Back to Journals » Vascular Health and Risk Management » Volume 12
SGLT2 inhibitors or GLP-1 receptor agonists as second-line therapy in type 2 diabetes: patient selection and perspectives
Authors Gurgle H, White K, McAdam-Marx C
Received 14 November 2015
Accepted for publication 11 March 2016
Published 4 June 2016 Volume 2016:12 Pages 239—249
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/VHRM.S83088
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Dr Daniel Duprez
Holly E Gurgle, Karen White, Carrie McAdam-Marx
Department of Pharmacotherapy, University of Utah College of Pharmacy, Salt Lake City, UT, USA
Abstract: Controversy exists regarding the selection of second-line therapy for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) who are unable to achieve glycemic control with metformin therapy alone. Newer pharmacologic treatments for T2DM include glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors. Both the classes of medication are efficacious, exhibit positive effects on weight, and are associated with minimal risk of hypoglycemia. The purpose of this review is to compare the clinical trial and real-world effectiveness data of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists versus sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors related to A1c reduction, weight loss, cost-effectiveness, cardiovascular outcomes, and safety in patients with T2DM. This review summarizes comparative evidence for providers who are determining which of the two classes may be the most appropriate for a specific patient.
Keywords: type 2 diabetes mellitus, GLP-1 receptor agonist, SGLT2 inhibitor, A1c, weight loss, adverse effect
Introduction
It is estimated that one in three people in the US will develop type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in their lifetime.1 T2DM is a progressive disorder characterized by insulin resistance and a progressive insulin secretory defect.2 Diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death in the US and associated with severe microvascular and macrovascular complications.1 Glycemic control reduces the risk for diabetes-related morbidity and mortality.2 In order to control glucose levels as the disease progresses, patients require lifestyle changes, dietary modifications, exercise, weight loss, and pharmacologic treatment, often with multiple classes of diabetes medications.2
Metformin (MET) is recommended as the first-line treatment for patients with T2DM due to well-established efficacy, safety, low cost, and data demonstrating a reduction in risk of cardiovascular (CV) events.2 However, controversy exists regarding the selection of second-line treatment in patients optimized on MET but not achieving glycemic targets, with contraindications to use of MET, or unable to tolerate MET.2,3 Pharmacologic options for the treatment of T2DM have expanded over the last decade. Second-line treatments include basal insulin, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA), sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2-I), sulfonylureas (SU), or thiazolidinediones (TZD).2
The American Diabetes Association 2016 guideline details a number of second-line options for use following MET and does not give preference to one drug class over the other.2 The American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology 2015 guideline does, however, give preference to GLP-1RA and SGLT2-I over older medication classes including SU and TZD.3 Both the American Diabetes Association and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology recommend that a patient-centered approach should guide the selection of pharmacologic agents.2,3 Considerations may include efficacy, cost, potential adverse effects, weight consideration, comorbid medication conditions, risk of hypoglycemia, and patient preferences.2 Two newer pharmacologic classes, GLP-1RA and SGLT2-I, in particular show promise as second-line treatment options given their favorable effects on weight and low potential for hypoglycemia. No head-to-head trials comparing agents in these two classes are currently available to guide decision-making. The purpose of this review is to compare the clinical trial and real-world effectiveness data of second-line therapy with SGLT2-I and GLP-1RA related to A1c reduction, weight loss, cost-effectiveness, and safety in patients with T2DM. Thus, this review will summarize comparative evidence for providers who are considering which of the two classes might be the most appropriate for a specific patient.
Methods
A Medline search was performed in August 2015 to identify clinical trials and observational studies related to SGLT2-I and GLP-1RA for the treatment of T2DM. Articles included data from human studies published within the past 10 years evaluating A1c, weight, or CV outcomes, and/or reporting adverse drug event (ADE) data versus placebo or versus other classes of interest. MeSH terms searched included SGLT2 or sodium glucose transport proteins, GLP-1 or glucagon-like peptides, and T2DM. Included articles were limited to evaluations of GLP-1RA or SGLT2-I versus placebo, with or without background MET therapy. In the case of articles containing multiple arms including comparisons to other treatments for T2DM, only the arm meeting inclusion criteria is presented due to the scope of this review. Articles on GLP-1RA or SGLT2-I used in combination with therapies other than MET were excluded. Articles evaluating liraglutide (Saxenda), which is US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved for weight management in individuals with or without diabetes, were also excluded.
Results
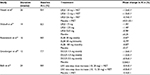
As described in Figures 1 and 2, a total of 2,232 articles were found in an initial Medline search, of which 846 articles were regarding GLP-1RA and 1,386 articles were related to SGLT2-I. Duplicate articles were removed and the remaining articles were screened for outcomes for comparisons of interest. Following our initial search, we identified five additional articles which met our inclusion criteria, bringing the total to 46 studies which were included in this review. Articles were reviewed for efficacy at reducing A1c (Tables 1 and 2) or for other clinical effects including effect on weight, blood pressure (BP), or other drug-related outcomes.
  | Figure 1 Flow diagram of GLP-1 study selection. Abbreviations: GLP-1RA, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists; RCT, randomized controlled trial; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide-1. |
  | Figure 2 Flow diagram of SGLT2-I study selection. Abbreviation: SGLT2-I, sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors; RCT, randomized controlled trial; |
GLP-1 receptor agonists
GLP-1RA, or incretin mimetics, activate GLP-1 receptors, causing a glucose-dependent increase in insulin with a decrease in glucagon secretion while increasing satiety and slowing gastric emptying.4 GLP-1RA are injected subcutaneously twice daily, daily, or weekly depending on the formulation. The US FDA approved the first GLP-1RA exenatide (Byetta) for the treatment of T2DM in 2005.4 Other GLP-1RA approved by the US FDA for the treatment of T2DM include liraglutide (Victoza, 2010), exenatide extended-release (Bydureon, 2012), albiglutide (Tanzeum, 2014), and dulaglutide (Trulicity, 2014).5–8 Lixisenatide (Lyxumia) is not available in the US, but was approved in the European Union in 2013.9 Liraglutide (Saxenda) at a higher dose was also approved by the US FDA in 2014 for weight management in certain obese or overweight individuals.10
Glycemic control
A1c reductions in patients with T2DM, currently treated with MET or no therapy, resulting from treatment with GLP-1RA in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are summarized in Table 1. The mean reduction in A1c with GLP-1RA ranged from 0.7% to 1.7% and was dose dependent. Clinical trials were performed in patients with moderate glycemic control (baseline A1c 7.7–8.4%), and may not be generalizable to patients with more uncontrolled diabetes. Many head-to-head trials have been performed comparing GLP-1RA directly to one another.11–18 Several comparative trials have found liraglutide to be superior to other GLP-1RA, including albiglutide,17 exenatide twice daily,15 and exenatide weekly.13 Dulaglutide was found to be non-inferior to liraglutide,16 and lixisenatide was found to be non-inferior to twice-daily exenatide.18 Exenatide weekly improves glycemic control as compared to twice-daily exenatide injections.19 Dulaglutide, exenatide, lixisenatide, and liraglutide have all been shown to significantly reduce postprandial blood glucose in clinical trials.19–22 Hypoglycemia was not found to be increased with GLP-1RA when compared to placebo.15,20,21,23
Effects on weight
Weight loss is a desirable outcome in most patients with T2DM due to the positive impact on glycemic control, insulin sensitivity, and comorbid health conditions. GLP-1RA cause weight loss in a dose-dependent manner, possibly through early satiety and delayed gastric emptying. Generally considered a class effect, weight loss is modest at doses approved for T2DM. A higher dose of liraglutide, up to 3 mg daily (Saxenda), has been approved by the US FDA for weight management in certain obese or overweight individuals.10
Virtually, all RCTs evaluating GLP-1RA were designed to evaluate weight change as a primary outcome. In a 56-week RCT of 846 overweight or obese patients with T2DM, liraglutide 1.8 mg daily resulted in percent body weight reduction of –2.71% (95% confidence interval [CI] –4.00%, –1.42%) (P<0.001) versus placebo.24Not all GLP-1RA and formulations appear to be equally effective at reducing weight. Bolli et al demonstrated significant weight loss with lixisenatide after 24 weeks as compared to placebo (–1.1 to –1.0 kg least squares mean difference; P<0.01).25 At 26 weeks, patients using liraglutide or exenatide weekly experienced weight loss (–3.57 and –2.68 kg, respectively), (95% CI 0.39, 1.40).13 Dulaglutide has also shown significant weight reduction compared to placebo (–1.3 kg ±0.29, P<0.001).14 Several studies have compared weight loss with exenatide weekly versus twice daily, suggesting minimal additional benefit with weekly dosing.12,19,26 Clinical trials with albiglutide for the treatment of T2DM did not show a statistically significant reduction in weight loss compared to placebo.20,23
Cardiovascular outcomes
Data from randomized clinical trials evaluating the effect of GLP-1RA on CV outcomes are limited. In the ELIXA trial, Pfeffer et al27 evaluated the effect of lixisenatide in patients with type 2 diabetes with myocardial infarction or unstable angina admission in the previous 180 days. After an average of 25 months, the primary composite outcome of CV death, myocardial infarction, stroke, or hospitalization for unstable angina occurred in 13.4% of individuals in the lixisenatide group compared to 13.2% in the placebo group (hazard ratio [HR] 1.02; 95% CI 0.89, 1.17). The addition of lixisenatide to standard therapy did not significantly alter the rates of CV events or hospitalizations in high-risk patients, although it did result in modest but significant reductions in A1c, weight, and systolic BP compared to standard therapy. Currently, the ELIXA trial is the only published clinical trial evaluating major CV outcomes with the use of GLP-1RA, although other trials evaluating liraglutide are currently in progress.
Other data evaluating surrogate markers of CV risk are available. Monami et al evaluated changes in lipid levels with GLP-1RA versus placebo in a meta-analysis.28 This analysis was based on four trials reporting change in total cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein and five trials reporting change in triglycerides. In these analyses, the only significant change relative to placebo found with GLP-1RA therapy was a reduction in triglycerides of –0.29 mmol/L (95% CI –0.57, –0.01) relative to placebo.
In their meta-analysis, Monami et al also considered the occurrence of any major cardiovascular event, a composite end point of CV death, stroke, nonfatal myocardial infarction, heart failure, or acute coronary syndrome.28 Relative to placebo, GLP-1RA therapy was associated with significant (65%) reduction in major CV event with an odds ratio (OR) of 0.51 (95% CI 0.28, 0.93; P=0.03). However, based on six exenatide and five liraglutide placebo-controlled studies (P=0.055 and P=0.31, respectively), significance was not reached for individual GLP-1RA with an OR of 0.45 (95% CI 0.20, 1.02) for exenatide and 0.60 (95% CI 0.22, 1.62) for liraglutide. In an 8-month prospective study of 64 patients with T2DM, liraglutide was shown to decrease carotid intima-media thickness from 1.19±0.47 to 0.94±0.21 mm (P<0.01 vs baseline). However, the impact of reduced carotid intima–media thickness on reduction of CV events has not been elucidated.29
Patients with T2DM commonly have hypertension, which increases their risk for many microvascular and macrovascular complications. RCT data have shown that GLP-1RA may lead to small but significant decreases in systolic BP, which appears to be independent of weight loss and may occur through increased renal excretion of sodium and endothelial vasodilation.30,31 In clinical trials, systolic BP reduction ranged from –2.8 to –4.4 mmHg.32–34 Others have found no significant reduction in BP with GLP-1RA treatment.23,35
Any BP reduction with GLP-1RA therapy is modest and thus has generally been a secondary outcome in clinical trials. As such, most trials were not powered to assess BP outcomes. Investigators have conducted pooled data analyses and meta-analyses of RCTs to assess the impact of GLP-1RA treatment on BP in patients with T2DM. Pooled analysis of registration trial data for liraglutide and exenatide twice daily (BID)36,37 found modest but statistically significant reductions in systolic BP for these agents relative to placebo, with liraglutide 1.2 and 1.8 mg daily leading to a mean reduction (SD) of 2.7±0.8 mmHg (P=0.003) and –2.9±0.7 mmHg (0.7) (P<0.001), respectively, compared to placebo.36 Exenatide twice daily leads to a reduction of –2.8 ±0.75 mmHg (P<0.001) in systolic BP.37 The exenatide analysis identified that systolic BP reductions were somewhat larger (–3.8 ±1.1 mmHg; P<0.001) in those with systolic BP at randomization ≥130 mmHg. While the liraglutide pooled analysis did not report diastolic BP results, exenatide did not lead to a significant reduction in diastolic BP (–0.5 mmHg; P=0.21). Wang et al conducted a broader meta-analysis of exenatide (twice daily and weekly) and liraglutide studies and estimated a slightly larger BP effect with these agents.38 Seven exenatide studies included a placebo arm, and in these studies the mean (95% CI) change in systolic BP relative to placebo was –5.2 mmHg (95% CI –6.9, –3.6) and the diastolic BP change was –5.9 mmHg (95% CI – 7.5, –4.3). Liraglutide results in two placebo-controlled studies were similar with a systolic BP change of –5.6 mmHg (95% CI –5.8, –5.4) and diastolic BP change of –4.5 mmHg (95% CI –4.7, –4.3). Thus, the pooled and meta-analysis data suggest that GLP-1RA has a small, favorable effect on systolic BP in patients with T2DM.38
GLP-1RA effect on heart rate has also been investigated, with several RCTs noting increases in heart rate of 3–4 bpm.34,35 One pooled analysis and one meta-analysis also evaluated data related to heart rate and pulse pressure. In both the studies, there was a significant increase in heart rate or pulse rate. In the pooled analysis of the liraglutide registration RCTs, liraglutide 1.2 mg led to an increase of 2.33±0.49 bpm in pulse rate relative to placebo, and liraglutide 1.8 mg led to an increase of 2.57±0.45 bpm (P<.001).36 While there was no effect on mean arterial pressure, pulse pressure was reduced by –3.3 and –4.51 mmHg with liraglutide 1.2 and 1.8 mg, respectively (P<0.005 for both). The meta-analysis identified a nonsignificant increase of 2.4 bpm (95% CI –0.24, 5.05) with GLP-1RA treatment relative to placebo.39
Gastrointestinal effects
The most common adverse effect noted in clinical trials with GLP-1RA was gastrointestinal upset.20,21,23 Nauck et al found that 35%–44% of patients treated with GLP-1RA complained of one or more adverse gastrointestinal effects including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.21 Gastrointestinal adverse effects are dose dependent and reported as the reason for withdrawal of 36 liraglutide-treated subjects (5% of all liraglutide subjects).21 In head-to-head trials, gastrointestinal effects appeared to be greater with liraglutide than exenatide extended-release (DURATION-6)13 and albiglutide (HARMONY-7)17, but liraglutide-treated patients experienced less nausea than those receiving exenatide twice daily (LEAD-6).15
Pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer
The risk of pancreatitis is higher in patients with diabetes than those without diabetes.40 Following early reports of acute pancreatitis with GLP-1RA, extensive study has been conducted to understand the risks. Because pancreatitis is a relatively uncommon event, investigators have utilized large ADE reporting datasets or administrative claim datasets to investigate this risk. Raschi et al utilized the US Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System in an early study.41 The authors identified all ADEs reported with diabetes medications, including oral drugs, exenatide, and insulin. Between 2004 and 2009, a total of 2,625 cases of pancreatitis were reported. Of these, 709 were exenatide users, corresponding to a reporting odds ratio of 1.76 (95% CI 1.61, 1.92; P<0.001). Liraglutide was not included in the pancreatitis evaluation as it was not launched until 2010.
A limitation of ADE reporting systems is that the true number of users is not known, and there is a risk of reporting bias. Thus, subsequent studies were based on administrative claim datasets comparing GLP-1RA patients to those with diabetes treated with other agents including MET, SU, TZD, sitagliptin, and insulin. Studies were conducted with 3- to 4-year time frames between 2005 and 2013.40,42–45 While studies varied in size and whether or not the definition of a case was based on hospitalization, none found an association between liraglutide or exenatide and pancreatitis. A study of liraglutide identified 0.188 cases per 100 person-years (PY) versus 0.154 in patients taking MET (an SU) or pioglitazone (a TZD). The adjusted relative risk (RR) for the risk of pancreatitis for liraglutide versus the comparator drugs was 1.10 (95% CI 0.81, 1.49).42 This study also evaluated the risk of pancreatic cancer with liraglutide use, and identified a 1-year incidence rate of 0.012 cases per 100 PY corresponding to a RR of 0.65 (95% CI 0.26, 1.60). Three of the four exenatide studies compared the odds of having pancreatitis requiring hospitalization relative to patients using other diabetes medications, and identified 1-year incidence rates from 0.132% to 0.196% versus 0.133% to 0.249% in comparison patients.43–45 This corresponds to adjusted OR of 0.923 (95% CI 0.63, 1.36) and 0.99 (95% CI 0.73, 1.33), respectively, and RR of 1.0 (95% CI 0.6, 1.7) for the risk of pancreatitis with exenatide use relative to comparison patients. The third exenatide study, which did not require hospitalization as a criterion for defining acute pancreatitis, identified an incidence rate of 0.570 cases per 100 PY and an adjusted HR of 0.9 (95% CI 0.6, 1.5) for exenatide versus comparison patients. Thus, the current evidence, based on large cohort studies, suggests that GLP-1RA are not associated with an increased risk of pancreatitis, and liraglutide does not appear to be associated with pancreatic cancer, although data are limited regarding pancreatic cancer.
Thyroid tumors and cancers
In addition to pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer, there has been concern that GLP-1RA therapy may be associated with thyroid tumors and cancer. A retrospective cohort study based on administrative claims data of 32,800 exenatide patients who were propensity score matched to patients treated with MET or glyburide found no increased risk for either benign thyroid neoplasms (RR 0.7; 95% CI 0.3, 1.7) or thyroid malignancies (RR 1.4; 95% CI 0.8, 2.4).46
SGLT2 inhibitors
SGLT2-I are the newest class of diabetes medication and were first approved by the European Union in 2011 and then by the US FDA in March 2013 for the treatment of T2DM. SGLT2-I act in the proximal nephrons to block glucose reabsorption by the kidneys, thereby increasing glucosuria.47 SGLT2-I approved in the US for the treatment of T2DM include canagliflozin (Invokana, 2013), dapagliflozin (Farxiga, 2014), and empagliflozin (Jardiance, 2014).47–49
Glycemic control
A1c reductions resulting from treatment with SGLT2-I with or without background therapy of MET in randomized trials are summarized in Table 2. The mean reduction in A1c with SGLT2-I ranged from 0.32% to 1.17%. Larger reductions in A1c were generally seen with higher doses of SGLT2-I and amongst patients with higher baseline A1c values.50,51 Clinical trials were performed in patients with moderate glycemic control (baseline A1c 7.2%–8.5%) and may not be generalizable to patients with more uncontrolled diabetes. However, the reduction in glucotoxicity with SGLT2-I and improved insulin sensitivity may result in increased benefit in patients with more elevated baseline A1c.52 SGLT2-I have varying selectivity for SGLT2 receptors, which likely results in variable A1c reduction. However, without head-to-head comparisons of different SGLT2-I in clinical trials, selection amongst the three available agents is difficult. The mechanism of action of SGLT2-I is glucose dependent, and hypoglycemia is not found to be increased with any of the agents.50,51,53,54 Furthermore, the mechanism of action of SGLT2-I is independent of insulin. This makes SGLT2-I a tempting treatment for T2DM, which is associated with a progressive loss of beta-cell function and insulin resistance, thereby limiting the long-term durability of other diabetes treatments. Unfortunately, limited long-term data are available for SGLT2-I, with the longest study to date having duration of only 2 years.
Effects on weight
SGLT2-I on average result in a small reduction in weight, possibly due to reduction in glucose reabsorption. The mean weight loss associated with SGLT2-I in clinical trials averaged from 1.5 to 3 kg compared to placebo.50,54 The weight loss appears to be sustained for up to 102 weeks.54,55
Cardiovascular outcomes
The EMPA-REG OUTCOME study by Zinman et al was designed specifically to evaluate the effect of empagliflozin in patients with T2DM and established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).56 After 3 years, the primary composite outcome (nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, or CV death) occurred in fewer patients assigned to the SGLT2-I versus placebo (10.5% vs 12.1%; HR 0.86; 95% CI 0.74, 0.99). Statistically significant reductions in the risk of death from CV causes (HR 0.62; 95% CI 0.49, 0.77), death from any cause (HR 0.68; 95% CI 0.57, 0.85), and heart failure hospitalizations (HR 0.65; 95% CI 0.50, 0.85) were also observed with empagliflozin versus placebo. There was no significant difference in the risk of myocardial infarction or stroke in those receiving empagliflozin compared with placebo. Although the achieved level of glycemic control differed between groups (7.8% vs 8.2%), this small difference seems unlikely to fully account for identified benefits. Patients in the placebo group were more likely to use SU and insulin. Although these results are highly promising, long-term data including primary CV prevention populations and utilizing other SGLT2-I will be needed to fully assess the CV outcomes with this class of medications.56
BP is an important surrogate marker for CV complications. SGLT2-I are mild osmotic diuretics associated with modest reductions in systolic (3–5 mmHg) and diastolic (1–2 mmHg) BP.50,53 In normotensive patients, this diuresis may result in hypovolemia or hypotension. SLGT2-I are also associated with modest increases in low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (1.9%–6.1%).50 Neither the effects on BP or lipids are likely to necessitate changes to antihypertensive or cholesterol therapy for most patients with T2DM.
Genitourinary effects
SGLT2-I have been associated with increased risks of genitourinary infections and polyuria due to increased glucose concentrations in the urine. RCT data evaluating the risk of urinary tract infections are conflicting with some identifying no increase in risk50,53–55 and others reporting a small increase in risk.51 Rates of genital infection, predominately vulvovaginal candidiasis amongst women, appear modestly increased in most studies by 2.0%–8.9% when compared to placebo.50,51,54 Early studies with dapagliflozin raised concerns about a potential increased incidence of bladder cancer. Although a causal relationship was not established, the US FDA has requested postmarketing surveillance studies, and its use in patients with active or history of bladder cancer should be avoided.57
Diabetic ketoacidosis
Although not readily apparent in RCT data, in May 2015 the US FDA added a warning that the use of SGLT2-I may lead to diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA).58 In some cases, diagnosis was delayed given a patient’s atypical euglycemic glucose levels (<250 mg/dL) at the time of presentation. Observational data support the finding that DKA in patients treated with SGLT2-I is likely rare with incidence rates of 0.763 versus 0.238 per 1,000 PY in patients treated with placebo.59 Patients with T2DM treated with SGLT2-I who experience gastrointestinal upset and malaise or develop metabolic acidosis should be promptly evaluated for the presence of ketones, even in the absence of severely elevated blood glucose.60 Risk factors for experiencing DKA with SGLT2-I are not fully understood but may include type 1 diabetes, treatment with insulin, volume depletion, alcohol use, illness, and those in postoperative status.59–61
Bone fractures
The US FDA added a warning in September 2015 about reductions in bone density and increased risk for bone fractures with the use of canagliflozin in patients with T2DM. It has been hypothesized that SGLT2-I may alter the absorption and excretion of calcium and phosphate, resulting in reductions in bone health. A 2-year RCT in older adults was conducted at the request of the US FDA. Findings are not yet published but available from the US FDA including placebo-corrected and dose-dependent declines in bone mineral density of 0.9%–1.2% at total hip, 0.3%–0.7% at lumbar spine, and 0.1% at femoral neck with the use of canagliflozin. Low trauma fractures were more common and appeared as early as 12 weeks after starting the drug.62
Discussion
Second-line pharmacotherapy selection for patients with T2DM optimized on MET, or with intolerance or contraindication to MET, is debated.2 Experts recommend that patient-specific considerations and shared decision-making should be incorporated into treatment decisions.2 GLP-1RA and SGLT2-I are two promising new classes of diabetes pharmacotherapy.
Key considerations for patient selection are outlined in Table 3. Currently, no head-to-head studies evaluating GLP-1RA versus SGLT2-I are available. A review of placebo-controlled trials of GLP-1RA and SGLT2-I in T2DM, with or without baseline MET therapy, suggests that both the classes are likely similar in efficacy, lowering A1c by ˜1%–1.5%. GLP-1RA, especially at higher doses, may be slightly more efficacious in terms of glucose lowering and weight loss than SGLT2-I. Most clinical trials evaluated patients with only moderately uncontrolled diabetes (average A1c <9% at baseline), and limited data are available describing the efficacy of these agents in patients with poorer level of control. Some evidence suggests that some patients may be nonrespondent to treatment with GLP-1RA, although the reason for the lack of response is unclear; such patients should have therapy discontinued.63 Both GLP-1RA and SGLT2-I offer minimal risk of hypoglycemia and appear to have positive, although modest, effects on weight and BP. The ELIXA trial identified a neutral CV effect of lixisenatide in patients with T2DM and recent acute coronary syndrome. Conversely, the EMP-REG OUTCOME trial found an exciting reduction in CV outcomes in patients with T2DM and known ASCVD that were treated with empagliflozin. In addition to needing long-term data in primary CV prevention populations, further research evaluating the CV effects of other GLP-1RA and SGLT2-I is required to understand whether such findings are agent or dose dependent. In the meantime, both ELIXA and EMP-REG OUTCOME trials should be accepted as strong evidence supporting the potential role of both GLP-1RA and SGLT2-I in patients with T2DM and known CV diseases.
Practical administration requirements may be important considerations for those with limited dexterity, poor eyesight, or aversion to the use of injectable medications. Patients treated with GLP-1RA will need to self-inject agents or have them administered subcutaneously anywhere from twice daily to once weekly depending on formulation. Learning to self-inject GLP-1RA requires learning to use prefilled pens and steps for reconstitution with diluents. Conversely, SGLT2-I are oral formulations that may be preferred by some patients due to ease of administration.
As relatively new classes of diabetes medications, GLP-1RA and SGLT2 agents are available as branded products with no generic equivalents. Costs per day are considerable and higher for GLP-1RA than for SGLT2-I (Table 3). However, peer-reviewed published pharmacoeconomic evaluations have generally found that GLP-1RA, specifically exenatide BID and exenatide weekly, are cost-effective when used as second-line treatment relative to analog basal insulins with costs per quality-adjusted life year within the generally accepted range for cost-effectiveness (Table 3).64–67 Investigators found that costs per quality-adjusted life year were dependent on analysis time horizon, baseline body mass index, degree of weight loss, and assumptions on A1c trends over time.67 Peer-reviewed published cost-effectiveness data for SGLT2-I are currently limited, with most data reported for dapagliflozin. Relative to SU or dipeptidyl peptidase-4 therapy, dapagliflozin is estimated to be cost-effective below the generally accepted cost-effectiveness thresholds (Table 3).68,69
Adverse effects of GLP-1RA include gastrointestinal side effects (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea), increased heart rate, and injection site reactions. While there is mixed evidence regarding whether GLP-1RA increase risk for acute pancreatitis and they are associated with thyroid tumors in animals, prescribers should consider these possible adverse effects in patients at elevated risk for either outcome. Adverse effects of SGLT2-I include genitourinary infections, a possible association with bladder cancer, DKA, and bone fractures. Patients should be engaged in shared decision-making and discussion about potential benefits and adverse effects with either class prior to initiating therapy.
Renal function should be assessed before initiating therapy with either GLP-1RA or SGLT2-I. Use of the GLP-1RA exenatide has been associated with cases of acute renal insufficiency or worsening of chronic renal failure.70 Caution is suggested in patients with glomerular filtration rate (GFR) less than 50 mL/min/1.73 m2, and use is not recommended or contraindicated in patients with a GFR less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m2. Limited data exist regarding the use of other GLP-1RA in patients with renal insufficiency and similar caution is recommended for all GLP-1RA until more data are available. Generally, use of SGLT2-I in patients with GFR less than 45–60 mL/min/1.73 m2 is not recommended or contraindicated, depending on the particular agent. SGLT2-I may be less efficacious and increase the risk of adverse effects. There is a contraindication for all SGLT2-I in patients with GFR less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m2.
Patients who have a history of ASCVD, no significant history of recurrent genitourinary infections or bladder cancers, and without risk factors for DKA or fractures may be good candidates for SGLT2-I. Patients able to self-inject, desiring weight loss, and without history of pancreatitis or thyroid tumors may be reasonable candidates for treatment with GLP-1RA. In either case, patients should be closely monitored for both efficacy and adverse effects. Given the expense of both the classes, therapy should be stopped in patients that fail to respond.
Differences also exist within drug classes. Exenatide and liraglutide have slightly better weight and efficacy outcomes compared to other GLP-1RA. Once-daily or weekly formulations may be preferred by patients and improve adherence. Longer acting agents also tend to have greater effect on fasting blood glucose, whereas shorter acting agents target postprandial glucose. Amongst SGLT2-I, canagliflozin specifically has raised concerns about risk of bone fracture, although it is unclear whether an association exists with other SGLT2-I. Empagliflozin appears to reduce CV risk in patients with known ASCVD, although it has more modest improvements in glycemic control when compared to other SGLT2-I. Further data are needed to understand if the reduction in CV outcomes with empagliflozin is a class effect.
Conclusion
GLP-1RA and SGLT2-I are efficacious second-line treatments for T2DM with limited risk of hypoglycemia and positive or neutral effects on CV risk, weight, and BP. While expensive relative to other agents, these classes of drugs are generally cost-effective as second-line treatment, although cost-effectiveness data are limited. Selection of treatment for T2DM should be patient specific and incorporate knowledge of potential adverse effects, required A1c reduction to achieve goal, cost, weight consideration, comorbid medication conditions, and patient preferences.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank Alisyn Hansen, PharmD, for her assistance with editing.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
CDC. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Statistics Report: Estimates of Diabetes and its Burden in the United States. 2014. | ||
American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes-2016: summary of revisions. Diabetes Care. 2016;39(Suppl 1):S4–S5. | ||
Handelsman Y, Bloomgarden ZT, Grunberger G, et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology - clinical practice guidelines for developing a diabetes mellitus comprehensive care plan - 2015. Endocr Pract. 2015;21(Suppl 1):1–87. | ||
Byetta [prescribing information]. Amylin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; 2014. Available from: http://www.byettahcp.com. Accessed October 1, 2015. | ||
Victoza [prescribing information]. Novo Nordisk; 2010. Available from: https://http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2010/022341lbl.pdf. Accessed October 1, 2015. | ||
Bydureon [prescribing information]. Amylin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; 2012. Available from: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/022200s000lbl.pdf. Accessed October 1, 2015. | ||
Tanzeum [prescribing information]. GlaxoSmithKline LLC; 2014. Available from: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/125431s000lbl.pdf. Accessed October 1, 2015. | ||
Trulicity [prescribing information]. Eli Lilly and Company; 2014. Available from: http://pi.lilly.com/us/trulicity-uspi.pdf. Accessed October 1, 2015. | ||
Lyxumia [prescribing information]. Sanofi-Aventis Group; 2013. Available from: http://www.medsafe.govt.nz/Profs/Datasheet/l/lyxumiainj.pdf. Accessed October 1, 2015. | ||
Saxenda [prescribing information]. Novo Nordisk; 2014. Available from: http://www.novo-pi.com/saxenda.pdf. Accessed October 1, 2015. | ||
Buse JB, Drucker DJ, Taylor KL, et al. DURATION-1: exenatide once weekly produces sustained glycemic control and weight loss over 52 weeks. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(6):1255–1261. | ||
Blevins T, Pullman J, Malloy J, et al. DURATION-5: exenatide once weekly resulted in greater improvements in glycemic control compared with exenatide twice daily in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96(5):1301–1310. | ||
Buse JB, Nauck M, Forst T, et al. Exenatide once weekly versus liraglutide once daily in patients with type 2 diabetes (DURATION-6): a randomised, open-label study. Lancet. 2013;381(9861):117–124. | ||
Wysham C, Blevins T, Arakaki R, et al. Efficacy and safety of dulaglutide added onto pioglitazone and metformin versus exenatide in type 2 diabetes in a randomized controlled trial (AWARD-1). Diabetes Care. 2014;37(8):2159–2167. | ||
Buse JB, Rosenstock J, Sesti G, et al. Liraglutide once a day versus exenatide twice a day for type 2 diabetes: a 26-week randomised, parallel-group, multinational, open-label trial (LEAD-6). Lancet. 2009;374(9683):39–47. | ||
Dungan KM, Povedano ST, Forst T, et al. Once-weekly dulaglutide versus once-daily liraglutide in metformin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes (AWARD-6): a randomised, open-label, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2014;384(9951):1349–1357. | ||
Pratley RE, Nauck MA, Barnett AH, et al. Once-weekly albiglutide versus once-daily liraglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on oral drugs (HARMONY 7): a randomised, open-label, multicentre, non-inferiority phase 3 study. Lancet. 2014;2(4):289–297. | ||
Rosenstock J, Raccah D, Koranyi L, et al. Efficacy and safety of lixisenatide once daily versus exenatide twice daily in type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin: a 24-week, randomized, open-label, active-controlled study (GetGoal-X). Diabetes Care. 2013;36(10):2945–2951. | ||
Drucker DJ, Buse JB, Taylor K, et al. Exenatide once weekly versus twice daily for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: a randomised, open-label, non-inferiority study. Lancet. 2008;372(9645):1240–1250. | ||
Grunberger G, Chang A, Garcia Soria G, Botros FT, Bsharat R, Milicevic Z. Monotherapy with the once-weekly GLP-1 analogue dulaglutide for 12 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes: dose-dependent effects on glycaemic control in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Diabet Med. 2012;29(10):1260–1267. | ||
Nauck M, Frid A, Hermansen K, et al. Efficacy and safety comparison of liraglutide, glimepiride, and placebo, all in combination with metformin, in type 2 diabetes: the LEAD (liraglutide effect and action in diabetes)-2 study. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(1):84–90. | ||
Lorenz M, Pfeiffer C, Steinstrasser A, et al. Effects of lixisenatide once daily on gastric emptying in type 2 diabetes--relationship to postprandial glycemia. Regul Pept. 2013;185:1–8. | ||
Rosenstock J, Reusch J, Bush M, Yang F, Stewart M. Potential of albiglutide, a long-acting GLP-1 receptor agonist, in type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial exploring weekly, biweekly, and monthly dosing. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(10):1880–1886. | ||
Davies MJ, Bergenstal R, Bode B, et al. Efficacy of liraglutide for weight loss among patients with type 2 diabetes: the SCALE Diabetes Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2015;314(7):687–699. | ||
Bolli GB, Munteanu M, Dotsenko S, et al. Efficacy and safety of lixisenatide once daily vs. placebo in people with type 2 diabetes insufficiently controlled on metformin (GetGoal-F1). Diabet Med. 2014;31(2):176–184. | ||
Ji L, Onishi Y, Ahn CW, et al. Efficacy and safety of exenatide once-weekly vs exenatide twice-daily in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Investig. 2013;4(1):53–61. | ||
Pfeffer MA, Claggett B, Diaz R, et al. Lixisenatide in patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Acute Coronary Syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(23):2247–2257. | ||
Monami M, Dicembrini I, Nardini C, Fiordelli I, Mannucci E. Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on cardiovascular risk: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014;16(1):38–47. | ||
Rizzo M, Chandalia M, Patti AM, et al. Liraglutide decreases carotid intima-media thickness in patients with type 2 diabetes: 8-month prospective pilot study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014;13:49. | ||
Gutzwiller JP, Hruz P, Huber AR, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 is involved in sodium and water homeostasis in humans. Digestion. 2006;73(2–3):142–150. | ||
Nystrom T, Gutniak MK, Zhang Q, et al. Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 on endothelial function in type 2 diabetes patients with stable coronary artery disease. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2004;287(6):E1209–E1215. | ||
Blonde L, Klein EJ, Han J, et al. Interim analysis of the effects of exenatide treatment on A1C, weight and cardiovascular risk factors over 82 weeks in 314 overweight patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2006;8(4):436–447. | ||
Garber A, Henry R, Ratner R, et al. Liraglutide versus glimepiride monotherapy for type 2 diabetes (LEAD-3 Mono): a randomised, 52-week, phase III, double-blind, parallel-treatment trial. Lancet. 2009;373(9662):473–481. | ||
Ferdinand KC, White WB, Calhoun DA, et al. Effects of the once-weekly glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist dulaglutide on ambulatory blood pressure and heart rate in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Hypertension. 2014;64(4):731–737. | ||
Gill A, Hoogwerf BJ, Burger J, et al. Effect of exenatide on heart rate and blood pressure in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized pilot study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2010;9:6. | ||
Fonseca VA, Devries JH, Henry RR, Donsmark M, Thomsen HF, Plutzky J. Reductions in systolic blood pressure with liraglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes: insights from a patient-level pooled analysis of six randomized clinical trials. J Diabetes Complications. 2014;28(3):399–405. | ||
Okerson T, Yan P, Stonehouse A, Brodows R. Effects of exenatide on systolic blood pressure in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Am J Hypertens. 2010;23(3):334–339. | ||
Wang B, Zhong J, Lin H, et al. Blood pressure-lowering effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists exenatide and liraglutide: a meta-analysis of clinical trials. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013;15(8):737–749. | ||
Liu R, Li L, Chen Y, Yang M, Liu H, Yang G. Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 agents on left ventricular function: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Med. 2014;46(8):664–671. | ||
Garg SK. The role of basal insulin and glucagon-like peptide-1 agonists in the therapeutic management of type 2 diabetes--a comprehensive review. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2010;12(1):11–24. | ||
Raschi E, Piccinni C, Poluzzi E, Marchesini G, De Ponti F. The association of pancreatitis with antidiabetic drug use: gaining insight through the FDA pharmacovigilance database. Acta Diabetol. 2013;50(4):569–577. | ||
Funch D, Gydesen H, Tornoe K, Major-Pedersen A, Chan KA. A prospective, claims-based assessment of the risk of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer with liraglutide compared to other antidiabetic drugs. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014;16(3):273–275. | ||
Wenten M, Gaebler JA, Hussein M, et al. Relative risk of acute pancreatitis in initiators of exenatide twice daily compared with other anti-diabetic medication: a follow-up study. Diabet Med. 2012;29(11):1412–1418. | ||
Romley JA, Goldman DP, Solomon M, McFadden D, Peters AL. Exenatide therapy and the risk of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer in a privately insured population. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2012;14(10):904–911. | ||
Dore DD, Seeger JD, Arnold Chan K. Use of a claims-based active drug safety surveillance system to assess the risk of acute pancreatitis with exenatide or sitagliptin compared to metformin or glyburide. Curr Med Res Opin. 2009;25(4):1019–1027. | ||
Dore DD, Seeger JD, Chan KA. Incidence of health insurance claims for thyroid neoplasm and pancreatic malignancy in association with exenatide: signal refinement using active safety surveillance. Ther Adv Drug Saf. 2012;3(4):157–164. | ||
Invokana [prescribing information]. Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; 2013. Available from: https://http://www.invokanahcp.com/prescribing-information.pdf. Accessed October, 2015. | ||
Farxiga [prescribing information]. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; 2014. Available from: http://www1.astrazeneca-us.com/pi/pi_farxiga.pdf. Accessed October 1, 2015. | ||
Jardiance [prescribing information]. Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; 2015. Available from: http://docs.boehringer-ingelheim.com/Prescribing Information/PIs/Jardiance/jardiance.pdf. Accessed October 1, 2015. | ||
Stenlof K, Cefalu WT, Kim KA, et al. Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin monotherapy in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with diet and exercise. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013;15(4):372–382. | ||
Ferrannini E, Berk A, Hantel S, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of empagliflozin, sitagliptin, and metformin: an active-controlled, parallel-group, randomized, 78-week open-label extension study in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(12):4015–4021. | ||
Chao EC. SGLT-2 inhibitors: a new mechanism for glycemic control. Clin Diabetes. 2014;32(1):4–11. | ||
Haring HU, Merker L, Seewaldt-Becker E, et al. Empagliflozin as add-on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Care. 2014;37(6):1650–1659. | ||
Rosenstock J, Jelaska A, Frappin G, et al. Improved glucose control with weight loss, lower insulin doses, and no increased hypoglycemia with empagliflozin added to titrated multiple daily injections of insulin in obese inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2014;37(7):1815–1823. | ||
Bolinder J, Ljunggren O, Johansson L, et al. Dapagliflozin maintains glycaemic control while reducing weight and body fat mass over 2 years in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled on metformin. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014;16(2):159–169. | ||
Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(22):2117–2128. | ||
FDA.gov: FDA. FDA approves Farxiga to treat type 2 diabetes [press release]. 2014 [January 8]. Available from: http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm380829.htm. Accessed January 5, 2016. | ||
FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA warns that SGLT2 inhibitors for diabetes may result in a serious condition of too much acid in the blood. May 15, 2015. Available from: http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm446845.htm. Accessed October 1, 2015. | ||
Erondu N, Desai M, Ways K, Meininger G. Diabetic ketoacidosis and related events in the canagliflozin type 2 diabetes clinical program. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(9):1680–1686. | ||
Peters AL, Buschur EO, Buse JB, Cohan P, Diner JC, Hirsch IB. Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis: a potential complication of treatment with sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(9):1687–1693. | ||
Rosenstock J, Ferrannini E. Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis: a predictable, detectable, and preventable safety concern with sglt2 inhibitors. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(9):1638–1642. | ||
IMS Health: Total Patient Tracker (TPT). July 2014 through June 2015. Extracted August 2015. File: DATA 2015- Canagliflozin DSC. Accessed November 11, 2015. | ||
Imai K, Tsujimoto T, Goto A, et al. Prediction of response to GLP-1 receptor agonist therapy in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2014;6(1):110. | ||
Fonseca T, Clegg J, Caputo G, Norrbacka K, Dilla T, Alvarez M. The cost-effectiveness of exenatide once weekly compared with exenatide twice daily and insulin glargine for the treatment of patients with type two diabetes and body mass index >/=30 kg/m(2) in Spain. J Med Econ. 2013;16(7):926–938. | ||
Samyshkin Y, Guillermin AL, Best JH, Brunell SC, Lloyd A. Long-term cost-utility analysis of exenatide once weekly versus insulin glargine for the treatment of type 2 diabetes patients in the US. J Med Econ. 2012;15(Suppl 2):6–13. | ||
Beaudet A, Palmer JL, Timlin L, et al. Cost-utility of exenatide once weekly compared with insulin glargine in patients with type 2 diabetes in the UK. J Med Econ. 2011;14(3):357–366. | ||
Waugh N, Cummins E, Royle P, et al. Newer agents for blood glucose control in type 2 diabetes: systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess. 2010;14(36):1–248. | ||
Charokopou M, McEwan P, Lister S, et al. Cost-effectiveness of dapagliflozin versus DPP-4 inhibitors as an add-on to metformin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus from a UK healthcare system perspective. BMC Health Serv Res. 2015;15:496. | ||
Charokopou M, McEwan P, Lister S, et al. The cost-effectiveness of dapagliflozin versus sulfonylurea as an add-on to metformin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med. 2015;32(7):890–898. | ||
FDA.gov: Food and Drug Administration. The FDA Safety Information and Adverse Event Reporting Program: Safety Information - Byetta (exenatide) - Renal Failure [press release]. 2009 [November 2]. Available from: http://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch/SafetyInformation/SafetyAlertsforHumanMedicalProducts/ucm188703.htm. Accessed January 5, 2016. | ||
Vilsboll T, Zdravkovic M, Le-Thi T, et al. Liraglutide, a long-acting human glucagon-like peptide-1 analog, given as monotherapy significantly improves glycemic control and lowers body weight without risk of hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2007;30(6):1608–1610. | ||
Wholesale Acquisition Cost, Redbook Online®. Truven Health. Available from: http://www.redbook.com/redbook/awp/. Accessed November 12, 2015. |
 © 2016 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2016 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.