Back to Journals » Psychology Research and Behavior Management » Volume 16
Sinicization Innovation of Marxist Humanistic Theory in Colleges and Universities Under the Background of Innovative Thinking
Received 18 January 2023
Accepted for publication 19 April 2023
Published 24 May 2023 Volume 2023:16 Pages 1897—1909
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PRBM.S405168
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Mei-Chun Cheung
Qi Li,1 Yan Ma2
1Faculty of Marxism, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, Jilin, 130024, People’s Republic of China; 2College of Philosophy and Sociology, Jilin University, Changchun, Jilin, 130024, People’s Republic of China
Correspondence: Yan Ma, Email [email protected]
Introduction: It is urgent to explore and solve the problems in China’s current Marxist psychological education. The main goal of the research is to promote the sinicization innovation of Marxist humanistic theory in colleges and universities.
Methods: Combined with Marxist humanist theory, this paper designs a science, technology, engineering, and mathematics teaching mode for cultivating innovative thinking in an attempt to change the way college students cultivate innovative thinking. The research method is to discuss the status, problems, causes, and countermeasures of the sinicization innovation of Marxist humanistic theory in colleges and universities through literature research, logical analysis, and empirical research.
Results: The progress and existing problems of college students’ current psychological education logic are summarized based on empirical research. The research results show that the innovation of Marxist humanistic theory in colleges and universities needs to be innovated in terms of theory, method, content, and form and integrated into the development needs and innovation requirements of contemporary Chinese society. The countermeasures implemented include promoting the intersectionality, interdisciplinarity, and innovation of Marxist humanistic theory research in colleges and universities, strengthening the close integration of Marxist humanistic theory education and practice in colleges and universities, and enhancing the effectiveness and orientation of Marxist humanistic theory education in colleges and universities.
Discussion: In the context of innovative thinking, the effectiveness of psychological logic education should be further improved through innovative research on the sinicization of Marxist humanistic theory in colleges and universities.
Keywords: innovative thinking, Marxism, humanism theory, sinicization innovation, psychological education
Introduction
The informatization process has changed people’s thinking, cognition, and life and has also driven society’s demand for innovative talents. The information age urgently needs high-level innovative talents. China continues to regard innovation as the keyword for cultivating talents to deal with the challenges of the information and digital age.1 In the 21st century, with the development of the market economy, ideas have been impacted by ideas from all over the world. People’s excessive pursuit of material leads to the neglect of spiritual and cultural progress.
First, the environment creates people. Marx did not completely reject the idea of “environment creates man” put forward by the old materialism but used materialist dialectics as a guide to advance the view of “environment creates man” to a new era height. Marx wrote:
The materialist doctrine of the transformative role of environment and education forgets that man changes the environment and that the educator himself must be educated.
This shows that Marx recognizes that people can create the environment. Still, the environment also restricts and affects people, and people and the environment interact with each other and are simultaneous. The environment creates man. The environment includes the natural and social environments, which is first manifested that man is a product of nature. People’s concept of consciousness changes with the change of the specific environment in which they live due to the influence of the socio-economic system and social relations, which reflects that the social consciousness of each era is determined by specific social existence. People in every era live in different natural and social environments. Therefore, the practical activities carried out by people will have the imprint and characteristics of that era, and the environment will limit the level of productivity.
Although education plays an important role in human development, it also has its limitations. The socio-historical background and the laws of social development are factors that limit education. The subjective initiative of the education object refers to the ability of the educated person to think for themselves, make decisions, and practice himself in education. Also, they can actively participate in and promote their learning and development. Therefore, people need to correctly recognize the subjective initiative of the educated. Only in this way can education really positively impact people. The relationship between human development and education must be viewed dialectically. At present, college students think that Marxism is ethereal because the Marxist belief education of college students is only the indoctrination of theory and the passive study of students. It lacks connections to the real lives of college students. The value demands of college students are not being answered. As a result, the psychological prejudgment of Marxist beliefs on the realization of individual life ideals has been reduced, and students cannot have emotional sustenance. This leads to the inability to produce sensations that shock and touch the heart. As a result, faith education has little effect.
From the perspective of theoretical and practical research on creativity, innovative thinking can be said to be divergent thinking or convergent thinking. In terms of logical classification, it is both logical thinking and illogical thinking. Therefore, it organically combines various forms of thinking and dialectically unifies the process of various forms of thinking. In addition, rich humanistic thought has been fully reflected in the proletarian ideology system founded by Marx. In the history of humanism research, what is called a major change is the formation of Marxist humanism. In the process of studying Marxism in modern Chinese history, a preliminary understanding of Marxism is obtained through the Soviet Union.2 At that time, China paid great attention to the research on the theory of revolutionary practice. China solves the revolutionary problems faced in modern times guided by the practice of Marxism. After the reform and opening up, people pay attention to the value differences and feelings of the person while emphasizing collectivism due to emancipation and progress of thought. The thought of Marxist humanism has gradually come to the forefront of academic research. Psychological education is an innovation of Marxism.3 The development of psychological education in mainland China only has a history of nearly 30 years. Mental health education has developed rapidly and achieved great results. However, many problems such as weak foundation and low levels restrict the development of mental health education. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out the innovation of Marxism in China and the education of psychological logic.4,5
Based on the above situation, this paper designs a Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) innovative thinking training teaching mode, trying to change the training mode of college students’ innovative thinking. The research is carried out combined with the theoretical content of Marxist humanism. This paper uses literature, questionnaires, interviews, and case analysis to study the logical work of effective psychological education for college students from the aspects of people’s needs, values, and development. The progress and existing problems of the current logical work of college students’ mental health education are summarized based on empirical research. Besides, it also studies the deficiencies and prospects of the current research issues. This paper also studies how to integrate the Marxist theory of humanism into all aspects of Chinese innovation and psychological education logic to further improve the effectiveness of psychological logic education. The main scope of research is to focus on designing a teaching model for STEM innovative thinking training. It aims to change the cultivation mode of innovative thinking of college students and integrate Marxist humanistic theory into all aspects of Chinese innovative logic and psychological education to improve the effectiveness of psychological logic education.
Literature Review
Human society has undergone a dynamic historical development process from low to high. Human society has continued to develop and progress throughout history. It is a long process of gradual development from the original primitive society to modern society. In this process, human society gradually got rid of the crude primitive mode of production and way of life, developed more and more advanced production methods and civilizations, and experienced stability in dynamics, from feudal and slave institutional methods to modern capitalist institutional methods. This embodies the infinite possibilities for human innovation, change, and progress. Society is not abstract but a concrete social formation in historical development. Each social formation has its socio-historical environment. Each historical, social formation will provide the necessary social environment for human survival. According to Marx,
the historically formed relationship between man and nature and between individuals encounters a great deal of productivity, capital, and environment transmitted from one generation to the next.6
Human beings use the natural conditions and social environment left over from history to create a new generation of environment. Likewise, the historical environment dictates the living conditions of the new generation. The relationship between man and the environment has been gradually formed and developed in history. Marx’s relationship with the environment is a dynamic development relationship. Pléh7 pointed out that Marxist beliefs belonged to the mental activity of man. Faith education was a process in which the three elements of cognition, emotion, and will were established in turn. Comprehensive and profound understanding is the foundation of Marxist faith education. It is not only the perception and memory of external information but also an internalized and highly stable cognitive structure.
The importance of understanding the relationship between material humans and their environment is the foundation of Marxism and the key to Marxist analysis. People should have a correct and profound understanding of the social adaptation of young students when thinking about the social adaptation of young students from a Marxist perspective. Social relations are gradually formed and unfolded in the practice of communication. Gao8 argued that from the perspective of psychology, Marxist faith education was student-oriented. It started from the three psychological processes of knowledge, affection, and intention and helped students use Marxist theories and methods to realize the unity of human reality and idealism, will, and belief. Øversveen9 pointed out that alienation in the Marxist sense could be understood as an objective process. It arose from appropriating the fruits of production and transformation into capital. All previous materialism included Feuerbach’s materialism. Its main disadvantage was that objects, reality, and sensibility were understood only in terms of the object or intuitive form rather than as human perceptual activities and practices. It was not understood from the subjective side.
Based on the above research background, this paper mainly constructs a STEM teaching model for cultivating innovative thinking from the perspective of the innovation of Marxist in colleges and universities combined with the theory of Marxist humanism to improve the effectiveness of psychological logic education.
Materials and Methods
Analysis of the Principles of Marxist Humanism Theory
As an important part of Marxist philosophy, Marxist humanism runs through Marxist theory from beginning to end. It is mainly about people’s problems. Specifically, it includes the following parts.
The first is the essence of man. In a certain social relationship, all voluntary and conscious labor activities of people revolve around people. If social relations are determined, people can carry out social practice activities smoothly. In other words, only when people’s practical activities are carried out smoothly, can they have human social connections, so people’s needs can be met. In addition, all the practical activities of people and all social connections can be formed smoothly through the needs of people. In general, the content of human labor is a practical activity. It takes the form of connecting through society. The needs of people are met, and the three factors are indispensable. Then, an organic and unified whole forms.
The second is the theory of human needs. The core concept of Marxist humanism is the theory of human needs. People’s problems are studied by exploring people’s needs. For the theory of human needs, Marx and Engels have long put forward related concepts. They believe that human needs are human nature.10 In general, Marx divides human needs into four parts. First, the most basic human need is the human need for material life and interests. Second, the need for spiritual culture is also a basic human need. Third, human needs also include the need for labor and communication. This is not just a low-level need but a high-level need as well. Fourth, “the highest level of human needs is the need for human self-realization and human comprehensive and free development.”
The third is the theory of human value. An important subject of Marxist humanism is the value of human beings. As a relational category, the three basic elements of value subject, value object, and value intermediary constitute the entire value. For the discussion of value, the following conclusions are drawn. First of all, the basis of social value is the individual value of human beings. Social value is also the most fundamental value of human value. Secondly, what promotes the realization of social value is the individual value of human beings. The realization of social value can also provide conditions for the realization of individual value.
The fourth is the theory of human development. The theory of human development is the core content and goal orientation of the Marxist humanistic theory. The theory of human development is the inevitable destination for all proletarian Marxist parties to carry out ideological and political education.11 Marx emphasizes,
The complete liberation of human beings and the all-around free development of human beings are an inevitable process of the law of social development. This process undergoes the continuous development of different social forms and reaches the ideal state.12
Analysis of Innovative Thinking Training Methods
The innovative thinking training method refers to stimulating people’s creativity and innovation ability by cultivating people’s creative thinking and innovative awareness to promote the production of innovative results. Innovative thinking training methods include methods to improve people’s ability to observe, associate, think, and express. It can be applied to the practice of sinicization innovation of Marxist humanistic theory in colleges and universities to promote the innovation of curriculum construction, teaching reform, and educational practice. The cultivation of innovative thinking can generally be divided into two categories. One is to cultivate innovative thinking through special thinking training. One is integrating thinking training into subject teaching, especially in comprehensive interdisciplinary teaching.13
Creative Problem Solving (CPS) Model
The CPS model proposed by Parnes in 1966 is designed to specifically address the problem of students’ lack of creativity.14 In 2000, Teffinger, Isaksen, and Dorval released version 6.1 of the CPS: the “four-component eight-stage” model. This model described CPS as a dynamic, open, and flexible system. This system emphasized the alternate application of divergent thinking and convergent thinking. The model referred to in the model construction process of this study was the dynamic and open CPS “four-component eight-stage” model. The CPS model could be continuously developed and improved through the research and revision of scholars such as Isakson and Dorval.15 Figure 1 shows the evolutionary process of the CPS model.
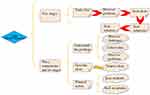 |
Figure 1 Diagram of the evolutionary process of CPS model development. |
The four-component eight-stage model of Dorval et al is drawn on here.16 This version of the CPS model is dynamic, open, and flexible. The CPS four-component eight-stage model focuses on the alternate application of divergent thinking and convergent thinking in the process of problem-solving17 and group cooperation. The form of group cooperation runs through the whole process of the CPS model.18 The specific content of the four-component eight-stage model of CPS is shown in Figure 2.
 |
Figure 2 Four-component eight-stage model of CPS. |
Five E Study (5EX) Mode
Scholars propose the 5EX model (as shown in Figure 3) based on the interdisciplinary learning characteristics of STEM education to further study the STEM model.19 The model is divided into five learning links. The first link is to get into the situation and ask questions. The second link is inquiry learning and mathematics application activities. The third link is engineering design and technical production. The fourth link is knowledge development and creative design activities. The fifth link is multiple evaluation and design reflection activities.20 The specific content is demonstrated in Figure 3. The 5EX model includes: (1): Enter and Question; (2) Exploration and Mathematics application activities; (3) Engineering and Technology production activities; (4) Expansion and Creativity design activities; (5) Evaluation and Reflection activities.
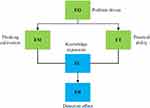 |
Figure 3 5EX design model. |
Analysis of STEM Model Construction Principles
The following principles must be followed in constructing the STEM teaching model for cultivating innovative thinking: directivity, integrity, and operability.21 The specific content of the STEM model construction principles is shown in Figure 4.
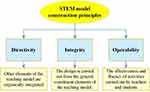 |
Figure 4 Principles of STEM model building. |
Research on Innovation and Psychological Education of Contemporary College Students
The design of this questionnaire is mainly divided into three parts. The first is a questionnaire on the cognitive status of contemporary college students on the Marxist theory of humanism. The second is a questionnaire on the status of contemporary college students’ identification with the sinicization and innovation of Marxist humanism theory. The third is a questionnaire on the practice of the psychological logic of the Marxist humanism theory among contemporary college students. Each part is designed according to the current situation, cause, and countermeasure investigation, a total of 46 questions. They are embodied in the following aspects in the preparation and design of the questionnaire program.
The first is the basic information of the investigation object. Six questions are designed in the questionnaire to understand the basic information of the respondents, such as gender, ethnicity, school stage, major, political affiliation, and whether they have served as student leaders. The professional information includes humanities and social sciences, science, engineering, agriculture, and medicine, arts and sports, and national defense.
The second is the sampling method of the questionnaire sample. It is difficult for college students to obtain the knowledge, identification, and practice of Marxist ideology through a comprehensive survey method, so a sample survey is adopted.
The third is the preparation procedure of the questionnaire. The first step is literature reading. It refers to reading the literature on Marxist ideology and subdividing the cognitive, identification, and practice dimensions of Marxist ideology.29–31 The second step is to determine the question of the questionnaire. The three dimensions of Marxist ideology are subdivided into different questions, and the dimensions of the questionnaire are obtained for the first time. The third step is to design the questionnaire. The test paper is designed according to the dimensions of the questionnaire obtained for the first time. The fourth step is to check the questionnaire. Non-major students and teachers are invited to check the questionnaire and correct the errors in the questionnaire. The fifth step is to determine the number of questions. The questionnaire is further refined to include all questions. There are 91 questions in the primary selection questionnaire. The sixth step is the initial test. The seventh step is to formally issue the questionnaire. According to the results of the initial test, 46 questions are finally determined. The reliability and validity of the questionnaire are within a reasonable range by testing. The eighth step is data processing and analysis. The performance of college students’ cognition, recognition, and practice of Marxist humanistic theory is analyzed through SPSS19.0 statistical software.
Results
Basic Information on the Research Object
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Jilin University and complied with the Declaration of Helsinki. Before the survey, the written informed consent form, and an introduction of the purpose of our survey research were provided to all participants together with the questionnaires. Explanations were made to the participators that this research adopts the principle of voluntary participation, and all the collected data would be kept strictly confidential, and the survey is only for research purposes so no individual or organization can access the data except our researchers.
Six questions are designed in the questionnaire to understand the basic information of the respondents, such as gender, ethnicity, school stage, major, political affiliation, and whether they have served as student leaders. Among them, professional information is divided into four categories: humanities and social sciences (127 people), science, engineering, agriculture, and medicine (91 people), art and sports (40 people), and national defense (42 people). The sample size is 310 people. Data collection is carried out using questionnaires. A total of 310 questionnaires are distributed, and 300 questionnaires are recovered, with a recovery rate of 96.77%. In addition, 73 invalid questionnaires are screened. The subjects of the questionnaire are selected by random sampling. The specific operation process of the questionnaire includes the steps of determining the research objectives, sample selection, questionnaire design, distribution method selection, data screening, and statistical analysis. It is necessary to ensure the legitimacy of the questionnaire and to guarantee the reliability and confidentiality of the data. Table 1 shows the basic information of the sample.
 |
Table 1 Basic Information on Research Objects |
The Main Problems of Contemporary College Students’ Cognition of Marxist Ideology
Lack of Cognition of the Basic Knowledge of Marxist Humanism Theory
Question seven of the questionnaire: As a complete scientific system, the three main components of the Marxist humanistic theoretical system do not include ().
From Table 2, the three components of the Marxist anthropological theory system are the basic common sense of Marxism, which does not contain the relevant content of human development. Still, only 41% of the surveyed college students correctly answer this common sense question. More than half of college students answer incorrectly. This reflects the lack of cognition of the basic common sense of the Marxist humanism theory among college students. The goal of the sinicization of Marxist humanistic theory requiring college students to “understand and grasp what Marxism is in general” has not been fully realized. In addition, the theoretical basis of Marxist humanism is a people-oriented social theory, including the objective nature of man, social historical status, and free creativity, which are interrelated and constitute the core of the theoretical system.
 |
Table 2 Answers to Question Seven |
Lack of Cognition of Relevant Theoretical Knowledge of Marxism
Question nine of the questionnaire: Marxism believes that the true unity of the world lies in ().
From Table 3, only 47% of the interviewed college students correctly answer that the real unity of the world is materiality, while 43% of the interviewed college students believe that practicality is the real unity of the world. This shows that college students do not have a firm grasp of the knowledge of the basic principles of Marxism, and the phenomenon of memory dislocation occurs. The lack of knowledge of Marxist theory will affect people’s correct interpretation and practice of this ideological system. Strengthening the study and understanding of the basic tenets of Marxism is conducive to promoting the healthy development of the socialist cause and the comprehensive deepening of socialism with Chinese characteristics.
 |
Table 3 Answers to Question Nine |
Lack of Cognition of the Sinicization of Marxist Humanism Theory
Question 11 of the questionnaire: The latest theoretical achievement of the sinicization of Marxism is ().
A. Reform and opening up B. The important thought of “Three Represents” C. Scientific outlook on development D. Socialism with Chinese characteristics for a new era.
From Table 4, only 42% of the interviewed college students correctly choose the answer, which reflects Xi Jinping’s thoughts on socialism with Chinese characteristics for a new era that has not entered the minds or hearts of some college students. The lack of recognition of the sinicization of Marxist humanism will hinder the understanding and application of this important theory. In-depth study and practice of the ideological essence of the sinicization of Marxist humanism will help promote the innovative development of Chinese culture and promote the progress of human social civilization.
 |
Table 4 Answers to Question 11 |
Fragmentation of the Innovative Cognitive Structure of Marxism in China
The division of society also affects the division of Marxist thought and its education. From the perspective of division learning, divided reading, time, and space are important factors affecting the cognitive structure of current college students’ Marxist ideology. Marxist ideology and its education also show fragmentation affected by social fragmentation. From the perspective of fragmented learning, fragmented reading, time, and space are important factors that impact the current college students’ Marxist ideological cognitive structure. Meanwhile, new methods for sinicization innovation of Marxist humanistic theory in colleges and universities are proposed, such as using network technology for knowledge promotion and interdisciplinary exchange, using cross-border integrated thinking methods to break the shackles of disciplines and colleges, and exploring the integration of innovation and entrepreneurship education of college students and Marxist humanistic theory. These new research methods and achievements can lead the development of the field, reflecting the innovation of research thinking and methods. The studied data are weighted in various ways, and the reliability of the data is verified.
Fragmented Reading Has Gradually Become the Main Reading Method of College Students
Table 5 is obtained according to the survey and statistical analysis of Tong Ling’s Exploration and Analysis of Ideological and Political Education of College Students under the Background of “Fragmented Reading”.
 |
Table 5 Percentage of Information Obtained by Fragmented Reading in Total Information Obtained |
The data in Table 5 reveals that fragmented reading has become the main way of reading and information acquisition for college students.
Fragmented Time
It is found that the online time of “micro-media” audiences is mainly after getting up in the morning, before and after lunch, before and after dinner, and before going to bed by observation. The traditional Marxist ideological education is accustomed to focusing on a period to instill relevant theoretical knowledge in college students. The immediacy of new media brings challenges to ideological education.
Question 18 of the questionnaire: What is the status of communication with the ideological and political teachers?
A. Frequent and frank exchanges of opinions with each other B. Infrequent exchanges of opinions with each other C. Lack of minimal communication D. Other.
As Figure 5 suggests, the fragmentation of college students’ acceptance of Marxist ideology is reflected in two aspects both inside and outside the classroom. Some students and teachers are in close contact with each other. Some students have no communication with their teachers. It greatly reduces the effectiveness of college students’ Marxist ideological education.
 |
Figure 5 Answers to question 18. |
Fragmentation of Audience
Fragmentation of cognitive audiences is a one-dimensional group with the same interests in the social relationship structure. College students have different personalities, family backgrounds, knowledge structures, and behavioral patterns, so their acceptance of Marxist ideological education will also be different, as shown in Table 6.
 |
Table 6 Survey on Fragmented Views of the Audience of Marxist Ideology |
The results of the questionnaire show that when students are asked “about the narrow definition of Marxism”, the proportion of students who answer correctly is quite different for different subject types. Besides, 42% of college students in humanities and social sciences answer this question correctly, ranking first among all majors. This also conforms to the characteristics of the humanities and social sciences with a good understanding of relevant knowledge. The second, third, and fourth students are college students in science, engineering, agriculture, medicine, arts and sports, and national defense. The results of this survey conform to the cognitive laws of Marxism among students of different majors and also confirm the fragmentation of the audience of Marxist ideology. In addition, descriptive statistics are used for data from the questionnaire sample, and the analyzed data should show percentages, mean weighted averages, and standard deviations. The results of the questionnaire are revealed in Table 7.
 |
Table 7 Descriptive Statistical Results of Survey Participants on Marxist Theoretical Innovations |
Discussion
The sinicization innovation strategy of Marxism and humanistic theory in college and university in the context of innovative thinking is studied. The empirical results show the timeliness of psychoeducation. Related studies on the development of Marxism and teacher teaching are compared. Rikowski et al32 first reviewed the development of Marxist educational thought. Then, they showed the influence of this idea in different periods, including the revolutionary period, the trade union movement period, and the post-industrial period. Then, the concept of transhumanism and its relationship with education were introduced. It was believed that transhumanism had brought new thinking and prospects to education. Finally, they called for paying attention to the inheritance and development of Marxist educational thought in contemporary educational practice and in-depth discussion and thinking on transhumanism. Marx et al33 first outlined the emerging situation of technology in education and raised the question of how technology should contribute to the cause of educational equity and social justice. Next, the seven papers included in this special topic were presented. These papers analyzed the impact of technology on educational equity and social justice from different perspectives and approaches, including how technology could be used to help vulnerable groups access knowledge, how to bridge the digital divide, and how technology could be used to improve the educational experience. Finally, the potential problems and challenges of technology in education were discussed, and future research directions were proposed. Frenzel et al34 explored the link between teachers’ evaluation of teaching and emotion and in what situations and among which teachers. The study found a significant positive correlation between the degree to which teachers rated their teaching positively and the positive emotions they experienced. The strength and direction of this relationship might vary between different teaching settings and individuals. The results helped to deeply understand the relationship between teachers’ emotional experience and teaching quality to provide useful references for improving teaching effectiveness. In summary, this paper reviews the development of Marxist educational thought and introduces the new thinking of transhumanism on education. Through the possibility of technology playing a role in justice and equity in education, the possible problems and challenges that technology may face in education are analyzed. It is helpful to deeply understand the relationship between teachers’ emotional experience and teaching quality to provide a useful reference for improving teaching effectiveness.
Conclusion
There are problems in the current Chinese Marxist psychological education. This paper designs a STEM teaching mode of innovative thinking training, trying to change the way of cultivating innovative thinking of college students. The research is carried out combined with the theoretical content of Marxist humanism. This paper uses literature, questionnaire, interview, and case analysis to study the logical work of college students’ psychological education from the aspects of people’s needs, values, and development. The results show that the cognitive audience of Marxist anthropological theory has fragmented characteristics in innovation and thinking training. This also means that the research should be in the context of innovative thinking. Besides, the effectiveness of psychological logic education should be improved through innovative research on the sinicization of Marxist anthropological theory in colleges and universities. In addition, it is necessary to deeply study the innovative thinking of college students to promote the development of innovation ability and thinking ability of college students. According to this characteristic, the effectiveness of psychological logic education should be further improved through innovative research on the sinicization of Marxist humanism theory in colleges and universities in the context of innovative thinking. It is found that although some achievements have been obtained, the study still has many shortcomings due to the author’s limitations through the review of this study. For example, the selection of research objects needs to be further expanded. Researchers can choose to further expand the sample size for more schools, more grades, and more classes. In addition, in terms of teaching content, the scope of practical content can be expanded, and courses such as Scratch, Lego, and EV3 can be selected. The experimental data should be more abundant, and the research will be more credible. Studies have indicated that the risk-taking dimension of creative tendencies has no significant change before and after the experiment. The reasons for this phenomenon still require follow-up research. In future research, the teaching methods and content of Marxist theory courses in colleges and universities can be innovated. For example, multimedia technology and case analysis methods are used to increase classroom interaction and guide students’ thinking to focus on integrating interdisciplinary and international teaching resources to provide students with a broad vision and cutting-edge theoretical knowledge.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Barak M, Watted A, Haick H. Establishing the validity and reliability of a modified tool for assessing innovative thinking of engineering students. Assess Eval High Educ. 2020;45(2):212–223. doi:10.1080/02602938.2019.1620680
2. Chunyan Z. The design in the course of economic management cultivation of innovative thinking in applied university. Theor Pract Innov Enntrepr. 2020;3(5):37.
3. Mengjia LI, Kai HUO. Research on cultivation of innovative thinking and reform of practical teaching for art majors. Theor Pract Innov Enntrepr. 2021;4(6):61.
4. Neveling P, Steur L. Introduction: Marxian anthropology resurgent. Focaal. 2018;2018(82):1–15. doi:10.3167/fcl.2018.820101
5. Rikowski G. Marxism and education: fragility, crisis, critique. Cadernos Do GPOSSHE On-Line. 2018;1(1):142–170. doi:10.33241/cadernosdogposshe.v1i1.488
6. Ahmed Z, Asghar MM, Malik MN, et al. Moving towards a sustainable environment: the dynamic linkage between natural resources, human capital, urbanization, economic growth, and ecological footprint in China. Resour Policy. 2020;67:101677. doi:10.1016/j.resourpol.2020.101677
7. Pléh C. Two versions of Marxist concrete psychology: politzer and mérei compared. Hist Psychol. 2022;25(1):68. doi:10.1037/hop0000190
8. Gao Z. Forging Marxist psychology in China’s cold war geopolitics, 1949–1965. Hist Psychol. 2019;22(4):309. doi:10.1037/hop0000097
9. Øversveen E. Capitalism and alienation: towards a Marxist theory of alienation for the 21st century. Eur J Soc Theory. 2022;25(3):440–457. doi:10.1177/13684310211021579
10. Zhang Z. “how is innovation possible?”: an analysis of Rancière’s post-Marxist view on innovation. Soc Sci Res. 2022;4(2):20–23. doi:10.26689/ssr.v4i2.3625
11. Sureeyatanapas P, Poophiukhok P, Pathumnakul S. Green initiatives for logistics service providers: an investigation of antecedent factors and the contributions to corporate goals. J Clean Prod. 2018;191:1–14. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.04.206
12. Chemhuru M. Interpreting ecofeminist environmentalism in African communitarian philosophy and Ubuntu: an alternative to anthropocentrism. Philos Pap. 2019;48(2):241–264. doi:10.1080/05568641.2018.1450643
13. Li H, Zhang R. Multi-angle analysis of technological innovation. Open Access Libr. 2021;8(7):1–7.
14. Padmanabhan S. Psychoeducation intervention for the mental health of college students. Sci Front. 2022;3(1):17.
15. Maher S, Aquanno SM. Conceptualizing neoliberalism: foundations for an institutional Marxist theory of capitalism. New Political Sci. 2018;40(1):33–50. doi:10.1080/07393148.2017.1416729
16. Garegnani P. On the labour theory of value in Marx and in the Marxist tradition. Rev Political Econ. 2018;30(4):618–642. doi:10.1080/09538259.2018.1509546
17. Osorio J. Assessing a proposal for updating the Marxist theory of dependency. Lat Am Perspect. 2022;49(1):153–165. doi:10.1177/0094582X211047906
18. Özsu U. Grabbing land legally: a Marxist analysis. Leiden J Int Law. 2019;32(2):215–233. doi:10.1017/S0922156519000025
19. Neilson D. In-itself for-itself: towards second-generation neo-Marxist class theory. Cap Cl. 2018;42(2):273–295. doi:10.1177/0309816817723299
20. Cheng E. Marxism and its sinicized theory as the guidance of the Chinese model: the “Two Economic Miracles” of the New China. World Rev Political Econ. 2018;9(3):296–314. doi:10.13169/worlrevipoliecon.9.3.0296
21. Zhu C. Marxist ethnic theory and its development to sinicization. J Sociol Ethnol. 2021;3(4):86–92.
22. Qingxiang H, Yuanzhang C. How the CPC Promotes the Sinicization, Contemporization, and Popularization of Marxism: a Centenary History and Historical Experiences. Teach Res. 2021;55(5):5.
23. Rosker JS. Transforming knowledge to wisdom: Feng Qi and the new Neo-Marxist humanism. Asian Philos. 2022;2022:1–21.
24. Maoze Z. On Marxist Confucianism: the new direction of China’s ideological development in the 21 st century. Int J Philos. 2021;9(2):90. doi:10.11648/j.ijp.20210902.13
25. Meng Z. Research on theoretical achievements of sinicization of Marxist legal thought. Insight Inf. 2021;3(4):35–37.
26. Fuchs C. Towards a critical theory of communication as renewal and update of Marxist humanism in the age of digital capitalism. J Theory Soc Behav. 2020;50(3):335–356. doi:10.1111/jtsb.12247
27. Bennett EA. Alienation and its consequence: an exploration of Marxism, hikikomori, and authenticity via relational connection. Humanist Psychol. 2020;48(3):257. doi:10.1037/hum0000153
28. Yakushko O, Blodgett E. Negative reflections about positive psychology: on constraining the field to a focus on happiness and personal achievement. J Humanist Psychol. 2021;61(1):104–131. doi:10.1177/0022167818794551
29. Kostkiewicz J. Child and family as proletarians of the educational ideology of Bolshevik Marxism in the critical reflection of polish humanists from the period 1917–1939. Polska Mysl Pedagogiczna. 2020;6(6):17–38. doi:10.4467/24504564PMP.20.002.12236
30. Peters MA. Educational philosophies of self-cultivation: Chinese humanism. Educ Philos Theory. 2020;1–7.
31. Rich GJ. Positive psychology and humanistic psychology: evil twins, sibling rivals, distant cousins, or something else? J Humanist Psychol. 2018;58(3):262–283. doi:10.1177/0022167817698820
32. Rikowski G, Ford DR. Marxist education across the generations: a dialogue on education, time, and transhumanism. Postdigit Sci Educ. 2019;1:507–524. doi:10.1007/s42438-018-0028-1
33. Marx S, Kim Y. Technology for equity and social justice in education: introduction to the special issue. Int J Multicult Educ. 2019;21(1):1–4. doi:10.18251/ijme.v21i1.1939
34. Frenzel AC, Fiedler D, Marx AKG, et al. Who enjoys teaching, and when? Between-and within-person evidence on teachers’ appraisal-emotion links. Front Psychol. 2020;11:1092. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01092
 © 2023 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2023 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
