Back to Journals » International Journal of Nanomedicine » Volume 15
Graphene Oxide/Copper Nanoderivatives-Modified Chitosan/Hyaluronic Acid Dressings for Facilitating Wound Healing in Infected Full-Thickness Skin Defects
Authors Yang Y , Dong Z, Li M, Liu L, Luo H, Wang P, Zhang D, Yang X, Zhou K, Lei S
Received 26 August 2020
Accepted for publication 25 September 2020
Published 27 October 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 8231—8247
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S278631
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Farooq A. Shiekh
Ying Yang,1,2 Zhonggen Dong,3 Min Li,4 Lihong Liu,1,3 Hang Luo,1 Pu Wang,2 Dou Zhang,1 Xinghua Yang,2 Kechao Zhou,1 Shaorong Lei2
1State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Research Institute of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, People’s Republic of China; 2Department of Plastic Surgery, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410008, People’s Republic of China; 3Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410011, People’s Republic of China; 4Department of Oncology, Changsha Central Hospital, University of South China, Changsha 410004, People’s Republic of China
Correspondence: Shaorong Lei
Department of Plastic Surgery, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, 87 Xiangya Road, Changsha 410008, Hunan, People’s Republic of China
Tel +86 73189753014
Fax +86 73184327332
Email [email protected]
Kechao Zhou
State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Research Institute of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, 932 South Lushan Road, Changsha 410083, Hunan, People’s Republic of China
Tel +86 7318836264
Fax +86 7318883646
Email [email protected]
Purpose: Wound healing, especially of infected wounds, remains a clinical challenge in plastic surgery. This study aimed to manufacture a novel and multifunctional wound dressing by combining graphene oxide/copper nanocomposites (GO/Cu) with chitosan/hyaluronic acid, providing significant opportunities for the therapy of wound repair in wounds with a high risk of bacterial infection.
Methods: In this study, GO/Cu-decorated chitosan/hyaluronic acid dressings (C/H/GO/Cu) were prepared using sodium trimetaphosphate (STMP) crosslinking and the vacuum freeze-drying method, and chitosan/hyaluronic acid dressings (C/H) and GO-incorporated chitosan/hyaluronic acid dressings (C/H/GO) served as controls. The surface characterization, in vitro degradation under various pH values, antimicrobial potential, cytocompatibility and in vivo therapeutic efficacy in a bacteria-infected full-thickness skin defect model were systematically evaluated.
Results: Our experimental results indicated that the acidic environment facilitated the release of copper (CuNPs and Cu2+) from the dressings, and prepared C/H/GO/Cu dressings exhibited significant in vitro antimicrobial activities against the two tested bacterial strains (ATCC35984 and ATCC25923). All three dressings showed satisfactory cytocompatibility with mouse fibroblasts (NIH/3T3-L1). Moreover, remarkably accelerated wound healing was found in the C/H/GO/Cu group, with controlled inflammatory infiltration and improved angiogenesis in granulation tissues. In addition, no pathological damage was noted in the tissue structures of the tested organs (heart, lung, liver and kidney) in any of the four groups.
Conclusion: Collectively, GO/Cu-incorporated chitosan/hyaluronic acid dressings suggested a synergistic antimicrobial efficacy and acceptable biocompatibility both in vitro and in vivo, as well as a significantly accelerated healing process of bacteria-infected wounds. Thus, the multifunctional C/H/GO/Cu composite is expected to be a potential alternative for wound dressings, especially for the management of intractable wounds caused by bacterial infection.
Keywords: graphene oxide, copper nanoparticles, wound dressing, bacterial infection, wound healing
Introduction
Severe skin injury resulting from burn, surgery, trauma or chronic disease (such as diabetes or peripheral vascular diseases) has become one of the most critical issues clinically.1 Generally, damage to the structural integrity of skin represents a loss of the protective barrier against external bacteria colonization, which could promote susceptibility to bacterial infection, especially for immunocompromised patients.2 The healing of damaged skin is a complex process and occurs in a systematic manner. There are four continuous and overlapping phases regarding wound healing, as follows: hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation and remodeling.3,4 Pathogenic contamination of wounds is considered to be a major disturbance during the healing process, aggravating wound deterioration and increasing the healthcare burden of patients suffering from skin defects.5 Therefore, it is clinically imperative to develop feasible therapeutic methods for the prevention and/or treatment of bacterial infection to recover a favorable microenvironment for wound regeneration.
Conventionally, a number of therapies, such as surgical wound dressing therapy, negative pressure wound therapy or hyperbaric oxygen treatment, are applied for wound management at early stages after injury.6 However, advanced therapies, including autogenous skin grafts, artificial tissue engineered products, or even flap transplantation, must be employed for wound closure if the strategies mentioned above do not provide the desired therapeutic effects.7–9 Although commercially available wound dressings have been widely used in the clinic, they are usually expensive and not suitable for the coverage of infected wound defects. To improve the treatment outcomes of infected wounds, functional wound dressings with antimicrobial properties were prepared and investigated as previously reported.10–13 As a derivative of graphene, graphene oxide (GO) nanosheets have drawn significant attention because of their broad-spectrum antibacterial properties and tolerable cytotoxicity in mammalian cells.14,15 The dominant perceptions regarding the antimicrobial mechanism of GO nanosheets could be summarized as follows: physical damage to bacterial membranes is mediated by reactive oxygen species (ROS)-relevant or irrelevant oxidative stress and destructive extraction of phospholipids from the lipid bilayers.16,17 These actions eventually contribute to the damage of the integrity of the cell membrane and then bacterial death.18 Nevertheless, whether GO nanosheets can selectively kill bacterial cells without affecting normal mammalian cells remains unknown, and the primary determinant of their antimicrobial actions is still under debate.14,16
GO-based multicomponent nanocomposites, including polymers, quaternary ammonium salts, antibiotics and nanometals, have emerged as promising candidates to overcome the limitations of individual components.14,19–22 As one of the most abundant natural biopolymers extracted from alkaline deacetylation of chitin, chitosan (CS) is extensively applied in wound healing applications because of its antibacterial activity, biocompatibility and biodegradability.23 Interestingly, enhancement of antimicrobial activity and cytocompatibility was observed after the attachment of CS to GO, indicating that GO-CS nanohybrids exhibit improved bactericidal and biosafety performances.24 In addition, the biodegradation time of GO-CS nanohybrids was suspected to be much slower than that of CS only due to the incorporation of GO-based nanomaterials, which may be beneficial for long time coverage of dressing scaffolds in wound treatment. Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a well-known high-molecular-weight linear natural glycosaminoglycan that serves as an indispensable component of the extracellular matrix (ECM) in human connective tissue and skin.25 The synergic action between CS and HA is of great importance to accelerate the wound healing process with satisfactory aesthetic and functional outcomes in wound closure.26 Therefore, we expected that a CS/HA-based platform could be an effective therapeutic strategy for developing multifunctional dressings for local treatment of infected wounds.
Copper (Cu) is a cost-effective antimicrobial agent that kills pathogens efficiently on its metallic surface, leading to the disruption of the respiratory chain and gene replication in bacteria.27 Meanwhile, cellular damage including oxidation of lipids and proteins, was found to contribute to lethality to microorganisms due to the redox properties of copper nanoparticles (CuNPs).28 Moreover, copper ions (Cu2+) have been reported to facilitate angiogenesis by maintaining the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1α).29 Inspired by their excellent antibacterial activity and angiogenesis capacity, Cu-incorporated wound dressings were prepared to stimulate angiogenesis and suppress infection in the management of bacteria-infected wounds.30,31 Additionally, CuNP-decorated GO membranes fabricated by an in situ chemical reduction method also exhibited enhanced antimicrobial performances.32 However, few investigations have emphasized the application of GO/Cu-based dressings for wound care under high risk of infection as far as we know. Taken together, this research aimed to prepare a multifunctional wound dressing by combining GO/Cu nanocomposites with chitosan/hyaluronic acid, and we anticipate the use of this novel dressing as a promising alternative for efficient therapeutic intervention of bacteria-infected wound healing in plastic surgery clinics (Scheme 1).
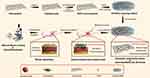 |
Scheme 1 Schematic illustration for the synthesis, synergistic antibacterial effects, cytocompatibility with fibroblasts and in vivo wound healing efficacy of C/H/GO/Cu dressing scaffolds. |
Materials and Methods
Synthesis of Graphene Oxide/Copper (GO/Cu) Nanocomposites
Graphene oxide (GO) was synthesized by the modified Hummer method from flake graphite (Aladdin, Shanghai, China) in accordance with the previously reported protocol.33 Then, a GO suspension (2 mg/mL, 100 mL) was prepared using an ultrasonic bath (SB-5200DT, SCIENTZ, Ningbo, China). In situ chemical reduction was performed to achieve the growth of copper nanoparticles (CuNPs) in the GO suspension as described previously.34 In brief, the desired amounts of cupric sulfate pentahydrate (CuSO4.5H2O, 100 mg, Aladdin) and ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid disodium salt dihydrate (EDTA.2Na.2H2O, 60 mg, Aladdin) were added into the as-prepared GO suspension and agitated sufficiently at 30 °C for 1 h, and then 20 mL of a solution containing sodium hydroxide (NaOH, 80 mg, Aladdin) and sodium borohydride (NaBH4, 10 mg, Aladdin) was added into the mixture slowly and stirred at 30 °C for 30 min. The collected mixture was centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 15 min, washed using deionized (DI) water three times and dried at 37 °C for 24 h to obtain homogeneous GO/Cu nanocomposite (mass ratio = 2:1).
Preparation of GO/Cu-Decorated Chitosan/Hyaluronic Acid Dressings
The composite dressings were prepared using sodium trimetaphosphate (STMP) crosslinking and then vacuum freeze-dried.35 As a food-safe crosslinking agent, STMP can produce stable phosphate linkages between intermolecular hydroxyl groups that exist in chitosan and hyaluronic acid (HA).36 Briefly, 5% wt chitosan (100–200 mPa.s viscosity, 97% N-deacetylation, Aladdin)/sodium hyaluronate (solution A) (80–2000 kDa, Solarbio, Beijing, China) mixture solutions (dissolved in 100 mL of 1 wt% acetic acid) were prepared. Meanwhile, 2.5% wt GO/Cu solution (solution B) (dispersed in 100 mL of DI water) was prepared after sonication for 45 min. Then, aliquots of solutions A and B (volume ratio=4:1) were mixed uniformly by mechanical agitation (1000 rpm, 30 min). Subsequently, the mixtures were crosslinked using STMP solutions (10% w/v, Aladdin) and agitated at 37 °C for 1 h. The solutions were poured into the customized polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) mold (100 mm in diameter and 5 mm in height) after being washed thoroughly with distilled water to remove the residual STMP and acetic acid, and the pH value of the final formulation upon hydration in water was approximately neutral (6.8–7.0) after washing. Then, the obtained solutions were kept at −80 °C for 12 h and further freeze-dried under vacuum (FD8-5T, SIM International Group CO., LTD, LA, USA) for 48 h. To serve as the controls, chitosan/hyaluronic acid dressings (C/H) and GO-incorporated chitosan/hyaluronic acid dressings (C/H/GO) were also fabricated in a similar manner. These prepared dressings were sterilized using 48 h ultraviolet radiation before carrying out the in vitro and in vivo biological experiments.
Morphological and Chemical Characterizations
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images of GO and GO/Cu were collected by a Tecnai G2 F20 electron microscope (JEM-2100F, JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) with an accelerating voltage of 200 kV. A field-emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM, ZEISS SIGMA HD, Jena, Germany) with an accelerating voltage of 10 kV was applied to examine the surface morphologies of the prepared dressings. The surface functional groups of the dressings were analyzed by a Fourier transform- infrared (FT-IR) spectrophotometer (NICOLET iS10, Thermo Fisher Scientific, MA, USA). The spectra were acquired with 32 scans per sample from 4000 to 400 cm−1 at a resolution of 4.0 cm−1. The thermal properties of the dressings were examined by a thermogravimetric (TG) analyzer (DTA-7300, SEIKO Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) with a heating rate of 10 mL/min from 30 to 1000 °C under nitrogen flow (80 mL/min) to investigate the amount of incorporated GO and CuNPs in the dressings.
The Copper Release Behaviors of the Dressings
To examine the effect of pH on the release kinetics of copper (CuNPs and Cu2+) from the dressings, samples with areas of 12.6 cm2 were cut and prepared and then immersed in 50 mL of HEPES (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) buffers with pH values of 5.5, 7.0 or 8.5. The solutions were collected at the indicated intervals (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13 and 14 d) after incubation at 37 °C with orbital shaking at 80 rpm and then supplemented by fresh buffer at each sampling time point. The concentration of released copper was analyzed using inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES, Perkin Elmer, Optima 5300 DV, USA) after being treated with strong acid to evaluate the amount of Cu released from the dressings at each interval.
Determination of Antibacterial Properties
The antibacterial properties of the dressings were determined by confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) observation, bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation evaluation. Two types of bacterial strains commonly seen in skin and soft tissue infections, methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA, ATCC25923) and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus epidermidis (MSSE, ATCC35,984), were used in the present study. Bacteria were suspended in Mueller-Hinton Broth (MHB, Solarbio) at a concentration of 1×108 colony-forming units (CFUs)/mL for subsequent experiments after overnight culture in 20 mL of tryptic soy broth (TSB).37 The MICs (minimal inhibitory concentrations) and MBCs (minimal bactericidal concentrations) of GO, CuNPs and GO/Cu nanomaterials against the two tested bacterial strains were determined as described in previous studies.38,39
Bacterial inactivation of the dressings was observed by CLSM (TCS SP8, Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany) with fluorescent green and red indicating live and dead cells, respectively.37 Dressings coated with bacteria were stained with 300 µL of combination dye (LIVE/DEAD BacLight viability kits, Life Technologies, CA, USA) after 6 and 48 h of contact according to the provided product manual. The survival status of the bacteria on the dressings was then examined using CLSM, and images were collected from random positions of the samples.
To further investigate the antimicrobial efficacy of the dressings, bacterial attachment and biofilm formation were quantitatively analyzed by the spread plate method and tissue culture plate method, respectively.40,41 First, 1 mL of MHB solution with 1×106 CFU bacteria was added into glass bottom cell culture dishes (NEST Biotechnology Ltd., Wuxi, China) containing C/H, C/H/GO and C/H/GO/Cu dressings, and dishes containing only MHB medium and bacteria served as blank controls. After incubation for 6 h at 37 °C, bacteria attached over the surface of the samples were thoroughly dislodged by ultrasonication (30 kHz, 5 min). The collected solutions were 10-fold serially diluted and then placed onto TSA plates for a 24 h incubation at 37 °C. The CFUs on the plates were counted to quantify the number of attached live bacterial cells in each group. The normalized CFUs were obtained by comparing the CFUs in the controls with groups containing dressings. Second, the samples were fixed by 2.5% glutaraldehyde for 30 min and dried at 60 °C for 1 h after 48-h incubation with the tested strains as aforementioned. Then, biofilms formed on the samples were stained with 1 mL of crystal violet (CV) solution (0.1% wt/vol, Sigma-Aldrich) at 37 °C for 10 min and dried for 2 h at 37 °C. Biofilms on the surfaces of the samples were quantified by solubilizing the CV stain in 300 μL of glacial acetic acid (30% wt/vol, Sigma-Aldrich) for 10 min. The CV concentration was confirmed at 492 nm on a microplate reader (M200 PRO, TECAN, Männedorf, Switzerland).
Determination of Cytocompatibility
The in vitro cytocompatibility of GO/Cu nanocomposites was investigated with mouse fibroblasts (NIH/3T3-L1) using apoptosis analysis and cell proliferation observation.42,43 In brief, sterile specimens were placed in 6-well plates containing cells at a density of 5.0×105 cells/well for coculture for 48 h, with culture medium and specimens as blank controls. Cells were collected and suspended in 500 μL of 1×binding buffer, and ten microliters of a mixture containing Annexin-V FITC and propidium iodide (PI) (BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) was added into the cell suspension. Subsequently, 100 μL of binding buffer was added into the suspension after being washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) twice. The effects of different specimens on cell apoptosis were confirmed by flow cytometry (FACS Canto II, BD Biosciences), and relevant data were analyzed using FlowJo software (TreeStar, OR, USA). In addition, the proliferative activities of cells over the surface of the dressings at days 1, 3 and 5 were evaluated by CCK-8 assay. Dressings were placed in 48-well plates containing cells at a density of 1.0×104 cells/well, and wells containing only medium and dressings served as blank controls. At the indicated time points, the medium was removed, and 100 μL of cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) solution (Dojindo Molecular Technologies Inc., Kumamoto, Japan) was added into the wells and incubated for an additional 4 h at 37 °C. The absorbance was measured on a microplate reader at 450 nm (OD450) in strict accordance with the manufacturer’s protocol.
In vivo Therapeutic Efficacy of Infected Wound Defects
In our study, a modified infected full-thickness skin defect model was established to investigate the anti-infection and wound healing effects of GO/Cu-decorated chitosan/hyaluronic acid dressings in vivo.10,44 All surgical procedures for the animal experiments were examined and approved by the Animal Experimentation Medical Ethics Committee of Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, and performed according to “3R” principles (Reduction, Replacement and Refinement) as indicated in the “Guidelines on Treating Experimental Animals Well” issued by the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Twenty male BALB/c mice weighing approximately 25–30 g (7–8 w age) were purchased from Shanghai SLAC Laboratory Animal Co., Ltd. (SLAC, Shanghai, China). The groupings (n=5 for each group) in the in vivo experiments were as follows: 1) Group without coverage by dressings (CTRL); 2) Group with coverage by chitosan/hyaluronic acid dressings (C/H); 3) Group with coverage by GO-incorporated chitosan/hyaluronic acid dressings (C/H/GO); 4) Group with coverage by GO/Cu-decorated chitosan/hyaluronic acid dressings (C/H/GO/Cu). Briefly, mice were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 5% chloral hydrate (10 μL/g body weight). The dorsal skin of mice was shaved and sterilized with iodophors. Then, a 10 mm diameter full-thickness defect was created with immobilization by a customized rubber ring. Subsequently, 50 μL of PBS containing Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC25923) at the indicated concentration (1.0×106 CFU/mL) was inoculated onto the wound surface and covered with different dressings. Each mouse was placed into an individual cage after operation, and all dressings were changed every two days. No antibiotics were administered after operation. No mortality occurred during the follow-up period.
Evaluation of Wound Healing Process
The general appearance of wounds in each group (n=5) was photographed by a digital camera (Sony, DSC-H300) at days 1, 3, 7, 10 and 14 postsurgery. The wound margin was carefully marked, and the wound area was quantified by ImageJ software (NIH, Maryland, USA).45 Wound area proportion was defined as the percentage change from the initial wound area at day 1 of the experiments, and the proportion of wound closure at the day of sacrifice (day 14) was also calculated and compared. The tissues containing the wound area and surrounding normal skin, as well as the vital organs (including the heart, lung, liver and kidney) in each group were collected for histopathological evaluation.
Histopathological and Immunofluorescence Examination
The prepared tissue specimens from each group (n=3) were fixed by 4% neutral-buffered paraformaldehyde (PFA) for 48 h, with sufficient washing overnight to remove the PFA.37 Then, samples were embedded in paraffin (EG1150, Leica) and cut into sections with a thickness of 5 μm (RM2245, Leica). Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and Masson’s trichrome staining were used to examine the morphological changes of infected wound defects and vital organs in order to evaluate the wound repair efficacy and potential toxicity of the C/H/GO/Cu dressing. In addition, immunofluorescence was performed to investigate the inflammatory infiltration and angiogenesis in granulation tissues as described previously.37,45 The prepared sections for immunofluorescence staining were incubated with rabbit anti-CD3 antibody (1:300, ab16669, Abcam, Cambridge, UK) or rabbit anti-CD31 antibody (1:200, ab124432, Abcam) overnight at 4 °C and then washed with PBS three times. Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti-rabbit IgG (1:200, ab150077, Abcam) was applied as the secondary antibody, and nuclei were counterstained with 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, Molecular Probe, Sigma-Aldrich). Images of five randomly selected fields from the wound site in each group were observed by an inverted fluorescence microscope (DMI4000B, Leica) to determine the biological effects of C/H/GO/Cu dressing on inflammatory infiltration and angiogenesis.
Statistical Analysis
All quantitative data obtained from both the in vitro and in vivo experiments were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and nonparametric tests (the Mann–Whitney U-test) were used for statistical analysis in SPSS software (version 19.0, IBM Corp, NY, USA). p-values less than 0.05 were considered to be statistically significant.
Results and Discussion
Synthesis and Characterization
In the present work, an environmentally friendly and easily accessible method was utilized to prepare the GO-Cu nanocomposites, which were synthesized via in situ chemical reduction as previously reported.34 As demonstrated in Figure 1A, ultrathin, smooth sheets with several surface wrinkles were observed through TEM observation, confirming the successful synthesis of the GO nanosheets. In addition, the morphological aspect of the CuNPs presented on the GO nanosheets was highly similar to the nanoparticle appearance described by Zhu et al.46 High-resolution TEM images of single copper nanoparticles displayed a measured lattice spacing of 0.352 nm, indicating a high crystallinity of the CuNPs. The gross appearance of the prepared dressings as shown in Figure 1B indicated that the GO nanosheets and GO/Cu nanocomposites were well dispersed and embedded throughout the chitosan/hyaluronic acid matrix, and the color of the dressings gradually deepened with the addition of GO and GO/Cu. Moreover, SEM images as displayed in Figure 1C indicated that the dressings had interconnected hybrid networks with porous structures. The GO nanosheets and GO/Cu nanocomposites were also uniformly incorporated into the interconnected micropores as shown in the SEM images with higher magnification. Overall, the morphological observation described above confirmed the successful preparation of GO/Cu nanocomposites and GO/Cu-decorated chitosan/hyaluronic acid dressings.
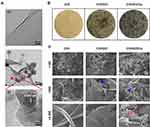 |
Figure 1 Characterization of GO/Cu nanocomposites and C/H/GO/Cu dressings. |
The FT-IR spectra of the prepared dressings are shown in Figure 2A. Absorption bands of carboxyl (-COO-) and acetyl groups (-C=O) of hyaluronic acid (HA) were observed at approximately 1620 cm−1, and a combined peak at approximately 1425 cm−1 was assigned to the N-acetyl moiety (-C-N-) of the amide II group and the carboxyl group as previously reported.47 The bands at 3350 cm−1 and 1640 cm−1 were related to the OH-, NH- and C=O stretching vibrations of chitosan,48 which are mostly overlapped by the oxygen-containing functional groups from GO and carboxyl and acetyl groups from HA. It is clearly illustrated that absorption bands of some oxygen-containing functional groups of GO nanosheets, such as 3500 cm−1, 1600 cm−1 and 1080 cm−1, were partially weakened or removed after chemical reduction. Meanwhile, absorption peaks for CuNPs in the FT-IR spectra were not obvious because there was no observable absorption peak above 1000 cm−1 as previously confirmed.34
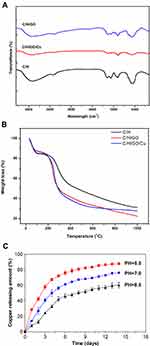 |
Figure 2 Surface and in vitro degradation features of the dressings. |
Variation of the thermal stability ranging from 30 to 1000 °C of the C/H, C/H/GO and C/H/GO/Cu dressings under nitrogen flows was further investigated by TGA as shown in Figure 2B. Overall, the TGA curves of the three dressings consisted of three stages. Weight loss of approximately 16% for the C/H dressings and 18% for the C/H/GO and C/H/GO/Cu dressings constituted the first stage at 30 to 110 °C, which resulted from the evaporation of moisture and residual acetic acid as previously verified.49–51 The initial changes of TGA curves indicated a certain amount of absorbed water in their porous structure. Then, the major decomposition of the C/H/GO and C/H/GO/Cu dressings ranged from 200 to 300 °C and the C/H dressings ranged from 200 to 400 °C, respectively, which was attributed to the cleavage of intermolecular bonds and molecular structures among the incorporated chitosan, hyaluronic acid and graphene oxide.49,51 We found an approximately 35% loss in weight for the C/H dressings and 40% loss in weight for the C/H/GO and C/H/GO/Cu dressings at the second stage, suggesting a discrepant thermal degradation behavior after the addition of GO and GO/Cu nanocomposite for the CS/HA dressings. Eventually, residues of the dressings were further degraded until the end of the thermogravimetric examination, and the weight loss during this process was approximately 23%, 27% and 22% for the C/H, C/H/GO and C/H/GO/Cu dressings, respectively. It could be observed that the mass ratio of CuNPs in the C/H/GO/Cu dressings was approximately 5% based on the above analysis.
Additionally, we evaluated the cumulative release profiles of copper (CuNPs and Cu2+) from the C/H/GO/Cu dressings under different pH values over two weeks. It was found that the acidic environment (pH=5.5) facilitated the release of copper from the dressings as demonstrated in Figure 2C, and the amounts of copper released from the dressings within 14 d were 88.1%, 76.2% and 60.3% under acidic, neutral and alkaline conditions, respectively. We found that a part of CuNPs were detached from the dressing scaffolds using TEM observation, and the release of Cu2+ from the C/H/GO/Cu dressings was highly pH-dependent and may be closely related to the extent of Cu oxidation and H+ concentration formed in the degradation medium, similar to the release behaviors of Ag+ under different pH conditions.52 Subcutaneous abscesses resulting from bacterial infection have been reported to generate an acidic microenvironment (pH ~6.0).53,54 Therefore, it is reasonable to expect an acidity-responsive and accelerated release behavior of copper from the C/H/GO/Cu dressings used for the treatment of acidity-related focal infections with skin defects.
In vitro Antibacterial Performances
The antimicrobial activities of GO-Cu nanocomposites and GO/Cu-incorporated chitosan/hyaluronic acid dressings were investigated against two methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus strains (ATCC25923 and ATCC 35984), which are the most common pathogens found in wound and surgical infections.53,55 First, we examined the MIC and MBC values of GO, CuNPs and GO/Cu nanocomposites against the two tested Staphylococcus strains as demonstrated in Table 1. The MICs of GO/Cu nanocomposites against ATCC25923 and ATCC35984 were 8 μg/mL and 4 μg/mL, respectively. In addition, the MBCs of GO/Cu nanocomposites were 16 μg/mL and 8 μg/mL, respectively. The MICs and MBCs of GO/Cu nanocomposites against the two strains were both lower than that of CuNPs and GO (p<0.01). The MBC/MIC ratio provides important information regarding the antimicrobial potential of tested agents. In general, an antimicrobial agent with a MBC/MIC ratio higher than 4 is defined as a bacteriostatic agent, and an MBC/MIC ratio less than 4 is defined as a bactericidal agent.56 We found that the MBC/MIC ratios of GO/Cu nanocomposites were both 2 against the tested microbes, indicating an evident bactericidal effect on the bacterial strains caused by GO/Cu nanocomposites.
 |
Table 1 The Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) and Minimal Bactericidal Concentration (MBC) Values of Different Nanomaterials Against the Two Tested Bacterial Strains |
Then, observation of bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation on the surfaces of the dressings was performed by CLSM after the Live/Dead staining as shown in Figure 3A. Viable cells stained by green fluorescent SYTO9 have intact cytoplasmic membranes, whereas inviable cells stained by red fluorescent PI have damaged cytoplasmic membranes.27 The fluorescence microscopy images demonstrated that bacterial cells of the C/H/GO/Cu group showed scattered distributed red fluorescence at 4 and 48 h, whereas the other groups showed intense green fluorescence at the two time points, especially at 48 h. Our results displayed that the C/H/GO/Cu dressings showed strong inhibiting effects on the bacterial adherence and subsequent biofilm formation of the two tested Staphylococcus strains. It has been reported that GO-based nanocomposites, whether directly used on wounds as antimicrobial agents or added into scaffolds as antimicrobial wound dressings, could significantly facilitate the healing process of bacteria-infected wounds.22,44 The inactivation of bacterial cells is primarily ascribed to the physicochemical interactions between GO and microorganisms, leading to compromised cell membrane integrity and disruption of lipids, proteins and DNA/RNA.16 Apart from the physical damage, chemical damage arising from oxidative stress was also proven to be closely related to the antibacterial activities of GO nanosheets.14 However, whether physical or chemical damage dominates the antibacterial behaviors is still unclear, and the antimicrobial efficacy remains controversial.14,16 Studies have indicated that copper ions inhibit bacterial growth by affecting the permeability of the cell membrane and then interfering with respiratory chains, producing ROS-related DNA/RNA dysfunction.27,31 Considering the similar antibacterial mechanisms of GO nanosheets and copper ions, we prepared GO/Cu nanocomposite-incorporated dressings to suggest a synergistic antimicrobial effects to combat bacteria-infected wound defects. It has been reported that Live/Dead bacterial staining could be used for rapid examination of the integrity of cell membranes;27 therefore, our results suggested that the plasma membrane integrity of tested bacterial cells was irreversibly damaged during the process of coculture with C/H/GO/Cu dressing scaffolds.
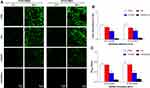 |
Figure 3 Determination of in vitro antibacterial properties of the dressings. |
Meanwhile, the amounts of live bacteria on the surface of different dressings at 6 h were examined by the spreading plate method as shown in Figure 3B. The numbers of viable bacteria attached on the C/H/GO/Cu dressings were considerably lower than those of the other groups (p<0.01). Moreover, biofilm formation on the surface of various samples was investigated using the tissue culture plate method at 48 h as presented in Figure 3C. The OD492 values of the two bacterial strains in the C/H/GO/Cu group were significantly lower than those in the other groups (p<0.01). The initial bacterial inoculation of the surfaces of injured wounds is regarded as a significant event in the development of wound infections, leading to aggravated wound deterioration and delayed wound healing.5 Thus, the inhibition of bacterial adherence and subsequent biofilm formation is of great significance for the application of biomaterials used for eradicating bacteria to restore a normal microenvironment for wound healing. These quantitative analyses indicated that bacterial attachment and biofilm formation were considerably inhibited on the surface of the C/H/GO/Cu dressings, which is consistent with the CLSM observation described above. Our results indicated that the C/H/GO/Cu dressing scaffold could be applied as a feasible candidate for facilitating the healing process of infected wounds in our established animal model.
In vitro Cytocompatibility Evaluation
To meet the requirements of cytocompatibility for potential application in tissue engineering,52 cell apoptosis analysis and proliferation observation were performed to clarify the potential cytotoxicity of C/H/GO/Cu dressing scaffolds to mouse fibroblasts. As shown in Figure 4A and B, the proportion of apoptotic cells in the C/H/GO and C/H/GO/Cu groups was slightly higher than that in the CTRL group (p<0.01 and p<0.05, respectively). In addition, there were no significant differences in cell proliferation among the four groups during the 5 d coculture period (p>0.05), as demonstrated in Figure 4C. Concerning the potential for oxidative damage to normal mammalian cells, it is critical to clarify the impact of GO-based nanocomposites on the biological behavior of NIH/3T3-L1 cells prior to performing in vivo investigation of the restoration of infected wound defects. Our in vitro results indicated that the C/H/GO/Cu dressing scaffold showed no obvious cytotoxicity to the tested cell lines, and its cytocompatibility is also acceptable in consideration of the aforementioned in vitro antimicrobial activities.
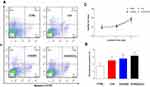 |
Figure 4 Determination of in vitro cytocompatibility of the dressings. |
It is still controversial whether GO-based materials can selectively kill bacterial cells without affecting normal mammalian cells due to the use of different biomaterials and cell lines.16 In the present study, mouse fibroblasts exhibited satisfactory viability in all the four groups based on the results of Annexin-V FITC staining and CCK-8 assay. Additionally, it has been reported that the cell proliferation rate was obviously reduced when the concentration of copper ions exceeded 0.1 mM, although this concentration showed good antimicrobial effects.31 Consequently, it is of great importance to find an appropriate balance between antibacterial function and cytotoxicity when GO/Cu nanocomposites are used for wound healing enhancement. As demonstrated above, the combination of GO and CuNPs suggested a synergistic antimicrobial effects, which may be closely associated to their similar antibacterial mechanisms, leading to significantly reduced dosages of the GO/Cu nanocomposites with desired antibacterial efficacy when compared with the GO or CuNPs used individually. Meanwhile, chitosan and hyaluronic acid, which are the most widely applied biopolymers, with excellent biocompatibility and biodegradability for local treatment of wounds,26 were used to establish a platform for manufacturing multifunctional bioactive dressings. To sum up, the cytocompatibility and biocompatibility of C/H/GO/Cu dressings could be obviously improved without affecting the required antimicrobial potential for overcoming bacterial infections thanks to decreased employment of nanomaterials and suitable incorporation of biopolymers.
Anti-Infection and Wound Healing Effect of GO/Cu Nanocomposite- Modified Dressings
In this study, we used a modified full-thickness cutaneous defect infection model to evaluate the in vivo anti-infection and wound healing capacity of the C/H/GO/Cu dressings. Representative digital images of wounds in each group as demonstrated in Figure 5A indicated that obvious abscesses were found in the CTRL, C/H and C/H/GO groups within one week, and milder abscesses were observed in the C/H/GO/Cu group compared with the other groups. Nevertheless, the difference in wound area and conditions became evident with the increase in treatment time from day 10 to 14. Wounds treated with the C/H/GO/Cu dressings displayed the best results in terms of decreased wound size and abscesses, and the C/H/GO group also demonstrated a smaller wound size compared to the CTRL and C/H groups. On the day of sacrifice, minimal wounds covered by slight scabs without any abscesses were found in the C/H/GO/Cu group, whereas nonhealing wound areas with mild abscesses remained visible in the other groups, especially in the CTRL and C/H groups. Furthermore, the quantitative analysis shown in Figure 5B confirmed that accelerated wound healing occurred in the C/H/GO and C/H/GO/Cu groups compared to the CTRL and C/H groups on days 10 and 14 (p<0.01), and the C/H/GO/Cu group exhibited the best wound closure rate among all groups (p<0.01). On day 14 postsurgery, the proportions of wound closure area were 18.5 ± 2.1%, 39.2 ± 8.0%, 61.7 ± 3.7% and 93.1 ± 1.2% in the CTRL, C/H, C/H/GO and C/H/GO/Cu groups, respectively (Figure 5C). Our results indicated that the healing process of infected cutaneous wound defects treated with C/H/GO/Cu dressing scaffolds was significantly accelerated, producing relatively satisfactory functional and aesthetic outcomes.
 |
Figure 5 The effect of GO/Cu nanocomposite-modified dressings on infected wound healing. |
Wound healing is a dynamic process including several molecular and cellular events aimed at recovery of the functionality and integrity of damaged skin.26 Bacterial infection is one of the major challenges in wound management due to the disorganized stages of wound repair and deteriorated microenvironment for re-epithelialization, and epithelialization has been regarded as one of the most important preconditions for successful wound regeneration.12,35 Given the abovementioned difficulty and complexity of healing infected wounds, dressings with antibacterial properties are increasingly needed for effective wound disinfection. In the present study, we prepared GO/Cu nanocomposite-decorated chitosan/hyaluronic acid dressings for bacteria-infected wound management. The re-epithelialization and wound contraction of full-thickness cutaneous wounds in mice were noticeably improved in the dressing groups compared to the respective controls. The inhibited progression of bacterial infection was mainly attributed to the GO/Cu nanocomposites and the CuNPs and Cu2+ released from the dressing scaffolds during the wound healing process. Additionally, the wettability and biocompatibility of the dressings were improved thanks to the hydrogel-like porous structure and to the addition of chitosan and hyaluronic acid, respectively. As a consequence, such a multifunctional dressing may be an ideal alternative for in vivo treatment of infected wounds in consideration of its particular advantages in maintaining a moist wound environment, providing bacterial protection, and allowing effective fluid management and low adhesion to the wound surface as required in previous studies.11,45
Histopathological and Immunofluorescence Analysis
The migration, proliferation and differentiation of several cell types, such as macrophages, fibroblasts and endothelial cells, constitute a multicellular and interactive process that leads to new tissue formation and ultimately wound healing.1 As shown in Figure 6, H&E and Masson’s trichrome staining were performed to observe the tissue regeneration morphological changes at the defect sites in all four groups at the day of sacrifice. Consistent with the representative digital images of wounds analyzed above, better re-epithelialization and organized granulation tissues were found in wounds treated with C/H/GO/Cu dressings than in the other groups at day 14. In contrast, typical signs of cutaneous infection around the defect sites as demonstrated by the development of inflammatory cell infiltration, local abscesses, fibrosis and hyperplasia were observed in the CTRL, C/H and C/H/GO groups, especially in groups CTRL and C/H. It was found that wounds treated with C/H/GO/Cu dressings exhibited relatively intact cutaneous regeneration with significantly reduced inflammatory reactions compared with the other groups.
 |
Figure 6 The effect of GO/Cu nanocomposite-modified dressings on wound healing in wounds under high risk of bacterial infection. |
Meanwhile, we examined the potential organ toxicity and in vivo biocompatibility of GO/Cu nanocomposite-modified dressings through histopathological analysis of the heart, lung, liver and kidney. As shown in Figure 7, the H&E-stained slices from these vital organs displayed no evident pathological changes or signs of infection-related inflammation, indicating that good in vivo biosafety of the used dressings and no systemic sepsis occurred in all four groups during the two weeks after surgery. Studies about GO-based materials for in vivo bactericidal applications are still in their initial stages, and the biocompatibility of GO-based materials must be more systematically investigated for future clinical application. Therefore, computational simulations and comprehensive observations should be introduced to clarify the interactions between GO-based materials and biosystems. Furthermore, immunofluorescence analysis of samples from each group was performed to investigate the effect of GO/Cu nanocomposite-modified dressings on the inflammatory infiltration and angiogenesis in granulation tissues. Close observation of the microstructure of newly formed tissues at the defect sites as shown in Figure 8 provided in-depth insight into the multicellular process during wound healing. In our study, immunofluorescent CD31 staining was used to evaluate the angiogenesis in wound sites after relevant interventions.45 Obviously greater density of microvessels in randomly selected fields was found in the regenerated tissues treated with C/H/GO/Cu dressings compared with the other groups (p<0.01), indicating greater vascularization in granulation tissues during the repair process. The blood vessel density exhibited no significant differences among the CTRL, C/H and C/H/GO groups at day 14 (p>0.05). On the other hand, immunofluorescent CD3 staining was applied to clarify the inflammatory infiltration in the wound sites.37 CD3+ T lymphocytes with varying densities were microscopically identified in all groups, and quantitative analysis further confirmed that the number of infiltrated lymphocytes was significantly lower in the wounds treated with C/H/GO/Cu dressings than in the other three groups (p<0.01). The quantity of infiltrated lymphocytes exhibited a decreasing trend from the CTRL to the C/H/GO/Cu group, indicating a significant reduction of inflammatory aggregates closely related to bacterial infections in wounds treated with C/H/GO/Cu dressings, which was consistent with the images of the wound healing process and histological observation of the newly formed tissues at the defect sites as demonstrated in Figures 5 and 6, respectively.
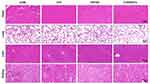 |
Figure 7 Examination of potential organ toxicity of GO/Cu nanocomposite-modified dressings. |
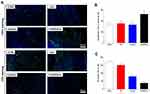 |
Figure 8 The effect of GO/Cu nanocomposite-modified dressings on inflammatory infiltration and angiogenesis in regenerated tissues. |
It has been reported that injured wounds, especially for serious open injury, are susceptible to bacterial infections due to the disrupted skin barrier, available microbial nutrients and damaged vascular supply.5 Angiogenesis is regarded as an important process for tissues to obtain needed oxygen and nutrients, and the early angiogenic response is essential for tissue regeneration and wound healing.35 Therefore, the successful management of bacteria-infected wounds mainly depends on the effectiveness of antimicrobial performance and revascularization. Currently, the introduction of nanotechnology to wound treatment has been widely investigated by means of diverse routes.5 Copper is a well-studied broad-spectrum antibacterial agent with a reliable angiogenesis stimulation effect, making it a promising bioactive substance for incorporation into biomaterials for skin regeneration in cases with a high risk of bacterial infection.30,31 In addition, a previous study reported that graphene oxide (GO) promotes angiogenesis by increasing nitric oxide (NO) production via the activation of phospho-eNOS,57 and the incorporation of reduced GO showed increased angiogenesis and completely vascularized architecture in diabetic wounds.35 In our research, a multifunctional wound dressing was prepared by combining GO/Cu nanocomposites with chitosan/hyaluronic acid. We found that the density of microvessels in granulation tissues obtained from the C/H/GO group was significantly reduced compared with that in the C/H/GO/Cu groups due to poor anti-infection performances; the addition of only GO to the dressing scaffolds led to no visible angiogenesis during the healing process. Meanwhile, systemic activation of CD3+ T lymphocytes was noted in tissues of patients with implant-associated infection,58 and the levels of inflammatory infiltration proportional to bacterial burden were significantly reduced at the wound sites in the C/H/GO/Cu group. Our results suggested that effective antimicrobial action is a prerequisite for subsequent new capillary and tissue formation during infected wound repair, and wound dressing with improved antibacterial and angiogenic properties offers evident advantages over single-function dressings for the regeneration of challenging infected wound defects. Apart from the excellent performances of C/H/GO/Cu scaffolds as wound dressings, several limitations should also be pointed out as follows. First, tensile strength of the dressings remains to be improved for convenient usage, and controlled release of Cu ions from the dressings should also be considered in subsequent material modification. Second, we must determine the long-term biosafety (including the metabolic pathways of GO nanosheets and copper) of GO/Cu nanocomposites based dressings prior to applying for a medical device license. Third, larger animal models, such as mini pigs with similar structure of dermal tissue of human beings, are needed to be established to further examine the therapeutic efficacy of the dressings.
Conclusion
In summary, we successfully manufactured GO/Cu nanocomposite-incorporated bioactive dressing scaffolds with significantly improved antimicrobial performance and angiogenesis capacity and good biocompatibility. Potentially due to the similarity of their antibacterial mechanisms, as discussed above, enhanced antimicrobial effects of GO and CuNPs against two Staphylococcus strains commonly found in wound infections were observed. Furthermore, the wound-healing quality was evidently improved by the prepared C/H/GO/Cu dressings, as indicated by the promotion of in vivo angiogenesis and cutaneous restoration as well as significantly reduced inflammatory infiltration caused by bacterial infection. Based on these findings, a multifunctional GO/Cu nanocomposite-decorated chitosan/hyaluronic acid dressing could have great potential in accelerating the healing process of infected wounds in plastic clinics.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation for Youth of China (81802136), Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (2018M643005), Natural Science Foundation for Youth of Hunan Province (2020JJ5939), Science Foundation for Youth of Xiangya Hospital, Central South University (2017Q18), and Postdoctoral Science Foundation of Central South University (205432).
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Singer AJ, Clark RAF, Epstein FH. Cutaneous wound healing. N Engl J Med. 1999;341(10):738–746. doi:10.1056/NEJM199909023411006
2. Huang X, Zhang YQ, Zhang XM, et al. Influence of radiation crosslinked carboxymethyl-chitosan/gelatin hydrogel on cutaneous wound healing. Mater Sci Eng C. 2013;33(8):4816–4824. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2013.07.044
3. Diegelmann RF. Wound healing: an overview of acute, fibrotic and delayed healing. Front Biosci. 2004;9(1–3):283–289. doi:10.2741/1184
4. Mahdavian Delavary B, van der Veer WM, van Egmond M, et al. Macrophages in skin injury and repair. Immunobiology. 2011;216(7):753–762. doi:10.1016/j.imbio.2011.01.001
5. Jahromi MAM, Zangabad PS, Basri SMM, et al. Nanomedicine and advanced technologies for burns: preventing infection and facilitating wound healing. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018;123:33–64. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2017.08.001
6. Rosenbaum AJ, Banerjee S, Rezak KM, et al. Advances in wound management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2018;26(23):833–843. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-17-00024
7. Tam J, Wang Y, Farinelli WA, et al. Fractional skin harvesting: autologous skin grafting without donor-site morbidity. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2013;1(6):e47.
8. Hart CE, Loewen-Rodriguez A, Lessem J. Dermagraft: use in the treatment of chronic wounds. Adv Wound Care. 2012;1(3):138–141. doi:10.1089/wound.2011.0282
9. Wei J-W, Ni J-D, Dong Z-G, et al. A modified technique to improve reliability of distally based sural fasciocutaneous flap for reconstruction of soft tissue defects longitudinal in distal pretibial region or transverse in heel and ankle. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2016;55(4):753–758. doi:10.1053/j.jfas.2016.02.011
10. Zhou DJ, Yang T, Qian W, et al. Study of the mechanism of environmentally friendly translucent balsa-modified lysozyme dressing for facilitating wound healing. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13:4171–4187. doi:10.2147/IJN.S165075
11. Dong W-H, Liu J-X, Mou X-J, et al. Performance of polyvinyl pyrrolidone-isatis root antibacterial wound dressings produced in situ by handheld electrospinner. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020;188:110766. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110766
12. Huang X-W, Wei -J-J, Liu T, et al. Silk fibroin-assisted exfoliation and functionalization of transition metal dichalcogenide nanosheets for antibacterial wound dressings. Nanoscale. 2017;9(44):17193–17198. doi:10.1039/C7NR06807G
13. Chen HL, Lan GQ, Ran LX, et al. A novel wound dressing based on a konjac glucomannan/silver nanoparticle composite sponge effectively kills bacteria and accelerates wound healing. Carbohydr Polym. 2018;183:70–80. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.11.029
14. Ji HW, Sun HJ, Qu XG. Antibacterial applications of graphene-based nanomaterials: recent achievements and challenges. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016;105:176–189. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2016.04.009
15. Xia M-Y, Xie Y, Yu C-H, et al. Graphene-based nanomaterials: the promising active agents for antibiotics-independent antibacterial applications. J Control Release. 2019;307:16–31. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.06.011
16. Zou XF, Zhang L, Wang ZJ, et al. Mechanisms of the antimicrobial activities of graphene materials. J Am Chem Soc. 2016;138(7):2064–2077. doi:10.1021/jacs.5b11411
17. Rojas-Andrade MD, Chata G, Rouholiman D, et al. Antibacterial mechanisms of graphene-based composite nanomaterials. Nanoscale. 2017;9(3):994–1006. doi:10.1039/C6NR08733G
18. Tu YS, Lv M, Xiu P, et al. Destructive extraction of phospholipids from Escherichia coli membranes by graphene nanosheets. Nat Nanotechnol. 2013;8(8):594–601. doi:10.1038/nnano.2013.125
19. Carpio IEM, Santos CM, Wei X, et al. Toxicity of a polymer–graphene oxide composite against bacterial planktonic cells, biofilms, and mammalian cells. Nanoscale. 2012;4(15):4746–4756. doi:10.1039/c2nr30774j
20. Wang YL, El-Deen AG, Li P, et al. High-performance capacitive deionization disinfection of water with graphene oxide-graft-quaternized chitosan nanohybrid electrode coating. ACS Nano. 2015;9(10):10142–10157. doi:10.1021/acsnano.5b03763
21. Xu LQ, Liao YB, Li NN, et al. Vancomycin-assisted green synthesis of reduced graphene oxide for antimicrobial applications. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2018;514:733–739. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2018.01.014
22. Ran X, Du Y, Wang ZZ, et al. Hyaluronic acid-templated Ag nanoparticles/graphene oxide composites for synergistic therapy of bacteria infection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(23):19717–19724. doi:10.1021/acsami.7b05584
23. Moeini A, Pedram P, Makvandi P, et al. Wound healing and antimicrobial effect of active secondary metabolites in chitosan-based wound dressings: a review. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;233:115839. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.115839
24. Majidi HJ, Babaei A, Bafrani ZA, et al. Investigating the best strategy to diminish the toxicity and enhance the antibacterial activity of graphene oxide by chitosan addition. Carbohydr Polym. 2019;225:115220. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115220
25. Bukhari SNA, Roswandi NL, Waqas M, et al. Hyaluronic acid, a promising skin rejuvenating biomedicine: a review of recent updates and pre-clinical and clinical investigations on cosmetic and nutricosmetic effects. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;120:1682–1695. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.09.188
26. Vigani B, Rossi S, Sandri G, et al. Hyaluronic acid and chitosan-based nanosystems: a new dressing generation for wound care. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2019;16(7):715–740. doi:10.1080/17425247.2019.1634051
27. Li M, Ma Z, Zhu Y, et al. Toward a molecular understanding of the antibacterial mechanism of copper-bearing titanium alloys against Staphylococcus aureus. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(5):557–566. doi:10.1002/adhm.201500712
28. Wei YH, Chen S, Kowalczyk B, et al. Synthesis of stable, low-dispersity copper nanoparticles and nanorods and their antifungal and catalytic properties. J Phys Chem C. 2010;114(37):15612–15616. doi:10.1021/jp1055683
29. Wu CT, Zhou YH, Xu MC, et al. Copper-containing mesoporous bioactive glass scaffolds with multifunctional properties of angiogenesis capacity, osteostimulation and antibacterial activity. Biomaterials. 2013;34(2):422–433. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.09.066
30. Li JY, Zhai D, Lv F, et al. Preparation of copper-containing bioactive glass/eggshell membrane nanocomposites for improving angiogenesis, antibacterial activity and wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2016;36:254–266. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2016.03.011
31. Xu Q, Chang ML, Zhang Y, et al. PDA/Cu bioactive hydrogel with “hot ions effect” for inhibition of drug-resistant bacteria and enhancement of infectious skin wound healing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(28):31255–31269.
32. Ma W, Soroush A, Luong TVA, et al. Cysteamine- and graphene oxide-mediated copper nanoparticle decoration on reverse osmosis membrane for enhanced anti-microbial performance. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2017;501:330–340. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2017.04.069
33. Stankovich S, Dikin DA, Dommett GHB, et al. Graphene-based composite materials. Nature. 2006;442(7100):282–286. doi:10.1038/nature04969
34. Chen QW, Zhang LY, Chen G. Facile preparation of graphene-copper nanoparticle composite by in situ chemical reduction for electrochemical sensing of carbohydrates. Anal Chem. 2012;84(1):171–178. doi:10.1021/ac2022772
35. Thangavel P, Kannan R, Ramachandran B, et al. Development of reduced graphene oxide (rGO)-isabgol nanocomposite dressings for enhanced vascularization and accelerated wound healing in normal and diabetic rats. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2018;517:251–264. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2018.01.110
36. Lack S, Dulong V, Picton L, et al. High-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies of polysaccharides crosslinked by sodium trimetaphosphate: a proposal for the reaction mechanism. Carbohydr Res. 2007;342(7):943–953. doi:10.1016/j.carres.2007.01.011
37. Yang Y, Yang S-B, Wang Y-G, et al. Bacterial inhibition potential of quaternised chitosan-coated VICRYL absorbable suture: an in vitro and in vivo study. J Orthop Translat. 2017;8:49–61. doi:10.1016/j.jot.2016.10.001
38. Wiegand I, Hilpert K, Hancock REW. Agar and broth dilution methods to determine the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antimicrobial substances. Nat Protoc. 2008;3(2):163–175. doi:10.1038/nprot.2007.521
39. Lallemand EA, Lacroix MZ, Toutain P-L, et al. In vitro degradation of antimicrobials during use of broth microdilution method can increase the measured minimal inhibitory and minimal bactericidal concentrations. Front Microbiol. 2016;7:2051. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2016.02051
40. Van de Belt H, Neut D, Schenk W, et al. Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation on different gentamicin-loaded polymethylmethacrylate bone cements. Biomaterials. 2001;22(12):1607–1611. doi:10.1016/S0142-9612(00)00313-6
41. Mathur T, Singhal S, Khan S, et al. Detection of biofilm formation among the clinical isolates of Staphylococci: an evaluation of three different screening methods. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2006;24(1):25–29. doi:10.4103/0255-0857.19890
42. Thangavel P, Ramachandran B, Muthuvijayan V. Fabrication of chitosan/gallic acid 3D microporous scaffold for tissue engineering applications. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2016;104(4):750–760. doi:10.1002/jbm.b.33603
43. Yang Y, Liu LH, Luo H, et al. Dual-purpose magnesium-incorporated titanium nanotubes for combating bacterial infection and ameliorating osteolysis to realize better osseointegration. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2019;5(10):5368–5383. doi:10.1021/acsbiomaterials.9b00938
44. Liu TF, Liu YQ, Liu ML, et al. Synthesis of graphene oxide-quaternary ammonium nanocomposite with synergistic antibacterial activity to promote infected wound healing. Bruns Trauma. 2018;6:16.
45. Zhou X, Wang H, Zhang JM, et al. Functional poly(ε-caprolactone)/chitosan dressings with nitric oxide-releasing property improve wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2017;54:128–137. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2017.03.011
46. Zhu JY, Wang J, Uliana AA, et al. Mussel-inspired architecture of high-flux loose nanofiltration membrane functionalized with antibacterial reduced graphene oxide–copper nanocomposites. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(34):28990–29001. doi:10.1021/acsami.7b05930
47. Ramachandran B, Chakraborty S, Kannan R, et al. Immobilization of hyaluronic acid from Lactococcus lactis on polyethylene terephthalate for improved biocompatibility and drug release. Carbohydr Polym. 2019;206:132–140. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.10.099
48. Pereira JR, Bezerra GS, Furtado AA, et al. Chitosan film containing Mansoa hirsuta fraction for wound healing. Pharmaceutics. 2020;12(6):E484. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics12060484
49. Figueroa T, Aguayo C, Fernández K. Design and characterization of chitosan-graphene oxide nanocomposites for the delivery of proanthocyanidins. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:1229–1238. doi:10.2147/IJN.S240305
50. Yang Y, Yang SB, Wang YG, et al. Anti-infective efficacy, cytocompatibility and biocompatibility of a 3D-printed osteoconductive composite scaffold functionalized with quaternized chitosan. Acta Biomater. 2016;46:112–128. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2016.09.035
51. Lewandowska K, Sionkowska A, Grabska S, et al. Surface and thermal properties of collagen/hyaluronic acid blends containing chitosan. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;92:371–376. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.07.055
52. Shao W, Liu XF, Min HH, et al. Preparation, characterization, and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticle-decorated graphene oxide nanocomposite. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(12):6966–6973. doi:10.1021/acsami.5b00937
53. Qian W, Yan C, He DF, et al. pH-triggered charge-reversible of glycol chitosan conjugated carboxyl graphene for enhancing photothermal ablation of focal infection. Acta Biomater. 2018;69:256–264. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2018.01.022
54. Korupalli C, Huang -C-C, Lin W-C, et al. Acidity-triggered charge-convertible nanoparticles that can cause bacterium-specific aggregation in situ to enhance photothermal ablation of focal infection. Biomaterials. 2017;116:1–9. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.11.045
55. Chiu IM, Heesters BA, Ghasemlou N, et al. Bacteria activate sensory neurons that modulate pain and inflammation. Nature. 2013;501(7465):52–57. doi:10.1038/nature12479
56. Pankey GA, Sabath LD. Clinical relevance of bacteriostatic versus bactericidal mechanisms of action in the treatment of gram-positive bacterial infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;38(6):864–870.
57. Mukherjee S, Sriram P, Barui AK, et al. Graphene oxides show angiogenic properties. Adv Healthc Mater. 2015;4(11):1722–1732. doi:10.1002/adhm.201500155
58. Dapunt U, Giese T, Prior B, et al. Infectious versus non-infectious loosening of implants: activation of T lymphocytes differentiates between the two entities. Int Orthop. 2014;38(6):1291–1296. doi:10.1007/s00264-014-2310-5
 © 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
