Back to Journals » Journal of Pain Research » Volume 11
Supracondylar process syndrome: two cases of median nerve neuropathy due to compression by the ligament of Struthers
Authors Shon HC, Park JK, Kim DS , Kang SW , Kim KJ, Hong SH
Received 26 December 2017
Accepted for publication 2 March 2018
Published 16 April 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 803—807
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S160861
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Katherine Hanlon
Hyun-Chul Shon, Ji-Kang Park, Dong-Soo Kim, Sang-Woo Kang, Kook-Jong Kim, Seok-Hyun Hong
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea
Abstract: The supracondylar process is a beak-shaped bony process on the anteromedial aspect of the distal humerus. The ligament of Struthers is a fibrous band extending from the tip of the process to the medial epicondyle. The median nerve and brachial artery pass under the ligament of Struthers and consequently can be compressed, causing supracondylar process syndrome. As a rare cause of proximal median nerve entrapment, supracondylar process syndrome is triggered when the median nerve is located in the superficial or deep layer of the ligament of Struthers as a result of anatomical variation. The supracondylar process can be easily detected on X-ray images obtained in oblique views but may not be identified in only anteroposterior or lateral views. In this article, we present 2 cases of supracondylar process syndrome and describe the process of diagnosis and treatment and results of a literature review.
Keywords: supracondylar process syndrome, ligament of Struthers, median nerve, nerve entrapment
Introduction
Struthers named the ligament of Struthers in 1854, describing it as a ligament or muscle fiber connecting the supracondylar process to the medial epicondyle.1 The supracondylar process is a congenital bony protuberance on the anteromedial aspect of the distal humerus, ~5 cm proximal to the medial epicondyle.2 It has been detected in 0.1%–2.7% of the healthy population and ranges from 2 to 20 mm in size as a distal projection.3 Without symptoms in most cases, supracondylar process syndrome can develop when neurovascular structures are compressed by the supracondylar process or ligament of Struthers.4 The median nerve and brachial artery can be entrapped while passing through the deep layer of the tunnel formed by the supracondylar process and ligament of Struthers, and symptoms can manifest at the time of entrapment5 or when the nerve passes the superficial layer and continues its course.6 Symptomatic supracondylar process syndrome can be treated with a restriction of movement and conservative therapy, with relief of local compression. However, surgical decompression improved symptoms in most reports.6 The supracondylar process can be easily detected on X-ray images taken in oblique views but may not be identified if only anteroposterior or lateral views are taken. Magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasound are also used for diagnosis.2,3 We report 2 cases of supracondylar process for the first time in Korea, treated with surgical excision and decompression, and describe the diagnosis and treatment, along with the results of a literature review.
Case series
Case 1
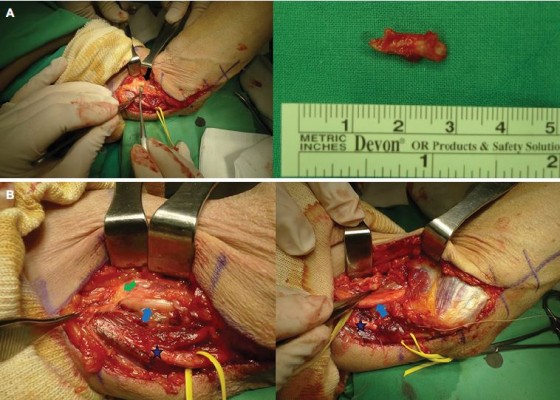
A 36-year-old right-handed woman presented with pain in the medial aspect of the right elbow joint, which progressively worsened 3 months ago, with numbness in the distribution of the median nerve. Her symptoms were aggravated by continuous movement and local compression. Because of pain, the patient had visited a private clinic and received injections several times without any benefit. Physical examination revealed tenderness and a Tinel’s sign in the medial epicondyle. Her ulnar nerve was normal without weakness or sensory abnormality, and normal muscle strength was observed in the flexor pollicis longus and flexor digitorum profundus. A bony projection was felt at a site ~8 cm proximal to the medial epicondyle. A supracondylar process was found on X-ray images and computed tomography (Figure 1A and 1B). Surgery was performed under general anesthesia. The supracondylar process, which was 11 mm in length and 6 cm above the medial epicondyle, was exposed through a medial approach (Figure 2A). The ligament of Struthers connected the supracondylar process and medial epicondyle, and the median nerve passed under the ligament of Struthers (Figure 2B). The brachial artery crossed the lateral surface layer of the ligament of Struthers. The median nerve appeared to be deviated by the supracondylar process and ligament of Struthers along its course. However, it showed a normal structural appearance without direct compression. The supracondylar process and ligament of Struthers were removed to free the median nerve. The symptoms improved, and the patient could perform normal daily activities without symptoms on follow-up at 5 months postoperatively. Pathology showed the excised tissue was lamellated bone with no indication of malignancy.
  | Figure 1 (A) Simple X-ray image with anteroposterior and lateral radiographs showing the supracondylar process. (B) Supracondylar process observed on 3-dimensional computed tomography. |
Case 2
A 68-year-old right-handed man presented with pain in the medial aspect of the left elbow joint and hand numbness in the distribution of the median and ulnar nerves. The symptoms worsened when the elbow was flexed and internally rotated. The patient had chronic obstructive lung disease. One year prior to admission, he had undergone open reduction and internal fixation using a plate for a fall-induced fracture of the ipsilateral distal radius in another hospital. However, surgical malunion led to secondary osteoarthritis in the wrist joint, causing chronic pain. He underwent arthrodesis at our hospital. Before surgery, the patient complained of worsening sensory abnormalities. Examination revealed tenderness and Tinel’s sign in the medial and lateral epicondyles. X-ray imaging showed a supracondylar process located 5 cm proximal to the medial epicondyle (Figure 3). Surgery was performed under general anesthesia. The supracondylar process, which was 15 mm in length and 6 cm above the medial epicondyle, was exposed through a medial approach (Figure 4A). The ligament of Struthers connected the supracondylar process and medial epicondyle, and the median nerve passed under the ligament of Struthers. The ulnar nerve was not affected (Figure 4B). Although the median nerve was compressed by the supracondylar process and ligament of Struthers, there was no structural change. We released the nerve by removing the supracondylar process and ligament of Struthers and performed adhesiolysis to treat the ulnar nerve at the previous surgical site in the wrist joint. The symptoms improved, and the patient showed complete union 1 year after surgery, with the ability to resume normal daily activities. Pathology exam showed the excised tissue was lamellated bone.
  | Figure 3 Supracondylar process is seen on simple X-ray anteroposterior and lateral (lat) radiographs. |
Consent statement
Written informed consent was obtained from the patients for publication of this case series and any accompanying images.
Discussion
In 1930, Lund described entrapment of the median nerve caused by the supracondylar process and its fractures.7 However, the supracondylar process may not cause symptoms and may be felt as a painless lump on examination or detected incidentally on an X-ray image. It can be mistaken for an osteochondroma or malignant tumor. The supracondylar process can easily be found with X-ray images taken from oblique views when the elbow joint is internally rotated.1 Magnetic resonance imaging can also be used to identify the supracondylar process and its anatomical relationships with surrounding structures, including the ligament of Struthers, nerves, and vessels.6 A supracondylar process was found in 0.1%–2.7% of the population.3 Gessini et al8 reported that entrapment of the median nerve led to the supracondylar process in 0.5% of the population.
Opanova and Atkinson4 previously reported that sensory abnormalities, with numbness and weakness, were the primary symptoms of median nerve compression after evaluating 43 cases of supracondylar process syndrome. Pain tends to worsen when the forearm is medially rotated.4 In this study, we also found that symptoms were exacerbated with flexion and internal rotation of the elbow joint. A process felt on the area proximal to the medial epicondyle and tenderness were the most common findings. Symptoms of median nerve compression alone were most common and were observed in 18 cases. A supracondylar process fracture was reported in 9 cases, and pain around the supracondylar process was reported in 6 cases. In 9 cases, vascular symptoms of varying severity were reported and ischemic pain caused by peripheral embolism and thrombosis had occurred. A sole manifestation of ulnar nerve compression was reported in 1 case only.
Because supracondylar process syndrome is very rare, treatment modalities have not been defined, making comparisons difficult. A proximal median nerve compression neuropathy such as pronator syndrome and anterior interosseous nerve syndrome can heal with conservative therapy, including rest and anti-inflammatory drugs,9 whereas supracondylar process syndrome requires surgical decompression.6 In this article, conservative treatment failed to improve symptoms and surgery resulted in good outcomes. Although the duration of symptoms varied among case reports, surgical treatment was effective in resolving symptoms, regardless of the duration.4
Conclusion
In summary, supracondylar process syndrome manifests with nerve compression and requires careful differential diagnosis because it can easily be missed on imaging. Although the symptoms do not improve with conservative therapy, surgery can ensure a favorable outcome and is easy to perform. Once the correct diagnosis is accurately made, treatment is not considered difficult. There is no study of the control group which shows abnormalities on X-ray imaging but has no symptoms. This is because there are not many cases yet, and the control group should be studied in the future.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Loukas M, Pennell C, Tubbs RS, Cohen-Gadol AA. Sir John Struthers (1823–1899) and his ligament and arcade. Neurosurgery. 2010;66(6):1170–1173. | ||
Lordan J, Rauh P, Spinner RJ. The clinical anatomy of the supracondylar spur and the ligament of Struthers. Clin Anat. 2005;18(7):548–551. | ||
Camerlinck M, Vanhoenacker FM, Kiekens G. Ultrasound demonstration of Struthers’ ligament. J Clin Ultrasound. 2010;38(9):499–502. | ||
Opanova MI, Atkinson RE. Supracondylar process syndrome: case report and literature review. J Hand Surg Am. 2014;39(6):1130–1135. | ||
Horak BT, Kuz JE. An unusual case of pronator syndrome with ipsilateral supracondylar process and abnormal muscle mass. J Hand Surg Am. 2008;33(1):79–82. | ||
Ay S, Bektas U, Yilmaz C, Diren B. An unusual supracondylar process syndrome. J Hand Surg Am. 2002;27(5):913–915. | ||
Symeonides PP. The humerus supracondylar process syndrome. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1972;82:141–143. | ||
Gessini L, Jandolo B, Pietrangeli A. Entrapment neuropathies of the median nerve at and above the elbow. Surg Neurol. 1983;19(2):112–116. | ||
Rodner CM, Tinsley BA, O’Malley MP. Pronator syndrome and anterior interosseous nerve syndrome. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2013;21(5):268–275. |
 © 2018 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2018 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.


