shi L, Roy K. Nanoimprint lithography based fabrication of shape-specific, enzymatically-triggered smart nanoparticles. J Control Release. 2008;125(3):263–272. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2007.10.021
7. Kim J, Lee N, Hyeon T. Recent development of nanoparticles for molecular imaging. Philos T R Soc A. 2017;375(2107). doi:10.1098/rsta.2017.0022
8. Pu KY, Shuhendler AJ, Jokerst JV, et al. Semiconducting polymer nanoparticles as photoacoustic molecular imaging probes in living mice. Nat Nanotechnol. 2014;9(3):233–239. doi:10.1038/Nnano.2013.302
9. Cheng Z, Yan XF, Sun XL, Shen BZ, Gambhir SS. Tumor molecular imaging with nanoparticles. Engineering-Prc. 2016;2(1):132–140. doi:10.1016/J.Eng.2016.01.027
10. Sharifi S, Seyednejad H, Laurent S, Atyabi F, Saei AA, Mahmoudi M. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for in vivo molecular and cellular imaging. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2015;10(5):329–355. doi:10.1002/cmmi.1638
11. Culver KS, Shin YJ, Rotz MW, Meade TJ, Hersam MC, Odom TW. Shape-dependent relaxivity of nanoparticle-based T1 magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2016;120(38):22103–22109. doi:10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b08362
12. Cole LE, Ross RD, Tilley JMR, Vargo-Gogola T, Roeder RK. Gold nanoparticles as contrast agents in x-ray imaging and computed tomography. Nanomedicine-Uk. 2015;10(2):321–341. doi:10.2217/Nnm.14.171
13. Key J, Leary JF. Nanoparticles for multimodal in vivo imaging in nanomedicine. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;9:711–726. doi:10.2147/IJN.S53717
14. Zhang Y, Wang G, Yang L, Wang F, Liu AH. Recent advances in gold nanostructures based biosensing and bioimaging. Coordin Chem Rev. 2018;370:1–21. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2018.05.005
15. Hwang DK, Dendukuri D, Doyle PS. Microfluidic-based synthesis of non-spherical magnetic hydrogel microparticles. Lab Chip. 2008;8(10):1640–1647. doi:10.1039/b805176c
16. Tran S, DeGiovanni PJ, Piel B, Rai P. Cancer nanomedicine: a review of recent success in drug delivery. Clin Transl Med. 2017;6(1):44 . doi:10.1186/s40169-017-0175-0
17. Leifer K, Welch K, Jafri SH, Blom T. Nanoparticle bridges for studying electrical properties of organic molecules. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;906:535–546. doi:10.1007/978-1-61779-953-2_43
18. Scott RW, Wilson OM, Crooks RM. Synthesis, characterization, and applications of dendrimer-encapsulated nanoparticles. J Phys Chem B. 2005;109(2):692–704. doi:10.1021/jp0469665
19. Wetterskog E, Agthe M, Mayence A, et al. Precise control over shape and size of iron oxide nanocrystals suitable for assembly into ordered particle arrays. Sci Technol Adv Mat. 2014;15(5). doi:10.1088/1468-6996/15/5/055010
20. Bianco A, Kostarelos K, Prato M. Applications of carbon nanotubes in drug delivery. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2005;9(6):674–679. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2005.10.005
21. Moghimi SM, Hunter AC, Murray JC. Nanomedicine: current status and future prospects. Faseb J. 2005;19(3):311–330. doi:10.1096/fj.04-2747rev
22. Hao Y, Huang YX, He YQ, et al. The evaluation of cellular uptake efficiency and tumor-targeting ability of MPEG-PDLLA micelles: effect of particle size. RSC Adv. 2016;6(17):13698–13709. doi:10.1039/c5ra26563k
23. Agarwal R, Singh V, Jurney P, Shi L, Sreenivasan SV, Roy K. Mammalian cells preferentially internalize hydrogel nanodiscs over nanorods and use shape-specific uptake mechanisms. P Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110(43):17247–17252. doi:10.1073/pnas.1305000110
24. Zhang P, Xia J, Luo S. Generation of well-defined micro/nanoparticles via advanced manufacturing techniques for therapeutic delivery. Materials (Basel). 2018;11(4). doi:10.3390/ma11040623
25. Lebre F, Sridharan R, Sawkins MJ, Kelly DJ, O’Brien FJ, Lavelle EC. The shape and size of hydroxyapatite particles dictate inflammatory responses following implantation. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):2922. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-03086-0
26. Zaki NM, Nasti A, Tirelli N. Nanocarriers for cytoplasmic delivery: cellular uptake and intracellular fate of chitosan and hyaluronic acid-coated chitosan nanoparticles in a phagocytic cell model. Macromol Biosci. 2011;11(12):1747–1760. doi:10.1002/mabi.201100156
27. Key J, Palange AL, Gentile F, et al. Soft discoidal polymeric nanoconstructs resist macrophage uptake and enhance vascular targeting in tumors. ACS Nano. 2015;9(12):11628–11641. doi:10.1021/acsnano.5b04866
28. Sanchez-Iglesias A, Winckelmans N, Altantzis T, Bals S, Grzelczak M, Liz-Marzan LM. High-yield seeded growth of monodisperse pentatwinned gold nanoparticles through thermally induced seed twinning. J Am Chem Soc. 2017;139(1):107–110. doi:10.1021/jacs.6b12143
29. Palomba R, Palange AL, Rizzuti IF, et al. Modulating phagocytic cell sequestration by tailoring nanoconstruct softness. ACS Nano. 2018;12(2):1433–1444. doi:10.1021/acsnano.7b07797
30. Xu QB, Hashimoto M, Dang TT, et al. Preparation of monodisperse biodegradable polymer microparticles using a microfluidic flow-focusing device for controlled drug delivery. Small. 2009;5(13):1575–1581. doi:10.1002/smll.200801855
31. Qin D, Xia Y, Whitesides GM. Soft lithography for micro- and nanoscale patterning. Nat Protoc. 2010;5(3):491–502. doi:10.1038/nprot.2009.234
32. Xu R, Zhang G, Mai J, et al. An injectable nanoparticle generator enhances delivery of cancer therapeutics. Nat Biotechnol. 2016;34(4):414–418. doi:10.1038/nbt.3506
33. Xie JW, Ng WJ, Lee LY, Wang CH. Encapsulation of protein drugs in biodegradable microparticles by co-axial electrospray. J Colloid Interf Sci. 2008;317(2):469–476. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2007.09.082
34. Yao J, Lim LK, Xie JW, Hua JS, Wang CH. Characterization of electrospraying process for polymeric particle fabrication. J Aerosol Sci. 2008;39(11):987–1002. doi:10.1016/j.jaerosci.2008.07.003
35. Yuan S, Lei F, Liu Z, Tong Q, Si T, Xu RX. Coaxial electrospray of curcumin-loaded microparticles for sustained drug release. PLoS One. 2015;10(7):e0132609. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0132609
36. Priyadarshana G, Kottegoda N, Senaratne A, de AA, Karunaratne V. Synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles by top-down approach from a high purity ore. J Nanomater. 2015. doi:10.1155/2015/317312
37. Merkel TJ, Herlihy KP, Nunes J, Orgel RM, Rolland JP, DeSimone JM. Scalable, shape-specific, top-down fabrication methods for the synthesis of engineered colloidal particles. Langmuir. 2010;26(16):13086–13096. doi:10.1021/la903890h
38. Doshi N, Zahr AS, Bhaskar S, Lahann J, Mitragotri S. Red blood cell-mimicking synthetic biomaterial particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(51):21495–21499. doi:10.1073/pnas.0907127106
39. Aryal S, Hu CM, Fang RH, et al. Erythrocyte membrane-cloaked polymeric nanoparticles for controlled drug loading and release. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2013;8(8):1271–1280. doi:10.2217/nnm.12.153
40. Merkel TJ, Jones SW, Herlihy KP, et al. Using mechanobiological mimicry of red blood cells to extend circulation times of hydrogel microparticles. P Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108(2):586–591. doi:10.1073/pnas.1010013108
41. Lin LH, Peng XL, Mao ZM, et al. Bubble-Pen Lithography. Nano Lett. 2016;16(1):701–708. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b04524
42. Rothen-Rutishauser BM, Schurch S, Haenni B, Kapp N, Gehr P. Interaction of fine particles and nanoparticles with red blood cells visualized with advanced microscopic techniques. Environ Sci Technol. 2006;40(14):4353–4359.
43. Gratton SE, Ropp PA, Pohlhaus PD, et al. The effect of particle design on cellular internalization pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(33):11613–11618. doi:10.1073/pnas.0801763105
44. Unezaki S, Maruyama K, Hosoda J, et al. Direct measurement of the extravasation of polyethyleneglycol-coated liposomes into solid tumor tissue by in vivo fluorescence microscopy. Int J Pharm. 1996;144(1):11–17. doi:10.1016/S0378-5173(96)04674-1
45. Roy E, Patra S, Saha S, Kumar D, Madhuri R, Sharma PK. Shape effect on the fabrication of imprinted nanoparticles: comparison between spherical-, rod-, hexagonal-, and flower-shaped nanoparticles. Chem Eng J. 2017;321:195–206. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2017.03.050
46. Hager R, Halilovic A, Burns JR, Schaffler F, Howorka S. Arrays of individual DNA molecules on nanopatterned substrates. Sci Rep. 2017;7:42075. doi:10.1038/srep42075
47. Huanbutta K, Sangnim T, Limmatvapirat S, Nunthanid J, Sriamornsak P. Design and characterization of prednisolone-loaded nanoparticles fabricated by electrohydrodynamic atomization technique. Chem Eng Res Des. 2016;109:816–823. doi:10.1016/j.cherd.2016.03.004
48. Bowerman CJ, Byrne JD, Chu KS, et al. Docetaxel-loaded PLGA nanoparticles improve efficacy in taxane-resistant triple-negative breast cancer. Nano Lett. 2017;17(1):242–248. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b03971
49. Ishida T, Tachikiri Y, Sako T, Takahashi Y, Yamada S. Structural characterization and plasmonic properties of two-dimensional arrays of hydrophobic large gold nanoparticles fabricated by Langmuir-Blodgett technique. Appl Surf Sci. 2017;404:350–356. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.01.304
50. Zhan Z, Lei Y. Sub-100-nm nanoparticle arrays with perfect ordering and tunable and uniform dimensions fabricated by combining nanoimprinting with ultrathin alumina membrane technique. ACS Nano. 2014;8(4):3862–3868. doi:10.1021/nn500713h
51. Zhang HJ, Xu HJ, Wu MH, Zhong YF, Wang DH, Jiao Z. A soft-hard template approach towards hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles with rough surfaces for controlled drug delivery and protein adsorption. J Mater Chem B. 2015;3(31):6480–6489. doi:10.1039/c5tb00634a
52. Champion JA, Katare YK, Mitragotri S. Making polymeric micro- and nanoparticles of complex shapes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(29):11901–11904. doi:10.1073/pnas.0705326104
53. Gates BD, Xu Q, Stewart M, Ryan D, Willson CG, Whitesides GM. New approaches to nanofabrication: molding, printing, and other techniques. Chem Rev. 2005;105(4):1171–1196. doi:10.1021/cr030076o
54. Zhang L, Guan C, Wang Y, Liao J. Highly effective and uniform SERS substrates fabricated by etching multi-layered gold nanoparticle arrays. Nanoscale. 2016;8(11):5928–5937. doi:10.1039/c6nr00502k.
55. Blanco E, Shen H, Ferrari M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat Biotechnol. 2015;33(9):941–951. doi:10.1038/nbt.3330
 © 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
