Back to Journals » Drug Design, Development and Therapy » Volume 10
Efficacy and safety of gemcitabine plus erlotinib for locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Authors Wang Y, Hu G, Zhang Q, Tang N, Guo J, Liu L, Han X, Wang X, Wang Z
Received 30 January 2016
Accepted for publication 31 March 2016
Published 13 June 2016 Volume 2016:10 Pages 1961—1972
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S105442
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Wei Duan
Yuan Wang,1 Guo-fang Hu,1 Qian-qian Zhang,1 Ning Tang,1 Jun Guo,2 Li-yan Liu,2 Xiao Han,2 Xia Wang,2 Zhe-hai Wang2
1School of Medicine and Life Sciences, Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences, University of Jinan, 2Shandong Cancer Hospital, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, People’s Republic of China
Background: Pancreatic cancer is considered as a chemoresistant neoplasm with extremely dismal prognosis. Gemcitabine is recommended as the standard agent for locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer. A series of trials have been conducted to improve the outcome of advanced pancreatic cancer with other anticancer drugs in combination with gemcitabine. Unfortunately, the designers of the clinical trials failed to improve the poor prognosis of patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Erlotinib was the first additional drug that improved the overall survival of patients with advanced pancreatic cancer with gemcitabine. We performed this systematic review and meta-analysis to explore the efficacy and safety of the combination of gemcitabine with erlotinib (GemErlo) for patients with advanced pancreatic cancer using the currently available evidence.
Methods: PubMed/MEDLINE, EMBASE, the Cochrane Library, and relevant abstracts of major conferences were comprehensively searched. Data results on objective response rate, disease control rate, and 1-year survival were pooled by using MetaAnalyst with a random-effects model. Results on progression-free survival and overall survival were only summarized descriptively.
Results: A total of 24 studies with 1,742 patients with locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer treated with GemErlo were included. Combined objective response rate was 14.4% (95% CI: 11.6%–17.7%), disease control rate was 55.0% (95% CI: 51.5%–58.5%), and 1-year survival rate was 28.5% (95% CI: 24.0%–33.4%). Progression-free survival ranged from 2.63 to 9.6 months, and overall survival varied from 6 to 10 months. As for the toxicity profile, the most common adverse events (AEs) were hematologic reactions, skin rash, and gastrointestinal reactions. Other severe AEs, which had low incidence, included treatment-induced death and interstitial lung disease.
Conclusion: Our study showed that GemErlo is associated with reasonable activity in treating patients with locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer. Most of the AEs were tolerable, while some severe AEs needed careful detection.
Keywords: advanced pancreatic cancer, chemotherapy, targeted agent, meta-analysis
Background
Pancreatic cancer is considered as a chemoresistant solid neoplasm, has the eighth highest mortality rate, and is the fourth most common cause of cancer-related deaths in the world (both in industrial countries as well as in nonindustrial countries).1–3 Approximately 80% of the patients have an unresectable tumor (locally advanced and/or metastatic) at the time of diagnosis, which leads to extremely poor prognosis of advanced pancreatic cancer.4 Some reports declared that patients with advanced pancreatic cancer only have 2–4 months as the median expected life span without chemotherapy treatment,5 and they were also reported to have the lowest 5-year survival rate, which was 6% compared with patients with cancers at other sites.2
Single-agent gemcitabine has been the standard backbone of first-line chemotherapy for advanced pancreatic cancer based on the results of a Phase III trial comparing gemcitabine versus 5-fluorouracil, wherein gemcitabine demonstrated a modest survival advantage (5.65 vs 4.41 months, P=0.0025) and less toxicity.6 However, the improvement it brings is very modest because the median overall survival (OS) still remains less than 6 months.6 Subsequent trials designed to improve the poor clinical outcome of advanced pancreatic cancer by combining other cytotoxic drugs, such as fluorouracil, irinotecan, pemetrexed, oxaliplatin, exatecan, cisplatin, and capecitabine,7–14 or targeted agents, such as bevacizumab15 with gemcitabine, have been conducted widely since then. However, most trials failed to show significant improvement in survival or response rate when compared with gemcitabine monotherapy. The failure of combination chemotherapy to improve the dismal prognosis of advanced pancreatic cancer means that new treatment regimens are urgently needed to further improve the outcomes of advanced pancreatic cancer.
Erlotinib was the first additional anticancer drug that statistically improved the OS according to the results of a randomized controlled trial (RCT) conducted by Moore et al, which directly compared gemcitabine with erlotinib (GemErlo) with gemcitabine alone.16 After that, in November 2005, erlotinib, in combination with gemcitabine, received US Food and Drug Administration approval for use as the front-line therapy for locally advanced and/or metastatic pancreatic cancer. Since then, more studies aimed at exploring the efficacy and safety of the combination of GemErlo were performed all over the world.16–39 In those studies, some were retrospective trials and some were RCTs, whereas some were single-arm trials, but one thing these studies all had in common was that all or part of the patients enrolled received GemErlo regimen with or without comparison of gemcitabine alone.
We conducted this systematic review of available studies to further examine more comprehensively the efficacy and safety profiles of GemErlo for treating patients with locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer.
Methods
Search strategy
An electronic search of scientific literature published in the databases of PubMed/MEDLINE, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library was performed using the MeSH terms and various free words such as “pancreatic neoplasm” or “pancreas neoplasm” or “pancreatic carcinoma” or “pancreatic cancer” and so on, which were simplified into “pancrea*” in combination with “erlotinib or tarceva” and “gemcitabine” without language restrictions. It should be specially explained that the literature search was limited to “human studies” and “controlled clinical trial” or “randomized controlled trial” when using the EMBASE database due to the huge amounts of search results. The search period was from the establishment of each database up to October 2015. We also reviewed conference abstracts of American Society of Clinical Oncology to identify “gray literature”. References of previous systematic reviews were scanned for any other relevant trials.
Selection criteria
Studies meeting the following inclusion criteria were considered eligible for inclusion in the analysis: 1) patients with locally advanced and/or metastatic pancreatic cancer; 2) treatment with gemcitabine plus erlotinib at any line; 3) patients reporting at least one of the following outcomes – objective response rate (ORR; the percentage of the complete response and partial response in total measurable lesions after treatment), disease control rate (DCR; the percentage of the complete response, partial response, and stable disease in total measurable lesions after treatment), 1-year survival rate (the percentage of the patients who survive over 1-year in total patients), progression-free survival (PFS; time between diagnosis and progression or death for any cause), OS (time between diagnosis and death for any cause), and adverse events (AEs); and 4) studies having GemErlo-treated arm or single-arm prospective or retrospective.
Two independent reviewers assessed the eligibility of abstracts identified by the search. If the eligibility was ambiguous from the abstract, the full article was retrieved for clarification. Any disagreements between the two reviewers were resolved by discussion or through consultation with a third expert for final decision.
Data extraction
The extracted data are summarized as follows: 1) general information, including the first author’s name and the year of publication; 2) design and implementation, including the study design, number of patients treated by GemErlo, age (median and range), percentage of male patients, performance status, original status before treatment, treatment line, specific dosage, and administration interval of GemErlo regimen; 3) ORR, DCR, 1-year survival rate, PFS, OS, number of each type of AEs stratified by severity; and 4) hazard ratio (HR), which identified the difference of PFS, and OS between GemErlo-treated arm and gemcitabine monotherapy arm. We also performed subgroup analysis according to the suspected factors, which may lead to heterogeneity between selected studies.
Statistical analysis
We employed standard meta-analytic methods. The indicators of rates such as ORR, DCR, and 1-year survival rate were analyzed by applying MetaAnalyst with the random-effects mode.40 Between-study heterogeneity was evaluated with the Cochran’s Q-test and the I2 statistic. A P-value ≤0.10 rather than P-value ≤0.05 for the Q-test or I2>50% indicated significant heterogeneity between the studies.41,42 We further investigated potential sources of heterogeneity by arranging groups of the selected studies. The dosages of gemcitabine were divided into two groups: one was 1,000 mg/m2, while the other was >1,000 mg/m2. Similarly, the dosages of erlotinib were divided into three groups, which were 100 mg/d, 100 or 150 mg/d, and 150 mg/d, respectively. According to the sample size, the studies were separated into the small studies and the large studies. The survival indexes (PFS and OS) in the GemErlo-treated arm and the gemcitabine monotherapy arm, as well as the difference between the two arms, were summarized descriptively because of the limited number of eligible studies that directly compared GemErlo with gemcitabine alone. Finally, publication bias was evaluated by using funnel plots.
Results
Characteristics of the studies
A total of 519 individual studies were identified from our literature search, of which 117 duplicate researches were removed. After reviewing titles and abstracts, 342 were excluded initially, and 60 studies were thoroughly assessed by full-text reading. Finally, 24 eligible studies with sample sizes ranging from 15 to 301 and involving 1,742 advanced pancreatic cancer patients met the inclusion criteria.16–39 The selection procedure of the eligible studies is presented in Figure 1. The detailed description of the selected studies is listed in Table 1. Within the selected studies, there were five retrospective studies,21,25,30,34,37 nine single-arm Phase II trials,18,19,22,23,27–29,32,38 six Phase II RCTs,26,31,33,35,36,39 three Phase III RCTs,16,20,24 and one Phase Ib trial.17 Among the studies, one RCT16 and a retrospective study34 investigated the difference between the GemErlo-treated arm and the gemcitabine monotherapy arm directly. The percentage of all the subjects that were male ranged from 44% to 72%. The median ages of patients in the selected studies were roughly equivalent, at approximately 59.5–68 years old. The performance status of the patients before treatment was found to be either over 60% according to the Karnofsky performance score or less than 2 according to the World Health Organization (WHO) performance score or less than 2 according to the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance score. Most of the studies presented the initial status of the primary tumors of the patients. According to the international standard of tumor, node, and metastasis classification, locally advanced tumors are defined as Stage III, whereas metastatic tumors are defined as Stage IV, which accounted for much bigger proportion of the included advanced pancreatic cancer patients.43
  | Figure 1 Eligibility of studies for inclusion in the meta-analysis. |
Among the studies that specified relevant issues, patients in one study were given GemErlo as first- or second-line therapy,35 whereas patients in other studies received GemErlo as first-line chemotherapy.16,20–30,32–34,36–39 In all studies that provided relevant information, responses of tumor were evaluated according to the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors, and the grades of AEs were assessed in terms of National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria or the WHO criteria. The relatively common administration dosage of gemcitabine was the recommended dosage of 1,000 mg/m2,16,17,20–26,29–39 while some studies used more than 1,000 mg/m2.18,19,27,28 The first and second most common patterns of administration interval were “weekly for the first 3 weeks in a 4-week cycle”23,27–30,33,35,36,39 and “weekly for the first 7 weeks in the first 8-week cycle then weekly for the first 3 weeks in a 4-week cycle”.16,20,24,31,37 Erlotinib was administered at the dose of 100 mg/d in 17 studies,19,20,23,25–36,38,39 100 or 150 mg/d in three studies,16,17,21 and 150 mg/d in the remaining three studies.18,22,24
Objective response rate
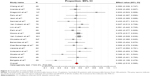
ORRs were reported in 20 studies,16–18,20–23,25,27–30,32–39 varying from 0% to 28.6%. Obvious heterogeneity (I2=35.7%, P=0.001) was present among the aforementioned studies. The pooled estimated ORR by the random-effects model was 14.4% (95% CI: 11.6%–17.7%; Figure 2). The results of subgroup analysis showed that heterogeneity was significantly reduced in the subgroup of sample size. According to the subgroup analysis, we concluded that the sample size was the potential source of the heterogeneity of ORR between studies. The combined ORR for the subgroups of the large studies and the small studies were 9.0% and 16.8%, respectively, which were close to the overall ORR (Table 2).
  | Table 2 Results of subgroup analysis for ORR and DCR |
Disease control rate
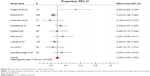
DCRs were revealed in 19 studies,16–23,25,27–30,32–34,37–39 varying from 25.0% to 83.3%. Modest heterogeneity was reported among studies (I2=23.3%, P=0.094). The combined estimated DCR was 55.0% (95% CI: 51.5%–58.5%; Figure 3). The results of subgroup analysis showed that heterogeneity still existed between studies; this meant that we could not satisfactorily explain the source of the heterogeneity by the dosage and sample size (Table 2).
Survival rate
Eight studies reported 1-year survival rates,16–18,22,23,27,29,37 which was 28.5% (95% CI: 24.0%–33.4%), with modest heterogeneity between the studies (I2=29.4%, P=0.082; Figure 4). We did not conduct subgroup analyses due to the limited number of studies that provided relevant data of 1-year survival rates. In addition, three studies reported 6-month survival rates, which were 53.0%, 52.9%, and 41.2%, respectively.22,30,35
PFS and overall survival
PFS, which was reported in 13 studies, ranged from 2.63 to 9.6 months, but was mostly less than 5 months.16,17,20,21,23,26,28–30,34–36,39 Eighteen studies reported information of OS, which varied from 6 to 10 months.16–18,20,21,23,25,27–30,32,34–37,39
Adverse events
In total, 48 kinds of AEs caused by GemErlo in the patients were available in 21 studies (Table 3).16–24,27–30,32–39 The most common AEs (based on the number of the total patients who experienced the specific AEs) were hematologic reactions, such as leukocytopenia (61.4%), anemia (32.6%), neutropenia (27.8%), thrombocytopenia (25.9%); skin-related disease, namely rash (34.3%); gastrointestinal reactions such as nausea or vomiting (43.1%), diarrhea (34.2%), anorexia (22.4%), stomatitis (16.8%), drug-induced hepatic injury (36.1%); and some other treatment-related signs and syndromes such as fatigue (29.9%), infection (25.2%), and fever (19.2%). Other severe AEs, which had low incidence, included treatment-related deaths (3.0%) and interstitial lung disease (3.9%).
Comparison between GemErlo with gemcitabine alone
There are two studies that compared GemErlo versus gemcitabine monotherapy.16,34 Moore et al16 conducted an RCT aimed at examining the benefit brought by the addition of erlotinib to gemcitabine. Patients were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive gemcitabine at the standard dosage of 1,000 mg/m2 plus erlotinib at the dosage of 100–150 mg/d or gemcitabine plus placebo. The ORRs in GemErlo and gemcitabine/placebo arms were 8.6% and 8.0%, respectively, and DCRs were 57.5% and 49.2%, respectively; however, both of the response rates did not achieve statistical significance. On the other hand, however, patients treated with GemErlo gained statistically significant benefits in PFS (3.75 vs 3.55 months, HR =0.77, 95% CI: 0.64–0.92), OS (6.24 vs 5.91 months, HR =0.82, 95% CI: 0.69–0.99), and 1-year survival rate (23% vs 17%) compared with the gemcitabine plus placebo arm. As for the toxicity profile, patients who received GemErlo experienced higher frequencies of rash (72 vs 69), diarrhea (56 vs 41), stomatitis (23 vs 14), interstitial lung disease (7 vs 1), and treatment-related deaths (6 vs 0).
The other study conducted by Lim et al34 retrospectively compared the efficacy and tolerability between three regimens – gemcitabine plus capecitabine, gemcitabine plus erlotinib, and gemcitabine alone for patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. We chose the latter two regimens for our meta-analysis. The ORRs in GemErlo and gemcitabine monotherapy arms were 15.9% vs 12.7%, DCRs were 59.1% vs 63.8%, 1-year survival rates were 22.7% vs 25.5%, PFS was 2.9 vs 5.2 months, and OS was 9.9 vs 10.4 months, respectively. Unfortunately, we could not obtain the data that identified whether the aforementioned indicators were statistically significant or not because the authors did not mention it in the literature. As for the toxicity profile, the frequencies of diarrhea (16 vs 9) and skin rash (11 vs 1) were higher in the GemErlo arm than the gemcitabine arm, while it was just the opposite for other AEs.
Analysis of publication bias
The shape of the funnel plots for the ORR (Figure 5A) and DCR (Figure 5B) appeared to be approximately symmetrical and indicated that publication bias might not have a significant effect on our results.
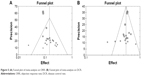  | Figure 5 (A) Funnel plot of meta-analysis on ORR. (B) Funnel plot of meta-analysis on DCR. |
Discussion
According to the recommendations of the latest version of National Comprehensive Cancer Network guideline, gemcitabine was regarded as the standard chemotherapy for locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer.43 Many previous studies tried to combine gemcitabine with many cellulotoxic or targeted agents to improve the poor prognosis of advanced pancreatic cancer; however, they all failed to obtain satisfactory results. Erlotinib was the first additional anticancer agent used in therapy since Moore et al’s16 RCT directly comparing GemErlo with gemcitabine alone.
Erlotinib is an oral small-molecule epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor that blocks the signal transduction pathway, which plays a critical role in the differentiation, proliferation, programmed cell death (apoptosis), angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis of cancer cells.44 Erlotinib has shown antitumor activity in pancreatic cell lines.45 Human pancreatic tumors contain high levels of epidermal growth factor receptor expression, which is associated with worse prognosis.46–48
This systematic review and meta-analysis comprehensively evaluated the benefits and toxicities of GemErlo with or without gemcitabine alone for patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. In this review, 24 reports were identified by systematic search strategy. The heterogeneity in ORRs between the studies was reduced by the subgroup analysis of sample size.
According to this systematic review, the ORR in GemErlo-treated patients ranged from 0% to 28.6%, with a weighted estimate of 14.4%, while previous reports had indicated that gemcitabine monotherapy resulted in an ORR of 4.4%–23.8%.6–15,49,50 The DCR produced by gemcitabine alone in the previous studies varied from 34% to 57.1%,12–15,49,50 while GemErlo regimen increased DCR to a range of 25.0%–83.3%, with weighted estimate of 55%. Judging from the present data, the results of ORR and DCR seemed consistent with that of Moore et al16 who found no significant differences according to ORR and DCR. Weighted estimate of 1-year survival rate was 28.5%, which varied from 18.5% to 53.3%, which was superior to the result of the previous studies in which 1-year survival rate ranged from 11% to 37.2%.6,8,10–14,50 The PFS of the included studies ranged from 2.63 to 9.6 months and the OS varied from 6 to 10 months, which were slightly longer than the PFS (2.2–4.0 months)7,9,10,12,13,15,49 and OS (5.0–8.2 months)6–15,49,50 demonstrated in the previous studies that used gemcitabine alone. This is also consistent with the results of Moore et al’s trial.16 Taken together, GemErlo treatment brought slight improvement according to the PFS, OS, and 1-year survival rate compared with gemcitabine alone; however, GemErlo regimen failed to improve the tumor response rate.
As GemErlo treatment has been shown to bring slight improvement for patients with advanced pancreatic cancer compared with gemcitabine alone, when facing the choice of treating with GemErlo or gemcitabine in combination with other anticancer drugs, the clinical efficacy and safety should be taken into consideration. However, few studies have compared GemErlo or gemcitabine plus other chemotherapies directly in a single trial. Only one retrospective multivariate matched-pair analysis performed by Stuebs et al25 compared GemErlo with the combination of gemcitabine plus docetaxel. They found no significant differences between the two combinations in the efficacy profile. On the basis of the available studies that investigated the comparison between gemcitabine with other anticancer agents and gemcitabine alone, the ranges of ORR, DCR, 1-year survival rate, PFS, and OS of the combined treatment arms were 6.8%–26.8%,7–15,49,50 48.7%–79.3%,12–15,49,50 11.3%–34.7%,8,10,11–14,50 3.4–5.8 months,7,9,10,12,13,15,49,50 and 5.8–9.5 months,7–15,49,50 respectively. Our results seemed to be roughly equal to all the aforementioned indicators except for the PFS and 1-year survival rate, which were slightly better than the combination of gemcitabine plus other chemotherapies.
Each chemotherapy regimen, including the GemErlo treatment regimen, has treatment-related AEs. According to our review, the most common AEs were hematologic toxicities, rash, and diarrhea. Four studies regarded the grade of skin rash as a potential prognosis factor.16,20,29,32 Moore et al16 found that the median OS for patients with grades 0, 1, and 2+ rash were 5.3, 5.8, and 10.5 months, respectively; the 1-year survival rates were 16%, 9%, and 43% (P<0.001). Coincidentally, Van Cutsem et al,20 Aranda et al,29 and Park et al32 also noted that the more severe the skin rash of the patients treated with GemErlo, the better the response rates and survival rates.
Nevertheless, our meta-analysis also had some limitations, which need to be addressed. First and most important, relevant RCTs exploring the difference of efficacy and safety between the GemErlo-treatment arm and gemcitabine monotherapy arm have not been conducted extensively; for this reason, most of the selected studies were a series of single-arm prospective studies and retrospective studies, which could lead to heterogeneity between studies. Second, some of the included studies were the abstracts of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, thus preventing us from obtaining more complete information regarding the characteristics of the patients, regimens, and outcomes. Third, the sample sizes of the selected studies were small, which could lead to bias. Future studies are needed to further assess the other nontherapeutic factors, such as the economic conditions, primary disease, and nutrition status, which might also affect the outcomes of GemErlo treatment. More high-quality, large-sample, multicenter, randomized controlled clinical trials, which report detailed tumor response, survival, quality of life, and AEs on a deeper level, are urgently needed to determine the efficacy and safety of GemErlo treatment.
Conclusion
Based on the results of this meta-analysis, GemErlo treatment was shown to have a favorable therapeutic effect in patients with locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer. Most of the AEs were tolerable, while some severe AEs needed careful detection. To make more efficient regimens for patients with advanced pancreatic cancer, the comparison between the GemErlo treatment and gemcitabine in combination with other cytotoxic drugs or targeted drugs warrants further study.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Lowenfels AB, Maisonneuve P. Epidemiology and risk factors for pancreatic cancer. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2009;20:197–209. | ||
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics. 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29. | ||
Ferlay J, Steliarova-Foucher E, Lortet-Tieulent J, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: estimates for 40 countries in 2012. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49:1374–1403. | ||
Bond-Smith G, Banga N, Hammond TM, Imber CJ. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma. BMJ. 2012;344:e2476. | ||
Cascinu S, Graziano F, Catalano G. Chemotherapy for advanced pancreatic cancer: it may no longer be ignored. Ann Oncol. 1999;10:105–109. | ||
Burris HA 3rd, Moore MJ, Andersen J, et al. Improvements in survival and clinical benefit with gemcitabine as first-line therapy for patients with advanced pancreas cancer: a randomized trial. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15:2403–2413. | ||
Berlin JD, Catalano P, Thomas JP, Kugler JW, Haller DG, Benson AB 3rd. Phase III study of gemcitabine in combination with fluorouracil versus gemcitabine alone in patients with advanced pancreatic carcinoma: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Trial E2297. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:3270–3275. | ||
Rocha Lima CM, Green MR, Rotche R, et al. Irinotecan plus gemcitabine results in no survival advantage compared with gemcitabine monotherapy in patients with locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer despite increased tumor response rate. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:3776–3783. | ||
Oettle H, Richards D, Ramanathan RK, et al. A phase III trial of pemetrexed plus gemcitabine versus gemcitabine in patients with unresectable or metastatic pancreatic cancer. Ann Oncol. 2005;16:1639–1645. | ||
Louvet C, Labianca R, Hammel P, et al. Gemcitabine in combination with oxaliplatin compared with gemcitabine alone in locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer: results of a GERCOR and GISCAD phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:3509–3516. | ||
Abou-Alfa GK, Letourneau R, Harker G, et al. Randomized phase III study of exatecan and gemcitabine compared with gemcitabine alone in untreated advanced pancreatic cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:4441–4447. | ||
Heinemann V, Quietzsch D, Gieseler F, et al. Randomized phase III trial of gemcitabine plus cisplatin compared with gemcitabine alone in advanced pancreatic cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:3946–3952. | ||
Scheithauer W, Schüll B, Ulrich-Pur H, et al. Biweekly high-dose gemcitabine alone or in combination with capecitabine in patients with metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a randomized phase II trial. Ann Oncol. 2003;14:97–104. | ||
Colucci G, Giuliani F, Gebbia V, et al. Gemcitabine alone or with cisplatin for the treatment of patients with locally advanced and/or metastatic pancreatic carcinoma: a prospective, randomized phase III study of the Gruppo Oncologia dell’Italia Meridionale. Cancer. 2002;94:902–910. | ||
Kindler HL, Niedzwiecki D, Hollis D, et al. Gemcitabine plus bevacizumab compared with gemcitabine plus placebo in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: phase III trial of the Cancer and Leukemia Group B (CALGB 80303). J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:3617–3622. | ||
Moore MJ, Goldstein D, Hamm J, et al. Erlotinib plus gemcitabine compared with gemcitabine alone in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: a phase III trial of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:1960–1966. | ||
Dragovich T, Huberman M, Von Hoff DD, et al. Erlotinib plus gemcitabine in patients with unresectable pancreatic cancer and other solid tumors: phase IB trial. Cancer Chemoth Pharm. 2007;60:295–303. | ||
Ardavanis A, Kountourakis P, Karagiannis A, Doufexis D, Tzovaras AA, Rigatos G. Biweekly gemcitabine (GEM) in combination with erlotinib (ERL): an active and convenient regimen for advanced pancreatic cancer. Anticancer Res. 2009;29:5211–5217. | ||
Bengala C, Sternieri R, Malavasi N, et al. Phase II trial of erlotinib in combination with increasing dose of gemcitabine given as fixed dose rate infusion in advanced pancreatic cancer (advanced pancreatic cancer). 2009 ASCO Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium [abstract number: 156]. Available from: http://meetinglibrary.asco.org/content/10332-63. Accessed January 28, 2009. | ||
Van Cutsem E, Vervenne WL, Bennouna J, et al. Phase III trial of bevacizumab in combination with gemcitabine and erlotinib in patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:2231–2237. | ||
Cheng YJ, Bai CM, Zhang ZJ. Efficacy of gemcitabine combined with erlotinib in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2010;32:421–423. | ||
Milella M, Vaccaro V, Sperduti I, et al. Phase II study of erlotinib (E) combined with fixed dose-rate gemcitabine (FDR-Gem) as first-line treatment for advanced adenocarcinoma of the pancreas (PDAC). 2010 ASCO Annual Meeting [abstract number: e14565]. Available from: http://meetinglibrary.asco.org/content/51951-74. Accessed June 4, 2010. | ||
Okusaka T, Furuse J, Funakoshi A, et al. Phase II study of erlotinib plus gemcitabine in Japanese patients with unresectable pancreatic cancer. Cancer Sci. 2011;102:425–431. | ||
Boeck S, Vehling-Kaiser U, Waldschmidt D, et al. Erlotinib 150 mg daily plus chemotherapy in advanced pancreatic cancer: an interim safety analysis of a multicenter, randomized, cross-over phase III trial of the “Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie.” Anticancer Drugs. 2010;21:94–100. | ||
Stuebs P, Habermann P, Zierau K, et al. First-line therapy for advanced pancreatic cancer with gemcitabine and docetaxel versus gemcitabine and erlotinib: a multivariate matched pair analysis. 2010 ASCO Annual Meeting [abstract number: e14572]. Available from: http://meetinglibrary.asco.org/content/52331-74. Accessed: June 4 2010. | ||
Kim GP, Foster NR, Salim M, et al. Randomized phase II trial of panitumumab (P), erlotinib (E), and gemcitabine (G) versus erlotinib-gemcitabine in patients with untreated, metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma. 2011 ASCO Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium [abstract number: 238]. Available from: http://meetinglibrary.asco.org/content/71370-103. Accessed January 20, 2011. | ||
Feliu J, Borrega P, León A, et al. Phase II study of a fixed dose-rate infusion of gemcitabine associated with erlotinib in advanced pancreatic cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011;67:215–221. | ||
Llarena MA, Mane J, Lopez-Vivanco G, et al. Gemcitabine (G) fixed-dose-rate infusion (FDR) plus erlotinib (E) in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer (advanced pancreatic cancer). 2011 ASCO Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium [abstract number: 304]. Available from: http://meetinglibrary.asco.org/content/71207-103. Accessed January 20, 2011. | ||
Aranda E, Manzano JL, Rivera F, et al. Phase II open-label study of erlotinib in combination with gemcitabine in unresectable and/or metastatic adenocarcinoma of the pancreas: relationship between skin rash and survival (Pantar study). Ann Oncol. 2012;23:1919–1925. | ||
Jeon EK, Won HS, Ko YH, et al. Comparison of the efficacy and the toxicity between gemcitabine with capecitabine (GC) and gemcitabine with erlotinib (GE) in unresectable pancreatic cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012;138:1625–1630. | ||
Modiano M, Keogh GP, Manges R, et al. Apricot-P: a randomized placebo-controlled phase II study of COX-2 inhibitor apricoxib or placebo in combination with gemcitabine and erlotinib in advanced or metastatic adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. 2012 ASCO Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium [abstract number: 253]. Available from: http://meetinglibrary.asco.org/content/87740-115. Accessed January 19, 2012. | ||
Park S, Chung MJ, Park JY, et al. Phase II trial of erlotinib plus gemcitabine chemotherapy in Korean patients with advanced pancreatic cancer and prognostic factors for chemotherapeutic response. Gut Liver. 2013;7:611–615. | ||
Van Cutsem E, Li CP, Nowara E, et al. Dose escalation to rash for erlotinib plus gemcitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancer: the phase II RACHEL study. BJC. 2014;111:2067–2075. | ||
Lim JY, Cho JH, Lee SJ, Lee DK, Yoon DS, Cho JY. Gemcitabine combined with capecitabine compared to gemcitabine with or without erlotinib as first-line chemotherapy in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res Treat. 2015;47:266–273. | ||
Wilmink J, Kordes S, Zwinderman K, Mathot R, Punt CJA, Richel D. A phase II randomized, placebo controlled study to evaluate the efficacy of the combination of gemcitabine, erlotinib and metformin in patients with locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer. 2014 ASCO Annual Meeting [abstract number: 4021]. Available from: http://meetinglibrary.asco.org/content/129089-144. Accessed May 30, 2014. | ||
Philip PA, Goldman B, Ramanathan RK, et al. Dual blockade of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 (IGF-1R) signaling in metastatic pancreatic cancer: phase Ib and randomized phase II trial of gemcitabine, erlotinib, and cixutumumab versus gemcitabine plus erlotinib (SWOG S0727). Cancer. 2014;120:2980–2985. | ||
Diaz Beveridge R, Alcolea V, Aparicio J, et al. Management of advanced pancreatic cancer with gemcitabine plus erlotinib: efficacy and safety results in clinical practice. JOP. 2014;15:19–24. | ||
Semrad T, Barzi A, Lenz HJ, et al. Pharmacodynamic separation of gemcitabine and erlotinib in locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer: therapeutic and biomarker results. Int J Clin Oncol. 2015;20:518–524. | ||
Benavides M, Plazas JG, Guillen C, et al. Gemcitabine (G)/erlotinib (E) versus gemcitabine/erlotinib/capecitabine in the first line treatment of patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer (mPC): efficacy and safety results of a phase IIb randomized study from the Spanish TTD. 2014 ASCO Annual Meeting [abstract number: 4122]. Available from: http://meetinglibrary.asco.org/content/129070-144. Accessed May 30, 2014. | ||
DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986;7:177–188. | ||
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327:557–560. | ||
Hardy RJ, Thompson SG. Detecting and describing heterogeneity in meta-analysis. Stat Med. 1998;17:841–856. | ||
NCCN guidelines for pancreatic cancer. Available from: http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/pancreatic.pdf. Accessed January 30, 2016. | ||
Bareschino MA, Schettino C, Troiani T, Martinelli E, Morgillo F, Ciardiello F. Erlotinib in cancer treatment. Ann Oncol. 2007;18(Suppl 6):vi35–vi41. | ||
Durkin AJ, Bloomston PM, Rosemurgy AS, et al. Defining the role of the epidermal growth factor receptor in pancreatic cancer grown in vitro. Am J Surg. 2003;186:431–436. | ||
Fjällskog ML, Lejonklou MH, Oberg KE, Eriksson BK, Janson ET. Expression of molecular targets for tyrosine kinase receptor antagonists in malignant endocrine pancreatic tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:1469–1473. | ||
Xiong HQ. Molecular targeting therapy for pancreatic cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2004;54(Suppl 1):S69–S77. | ||
Ueda S, Ogata S, Tsuda H, et al. The correlation between cytoplasmic overexpression of epidermal growth factor receptor and tumor aggressiveness: poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreas. 2004;29:e1–e8. | ||
Philip PA, Benedetti J, Corless CL, et al. Phase III study comparing gemcitabine plus cetuximab versus gemcitabine in patients with advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Southwest Oncology Group-directed intergroup trial S0205. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:3605–3610. | ||
Cunningham D, Chau I, Stocken DD, et al. Phase III randomized comparison of gemcitabine versus gemcitabine plus capecitabine in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:5513–5518. |
 © 2016 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2016 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.