Back to Journals » OncoTargets and Therapy » Volume 8
Expression and clinical significance of fibroblast growth factor 1 in gastric adenocarcinoma
Authors Liu N, Zhang J, Sun S, Yang L, Zhou Z, Sun Q, Niu J
Received 13 December 2014
Accepted for publication 19 January 2015
Published 9 March 2015 Volume 2015:8 Pages 615—621
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S79204
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Professor Daniele Santini
Naiqing Liu,1,2,* Jingyu Zhang,2,* Shuxiang Sun,2 Liguang Yang,2 Zhongjin Zhou,2 Qinli Sun,2 Jun Niu1
1Department of General Surgery, Qilu Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University, Jinan, People’s Republic of China; 2Department of General Surgery, Yishui Central Hospital, Linyi, People’s Republic of China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Background: The clinical significance of fibroblast growth factor 1 (FGF1) has been revealed in several cancers, including ovarian cancer, breast cancer, and bladder cancer. However, the clinical significance of FGF1 in gastric adenocarcinoma has not been explored.
Patients and methods: In our experiments, we systematically evaluated FGF1 expression in 178 cases of gastric adenocarcinoma with immunohistochemistry, and subsequently analyzed the correlation between FGF1 expression and clinicopathologic features. Moreover, FGF1 expression in tumor tissue and corresponding adjacent tissue was detected and compared by real-time polymerase chain reaction. The Kaplan–Meier method and the Cox-regression model were used with univariate and multivariate analysis, respectively, to evaluate the prognostic value of FGF1 in gastric adenocarcinoma.
Results: Higher FGF1 expression rate is 56.7% (101/178) in gastric adenocarcinoma. FGF1 expression in gastric adenocarcinoma was significantly higher than adjacent tissue (P<0.0001). Expression of FGF1 is significantly associated with lymph node invasion (P<0.001), distant metastasis (P=0.013), and differentiation (P=0.015). Moreover, FGF1 overexpression was closely related to unfavorable overall survival rate (P=0.021), and can be identified to be an independent unfavorable prognostic factor (P=0.004).
Conclusion: FGF1 is an independent prognostic factor, indicating that FGF1 could be a potential molecular drug target in gastric adenocarcinoma.
Keywords: fibroblast growth factor 1, gastric adenocarcinoma, prognosis, biomarker, lymph node, gene fusion
Introduction
The incidence of gastric cancer is the fourth highest in men and the fifth highest in women globally.1 It constitutes about 8% of all cancer cases worldwide, but accounts for over 10% of all cancer deaths because of its high mortality.2 The high mortality of gastric cancer results partly from its silent clinical features, early lymph metastasis and easy recurrence. In gastric cancer, gastric adenocarcinoma is the most common histological type and makes up more than 90% of gastric cancer.3,4 Thanks to decades of research, many genetic alterations and many kinds of biomarkers have been observed,5 which have directly resulted in chemotherapy drugs used for gastric cancer, such as Herceptin. This translational medicine of biomarker discovery enormously increases the survival time and life quantity of patients. However, gastric cancer is still a major health burden worldwide. More effective diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers should be researched and unearthed.
In human beings, the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family comprises 22 members, and the fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) family consists of four members. These FGFs trigger a complex signaling network by interacting with different FGFRs and initiate a signaling cascade, which is essential in many cellular processes such as cell proliferation, migration, and differentiation.6 In the four members of the FGFR family, it is generally acknowledged that FGFR2 is an effective biomarker and also a potential molecular target in gastric cancer.7 FGFR2 has been demonstrated to promote progression of gastric cancer in both in vivo and in vitro studies. The correlation of FGFR2 with gastric cancer progression can be explained by factors including FGFR2 abnormal amplification,7 FGFR2 gene fusion,8 and FGF10/FGFR2 ectopic stimulation.9 FGFR2 has been proved in in vitro studies to interact with FGF1, FGF2, FGF3, FGF4, FGF6, FGF7, FGF8, FGF9, FGF10, FGF17, FGF18, and FGF22. The binding of FGFR2 with FGF1 and FGF2 is more predominant than other ligands.10 Additionally, FGF1 ectopic overexpression has been found to be correlated with progression or prognosis of several cancers, including ovarian cancer, bladder cancer, and breast cancer.11–13 However, as the most potent ligand for FGFR2, the value of FGF1 on diagnosis, prediction, and prognosis in gastric cancer has not been studied.
In our study, we retrospectively analyzed FGF1 expression in 178 gastric adenocarcinoma samples and compared the FGF1 mRNA levels from gastric cancer tissues and adjacent tissues. Moreover, we assessed the correlation between FGF1 and clinicopathologic parameters by the chi-square test. Moreover, we evaluated the prognostic value of FGF1 with univariate and multivariate analysis and finally identified FGF1 as an independent prognostic factor in gastric adenocarcinoma.
Patients and methods
Patients and follow-up
From 2004 to 2010, 225 patients underwent surgical operation and were diagnosed as gastric adenocarcinoma in Qilu Hospital and Yishui Central Hospital, which consisted of the primary cohort. The validation cohort, composed of 178 patients, was selected from the primary cohort on the basis of the following criteria: 1) available tissue samples and medical records, 2) available follow-up, and 3) no severe perioperative complications. In the validation cohort, there were 134 males and 44 females, with an average follow-up of 21.6 months. Moreover, 33 patients who underwent gastric adenocarcinoma surgery from 2011 to 2013 were enrolled in a prospective cohort. In this cohort, tumor tissue and adjacent tissue were preserved in liquid nitrogen immediately after tumor resection, and used for FGF1 mRNA extraction later. All the samples were obtained after obtaining prior patient consent and approval of the Institutional Clinical Ethics Review Board. The diagnosis of the validation cohort was reconfirmed by two senior pathologists. The tumor TNM stage was identified according to the guidelines of seventh American Joint Committee on Cancer/Union for International Cancer Control.
Immunohistochemistry
The tissue specimens were first formalin (10%) fixed and paraffin-embedded. After that, the slides were deparaffinized at 55°C for 20 minutes followed by three washes with xylene, and then rehydrated with graded ethanol with concentrations at 100%, 95%, and 80%. The endogenous peroxidase activity was blocked by 3% hydrogen peroxide, and antigen retrieval was achieved by heating in citrate buffer (pH=6.0) in a microwave oven for 10 minutes. After being incubated in primary antibody dilution (1:100) at 4°C overnight, the slides were then incubated for 30 minutes each in a biotin-labeled secondary antibody (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology, Shanghai, People’s Republic of China), followed by incubation in streptavidin-peroxidase (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology). The visualization of slides was achieved with a 3,3′-diaminobenzidine substrate. Finally, the sections were counterstained with hematoxylin, dehydrated, and mounted. In the IHC test, the negative control was the sample with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) incubation instead of primary antibody, with all the other procedures remaining the same, while positive control was placental tissue sections, which had high FGF1 expression.14,15
Immunohistochemistry score and evaluation
Each stained section was blindly evaluated by two senior pathologists who were unaware of the clinical information. All conflicting cases on scoring were adjudicated by a third individual. Five sights were selected randomly and observed with a light microscope. The score of FGF1 was obtained as the product of positive cells multiplied by staining intensity. The scoring system for positive cell percentages was as follows: 0, less than 10% positive cells; 1, 10%–30% positive cells; 2, 30%–50% positive cells; 3, >50% positive cells. The score system for staining intensity was defined as: 0 for negative staining, 1 for weak staining, 2 for moderate staining, 3 for strong staining. The cut-off was arbitrarily defined as: score ≥4 is high FGF1 expression and score <4 is low FGF1 expression.
RNA extraction and real-time PCR
The mRNA of tumor and corresponding tissue was extracted with Trizol (Life Technologies, Paisley, UK) and quantified by a Nanodrop spectrophotometer. The total amount of 500 ng mRNA was used for cDNA synthesis and quantitative PCR by the StepOnePlus real-time PCR system (Applied Biosystems, CA, USA) according to the manual. GAPDH (glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase) was considered as an internal control. The sequences of primers used for real-time PCR experiments are designed following previous study and shown below.16
Human FGF1 forward ACACCGACGGGCTT TTATACG.
Human FGF1 reverse CCCATTCTTCTTGAGG CCAAC.
Statistical analysis
All data were analyzed with software SPSS 13.0 (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA). The correlation between FGF1 expression and other clinicopathologic parameters were evaluated by the chi-square test. The relationship between FGF1 and the overall survival rate was analyzed by univariate analysis using the Kaplan–Meier method. Independent prognostic factors were identified by the Cox proportional hazards regression model. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
FGF1 expression in gastric cancer
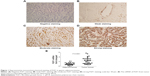
In our experiments, FGF1 was observed mainly in the cytoplasm of gastric cancer cells. The patients with FGF1 expression were divided into a high-expression group and a low-expression group according to the score of immunohistochemistry, which was the product of staining intensity multiplied by positive cell percentage. Figure 1A, B, C, and D represent the negative, weak, moderate, and strong staining intensity, respectively. By detecting the mRNA level of FGF1 from tumor tissue and adjacent tissue, we proved that FGF1 was remarkably overexpressed in tumor tissue compared with the corresponding adjacent tissue (P<0.0001), indicating that FGF1 may play an important role in gastric cancer tumorigenesis or progression (Figure 1E).
Correlation between FGF1 and clinicopathologic features
In the validation cohort, the percentage of high FGF1 is 56.7% (101/178) (Table 1). In the validation cohort, N stage 1/2/3 makes up 72.5% of all cases, indicating that lymph invasion is the most early and dominating metastatic way of gastric adenocarcinoma. Moreover, more males appeared to be suffering from gastric adenocarcinoma than females, which corresponded with the results of previous studies.14,15 We further evaluated FGF1 association with other clinicopathologic parameters using the chi-square test (Table 1). High FGF1 expression was significantly associated with easier lymph node metastasis (P<0.001) and distant metastasis (P=0.013), indicating that FGF1 may be involved in tumor invasion and metastasis. Moreover, the group of high FGF1 expression had more cases of poor tumor differentiation, which was statistically significant (P=0.015) and strongly suggested that FGF1 may promote gastric cancer progression by epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) or other differentiation-related progression.
  | Table 1 Correlation between FGF1 and clinicopathologic parameters |
FGF1 prognostic significance in gastric cancer
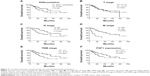
The prognostic value of FGF1 was evaluated by univariate analysis and multivariate analysis. Kaplan–Meier survival curves were made to analyze overall 5-year cumulative survival rate differences between FGF1 high and low expressions (Table 2). With the Kaplan–Meier method, we demonstrated that FGF1 was significantly associated with 5-year overall survival rate in gastric cancer (P=0.021). In addition, differentiation (P=0.047), lymph node invasion (P=0.003), distant metastasis (P<0.001), and TNM stage (P=0.005) were also found to be closely related to poor prognosis of gastric cancer (Figure 2).
  | Table 2 Univariate analysis of FGF1 and clinicopathologic parameters |
Multivariate analysis was further performed to identify the independent prognostic factors (Table 3). Clincopathologic parameters were enrolled in the Cox-Regression model, including sex, age, tumor diameter, T stage, N stage, M stage, differentiation, and FGF1 expression. FGF1 overexpression was proved to be an independent unfavorable prognostic factor in gastric adenocarcinoma (P=0.004). Besides FGF1, lymph node invasion (P=0.007), distant metastasis (P<0.001), and differentiation (P=0.003) were also confirmed as independent unfavorable prognostic factors in gastric adenocarcinoma.
Discussion
In our study, we investigated the expression of FGF1, the most predominant ligand of FGFR2, and evaluated the prognostic value of FGF1 in gastric adenocarcinoma in a large cohort. Consequently, we found that the rate of FGF1 overexpression was very high (56.7%) in gastric adenocarcinoma, and that FGF1 expression in tumor tissue was significantly higher than in adjacent tissue. Moreover, we demonstrated that high FGF1 expression is significantly associated with a poorer overall survival rate (P=0.021) with univariate analysis. Additionally, we identified FGF1 as an independent prognostic biomarker in gastric adenocarcinoma with multivariate analysis (P=0.004).
Tumor cells can secrete several kinds of proteins by themselves, especially growth factors like VEGF, to fulfill the growth demand. This kind of autocrine and paracrine is an important way of tumor cell progression.17 Our study demonstrated that FGF1 overexpression could result in unfavorable prognosis in gastric cancer, which may provide a new insight into the study of autocrine and paracrine of gastric cancer.
As a growth factor receptor, lots of previous proofs demonstrated that FGFR2 was a prognostic biomarker in gastric cancer,6,18 and FGF10-FGFR2 signaling is required in gastric development.9 Considering that FGF1 is the most predominant ligand of FGFR2, this finding may supply a profound mechanism of pathologic stimulation of the FGF1–FGFR2 signaling pathway. FGFR2 was proved to promote gastric cancer progression and correlate with poor prognosis by inducing EMT of gastric cancer. In previous studies, FGF1 was proved to stimulate FGFR2 by interaction and subsequently induce the downstream signaling cascade including RAS, MAPK/ERK signaling pathway in several cancers.11,19,20 Fortunately, inhibitors targeting FGFR2 have the antigastric cancer activity in both in vivo and in vitro studies,21,22 which enlighten us that inhibitors blocking the FGF1–FGFR2 signaling pathway could be a potential therapeutic drug target. On the basis of the clinical data and statistical analysis of our experiments, we boldly hypothesized that FGF1 overexpression in gastric adenocarcinoma may cause ectopic activation of FGFR2 and subsequently result in unfavorable prognosis.
More experiments are needed to reveal the deeper molecular mechanisms and details, such as how FGF1 is secreted into the intracellular space and how FGF1 triggers the oncogenic pathway finally. Moreover, four FGFRs and 21 FGFs form a complicated signaling network. One FGFR can be activated by different FGFs, and one FGF may stimulate different FGFRs. Even FGFR2, the well-known prognostic biomarker in gastric cancer, has three distinct isoforms that have different affinities for different FGFs and may result in different outcomes of cancer. We hope our study may trigger more interest in the oncogenic role of FGF1 and help find a new and effective drug target of gastric cancer.
The value of FGF1 as a tumor biomarker has been revealed in several kinds of tumors in previous studies, such as in colorectal cancer and ovarian adenocarcinomas.23,24 Additionally, many fundamental researches have demonstrated that FGF1 can promote cancer progression and anti-FGF1 therapy can reduce cancer growth.25–28 However, there is still no available inhibitor targeting at FGF1. On the basis of our research, we suspected that an inhibitor that mimics FGF1 and inhibits FGFR2 competitively is a potential and very promising drug in gastric cancer treatment. In addition, we hope our new finding can help find a new molecular target and develop a new chemotherapeutic agent of gastric cancer.
In conclusion, we systematically analyzed the expression of FGF1 in 178 cases of gastric cancer, and identified FGF1 as an independent prognostic biomarker in gastric adenocarcinoma with univariate and multivariate analysis. Moreover, FGF1 expression was proved to be significantly associated with lymph invasion, distant metastasis, and differentiation. Furthermore, we suspected that ectopic FGF1 overexpression may stimulate FGFR2 continuously, and expected FGF1 to be a promising molecular drug target in gastric adenocarcinoma.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Wadhwa R, Song S, Lee JS, Yao Y, Wei Q, Ajani JA. Gastric cancer-molecular and clinical dimensions. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013;10:643–655. | ||
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. | ||
Ma BB, Hui EP, Mok TS. Population-based differences in treatment outcome following anticancer drug therapies. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:75–84. | ||
Macdonald JS. Gastric cancer – new therapeutic options. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:76–77. | ||
Yasui W, Sentani K, Sakamoto N, Anami K, Naito Y, Oue N. Molecular pathology of gastric cancer: research and practice. Pathol Res Pract. 2011;207:608–612. | ||
Katoh M, Nakagama H. FGF receptors: cancer biology and therapeutics. Med Res Rev. 2014;34:280–300. | ||
Kunii K, Davis L, Gorenstein J, et al. FGFR2-amplified gastric cancer cell lines require FGFR2 and ERBB3 signaling for growth and survival. Cancer Res. 2008;68:2340–2348. | ||
Arai Y, Totoki Y, Hosoda F, et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 tyrosine kinase fusions define a unique molecular subtype of cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology. 2014;59:1427–1434. | ||
Spencer-Dene B, Sala FG, Bellusci S, Gschmeissner S, Stamp G, Dickson C. Stomach development is dependent on fibroblast growth factor 10/fibroblast growth factor receptor 2b-mediated signaling. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:1233–1244. | ||
Lew ED, Bae JH, Rohmann E, Wollnik B, Schlessinger J. Structural basis for reduced FGFR2 activity in LADD syndrome: implications for FGFR autoinhibition and activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:19802–19807. | ||
Smith G, Ng MT, Shepherd L, et al. Individuality in FGF1 expression significantly influences platinum resistance and progression-free survival in ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer. 2012;107:1327–1336. | ||
Rogala E, Skopinska-Rozewska E, Sommer E, et al. Assessment of the VEGF, bFGF, aFGF and IL8 angiogenic activity in urinary bladder carcinoma, using the mice cutaneous angiogenesis test. Anticancer Res. 2001;21:4259–4263. | ||
Blanckaert VD, Hebbar M, Louchez MM, Vilain MO, Schelling ME, Peyrat JP. Basic fibroblast growth factor receptors and their prognostic value in human breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 1998;4:2939–2947. | ||
Relf M, LeJeune S, Scott PA, et al. Expression of the angiogenic factors vascular endothelial cell growth factor, acidic and basic fibroblast growth factor, tumor growth factor beta-1, platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor, placenta growth factor, and pleiotrophin in human primary breast cancer and its relation to angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 1997;57:963–969. | ||
el-Hariry I, Pignatelli M, Lemoine N. Fibroblast growth factor 1 and fibroblast growth factor 2 immunoreactivity in gastrointestinal tumours. J Pathol. 1997;181:39–45. | ||
Jiang S, Yan C, Fang QC, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 21 is regulated by the IRE1alpha-XBP1 branch of the unfolded protein response and counteracts endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced hepatic steatosis. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:29751–29765. | ||
Sporn MB, Roberts AB. Autocrine growth factors and cancer. Nature. 1985;313:745–747. | ||
Su X, Zhan P, Gavine PR, et al. FGFR2 amplification has prognostic significance in gastric cancer: results from a large international multicentre study. Br J Cancer. 2014;110:967–975. | ||
Brown A, Robinson CJ, Gallagher JT, Blundell TL. Cooperative heparin-mediated oligomerization of fibroblast growth factor-1 (FGF1) precedes recruitment of FGFR2 to ternary complexes. Biophys J. 2013;104:1720–1730. | ||
Steele IA, Edmondson RJ, Leung HY, Davies BR. Ligands to FGF receptor 2-IIIb induce proliferation, motility, protection from cell death and cytoskeletal rearrangements in epithelial ovarian cancer cell lines. Growth Factors. 2006;24:45–53. | ||
Kim ST, Jang HL, Lee SJ, et al. Pazopanib, a novel multitargeted kinase inhibitor, shows potent in vitro antitumor activity in gastric cancer cell lines with FGFR2 amplification. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014;13:2527–2536. | ||
Chang J, Wang S, Zhang Z, et al. Multiple receptor tyrosine kinase activation attenuates therapeutic efficacy of the fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 inhibitor AZD4547 in FGFR2 amplified gastric cancer. Oncotarget. Epub December 10, 2014. | ||
Birrer MJ, Johnson ME, Hao K, et al. Whole genome oligonucleotide-based array comparative genomic hybridization analysis identified fibroblast growth factor 1 as a prognostic marker for advanced-stage serous ovarian adenocarcinomas. J Clin Oncol. 2007;250:2281–2287. | ||
Sato T, Oshima T, Yoshihara K, et al. Overexpression of the fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 gene correlates with liver metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 2009;21:211–216. | ||
Moya ML, Lucas S, Francis-Sedlak M, et al. Sustained delivery of FGF-1 increases vascular density in comparison to bolus administration. Microvasc Res. 2009;78:142–147. | ||
Billottet C, Tuefferd M, Gentien D, et al. Modulation of several waves of gene expression during FGF-1 induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of carcinoma cells. J Cell Biochem. 2008;104:826–839. | ||
Hayrabedyan S, Kyurkchiev S, Kehayov I. FGF-1 and S100A13 possibly contribute to angiogenesis in endometriosis. J Reprod Immunol. 2005;67:87–101. | ||
Zhang L, Kharbanda S, McLeskey SW, Kern FG. Overexpression of fibroblast growth factor 1 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells facilitates tumor cell dissemination but does not support the development of macrometastases in the lungs or lymph nodes. Cancer Res. 1999;59:5023–5029. |
 © 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.