Back to Journals » OncoTargets and Therapy » Volume 11
NOP7 interacts with β-catenin and activates β-catenin/TCF signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
Authors Wu N, Zhao J, Yuan Y, Lu C, Zhu W, Jiang Q
Received 4 February 2018
Accepted for publication 23 June 2018
Published 1 October 2018 Volume 2018:11 Pages 6369—6376
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S164601
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Samir Farghaly
Nan Wu,1 Jing Zhao,2,3 Youhua Yuan,4 Chuanjia Lu,1 Wenjing Zhu,1 Qun Jiang1
1Department of Clinical Laboratory, Shanghai Stomatological Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, People’s Republic of China; 2Department of General Surgery, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, People’s Republic of China; 3Cancer Metastasis Institute, Fudan University, Shanghai, People’s Republic of China; 4Department of Clinical Laboratory, Henan Provincial People’s Hospital, Zhengzhou, People’s Republic of China
Background: The hyperactivation of β-catenin signaling is frequently observed in clinical hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) samples. Further understanding the mechanisms involved in activating β-catenin/TCF signaling would benefit the treatment of HCC.
Method and results: Here, it was found that NOP7 was a binding partner of β-catenin. NOP7 strengthened the interaction between β-catenin and TCF4, which led to the activation of β-catenin/TCF signaling. The upregulation of NOP7 in HCC promoted the growth (in both liquid culture and soft agar) and migration of HCC cancer cells.
Conclusion: Taken together, we have demonstrated the oncogenic functions of NOP7 in HCC, suggesting that targeting NOP7 would benefit the treatment of HCC.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, NOP7, β-catenin/TCF pathway, cell growth, cell migration
Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a very common malignancy in Asian countries, and its outcome is still very poor.1 Therefore, illustrating the mechanisms involved in HCC would help in designing treatments for this disease.
An inactive mutation of Axin or a constitutive mutation of β-catenin are very common in HCC, which leads to the activation of β-catenin/TCF signaling.2,3 Cytoplasmic and nuclear accumulation of β-catenin in HCC cells was found in approximately 80% HCC tissues, suggesting a role for the overactivation of β-catenin/TCF signaling in the development of HCC.3,4 In the absence of Wnt ligand, β-catenin is phosphorylated and destroyed by the destruction complex.5,6 The stimulation of Wnt ligand disassociates the β-catenin destruction complex, and the β-catenin protein level becomes elevated in the cytoplasm, β-catenin then translocates to the nucleus. In the nucleus, β-catenin interacts with TCF4 to promote the expression of downstream genes (N-cadherin, vimentin, Snail, and cyclinD1).7,8 The activity of β-catenin/TCF signaling is critical for the malignant behaviors of HCC cells.9–11 The regulation of β-catenin/TCF signaling occurs at multiple levels.12,13 However, how the β-catenin/TCF complex is regulated remains largely unknown.
NOP7 is localized in the nucleus and includes a BRCA1 interaction domain in the C-terminus.14 NOP7, BOP1, and WDR12 form the PeBoW complex and promote cell proliferation.15,16 Moreover, NOP7 is essential for the proliferation and tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells.17 However, its roles in HCC remain largely unknown. In this study, the expression of NOP7 in HCC tissues and its functions and molecular mechanisms were studied.
Materials and methods
Cell culture
All of the cell lines used in this study were purchased from the Cell Bank of Shanghai Institutes for Biological Science (Shanghai, People’s Republic of China). Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Gibco, Waltham, MA, USA), 100 units/mL penicillin, and 100 g/mL streptomycin were used to culture these cell lines, which were incubated with 5% CO2 at 37°C.
Clinical samples
The clinical samples and paired noncancerous tissues were obtained from patients at Shanghai Stomatological Hospital after obtaining their consent. The clinical samples were kept in liquid nitrogen. This study was performed after being approved by the ethics committee of Fudan University. All patients provided written, informed consent. All experiments were performed following relevant and national guidelines and regulations of Fudan University.
Western blot analysis
Cellular proteins and proteins from the tissues were extracted using RIPA buffer. After separating the proteins by SDS-PAGE, they were then transferred to PDVF membranes. The blocking was performed using 5% BSA solution at room temperature for approximately 40 minutes. Then, the membrane was incubated with primary antibodies overnight. On the second day, TBST solution was used to wash the membrane, and the membrane was then sequentially incubated with secondary antibody for 1 hour at room temperature. The proteins were visualized by an ECL kit.
Immunohistochemistry
After deparaffinizing and rehydrating fixed sections using gradually decreasing concentrations of xylene and ethanol, the sections were incubated with 0.3% H2O2 solution for 30 minutes at room temperature. Sodium citrate solution (pH 6.0) was used for antigen retrieval. The sections were blocked with BSA solution to diminish nonspecific binding. Then, the sections were stained with NOP7 antibody and were visualized with secondary antibody (Envision, Gene Technology, Shanghai, China). Slides were then developed with DAB and counterstained with hematoxylin.
GST pull-down
A fusion protein was obtained by cloning the coding sequence of β-catenin into the pGEX-4T-1 vector. A 7404 cell lysate was prepared using lysis buffer containing 50 mM Tris-Cl (pH 7.5), 150 mM NaCl, 0.1% NP40, and protease inhibitor cocktail. A total of 5 μg of GST-NOP7 fusion protein was mixed with 500 μg of cell lysate and was incubated at 4°C for 4 hours. Then, glutathione-Sepharose-4B beads were mixed with the samples and incubated at 4°C for an additional 1 hour. The beads were collected by centrifugation and washed with lysis buffer. Finally, Laemmli buffer was used to elute the proteins bound to the beads, and SDS-PAGE was performed.
Immunoprecipitation assay
Cell lysates were prepared with RIPA buffer. After centrifugation, the supernatant was incubated with the antibody overnight at 4°C. Then, the protein A beads were mixed with the supernatant for another 4 hours. Finally, Laemmli buffer was used to elute the proteins bound to the beads, and SDS-PAGE was performed.
Plasmids
The coding sequences of NOP7, β-catenin, and TCF4 were amplified by PCR and were inserted into pCMVTag2B (Flag tag), pcDNA3.1 (myc tag), and pCMV-HA (HA tag) plasmids, respectively.
Downregulation of NOP7 in HCC cells
RNAi lentivirus particles (sh con and sh NOP7) were provided by GeneChem (Shanghai, People’s Republic of China). The same multiplicity of infection of virus was incubated with cells for 8 hours to knock down NOP7 expression. Then, the cells were incubated with medium containing puromycin for 2 weeks, and the puromycin-resistant cells were pooled.
Topflash
Then, 7404 cells were seeded in 24-well plates. On the next day, the Topflash assay was performed by cotransfection of Topflash (0.1 μg), expression vector (0.5 μg) and TK Renilla (0.05 μg). Two days later, cells were incubated with Wnt3a (100 ng/mL) protein. Then, the reporter activity was measured using the dual-luciferase reporter assay system (Promega, Madison, WI, USA).
Cell motility assay
The upper Boyden chamber was filled with 0.05 mL of medium (1% FBS) containing 2×105 cells, and the lower chamber was filled with 0.15 mL of medium (10% FBS). Eight hours later, traditional hematoxylin and eosin staining was performed to examine cells that had migrated to the lower surfaces of the filters. Cells were photographed, and statistical analysis was performed.
MTT assay
The growth rate of HCC cells was determined using MTT. Every 48 hours, the growth rate of the HCC cells was determined by incubating the cells with MTT solution (50 μg/well) for 4 hours. Then, DMSO was used to dissolve the cells, and the OD value was measured at 540 nm.
Soft agar assay
First, a bottom layer with 0.5% agarose and 10% FBS in DMEM was used to coat the 24-well plate. An upper layer with 0.35% agarose and 10% FBS in DMEM containing HCC cells (2,000 cells/well) was then laid on the bottom layer. Two weeks later, the foci were photographed, and statistical analysis was performed.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t-test (2-tailed) with GraphPad Prism software (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA). Differences with P<0.05 were considered statistically significant. Data are represented as the means ± standard error of the mean.
Results
The NOP7 mRNA and protein levels were elevated in HCC
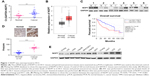
We first tested the NOP7 mRNA levels in the paired HCC tissues and noncancerous tissues. Compared with the noncancerous tissues, the NOP7 mRNA level in the HCC tissues was higher (Figure 1A), which was consistent with the observation after searching the GEPIA database (Figure 1B). We next examined the NOP7 protein levels in the HCC tissues and paired normal tissues. Both Western blot (6/6) and immunohistochemical staining revealed that the NOP7 protein level was increased in HCC samples (Figure 1C and D). Moreover, the NOP7 protein levels in normal liver cell lines (L02 and Chang) and HCC cell lines (7404, Hep3B, HepG2, QGY, MHCC97H, HLE, HLF, and Huh7) were tested. The NOP7 protein level was lower in normal liver cells and higher in HCC cells (Figure 1E). In addition, we searched the GEPIA database and correlated the expression of NOP7 with survival and found that NOP7 expression predicted poor survival (Figure 1F). Collectively, these data revealed that NOP7 was upregulated in HCC.
NOP7 accelerated the growth and enhanced the migration of HCC cells
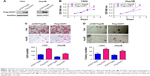
To further investigate the functions of NOP7 in HCC, NOP7 (Flag-NOP7) vectors were transfected into 7404 and Hep3B cells, and the expression of Flag-NOP7 was confirmed by Western blot analysis (Figure 2A). Then, we used the MTT assay, the Boyden chamber assay and the soft agar assay to examine the growth and motility of HCC cells. Forced expression of NOP7 in 7404 and Hep3B cells accelerated cellular growth in the MTT assay (Figure 2B), enhanced migration (Figure 2C) in the Boyden chamber assay, and promoted colony formation in the soft agar assay (Figure 2D).
To test the endogenous functions of NOP7 in HCC, NOP7 expression in 7404 and Hep3B cells was knocked down using 2 independent sequences (Figure 3A). Knocking down NOP7 impaired the growth (Figure 3B), migration (Figure 3C), and colony formation (Figure 3D) of 7404 and Hep3B cells. In summary, these results demonstrated that NOP7 is important for the growth and migration of HCC cells.
NOP7 elevated the transcriptional activity of the β-catenin/TCF complex in HCC cells
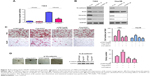
Next, we screened the pathways regulated by NOP7 using a reporter assay. Downregulation of NOP7 impaired the activity of Topflash (Figure 4A). Furthermore, downregulation of NOP7 in 7404 and Hep3B cells decreased the protein expression levels of N-cadherin, Snail, vimentin, and CyclinD1 (β-catenin/TCF complex downstream genes) (Figure 4B). These results indicated that NOP7 was essential for the activation of β-catenin/TCF signaling. Moreover, downregulation of β-catenin rescued the functions of NOP7, such as the migration and colony formation of HCC cells (Figure 4C and D).
NOP7 bound to β-catenin
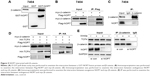
Next, we examined the position of NOP7 in the β-catenin/TCF signaling pathway. A GST pull-down assay showed that NOP7 interacted with β-catenin (Figure 5A). Immunoprecipitation using 7404 cell lysate demonstrated that exogenously expressed NOP (Flag-NOP) and β-catenin (myc-β-catenin) formed a complex (Figure 5B). Moreover, endogenously expressed NOP7 and β-catenin were in the same complex (Figure 5C). These observations demonstrated that NOP interacted with β-catenin. Furthermore, NOP7 bridged β-catenin and TCF4 together (Figure 5D and E). Collectively, these findings indicated that NOP7 activated β-catenin/TCF4 by strengthening the binding between β-catenin and TCF4.
NOP7 promoted the tumorigenesis of 7404 cells
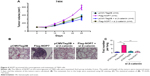
To examine the functions of NOP7 in vivo, we subcutaneously injected 7404 cells into nude mice. The growth of tumors was represented by the tumor volume. As shown in Figure 6A, NOP7 overexpression promoted the tumorigenesis of 7404 cells, which was impaired by knocking down β-catenin (Figure 6A). After the mice were sacrificed, the metastatic foci in the lung tissues were examined. More metastatic foci were observed in the lungs of the mice injected with 7404 cells overexpressing NOP7 (Figure 6B and C). Taken together, these data suggested that NOP7 promoted the tumorigenesis and metastasis of 7404 cells.
Discussion
Although the functions of NOP7 in the assembly of Pre-60S ribosomal subunit have been investigated,18,19 the functions of NOP7 in cancer have been rarely studied. This study has clearly shown that NOP7 expression was elevated in HCC tissues. NOP7 promoted cellular growth, migration, and colony formation and positively regulated the growth, migration, and colony formation of cancer cells. Moreover, NOP7 was determined to be a binding protein of β-catenin and bridged the interaction of β-catenin and TCF4. These observations clearly demonstrated the tumor-promoting roles of NOP7 in the progression of HCC. In addition, these observations suggested that NOP7 regulated β-catenin/TCF signaling. Based on the finding that β-catenin/TCF signaling is aberrantly active in HCC, targeting NOP7 might be a promising strategy.
The most interesting observation in this study is the identification of NOP7 as the binding protein for β-catenin. The regulation of β-catenin/TCF signaling remains largely unknown. Several proteins have been reported to modulate the interaction between β-catenin and TCF4. For example, ICAT has been found to destroy the binding between β-catenin and TCF4 and, thus, to inhibit β-catenin/TCF signaling.20 Therefore, further determination of the binding domain between β-catenin and NOP7 would provide novel insights.
In summary, we have shown that NOP7 enhanced the motility of HCC cancer cells. NOP7 also activated β-catenin/TCF signaling, a major modulator of the epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Moreover, knocking down NOP7 expression inhibited the expression of mesenchymal markers (N-cadherin and vimentin). These observations indicated that NOP7 might promote the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of HCC cells.
In conclusion, NOP7 promoted the progression of HCC, suggesting that NOP7 might be a potential target for the treatment of this disease.
Ethical approval
Ethical and legal approval was obtained prior to the commencement of the study. Fudan University gave the approval. Written confirmation has been given, and all experiments were performed following relevant and national guidelines and regulations of Fudan University.
Author contribution
Nan Wu designed this project. Jing Zhao, Youhua Yuan, Chuanjia Lu, Wenjing Zhu, and Qun Jiang did the assay. All authors contributed toward data analysis, drafting and critically revising the paper and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67(1):7–30. | ||
Mazzoni SM, Fearon ER. AXIN1 and AXIN2 variants in gastrointestinal cancers. Cancer Lett. 2014;355(1):1–8. | ||
Park JY, Park WS, Nam SW, et al. Mutations of beta-catenin and AXIN I genes are a late event in human hepatocellular carcinogenesis. Liver Int. 2005;25(1):70–76. | ||
Taniguchi K, Roberts LR, Aderca IN, et al. Mutational spectrum of beta-catenin, AXIN1, and AXIN2 in hepatocellular carcinomas and hepatoblastomas. Oncogene. 2002;21(31):4863–4871. | ||
Heintze JM. Developmental biology: renewal of NPCs requires MYC and β-catenin. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017;13(12):723. | ||
Buckland J. Bone: anabolic Wnt/β-catenin signalling: osteocytes are key. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11(3):128. | ||
Kypta RM, Waxman J. Wnt/β-catenin signalling in prostate cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 2012;9(8):418–428. | ||
Leavy O. Mucosal immunology: β-catenin calms the gut. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10(10):682. | ||
Tuo H, Wang Y, Wang L, et al. MiR-324-3p promotes tumor growth through targeting DACT1 and activation of Wnt/β-catenin pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2017;8(39):65687–65698. | ||
Dong L, Li Z, Xue L, et al. DIAPH3 promoted the growth, migration and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by activating beta-catenin/TCF signaling. Mol Cell Biochem. 2018;438(1–2):183–190. | ||
Liu L, Wu J, Wang S, et al. PKMYT1 promoted the growth and motility of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by activating beta-catenin/TCF signaling. Exp Cell Res. 2017;358(2):209–216. | ||
Nusse R, Clevers H. Wnt/β-catenin signaling, disease, and emerging therapeutic modalities. Cell. 2017;169(6):985–999. | ||
Clevers H, Nusse R. Wnt/β-catenin signaling and disease. Cell. 2012;149(6):1192–1205. | ||
Adams CC, Jakovljevic J, Roman J, Harnpicharnchai P, Woolford JL Jr. Saccharomyces cerevisiae nucleolar protein Nop7p is necessary for biogenesis of 60S ribosomal subunits. RNA. 2002;8(2):150–165. | ||
Thoms M, Ahmed YL, Maddi K, Hurt E, Sinning I. Concerted removal of the Erb1-Ytm1 complex in ribosome biogenesis relies on an elaborate interface. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44(2):926–939. | ||
Romes EM, Sobhany M, Stanley RE. The crystal structure of the ubiquitin-like domain of ribosome assembly factor Ytm1 and characterization of its interaction with the AAA-ATPase midasin. J Biol Chem. 2016;291(2):882–893. | ||
Killian A, Le Meur N, Sesboüé R, et al. Inactivation of the RRB1-Pescadillo pathway involved in ribosome biogenesis induces chromosomal instability. Oncogene. 2004;23(53):8597–8602. | ||
Tang L, Sahasranaman A, Jakovljevic J, Schleifman E, Woolford JL Jr. Interactions among Ytm1, Erb1, and Nop7 required for assembly of the Nop7-subcomplex in yeast preribosomes. Mol Biol Cell. 2008;19(7):2844–2856. | ||
Miles TD, Jakovljevic J, Horsey EW, Harnpicharnchai P, Tang L, Woolford JL Jr. Ytm1, Nop7, and Erb1 form a complex necessary for maturation of yeast 66S preribosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25(23):10419–10432. | ||
Tago K, Nakamura T, Nishita M, et al. Inhibition of Wnt signaling by ICAT, a novel beta-catenin-interacting protein. Genes Dev. 2000;14(14):1741–1749. |
 © 2018 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2018 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.