Back to Journals » Vascular Health and Risk Management » Volume 11
Hypoglycemia hospitalization frequency in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a comparison of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors and insulin secretagogues using the French health insurance database
Authors Detournay B, Halimi S, Robert J, Deschaseaux C, Dejager S
Received 12 March 2015
Accepted for publication 28 April 2015
Published 17 July 2015 Volume 2015:11 Pages 417—425
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/VHRM.S84507
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Dr Daniel Duprez
Bruno Detournay,1 Serge Halimi,2,3 Julien Robert,1 Céline Deschaseaux,4 Sylvie Dejager5,6
1Cemka-Eval, Bourg-la Reine, France; 2Department of Diabetology, Endocrinology and Nutrition, Grenoble University Hospital Center, Grenoble, France; 3University Joseph Fourier, Grenoble, France; 4Novartis Pharma SAS, Market Access Department, Rueil-Malmaison, France; 5Novartis Pharma SAS, Medical and Scientific Affairs, Rueil Malmaison, France; 6Department of Diabetology, Metabolism and Endocrinology, Pitié-Salpétrière Hospital, Paris, France
Aim: We aimed to compare the frequency of severe hypoglycemia leading to hospitalization (HH) and emergency visits (EV) for any cause in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus exposed to dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) inhibitors (DPP4-i) versus those exposed to insulin secretagogues (IS; sulfonylureas or glinides).
Methods: Data were extracted from the EGB (Echantillon Généraliste des Bénéficiaires) database, comprising a representative sample of ~1% of patients registered in the French National Health Insurance System (~600,000 patients). Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients exposed to regimens containing either a DPP4-i (excluding treatment with IS, insulin, or glucagon-like peptide 1 analog) or IS (excluding treatment with insulin and any incretin therapy) between 2009 and 2012 were selected. HH and EV during the exposure periods were identified in both cohorts. A similar analysis was conducted considering vildagliptin alone versus IS. Comparative analyses adjusting for covariates within the model (subjects matched for key characteristics) and using multinomial regression models were performed.
Results: Overall, 7,152 patients exposed to any DPP4-i and 1,440 patients exposed to vildagliptin were compared to 10,019 patients exposed to IS. Eight patients (0.11%) from the DPP4-i cohort and none from the vildagliptin cohort (0.0%) were hospitalized for hypoglycemia versus 130 patients (1.30%) from the IS cohort (138 hospitalizations) (P=0.02 and P<0.0001, respectively). Crude rates of HH/1,000 patient-years were 1.4 (95% CI: 0.7; 2.4) in the DPP4-i cohort, 0.0 in the vildagliptin cohort (95% CI: 0.0; 4.0), versus 5.6 (95% CI, 4.7; 6.6) in the IS cohort (P<0.0001). After adjustments, rates per 1,000 patient-years of HH were 1.4 (95% CI: 0.7; 2.4) with DPP4-i versus 7.5 (95% CI: 6.0; 9.2) with IS (P<0.0001), and 0.0 (95% CI: 0.0; 4.0) with vildagliptin versus 13.6 (95% CI: 10.4; 17.5) with IS (P<0.0001). Adjusted EV rates were also significantly lower with all DPP4-i or with vildagliptin, as compared to IS (P<0.0001). Consistent results were found when considering only treatment initiations for all compared cohorts.
Conclusion: HH and EV were significantly less frequent in patients exposed to any DPP4-i or to vildagliptin versus IS. These real-life data should be considered in the benefit/risk evaluation of the drugs.
Keywords: type 2 diabetes, severe hypoglycemia, hospitalization, sulfonylureas, DPP4 inhibitors, vildagliptin
Introduction
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) represents a considerable health burden, with a steadily increasing prevalence worldwide.1 Currently, the disease affects about 25 million persons in the US and nearly 5% of the French population.2
Hypoglycemia is a common problem in treated patients with T2DM,3 responsible for increased health care costs4 and associated with multiple and potentially severe adverse consequences3 that can lead to hospitalization.5,6 Recent data show that rates of hospital admission for hypoglycemia now exceed those for hyperglycemia among US Medicare beneficiaries.7
Hypoglycemia occurs most frequently with antidiabetic treatments that increase insulin levels independently of the blood glucose level, such as oral insulin secretagogues (IS; sulfonylureas and glinides) and exogenous insulin.3,8 Unlike indiscriminate IS, dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors (DPP4-i) regulate glucose homeostasis in a glucose-dependent manner and are consequently associated with a lower risk of hypoglycemia.8
In particular, this overall low risk of hypoglycemia has been extensively documented throughout the clinical development program with the DPP4-i vildagliptin, across a wide range of clinical settings,9 including populations particularly vulnerable to hypoglycemia such as elderly10,11 patients with renal impairment12 and patients treated with insulin.13 This low hypoglycemic potential has a solid mechanistic basis.14
However, this lower frequency of hypoglycemia has mainly been observed in clinical trials15–17 comparing closely monitored treatments in selected T2DM populations. Large claims databases may now be used to confirm the better tolerability of DPP4-i as compared to sulfonylureas and glinides in the real-life setting, at least in severe hypoglycemic events, and to estimate the magnitude of this beneficial effect. In France, in the early 2000s, legislators requested the three main French National Sickness Funds’ beneficiaries covering more than 95% of the French population (66 million individuals) to develop an information system aimed at better understanding and evaluating beneficiaries’ health care consumption. In addition, a random permanent sample of beneficiaries enrolled in this database was created (Echantillon Généraliste des Bénéficiaires [EGB]).18 This large sample can now be used to conduct longitudinal studies as it permits audits of patients’ care paths and patients’ use of both hospital- and office-based care.18 Therefore, it was of interest to compare the real-life frequency of severe hypoglycemic episodes leading to hospitalization and of emergency visits (EV) in patients exposed to DPP4-i versus those exposed to IS in this nationwide health insurance database.
Methods
Setting and subjects
The EGB database contains anonymous sociodemographic and medical characteristics and records of health care reimbursements, both in ambulatory and hospital settings. It was created using a systematic sampling method (survey rate of 1/97th), resulting in a permanent representative national sample of about 600,000 anonymous individuals from the whole population covered by the main French National Sickness Funds. The EGB can be used for research purposes to conduct longitudinal studies, as it permits tracing back patients’ care paths and hospital or outpatient claims, and enables calculation of individual expenditures over the course of time.18 It has been used successfully to investigate important public health questions, such as the risk of cancer in insulin glargine users.19
On the other hand, EGB has the same limitations as most other claims systems: data include age, sex, date of death, health care insurance status including long-standing conditions (ALD [a specific status providing 100% reimbursement for long-standing conditions]), and CMU (a specific status providing 100% coverage for deprived people), but no other sociodemographic data. While the database contains information on all health care expenditures effectively reimbursed (ambulatory or in hospital setting), it does not record over-the-counter drugs, and cannot identify patients who do not use their doctors’ prescriptions. Finally, it contains few medical data (ie, biological results and reasons for physician visits in ambulatory settings or for EV are not collected).
Because of these limitations, especially the lack of information on glycemic control, an additional study (HYPOVI study) was set up in parallel to further describe the profiles of patients exposed to IS and to the DPP4-i vildagliptin during the same period in France. This study was based on a longitudinal patient database supplied with anonymous information, collected during daily practice from a sample of 1,200 office-based physicians (general practitioners [GPs]) via their practice management software.20 The sample was representative of French GPs in terms of age, sex, and area of coverage. Two cohorts were defined: patients exposed to regimens comprising either vildagliptin (excluding treatment with IS, insulin, or any other incretin therapy) or to IS (excluding treatment with insulin and with any incretin therapy). Data collected in this additional study included all hypoglycemic episodes that occurred within the previous 12 months (requiring/not requiring third party or medical assistance) as reported to patients’ GPs during routine visits, as well as clinical data (body mass index, diabetes duration, complications and comorbidities, and glycemic control from available biological data).
Study design and exposures
The main study in our current research was based on retrospective data extracted from the EGB database. Patients with T2DM exposed to regimens containing either a DPP4-i (excluding treatment with IS, insulin, or GLP1 analogs) or IS (excluding treatment with insulin and with any incretin therapy) between 2009 and 2012 were selected. This exposure period was based upon the availability of most DPP4-i in France. For each individual patient, the start date was that of the first delivery of the antidiabetic drug considered (IS or DPP4-i), starting from January 2009, and the end date was the last delivery plus 90 days, which is the usual length of a medical prescription in France, or the date of delivery of any excluded treatment or death. A similar analysis was conducted to evaluate the same endpoints with vildagliptin (available in France from September 2009) versus IS during the same period; the data with vildagliptin was needed to provide new insights to the Economic Committee for Healthcare Products which is in charge of drug reimbursement and pricing in France.
Since IS have been available for many years in France, unlike DPP4-i, the exposure time was expected to be longer in the IS cohort. To examine the impact of a potential over-representation of patients with shorter exposure period to IS due to the necessary adjustments, an additional supportive analysis was further conducted considering treatment initiations in the IS cohort.
Assessments/endpoint definitions
Data collected in the EGB comprised patients’ characteristics (age, sex, date of death, CMU and ALD affiliation [see the “Settings and subjects” section]), treatments codes with delivery dates and quantities, and information regarding hospitalizations and EV. Hospitalizations related to severe hypoglycemia during the exposure periods were identified in both cohorts using the following International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, Version 10 (ICD10) codes: E160, E161, E162, E140, or T383. Emergency visits for any cause were also captured. The reasons for the EV were not recorded in EGB, and all visits were thus taken into account as a global surrogate for higher medical needs and health care utilization.
Statistical analyses
In order to compare the two cohorts and to take into account possible confounders, two methods of adjustment were subsequently used. The first method used direct standardization, adjusting for key covariates defined a priori as likely to be confounding factors: subjects were matched for age, sex, CMU status (as a reflection of socioeconomic status and potential different management), and drug exposure duration. The reference population was the DPP4-i cohort, taking into account the much larger sample size in the IS cohort. The adjusted results were then expressed in the same way as the raw data and were compared using conventional tests including estimation of 95% confidence intervals (CI95% [x; y]).
Additionally and when possible, multivariate methods involving the use of multinomial regression models, either a logistic model or a generalized linear model (Poisson model) were used depending on the nature of the dependent variable (dichotomous or cardinal); use was determined by simultaneously considering as explanatory factors of the events (hypoglycemia requiring hospital admission, and EV) the potential confounding factors mentioned previously in this section and the treatment group to which the patient belonged. The differences between groups were expressed using odds ratios (ORs). Similar analyses were conducted considering the comparison between exposure to vildagliptin and IS. In the additional HYPOVI study performed as part of the current research, similar multivariate analyses were conducted but with additional consideration of the glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level as an adjustment factor.
Ethics
The current study was conducted in accordance with the rules of the French National Order of Physicians and the Recommendations for Professional Standards and Good Epidemiological Practices. All data processing was carried out in compliance with French information technology and privacy law.
Results
Patient characteristics
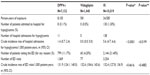
Patient characteristics are described in Table 1. Between 2009 and 2012, a total of 7,152 patients were exposed to a DPP4-i, with 1,440 patients exposed to vildagliptin (versus 10,019 patients exposed to an IS) in the EGB database. Patients in the IS cohort were older than in the DPP4-i or in the vildagliptin cohort (mean age 67.3±12.8 years versus mean age 63.7±11.9 years [P<0.0001] and mean age 63.5±11.9 years [P<0.0001], respectively) and had a longer exposure duration over the study period, which was expected, because DPP4-i have been marketed only since 2007 in France (September 2009 for vildagliptin).21
Patients were in their early sixties, and there were slightly more males (53%) in both cohorts. In both cohorts, most patients had long-standing condition status (ALD), as anticipated for patients with T2DM, the proportion being higher in the DPP4-i (86.7%) versus IS (78.7%) cohort. About 9% of the population in both cohorts was under a special coverage program for deprived people (CMU).
Endpoints
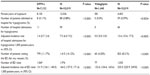
Eight patients (0.11%) from the DPP4-i cohort and none from the vildagliptin cohort (0.0%) were hospitalized for hypoglycemia versus 130 patients (1.30%) with IS (138 hospitalizations) (P=0.02 and P<0.0001, respectively). When expressed as a rate per 1,000 patient-years, the crude hospitalization rates for hypoglycemia were 1.4/1,000 patient-years (95% CI: 0.7; 2.4) in the DPP4-i cohort, 0.0/1,000 patients-years in the vildagliptin cohort (95% CI: 0.0; 4.0) versus 5.6/1,000 patient-years (95% CI: 4.7; 6.6) in the IS cohort (P<0.0001) (Table 2).
Exactly 799 patients in the DPP4-i cohort (11.2%) and 60 patients in the vildagliptin cohort (4.2%) versus 2,144 patients (21.4%) in the IS cohort visited the emergency department (ED) for any cause (P<0.0001 in both comparisons). When expressed as a rate per 1,000 patient-years, the corresponding crude incidence rates of EV/1,000 patient-years was not significantly different between the cohorts compared (P=0.5 and P=0.2, respectively).
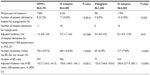
After adjustment, rates of hospital admissions for hypoglycemia and of EV were all significantly lower with DPP4-i or vildagliptin versus IS (P<0.0001) (Table 3). Further, two multivariate regression models were used to compare rates of all EV, one analysis focusing on the explanation of a dichotomous variable (patient making an EV: yes/no) and the other of a quantitative variable (number of visits). This method was not applied to the comparative analysis of hospitalization as no cases were observed in the group exposed to vildagliptin. The logistic regression analysis showed that the rate of EV was lower in patients treated with DPP4-i compared with patients treated with IS (OR: 0.769; 95% CI: 0.697; 0.849; P<0.0001) and was two-fold lower with vildagliptin compared with IS (OR: 0.486; 95% CI: 0.386; 0.651; P<0.0001) after adjusting for age, sex, CMU affiliation, and exposure durations. The application of a Poisson model yielded very similar results, with estimated OR in favor of DPP4-i (OR: 0.765; 95% CI: 0.693; 0.845; P<0.0001) or in favor of vildagliptin (OR: 0.533; 95% CI: [0.385; 0.738]; P<0.0001).
Additional supportive analysis (treatment initiations)
Consistent results were also found when considering treatment initiations only in the IS cohort (Table 4). This was important to eliminate the possible bias of an over-representation of patients with shorter exposure period to IS after adjustments, since patients in the DPP4-i cohort had much shorter exposure periods.
Exactly 4,005 patients were initiated with an IS drug in the EGB database between 2009 and 2012. Over half (53.8%) were male, 76% were under ALD, and 12.4% had a CMU affiliation. Patients in this cohort were slightly younger on average than the overall IS cohort (mean age 64.3±13.7 years), and their mean exposure duration was 18.7 months. After adjustment for age, sex, CMU status, and drug exposure duration, rates of hospital admissions for hypoglycemia and of EV per 1,000 patient-years were also significantly lower when compared either to the whole DPP4-i cohort or to the vildagliptin cohort versus IS initiators (Table 4).
Complementary data from the observational HYPOVI study
In the parallel study, data were analyzed for 487 patients (381 and 106 patients in the IS and vildagliptin cohorts, respectively). The final analysis was based on 304 patient-years of exposure to IS treatment and 79 patient-years of exposure to vildagliptin treatment. Patients were generally representative of the T2DM population treated with oral agents in France, and their characteristics did not differ substantially between the two cohorts. About 57% of patients were males, mean age was 66 years, mean body mass index was 30 kg/m2, and the median diabetes duration was 6.0 years in both cohorts.
Glycemic control was not different in the vildagliptin cohort (mean HbA1c, 7.1%±1.0%) than in the IS cohort (mean HbA1c, 7.3%±1.2%; P = not significant [NS]). Exactly 50.8% of the patients in the vildagliptin cohort had an HbA1c level of <7.0% versus 43.9% of those in the IS cohort (P = NS).
Incidences of all episodes of hypoglycemia were collected. Interestingly (considering also the HbA1c level as a covariate), adjusted estimates/1,000 patient-years of severe hypoglycemia leading to hospitalization (0.0 [95% CI: 0.0; 47.7] with vildagliptin versus 13.2 [95% CI: 3.6; 33.8] with IS; P=0.3958) were similar to those observed in the EGB analysis (0.0 with vildagliptin versus 13.6 with IS; P=0.0003). In addition, when considering severe hypoglycemia requiring medical assistance (hospital admission or the help of a health care professional), the difference in favor of vildagliptin was pronounced, even if it did not reach statistical significance due to lower numbers of patients included in this study: 0.0/1,000 patient-years (95% CI: 0.0; 47.7) with vildagliptin versus 29.7/1,000 patient-years (95% CI 13.6; 56.4) with IS (P=0.1243). Furthermore, all hypoglycemic events were captured in the current HYPOVI study, and their rates were significantly lower with vildagliptin relative to IS after adjustments: 63.3/1,000 patient-years (95% CI: 7.8; 118.8) versus 168.3/1,000 patient-years (95% CI: 122.1; 214.5) (P=0.0214).
Discussion
The analysis of this large French health insurance database showed that emergency health care resource utilization by patients with T2DM was markedly lower in patients treated with DPP4-is compared to those treated with IS drugs (ie, sulfonylureas and glinides) in real-life situations. Notably, there was a significant reduction in the frequency of the most severe hypoglycemic events, those requiring hospitalization, which was consistent with reduced use of the ED, whatever the cause, by patients in the DPP4-i cohort versus those in the IS cohort. Similar results were also obtained when considering exposure after IS treatment initiations only compared to DPP4-i exposure.
The analysis conducted with vildagliptin alone provided consistent results to those of the whole DPP4-i class that were available on the French market (predominantly sitagliptin) compared to IS, showing a significant benefit in the reduction of hospitalizations for severe hypoglycemia with vildagliptin (0.0/1,000 patient-years) as compared to IS drugs (13.6/1000 patient-years; P<0.0001). When considering these results, one should keep in mind that they reflect the frequency of hypoglycemia resulting in hospital admission, which represents only a small minority of all severe hypoglycemic events. The EGB analysis could not assess severe hypoglycemia treated in outpatient settings and those treated without formal medical intervention. Furthermore, patients treated in hospital but coded with diagnoses such as syncope or fall and not including hypoglycemia were missed. Thus, the estimated rates of severe hypoglycemic episodes in the present EGB analysis were quite conservative in all cohorts.
For this reason, it was of interest to complement our main analysis with data, certainly less robust and subject to declaration bias, but nevertheless covering a wider range of hypoglycemic events, collected by GP interviews at routine patients’ visits in the concomitant HYPOVI panel. All hypoglycemic episodes that patients recalled at the visit were reported, whatever the consequences. More severe events were more likely to be reported accurately with less memory bias, particularly those that had led to hospitalization. It is remarkable in this regard that the adjusted estimates of hypoglycemia leading to hospitalization were almost identical to those derived from the EGB database (0.0/1,000 patient-years [95% CI: {0.0; 47.7}] with vildagliptin versus 13.2/1,000 patient-years [95% CI: {3.6; 33.8}] with IS; P=0.3958). Adjusted rates of the more common hypoglycemia (all events) were also markedly reduced with vildagliptin relative to IS (63.3/1,000 patient-years [95% CI: {7.8; 118.8}] versus 168.3/1,000 patient-years [95% CI: {122.1; 214.5}]; P=0.0214).
The possibilities to adjust for potential confounding factors were limited by the unavailability of some important variables in the EGB, such as glycemic control. Indeed, when comparing rates of hypoglycemia, is it important to take into account the level of glucose control.22 In this regard, data from HYPOVI during the same period were reassuring in showing that a cohort of patients treated with IS did not have tighter levels of glucose control than patients treated with vildagliptin (mean HbA1c of 7.3% and 43.9% of patients with HbA1c <7.0% in IS-treated patients, versus mean HbA1c of 7.1% and 50.8% of patients with HbA1c <7.0% in the vildagliptin cohort). In addition, the relationship between glucose control and hypoglycemia may not be that simple. In the Lipska et al study, severe hypoglycemia was common among elderly patients with T2DM in general, but tended to be more frequent in patients with either near-normal glycemia or very poor glycemic control.22
This lower risk of severe hypoglycemia with DPP4-i15,23 and with vildagliptin versus IS drugs is in line with previous results from numerous clinical trials16,24 and real-life studies.25–27 The mechanism underlying this low hypoglycemic risk has been thoroughly examined under experimental conditions, particularly with vildagliptin. Three randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover studies have assessed the effects of vildagliptin on hormonal counter-regulation to hypoglycemia in diabetic patients. The first showed a 38% increase in the glucagon response with vildagliptin versus placebo during hypoglycemic (2.5 mmol/L) clamp in T2DM patients treated orally.14 These results were later confirmed in T2DM patients treated with insulin28 and in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus.29
For informed decision making when faced with the multiple and increasingly complex therapeutic choices now available, physicians should take into consideration all known aspects of antidiabetic drugs, and notably the potentially devastating consequences of severe hypoglycemia. Antidiabetic drugs account for a significant proportion of preventable hospitalizations for adverse drug events in older adults in the US.5 Hospitalizations for iatrogenic hypoglycemia represent a well-recognized public health issue of increasing frequency, to the point that rates of hospitalizations for hypoglycemia in the US now exceed those for hyperglycemia.7 Visits to the ED because of hypoglycemia requiring medical assistance were evaluated in a recent prospective multicenter survey in tertiary hospitals in Greece: most cases (90.8%) were observed in patients with T2DM, and use of sulfonylureas was the strongest independent predictor (OR: 4.0; 95% CI: 2.5; 6.4) of these events.30 It is therefore essential to know the real incidence of hospital admissions and EV for hypoglycemia with different antidiabetic drugs, and to the best of our knowledge, this study is the first to investigate this question in France with documented events in the National Health Insurance database. The current EGB analysis shows meaningful reductions in the frequency of the most severe hypoglycemic episodes when patients were treated with DPP4-is as compared to IS drugs.
Moreover, severe hypoglycemia has been associated with serious sequelae, including falls and fractures in older persons that may permanently affect their autonomy;31 dementia;32 cardiovascular events;33,34 and significant mortality.33,35 Interestingly, a reduction in all-cause mortality was recently shown in a cohort of patients initiated with a combination of metformin plus DPP4-i versus metformin plus sulfonylureas between 2007 and 2012; these data were found in the UK Clinical Practice Research Datalink (CPRD), along with a similar trends for major cardiovascular events.36
Although severe hypoglycemic events can clearly have dramatic consequences, milder events also place a significant psychological burden on patients;37 they may also result in reduced quality of life38 and major anxiety and fear of hypoglycemia;39 and their repetition predicts future severe episodes.3 Even non-severe events lead to poor adherence and more treatment discontinuations,4 and have a major negative impact on the worldwide economic burden of diabetes.4,40
Strengths and limitations of the current study
The current EGB analysis reports data from a large nationwide sample of representative T2DM persons; these are official data not subject to record bias, and are therefore indisputable. In addition, the representativeness of the sampled population is guaranteed. However, the current study’s main limitation is the impossibility to adjust for all potential confounding factors because of unavailable variables. Nonetheless, in the paired HYPOVI study, the clinical profiles of patients treated with IS did not differ in any clinically relevant manner to those of patients treated with the DPP4-i; in particular, glucose control was similar.
On the other hand, the complementary HYPOVI study consisted of softer data subject to recall bias.41 Even with severe events, there is under-reporting when events are collected retrospectively, as was recently shown in the DIALOG study: physicians reported severe hypoglycemia in 11.9% of T2DM patients treated with insulin over 1 year in the retrospective survey, while in the prospective survey, 6.4% of patients reported a severe event during the first month following insulin initiation.42 Despite these limitations, both databases have been used successfully in France to investigate major public health issues in different domains regarding diabetes19 or other medical situations.20
Conclusion
The analysis of events recorded in the current nationwide population-based study shows a markedly lower frequency of hospitalization for severe hypoglycemia and of all-cause EV, in patients with T2DM exposed to DPP4-i versus those exposed to insulin secretagogues. These real-life data have meaningful clinical and public health consequences and should be taken into consideration in the benefit/risk evaluation of drug strategies and in any care plan for patients with T2DM.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Rémy Soulhol for coordinating the study and Stéphane Quéré for statistical support. This work was funded by Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation.
Author contributions
BD conceived the study, was the key contributor to data analysis and overall data interpretation, and was involved in reviewing the paper. JR was responsible for the statistical analysis. CD participated in the study conception and design. SH contributed to overall data interpretation and was involved in reviewing the paper. SD participated in the study conception and design, overall clinical interpretation, and wrote the first draft of the paper; SD was also the key contributor in the writing of the paper. All authors were involved in paper revisions, approved the final paper, and are responsible for its intellectual content.
Disclosure
BD is employed by Cemka-Eval, a consultancy team working for numerous private companies and public French national and international institutions in health care. SH has received fees for consultancy, advisory boards, speaking, clinical studies, travel, or accommodation from Novo Nordisk, Lilly, Sanofi, Novartis Pharma SAS, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck & Co. Inc, Bristol-Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca, and Roche Pharmaceuticals. CD and SD are employees of Novartis Pharma SAS, the sponsor of the present study. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Guariguata L, Whiting DR, Hambleton I, Beagley J, Linnenkamp U, Shaw JE. Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2013 and projections for 2035. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014;103:137–149. | |
Mandereau-Bruno L, Denis P, Fagot-Campagna A, Fosse-Edorh S. Prevalence of people pharmacologically treated for diabetes and territorial variations in France in 2012. Bull Epidémiol Hebd. 2014;30–31:493–499. | |
Amiel SA, Dixon T, Mann R, Jameson K. Hypoglycaemia in type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2008;25:245–254. | |
Bron M, Marynchenko M, Yang H, Yu AP, Wu EQ. Hypoglycemia, treatment discontinuation, and costs in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus on oral antidiabetic drugs. Postgrad Med. 2012;124:124–132. | |
Budnitz DS, Lovegrove MC, Shehab N, Richards CL. Emergency hospitalizations for adverse drug events in older Americans. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:2002–2012. | |
Majumdar SR, Hemmelgarn BR, Lin M, McBrien K, Manns BJ, Tonelli M. Hypoglycemia associated with hospitalization and adverse events in older people: population-based cohort study. Diabetes Care. 2013;36:3585–3590. | |
Lipska KJ, Ross JS, Wang Y, et al. National trends in US hospital admissions for hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia among Medicare beneficiaries, 1999 to 2011. JAMA Intern Med. 2014;174:1116–1124. | |
Ahren B. Are sulfonylureas less desirable than DPP-4 inhibitors as add-on to metformin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes? Curr Diab Rep. 2011;11:83–90. | |
Dejager S, Schweizer A. Minimizing the risk of hypoglycemia with vildagliptin: Clinical experience, mechanistic basis, and importance in type 2 diabetes management. Diabetes Ther. 2011;2:51–66. | |
Halimi S, Raccah D, Schweizer A, Dejager S. Role of vildagliptin in managing type 2 diabetes mellitus in the elderly. Curr Med Res Opin. 2010;26:1647–1656. | |
Schweizer A, Dejager S, Foley JE, Shao Q, Kothny W. Clinical experience with vildagliptin in the management of type 2 diabetes in a patient population ≥75 years: a pooled analysis from a database of clinical trials. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011;13:55–64. | |
Dejager S, Schweizer A. Incretin therapies in the management of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and renal impairment. Hosp Pract (1995). 2012;40:7–21. | |
Charbonnel B, Schweizer A, Dejager S. Combination therapy with DPP-4 inhibitors and insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: what is the evidence? Hosp Pract (1995). 2013;41:93–107. | |
Ahrén B, Schweizer A, Dejager S, et al. Vildagliptin enhances islet responsiveness to both hyper- and hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94:1236–1243. | |
Göke B, Gallwitz B, Eriksson J, Hellqvist A, Gause-Nilsson I; D1680C00001 Investigators. Saxagliptin is non-inferior to glipizide in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled on metformin alone: a 52-week randomised controlled trial. Int J Clin Pract. 2010;64:1619–1631. | |
Matthews DR, Dejager S, Ahrén B, et al. Vildagliptin add-on to metformin produces similar efficacy and reduced hypoglycaemic risk compared with glimepiride, with no weight gain: results from a 2-year study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2010;12:780–789. | |
Nauck MA, Meininger G, Sheng D, Terranella L, Stein PP; Sitagliptin Study 024 Group. Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, sitagliptin, compared with the sulfonylurea, glipizide, in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin alone: a randomized, double-blind, non-inferiority trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2007;9:194–205. | |
Tuppin P, de Roquefeuil L, Weill A, Ricordeau P, Merlière Y. French national health insurance information system and the permanent beneficiaries sample. Rev Epidemiol Sante Publique. 2010;58:286–290. | |
Blin P, Lassalle R, Dureau-Pournin C, et al. Insulin glargine and risk of cancer: a cohort study in the French National Healthcare Insurance Database. Diabetologia. 2012;55:644–653. | |
Sabouret P, Depret-Bixio L, Cotte FE, Marie P, Bedira N, Blin P. Sex differences in stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation in French primary care. Results of the AFIGP (Atrial Fibrillation In General Practice) Database. Clin Res Cardiol. 2014; 103:887–893. | |
Haute Autorité de Santé, Avis de la Comission de Transparence. Galvus, 10 Décembre 2008. Available from: www.has-sante.fr/portail/plugins/ModuleXitiKLEE/types/FileDocument/doXiti.jsp?id=c_749360. Accessed June 8, 2015. French. | |
Lipska KJ, Warton EM, Huang ES, et al. HbA1c and risk of severe hypoglycemia in type 2 diabetes: the diabetes and aging study. Diabetes Care. 2013;36:3535–3542. | |
Krobot KJ, Ferrante SA, Davies MJ, et al. Lower risk of hypoglycemia with sitagliptin compared to glipizide when either is added to metformin therapy: a pre-specified analysis adjusting for the most recently measured HbA(1c) value. Curr Med Res Opin. 2012;28:1281–1287. | |
Ahrén B, Foley JE, Dejager S, et al. Higher risk of hypoglycemia with glimepiride versus vildagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes is not driven by high doses of glimepiride: divergent patient susceptibilities? Diabetes Ther. 2014;5:459–469. | |
Penfornis A, Bourdel-Marchasson I, Quere S, Dejager S. Real-life comparison of DPP4-inhibitors with conventional oral antidiabetics as add-on therapy to metformin in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes: the HYPOCRAS study. Diabetes Metab. 2012;38:550–557. | |
Simon D, Detournay B, Eschwege E, et al. Real-life comparison of DPP4-inhibitors with conventional oral antidiabetics as add-on therapy to metformin in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes: the HYPOCRAS study. Diabetes Ther. 2014;5:207–224. | |
Mathieu C, Barnett AH, Brath H, et al. Effectiveness and tolerability of second-line therapy with vildagliptin vs other oral agents in type 2 diabetes: a real-life worldwide observational study (EDGE). Int J Clin Pract. 2013;67:947–956. | |
Farngren J, Persson M, Schweizer A, Foley JE, Ahrén B. Glucagon dynamics during hypoglycemia and food-re-challenge following treatment with vildagliptin in insulin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014;16:812–818. | |
Farngren J, Persson M, Schweizer A, Foley JE, Ahrén B. Vildagliptin reduces glucagon during hyperglycemia and sustains glucagon counterregulation during hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97:3799–3806. | |
Liatis S, Mylona M, Kalopita S, et al. Hypoglycaemia requiring medical assistance in patients with diabetes: a prospective multicentre survey in tertiary hospitals. Diabetes Metab. 2015;41:126–131. | |
Nelson JM, Dufraux K, Cook PF. The relationship between glycemic control and falls in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2007;55:2041–2044. | |
Whitmer RA, Karter AJ, Yaffe K, Quesenberry CP Jr, Selby JV. Hypoglycemic episodes and risk of dementia in older patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA. 2009;301:1565–1572. | |
Hsu PF, Sung SH, Cheng HM, et al. Association of clinical symptomatic hypoglycemia with cardiovascular events and total mortality in type 2 diabetes: a nationwide population-based study. Diabetes Care. 2013;36:894–900. | |
Stahn A, Pistrosch F, Ganz X, et al. Relationship between hypoglycemic episodes and ventricular arrhythmias in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases: silent hypoglycemias and silent arrhythmias. Diabetes Care. 2014;37:516–520. | |
McCoy RG, Van Houten HK, Ziegenfuss JY, Shah ND, Wermers RA, Smith SA. Increased mortality of patients with diabetes reporting severe hypoglycemia. Diabetes Care. 2012;35:1897–1901. | |
Morgan CL, Mukherjee J, Jenkins-Jones S, Holden SE, Currie CJ. Combination therapy with metformin plus sulphonylureas versus metformin plus DPP-4 inhibitors: association with major adverse cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014;16:977–983. | |
Fulcher G, Singer J, Castañeda R, et al. The psychosocial and financial impact of non-severe hypoglycemic events on people with diabetes: two international surveys. J Med Econ. 2014;17:751–761. | |
Barendse S, Singh H, Frier BM, Speight J. The impact of hypoglycaemia on quality of life and related patient-reported outcomes in type 2 diabetes: a narrative review. Diabet Med. 2012;29:293–302. | |
Wild D, von Maltzahn R, Brohan E, Christensen T, Clauson P, Gonder-Frederick L. A critical review of the literature on fear of hypoglycemia in diabetes: implications for diabetes management and patient education. Patient Educ Couns. 2007;68:10–15. | |
Brod M, Wolden M, Christensen T, Bushnell DM. Understanding the economic burden of nonsevere nocturnal hypoglycemic events: impact on work productivity, disease management, and resource utilization. Value Health. 2013;16:1140–1149. | |
Hill HA and Kleinbaum DG. Bias in Observational Studies. Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online, 2014. Available from: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/9781118445112.stat05111/abstract. Accessed June 10, 2015. | |
Cariou B, Fontaine P, Eschwege E, et al. Frequency and predictors of confirmed hypoglycaemia in type 1 and insulin-treated type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in a real-life setting: results from the DIALOG study. Diabetes Metab. 2015;41:116–125. |
 © 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.