Back to Journals » Cancer Management and Research » Volume 13
Predictive Factors Among Clinicopathological Characteristics for Sentinel Lymph Node Metastasis in T1-T2 Breast Cancer
Authors Minami S , Sakimura C, Irie J, Tokai Y, Okubo H, Ohno T
Received 1 October 2020
Accepted for publication 23 November 2020
Published 11 January 2021 Volume 2021:13 Pages 215—223
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S284922
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Shigeki Minami,1 Chika Sakimura,1 Junji Irie,2 Yukiko Tokai,3 Hitoshi Okubo,4 Tsuyoshi Ohno5
1Department of Breast and Endocrine Surgery, Nagasaki Harbor Medical Center, Nagasaki 850-8555, Japan; 2Department of Pathology, Nagasaki Harbor Medical Center, Nagasaki, Japan; 3Department of Breast Surgery, Imamura Women’s Clinic, Nagasaki, Japan; 4Okubo Breast Clinic, Nagasaki, Japan; 5Ohno Breast and Thyroid Clinic, Nagasaki, Japan
Correspondence: Shigeki Minami
Department of Breast and Endocrine Surgery, Nagasaki Harbor Medical Center, 6-39 Shinchi-machi, Nagasaki 850-8555, Japan
Tel +81-95-822-3251
Fax +81-95-826-8798
Email [email protected]
Background: The axillary lymph node status is an important prognostic factor of breast cancer. This study explores the predictive factors for sentinel lymph node (SLN) metastasis among the preoperative clinicopathological features, including impaired glucose tolerance (IGT).
Methods: This study comprised patients diagnosed with breast cancer who underwent surgery at Nagasaki Harbor Medical Center between April 2014 and December 2019. The factors assessed using univariate and multivariate analyses were the clinicopathological data of these cancers, including the patient age, gender, menstrual status, breast or ovarian cancer family history, body mass index, glycosylated hemoglobin, clinical tumor size, nipple-tumor distance (NTD), tumor histology, histological grade, node status, estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, human epidermal growth factor receptor type 2 status, and Ki67 labeling index.
Results: In the cohort of 313 cases, the ratio of SLN metastasis was 17.3%. A univariate analysis found that the tumor size, NTD, IGT, and clinical tumor stage were associated with SLN metastasis. In a multivariable analysis, the tumor size, NTD, and IGT were associated with SLN metastasis. The receiver operating characteristic curve showed a sensitivity and specificity of 61.1% and 65.6%, respectively, at a cut-off of 1.7 cm for the tumor size (area under the curve [AUC]: 0.664; 95% confidence interval: 0.592– 0.736), and a sensitivity and specificity of 60.4% and 62.9%, respectively, at a cut-off of 2.0 cm for NTD (AUC: 0.651; 95% confidence interval: 0.571– 0.731) to predict the risk of SLN metastasis.
Conclusion: T1 and T2 breast cancer patients with a larger tumor size, tumor located closer to the nipple, and IGT have a higher risk of SLN metastases than others.
Keywords: breast cancer, sentinel lymph node metastasis, predictive factor, nipple-tumor distance, impaired glucose tolerance
Introduction
The axillary lymph node (LN) status is an important prognostic factor for predicting the survival of breast cancer patients. At present, a sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) is the standard approach for axillary LN staging in clinical node-negative breast cancer patients and is less invasive than axillary lymph node dissection (ALND).1,2 However, an SLNB is not only still invasive, it is also associated with several postoperative complications, such as lymphedema, sensory loss, and upper limb pain.3,4 Furthermore, the incidence of SLN metastasis in clinical axillary LN-negative patients was reported to be 23.0–37.1%,5–8 and approximately 70–80% of patients receive excessive invasive axillary surgery. If predictive factors of SLN metastasis could be identified, we might be able to select candidate patients for an SLNB. Previous studies have shown that clinicopathological features such as the tumor size, age at the diagnosis, body mass index (BMI), tumor location, etc., are related to SLN metastasis.5–11
The association between cancer and diabetes has been reported by the American Diabetes Association and the American Cancer Society, including the relationship between diabetes and the cancer morbidity or prognosis, common risk factors for diabetes and cancer, and molecular mechanisms linking diabetes and cancer.12,13 Diabetes is reportedly associated with an increased risk of breast cancer. However, the association between diabetes and SLN metastasis has not yet been clarified.
Therefore, the present study explored the predictive factors of SLN metastasis among preoperative clinicopathological features, including impaired glucose tolerance (IGT).
Methods
Patient Selection
We identified breast cancer patients who underwent breast surgery and an SLNB at Nagasaki Harbor Medical Center between April 2014 and December 2019. The exclusion criteria were in situ carcinoma, preoperative systemic therapy, bilateral breast cancer, tumor size larger than 5 cm, male breast cancer, and patient with a history of treatment for breast cancer.
The clinicopathological data of these cases, including the patient age, gender, menstrual status, breast or ovarian cancer family history, body mass index (BMI), glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), clinical tumor size, nipple-tumor distance (NTD), tumor histology, histological grade, node status, estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PgR), human epidermal growth factor receptor type 2 (HER2) status, and Ki67 labeling index, were retrieved from our database and the patient’s medical records. ER and PgR were considered positive if there were any instances of positive staining and negative otherwise; HER2 was considered positive if a value of 3+ was obtained on immunohistochemical staining or a positive value on fluorescence in situ hybridization.
Definition of IGT
HbA1c was adopted as a diagnostic test for diabetes mellitus by the American Diabetes Association in 2010 and by the World Health Organization in 2011.14,15 An HbA1c of ≥6.5% is recommended as the cut-off point for diagnosing diabetes in both reports. In the present study, IGT was defined as HbA1c >6.0% according to our institutional normal range of HbA1c (4.9–6.0%) using a method certified by the National Glycohemoglobin Standardization Program. The patients with a diagnosis of diabetes and/or those with HbA1c >6.0% were considered to have IGT.
Measurement of NTD
In this study, the NTD (in cm), which was the distance of the proximal edge of the tumor from the nipple, was measured using slide calipers at a physical examination. The data were collected from patient’s medical records.
Statistical methods
All statistical analyses were performed with EZR on R Commander Version 2.5–1 (Saitama Medical Center, Jichi Medical University, Saitama, Japan),16 which is a graphical user interface for R (The R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria). The data are presented as the median (interquartile range) for not normally distributed variables. Differences in continuous variables between groups were assessed using the Mann–Whitney U-test for not normally distributed variables. Differences in categorical variables between groups were assessed using Fisher’s exact test. Associations with positive LNs were evaluated using logistic regression models. A multivariate logistic regression model was conducted including all variables from the univariate analysis that were related to the SLN status. The cut-off values, sensitivity, and specificity were determined by the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve method with the area under the curve (AUC) to estimate the strength of the relationship between LN metastasis and the clinical outcomes.
Results
Clinical Characteristics
A total of 454 breast cancer patients who had undergone breast surgery and an SLNB at Nagasaki Harbor Medical Center between April 2014 and December 2019 were considered for the study. Of these, 141 cases were excluded from this study for the following reasons: in situ carcinoma (74 cases), preoperative systemic therapy (46 cases), bilateral breast cancer (11 cases), tumor size larger than 5 cm (5 cases), male breast cancer (3 cases), and history of breast cancer (2 cases). Thereafter, 313 cases were enrolled in this study.
All patients were female, with a median age of 63 years old (range 31–89 years old). A total of 259 patients (82.7%) were SLN-negative, and 54 (17.3%) were SLN-positive. Of the 54 SLN-positive patients, 45 underwent both an SLNB and ALND, and 9 underwent an SLNB without ALND because of micro-metastasis <2 mm in size.
The clinical and pathologic features of the 313 cases and comparisons of the SLN-positive and SLN-negative patients are summarized in Table 1. Our study found that the tumor size, NTD, IGT, tumor location, and clinical tumor stage were associated with the presence of SLN metastasis, while other factors had no relationship with SLN metastasis.
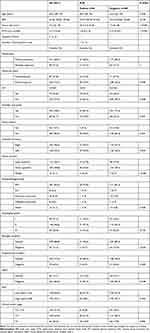 |
Table 1 Clinicopathologic Characteristics and the Comparison of Features Between SLN-Positive and SLN-Negative Cases |
The results of the univariate logistic regression models for predicting positive LNs are summarized in Table 2. The factors associated with SLNB positivity on a univariate analysis were BMI, tumor size, NTD, IGT, and clinical tumor stage.
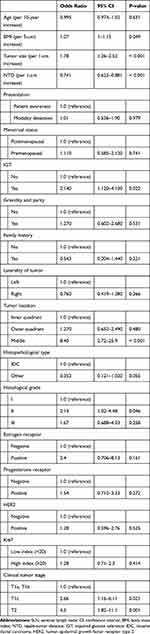 |
Table 2 Results of a Univariate Analysis for SLN Metastasis Predictive Parameters |
All features from Table 2 were included in the multivariate analysis. Only those features reported in Table 3 were statistically significant in the multivariate model. In the multivariable analysis, the tumor size, NTD, and IGT were associated with SLN positivity.
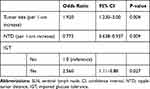 |
Table 3 Results of a Multivariate Analysis for SLN Metastasis Predictive Parameters |
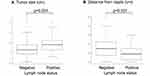
Figure 1A and B show a box plot of the node-negative and node-positive cases. The median tumor size of the node-negative cases was 13 mm, compared with 18 mm in the node-positive cases (p < 0.001). The median NTD for the SLN-negative cases was 3.0 cm, compared with 1.8 cm for the SLN-positive cases (p < 0.001).
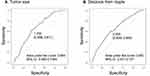
The ROC curves corresponding to the tumor size and NTD are shown in Figure 2A and B, respectively. Regarding the tumor size, the AUC was 0.664 (95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.592–0.736), and for a cut-off value of 1.7 cm, the sensitivity was 61.1%, and the specificity was 65.6%. Regarding the NTD, the AUC was 0.651 (95% CI = 0.571–0.731), and for a cut-off value of 2.0 cm, the sensitivity was 60.4%, and the specificity was 62.9%.
Among the 54 patients with SLN-positive status, there were 41 (75.9%) with macro-metastases and 13 (24.1%) with micro-metastases. Of the 41 patients with macro-metastases, all underwent ALND and 15 patients (36.6%) had additional metastatic lymph nodes on ALND. The median number of positive LNs was 1 (range 1–13), and the median number of LNs subjected to ALND was 11 (range 3–24). Of the 13 patients with micro-metastases, 5 (38.5%) underwent ALND, while 8 (61.5%) did not undergo ALND. All 13 patients with micro-metastases had 1 LN metastasis.
Discussion
The present study determined the value of the clinicopathological features of clinical node-negative breast cancer for predicting the status of axillary SLN positivity. We found that the tumor size, distance of the tumor from the nipple, and IGT were independent predictors of SLN positivity. The BMI and histological grade did not retain relevance in a multivariate analysis.
In our series of 313 early breast cancer patients, SLN metastasis was detected in 17.3%, which was lower than in previous reports, with an incidence range reported in the literature of 23.0–37.1%.5–8 This difference may be due to the selection of the SLNB. We perform ultrasound (US)-guided fine-needle-aspiration cytology of LNs in all cases suspected of ALN metastasis on preoperative US and/or computed tomography (CT) and perform ALND in cases with positive cytology results.
The tumor size was shown to be a threshold predictor of SLN metastasis in this study; 21/191 (11.0%) patients with tumors <17 mm and 33/122 (24.8%) of those with tumors ≥17 mm had SLN metastasis. Previous studies have also shown that the tumor size is a strong predictor of SLN and ALN metastasis.5–11
It is reasonable to conclude that tumors closer to the rich plexus of lymphatics in the subareolar locations are likely to have strong access to the lymphatic network, thereby resulting in a greater risk of lymphatic dissemination and consequently ALN metastases.17 Previous studies have shown that breast cancer located closer to the nipple has a higher incidence of ALN metastasis than that located farther away.5,7,9 In our study, an NTD of 20 mm was found to be the threshold value, and 22/180 (12.2%) of patients with an NTD <20 mm and 31/124 (25.0%) of those with an NTD ≥20 mm had SLN metastasis. The NTD was easily measured using slide calipers on a routine physical examination and was found to be a predictive factor of SLN metastasis.
The American Diabetes Association and American Cancer Society reported that diabetes is associated with an increased risk of breast cancer,12,13 while the Japan Diabetes Society/Japanese Cancer Association Joint Committee have suggested no increased risk of breast cancer associated with diabetes in Japanese patients.18 Recently, several studies reported that type 2 diabetes and impaired glucose metabolism were associated with the prognosis of breast cancer.19–22 In our study, an IGT was associated with SLN metastasis. Our findings suggest that having IGT may lead to LN progression despite early breast cancer.
Several limitations associated with the present study warrant mention. First, it is a retrospective, single-institution study with a small sample size; thus, the generalizability of the findings is limited. This work represents the preliminary results of a large study. Second, the NTD was measured using slide calipers on a physical examination, an approach wherein accurate measurements are difficult to obtain in cases with poorly defined borders. The breast size was also not mentioned in this study, even though it might affect the NTD. However, we did not detect any correlation between the BMI and nodal status. Third, IGT in this study was not determined through rigorous tests of IGT or insulin resistance or a diagnosis of diabetes. However, to our knowledge, our study is the first to determine IGT as a predictive factor for evaluating SLN metastasis. Third, we could not evaluate lymphovascular invasion (LVI), which has been reported as a predictive factor of node metastasis.5,6,10,11 In this study, we performed a preoperative core-needle-biopsy of the tumor, which has limited ability to assess lymphovascular invasion.
The ALN status is an important prognostic factor for predicting the survival of breast cancer patients. Recently, the Z0011 trial and AMAROS trial showed that the therapeutic value of patients with SLN metastasis treated with an SLNB and radiation therapy was not inferior to that of patients with SLN metastasis treated with ALND.23–26 The treatment strategy and axillary staging methodology of breast cancer may change in the future.
In conclusion, breast cancer patients with a larger tumor size, lesion located closer to the nipple, and IGT have a higher risk of SLN metastases than others. These results may be used to make decisions in the management of patients with breast cancer in order to minimize therapeutic and surgical procedures as much as possible.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Nagasaki Harbor Medical Center (NIRB No. R01-025) and was conducted in accordance with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Consent to participate was obtained in the form of an opt-out option on the web-site. The data were anonymized for the analysis.
Author Contributions
All authors made substantial contributions to the conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data, took part in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content, agreed to submit to the current journal, gave final approval of the version to be published, and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Funding
The authors declare that this study was not funded.
Disclosure
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Veronesi U, Paganelli G, Viale G, et al. Sentinel-lymph-node biopsy as a staging procedure in breast cancer: update of a randomised controlled study. Lancet Oncol. 2006;7(12):983–990. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(06)70947-0
2. Krag DN, Anderson SJ, Julian TB, et al. Technical outcomes of sentinel-lymph-node resection and conventional axillary-lymph-node dissection in patients with clinically node-negative breast cancer: results from the NSABP B-32 randomised Phase III trial. Lancet Oncol. 2007;8(10):881–888. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(07)70278-4
3. Krag D, Weaver D, Ashikaga T, et al. The sentinel node in breast cancer–a multicenter validation study. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(14):941–946. doi:10.1056/NEJM199810013391401
4. Kuwajerwala NK, Feczko C, Dekhne N, et al. Comparison of lymphedema in patients with axillary lymph node dissections to those with sentinel lymph node biopsy followed by immediate and delayed ALND. Am J Clin Oncol. 2013;36(1):20–23. doi:10.1097/COC.0b013e31823a4956
5. Yoshihara E, Smeets A, Laenen A, et al. Predictors of axillary lymph node metastases in early breast cancer and their applicability in clinical practice. Breast. 2013;22(3):357–361. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2012.09.003
6. Viale G, Zurrida S, Maiorano E, et al. Predicting the status of axillary sentinel lymph nodes in 4351 patients with invasive breast carcinoma treated in a single institution. Cancer. 2005;103(3):492–500. doi:10.1002/cncr.20809
7. Zhang Y, Li J, Fan Y, et al. Risk factors for axillary lymph node metastases in clinical stage T1-2N0M0 breast cancer patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(40):e17481. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000017481
8. Ding J, Jiang L, Wu W. Predictive value of clinicopathological characteristics for sentinel lymph node metastasis in early breast cancer. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:4102–4108. doi:10.12659/msm.902795
9. Ji F, Xiao WK, Yang CQ, et al. Tumor location of the central and nipple portion is associated with impaired survival for women with breast cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 2019;11:2915–2925. doi:10.2147/CMAR.S186205
10. Ansari B, Morton MJ, Adamczyk DL, et al. Distance of breast cancer from the skin and nipple impacts axillary nodal metastases. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18(11):3174–3180. doi:10.1245/s10434-011-1957-z
11. La Verde N, Biagioli E, Gerardi C, et al. Role of patient and tumor characteristics in sentinel lymph node metastasis in patients with luminal early breast cancer: an observational study. Springerplus. 2016;5(1):114. doi:10.1186/s40064-016-1720-9
12. Giovannucci E, Harlan DM, Archer MC, et al. Diabetes and cancer: a consensus report. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60(4):207–221. doi:10.3322/caac.20078
13. Giovannucci E, Harlan DM, Archer MC, et al. Diabetes and cancer: a consensus report. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(7):1674–1685. doi:10.2337/dc10-0666
14. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes–2010 [published correction appears in diabetes care. 2010 Mar;33(3):692]. Diabetes Care. 2010;Suppl 33(Suppl Supplement_1):S11–S61. doi:10.2337/dc10-S011.
15. World Health Organization. Use of glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) in the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2011. Available from: https://www.who.int/diabetes/publications/report-hba1c_2011.pdf.
16. Kanda Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013;48(3):452–458. doi:10.1038/bmt.2012.244
17. Suami H, Pan W-R, Taylor GI. Historical review of breast lymphatic studies. Clin Anat. 2009;22(5):531–536. doi:10.1002/ca.20812
18. Kasuga M, Ueki K, Tajima N, et al. Report of the japan diabetes society/japanese cancer association joint committee on diabetes and cancer. Cancer Sci. 2013;104(7):965–976. doi:10.1111/cas.12203
19. Ferroni P, Riondino S, Laudisi A, et al. Pretreatment insulin levels as a prognostic factor for breast cancer progression. Oncologist. 2016;21(9):1041–1049. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0462
20. Monzavi-Karbassi B, Gentry R, Kaur V, et al. Pre-diagnosis blood glucose and prognosis in women with breast cancer. Cancer Metab. 2016;4(1):7. doi:10.1186/s40170-016-0147-7
21. Mu L, Zhu N, Zhang J, et al. Type 2 diabetes, insulin treatment and prognosis of breast cancer. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2017;33(1):e2823. doi:10.1002/dmrr.2823
22. Lee KN, Torres MA, Troeschel AN, et al. Type 2 diabetes, breast cancer specific and overall mortality: associations by metformin use and modification by race, body mass, and estrogen receptor status. PLoS One. 2020;15(5):e0232581. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0232581
23. Giuliano AE, Hunt KK, Ballman KV, et al. Axillary dissection vs no axillary dissection in women with invasive breast cancer and sentinel node metastasis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2011;305(6):569–575. doi:10.1001/jama.2011.90
24. Giuliano AE, Ballman KV, McCall L, et al. Effect of axillary dissection vs no axillary dissection on 10-year overall survival among women with invasive breast cancer and sentinel node metastasis: the ACOSOG Z0011 (Alliance) randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;318(10):918–926. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.11470
25. Galimberti V, Cole BF, Viale G, et al. Axillary dissection versus no axillary dissection in patients with breast cancer and sentinel-node micrometastases (IBCSG 23-01): 10-year follow-up of a randomised, controlled Phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19(10):1385–1393. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30380-2
26. Donker M, van Tienhoven G, Straver ME, et al. Radiotherapy or surgery of the axilla after a positive sentinel node in breast cancer (EORTC 10981-22023 AMAROS): a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(12):1303–1310. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70460-7
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.