Back to Journals » Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare » Volume 14
Multidisciplinary Provision of Food and Nutritional Care to Hospitalized Adult In-Patients: A Scoping Review
Authors Yinusa G, Scammell J , Murphy J , Ford G, Baron S
Received 18 August 2020
Accepted for publication 24 November 2020
Published 22 February 2021 Volume 2021:14 Pages 459—491
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JMDH.S255256
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Scott Fraser
Gladys Yinusa,1 Janet Scammell,1 Jane Murphy,2 Gráinne Ford,3 Sue Baron1
1Department of Nursing Science, Faculty of Health and Social Sciences, Bournemouth University, Bournemouth, Dorset, UK; 2Ageing and Dementia Research Centre, Faculty of Health and Social Sciences, Bournemouth University, Bournemouth, Dorset, UK; 3Dietetic Department, The Royal Bournemouth and Christchurch Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Bournemouth, Dorset, UK
Correspondence: Gladys Yinusa Email [email protected]
Purpose: Multidisciplinary approaches to nutritional care are increasingly emphasized and recommended. However, there is little evidence of how different disciplines work together collaboratively to deliver optimum quality care to adult in-patients. This scoping review aimed to describe the existing literature on multidisciplinary collaboration to identify the various disciplines involved and the features that influence collaborative working in implementing multidisciplinary food and nutritional care with adult in-patients.
Methods: Multiple databases were searched, including MEDLINE Complete, Embase, CINAHL Complete, HMIC, and Scopus, from their inception to December 2019. Data were retrieved from eligible studies. A narrative description of findings is reported with respect to the disciplines involved, the aspects of nutritional care explored, and the collaborative processes categorized using the input, process, and outcome framework.
Results: Thirty-one studies with heterogeneous study designs met the eligibility criteria. Studies were undertaken in six countries. Findings show a wide diversity of multidisciplinary collaborations in various aspects of nutritional care in all studies. Multidisciplinary nutritional care provision was facilitated by several processes, including training and development, communication and information sharing, and clinical leadership and management support. Outcomes were reported at the patient, team, and organizational levels.
Conclusion: This review reveals the significance of the interrelationship between different disciplines and their complementary contributions towards the delivery of optimal food and nutritional care. Key aspects include the involvement of different disciplines, the clarification of roles and multidisciplinary interrelationships, communication, information sharing, clinical leadership, and management support, all of which facilitated collaborative working. Our review uncovered that these features can significantly influence multidisciplinary working. This review is the first to present literature concerning the attributes that affect collaborative working. Further research is recommended specifically around multidisciplinary nutritional care processes and conditions that allow for better collaborative working.
Keywords: malnutrition, adult in-patient, hospital, multidisciplinary care, nutritional care
Introduction
Providing food and nutritional care in hospitals is integral to patient-centered care. This involves responding to changing nutritional requirements and patients’ needs, which will vary depending on their health status. In hospitals, malnutrition (as undernutrition) is a significant clinical concern with well documented adverse consequences, including a compromised immune system in affected patients and clinical complications, increased readmissions, and mortality.1,2 To prevent these complications, patients with or at risk of malnutrition must be identified and treated efficiently and effectively.3,4 There is a growing awareness of not only the prevalence of malnutrition but also compliance difficulties with standardized nutritional care practices, including the use of validated screening tools, referral for diagnosis, treatment, and nutritional management plans for patients.5,6 The consequences of malnutrition for patients are significant and have implications for healthcare providers. These require the skills of many disciplines if they are to be managed successfully.7,8
There is a growing emphasis in economically developed countries for healthcare professionals to collaborate in delivering nutritional care. In a call to action, the interdisciplinary body, the Alliance to Advance Patient Nutrition based in the United States, has stressed the importance of addressing malnutrition using an interdisciplinary approach and strategies.8 These depend on different stakeholders, including patients, families, volunteers, and multidisciplinary professionals.
Multidisciplinary roles and responsibilities are also significant in achieving improvements in overall care quality.9 In response to the need for a change in practice and improved service implementation approaches, an Australian action research study developed a Systematized, Interdisciplinary Malnutrition Pathway for imPLEmentation and Evaluation (SIMPLE) in hospitals. While it has yet to be evaluated, the interdisciplinary SIMPLE model aims to improve malnutrition management and nutritional care within hospital environments.10
A range of terms is sometimes used interchangeably to describe collaborative working practices such as “interdisciplinary,” “multidisciplinary,” and “transdisciplinary” care. However, for the purpose of this paper, the term multidisciplinary care will be used to refer to a group of professionals from two or more disciplines who work on the same project, independently or in parallel.11 The term team refers to a group of people with complementary skills who are committed to a common purpose (in this case, nutritional care), performance goals, and approach for which they hold themselves mutually accountable.12 Furthermore, in this review, the term nutritional care is taken to mean a coordinated approach to the delivery of food and fluids by different healthcare professionals and views the patient as an individual with needs and preferences.13 Volunteers and service users (patients) are included within this context of collaborative nutritional care.
Arguably, previous studies and reviews on nutritional care have had a narrower focus. For example, the effectiveness of mealtime interventions to improve nutritional intake for adult patients.14 While other studies investigated and reported findings on meal assistance or supportive interventions aimed at enhancing intake.15,16 However, the review undertaken by Rasmussen et al,17 specifically examined the effectiveness of multidisciplinary nutritional care, including nutritional support and dietary counseling in older hospitalized patients. It concluded that multidisciplinary nutritional support improves patients’ quality of life and has a positive effect on mortality. Conversely, our review focuses on exploring the different disciplines involved in the collaborative approach and activities undertaken not just with healthcare professionals but also with patients, relatives, and volunteers. In summary, despite support for the benefits of multidisciplinary care models, there is a dearth of information on the processes associated with effective collaborative working and the conditions that allow for the coordination of activities in delivering optimal nutritional care. Furthermore, multidisciplinary care is not without challenges.18–20,72 There appears to be a limited understanding of how the different components of a collaborative approach can individually and collectively affect nutritional care outcomes in this context. These also include the features that enable successful collaborative working to deliver optimum quality care to adult in-patients. Therefore, our review describes the existing literature on multidisciplinary collaboration to identify the different disciplines involved and explore the features of collaborative nutritional care approaches for adult in-patients receiving nutritional intake (excluding patients requiring specialized artificial nutritional support).
Review Question
The questions that guided this scoping review were:
What are the features of multidisciplinary collaborative care approaches in the provision of food and nutritional care to adult in-patients?
What disciplines are involved in multidisciplinary collaboration, and what aspects of nutritional care are explored?
What collaborative activities, processes, and outcomes of multidisciplinary nutritional care are reported?
Methods
This scoping review was conducted in accordance with the Joanna Briggs Institute’s (JBI)21 formal guidance for scoping reviews. This methodology was chosen to address the research questions as its exploratory nature allows for the synthesis of the different forms of existing literature uncovered.21 Results are reported following the guidelines for the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR).22 Our protocol is registered on protocols.io. (where doi.org/10.17504/protocols.io.bgzajx2e is the unique DOI).76
Search Strategy
The search strategy targeted primary studies and followed the three-step process recommended by JBI to identify both published studies and unpublished studies in gray literature. The text words contained in the titles and abstracts of relevant articles and the index terms used to describe the articles were used to develop a full search strategy. The search strategy was devised for the Medline Complete database and later adapted for each subsequent database. Databases were searched from the date of their inception to December 2019. An illustrative example from the search in Medline Complete is provided in Appendix 1. The reference list of articles selected for full-text review was screened for additional papers. Search terms included nutritional care, multidisciplinary, interdisciplinary, interprofessional, and collaborative (see Appendix 1).
Information Sources
The following electronic databases were searched: Medline Complete, Embase, Cochrane, CINAHL Complete, HMIC, BNI, and Scopus. Searches were also conducted in NICE Evidence, OpenGrey, ClinicalTrials.gov, and Epistomonikos for unpublished studies and gray literature.
Inclusion Criteria
The inclusion criteria for this scoping review follow the types of Participants, Concept, and Context (PCC) components stipulated by JBI. The PCC components specify the basis upon which sources were considered for inclusion as described in the next three sections.21
Types of Participants
The participant group of focus for this review was: any hospital staff whose role contributed to nutritional care provision. Such as those from allied health professions, medicine, nursing, clinical pharmacy, the wider healthcare team, and non-clinical support personnel, including volunteers, patients, and relatives. The review included studies focusing on patients who were adults or groups of adult in-patients with or at risk of malnutrition. The adult patient group was defined as patients aged 18 years and above.
Concept
The concepts of interest in this review were features of multidisciplinary collaborative care approaches in delivering nutritional care to patients in hospitals.
The aspects of nutritional care explored were identified using the guidelines on terminology and definitions set out by the European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism (ESPEN).23 For instance, nutritional care processes in a systematic sequence involve distinct, interrelated steps in the provision of nutritional care (such as malnutrition risk screening, nutritional assessment, diagnostic procedures, and nutritional care plan). While the classification of forms and products represents the many ways nutrition care and therapy can be provided (such as meal environment and diets).23 Only studies that focused on multidisciplinary nutritional care and adopted multidisciplinary collaborative approaches were considered for inclusion. Multidisciplinary interventions involving two or more professional groups across different stages of the patient’s nutrition pathway, such as assessment, eating support, and meal environment, were included.
In this review, literature that focused on multidisciplinary working with patients requiring specialized artificial nutritional support such as enteral and parenteral nutrition were excluded. Studies that focused primarily on the prevalence of disease conditions or risk factors leading to malnutrition were likewise excluded.
Context
Interventions with a primary focus on providing nutritional care outside the context of the hospital setting (as in the community and home care) were excluded. Only studies implemented within hospital settings and with a multidisciplinary follow-up after discharge were included. As original studies were of interest to this review, secondary sources of evidence such as case studies, systematic reviews, and literature reviews were not included in the analysis. However, their reference list was reviewed to identify any further primary research.
Types of Sources
The scoping review included qualitative, quantitative, and mixed-methods study designs. Published and unpublished (gray literature) papers in English that met the eligibility criteria were included. A formal quality assessment of the included studies was not conducted; however, research quality was discussed between authors with specific emphasis on the nature, reporting, and general quality of the evidence. Moreover, this is an optional step in the PRISMA extension checklist for scoping reviews.22
Study Selection
Study selection was an iterative process of screening abstracts and revising the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Following the search, all identified records were collated and uploaded into EndNote X9.2 Clarivate Analytics. The first author retrieved and screened titles and abstracts of all articles for relevance (GY). The selected abstracts were screened by three independent reviewers (JS, JM, GF) for assessment against the inclusion criteria to ensure validity. Full-text papers that did not meet the inclusion criteria were further excluded with reasons. Any disagreements that arose between the reviewers were resolved by arbitration involving a fourth reviewer and subsequently through discussion as a team.
Data Extraction
Information was collected using the data extraction tool presented in Appendix 2, developed and reviewed by the review team. The extracted data included the study aim, study population, and specific details about the professional disciplines involved, including patients, relatives, or volunteers. The reported collaborative approach to nutritional care, the study context, methods, and outcomes relevant to the review questions were also extracted. While the studies retrieved utilized different terminology (Interdisciplinary rounds or multi-disciplinary audit), the term “multidisciplinary care” is used in the presentation of the review findings. One author (GY) extracted data and subsequently verified by three reviewers (JS JM GF). All disagreements that arose between the reviewers were resolved through discussion.
Data Presentation
Studies were reviewed and reported based on their characteristics. They were structured in descriptive themes or a narrative format related to multidisciplinary care inputs, processes, and outcomes (IPO), using a framework adapted from McGrath.24 The IPO framework is a widely used guide for understanding and explaining group research; hence, it is especially valued in “teamwork” literature.25,26 The framework has also been applied in various ways in other literature, including systematic and scoping reviews.27,28
Results
In this section, the characteristics of the retrieved studies are described. A total of 1992 studies were retrieved from the literature search, and these were reduced to 1601 after the removal of duplicates. After title and abstract screening against eligibility criteria, 121 potential articles remained for a full review. A total of 31 studies published between January 1996 and December 2019 were identified as eligible for inclusion in the review.29,30 Excluded articles either did not focus on multidisciplinary collaborations in hospitals31 or as a nutritional care component or only examined the functionality and usage of a nutritional care tool by staff.32 A flow chart showing the number of studies at each stage is detailed in Figure 1.
 |
Figure 1 PRISMA diagram. Search strategy and study selection process. Abbreviations: NC, nutritional care; MD, multidisciplinary; MDT, multidisciplinary teams; PEG, percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy. Notes: PRISMA figure adapted from Liberati A, Altman D, Tetzlaff J, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. Journal of clinical epidemiology. 2009;62(10). Creative Commons.77 |
Study Characteristics
Location and Setting
The retrieved studies originated in six countries or regions, to wit: The United Kingdom (n=15), United States (n=1), Australia (n=11), Canada (n=2), and one each from the Netherlands and Scandinavian countries (Denmark, Norway, and Sweden). The majority of studies were conducted with patients aged 65 years or older. The studies were conducted in hospitals, including elderly care units or older persons’ wards, medical, orthopedic, trauma, geriatric, oncology, respiratory, or gastrointestinal wards. Some studies did not specify ward type or were carried out across several wards. A detailed description of the studies that were reviewed is presented in Table 1.
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
Table 1 Characteristics of Included Studies |
Designs of Included Studies
Studies adopted a range of research designs including clinical audit studies,29,33,37 quasi‐experimental studies34,35,58 randomized cluster trials,52 pilot studies,36,40,46 prospective or controlled prospective (cohort study or before and after comparative intervention) studies,41,48 pre-post observational,61 and quantitative39 and qualitative studies.44,45,47,50,51,54–57,59,60
Studies drew on diverse conceptual approaches ranging from participatory action research to frameworks promoting action on research implementation in health services (PARIHS),38,42,49,53 rapid spread clinical change methods,43 and collaborative best practice implementation studies.30 A variety of data collection methods were employed. These included surveys focus groups, meetings and discussions, face-to-face and telephone interviews, observations (structured and semi-structured), questionnaires, meeting reports, and patients’ medical records and data records from malnutrition screening and assessment (such as weight and height measurement).
As described in the data presentation section, the review findings are reported using the three-category framework of input, process, and outcome as a basis for categorizing and interpreting the evidence for collaborative working (see Figure 2).62 The term Input here refers to the contextual influences on collaborative working and, in this case, it includes the characteristics of the different disciplines and the aspects of nutritional care explored. The Process involves interactions between the participating team members and activities through which nutritional care is delivered in collaboration between different groups. The Outcomes consider the multidisciplinary activities’ results and impact at the patient, team, and organizational levels. It considers the extent to which the intervention has informed, improved the way nutritional care is provided (such as satisfaction and commitment).62
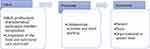 |
Figure 2 Application of input-process-outcome (IPO) framework. |
Input: Disciplines Involved and Aspects of Nutritional Care Explored
Multidisciplinary collaborations were mostly reported descriptively with a representation ranging between three or more different participant groups. A wide range of disciplines, including patients, relatives, and volunteers, were observed to have participated. All of them contributed to different aspects of nutritional care, depending on the objective of individual studies.
Nutritional care practices were examined from staff perspectives to understand the attributes that support change efforts towards improvement in several studies. For example, Laur et al,56 involved nurses, physicians, food service workers, dietitians, and hospital management staff. Whereas Brown and Jones40 included meal volunteers, speech and language therapists, and dietetic and nursing staff in a study that highlighted the importance of meal volunteers’ roles in ensuring patients receive nutritional care in a timely and comfortable manner.
The participants in the 31 studies comprised the following: registered nurses (n=26), dieticians (n=23), physicians (n=12), speech and language therapists (or speech pathologists) (n=12), occupational therapists (n=8), housekeepers (n=2), and social workers (n=3). Physiotherapists, healthcare assistants, and nursing assistants each participated in five studies while catering, and food production staff were reported to have participated in 13 studies.
The involvement of ward managers, unit leaders, and their assistants in promoting nutritional care practices is reflected in 11 studies. Also represented are the facilities staff, catering staff, student nurses, dietetic assistants, dietetic interns, nutritionists, pharmacists, food design researchers, radiographers, and food and service staff. Members of these professions were less frequently cited. Other auxiliary staff were not explicitly defined but were reported to have participated in two studies. Figure 3 summarizes the distribution of disciplines in the retrieved studies from the most represented to the least represented.
 |
Figure 3 Distribution of disciplines in the retrieved studies. |
The most frequently cited professions were registered nurses (n=26), who were involved in all aspects of nutritional care, except in studies whose aim was role-specific or when nurses did not play a key role in delivering the intervention being implemented. For example, nurses were not included in a study that sought to identify factors influencing hospital food services from the perspective of management staff (who supervise and complete administrative responsibilities), food service staff, and food service assistants (responsible for serving, delivering meals, and keeping the kitchen areas clean). Notably, nurses and dietitians are the most common participants in the same studies.
Meal volunteers and feeding assistants participated in seven studies; relatives or carers in two; and patients in five studies. In these studies, meal volunteers and feeding assistants mostly assisted patients during mealtimes, while patients’ and relatives’ participation involved sharing their experiences of nutritional care provision. Although the studies adopted collaborative approaches, the associations between participant input, processes, and outcomes were not their primary research aim.
The component of food and nutritional care explored varied depending on the aim of the study. Generally, the studies either focused on one or a combination of two or more aspects of the various components, processes, and products of nutritional care interventions, as grouped by the ESPEN guidelines (2017).23 Fifteen studies reported on the forms and products of nutritional care, such as changes in the meal environment, including meal support and eating support, to meet patients’ nutritional needs.35,38–40,42,44,47,48,51,53–55,58,60,61 Eight studies specified on nutritional care processes such as malnutrition risk screening, nutritional assessment, and documentation.33,43,45,46,52,56,57,59 Similarly, eight studies reported on both the forms and nutritional care processes.29,30,34,36,37,41,49,50
Although different research approaches were used, the majority of studies had a similar focus on efforts to promote patients’ food intakes, including feeding support and the meal environment. While most retrieved studies were conducted in the UK, the distribution of studies across other countries is significantly small in comparison. Also, it is notable that the studies that included patients or relatives or volunteers were mainly set in the UK,29,40,51,54,58 with one each in Netherlands,41 United States35 and Australia.30
Process: Collaborative Activities and Processes
Review findings indicate there are common characteristics of staff’s activities, processes, and interactions across different disciplines in the provision of nutritional care. These include co-design of nutritional care interventions, clarifying roles and responsibilities, developing existing roles (or creating a new role) to support ward processes, staff training and development, communication and information sharing, and clinical leadership support in the process of implementation.
Findings indicate that nutritional care interventions were either co-designed with or in consultation with other disciplines.29,30,33,36,37,52,64 For example, in an exploratory clinical audit study, a multidisciplinary group was formed consisting of the nursing, dietetic, and catering staff to examine the nutritional care practices. This also included the patients’ nutritional adequacy, documentation, and records of nutritional assessments, as well as nurses’ nutritional knowledge base, which resulted in the development of an audit.29 Similarly, Roberts et al,61 reported on a multifaceted intervention in which nutritional barriers were assessed. In response, color-coded nutrition intake magnets were placed at patient bedsides to identify those at risk of malnutrition. Foodservice system changes were implemented (breakfast meal timing), and discipline-specific staff training (co-developed by a multidisciplinary team) was provided at the ward level to nurses, doctors, and food service staff.
The co-creation and introduction of a new role or the development of an existing role were reported in studies with the aim to facilitate practice-based activities in delivering nutritional care on the wards.30,36,37 For example, upon identification of concerns specific to nutritional care practices on the ward, a multidisciplinary team consisting of nursing, dietetics, speech and language therapy, catering, occupational therapy, and management staff created the ward nutrition coordinator’s role to facilitate nutritional care through the ward team. Similarly, in another study, the ward housekeeper’s already existing role was expanded and incorporated within the multidisciplinary team to enhance nutritional care coordination.37 As exemplified in research by Sykes et al,30 the clarification of roles and responsibilities was reported to have facilitated improvement during mealtimes and in assisting patients. However, while team roles and responsibilities were entrusted to staff, supervision and “fallback” roles were introduced in the cases when the delegated staff member was unavailable to perform the required task.
To enhance knowledge and skills, training was delivered in different ways depending on the intervention being implemented. Nine studies reported and utilized training and education-based activities to enhance knowledge and develop skills in providing nutritional care.30,34,35,38,40,41,48,52,61 In a study undertaken to determine whether hospitalized older adults (mean age 78.2 years) would consume a more significant proportion of their meals when given feeding assistance by trained volunteers, Robison et al,54 provided multidisciplinary training delivered by a team comprising nurses, a dietitian, a speech and language therapist, and an occupational therapist. The study aimed to support volunteers in recognizing the complexities of feeding and developing the skills required to assist patients better. Dietitians provided specific training to nurses aimed at increasing awareness of patients’ dietary intake.41 In other research, facilitator pairs52 were used that included a nurse and a dietitian who led the intervention. They educated and trained staff on using the Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool (“MUST”) to support the implementation of feeding assistance. The facilitator pairs also worked with the hospital kitchen staff to introduce the use of red trays that identifies patients who require help at mealtimes.
To communicate and discuss ways of improving patients’ nutrition care, multidisciplinary team meetings, discussions, and feedback sessions were reported in thirteen studies and used to explore solutions and solve issues as a team.30,39,44,45,47,50,54–60 To explore multidisciplinary perspectives in identifying barriers and facilitators to various aspects of nutritional care, thirteen studies adopted research group interaction methods (focus group, discussion forums) and interviews and questionnaires. For instance, Cooper45 facilitated communication between stakeholders to investigate current practice at the ward level regarding adherence to a care plan, leading to the re-designing of the care plan. Similarly, two studies deployed practice-based multi-professional information-sharing activities such as patient records documentation (food and fluid).30,41 The influence of clinical leadership on the team was specified and identified to contribute to shaping team processes and multidisciplinary collaborations in delivering nutritional interventions.54,55 Related to this is commitment and enthusiasm from clinical staff reported in two studies as an essential component in the process of providing nutritional care.29,51
Outcomes: Reported Outcomes of Collaborative Nutritional Care
The reported outcomes identified from the studies are grouped into three categories according to the intervention level; these are outcomes at the patient, the team, and the organizational levels. Patient level outcomes are exemplified in studies that observe modifications to patients’ nutritional status and perception of satisfaction. Staff outcomes were evident in studies that reported changes in staff knowledge, skills, perceived satisfaction, and perceived impact of the interventions. The extent to which the intervention informed, changed or improved nutritional care provision is represented at the organizational level.
Patient Level
Patients’ access to improved quality of service, nutritional support actions, and practices was reported to have significantly increased.39,41,48,50 Patient outcomes were specifically described in twelve studies that reported outcome measures including increases in dietary energy and protein intakes, improved overall nutritional status, and patient responses such as their satisfaction with improved nutritional support and overall quality of care.34,35,37,40,41,43,49,51–54,61
However, with regards to patients’ nutritional care, only two of the studies reported the association between the multidisciplinary approach and patient outcomes. A controlled prospective cohort study41 analyzed the effectiveness of a multidisciplinary intervention on nutritional intake and the quality of life of older patients. They reported an increase in dietary energy and protein intake in patients who received multidisciplinary nutritional care (including nutritional support during hospitalization) as compared to patients who received the standard nutritional care where nutritional support was seldom provided. However, their findings found an association between multidisciplinary nutritional care and body cell mass (one of the parameters they measured). Bell et al,49 reported higher increases in protein and energy intake with multidisciplinary care compared with individualized care indicating an overall better and improved patient outcome.
Team Level
Team level outcomes were reported in 15 studies and are grouped into four main categories.
In one study, collaborative bottom-up and solution-focused practices that involved staff throughout the process were reported to result in enhanced ownership of nutrition care. Two studies specified that the collaborative approach and the targeted nutritional training patients received resulted in increased commitment and enthusiasm among staff.29,46
Four studies reported an increase in awareness of patients’ nutrition among staff groups.33,38,57,61 Eglseer et al,57 noted that healthcare staff’s knowledge, attitudes, and perceived practices are key components for successful nutritional care in malnourished patients and therefore recommended improvements for better patient outcomes. In three studies, staff confidence to assist in feeding patients34 and increased job satisfaction by mealtime volunteers were reported.35 One study in which staff explored solutions and solved issues as a team reported feeling empowered to make the changes required to better deliver patient nutritional care.43
Three studies in which staff and volunteers were engaged and involved during mealtimes reported that both patients and nursing staff felt supported during mealtimes.40,43,58
Two studies specified that introducing a new role36 and the development of an existing role in the ward improved nutritional care delivery.48 Farrer et al,46 created a collaborative team and introduced a nutritional coordinator’s role to facilitate the administration of patients’ nutritional needs. The results demonstrated a significant impact on nutritional screening, nutritional services, patients’ perceptions of their nutritional care, and enhanced staff support and satisfaction.36 However, Young et al,48 reported that existing staff’s involvement across disciplines might be as effective as introducing a dedicated feeding role.
Organizational Level
Of the 31 studies, none examined the effect of collaborative working on system changes; however, twelve studies reported diverse changes made to nursing practice, including follow-up on adherence to nutritional guidelines and implementation.30,33,38,40,42,43,49,50,53,56–58 Studies that reported changes in practice adopted collaborative participatory and action approaches. The ward staff were reported to have made changes to nursing practice, such as better adherence to protected mealtimes and more staff engagement with prioritizing mealtimes, ensuring sufficient time and expertise to assist patients with eating support.30,40
Discussion
The purpose of this scoping review was to identify and describe the features of multidisciplinary collaborative care approaches when implementing food and nutritional care interventions. The scoping review examined 31 studies and identified diverse disciplines’ involvement, including patients, relatives, and volunteers, indicating the developing evidence of collaborative working around various aspects of food and nutritional care. In summary, this review identified some collaborative activities, processes, and outcomes of multidisciplinary nutritional care in support of nutritional care practices. The findings reveal that although retrieved studies adopted collaborative approaches, examining the association of participant input, the collaborative processes, and outcomes were not the primary research aim of studies.
Features of Multidisciplinary Collaborative Care Approaches
Previous reviews have either examined the effectiveness of nutritional care,14 or the impact of specific interventions on patients’ nutritional outcomes or their cost implications.66 In contrast, our scoping review contributes to the literature in that the scope is focused on specific attributes that affect collaborative working in patients’ nutritional care. This section explores the features identified to be integral to collaborative working and their implications for nutritional care.
The Involvement of Different Disciplines and Varied Aspects of Nutritional Care
Despite the policy imperative for collaborative working to improve nutritional outcomes, our review did not identify any studies that specifically examined the role of collaborating disciplines and their relationship to nutritional care processes. This finding suggests this to be a potential area for future research. However, this review demonstrates that collaborative working is evident in nutritional care provision where different disciplines and wider team, including patients, relatives, and volunteers, all contributed to these collaborations. With the exception of two studies, the composition of all the participant groups was evident and clarified. This evidence of collaborative care underscores the importance of nutritional care as everybody’s responsibility.
In addition to professional healthcare providers, patients at the center of care, their families, and volunteers are key stakeholders, and they all make a valuable contribution to nutritional outcomes. The critical role of volunteers was highlighted, recognizing their contribution to patients’ nutritional care. However, their involvement, as suggested from the above findings, were relatively context specific. The countries where these studies were undertaken appears to be where there is a growing recognition within regulatory and accreditation systems on the role played by voluntary services.63 This may reflect policy implications regarding nutritional care interventions for patients.
Given that public policy has been reported to impact volunteers’ roles and responsibilities, effective policies and strategies for volunteering are essential, particularly for meal volunteers. Besides, previous studies have demonstrated that mealtime volunteers can be trained to provide mealtime assistance to older acute in-patients safely. This can improve the overall quality of mealtime care and benefit both patients and ward staff.68
As healthcare providers in hospitals, health care professionals have a shared role in providing optimal nutritional care to patients. Their engagement, as well as their interrelated roles in these collaborative activities, are critical, as each discipline brings specific expertise. Hence, in collaboration, they can better understand each other’s roles, plan, implement, and evaluate nutritional care (rather than doing so in isolation).8
The scoping review also highlights the growing evidence of collaborative working around different components of nutritional care. These not only include nutritional care processes, such as malnutrition risk screening and nutritional assessment and planning, but also involve the forms and products associated with nutritional care, such as meal environment, diets (regular hospital diet and food products), and therapeutic diets (functional and modified foods and fluids). These components reflect the recommendations found within policy and guideline documents concerning the management of malnutrition.67 However, while nutritional care standards and guidelines are essential, their implementation requires the coordination, engagement, and collaboration of these disciplines to meet patients’ needs.
Multidisciplinary Interrelationship and Role Clarity
Multidisciplinary collaboration, involving the wide range of professions identified in this review, is indicative of the complementary contributions each provides. The shared perspectives and the interrelationship between disciplines indicate that everyone plays a vital role in delivering optimal food and nutritional care.
The findings show that collaborative relationships and interdependence were evident among professionals. To coordinate ward-based nutritional care36 new roles were either introduced or were developed37 or delineated amongst staff, enabling collaborative working.41,48,49 Professional boundaries and role clarity benefit nutritional care coordination because they enable the multidisciplinary team members to possess a clear understanding of their own roles and an appreciation of the roles performed by other team members. This mutual understanding is also likely to ensure care gaps are identified, and appropriate care is provided to achieve shared goals.68
However, an important highlight was the notion of the interchangeability of roles in cases where roles delegated to staff or volunteers were not performed for different reasons, such as shift patterns or unavailability. For instance, when nursing staff had the fallback role of assisting patients during mealtimes, even though mealtime assistance responsibilities were delegated to other staff; in this case, nursing assistants and food services staff.30 While this reflects the nursing staff’s central role, it also emphasizes the importance of shared responsibility and role clarification within multidisciplinary working. Similar results were reported in two studies in which staff perceptions for in-patients’ poor nutritional intake were investigated or the feasibility of identifying nutritionally at-risk patients.7,70 Both these studies emphasized the imperative of integrating collaborative efforts. The significance of role clarification and shared responsibility to multidisciplinary collaboration has been highlighted in other literature, as have the challenges of achieving these objectives in practice.7,69,70 Nonetheless, it is pertinent these are recognized as fundamental elements of multidisciplinary approaches to nutritional care.
The Role of Communication, Knowledge and Information-Sharing in the Process of Collaborative Working
Several studies have focused on knowledge and information-sharing processes. Eide et al,74 support these findings. They reported from a study conducted from the nurses’ perspective that insufficient knowledge leads to inadequate nutritional practice, impacting treatment outcomes. Nutrition training and education programs were aimed at increasing the capacity of individuals to carry out their roles more effectively by either acquiring, upgrading, or enhancing their skill sets.30,35,38,61 For instance, nursing staff received training from the speech and language therapist on managing patients with swallowing difficulties to enable the identification of patients with dysphagia.34 While most studies did not measure the degree of the direct impact of training on patient outcomes, team-level outcomes reported indicated significant benefits. These included increased awareness and better engagement in providing nutritional care.38,57,61 For example, Eglseer et al’s,57 study found that increased exposure to malnutrition knowledge prompted the need for further training of nursing staff.
Although the benefits of education and training are well-established features in the literature,20,71,73 sustainability in providing appropriate nutritional care requires regular training updates and adapted structural processes to reinforce nutrition knowledge and support effective implementation.48 Problem identification and valuing the experiential perspectives of different disciplines, including patients, relatives, and volunteers30,54–60 reflected approaches that recognized and appreciated the expertise of different stakeholders and their contribution to addressing the concerns of malnutrition. Additionally, as a process of integrating patient care to ensure consistency and continuity of care, communication through multidisciplinary team meetings and discussions was reported in several studies.43,46,53, Whilst there was some significant value to team members, evidence that links the benefits of multidisciplinary meetings to improved care implementation was not apparent. Moreover, while multidisciplinary meetings are part of existing structural processes in hospitals, further research is required in establishing whether nutritional care is prioritized in such meetings amid competing clinical needs.
Clinical Leadership and Management Support
Leadership and management involvement were observed across multiple studies ranging from ward or unit managers and included nursing, dietetic, facilities, catering and food services managers.29,44,59 Although details of their roles and contributions were not often reported in the majority of the studies, indirect outcomes of their participation were associated with successful implementation. For instance, in Carson and Close,29 hospital managers were involved in investigating current nutrition practices following concerns raised and funds made available for further investigation. The involvement of hospital leaders is crucial. Their role has clinical and financial implications on malnutrition so that appropriate steps can be taken to address concerns and improve care.8
In contrast, the benefits of leadership were, however, not confined to senior management roles. In the clinical setting, the adoption of change was driven by influential nutrition advocates. Previous studies on nutritional care practices recognize the vital role of such advocates, often referred to as “nutrition champions”, in facilitating change.75 The hospital food service supervisors and food service assistants played a significant role as reported in Collins et al,55 by taking responsibility to lead by example and provide assistance on the wards. They also assumed the role of opinion leaders and spreaders of change amongst their peers. It seems likely that the concept of shared leadership, where mutual influence is embedded in the interactions of staff members or different disciplines, supports a positive multidisciplinary relationship, which may facilitate more collective effective change.
Also based on the premise of distributing leadership responsibility across multiple levels, a shared leadership approach to implementation has the potential to be a valuable concept for further research and may better inform sustainability and continuity of collaborative nutritional care practices in hospitals.
Managing in-practice challenges is also significant in multidisciplinary approaches. In the case of Collins et al,55 the food service supervisors were reported to have influenced teamwork where the burden of staffing and time constraints was evident. Outcomes of multidisciplinary collaborations appeared to have some benefit at the patient, team, and system levels. For example, at the patient level, an observed increase in energy and protein intake41,49 indicates a significant beneficial association between collaborative activities with improved clinical outcomes. Similarly reported are increased food and fluid intakes,49 staff confidence in their role and job satisfaction,34,54,57 a sense of empowerment,43 and staff feeling valued58 and supported.40 Systemic changes where improvements to nursing practice were implemented further highlight the impact of collaborative care. Moreover, some studies reported enablers and key success factors, which included commitment and enthusiasm about patient nutritional care from clinical staff;29,51 which was mentioned in passing rather than being a feature intended to be measured.
Notably, methodological approaches that demonstrated systemic practice changes used action research or implementation research, which influenced the change processes.38,53 These approaches seek to bring about change through action, developing and improving practice by actively engaging staff in the processes of diagnosing, planning action, taking action and evaluating action within their clinical area.65 Future studies examining the continuity and coordination of multidisciplinary nutritional care approaches are needed, given the increased imperative of guidelines and policies to increase collaborative multidisciplinary nutritional care initiatives that benefit care quality. Pertinent to this research is the role of organizational culture in understanding how the preconditions within healthcare institutions influence health professionals’ actions and behaviors to support or disrupt optimal nutritional care.
Limitations
As part of the extent of information covered, the scoping review had some limitations. Most studies did not explicitly focus on collaborative multidisciplinary processes. Therefore, related studies might have been missed in the searches and selection process. While in some retrieved studies, such processes featured within the findings. Although some actions and interactions that shaped implementations may not have been fully recognized and the nature of reporting might have been underplayed in the analysis.
Nonetheless, the review identified the characteristics of the various disciplines involved and processes from the retrieved studies to understand collaborative nutritional care further.
The IPO framework was applied to report the findings of the studies included in this review. Given our use of the framework, we did not determine the causal relationship between the input, process, and outcome due to the studies’ complexity and heterogeneous nature. Despite this limitation, the framework can be used to diagnose the degree of collaboration and the interrelationship of the IPO components in any multidisciplinary nutritional care intervention and identify further areas for future research and improvement.
Recommendations
Further research is recommended where different healthcare professionals are involved in nutritional care to identify the critical elements of multidisciplinary collaborative working more clearly. These insights will further our understanding of the impact on care outcomes.
It is recommended that participatory research approaches would be appropriate to maximize engagement and collaboration in proposing and embedding change.
Conclusion
The review demonstrates that multidisciplinary care approaches benefit from the engagement of the different disciplines, including volunteers, patients, and relatives. Some features are critical to the process of collaborative working, to wit: role clarity, effective multidisciplinary relationships facilitated by effective communication, knowledge, and information-sharing. In addition, the ways they are implemented may either facilitate or impede the effective provision of food and nutritional care in hospitals.
This review represents the first as of when conducted to evaluate existing literature concerning collaborative working features in implementing multidisciplinary care approaches to food and nutritional care. It indicates that to enhance collaborative approaches to nutritional care, activities such as team meetings, discussion and shared learning, role clarity, and processes that enable some nutritional interchangeability, and the support from clinical leadership and management should be considered and enacted in policy guidance to impact on practice. Achieving optimum nutritional care outcomes is a worthy goal for healthcare providers, as is the process by which they can be achieved and consequently requires consideration.
Gaps in the literature indicate a need for more focused research around multidisciplinary nutritional care processes and the conditions that allow for better collaborative working. This review provides a basis to inform for future research, particularly around investigating the nature of multidisciplinary group contributions to nutritional care quality. Given that “buy-in” from various key stakeholders is essential to change practice, the adoption of participatory action research approaches may be beneficial to collaboratively develop and better implement planned changes to food and nutritional care in hospital settings.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Agarwal E, Ferguson M, Banks M, et al. Malnutrition and poor food intake are associated with prolonged hospital stay, frequent readmissions, and greater in-hospital mortality: results from the nutrition care day survey 2010. Clin Nutrition. 2013;32(5):737–745. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2012.11.021
2. Cederholm T, Jensen GL, Correia MITD, et al. GLIM criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition–A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2019;10(1):207–217. doi:10.1002/jcsm.12383
3. Avelino-Silva TJ, Jaluul O. Malnutrition in hospitalized older patients: management strategies to improve patient care and clinical outcomes. Int J Gerontol. 2017;11(2):56–61. doi:10.1016/j.ijge.2016.11.002
4. Volkert D, Beck AM, Cederholm T, et al. Management of Malnutrition in Older Patients—Current Approaches, Evidence and Open Questions. J Clin Med. 2019;8(7):974. doi:10.3390/jcm8070974
5. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Nutrition Support in Adults: Evidence Update August 2013. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE), Department of Health England. 2013.
6. Correia MITD, Hegazi RA, Higashiguchi T, et al. Evidence-based recommendations for addressing malnutrition in health care: an updated strategy from the feedM. E. Global study group. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2014;15(8):544–550. doi:10.1016/j.jamda.2014.05.011
7. Ross LJ, Mudge AM, Young AM, Banks M. Everyone’s problem but nobody’s job: staff perceptions and explanations for poor nutritional intake in older medical patients. Nutrition Dietetics. 2011;68(1):41–46. doi:10.1111/j.1747-0080.2010.01495.x
8. Tappenden KA, Quatrara B, Parkhurst ML, Malone AM, Fanjiang G, Ziegler TR. Critical role of nutrition in improving quality of care: an interdisciplinary call to action to address adult hospital malnutrition. Medsurg Nursing. 2013;22(3):147–165.
9. Elia M; The ‘MUST’report. Nutritional screening of adults: a multidisciplinary responsibility. A Report by the Malnutrition Advisory Group of the British Association for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (BAPEN) Marinos Elia, British Association for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition. 2003.
10. Bell JJ, Young A, Hill J, et al. Rationale and developmental methodology for the SIMPLE approach: a systematised, interdisciplinary malnutrition pathway for implementation and evaluation in hospitals. Nutrition Dietetics. 2018;75(2):226–234. doi:10.1111/1747-0080.12406
11. D’Amour D, Ferrada-Videla M, San Martin Rodriguez L, Beaulieu M-D. The conceptual basis for interprofessional collaboration: core concepts and theoretical frameworks. J Interprof Care. 2005;19(sup1):116–131. doi:10.1080/13561820500082529
12. Carrier J, Kendall I. Professionalism and interprofessionalism in health and community care: some theoretical issues. In: Interprofessional Issues in Community and Primary Health Care. Springer. 1995:9–36.
13. Healthcare Improvement Scotland. Complex Nutritional Care Standards - Consultation Report: December 2015. Healthcare Improvement Scotland; 2015.
14. Whitelock G, Aromataris E. Effectiveness of mealtime interventions to improve nutritional intake of adult patients in the acute care setting: a systematic review. JBI Database Systematic Rev Impl Rep. 2013;11(3):263–305. doi:10.11124/01938924-201311030-00004
15. Baldwin C, Kimber KL, Gibbs M, Weekes CE. Supportive interventions for enhancing dietary intake in malnourished or nutritionally at‐risk adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;12:12. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009840.pub2
16. Edwards D, Carrier J, Hopkinson J. Mealtime assistance for older adults in hospital settings and rehabilitation units from the perspective of patients, families and healthcare professionals: a mixed methods systematic review. JBI Database Syst Rev Impl Rep. 2016;14(9):261–357. doi:10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-003100
17. Rasmussen NML, Belqaid K, Lugnet K, Nielsen AL, Rasmussen HH, Beck AM. Effectiveness of multidisciplinary nutritional support in older hospitalised patients: a systematic review and meta-analyses. Clinical Nutrition ESPEN. 2018;27:44–52. doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2018.07.002
18. Vogwill V, Reeves S. Challenges of information exchange between nurses and physicians in multidisciplinary team meetings. J Interprof Care. 2008;22(6):664–667. doi:10.1080/13561820802114772
19. Mehta NM, McAleer D, Hamilton S, et al. Challenges to optimal enteral nutrition in a multidisciplinary pediatric intensive care unit. J Parenteral Enteral Nutrition. 2010;34(1):38–45. doi:10.1177/0148607109348065
20. DiMaria-Ghalili RA, Mirtallo JM, Tobin BW, Hark L, Van Horn L, Palmer CA. Challenges and opportunities for nutrition education and training in the health care professions: intraprofessional and interprofessional call to action. Am J Clin Nutr. 2014;99(5):1184S–1193S. doi:10.3945/ajcn.113.073536
21. Peters M, Godfrey C, McInerney P, Soares C, Khalil H, Parker D. The Joanna Briggs Institute Reviewers’ Manual 2015: Methodology for JBI Scoping Reviews. The Joanna Briggs Institute. 2015.
22. Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, et al. PRISMA extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169:467. doi:10.7326/M18-0850
23. Cederholm T, Barazzoni R, Austin P, et al. ESPEN guidelines on definitions and terminology of clinical nutrition. Eur Society Clin Nutrition Metab. 2017.
24. McGrath JE. Social Psychology: A Brief Introduction. Holt: Rinehart and Winston; 1964.
25. Marks MA, Mathieu JE, Zaccaro SJ. A temporally based framework and taxonomy of team processes. Acad Management Rev. 2001;26(3):356–376. doi:10.5465/amr.2001.4845785
26. Ilgen DR, Hollenbeck JR, Johnson M, Jundt D. Teams in organizations: from input-process-output models to IMOI models. Annu Rev Psychol. 2005;56:517–543. doi:10.1146/annurev.psych.56.091103.070250
27. Künzle B, Kolbe M, Grote G. Ensuring patient safety through effective leadership behaviour: a literature review. Saf Sci. 2010;48(1):1–17. doi:10.1016/j.ssci.2009.06.004
28. Reeves S, Goldman J, Gilbert J, et al. A scoping review to improve conceptual clarity of interprofessional interventions. J Interprof Care. 2011;25(3):167–174. doi:10.3109/13561820.2010.529960
29. Carson M, Close J. A team approach to the audit of nutritional care in community hospitals. J Human Nutrition Dietetics. 1996;9(4):309–317. doi:10.1046/j.1365-277X.1996.00466.x
30. Sykes P, Norris I, Cook M, et al. Mealtime assistance. from chaos to calm: a collaborative best practice implementation project. J Nurs Care Qual. 2019;34(1):80–85. doi:10.1097/NCQ.0000000000000352
31. Hall K, Gilliland H. Changing the long-term care culture through interprofessional practice: a speech-language pathologist-led initiative. Perspectives ASHA Special Interest Groups. 2019;4(2):313–321. doi:10.1044/2019_PERS-SIG2-2018-0005
32. Smith S, Westergren A, Saunders J, Hagell P. Nutritional screening: a user-friendly tool adapted from Sweden. British J Nursing. 2016;25(4):208–211. doi:10.12968/bjon.2016.25.4.208
33. Gee P, Palk M, Thatcher C. Nutritional assessment in elderly care–a team approach. Int J Language Communication Disorders. 1998;33:
34. Biernacki C, Barratt J, Barratt J. Improving the nutritional status of people with dementia. British j Nursing. 2001;10(17):1104–1114. doi:10.12968/bjon.2001.10.17.9949
35. Robinson S, Clump D, Weitzel T. The memorial meal mates: a program to improve nutrition in hospitalized older adults. Geriatr Nurs (Minneap). 2002;23(6):332–335. doi:10.1067/mgn.2002.130279
36. Hayward J. Ward nutrition coordinators to improve patient nutrition in hospital. British j Nursing. 2003;12(18):1081–1089. doi:10.12968/bjon.2003.12.18.11781
37. Richmond J. Developing the role of a ward housekeeper within a multidisciplinary team. British J Nursing. 2007;16(1):56–59. doi:10.12968/bjon.2007.16.1.22716
38. Dickinson A, Welch C, Ager L, Costar A. Hospital mealtimes: action research for change? Proc Nutrition Society, 64 3 269–275 doi: 10.1079/PNS2005432.
39. Thoresen L, Rothenberg E, Beck AM, et al. Doctors and nurses on wards with greater access to clinical dietitians have better focus on clinical nutrition. J Human Nutrition Dietetics. 2008;21(3):239–247. doi:10.1111/j.1365-277X.2008.00869.x
40. Brown H, Jones L. The role of dining companions in supporting nursing care nursing standard (through 2013). Nursing Standard. 2009;23(41):40–46. doi:10.7748/ns2009.06.23.41.40.c7049
41. Hoekstra JC, Goosen JHM, de Wolf GS, Verheyen CCPM. Effectiveness of multidisciplinary nutritional care on nutritional intake, nutritional status and quality of life in patients with hip fractures: a controlled prospective cohort study. Clin Nutrition. 2011;30(4):455–461. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2011.01.011
42. Macdonald AS, Teal G, Bamford C, Moynihan PJ. Hospitalfoodie: an interprofessional case study of the redesign of the nutritional management and monitoring system for vulnerable older hospital patients. Qual Prim Care. 2012;20(3):169–177.
43. McKeane A. Using Rapid Spread to improve hospital nutrition. Nurs Times. 2012;108(42):24–25.
44. Walton K, Williams P, Tapsell L. Improving food services for elderly, long-stay patients in Australian hospitals: adding food fortification, assistance with packaging and feeding assistance. Nutrition Dietetics. 2012;69(2):137–144. doi:10.1111/j.1747-0080.2012.01587.x
45. Cooper C, Brierley ER, Burden ST. Improving adherence to a care plan generated from the malnutrition universal screen tool. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2013;67:174–179. doi:10.1038/ejcn.2012.196
46. Farrer K, Donaldson E, Blackett B, et al. Nutritional screening of elderly patients: a health improvement approach to practice. J Human Nutrition Dietetics. 2013;27(2):184–191. doi:10.1111/jhn.12073
47. Heaven B, Bamford C, May C, Moynihan P. Food work and feeding assistance on hospital wards. Sociol Health Illn. 2013;35(4):628–642. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9566.2012.01515.x
48. Young AM, Mudge AM, Banks MD, Ross LJ, Daniels L. Encouraging, assisting and time to EAT: improved nutritional intake for older medical patients receiving Protected Mealtimes and/or additional nursing feeding assistances. Clin Nutrition. 2013;32(4):543–549. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2012.11.009
49. Bell JJ, Rossi T, Bauer JD, Capra S. Developing and evaluating interventions that are applicable and relevant to inpatients and those who care for them; a multiphase, pragmatic action research approach. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2014;14(1):98. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-14-98
50. Keller HH, Vesnaver E, Davidson B, et al. Providing quality nutrition care in acute care hospitals: perspectives of nutrition care personnel. J Human Nutrition Dietetics. 2014;27(2):192–202. doi:10.1111/jhn.12170
51. Roberts HC, De Wet S, Porter K, et al. The feasibility and acceptability of training volunteer mealtime assistants to help older acute hospital inpatients: the southampton mealtime assistance study. J Clin Nurs. 2014;23(21–22):3240–3249. doi:10.1111/jocn.12573
52. Schultz TJ, Kitson AL, Long L, et al. Does a multidisciplinary nutritional intervention prevent nutritional decline in hospital patients? A stepped wedge randomised cluster trial. e-SPEN J. 2014;9:2. doi:10.1016/j.clnme.2014.01.002
53. Mudge AM, McRae P, Cruickshank M. Eat walk engage: an interdisciplinary collaborative model to improve care of hospitalized elders. Am J Med Qual. 2015;30(1):5–13. doi:10.1177/1062860613510965
54. Robison J, Pilgrim AL, Rood G, et al. Can trained volunteers make a difference at mealtimes for older people in hospital? A qualitative study of the views and experience of nurses, patients, relatives and volunteers in the Southampton mealtime assistance study. Int J Older People Nurs. 2015;10(2):136–145. doi:10.1111/opn.12064
55. Collins J, Huggins CE, Porter J, Palermo C. Factors influencing hospital foodservice staff’s capacity to deliver a nutrition intervention. Nutr Diet. 2017;74(2):129–137. doi:10.1111/1747-0080.12344
56. Laur C, Valaitis R, Bell J, Keller H. Changing nutrition care practices in hospital: a thematic analysis of hospital staff perspectives. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017;17:1–15. doi:10.1186/s12913-017-2409-7
57. Eglseer D, Halfens RJG, Lohrmann C. Use of an electronic malnutrition screening tool in a hospital setting: effects on knowledge, attitudes and perceived practices of healthcare staff. British J Nutrition. 2018;120(2):150–157. doi:10.1017/S0007114518001447
58. Howson FFA, Robinson SM, Roberts HC, et al. Can trained volunteers improve the mealtime care of older hospital patients?: an implementation study in one English hospital. BMJ Open. 2018;8:8. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2018-022285
59. Byrnes A, Young A, Mudge A, Banks M, Bauer J. EXploring practice gaps to improve PERIoperativE Nutrition CarE (EXPERIENCE Study): a qualitative analysis of barriers to implementation of evidence-based practice guidelines. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2019;73(1):94–101. doi:10.1038/s41430-018-0276-x
60. Ottrey E, Porter J, Huggins CE, Palermo C. Ward culture and staff relationships at hospital mealtimes in Australia: an ethnographic account. Nurs Health Sci. 2019;21(1):78. doi:10.1111/nhs.12559
61. Roberts S, Williams LT, Sladdin I, et al. Improving nutrition care, delivery, and intakes among hospitalised patients: a mixed methods, integrated knowledge translation study. Nutrients. 2019;11(6):1417. doi:10.3390/nu11061417
62. Mathieu J, Maynard MT, Rapp T, Gilson L. Team effectiveness 1997–2007: a review of recent advancements and a glimpse into the future. J Manage. 2008;34(3):410–476. doi:10.1177/0149206308316061
63. Baczynska AM, Lim SER, Sayer AA, Roberts HC. The use of volunteers to help older medical patients mobilise in hospital: a systematic review. J Clin Nurs. 2016;25(21–22):3102–3112.
64. Roberts HC, Lim SER, Cox NJ, Ibrahim K. The challenge of managing undernutrition in older people with Frailty. Nutrients. 2019;11(4):808. doi:10.3390/nu11040808
65. O’Neal H, Manley K. Action planning: making change happen in clinical practice. Nursing Standard. 2007;21(35):35–40. doi:10.7748/ns.21.35.35.s52
66. Weekes CE, Spiro A, Baldwin C, et al. A review of the evidence for the impact of improving nutritional care on nutritional and clinical outcomes and cost. J Human Nutrition Dietetics. 2009;22(4):324–335. doi:10.1111/j.1365-277X.2009.00971.x
67. BAPEN. Nutritional care tool report 2017. British Association for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (BAPEN); 2017.
68. Howson F, Sayer A, Roberts H. The impact of trained volunteer mealtime assistants on dietary intake and satisfaction with mealtime care in adult hospital inpatients: a systematic review. J Nutrition, Health Aging. 2017;21(9):1038–1049. doi:10.1007/s12603-016-0847-2
69. Orchard C, Bainbridge L, Bassendowski S, et al. A national interprofessional competency framework. Canadian Interprofessional Health Collaborative. 2010.
70. Kenworthy S, Agarwal E, Farlow L, Angus R, Marshall AP. Feasibility of using the “modified NUTrition Risk In the Critically ill” nutritional risk screening tool to identify nutritionally at-risk patients in an Australian intensive care unit. Australian Critical Care. 2020;33(3):259–263. doi:10.1016/j.aucc.2019.08.003
71. Brault I, Kilpatrick K, D’Amour D. et al. Role clarification processes for better integration of nurse practitioners into primary healthcare teams: a multiple-case study. Nurs Res Pract;2014. 2014. doi: 10.1155/2014/170514
72. Caldwell K, Atwal A. The problems of interprofessional healthcare practice in hospitals. British J Nursing. 2003;12(20):1212–1218. doi:10.12968/bjon.2003.12.20.11844
73. Reeves S, Perrier L, Goldman J, Freeth D, Zwarenstein M. Interprofessional education: effects on professional practice and healthcare outcomes. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;3. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002213.pub3
74. Eide HD, Halvorsen K, Almendingen K. Barriers to nutritional care for the undernourished hospitalised elderly: perspectives of nurses. J Clin Nurs. 2015;24(5–6):696–706. doi:10.1111/jocn.12562
75. Gerrish K, Laker S, Taylor C, Kennedy F, McDonnell A. Enhancing the quality of oral nutrition support for hospitalized patients: a mixed methods knowledge translation study (The EQONS study). J Adv Nurs. 2016;72(12):3182–3194. doi:10.1111/jan.13085
76. Yinusa G, Scammell J, Murphy J, Ford J. Multidisciplinary provision of food and nutritional care to hospitalised adult in-patients: a scoping review protocol. Protocolsio. 2020.
77. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Prisma G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLOS Medicine. 2009;6(7):e1000097.
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
