Back to Journals » Drug Design, Development and Therapy » Volume 10
The efficacy of nebulized magnesium sulfate alone and in combination with salbutamol in acute asthma
Authors Sarhan HA, EL-Garhy OH, Alhosseiny M, Youssef N
Received 25 December 2015
Accepted for publication 10 March 2016
Published 9 June 2016 Volume 2016:10 Pages 1927—1933
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S103147
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Wei Duan
Hatem A Sarhan,1 Omar H EL-Garhy,1 Mohamed A Ali,2 Nouran A Youssef1
1Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, 2Department of Chest Diseases, Faculty of Medicine, Minia University, Minia, Egypt
Objective: Evaluation of the efficacy of nebulized magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) alone and in combination with salbutamol in acute asthma.
Methods: A double-blind randomized controlled study was conducted in Chest and Emergency Departments. Thirty patients of acute attack of bronchial asthma were randomized into three groups: MgSO4 nebulization (group A), salbutamol nebulization (group B), and their combination (group C). All patients were monitored before and after nebulization (each 20 minutes) for peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR), respiratory rate (RR), heart rate (HR), blood pressure, pulsus paradoxus, oxygen saturation, clinical examination, and Fischl index.
Results: A highly significant improvement in PEFR, PEFR percentage, and Fischl index and significant decrease in RR and HR was observed in all groups. A similar improvement in PEFR was observed in group A and group B (P=0.389). The difference in peak expiratory flow (PEF) improvement was insignificant between group B and group C (P=0.101), while there was a significant difference between group A and group C (P=0.014) in favor of group C.
Conclusion: Nebulized MgSO4 alone or combined with salbutamol has a clinically significant bronchodilator effect in acute asthma and leads to clinical improvement, increase in PEFR, reduction in HR, and reduction in RR. The response to nebulized MgSO4 alone (PEFR improvement 54±35.6 L/min, P=0.001) is comparable (P=0.389) to that of nebulized salbutamol (PEFR improvement 67.0±41.9 L/min, P=0.001) and is significantly less than (P=0.014) that of nebulized combination (PEFR improvement 92.0±26.9 L/min, P=0.000).
Keywords: nebulized magnesium sulfate, salbutamol, acute asthma, peak expiratory flow rate, Fischl index
Introduction
Asthma is a heterogeneous disease, usually characterized by chronic airway inflammation. It is defined by the history of respiratory symptoms such as wheeze, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and cough that vary over time and in intensity, together with variable expiratory airflow limitation.1 It is the most common chronic lung disease in both the developed and developing countries.2,3 Multicenter studies conducted in large general populations indicate that asthma is a disease extremely prevalent with up to one out of ten adults and one out of three children worldwide.4,5 Asthma is responsible for a significant personal and social burden, due to staggering costs to the patient and the health care system, and the potential for adverse outcomes.6
Asthma exacerbations are acute or subacute episodes of breathlessness, cough, wheezing, and chest tightness, or any combination of these symptoms. Exacerbations are associated with airway obstruction that should be documented and quantified by peak expiratory flow (PEF) or forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) measurement.7,8 Standard treatments for asthma crisis include short-acting bronchodilator, β2-agonists, inhaled anticholinergic agents, and corticosteroids, in addition to general management.5,9 Use of oxygen in a patient with acute severe asthma is justified only if the partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood is <60 mmHg. In fact, there is some suggestion that excess oxygen may be harmful for some patients with acute severe asthma.10,11 Intravenous methyl xanthine agents, such as theophylline, are less effective,6,12 have a low therapeutic index, and exhibit frequent side effects, making them increasingly unpopular.13,14 Antibiotics have not been shown to improve outcomes.15
Some studies suggest MgSO4 as an additional bronchodilator treatment option in patients resistant to standard therapy. MgSO4 has been assessed in intravenous and nebulized forms. The nebulized route offers the potential advantage of a quick onset of action and reduced incidence of side effects. Its disadvantages include a reduced dose of drug delivered compared with the intravenous form, and increased respiratory effort of the patient to enhance the drug’s effectiveness. The intravenous route provides direct access to the venous system, allowing the delivery of high drug concentrations. Disadvantages include the need for intravenous access and drug administration by infusion lasting ~20 minutes.16 Several studies17–22 had confirmed the bronchodilating effects of intravenous magnesium, but its effects through inhalation are controversial.23–28 However, the Global Initiative in National Asthma recommendations approve the use of inhaled MgSO4 during a crisis.1
Magnesium, the second most abundant intracellular cation, has a wide range of biological actions that are of potential relevance to the airways.23,29 Magnesium is involved with cellular homeostasis through its role as an enzymatic cofactor, as well as being involved in acetylcholine and histamine release, from cholinergic nerve terminals and mast cells, respectively. Investigators have proposed that the effect of MgSO4 is related to its ability to block the calcium ion influx to the smooth muscles of the respiratory system. Magnesium may increase the bronchodilator response to salbutamol in acute asthma by increasing the affinity of β-receptors to salbutamol or by upregulating β-receptors.6,8 This agent has been shown to be easy to use, extremely safe, and inexpensive. However, given its recent demonstration of efficacy, the use of this agent by frontline emergency physicians is unknown.15
The aim of this study was to make a comparison between the efficacy of nebulized dosage forms of MgSO4, salbutamol, and a combination of them as bronchodilators in the treatment of acute asthma.
Methods
Materials/instruments
- Salbutamol respirator solution containing 5 mg of salbutamol per mL (Ventolin respirator solution, GlaxoSmithKline plc, London, UK)
- Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate MgSO4·7H2O (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA)
- Normal saline, 0.9% w/v of NaCl, sterile, pyrogen-free isotonic solution, blood pressure (BP) 2004 (Al Mottahedoon Pharma, El Sharkeya, Egypt)
- Sterile water for injection, pyrogen-free isotonic solution, BP 2004 (Al Mottahedoon Pharma, Egypt)
- 0.22 μm hydrophilic filter (Corning Incorporated, Corning, NY, USA)
- Ultrasonic nebulizer (Fazzini, Italy)
- Lungenfunktionsgerät Roland Pulmo Test peak flow meter.
Preparation of isotonic, sterile, aqueous solution of MgSO4 for inhalation
- 3 mL dose (3.3% solution, 100 mg)
Four grams of MgSO4·7H2O (molecular weight =246.48 g/mol) were dissolved in 100 mL sterile water for injection using ultrasonic stirrer. After MgSO4 was completely dissolved, 132 mg of sodium chloride was added to adjust isotonicity of the solution. The pH of the solution was adjusted to 3.4, and the volume was adjusted to 120 mL with sterile water for injection and mixed again. Finally, the solution was sterilized by passing through 0.22 μm filter unit and aliquoted into individual 3 mL volumes in sterile 10 mL falcon tubes. - 2.5 mL dose (4% solution, 100 mg)
Four grams of MgSO4·7H2O (molecular weight =246.48 g/mol) were weighed and then dissolved in 80 mL sterile water for injection using ultrasonic stirrer. The pH of the solution was adjusted to 3.4, and the volume was adjusted to 100 mL with sterile water for injection and mixed again. Finally, the solution was sterilized by passing through 0.22 μ filter unit and aliquoted into individual 2.5 mL volumes in sterile 10 mL falcon tubes.
All the processes were done aseptically in a laminar airflow hood in our research lab.
Patients
A double-blind, randomized controlled study was conducted in Minia University Hospital Chest and Emergency Departments, Minia, Egypt, between October 2013 and March 2015. The study was approved by the Minia University Research Committee and the Minia University Hospital Ethical Committee. Written informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Patients included were newly diagnosed or known cases of bronchial asthma. Thirty subjects aged between 11 years and 70 years were selected according to the criteria for diagnosis of bronchial asthma, which are
- Medical history and physical examination
- Spirometry.
Spirometry was performed in all selected patients to confirm the diagnosis of bronchial asthma. The parameters measured in spirometry were FEV1, forced vital capacity (FVC), and PEFR. Patients with PEF <300 L/min were included; the best of three attempts was considered.
Patients were excluded if any of the following conditions were present: fever, lower respiratory tract infection, cardiac, renal, or hepatic dysfunction, required ventilator care or endotracheal intubation, near-fatal asthma, pregnant or breastfeeding mothers, failed to use PEF meter, or had received oral, inhaled, or parenteral bronchodilators in the past 6 hours, or steroids in the past 12 hours.
Study design
Asthmatic patients were divided into three groups as shown in Table 1. A Fazzini ultrasonic nebulizer was used for the administration of the drugs. All patients were monitored before nebulization, and every 20 minutes up to 1 hour after completion of nebulization. Monitored parameters were PEF, with a handheld Lungenfunktionsgerät Roland Pulmo Test peak flow meter, respiratory rate (RR), heart rate (HR), BP, pulsus paradoxus (PP), oxygen saturation (SO2), clinical examination, and Fischl index30 (at 0 minute and 120 minutes only). The Fischl index takes into account dyspnea, accessory muscle use, wheeze, HR ≥120 beats/min, RR ≥30 breaths/min, PP ≥18 mmHg, and a PEF ≤120 L/min. The presence of each finding scores 1 point and a total score of 4 points or more implies severe asthma. Patients in group A and group C were also monitored for side effects of MgSO4 such as hypotension, arrhythmias, loss of deep tendon reflexes, and respiratory depression before and after each nebulization dose.
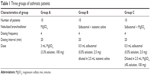  | Table 1 Three groups of asthmatic patients |
After the completion of the four nebulization doses, patients with unsustainable bronchodilatation effect were given supplemental treatment in the emergency department in the form of oxygen, salbutamol nebulization, hydrocortisone injection, and aminophylline infusion.
Results
Out of 45 patients screened over the study period, only 30 patients were included. Only single visits were taken into consideration in our study to avoid patient bias.
Our study showed that the MgSO4 nebulization, alone or combined with a bronchodilator, resulted in clinical improvement, increase in PEFR, reduction in HR, and reduction in RR. However, comparing MgSO4 with salbutamol, we found that salbutamol (PEFR improvement 67.0±41.9 L/min, PEFR percentage improvement 13.2±7.7, and Fischl index improvement 3.3±1.0) was slightly better (P=0.389, P=0.573, and P=0.594, respectively) than MgSO4 (PEFR improvement 54±35.6 L/min, PEFR percentage improvement 11.5±7.7, and Fischl index improvement 3.0±1.2) in the management of acute exacerbations of asthma, and a combination of them was the best (PEFR improvement 92.0±26.9 L/min, PEFR percentage improvement 17.1±5.4, and Fischl index improvement 3.4±1.5). Nebulized MgSO4 showed early but unsustainable relief, so it may be better used as an adjunct for standard treatment in acute attacks of asthma.
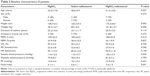
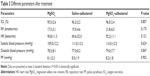
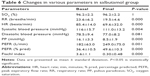
Baseline patient features are shown in Table 2. There was a significant difference between three groups in age, height, and weight. Regarding other baseline data, differences between the groups were not statistically significant. All patients were presented by dyspnea and wheeze. Tables 3 and 4 show that no statistically significant difference between groups in any parameter was observed after treatment.
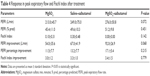
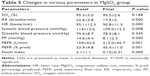
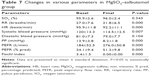
There was a highly significant improvement in PEFR, PEFR percentage, and Fischl index in all groups (Tables 5–7). A similar improvement in PEFR was observed in MgSO4 and salbutamol groups (P=0.389). The difference in PEF improvement was nonsignificant between salbutamol and combination groups (P=0.101); however, there was a significant difference between MgSO4 and combination groups (P=0.014) in favor of the combination group. There was no significant difference between any pair of groups in either PEFR percentage improvement (groups A and B [P=0.598], groups B and C [P=0.231], groups A and C [P=0.090]) or Fischl index improvement (groups A and B [P=0.613], groups B and C [P=0.866], groups A and C [P=0.501]).
The mean basal, as well as final, respiratory (basal: groups A and B [P=0.718], groups B and C [P=0.225], groups A and C [P=0.120]; final: groups A and B [P=0.378], groups B and C [P=0.312], groups A and C [P=0.065]) and heart (basal: groups A and B [P=0.102], groups B and C [P=0.078], groups A and C [P=0.890]; final: groups A and B [P=0.030], groups B and C [P=0.021], groups A and C [P=0.881]) rates were not significantly different between any pair of groups. According to Tables 5–7, a highly significant decrease in RR and HR was observed in each group.
The difference in both mean basal and final SO2 between any pair of three groups was nonsignificant (basal: groups A and B [P=0.455], groups B and C [P=0.803], groups A and C [P=0.618]; final: groups A and B [P=0.528], groups B and C [P=0.857], groups A and C [P=0.652]). In Tables 5–7, no significant increase in SO2 in any of three groups was noted.
The most common adverse reactions associated with MgSO4 were dry and bitter mouth and dizziness. One patient developed mild transient hypotension. None of the patients in the MgSO4 group showed any sign of toxicity such as depressed deep tendon reflexes. In the salbutamol group, two patients experienced fine tremors. No clinically significant adverse events were reported in the combination group. None of the adverse effects shown in the three groups was severe enough to necessitate withdrawal from the study.
Discussion
The results of our study revealed that nebulized MgSO4, either alone or combined with salbutamol, has a significant bronchodilator effect in acute bronchial asthma. Bronchodilator effect of nebulized MgSO4 alone is similar to that of nebulized salbutamol and is significantly less than that of nebulized combination.
The common adverse effects associated with MgSO4 administration are nausea, vomiting, flushing, thirst, hypotension, drowsiness, confusion, loss of deep tendon reflexes, muscle weakness, respiratory depression, and cardiac arrhythmias.31
A systematic review done by Blitz et al6 demonstrated that nebulization of MgSO4 as an adjunct for β2-agonists improved pulmonary function in patients experiencing asthma exacerbations. They found no treatment benefit of either MgSO4 or β2-agonist alone. Subsequently, it was recommended to administer nebulized MgSO4 as an addition to inhaled β2-agonists in acute asthma attacks.
Abdelnabi et al8 concluded that nebulized MgSO4 improved the clinical condition, increased both PEFR and SO2, and decreased both HR and RR in case of acute bronchial asthma. They reported a significant bronchodilatation that was significantly less than that of salbutamol when either was used alone.
Talukdar et al14 demonstrated a clinically significant bronchodilatory effect of nebulized MgSO4 in severe bronchial asthma, which was significantly less than that of salbutamol.
Nannini et al23 showed that in acutely ill asthmatic patients, the peak flow response to isotonic MgSO4 as an adjuvant to nebulized salbutamol was higher than salbutamol with normal saline. Single dose of 0.5 mL salbutamol (2.5 mg) diluted in either 3 mL normal saline or in 3 mL isotonic MgSO4 (225 mg) was administered to each patient.
In a study conducted by Bessmertny et al,24 nebulized MgSO4 combined with albuterol failed to show any benefit in addition to that provided by albuterol plus isotonic saline, in adults with mild-to-moderate asthma attacks. Patients received three doses of nebulized albuterol at 20-minute intervals. Either nebulized MgSO4 (384 mg) or isotonic saline solution was administered to patients immediately after each albuterol dose with a total of three doses.
In a randomized placebo-controlled trial, Hughes et al25 observed an enhanced bronchodilator response after nebulization of three doses of 2.5 mg salbutamol mixed with 2.5 mL isotonic MgSO4 at 30 minutes intervals, when compared with nebulization of salbutamol mixed with isotonic saline, in patients with severe asthma. FEV1 at 90 minutes was the primary outcome measure. They found that the improvement was greater in patients with a baseline FEV1 of <30% of the predicted value.
The results of our study are consistent with a randomized, double-blind, controlled study conducted by Mangat et al,31 in which the bronchodilator effectiveness of nebulized MgSO4 in acute asthma was assessed and compared with nebulized salbutamol. Patients received either four doses of nebulized 3 mL salbutamol (2.5 mg) or four doses of nebulized 3 mL MgSO4 (3.2% solution, 95 mg). They reported significant improvement in PEFR, PEFR percentage, and Fischl index, as well as significant decrease in RR, in both groups. However, the difference between the two groups was not significant. There was a significant decrease in HR and mean arterial pressure in MgSO4 group and salbutamol group, respectively. It was concluded that the bronchodilatory effect of nebulized MgSO4 was significant and similar to that of nebulized salbutamol.
Our results disagreed with a study32 of the efficacy of nebulized MgSO4 in acute severe asthma. Patients were divided into three groups (salbutamol, salbutamol with MgSO4, and MgSO4). There was no significant increase in any of measured parameters (PEFR, FEV1, FVC, and FEV1/FVC) in all three groups; however, the percentage increase was quite significant in the two groups where MgSO4 was used. Also the changes in vital parameters were not significant. It was noted that the response to MgSO4 was greater in patients with baseline PEFR <50%, thus MgSO4 may be a good choice in the management of acute severe asthma. Our study agreed with them in that the bronchodilator response to MgSO4 was early but unfortunately unsustainable, so a combination of MgSO4 with standard treatment may be better in treating acute severe asthma.
Conclusion
Nebulized MgSO4, either alone or combined with salbutamol, has a clinically significant bronchodilator effect in acute asthma. The response to nebulized MgSO4 alone is comparable to that of nebulized salbutamol and is significantly less than that of nebulized combination. The response to nebulized MgSO4 alone (PEFR improvement 54±35.6 L/min, P=0.001) is comparable (P=0.389) to that of nebulized salbutamol (PEFR improvement 67.0±41.9 L/min, P=0.001) and is significantly less than (P=0.014) that of nebulized combination (PEFR improvement 92.0±26.9 L/min, P=0.000).
This suggests that a combination of MgSO4 and salbutamol may be the best choice for the management of acute exacerbations of asthma.
Nebulized MgSO4 is a well-tolerated bronchodilator for acutely ill asthmatic patients, and can be administered safely. Being cheap and readily available, it can be commonly used.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). Global strategy for asthma management and prevention; 2015. Available from: www.ginasthma.org. Accessed on August 3, 2015. | ||
Morell F, Genover T, Reyes L, Benaqueb E, Rogera L, Ferrera J. [Monitoring of asthma outpatients after adapting treatment to meet international guidelines]. Archivos de Bronconeumología (English Edition). 2007;43(1):29–35. | ||
Refaat S, Aref H. Acute asthma in emergency department, prevalence of respiratory and non-respiratory symptoms. Egypt J Chest Dis Tuberc. 2014;63(4):776–771. | ||
Annesi-Maesano I. [Epidemiology of asthma in the world and in France]. Rev Prat. 2011;61(3):329–335. | ||
Shan Z, Rong Y, Yang W, et al. Intravenous and nebulized magnesium sulfate for treating acute asthma in adults and children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Respir Med. 2013;107(3):321–330. | ||
Blitz M, Blitz S, Hughes R, et al. Aerosolized magnesium sulfate for acute asthma: a systematic review. Chest. 2005;128(1):337–344. | ||
Busse WW, Banks-Schlegel S, Wenzel SE. Pathophysiology of severe asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000;106(6):1033–1042. | ||
Abdelnabi EA, Kamel MM, Ali AE. Nebulized magnesium sulphate versus nebulized salbutamol in acute bronchial asthma. Egypt J Chest Dis Tuberc. 2012;61(3):29–34. | ||
Bateman E, Hurd S, Barnes P, et al. Global strategy for asthma management and prevention: GINA executive summary. Eur Respir J. 2008;31(1):143–178. | ||
Chien JW, Ciufo R, Novak R, et al. Uncontrolled oxygen administration and respiratory failure in acute asthma. Chest. 2000;117(3):728–733. | ||
Agarwal R, Gupta D. No role for inhaled magnesium sulfate in the treatment of acute asthma? Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2007;20(5):494. | ||
Emond S. Addition of intravenous aminophylline to β2-agonist in adults with acute asthma. Ann Emerg Med. 2002;40(3):350–352. | ||
Siegel D, Sheppard D, Gelb A, Weinberg PF. Aminophylline increases the toxicity but not the efficacy of an inhaled beta-adrenergic agonist in the treatment of acute exacerbations of asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985;132(2):283–286. | ||
Talukdar T, Singhal P, Jain A, Kumar R, Gaur SN. Inhaled magnesium sulfate in the treatment of severe asthma. Indian J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2005;19(1):29–35. | ||
Rowe BH, Camargo CA, Multicenter Airway Research Collaboration. The use of magnesium sulfate in acute asthma: rapid uptake of evidence in North American emergency departments. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;117(1):53–58. | ||
Goodacre S, Cohen J, Bradburn M, Gray A, Benger J, Coats T; 3Mg Research Team. Intravenous or nebulised magnesium sulphate versus standard therapy for severe acute asthma (3Mg trial): a double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2013;1(4):293–300. | ||
Okayama H, Aikawa T, Okayama M, Sasaki H, Mue S, Takishima T. Bronchodilating effect of intravenous magnesium sulfate in bronchial asthma. JAMA. 1987;257(8):1076–1078. | ||
Skobeloff EM, Spivey WH, McNamara RM, Greenspon L. Intravenous magnesium sulfate for the treatment of acute asthma in the emergency department. JAMA. 1989;262(9):1210–1213. | ||
Noppen M, Vanmaele L, Impens N, Schandevyl W. Bronchodilating effect of intravenous magnesium sulfate in acute severe bronchial asthma. Chest. 1990;97(2):373–376. | ||
Okayama H, Okayama M, Aikawa T, Sasaki M, Takishima T. Treatment of status asthmaticus with intravenous magnesium sulfate. J Asthma. 1991;28(1):11–17. | ||
Singh AK, Gaur S, Kumar R. A randomized controlled trial of intravenous magnesium sulphate as an adjunct to standard therapy in acute severe asthma. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008;7(4):221–229. | ||
Kew KM, Kirtchuk L, Michell CI. Intravenous magnesium sulfate for treating adults with acute asthma in the emergency department. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;5:Cd010909. | ||
Nannini Jr LJ, Pendino JC, Corna RA, Mannarino S, Quispe R. Magnesium sulfate as a vehicle for nebulized salbutamol in acute asthma. Am J Med. 2000;108(3):193–197. | ||
Bessmertny O, DiGregorio RV, Cohen H, et al. A randomized clinical trial of nebulized magnesium sulfate in addition to albuterol in the treatment of acute mild-to-moderate asthma exacerbations in adults. Ann Emerg Med. 2002;39(6):585–591. | ||
Hughes R, Goldkorn A, Masoli M, Weatherall M, Burgess C, Beasley R. Use of isotonic nebulised magnesium sulphate as an adjuvant to salbutamol in treatment of severe asthma in adults: randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2003;361(9375):2114–2117. | ||
Kokturk N, Turktas H, Kara P, Mullaoglu S, Yilmaz F, Karamercan A. A randomized clinical trial of magnesium sulphate as a vehicle for nebulized salbutamol in the treatment of moderate to severe asthma attacks. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2005;18(6):416–421. | ||
Aggarwal P, Sharad S, Handa R, Dwiwedi SN, Irshad M. Comparison of nebulised magnesium sulphate and salbutamol combined with salbutamol alone in the treatment of acute bronchial asthma: a randomised study. Emerg Med J. 2006;23(5):358–362. | ||
Gallegos-Solórzano MC, Pérez-Padilla R, Hernández-Zenteno RJ. Usefulness of inhaled magnesium sulfate in the coadjuvant management of severe asthma crisis in an emergency department. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2010;23(5):432–437. | ||
Britton J, Pavord I, Richards K, et al. Dietary magnesium, lung function, wheezing, and airway hyper-reactivity in a random adult population sample. Lancet. 1994;344(8919):357–362. | ||
Fischl MA, Pitchenik A, Gardner LB. An index predicting relapse and need for hospitalization in patients with acute bronchial asthma. N Engl J Med. 1981;305(14):783–789. | ||
Mangat H, D’Souza G, Jacob M. Nebulized magnesium sulphate versus nebulized salbutamol in acute bronchial asthma: a clinical trial. Eur Respir J. 1998;12(2):341–344. | ||
Dadhich P, Vats M, Lokendra D, et al. Magnesium sulphate nebulization in acute severe asthma. Chest. 2003;124(4_MeetingAbstracts):107S. |
 © 2016 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2016 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.