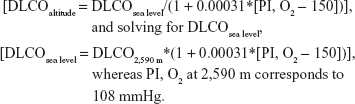Back to Journals » International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease » Volume 13
Exercise performance and symptoms in lowlanders with COPD ascending to moderate altitude: randomized trial
Authors Furian M , Flueck D, Latshang TD, Scheiwiller PM, Segitz SD, Mueller-Mottet S, Murer C , Steiner A, Ulrich S , Rothe T, Kohler M, Bloch KE
Received 4 May 2018
Accepted for publication 28 June 2018
Published 26 October 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 3529—3538
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S173039
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Richard Russell
Michael Furian,1,* Deborah Flueck,1,* Tsogyal D Latshang,1 Philipp M Scheiwiller,1 Sebastian Daniel Segitz,1 Séverine Mueller-Mottet,1 Christian Murer,1 Adrian Steiner,1 Silvia Ulrich,1 Thomas Rothe,2 Malcolm Kohler,1 Konrad E Bloch1
1Department of Respiratory Medicine, University Hospital of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland; 2Zuercher RehaZentrum Davos, Davos Clavadel, Switzerland
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Objective: To evaluate the effects of altitude travel on exercise performance and symptoms in lowlanders with COPD.
Design: Randomized crossover trial.
Setting: University Hospital Zurich (490 m), research facility in mountain villages, Davos Clavadel (1,650 m) and Davos Jakobshorn (2,590 m).
Participants: Forty COPD patients, Global Initiative for Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) grade 2–3, living below 800 m, median (quartiles) age 67 y (60; 69), forced expiratory volume in 1 second 57% predicted (49; 70).
Intervention: Two-day sojourns at 490 m, 1,650 m, and 2,590 m in randomized order.
Outcome measures: Six-minute walk distance (6MWD), cardiopulmonary exercise tests, symptoms, and other health effects.
Results: At 490 m, days 1 and 2, median (quartiles) 6MWD were 558 m (477; 587) and 577 m (531; 629). At 2,590 m, days 1 and 2, mean changes in 6MWD from corresponding day at 490 m were -41 m (95% CI -51 to -31) and -40 m (-53 to -27), n=40, P<0.05, both changes. At 1,650 m, day 1, 6MWD had changed by -22 m (-32 to -13), maximal oxygen uptake during bicycle exercise by -7% (-13 to 0) vs 490 m, P<0.05, both changes. At 490 m, 1,650 m, and 2,590 m, day 1, resting PaO2 were 9.0 (8.4; 9.4), 8.1 (7.5; 8.6), and 6.8 (6.3; 7.4) kPa, respectively, P<0.05 higher altitudes vs 490 m. While staying at higher altitudes, nine patients (24%) experienced symptoms or adverse health effects requiring oxygen therapy or relocation to lower altitude.
Conclusion: During sojourns at 1,650 m and 2,590 m, lowlanders with moderate to severe COPD experienced a mild reduction in exercise performance and nearly one quarter required oxygen therapy or descent to lower altitude because of adverse health effects. The findings may help to counsel COPD patients planning altitude travel.
Registration: ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT01875133
Keywords: CPET, cardiopulmonary exercise testing, acute mountain sickness, hypoxia, adverse health effects, dyspnea, altitude illness, arterial blood gas analysis, pulmonary function
Introduction
COPD is characterized by chronic airflow obstruction related to airway inflammation, remodeling, and parenchymal destruction of the lung.1 This causes dyspnea, exercise limitation, and an impaired quality of life. Worldwide, more than 200 million tourists are estimated to visit altitudes over 1,500 m each year.2 Among them, many patients with COPD are expected to experience adverse health effects including acute mountain sickness,3 excessive dyspnea, and impairment of exercise performance during everyday activities when exposed to hypobaric hypoxia during altitude sojourns. However, whether and to which extent impaired pulmonary gas exchange, reduced muscle strength, and cardiovascular and other limitations affect well-being and physical performance in COPD patients traveling to high altitude has not been extensively studied. In a recent physiological investigation, we observed a reduction of submaximal constant load bicycle exercise by about one half due to systemic and cerebral hypoxemia in a group of COPD patients at 2,590 m compared with the performance at their low altitude residence.4 To provide a scientific basis to counsel COPD patients planning altitude sojourns, the current study evaluated the effect of travel to altitudes of 1,650 and 2,590 m for a total of 4 days on exercise performance, general well-being, and several other outcomes in lowlanders with moderate to severe COPD.
Methods
Study design and setting
This randomized crossover trial evaluated the effect of a 4-day sojourn at moderate altitude on exercise performance, symptoms, and several physiological outcomes in patients with stable COPD, Global Initiative for Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) grades 2–3, living below 800 m. The studies were performed from June to August 2013 in Zurich (490 m, 1,608 ft, barometric pressure [PB] 719 Torr) and in Swiss alpine villages, Davos Clavadel (1,650 m, 5,413 ft, PB 628 Torr) and Davos Jakobshorn (2,590 m, 8,497 ft, PB 562 Torr). Participants spent 2 days at each study location, in random order, to undergo outcome assessments. Some physiological outcomes evaluating gas exchange, cerebral blood flow, and cerebral and muscle tissue oxygenation as a part of the current trial have been reported recently.4 Apart from baseline characteristics of study participants, the data presented here have not been published except previously in abstract form. The study was approved by the Cantonal Ethics Committee of Zurich (EK-2013-0088), subjects gave written informed consent, and the trial is registered at www.ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT01875133.
Participants
Subjects with stable COPD, GOLD grade 2–3, diagnosed according to the GOLD guidelines (forced expiratory volume in 1 second [FEV1]/forced vital capacity [FVC] ratio <0.7, FEV1 between 30% and 80% predicted), aged 18 to 75 years, both sexes, living below 800 m, were invited to participate. Subjects with very severe COPD (FEV1 <30% predicted), respiratory failure at lowland (PaO2 <7.3 kPa or PaCO2 >6.0 kPa), or those with known previous intolerance of altitude 2,600 m or lower, a history of sleep apnea syndrome, or more than mild or inadequately controlled cardiovascular disease were excluded. Patients having traveled to altitudes >1,500 m for >2 days within 4 weeks prior to the study were also excluded.
Randomization and intervention
Using a balanced block design, participants were randomized to one of the following four sequences of altitude exposure with sojourns of 2 days at each location: Group A 490/1,650/2,590 m; Group B 490/2,590/1,650 m; Group C 1,650/2,590/490 m; Group D 2,590/1,650/490 m. Participants traveled by train and car between Zurich and Davos Clavadel and by cable car between Davos Clavadel and Davos Jakobshorn.
As a safety precaution, the protocol required that any patient with intolerable discomfort (according to the patient’s own subjective assessment), symptoms or signs of relevant intercurrent illness, such as a COPD exacerbation, new onset or unstable cardiovascular disease including uncontrolled hypertension (systolic and/or diastolic blood pressure >220 and/or >110 mmHg), neurological impairment, gastrointestinal symptoms requiring treatment, or severe hypoxemia (arterial oxygen saturation <80% for >30 minutes) were withdrawn from the study, treated with oxygen and other measures as appropriate, and transported to low altitude. Maximal bicycle exercise tests to exhaustion were performed at 490 m and 1,650 m, but for safety reasons, not at 2,590 m. Patients were asked to continue their regular medication during the study.
Assessments
Exercise tests, pulmonary function, and arterial blood gas analysis
Six-minute walk tests with monitoring of pulse oximetry (SpO2) were performed.5
Lung function studies including spirometry, body plethysmography (only at 490 and 2,590 m due to logistical constraints), diffusing capacity (Bodystik™ and Diffustik™, Geratherm Respiratory GmbH, Bad Kissingen, Germany), and nasal sniff inspiratory pressure (Morgan P max, Morgan Medical Ltd., Gillingham, UK) were performed 15 minutes after inhalation of a short-acting bronchodilator.6,7 Pulmonary volumes and flows were expressed in body temperature, pressure, and saturated conditions. Diffusing capacity was measured by the single-breath technique. To allow for convenient comparisons between values measured at 490 m, 2,590 m, and predicted values for sea level, values measured at 2,590 m were corrected for the lower PB at altitude by transforming the equation recommended to predict values at high altitude:8
|
Cardiopulmonary cycle exercise tests were performed with a progressive ramp protocol to exhaustion9 at 490 m and 1,650 m. The target duration of the exercise test at 490 m was 8–12 minutes, and the slope (ie, increase in watts per minute) was selected accordingly, based on the individually predicted maximal work rate (Wmax). For each individual, an identical ramp protocol was applied at 490 m and 1,650 m. Ventilation, gas exchange, oxygen saturation, and electrocardiogram were recorded breath by breath (Ergostik™, Geratherm Respiratory GmbH). Radial artery blood was drawn at rest and during maximal exercise and analyzed immediately (RAPIDPOINT 405, Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics GmbH, Zurich, Switzerland). Maximal physiologic variables of exercise tests were defined as mean values during the final 30 seconds of maximal exercise. Patients indicated the perceived exertion on the Borg CR10 scale.10
Clinical examination, evaluation of acute mountain sickness (AMS), and dyspnea
A complete medical history was obtained. Physical examination included weight, height, blood pressure, pulse rate, and SpO2. Dyspnea was assessed by the modified Medical Research Council dyspnea score.11 AMS was assessed in the morning and evening by the Environmental Symptoms Questionnaire cerebral score (AMSc) comprising 11 questions on AMS symptoms rated from 0 (not at all) to 5 (extreme). The weighted sum of responses ranges from 0 to 5. Scores ≥0.7 are considered to reflect clinically relevant AMS.12
Outcomes
The primary outcome was the change in the 6-minute walk distance (6MWD). Secondary outcomes were the oxygen saturation by SpO2, heart rate, lung function, arterial blood gases, and measures derived from cardiopulmonary exercise testing.
Sample size
Sample size estimation indicated that at least 36 participants were required to detect a minimally important difference in the 6MWD of 30 m (SD 55 m) with a power of 80%, alpha 0.05.13 To account for dropouts, 40 participants were included.
Blinding
Investigators analyzing the data were blinded to altitude and altitude exposure sequence.
Statistical analysis
Due to non-normal distribution of the majority of the data, all variables were summarized by medians and quartiles. Overall effects were evaluated by Friedman ANOVA, and significant findings were further analyzed by post hoc analyses using Wilcoxon matched pairs tests. Effects of altitude exposure were evaluated by computing mean differences in outcomes with 95% CIs. The primary outcome was analyzed according to the intention-to-treat principle with missing data replaced by multiple imputations applying a multivariable regression model with baseline variables as independent predictors. Secondary outcomes were analyzed according to the per-protocol principle on all available data. Regression analyses were used to separately assess the effect of altitude (1,650 m and 2,590 m vs 490 m) on the 6MWD while controlling for baseline characteristics and potential confounders. Age, sex, and all predictor variables for which univariate analysis revealed an association with P<0.2 were entered into a subsequent multivariable model. A probability of P<0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
Results
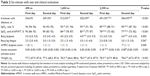
The study participant flow is shown in Figure 1. Of 191 screened subjects, 139 refused to participate and 12 met exclusion criteria. Thus, 40 subjects were included and randomized and their primary outcome (6MWD) was analyzed according to the intention-to-treat principle. One patient each in groups A to C and two in group D required nocturnal supplemental oxygen because of severe hypoxemia (as defined per protocol by a value of SpO2 <80% for ≥30 minutes) or dyspnea. These subjects felt well thereafter and remained at altitude but were excluded from exercise tests on the next day. Two subjects withdrew informed consent after baseline examination in Zurich and one refused to ascend to 2,590 m because of insomnia at 1,650 m. Thus, the per-protocol group consisted of 32 participants (Table 1). The age of patients ranged from 51 to 74 y, 25% were current smokers, and the median FEV1 was 59% predicted. The most prevalent comorbidities were cardiovascular diseases. The majority of participants (81%) used regular inhaled β-adrenergics or anticholinergics and 56% used inhaled glucocorticoids (Table 1).
Several participants experienced altitude-related adverse health effects. In addition to those mentioned above who were withdrawn because of severe hypoxemia, dyspnea, or other discomfort, patients had (on average) mild symptoms of AMS that were most pronounced on the first day at 2,590 m (Table 2). The incidence of clinically relevant AMS (AMSc score ≥0.7) on the first and second day at 1,650 m was 3% (1 out of 38) and 0%, and on the first and second day at 2,590 m was 5% (2 out of 38) and 0% in patients ascending to higher altitudes. The combined incidence of any altitude-related adverse health effect during the 4 days at altitude was 24% (9 out of 38).
Six-minute walk tests, pulmonary function, and arterial blood gases
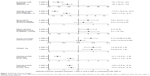
The 6MWD and SpO2 at the beginning and end of the 6-minute walk test were significantly reduced at 1,650 m and 2,590 m compared with those at 490 m, and the perceived dyspnea at the end of the 6MWD was greater at higher altitudes compared with values at 490 m (Table 2 and Figure 2).
Univariable regression analysis with the change in the 6MWD from 490 m baseline as the dependent variable revealed that altitude, second vs first day at altitude, the 6MWD, FEV1, and DLCO at 490 m were significant predictors. In a multivariable analysis, maintaining age, sex, and variables with P<0.2 in univariable analysis in the model, significant independent predictors for the 6MWD were altitude 1,650 m (predicted mean change −17 m [95% CI −27 to −6 m], P=0.001) and 2,590 m (predicted mean change −37 m [95% CI −47 to −27 m], P<0.001). Additional independent predictors were the baseline value of the 6MWD (+0.8 m [+0.7 to +0.9], P<0.001) and FEV1 % predicted at 490 m (+0.9 m [+0.1 to +1.7], P=0.029), while age (P=0.866), sex (P=0.333), and DLCO at 490 m (P=0.188) were not.
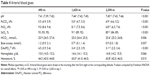
Spirometry revealed no significant changes in FVC and FEV1 (in liters) nor in their ratio over the course of the study at the different altitudes (Table 3). FVC (in % predicted) tended to be minimally greater at 1,650 m compared with other altitudes. Static lung volumes (total lung capacity, residual volume) were not different at 2,590 m vs 490 m. Peak expiratory flow improved significantly with increasing altitude, and correspondingly, airway resistance was reduced at 2,590 m vs 490 m. There was a slight but statistically significant reduction in the DLCO corrected for hemoglobin and for the reduced PB at 2,590 m.
The arterial blood gas analysis revealed a mild to moderate hypoxemia that increased with altitude (Figure 2, Table 4). The alveolar–arterial PO2 gradient was elevated at 490 m and decreased slightly at higher altitudes but remained elevated. According to inclusion criteria, patients were normocapnic at 490 m and their PaCO2 was slightly reduced at higher altitudes with an associated increase in pH.
Cardiopulmonary exercise tests
Compared with 490 m, endurance time, Wmax, and maximal oxygen uptake (V′O2 normalized for weight) were all significantly reduced at 1,650 m. The reduction in endurance time and thus Wmax was −7% (95% CI −13 to 0, P<0.01). The impairment in exercise performance at 1,650 m was associated with a reduced PaO2, SaO2, and alveolar–arterial PO2 gradient during maximal exercise; in addition, there was a lower PaCO2 and increased ventilatory equivalents for O2 uptake and CO2 output (V′E/O2 and V′E/CO2) compared with 490 m. Subjective perception of dyspnea and leg fatigue were similar at low and high altitude (Table 5).
Discussion
The results of the current randomized trial show that patients with moderate to severe COPD living below 800 m experienced a mild reduction in the 6MWD by a mean of 41 m at 2,590 m and by 22 m at 1,650 m. At 1,650 m, bicycle exercise tests revealed a mild reduction of maximal performance by 7% related to hypoxemia and ventilatory limitation. Over the course of the 4-day sojourn at higher altitude, 9 of the 38 patients (24%) experienced symptoms of AMS, dyspnea, or severe hypoxemia that required oxygen therapy for safety reasons. The current results represent a valuable reference that might help to counsel COPD patients planning altitude travel and prevent adverse effects on their health.
Data on exercise performance of COPD patients traveling to altitude are scant. In a study by Kelly et al,14 18 COPD patients (mean FEV1 42% predicted) were transported by car from sea level to Mt Hutt (2,086 m) for a sojourn of few hours. Not all patients were able to complete the 6-minute walk, and their mean walk distance was reduced to less than half of that at sea level (from 467 to 245 m). In eight COPD patients (FEV1 25%–78% predicted) traveling from sea level to Mount Washington (1,920 m), Vermont, PaO2 initially dropped from 8.8 to 6.8 kPa, but values increased to 7.3 kPa with acclimatization over 4 days; patients performed mild treadmill exercise without notable problems.15 In the Dutch Asthma Center Davos (1,560 m), 37 lowlanders with COPD (FEV1 63% predicted) underwent a 5-week rehabilitation training. Compared with baseline evaluation at sea level, their exercise capacity at arrival at 1,560 m was not significantly reduced and it increased over the course of rehabilitation.16 No other studies on exercise performance during intermediate or long-term altitude sojourns of COPD patients were identified.
Compared with the patients reported by Kelly et al,14 the participants in the current trial had a less pronounced reduction in the 6MWD, which might be due to less severe COPD in the current trial (FEV1 59% vs 42% predicted). Another explanation is the difference in the study design because half of the patients in the current trial already stayed for 2 days at 1,650 m before ascending further to 2,590 m (Figure 1), which might have led to improved physical performance at 2,590 m by acclimatization.
We have previously reported a reduction of endurance time during submaximal cycle exercise by 54% in COPD patients at 2,590 m.4 Underlying mechanisms were combined effects of hypobaric hypoxia on dyspnea and pulmonary gas exchange with arterial and cerebral hypoxemia (measured by near-infrared spectroscopy), while ventilatory limitation seemed not to have played a predominant role. Because exercise intensity during a 6MWD is submaximal, we assume that similar mechanisms may have contributed to the impaired performance at higher altitudes compared with 490 m in COPD patients participating in the current study. In turn, during progressive maximal ramp exercise at 1,650 m, our results suggest that mechanical ventilatory limitation has contributed to the reduction in maximal work performance. Thus, the breathing reserve was reduced, and there was a greater ventilatory inefficiency evidenced by the increased ventilatory equivalents for both O2 uptake and CO2 output (Table 3).
In the current patients, there were no relevant changes in static and dynamic lung volumes at 2,590 vs 490 m (Table 3). For comparison, previous studies in healthy individuals17 and in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome18 ascending to 2,590 m have shown a slight reduction in FVC that was not associated with a change in inspiratory muscle strength and was therefore possibly related to subclinical interstitial fluid accumulation. In the current study, a larger interindividual variability of baseline lung function in the COPD patients may have reduced the power to detect minor, altitude-induced changes. However, the current patients having an already reduced diffusing capacity to nearly half of the predicted value at 490 m revealed a further decrease at 2,590 m (Table 3). This was associated with an increase in body weight, suggesting a possible interstitial pulmonary fluid accumulation as suspected in healthy individuals in previous studies.19,20
In addition to the impairment of pulmonary gas exchange and consecutive hypoxemia related to the airflow limitation and parenchymal destruction of the lung, a potential further cause of exercise limitation in COPD patients at altitude relates to an excessive rise in pulmonary artery pressure due to hypoxic vasoconstriction in the presence of some degree of preexisting pulmonary hypertension. In support of this hypothesis, echocardiographic studies performed at rest revealed an elevated pulmonary artery pressure at 2,590 m compared with that at 490 m.21
In this trial, 9 of the 38 randomized patients (24%) ascending to higher altitude suffered from adverse altitude-related health effects including headaches and clinically relevant symptoms of AMS (5% at 1,650 m, 18% at 2,590 m), and 13% had severe hypoxemia at 2,590 m that prompted us to administer supplemental oxygen. While symptoms of AMS might have been controlled by pain suppressants and other drugs including acetazolamide or dexamethasone that are successfully used in healthy mountaineers suffering from AMS,22 we considered it unethical to expose the COPD patients to prolonged hypoxemia with SpO2<80%. The rules for administration of oxygen were arbitrary because there is no conclusive evidence to suggest that level and duration of hypoxemia represent an increased risk for COPD patients, some of them with cardiovascular comorbidities. It is conceivable, however, that the risk for relevant cardiac arrhythmias and possibly adverse cardiovascular events might have been elevated at 2,590 m because we have previously observed a prolongation of the QT interval in patients with COPD during a stay at 2,048 m23 or with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome at 2,590 m.24 Moreover, we suspect that those COPD patients who had severe hypoxemia would have developed more severe symptoms of AMS if they had stayed untreated at altitude for a longer time.
According to our study design, the order of exposure to the different altitudes was performed in random order to reduce the bias that might have been induced by a fixed sequence of stay at the three elevations. The fact that half of the patients had already spent 2 days at a higher altitude than that of their residence before assessments at 1,650 or 2,590 m, respectively (Figure 1), is a limitation that might have influenced the incidence of AMS and other altitude-related adverse health effects by acclimatization. In particular, we cannot exclude that a direct ascent from 490 m to 2,590 m by all participants might have resulted in a higher incidence of AMS and other adverse outcomes. However, in multivariable regression analysis, the altitude exposure sequence was not an independent predictor of the 6MWD. Although a relatively large number of well-characterized COPD patients participated in the current study, it included patients with moderate to severe COPD only; therefore, our results might not apply to patients with very severe (FEV1<30% predicted) or only mild (FEV1>80% predicted) COPD.
Conclusion
The results of the current study demonstrate that lowlanders with moderate to severe COPD experience a modest decrease in the 6MWD when ascending for 2 days to 1,650 m and 2,590 m and their maximal performance during bicycle exercise is decreased at 1,650 m due to hypoxemia and ventilatory limitation. Severe hypoxemia for prolonged time was prevented by oxygen administration. Therefore, more severe impairments and adverse health effects might have been avoided. Our data may serve as a valuable basis for counseling patients with COPD planning altitude travel taking the individual condition, the physical fitness, and comorbidities into account.
Acknowledgments
This study has been supported by grants of the Swiss National Science Foundation and Zurich Lung League. Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics GmbH, Zurich, Switzerland, provided the blood gas analyzer and some equipment.
Author contributions
MF, DF, TDL, and KEB contributed to study design, data collection, analysis and drafting, or critically revising the manuscript. PMS, SDS, SM-M, CM, and AS contributed to data collection, analysis, and took part in revising the manuscript. SU, TR, and MK contributed to study design, data analysis, and took part in revising the manuscript. All authors gave final approval of the version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Disclosure
SU reports grants from Swiss National Science Foundation, Zurich Lung League, grants and personal fees from Actelion SA, OrPha Swiss, personal fees from MSD, outside the submitted work. MK reports personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, CSL Behring, Mundipharma grants, and personal fees from Roche, AstraZeneca, and Bayer outside the submitted work. The other authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease. Global strategy for diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. GOLD; 2017. Available from: https://goldcopd.org/download/326/. Accessed August 28, 2018. | ||
Tourism statistics – intra-EU tourism flows 2017. Available from: http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/Tourism_statistics_-_intra-EU_tourism_flows. Accessed May 2, 2018. | ||
Meier D, Collet TH, Locatelli I, et al. Does this patient have acute mountain sickness? The rational clinical examination systematic review. JAMA. 2017;318(18):1810–1819. | ||
Furian M, Hartmann SE, Latshang TD, et al. Exercise performance of lowlanders with COPD at 2,590 m: data from a randomized trial. Respiration. 2018;95(6):422–432. | ||
ATS statement, ATS Committee on Proficiency Standards for Clinical Pulmonary Function Laboratories, Statement ATS. ATS statement: guidelines for the six-minute walk test. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;166(1):111–117. | ||
American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society. ATS/ERS Statement on respiratory muscle testing. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;166(4):518–624. | ||
Miller MR, Hankinson J, Brusasco V, et al. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur Respir J. 2005;26(2):319–338. | ||
Macintyre N, Crapo RO, Viegi G, et al. Standardisation of the single-breath determination of carbon monoxide uptake in the lung. Eur Respir J. 2005;26(4):720–735. | ||
American Thoracic Society, American College of Chest Physicians. ATS/ACCP Statement on cardiopulmonary exercise testing. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;167(2):211–277. | ||
Borg E, Kaijser L. A comparison between three rating scales for perceived exertion and two different work tests. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2006;16(1):57–69. | ||
Mahler DA, Wells CK. Evaluation of clinical methods for rating dyspnea. Chest. 1988;93(3):580–586. | ||
Sampson JB, Cymerman A, Burse RL, Maher JT, Rock PB. Procedures for the measurement of acute mountain sickness. Aviat Space Environ Med. 1983;54(12 Pt 1):1063–1073. | ||
Puhan MA, Mador MJ, Held U, Goldstein R, Guyatt GH, Schünemann HJ. Interpretation of treatment changes in 6-minute walk distance in patients with COPD. Eur Respir J. 2008;32(3):637–643. | ||
Kelly PT, Swanney MP, Stanton JD, Frampton C, Peters MJ, Beckert LE. Resting and exercise response to altitude in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Aviat Space Environ Med. 2009;80(2):102–107. | ||
Graham WG, Houston CS. Short-term adaptation to moderate altitude. Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. JAMA. 1978;240(14):1491–1494. | ||
Bijl D, Speelberg B, Folgering HT. Pulmonary rehabilitation at moderate altitude: a 1-year follow-up. Neth J Med. 1994;45(4):154–161. | ||
Latshang TD, Lo Cascio CM, Stöwhas A-C, et al. Are nocturnal breathing, sleep, and cognitive performance impaired at moderate altitude (1,630–2,590 m)? Sleep. 2013;36(12):1969–1976. | ||
Latshang TD, Nussbaumer-Ochsner Y, Henn RM, et al. Effect of acetazolamide and autoCPAP therapy on breathing disturbances among patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome who travel to altitude: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2012;308(22):2390–2398. | ||
Clarenbach CF, Senn O, Christ AL, Fischler M, Maggiorini M, Bloch KE. Lung function and breathing pattern in subjects developing high altitude pulmonary edema. PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41188. | ||
Senn O, Clarenbach CF, Fischler M, et al. Do changes in lung function predict high-altitude pulmonary edema at an early stage? Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2006;38(9):1565–1570. | ||
Lichtblau M, Latshang T, Furian M, et al. Right and left ventricular function in lowlanders with COPD travelling to moderate altitude. Eur Respir J. 2015;46(Suppl 59):PA3756. | ||
Luks AM, Mcintosh SE, Grissom CK, et al. Wilderness Medical Society practice guidelines for the prevention and treatment of acute altitude illness: 2014 update. Wilderness Environ Med. 2014;25(4 Suppl):S4–S14. | ||
Bisang M, Latshang TD, Furian M, et al. P156 Risk of cardiac arrhythmias in lowlanders with COPD travelling to high altitude. Randomized trial of nocturnal oxygen therapy. Chest. 2017;151(5):A54. | ||
Latshang TD, Kaufmann B, Nussbaumer-Ochsner Y, et al. Patients with obstructive sleep apnea have cardiac repolarization disturbances when travelling to altitude: randomized, placebo-controlled trial of acetazolamide. Sleep. 2016;39(9):1631–1637. | ||
Crapo RO, Jensen RL, Hegewald M, Tashkin DP. Arterial blood gas reference values for sea level and an altitude of 1,400 meters. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;160(5 Pt 1):1525–1531. |
 © 2018 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2018 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.