Back to Journals » Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity » Volume 7
Prevalence of diagnosed and undiagnosed diabetes mellitus in adults aged 19 years and older in Basrah, Iraq
Authors Mansour AA, Al-Maliky AA, Kasem B, Jabar A, Mosbeh KA
Received 23 December 2013
Accepted for publication 9 January 2014
Published 2 May 2014 Volume 2014:7 Pages 139—144
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S59652
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Abbas Ali Mansour, Ahmed A Al-Maliky, Bashar Kasem, Abdulsatar Jabar, Khalid Abdulabass Mosbeh
Al-Faiha Diabetes Endocrine and Metabolism Center (FDEMC) Basrah, Iraq
Background: Six of the top ten countries in the world with the highest prevalence of diabetes mellitus are in the Middle East. The objective of this investigation was to evaluate the prevalence of diabetes in Basrah, Southern Iraq.
Methods: A population-based, cross-sectional, simple random study screened 5,445 persons aged 19–94 years in Basrah, with glycated hemoglobin measured in 88.3% of the population and fasting plasma glucose in 18.7%. Body mass index and other demographic parameters were also measured.
Results: Of the 5,445 persons screened, 8.7% had already been diagnosed with diabetes and 11% were found by screening to have undiscovered diabetes, giving an age-adjusted prevalence of diabetes of 19.7%, with 55.7% of those with diabetes being previously undiagnosed. In addition, 29.1% of the screened population had prediabetes, giving a prevalence of dysglycemia of 48.8%, with only 51.2% of the persons screened being normoglycemic. The prevalence of diabetes in both sexes peaked at age 46–60 years. Diabetes was slightly more prevalent in females than in males, and about 70.3% of diabetic individuals had a body mass index ≥25 kg/m².
Conclusion: The prevalence of diabetes in Basrah, Iraq, is very high, affecting one in five adults. The epidemic of diabetes will result in strain on the financial resources of health care systems.
Keywords: diabetes mellitus, screening, epidemiology, glycated hemoglobin, Iraq
Introduction
Worldwide, it is estimated that 366 million people have diabetes, with half unaware they have the disease.1 Of the ten countries with the highest prevalence of diabetes, six are in the Middle East (Kuwait, Lebanon, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, and the United Arab Emirates). In the 20 Arab countries for which data are available, nearly 20.5 million people are living with diabetes and another 13.7 million are in the prediabetes stage, having impaired glucose tolerance. In contrast with developed countries, in which most people with diabetes are over the age of retirement, nearly three quarters (73.4%) of diabetics in Arab countries are under 60 years of age and hence in their most productive years, further increasing the burden of disability due to diabetes.1
In 2009, an international committee for the diagnosis of diabetes recommended use of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), an index of average plasma glucose over several weeks, as a marker for the disease.2 This recommendation was also made by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) in 2010,3 which suggested that HbA1c ≥6.5% (48 mmol/mol) be considered diagnostic of diabetes. HbA1c is considered equal to fasting plasma glucose (FPG) as a predictor of diabetes.4
Assessments of FPG concentrations have been associated with methodological, procedural, and practical problems, and the oral glucose tolerance test is tedious to perform. Measurements of HbA1c are considered an alternative diagnostic test, overcoming many of the problems associated with other tests.5 Moreover, a diagnosis of diabetes can be confirmed by measuring FPG and HbA1c at the same time.6 A comparison of the association of diabetic retinopathy with the results of three diagnostic tests (HbA1c, FPG, and 2-hour glucose) in 44,623 individuals showed that FPG (117 mg/dL [6.5 mmol/L]) and HbA1c (6.5% [48 mmol/mol]) were associated with retinopathy, whereas 2-hour glucose concentrations were not.7
The ADA does not recommend testing both FPG and HbA1c, because these tests are not completely (100%) concordant, which can lead to confusion. In contrast, the Japan Diabetes Society has recommended that individuals be simultaneously tested for FPG and HbA1c for the diagnosis of diabetes.6 Early diagnosis is important for effective management, significantly reducing the risk of complications such as diabetic nephropathy and diabetic retinopathy, but not mortality.8,9 The objective of this investigation was to assess the prevalence of diabetes mellitus in Basrah, Southern Iraq.
Materials and methods
Setting and design
Basrah is a governorate located in Southern Iraq, 550 km from the Iraqi capital, Baghdad, with a total population of 3 million. A population-based, cross-sectional, simple random study was performed to screen for diabetes in Basrah between January 2011 and October 2012. Using a Google map, we screened people from the Dur Nuwab Al Dubat, Duran Naft, Dur Al-Dhabaat, Yaseen Khrebit, Al Hayy alMarkazi, Al Iskan, Al-Abelah, Dur Alhindia, Hateen, Al Hadi, and Al Gzaiza districts of Basrah. The study was approved by the ethics committee of the Basrah Directorate of Health and written informed consent was taken from each study participant.
Study subjects
Subjects were invited via the media and during home visits performed as part of a vaccination program to come to the center to be screened for diabetes. The main outcome measure was the prevalence of diabetes among adults. Prior to screening, the participants were informed about the importance of establishing a database for diabetes in Iraq. Participants were excluded if they were younger than 19 years of age or pregnant.
The participants were invited to undergo examination at the Al-Faiha Diabetes Endocrine and Metabolism Center in Basrah, Southern Iraq. Information was collected using a structured, interviewer-administered questionnaire, followed by a physical examination. Age, sex, education level, smoking, and family history of diabetes (first-degree and/or second-degree relatives) were recorded.
Body mass index (BMI) was calculated as kg/m2. Participants were categorized according to World Health Organization BMI criteria as normal (<25 kg/m2), overweight (25–29.9 kg/m2), or obese (≥30 kg/m2).
Smokers were defined as those who reported smoking >100 cigarettes during their lifetime and were currently smoking every day or some days. Hypertension was defined as either a resting systolic blood pressure ≥140 mmHg or a resting diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mmHg recorded at a single visit or being prescribed an antihypertensive medication.
Laboratory tests
A blood sample was obtained after an overnight fast and parameters were measured at the center’s laboratory. Plasma glucose concentrations were measured using an automated glucose oxidase method (Biolyzer® 300; Analyticon Biotechnologies AG, Lichtenfels, Germany). In subjects unable to fast, HBA1c was measured by high-performance liquid chromatography (Variant™ hemoglobin testing system; Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc., Hercules, CA, USA). This minority agreed to come the next day fasting to do proper oral glucose tolerance test with 75 g anhydrous glucose powder dissolved into 250–300 mL of water.
Diagnosis of type 2 diabetes
Subjects were classified according to ADA criteria, with normal FPG being <100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L), impaired fasting glucose being FPG ranging from 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L) to 125 mg/dL (6.9 mmol/L), and diabetes being FPG ≥126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L).2 HbA1c concentrations <5.7% were considered normal, those ranging from 5.7% (39 mmol/mol) to 6.4% (46 mmol/mol) were considered prediabetes, and those ≥6.5% (48 mmol/mol) were considered to indicate diabetes. On an oral glucose tolerance test, diabetes was diagnosed if 2-hour plasma glucose was 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L), and the impaired glucose tolerance test was considered in those with plasma glucose 140–199 mg/dL (7.7–11 mmol/L). Persons with impaired fasting glucose or the impaired glucose tolerance test and prediabetes on HbA1c were considered to have prediabetes according to the ADA classification. Study participants were asked if they had ever been told by a physician that they had diabetes; if so, blood tests were performed to assess diabetes control. This group was defined as the known diabetes group.
Statistical analysis
Continuous variables are presented as the mean ± standard deviation, and categorical data as frequencies and percentages. The data collected were analyzed by the chi-squared test as appropriate. All statistical analyses were performed using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences version 15 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). A P-value <0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
Results
Demographic characteristics of the study population are shown in Table 1. Of the 5,445 individuals screened, 52.6% were women and 47.3% were men. Their mean age was 46.7±14.3 (range 19–94) years and their mean BMI was 27.4±6.4 kg/m2; 40.5% had a family history of diabetes, 16.9% were smokers, and 11.2% were hypertensive.
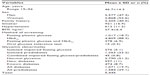  | Table 1 Baseline characteristics of the 5,445 screened individuals |
Screening was by HbA1c measurement in 88.3% of the study subjects, followed by FPG in 18.7%. Of the study subjects, 8.7% had been previously diagnosed with diabetes, whereas 11% were found by screening to have diabetes, resulting in an age-adjusted prevalence of diabetes of 19.7%. Of those with diabetes, 55.7% were previously undiagnosed. In addition, 29.1% were found to have prediabetes, indicating that dysglycemia was present in 48.8% of the study population, with only 51.2% being normoglycemic (Figure 1).
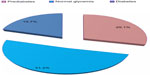  | Figure 1 Glycemic abnormalities. |
Table 2 shows the prevalence rates of diagnosed and undiagnosed diabetes according to subject age. The prevalence of diabetes in both sexes peaked at age 46–60 years (Figure 2), with 41.7% of men and 43.9% of women having diabetes. Prediabetes peaked at age 31–45 years in men and at age 46–60 years in women. The prevalence of diabetes was higher in women than in men (19.8% versus 19.6%; P<0.0001), as was the prevalence of prediabetes (29.5% versus 28.6%; P<0.0001).
  | Table 2 Prevalence of dysglycemia according to subject sex and age |
  | Figure 2 Prevalence of dysglycemia by age in both men and women. |
Table 3 shows the characteristics of study subjects according to glycemic abnormality. The mean age and BMI of those with diabetes and prediabetes was higher than that in those with normoglycemia. Hypertension and family history of diabetes were higher in the combined diabetes and prediabetes groups than in the normoglycemic group. The prevalence of smoking was lower in the diabetes group, but 44.4% of smokers had prediabetes or diabetes.
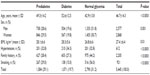  | Table 3 Associations between subject characteristics and glycemic abnormalities |
Distribution of glycemic abnormality according to BMI category is shown in Table 4. Combined diabetes and prediabetes was more common in overweight and obese people. About 70.3% of those with diabetes had a BMI ≥25 kg/m2.
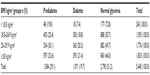  | Table 4 Glycemic abnormalities according to BMI categories |
Discussion
There is some uncertainty about the prevalence of diabetes mellitus in the Iraqi population. Iraq has undergone rapid economic development in the last 10 years. In December 2011, the International Diabetes Federation reported that, of the ten countries with the highest prevalence of diabetes in adults aged 20–79 years, six were in the Middle East, ie, Kuwait (21.1%), Lebanon (20.2%), Qatar (20.2%), Saudi Arabia (20.0%), Bahrain (19.9%), and the United Arab Emirates (19.2%).1 Iraq is considered as having a medium prevalence (9.3%) of diabetes in the Middle East based on surveys from 2006 to 2007.1,10–12 Diabetes was also found to affect 21.9% of Iraqis living in Sweden in 2010.13 In the present study of adults in Basrah, Southern Iraq, we found that one in five subjects had diabetes.
We found that the peak age of diabetes in both sexes was in the fourth through sixth decades of life. Studies in Saudi Arabia found that the age-adjusted prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus was 30.0%–31.6%, with the highest prevalence in those aged 46–60 years.14,15 High diabetes prevalence rates have been observed in other Gulf region countries, including Bahrain (25.7%) and Oman (16.1%).16,17 In Lebanon, the combined prevalence of previously diagnosed and newly diagnosed diabetes was 15.8%, with 17.6% in men and 13.4% in women.18 In Iran, 5.5% of individuals have diabetes, with one third of adults in Tehran having impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes,19,20 while in Jordan the age-standardized prevalence of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose was found to be 17.1% and 7.8%, respectively.21
In developed countries, in which most people are of European descent, diabetes affects mainly those older than 65 years of age. Similar findings were observed in Iran, where diabetes was more common among older people, with 10.9% of those aged >60 years having the disease.22 However, in most developing countries, the peak incidence of diabetes is between 45 and 64 years. We also observed an association between diabetes and BMI, with 70.3% of Iraqis with diabetes having a BMI ≥25 kg/m2, compared with 85.7% of Saudis with diabetes.14
Slightly more than half of those with diabetes in our study were undiagnosed at the time of screening, similar to findings in the United Arab Emirates.23 Reported rates of undiagnosed diabetes in the Middle East and North Africa region have been found to vary, with rates of 29% in Iraq, 50% in Algeria and Iran, 56% among women in Pakistan, and 86% in Tunisia.24
We found that diabetes was more prevalent in women than in men, similar to findings in Iran, but in Jordan there was no difference between sexes.19,21 In contrast, the prevalence was higher in men in Saudi Arabia and Lebanon.14,18
Study limitations
The present study had several limitations. First, the boundaries between rural and urban areas became blurred following the 2003 Iraq war. Many people from rural areas migrated to cities, especially when the government of Iraq could no longer control migration. Thus, dividing people into those living in rural and urban areas is no longer feasible. Second, we measured FPG only once. Duplicate measurements of FPG are required for a diagnosis of diabetes due to day-to-day variations.25 For epidemiological studies, however, estimation of diabetes prevalence and incidence using a single elevated HbA1c or FPG measurement is considered acceptable.26,27
Third, this work has the limitations inherent to cross-sectional studies.
Conclusion
The prevalence of diabetes in Basrah, Iraq, is very high, affecting one in five adults. This epidemic of diabetes will result in strain on the financial resources of health care systems.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank the staff of the Al-Faiha Diabetes Endocrine and Metabolism Center in Basrah for their contribution to this work.
Author contributions
All authors contributed equally to the collection and/or analysis of data, interpretation of the results, and the conclusion of this research.
Disclosure
The authors have no conflicts of interest to report in relation to this work.
References
International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas. 5th ed. Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation; 2011. Available from: http://www.idf.org/diabetesatlas/5e/the-global-burden. Accessed March 24, 2014. | |
American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2010;33 Suppl 1:S62–S69. | |
Selvin E, Steffes MW, Zhu H, et al. Glycated hemoglobin, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk in nondiabetic adults. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(9):800–811. | |
d’Emden MC, Shaw JE, Colman PG, et al, Australian Diabetes Society; Royal College of Pathologists of Australasia; Australasian Association of Clinical Biochemists. The role of HbA1c in the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus in Australia. Med J Aust. 2012;197(4):220–221. | |
Seino Y, Nanjo K, Tajima N, et al. Report of the Committee on the Classification and Diagnostic Criteria of Diabetes Mellitus. J Japan Diab Soc. 2010;53:450–467. | |
Colagiuri S, Lee CM, Wong TY, Balkau B, Shaw JE, Borch-Johnsen K; DETECT-2 Collaboration Writing Group. Glycemic thresholds for diabetes-specific retinopathy: implications for diagnostic criteria for diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2011;34(1):145–150. | |
The International Expert Committee. International Expert Committee report on the role of the A1c assay in the diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(7):1327–1334. | |
[No authors listed]. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Lancet. 1998;352(9131):837–853. | |
Simmons RK, Echouffo-Tcheugui JB, Sharp SJ, et al. Screening for type 2 diabetes and population mortality over 10 years (ADDITION-Cambridge): a cluster-randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2012;380(9855):1741–1748. | |
Mansour AA, Wanoose HL, Hani I, Abed-Alzahrea A, Wanoose HL. Diabetes screening in Basrah, Iraq: a population-based cross-sectional study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2008;79(1):147–150. | |
Boutayeb A, Lamlili M, Boutayeb W, Maamri A, Ziyyat A, Ramdani N. The rise of diabetes prevalence in the Arab region. Open J Epidemiol. 2012;2:55–60. | |
World Health Organization. Global Infobase. Available from: https://apps.who.int/infobase/CountryProfiles.aspx. Accessed October 1, 2012. | |
Bennet L, Johansson SE, Agardh CD, et al. High prevalence of type 2 diabetes in Iraqi and Swedish residents in a deprived Swedish neighborhood – a population based study. BMC Public Health. 2011;11:303. | |
Al-Daghri NM, Al-Attas OS, Alokail MS, et al. Diabetes mellitus type 2 and other chronic non-communicable diseases in the central region, Saudi Arabia (Riyadh cohort 2): a decade of an epidemic. BMC Med. 2011;9:76. | |
Alqurashi KA, Aljabri KS, Bokhari SA. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus in a Saudi community. Ann Saudi Med. 2011;31(1):19–23. | |
Hamadeh RR. Non communicable diseases among the Bahraini population: a review. East Mediterr Health J. 2000;6(5–6):1091–1097. | |
Lawati JA, Al Riyami AM, Mohammed AJ, Jousilahti P. Increasing prevalence of diabetes mellitus in Oman. Diabet Med. 2002;19(11):954–957. | |
Hirbli KI, Jambeine MA, Slim HB, Barakat WM, Habis RJ, Francis ZM. Prevalence of diabetes in greater Beirut. Diabetes Care. 2005;28(5):1262. | |
Azimi-Nezhad M, Ghayour-Mobarhan M, Parizadeh MR, et al. Prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Iran and its relationship with gender, urbanisation, education, marital status and occupation. Singapore Med J. 2008;49(7):571–576. | |
Hadaegh F, Bozorgmanesh MR, Ghasemi A, Harati H, Saadat N, Azizi F. High prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes and abnormal glucose tolerance in the Iranian urban population: Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study. BMC Public Health. 2008;8:176. | |
Ajlouni K, Khader YS, Batieha A, Ajlouni H, El-Khateeb M. An increase in prevalence of diabetes mellitus in Jordan over 10 years. J Diabetes Complications. 2008;22(5):317–324. | |
Cockram CS. The epidemiology of diabetes mellitus in the Asia-Pacific region. Hong Kong Med J. 2000;6(1):43–52. | |
Saadi H, Al-Kaabi J, Benbarka M, et al. Prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes and quality of care in diabetic patients followed at primary and tertiary clinics in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. Rev Diabet Stud. 2010;7(4):293–302. | |
MENA International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes: the Hidden Pandemic and its Impact on the Middle East and Northern Africa. 2010. Available from: http://www.novonordisk.com/images/about_us/changing-diabetes/PDF/Leadership%20forum%20pdfs/MENA%20Forum/MENA_Diabetes_briefing_book_EN.pdf. Accessed April 17, 2014. | |
Ollerton RL, Playle R, Ahmed K, Dunstan FD, Luzio SD, Owens DR. Day-to-day variability of fasting plasma glucose in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic subjects. Diabetes Care. 1999;22(3):394–398. | |
[No authors listed]. Report of the Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care. 1997;20(7):1183–1197. | |
Kuzuya T, Nakagawa S, Satoh J, et al; Committee of the Japan Diabetes Society on the diagnostic criteria of diabetes mellitus. Report of the Committee on the Classification and Diagnostic Criteria of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2002;55(1):65–85. |
 © 2014 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2014 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
