Back to Journals » Cancer Management and Research » Volume 11
Novel variants of unknown significance in the PMS2 gene identified in patients with hereditary colon cancer
Authors Liccardo R, Della Ragione C, Mitilini N , De Rosa M, Izzo P, Duraturo F
Received 10 October 2018
Accepted for publication 4 April 2019
Published 18 July 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 6719—6725
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S167348
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Raffaella Liccardo,1 Carlo Della Ragione,2 Nunzio Mitilini,2 Marina De Rosa,1 Paola Izzo,1 Francesca Duraturo1
1Department of Molecular Medicine and Medical Biotechnologies, School of Medicine, University of Naples “Federico II”, Naples, Italy; 2UOC Pathological Anatomy, AORN “A. Cardarelli”, Naples, Italy
Background: Lynch syndrome is associated with genetic variants in mismatch repair (MMR) genes. Pathogenic variants in the MLH1 and MSH2 genes occur in most families in which the phenotype is highly penetrant. These testing criteria are likely to miss individuals with Lynch syndrome due to the less penetrant MMR genes, such as MSH6, MLH3, MSH3, and PMS2. So far, several mutations in the PMS2 gene have been described as responsible for the clinical manifestation of Lynch syndrome. Recent data have reported that families with atypical Lynch phenotype were found to have primarily monoallelic mutations in the PMS2 gene.
Methods: We analyzed the PMS2 gene to detect mutations in members of 64 Lynch syndrome families by direct sequencing.
Results: We report the identification of several genetic variants in patients with LS, of which three are novel variants. The carriers of these novel variants were also carried of other variants in PMS2 gene and/or in other MMR genes.
Conclusion: Therefore, we think that these novel PMS2 variants may act in additive manner to manifestation LS phenotype.
Keywords: Lynch syndrome, PMS2 gene, MMR genes, PMS2 variants, synergist effect of MMR variants
Introduction
The primary clinical manifestation of Lynch Syndrome is the development of colon cancer at an average age of 45 years; this syndrome is also characterized by an increased risk of developing extra-colonic tumors such as endometrial, ovarian, stomach, urinary, and biliary tract cancer.1 Families affected by LS were identified using the Amsterdam Criteria (AC) and Bethesda guidelines (BG).2,3 Lynch syndrome (LS) testing criteria were developed based on families with cancer histories across multiple generations. LS is associated with genetic variants in DNA Mismatch Repair (MMR) genes and it is characterized at somatic level by high instability of microsatellite sequences (MSI).4,5 Pathogenic variants in the MLH1 and MSH2 genes occur in most families in which the phenotype is highly penetrant.6,7 Pathogenetic variants in the less penetrant MMR genes, such as MSH6, MLH3, MSH3, and PMS2 were also shown in LS patients.8–10
The PMS2 gene is located on chromosome 7p22 in a region spanning 16 kb and is made up of 15 exons and 862 codons.11 The PMS2 protein acts as a heterodimer together with MLH1 protein forming the MutLα complex that is associated with the MutSα complex, which primarily repairs single-nucleotide mismatches.12 Its function is redundant with the MLH3 gene product. Mice that have the PMS2 gene deleted develop lymphomas and sarcomas but not gastrointestinal tumors; instead, mice lacking PMS2 and MLH3 develop a non-distinguishable phenotype from MLH1 knock-out mice.13 Finally, it has also shown that the PMS2 gene is also involved in the apoptotic pathway.14
So far, several mutations in the PMS2 gene have been described as responsible for the clinical manifestation of Lynch syndrome.15–17 The large rearrangements in the PMS2 gene are rarely described.18,19 Recent studies have demonstrated a reduced penetrance for monoallelic carriers of PMS2 mutations compared to the other MMR genes.20 Moreover, very often homozygous and/or biallelic point mutations in the PMS2 gene have been reported to be responsible for Lynch phenotypes;21,22 as it has been also described that PMS2 mutations together with mutations in other MMR genes should also be considered in patients suspected to present a Lynch syndrome with an unusual early-onset of tumors.23
The aim of this study was to analyze the PMS2 gene to detect mutations in members of 64 LS families. We have identified 21 variants in the PMS2 gene; of which no variant was of certain pathogenetic significance. Most of these variants had previously been described in the literature, only three of these are novel, of which two are missense variants that could alter the functionality of the protein.
Materials and methods
Patients and isolation of genomic DNA
Sixty-four LS patients were recruited from several hospitals in southern Italy; patients were previously established to be negative for pathogenetic mutations in other MMR genes including MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and MLH3 and included large rearrangements in PMS2 gene.19 Twenty-three families with classic LS phenotype were selected by AC 2 and 41 families with atypical Lynch phenotype were selected by MSI analysis as suggested BG1 Sixty samples from healthy patients collected from the Clinical Department of Laboratory Medicine of the hospital affiliated with Federico II University (Naples, Italy) were used as negative controls. The experiments were performed on DNA extracted from peripheral blood lymphocytes. Total genomic DNA was extracted from 4 mL peripheral blood lymphocytes using a BACC2 Nucleon kit (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech, Amersham, UK). The Clinical Department of Laboratory Medicine of the hospital affiliated to Federico II University (Naples, Italy) recruited the subjects after receiving authorization from the local ethics committee “Comitato etico per le attività Biomediche Carlo Romano” of the University of Naples, Federico II (protocol no. 120/10). Once the authorization was obtained, the study received ethical approval, and participants’ informed and written consent was obtained. The experiments were performed on DNA and on cDNA extracted from peripheral blood lymphocytes.
Mutation analysis and in silico analysis
The entire coding region of the PMS2 gene was amplified in 17 fragments, 1 for each exon and 3 overlapping fragments for exon 11, using customized primer sets, available upon request. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products were separated on a 1–2% agarose gel to check for unspecific amplicons. Subsequently, the PCR products were sequenced in both the forward and reverse directions using an ABI 3100 Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems).
The Sorting Intolerant From Tolerant (SIFT) (http://blocks.fhcrc.org/sift/SIFT.html) and Polymorphism Phenotyping (PolyPhen) (http://genetics.bwh.harvard.edu/pph/) tools were used for functional impact prediction of the novel variants, as described in our previous studies.6
Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
IHC was performed on a Benchmark XT automatized immunostainer (Ventana Medical Biosystems, Tucson, AZ, USA). The antibodies used were anti-MSH6, mouse monoclonal clone 44; anti-MSH2, mouse monoclonal clone G219-1129; anti-MLH1, mouse monoclonal clone M1 (Ventana); and anti-PMS2. The procedure was performed as described previously on sections of colon cancer tissues.9
Results
The mutation detection analysis of the PMS2 gene, performed on samples from patients with LS, as described in the Materials and Methods section, identified 21 genetic variants (Table 1). These variants were shown in both families’ groups (AC and BG respecting), casually. No variant of certain pathogenetic significance was identified in this study. Most variants had previously been described in the literature and reported in the MMR variants database of Insight Group (https://insight-database.org/variants/), while three were novel variants, of which two were missense variants. The two novel missense variants were analyzed using a bioinformatic tool that predicted that both these variants were likely pathogenic. These missense variants were identified in three unrelated LS families (Table 2). The genetic variant, c.2248G>A, located in exon 13 of the gene, was identified in a subject who developed right-side colon carcinoma at the age of 34 years. This variant was also identified in the father of this proband, who also developed colon cancer at 40 and in a paternal uncle who developed colon cancer at age 45. Thus, the mutation segregates with the disease in this family. Moreover, this variant was not found in the 60 healthy subjects used as negative controls. In silico analysis indicated that protein function was likely altered as a result of the mutation. The IHC analysis did not provide results due to paraffin-embedded tumoral tissue of poor quality. The father and son of this family were also carriers of unclassified variants in MSH2 genes, a missense variant in exon 3, the c.573C>T (p.Pro125Ser), already reported in “Insight Variants Database” (Table 2). The second novel PMS2 missense variant, the c.2380C>T in exon 14, was identified in two unrelated LS patients, and it was also not found in the 60 healthy subjects used as negative controls. The in silico analysis revealed that this variation has also a high probability of altered protein function; the IHC analysis showed normal expression of the PMS2 protein at the somatic level, (Table 2).
 |
Table 1 Variants identified in the PMS2 gene in our study |
 |
Table 2 Lynch syndrome patients carrier of novel PMS2 variants identified in this study |
Discussion
For many years, the PMS2 gene has been considered a gene candidate for the development of cancer in Lynch Syndrome. However, to date, its role in the development of cancer in Lynch syndrome is still not well understood. It has been reported that monoallelic mutations in the PMS2 gene are responsible for the phenotype found in families that do not fully comply with the Amsterdam criteria or who develop non-LS-related tumors.20 This can be explained considering that mice lacking PMS2 develop lymphomas and sarcomas but not gastrointestinal tumors.12
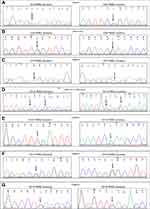
In this study, all variants identified in the PMS2 gene are unclassified, including also the novel variants. Bioinformatics studies have shown that two novel missense variants may be detrimental to the functionality of the protein. In particular, c.2248G>A, identified in exon 13 of the PMS2 gene, was found to segregate with the disease in the AC family and all family members’ carrier of this variant developed colon cancer. Our previous investigations showed that the index case of this family and his father were also carriers of a missense variant in the MSH2 gene, already described in literature as benign variant. Unfortunately, it was not possible to analyze the other affected family members because didn’t available. The MSI analysis performed on tumoral colon tissue of the index case showed a high MSI status (data not shown). Instead, the IHC investigations did not provide reliable results due to poor quality of the paraffin-embedded tumor tissue from the index case; therefore, we have not been able to escape a deficiency of MMR proteins at the somatic level associated with other causes, such as hypermethylation of the MLH1 promoter1 Thus, we speculated that likely these two variants identified in this family may act as low-risk alleles that together determine the deficiency of MMR system, as shown by high MSI status on tumoral DNA of index case. Also the other missense variant identified in this study, the c.2380C>T, in exon 14 of the PMS2 gene was found in two unrelated patients that both showed high MSI status on tumoral colon tissues (data not shown) but a poor one significant family history of LS-related cancers. However, the IHC analysis performed on colon cancer tissue of both index cases (07/6 and 00/12) showed normal expression of MMR proteins, MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2 (Table 2). This last data does not contrast with the result of the MSI rather it reinforces our hypothesis, first formulated; indeed, a missense mutation is predicted to alter the functionality of the protein but not its production. Moreover, also these two patients were carriers of other variants in MMR gene. In particular, the carrier 07/6 showed in addition to novel missense variant also a high numbers of other variants in PMS2 gene (Figure 1) and a variant in MLH3 gene (Table 2). Also, the carrier 00/12 showed two variants in PMS2 (included the novel variant) and one variant in MLH3 gene. Previously, literature data showed that the monoallelic mutations in the PMS2 gene are likely compatible with a more attenuated Lynch phenotype or a low-penetrance20 and, thus in the case of a classical phenotype, a second mutation may also be present in same PMS2 gene or in another MMR genes.23 Even if, all variants identified in this study seem unlikely to have pathogenic effects on protein function it cannot be ruled out that such variants represent low-penetrance alleles rather than benign variants or polymorphisms. Therefore, it is possible that the synergist effect of these low-risk alleles is causing disease manifestation in our patients.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Duraturo F, Liccardo R, De Rosa M, Izzo P. Genetics, diagnosis and treatment of Lynch syndrome: old lessons and current challenges (Review). Oncol Letters. 2019;17(3):3048–3054.
2. Vasen HFA, Watson P, Mecklin JP, Lynch HT. New clinical criteria for hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC, Lynch syndrome) proposed by the International Collaborative group on HNPCC. Gastroenterology. 1999;116:1453–1456.
3. Boland CR, Thibodeau SN, Hamilton SR, et al. A National Cancer Institute Workshop on Microsatellite Instability for cancer detection and familial predisposition: development of international criteria for the determination of microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 1998;58:5248–5257.
4. Duraturo F, Izzo P. Detection analysis of microsatellite instability status for the diagnosis and therapy of Lynch syndrome-related cancers. Biochim Clin. 2018;42(2):152–154.
5. Rasmussen LJ, Heinen CD, Royer-Pokora B, et al. Pathological assessment of mismatch repair gene variants in Lynch syndrome: past, present, and future. Hum Mutat. 2012;33(12):1617–1625. doi:10.1002/humu.22168
6. Duraturo F, Liccardo R, Cavallo A, De Rosa M, Rossi GB, Izzo P. Multivariate analysis as a method for evaluating the pathogenicity of novel genetic MLH1 variants in patients with colorectal cancer and microsatellite instability. Int J Mol Med. 2015;36:511–517. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2015.2255
7. Liccardo R, De Rosa M, Rossi GB, Rigler G, Izzo P, Duraturo F. Characterization of novel, large duplications in the MSH2 gene of three unrelated Lynch syndrome patients. Cancer Genet. 2018;221:19–24. doi:10.1016/j.cancergen.2017.11.008
8. Duraturo F, Liccardo R, Cavallo A, De Rosa M, Grosso M, Izzo P. Association of low-risk MSH3 and MSH2 variant alleles with Lynch syndrome: probability of synergistic effects. Int J Cancer. 2011;129:1643–1650. doi:10.1002/ijc.25824
9. Liccardo R, De Rosa M, Rossi GB, Carlomagno N, Izzo P, Duraturo F. Incomplete segregation of MSH6 frameshift variants with phenotype of Lynch syndrome. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(5). doi:10.3390/ijms18050999
10. Duraturo F, Liccardo R, Izzo P. Coexistence of MLH3 germline variants in colon cancer patients belonging to families with Lynch syndrome-associated brain tumors. J Neurooncol. 2016;129:577–578. doi:10.1007/s11060-016-2203-0
11. Thompson E, Meldrum CJ, Crooks R, et al. Hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer and the role of hPMS2 and hEXO1 mutations. Clin Genet. 2004;65(3):215–225.
12. Hegan DC, Narayanan L, Jirik FR, Edelmann W, Liskay RM, Glazer PM. Differing patterns of genetic instability in mice deficient in the mismatch repair genes Pms2, Mlh1, Msh2, Msh3 and Msh6. Carcinogenesis. 2006;27(12):2402–2408. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgl079
13. Chen PC, Dudley S, Hagen W, et al. Contributions by MutL homologues Mlh3 and Pms2 to DNA mismatch repair and tumor suppression in the mouse. Cancer Res. 2005;65(19):8662–8670. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0742
14. Marinovic-Terzic I, Yoshioka-Yamashita A, Shimodaira H, et al. Apoptotic function of human PMS2 compromised by the nonsynonymous single-nucleotide polymorphic variant R20Q. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(37):13993–13998. doi:10.1073/pnas.0806435105
15. Haraldsdottir S, Rafnar T, Frankel WL, et al. Comprehensive population-wide analysis of Lynch syndrome in Iceland reveals founder mutations in MSH6 and PMS2. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14755. doi:10.1038/ncomms14755
16. Carethers JM, Stoffel EM. Lynch syndrome and Lynch syndrome mimics: the growing complex landscape of hereditary colon cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(31):9253–9261. doi:10.3748/wjg.v21.i31.9253
17. van der Klift HM, Mensenkamp AR, Drost M, et al. Comprehensive mutation analysis of PMS2 in a large cohort of probands suspected of Lynch syndrome or Constitutional Mismatch Repair Deficiency Syndrome. Hum Mutat. 2016;37(11):1162–1179. doi:10.1002/humu.23052
18. van der Klift H, Wijnen J, Wagner A, et al. Molecular characterization of the spectrum of genomic deletions in the mismatch repair genes MSH2, MLH1, MSH6, and PMS2 responsible for hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC). Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2005;44(2):123–138. doi:10.1002/gcc.20219
19. Lo Monte AI, Cudia B, Liccardo R, Izzo P, Duraturo F. Involvement of large rearrangements in MSH6 and PMS2 genes in southern Italian patients with Lynch syndrome. EurJ Oncol. 2018;23(1):47–51.
20. Blount J, Prakash A. The changing landscape of Lynch syndrome due to PMS2 mutations. Clin Genet. 2018;94(1):61–69. doi:10.1111/cge.13205
21. Herkert JC, Niessen RC, Olderode-Berends MJ, et al. Paediatric intestinal cancer and polyposis due to bi-allelic PMS2 mutations: case series, review and follow-up guidelines. Eur J Cancer. 2011;47(7):965–982. Epub 2011 Mar 4. Review. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2011.01.013
22. Stark Z, Campbell LJ, Mitchell C, et al. Clinical problem-solving. Spot diagnosis. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(23):2229–2236. doi:10.1056/NEJMcps1302661
23. Bougeard G, Olivier-Faivre L, Baert-Desurmont S, et al. Diversity of the clinical presentation of the MMR gene biallelic mutations. Fam Cancer. 2014;13(1):131–135. doi:10.1007/s10689-013-9676-1
24. Hendriks YM, Jagmohan-Changur S, van der Klift HM, et al. Heterozygous mutations in PMS2 cause hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal carcinoma (Lynch syndrome). Gastroenterology. 2006;130(2):312–322
25. Nicolaides NC, Papadopoulos N, Liu B, et al. Mutations of two PMS homologues in hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer. Nature. 1994;371(6492):75–80
26. Viel A, Novella E, Genuardi M, et al. Lack of PMS2 gene-truncating mutations in patients with hereditary colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol. 1998;13(3):565–569
27. Wang Q, Lasset C, Desseigne F, et al. Prevalence of germline mutations of hMLH1, hMSH2, hPMS1, hPMS2, and hMSH6 genes in 75 French kindreds with nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. Hum Genet. 1999;105(1-2):79–85
 © 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.