Back to Journals » Cancer Management and Research » Volume 13
PRDX6 Overexpression Promotes Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration of A549 Cells in vitro and in vivo
Authors Li H, Zhang D, Li B, Zhen H, Chen W, Men Q
Received 28 September 2020
Accepted for publication 31 December 2020
Published 10 February 2021 Volume 2021:13 Pages 1245—1255
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S284195
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Seema Singh
Hao Li,1,* Donghua Zhang,2,* Bo Li,3 Honghua Zhen,4 Wenping Chen,4 Qingjuan Men5
1Department of Blood Transfusion, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated with Shandong First Medical University, Shandong, 271016, People’s Republic of China; 2Department of Oncology, Zhangqiu People’s Hospital Shandong Province, Shandong, 250200, People’s Republic of China; 3Department of Orthopaedics, Central Hospital of XinWen Mining Group Co., Ltd., Shandong, 271233, People’s Republic of China; 4Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Zhangqiu District People’s Hospital, Jinan City, Shandong Province, 250200, People’s Republic of China; 5Clinical Laboratory, People’s Hospital of Juxian, Shandong, 276500, People’s Republic of China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Correspondence: Qingjuan Men
Clinical Laboratory, People’s Hospital of Juxian, No. 151 Shennong Road, Ju County, Rizhao City, Shandong, 276500, People’s Republic of China
Tel +86 633-6889864
Email [email protected]
Purpose: Peroxiredoxin-6 (PRDX6) is frequently found in various cancers. However, its expression and relevance to proliferation, invasion, and migration in human non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) remain unclear. This study investigated the role and novel mechanism of PRDX6 in progression in an NSCLC cell line (A549).
Methods: We analyzed the expression of PRDX6 in NSCLC and adjacent normal tissues and explored the proliferation, migration, and invasion of A549 cells using either a PRDX6 plasmid or PRDX6 small interfering RNA (siRNA). We also assessed the effects of PRDX6 on the epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) and β-catenin-mediated transcription of target genes.
Results: PRDX6 expression was markedly higher in NSCLC tissues than in adjacent tissues. Proliferation, invasion, and migration of A549 cells were promoted by overexpression of PRDX6 but inhibited by its silencing. PRDX6 overexpression inhibited the protein expression of both phosphorylated β-catenin and E-cadherin, as well as the expression of vimentin, TWIST, and downstream targets of β-catenin including c-MYC, TCF-4, and MMP14. Conversely, PRDX6 silencing markedly decreased the expression of c-MYC, TCF-4, and MMP14, and inhibited EMT in A549 cells. Overexpression of PRDX6 in vivo notably increased the volume and weight of tumors.
Conclusion: PRDX6 overexpression promotes the proliferation, invasion, and migration of A549 cells in vitro and in vivo.
Keywords: PRDX6, non-small-cell lung cancer, β-catenin, metastasis, epithelial–mesenchymal transition
Introduction
NSCLC is the fourth leading cause of mortality worldwide.1 Despite an increasing number of patients benefitting from either surgery or chemoradiotherapy, recurrence and metastasis rates remain high and are regarded as the principal cause of death. As a result, it is crucial to identify the molecular pathogenesis underlying NSCLC progression in order to provide additional therapeutic targets.2,3 Peroxiredoxin-6 (PRDX6) is an important antioxidant protein that can effectively remove intracellular reactive oxygen species and maintain homeostasis. A member of the peroxidase family, PRDX6 is a bifunctional enzyme with phospholipase A2 (PLA2) and peroxidase activity.4,5 Studies have shown that in lung cancer and gastric cancer, PRDX6 promotes cell proliferation and inhibits cancer cell apoptosis; its peroxidase activity promotes the growth of cancer cells, whereas its PLA2 activity promotes the invasion and metastasis of cancer cells. Besides, PRDX6 promotes the occurrence and development of lung cancer by activating Akt, P3K, and p38 kinase, and the PRDX6-mediated CCL5-related JAK2/STAT3 pathway.6,7 Clinical studies have shown increased expression of PRDX6 in NSCLC, suggesting that PRDX6 may be closely related to the occurrence and development of NSCLC; however, its role and mechanism in NSCLC proliferation have not yet been elucidated. As a canonical mediator of the Wnt pathway, β-catenin is believed to be crucial in Wnt signaling transduction cascades and in activation of the transcription of downstream target genes, including T cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor (TCF/LEF) and c-Myc, when stabilized in the cytoplasm and translocated into the nucleus.8,9 Aberrant activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway contributes to various cancers. Nuclear expression of β-catenin is also linked to poor prognosis and chemo/radioresistance in human NSCLC. Further studies have suggested that the inhibition of β-catenin can suppress the proliferation, migration, and invasion of NSCLC cells.10,11 The data demonstrate that β-catenin has a crucial role in NSCLC inhibition. However, the mechanisms underlying the aberrant activation of the β-catenin signaling pathway and the regulation of β-catenin in NSCLC cells remain unknown. This study aimed to determine the expression and function of PRDX6, assess the relationship between PRDX6 and β-catenin in A549 cells, and explore the underlying molecular mechanisms. Taken together, the data indicated that PRDX6 overexpression promoted the proliferation, invasion, and migration of A549 cells in vitro and in vivo.
Materials and Methods
Screening of Differentially Expressed Genes
SangerBox (https://shengxin.ren/) was used to screen differentially expressed genes in NSCLC. The gene expression profiles of NSCLC and normal tissues were determined by V16, a simple TCGA download tool from SangerBox, and the differentially expressed genes were screened by DECenter. The differentially expressed genes were uploaded to the Cytoscape ClueGO software package, and gene ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) network analyses were performed. Volcano plots and heat maps of the differentially expressed genes were produced using the online tools at http://sangerbox.com/.
Materials and Samples
Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) was purchased from Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). Primary antibodies, including PRDX6 (dilution rate: 1:500), E-cadherin (dilution rate: 1:1000), vimentin (dilution rate: 1:1000), TWIST (dilution rate: 1:1500), total β-catenin (dilution rate: 1:500), p-β-catenin (dilution rate: 1:500), TCF-4 (dilution rate: 1:500), MMP-14 (dilution rate: 1:500), c-Myc (dilution rate: 1:500), and β-actin (dilution rate: 1:2000) antibodies, were bought from Chongqing Biomedicine Technology Co., Ltd. (Chongqing, China). A RevertAidTM First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit and Mammalian Protein Extraction Reagent, DMEM, fetal bovine serum (FBS), Opti-MEM, and 0.25% trypsin were bought from Life-iLab, (Shanghai, China). PCR Mix for real-time PCR was ordered from Tsingke Biological Technology (Beijing, China). Transwell® inserts were sourced from Corning Co., Ltd. (New York, USA). Protein beads were from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA, USA). Horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated secondary antibodies were ordered from Chongqing Biomedicine Technology Co., Ltd. (Chongqing, China), and Immobilon Western Chemiluminescent HRP Substrate was bought from Merck KGaA (Darmstadt, Germany). ViaFect™ transfection reagent was from Promega Co., Ltd. (Madison, WI, USA). The pcDNA3.1-PRDX6, pcDNA3.1(+)-β-catenin, and pcDNA3.1(+) (vector) plasmids were constructed by Tsingke Biotech Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). The small interfering RNA (siRNA) sequences were as follows:
PRDX6-siRNA1, 5′-GCTCTGTGGTGCACACTGGG-3′;
PRDX6-siRNA2, 5′-GTAGAGGATAGACAGCTTCA-3′;
PRDX6-siRNA3, 5′-GTTGGGAGCCACGTCCCCGA-3′;
β-catenin-siRNA, 5′-GUAGCUGAUAUUGAUGGACTT-3′;
si-NC, 5′-GACGAAAGCAGTTCGTCTA-3′.
Nude Mouse Tumorigenicity Assay
Human A549 cells were provided by the Cell Center of Beijing Beina Chuanglian Biotechnology Research Institute. Flag-PRDX6 lentivirus was prepared by Chongqing Biomedicine Technology Co., Ltd. Twelve BALB/C male nude mice aged 4–6 weeks, weighing 15–20 g, were provided by Chongqing Mcell Biotechnology Co., Ltd. The nude mice were kept in animal rooms at 23–25 °C and exposed to a 12 h light–dark cycle with free access to food and water. The experiments were carried out after 1 week of adaptive feeding. A549 cells in the logarithmic phase of growth were taken and diluted with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Subcutaneous right axillary inoculation was performed in nude mice at a dosage of 1×107 cells/mouse. Tumor growth was observed every 3 days following the tumor inoculation. The consecutive observations lasted 3 weeks. Following 30 min cell injection, the control group was injected with an empty virus, and the experimental group was injected with Flag-PRDX6 lentivirus (caudal vein injection, 5×107 IU/nude mice). Tumor growth was observed every 3 days following the tumor inoculation. Three weeks later, the nude mice were anesthetized with excessive pentobarbital sodium, and the tumors were removed for measurement.
RNA Isolation and Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
All of the NSCLC tumor tissues and adjacent tissues were collected from the Transfusion Department of the Provincial Hospital Affiliated with Shandong First Medical University, and stored in a freezer at −80 °C. Total RNA was isolated from NSCLC tissues and adjacent non-tumor tissues. The tissues were cut into pieces, placed in a mortar with liquid nitrogen, ground into powder, and mixed with 1 mL TRIzol solution in an EP tube. The tube was left undisturbed for 5 min, then 200 μL chloroform was added with violent shaking for 15 s with the EP tube covered tightly. The tube was centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 10 min, and the supernatant was removed into a new EP tube. Then, 500 μL isopropanol was added and mixed gently, and the tube was left to stand at room temperature for 10 min. Centrifugation was performed at 12,000 rpm for 10 min. The supernatant was discarded, and 1 mL 75% ethanol was added and mixed evenly, followed by centrifugation again at 4 °C and 12,000 rpm for 5 min. This procedure was repeated once. The supernatant was discarded, and the samples were dried at room temperature for 5 min, supplemented with 30 μL DEPC water to dissolve RNA, and stored at −70 °C. The primers used in qPCR were as follows: PRDX6: forward 5′-CAAGGTAGTGTCAGTGTGG-3′ and reverse 5′-GTA ATACGACTCACTATAGGGCG-3′; β-actin: forward 5′-GAGCACAGAGCCTCGCCTTT-3′ and reverse 5′-AGAGGCGTACAGGGATAGCA-3′. PRDX6 gene expression was normalized to that of β-actin. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Provincial Hospital Affiliated with Shandong First Medical University.
Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
Tissue sections were deparaffinized in xylene and rehydrated. After antigen retrieval, samples were blocked with 10% bovine serum albumin. The sections were then incubated with PRDX6 primary antibody and left undisturbed overnight at 4 °C, followed by incubation with the corresponding secondary antibody (BMS011, IGEE, China) at room temperature for 1 h. Finally, the binding antibodies were stained with diaminobenzidine, and the sections were counterstained with hematoxylin. Each test was repeated three times.
Cell Culture
A549 cells were sourced from the Cell Culture Collection Committee of the Chinese Academy of Sciences Library. These cells were cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS at 37 °C and 5% CO2.
PRDX6 Silencing and Overexpression in A549 Cells
Three PRDX6 siRNA oligos and a negative control (NC) were synthesized by RiboBio Co., Ltd. (Guangzhou, China). Cells were seeded in 6-cm dishes overnight and transfected with the three PRDX6 siRNA oligos. A nano fusion transfection reagent (Biomedicine, China) was used to deliver the siRNAs. Next, the medium was discarded and replaced with fresh complete medium for additional incubation of 48 h. Silencing efficiency at the mRNA level was evaluated by real-time PCR. Subsequently, the nano fusion transfection reagent was used to transfect A549 cells with pcDNA3.1-PRDX6 or the vector for 12 h. Finally, fresh complete medium was added for further study.
Co-Immunoprecipitation and Western Blotting
To investigate whether exogenous flagged PRDX6 bound to endogenous β-catenin in A549 cells, cells were infected with 3×Flag-PRDX6 adenovirus for 24 h, collected, and lysed with lysis buffer. Next, either β-catenin monoclonal antibody or control IgG was incubated with cell lysates at 4 °C overnight. Besides, protein A/G PLUS-agarose (Life-iLab, China) was added to cell lysates for incubation 2 h. The agarose beads were rinsed three times with lysis buffer. The precipitates were analyzed by Western blotting.
Cell Viability Assay
The A549 cell viability was determined by CCK-8 assay (Solarbio, China). Cells (5000 per well) were seeded in a 96-well plate, allowed to adhere for 12 h, and followed by cell transection in each group for an additional 48 h. The medium was discarded. Then, 10 μL of CCK-8 reagent was added to each well, and the plate was incubated at 37 °C for 4 h. The absorbance was detected at 450 nm in each well.
Migration and Invasion Assay
Cell migration and invasion ability were determined by transwell assays as per the manufacturer’s instructions. For the migration assay, 100 μL of serum-free medium containing 5×103 cells was incubated in the upper chamber. For the invasion assay, the upper chamber was coated with Matrigel and the lower chamber was coated with 700 μL of complete culture medium. Cells on the upper surface of the upper chamber were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h and then discarded. Invading cells on the lower surface of the upper chamber were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and stained with 1% crystal violet for 10 min.
Detection of Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis by Flow Cytometry
Cell proliferation was detected by flow cytometry according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Life-iLab, China). Cells with a density of 1.5×105/mL were inoculated in a 35 mm diameter petri dish and cultured for 1 day. The culture medium containing 0.4% FBS was synchronized for 3 days, leaving most cells at the G0 stage. Following an addition of 0.03 μg/mL BrdU, incubation was performed at 37 °C for 40 min. The culture medium was discarded and the cells were collected in a flow tube. After centrifugation at 350×g for 5 min, the supernatant was discarded. Each tube was fixed with 1 mL 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 min. The supernatant was discarded following centrifugation again at 600 ×g for 10 min. Each tube was cleaned with 2 mL of glycine, supplemented with 1 mL of 0.5% triton and incubated for 10 min. The cells were rinsed with PBS and resuspended. Cell apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Life-iLab, China). The cells were collected directly in a 10 mL centrifuge tube. The cell count of each specimen was 1×106/mL. Centrifugation was performed at 1000 rpm for 5 min, and the culture medium was discarded. Cells were washed once with incubation buffer, and centrifugation was performed again at 1000 rpm for 5 min. The cells were resuspended in 100 μL of Tag solution and incubated at room temperature in the dark for 10 min. The cells were precipitated and incubated following centrifugation at 1000 rpm for 5 min and then cleaned once with buffer solution. Fluorescence solution was added and incubated in the dark at 4 °C for 20 min with constant shaking. A flow cytometer was used at an excitation wavelength of 488 nm. FITC fluorescence was detected using a filter with a wavelength of 515 nm, and propidium iodide (PI) was detected using a filter with a 560 nm wavelength.
Statistical Analysis
Data from at least three independent experiments are presented as mean±SD. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 17.0. Comparisons between two groups were made with two-tailed Student’s t-tests, and one-way analysis of variance was used for comparison of three or more groups. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
PRDX6 is Highly Expressed in NSCLC
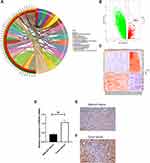
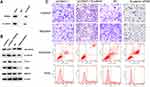
To determine the differences in PRDX6 expression between NSCLC and normal tissue, the gene expression profiles of NSCLC and the normal group were analyzed using SangerBox and Cytoscape. Volcano plots and heat maps of differentially expressed genes revealed that the PRDX6 gene was highly expressed in NSCLC (Figure 1A–C). In this study, the expression of PRDX6 mRNA in 40 NSCLC tissue samples and adjacent non-tumor tissues was determined by qPCR and IHC. The relative expression of PRDX6 mRNA was 1.07±0.12 in NSCLC tissues and 0.42±0.05 in adjacent non-tumor tissues (Figure 1D). PRDX6 mRNA expression in NSCLC tissues was higher than that in adjacent non-tumor tissues. PRDX6 protein was strongly stained in NSCLC tissues, whereas it was weakly stained in adjacent non-tumor tissues (Figure 1E and F), suggesting that PRDX6 was highly expressed in NSCLC tissues.
PRDX6 Overexpression Promotes A549 Cell Proliferation in vitro
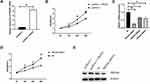
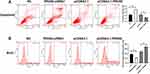
To clarify the regulatory effect of PRDX6 on the proliferation of A549 cells in vitro, PRDX6 was overexpressed and silenced in A549 cells. The effect of PRDX6 on A549 cell proliferation was explored. First, compared with the pcDNA3.1 vector group, the expression of PRDX6 was significantly increased in A549 cells following transfection with pcDNA3.1-PRDX6 (P<0.05) (Figure 2A and E). The CCK-8 results indicated that A549 cell viability was notably increased at 12, 24, and 48 h in the pcDNA3.1-PRDX6 group in comparison with the pcDNA3.1 vector group (P<0.05) (Figure 2B). Second, we silenced PRDX6 mRNA by applying three PRDX6 siRNAs (#1, #2, and #3 oligo sequences); the qPCR results demonstrated that the expression of PRDX6 mRNA in A549 cells was lower in the three PRDX6 siRNA groups than in the NC group (P<0.05) (Figure 2C). Moreover, PRDX6 siRNA #1 oligo silenced PRDX6 expression more effectively than the other siRNA oligos (Figure 2E) and was therefore selected for subsequent studies. The CCK-8 assay revealed that A549 cell viability in the PRDX6 siRNA group was lower than that in the NC group at 12, 24, and 48 h (P<0.05) (Figure 2D). These data demonstrate that PRDX6 regulates the proliferation of A549 cells. The flow cytometry results indicated that the apoptosis rate of A549 cells was decreased and the BrdU positive rate was increased following PRDX6 overexpression. By interfering with PRDX6 expression, the apoptosis rate of A549 cells was elevated and the BrdU positive rate was decreased (Figure 3A and B). The above results demonstrate that PRDX6 can promote proliferation of A549 cells and inhibit their apoptosis.
PRDX6 Overexpression Promotes Migration, Invasion, and EMT of A549 Cells
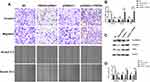
We further investigated the effects of PRDX6 on A549 cell migration and invasion through transwell assays. The results showed that overexpression of PRDX6 markedly promoted the migration and invasion of A549 cells. Compared with control cells, PRDX6 knockdown inhibited migration and invasion of A549 cells (Figure 4A).
Expression of EMT marker proteins (E-cadherin, vimentin, and TWIST) was detected by Western blotting. The results showed that levels of E-cadherin protein in the pcDNA3.1-PRDX6 group were lower than those in the pcDNA3.1-vector group, whereas levels of vimentin and TWIST protein were higher than those in the pcDNA3.1-vector group (P<0.05). Conversely, PRDX6 silencing upregulated E-cadherin in A549 cells but downregulated TWIST and vimentin (Figure 4B–D). Overall, these in vitro results suggested that PRDX6 promotes EMT, migration, and invasion of A549 cells.
PRDX6 Overexpression Promotes β-Catenin Mediated Signaling Pathway in A549 Cells
To clarify the regulatory mechanism of PRDX6, the protein–protein interactions of PRDX6 were analyzed using the STRING database. We found a binding interaction between PRDX6 and β-catenin. To verify this binding interaction, we performed a co-immunoprecipitation assay with A549 cells and found that endogenous PRDX6 interacted with β-catenin (Figure 5A). To explore the effects of PRDX6 on the β-catenin signaling pathway, protein expression of pβ-catenin, β-catenin, and its downstream targets including transcription factor 4 (TCF-4), cellular Myc (c-Myc), and matrix metalloproteinase-14 (MMP14) was evaluated. The Western blotting results indicated that protein levels of p-β-catenin in the PRDX6 overexpression group were markedly decreased, whereas those of β-catenin, TCF-4, c-Myc, and MMP14 were elevated in comparison with the control group (P<0.05) (Figure 5B).
β-Catenin Promotes A549 Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion
Next, to further verify the role of PRDX6 involving β-catenin, we detected the effects of β-catenin on cell invasion, migration, proliferation, and apoptosis of A549 cells. Overexpression of β-catenin promoted cell invasion, migration, and proliferation, and inhibited apoptosis. Silencing with β-catenin inhibited cell invasion, migration, and proliferation, and promoted apoptosis (Figure 5C). The regulatory effects of β-catenin on A549 cells were consistent with those of PRDX6.
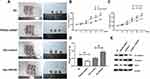
PRDX6 Overexpression Promotes Tumor Growth in vivo
Finally, we further verified the regulatory effect of PRDX6 on A549 in vivo through tumor formation tests in nude mice. A549 cells were injected into nude mice. Following 30 min cell injection, PRDX6 lentivirus and PRDX6-siRNA1 were injected into the tumorigenesis site. Body weight, tumor volume, and tumor weight were recorded every 3 days, for 21 days in total. The results showed a marked increase in tumor volume and weight at 12 days after PRDX6 overexpression. Silencing PRDX6 had the opposite results (Figure 6A–D). The expression change trends of E-cadherin, vimentin, and TWIST observed by Western blotting were consistent with the results of in vitro assays (Figure 6E). To sum up, PRDX6 could promote the proliferation, invasion, and migration of A549 cells, and facilitate tumor growth both in vivo and in vitro.
Discussion
In this study, we analyzed and compared the difference in PRDX6 expression between NSCLC and normal tissue, and overexpressed and silenced PRDX6 expression in NSCLC A549 cells and nude mice in vivo, so as to study the regulatory effect of PRDX6 on NSCLC and its molecular mechanism. The results showed that PRDX6 mRNA expression was upregulated in NSCLC tissues, and that this upregulation of PRDX6 promoted the proliferation, EMT, migration, and invasion of A549 cells. Conversely, PRDX6 silencing inhibited cell proliferation, EMT, and migration. Further research indicated that PRDX6 could interact with β-catenin and inhibit the phosphorylation and degradation of β-catenin, thereby activating downstream targets including c-MYC, TCF4, and MMP14. These results imply that PRDX6 regulates cellular proliferation and metastasis together with β-catenin. As a key regulator of cell proliferation, migration, and polarity, PRDX6 also plays an essential part in tumor evolution, affecting tumor cell proliferation by regulating downstream target genes.
Multiple previous studies have reported PRDX6 in tumors and have shown that the PRDX6 expression promotes the growth of lung cancer cells through its PLA2 activity. Overexpressed PRDX6 promoted the growth of lung cancer cells by upregulating AP-1 and JNK, thereby increasing peroxidase and PLA2 activity.12 Overexpressed PRDX6 also attenuated apoptosis of human ovarian cancer cells induced by TRAIL or cisplatin. In lung and breast cancer, PRDX6 has been shown to positively regulate tumorigenesis and development by activating the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Moreover, PRDX6 regulates Erk1/2 phosphorylation, and Erk1/2 activation also positively affects PRDX6 expression, resulting in a positive feedback loop.6,7 The expression of PRDX6 is upregulated in breast cancer cell lines. MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-435 cell lines overexpressing PRDX6 were established through stable transfection. Compared with untransfected cells, the proliferation potential of both transfected cell lines was markedly increased. However, some studies have found that low expression of PRDX6 increased apoptosis of peroxide-induced hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Decreased PRDX6 expression in liver cancer cells is related to poor prognosis. Furthermore, PRDX6 promoted apoptosis of liver cancer cells treated with TNF-α, indirectly proving that PRDX6 inhibited the growth of these cells. Some studies have found that PRDX6 had no significant effect on the proliferation and apoptosis of skin cancer cells during the occurrence and development of skin cancer. Therefore, PRDX6 may inhibit the formation of new tumors but also stimulate the growth of existing tumors via a dual effect on their occurrence and development. PRDX6 has been shown to promote invasion and metastasis of lung cancer cells by activating Akt, PI3K, and p38 kinases. Studies on human breast cancer cells in vitro have also demonstrated that PRDX6 overexpression could increase the proliferation and invasiveness of cancer cells, and in vivo experiments showed that PRDX6 could enhance in situ tumor growth in nude mice. On the contrary, breast cancer cells with low PRDX6 expression showed decreased growth, invasiveness, and metastasis. Similarly, PRDX6 overexpression could promote tumor cell growth, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer cells in vitro,15–18 as well as promoting the invasion and metastasis of lung cancer, breast cancer, and ovarian cancer cells.13,14 In this study, experiments on A549 cells in vitro and tumor formation in nude mice in vivo showed that PRDX6 could promote the proliferation, migration, and invasion of A549 cells. Our results are consistent with those of previous studies on lung cancer, breast cancer, and ovarian cancer.
β-catenin is an important component of the Wnt pathway. Studies in lung epithelial cells have shown that FoxM1 exerts a tumor inhibitory function by limiting the activity of the classical Wnt signaling pathway. Neuroblastoma represents the most common brain tumor in children; 15% of cases have abnormal activation caused by mutations of Wnt/β catenin signaling pathway components, including β-catenin. Downregulation of β-catenin in the nucleus can inhibit the proliferation and cell cycle progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells and reduce their migration, invasion, and metastasis. We found that overexpression of β-catenin promoted the proliferation of A549 cells, while overexpression of PRDX6 could promote the expression of β-catenin. The co-immunoprecipitation assay showed that PRDX6 was directly bound to β-catenin protein. These results suggest that PRDX6 may affect the proliferation, invasion, and migration of A549 cells by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
In conclusion, by downregulating expression or inducing inactivating mutations, PRDX6 functioned as a tumor promoter in various cancers. This research revealed that PRDX6 mRNA expression in NSCLC tissues was significantly higher than that in adjacent non-tumor tissues. The proliferation of A549 cells was promoted by overexpression of PRDX6 plasmid and inhibited by downregulation of PRDX6. The data demonstrated that PRDX6 was a tumor promoter in NSCLC. NSCLC metastasis is a major cause of death. It is closely related to EMT, which is characterized by loss of epithelial features and an increase in mesenchymal and migration features. Our results suggested that PRDX6 overexpression markedly decreased E-cadherin expression and elevated vimentin and TWIST expression, revealing its crucial role in EMT, migration, and invasion of A549 cells. Aberrant activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway promoted the carcinogenesis and progression of A549 cells. Overall, the current study showed that PRDX6 could bind β-catenin, inhibit phosphorylation, and activate downstream targets of c-Myc, TCF4, and MMP14. By contrast, PRDX6 silencing decreased levels of total β-catenin and expression of the target genes.
Conclusions
Briefly, the evidence suggests that PRDX6 can promote A549 proliferation, migration, and invasion. The findings also indicate that PRDX6, as a tumor promoter in A549 cells, is a potential target for new molecular therapeutic strategies to improve NSCLC patient prognosis.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
The tumor and adjacent tissues of 40 NSCLC patients admitted to the First Affiliated Hospital of Shandong First Medical University were collected. Written informed consent was obtained from each registered patient, and the study complied with the Declaration of Helsinki. The animal experiment complied with the “Regulations on the Management of Laboratory Animals” and the National Institutes of Health’s guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Shandong First Medical University (153633).
Author Contributions
All authors made substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; took part in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; agreed to submit to the current journal; gave final approval of the version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Funding
This work was supported by the Henan Provincial Department of Science and Technology Research Project (172102310116).
Disclosure
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
References
1. Muñoz-Unceta N, Burgueño I, Jiménez E, Paz-Ares L. Durvalumab in NSCLC: latest evidence and clinical potential. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2018;10:1758835918804151. doi:10.1177/1758835918804151
2. Socinski MA, Obasaju C, Gandara D, et al. Clinicopathologic features of advanced squamous NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol. 2016;11(9):1411–1422. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2016.05.024
3. Rolfo C, Caglevic C, Santarpia M, et al. Immunotherapy in NSCLC: a promising and revolutionary weapon. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;995:97–125. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-53156-4_5
4. Lu B, Chen XB, Hong YC, et al. Identification of PRDX6 as a regulator of ferroptosis. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019;40(10):1334–1342. doi:10.1038/s41401-019-0233-9
5. Jia G, Tan B, Ma J, Zhang L, Jin X, Li C. Prdx6 upregulation by curcumin attenuates ischemic oxidative damage via SP1 in rats after stroke. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:6597401. doi:10.1155/2017/6597401
6. Yun HM, Park KR, Park MH, et al. PRDX6 promotes tumor development via the JAK2/STAT3 pathway in a urethane-induced lung tumor model. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015;80:136–144. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.12.022
7. Zha X, Wu G, Zhao X, et al. PRDX6 protects ARPE-19 cells from oxidative damage via PI3K/AKT signaling. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36(6):2217–2228. doi:10.1159/000430186
8. Stewart DJ. Wnt signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014;106(1):djt356. doi:10.1093/jnci/djt356
9. Cai J, Fang L, Huang Y, et al. Simultaneous overactivation of Wnt/β-catenin and TGFβ signalling by miR-128-3p confers chemoresistance-associated metastasis in NSCLC. Nat Commun. 2017;8:15870. doi:10.1038/ncomms15870
10. Xu H, Lin D, Wang L, Liu N, Wang E. [Expression and mutation of β-catenin in non-small cell lung cancer]. Chin J Lung Cancer. 2004;7(5):409–413. doi:10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2004.05.08. Chinese.
11. Wang Y, Liu N, Dai S, Xu H, Wang E. [The relationship between expressions of β-catenin and TCF-4 in non-small cell lung cancer]. Chin J Lung Cancer. 2007;10(5):370–375. doi:10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2007.05.05. Chinese.
12. Yun HM, Park KR, Lee HP, et al. PRDX6 promotes lung tumor progression via its GPx and iPLA2 activities. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014;69:367–376. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.02.001
13. Rushefski M, Aplenc R, Meyer N, et al. Novel variants in the PRDX6 gene and the risk of acute lung injury following major trauma. BMC Med Genet. 2011;12:77. doi:10.1186/1471-2350-12-77
14. Lee HL, Park MH, Son DJ, et al. Anti-cancer effect of snake venom toxin through down regulation of AP-1 mediated PRDX6 expression. Oncotarget. 2015;6(26):22139–22151. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.4192
15. Lin LZ, Wang SM, Zhou JX. [Effects of yiqi chutan recipe on tumor growth, survival time and expressions of PRDX-1 and PRDX-6 in Lewis lung carcinoma model mice with pi-deficiency syndrome]. Chin J Integr Trad West Med. 2011;31(1):99–103. Chinese.
16. Xu R, Pan J, Mei J, Zhang Q. Systematic characterization of prognostic values of peroxiredoxin family in gastric cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:3948183. doi:10.1155/2020/3948183
17. Li Q, Wang N, Wei H, Li C, Wu J, Yang G. miR-24-3p regulates progression of gastric mucosal lesions and suppresses proliferation and invasiveness of N87 via peroxiredoxin 6. Digest Dis Sci. 2016;61(12):3486–3497. doi:10.1007/s10620-016-4309-9
18. Zhang J, Park HS, Kim JA, et al. Flavonoids identified from Korean Scutellaria baicalensis induce apoptosis by ROS generation and caspase activation on human fibrosarcoma cells. Am J Chin Med. 2014;42(2):465–483. doi:10.1142/s0192415x14500311
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.