Back to Journals » International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease » Volume 12
Dysregulation of microRNA-214 and PTEN contributes to the pathogenesis of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension
Authors Liu H, Yin T, Yan W, Si R, Wang B, Chen M, Li F, Wang Q, Tao L
Received 20 January 2016
Accepted for publication 25 February 2016
Published 19 June 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 1781—1791
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S104627
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Richard Russell
HaiTao Liu, Tao Yin, Wenjun Yan, Rui Si, Bo Wang, Mai Chen, Fei Li, Qiong Wang, Ling Tao
Department of Cardiology, Xijing Hospital, Fourth Military Medical University, Xi’an, Shaanxi, People’s Republic of China
Abstract: Hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension, which is characterized by vascular remodeling of blood vessels, is an important complication in COPD. In this study, we found that the expression of miR-214 was differentially expressed by screening 13 candidate miRNAs in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMCs). Additionally, using luciferase assay in PASMCs, we found that phosphatase-and-tensin homolog (PTEN) was a target of miR-214. Furthermore, the expression of PTEN was found to be substantially downregulated in PASMCs from COPD patients with pulmonary hypertension (PH) compared with normal controls by using real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR), immunohistochemistry, and Western blot. In addition, we transfected PASMCs with miR-214 mimics, using real-time PCR and Western blotting, to confirm the miRNA/mRNA relationship. Furthermore, the introduction of miR-214 significantly promoted the proliferation of PASMCs by suppressing apoptosis of the cells, which was mediated by the downregulation of PTEN. Exposure to hypoxia significantly increased the expression of miR-214 and decreased the expression of PTEN in PASMCs, and its proliferation was significantly promoted. Such effects could be significantly attenuated by the introduction of miR-214 inhibitors, which significantly downregulated miR-214 expression and upregulated the expression of PTEN. In conclusion, hypoxia-induced upregulation of miR-214 was found to promote PH development by targeting PTEN in PASMCs, and miR-214 could be a promising diagnostic tool and novel therapeutic target in the management of hypoxia-induced PH in COPD.
Keywords: hypoxia, pulmonary hypertension, miR-214, PTEN
Introduction
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a vascular disease of the lung characterized by the mean pulmonary arterial pressure reaching one-quarter of the systemic blood pressure. Stiffening or constriction of the pulmonary arteries that deliver blood to the lungs leads to PH.1 PH may result from thromboembolism, hypoxia caused by vascular or pulmonary parenchymal disease, heart failure, or a combination of these factors.2 Hypoxia exposure accelerates the remodeling of vessels, one of the pathological characteristics of PH, resulting in the development of vascular occlusion and neointimal formation.1 As a result, pumping blood from the heart forward into the lungs becomes increasingly difficult, and this leads to the enlargement of the right heart. The mechanisms underlying the progression and development remain largely unknown, and, if identified, it is possible that key therapeutic targets will be provided.3–5
Two mechanisms, vasoconstriction and the subsequent remodeling of medium- and small-sized pulmonary arteries, serve as hallmarks of advanced and severe PH and have been believed to contribute to PH.6 Abnormal proliferation and hypertrophy of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMCs), which leads to blockages in small pulmonary arteries, is the main pathological change associated with vascular remodeling.7,8 Lately, more attention has been focused on the dysfunction in the development of remodeling and hypoxic vasoconstriction in the context of microRNAs (miRNAs). Differential expression of miRNAs has been reported to participate in the peculiarly enhanced PASMC proliferation, and thus, it has been involved in the remodeling of vessels.9 Consequently, more attention is being paid to identify the miRNAs and their target genes, which are related to the pathogenesis of PH.
miRNAs, a group of small noncoding RNAs consisting of 18–25 nt, could bind to the 3′-untranslated region (3′-UTR) of mRNAs in order to negatively regulate the expression of target genes. This would lead to degradation or translational repression.10 Dysregulation of miRNAs has been shown to be functionally involved in the control of various biological processes, including proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and cell cycle progression.11 In recent years, a growing body of evidence is indicating that these molecules play substantial and important roles in the molecular mechanism underlying the physiological and pathophysiological adaptations to hypoxia. Among these miRNAs, those whose expression is dynamically regulated by hypoxia are called “hypoxamiRs”,12 and the upregulation or downregulation of the hypoxamiRs is implicated to be involved in the pathogenesis of the development of hypoxia-induced PH, an important complication in COPD patients, by suppressing the target gene expression or releasing physiologically inhibited expression of certain genes.13
In order to explore the role of candidate miRNAs in hypoxia-induced PH, we performed quantitative real-time-polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based screening for differentially expressed miRNAs, and identified miR-214 as the only significantly upregulated miRNA in the PASMCs harvested from COPD patients with PH. The objective of the present study was to determine whether differentially expressed miR-214 is responsible for the abnormally enhanced proliferation of PASMCs, as well as the underlying molecular mechanism.
Patients and methods
Patient samples
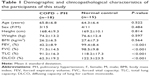
The participants in the study included patients with COPD and PH (N=18) and control subjects (N=15). Both groups received a pneumonectomy for a lung tumor (resection of lung) in Xijing Hospital, Fourth Military Medical University. Lung tissue samples were collected from normal-appearing areas of the pulmonary parenchyma (at least 2 cm from the tumor and free from pleura or large airways). The clinicopathological information relating to each patient in the two groups is displayed in Table 1. All patients were in stable medical condition, and they had not received medical attention and/or any change in their regular therapy in the period 3 months prior to their enrollment. This study was conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki Protocols after it was approved by the research ethics committee of Fourth Military Medical University. Written and informed consents were obtained from all participants prior to the study.
Tissue preparation and smooth muscle cell isolation
Segments of the pulmonary artery (50–500 μm external diameter) from the participants were incubated in Hanks’ solution containing collagenase (1.5 mg/mL) for 30 minutes. Next, the layers of adventitia and endothelium were stripped off, the smooth muscle was then digested by elastase (0.5 mg/mL) and collagenase (2.0 mg/mL), and the isolated smooth muscle cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum, penicillin (100 U/mL), and streptomycin (100 mg/mL) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) at 37°C. The cells at passages 3–8 were used for experiments.
Hypoxia treatment of PASMCs
PASMCs were exposed to hypoxia at 37°C in 1% O2, 5% CO2, and 94% N2 atmosphere for a period of 24 hours.
Western blotting
Proteins were extracted from the transfected cells using a lysis buffer (Upstate Biotechnology, Lake Placid, NY, USA). The protein level was determined using protein assay reagents following the standard protocols (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA). Briefly, 25 μg of total protein was loaded on 12% PAGE gel (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane (Bio-Rad Laboratories). Following the transfer, the membranes were blocked with Odyssey® blocking buffer (LI-COR Biosciences, Lincoln, NE, USA), and then they were incubated in primary antibodies buffer (primary antibodies, Odyssey Blocking Buffer, 0.1% Tween® 20) overnight at 4°C. Two primary antibodies, anti-phosphatase-and-tensin homolog (PTEN) antibody and anti-SMAD4 antibody, were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology Inc. (Beverly, MA, USA). The following day, the membranes were washed four times for 5 minutes in Tris-buffered saline and Tween 20 prior to being incubated in the secondary antibodies IRDye® 680LT Goat anti-Mouse lgG or IRDye 680LT Goat anti-Rabbit lgG (LI-COR) plus Odyssey blocking buffer and 0.1% Tween 20 at 1:20,000 dilution for 1 hour. Finally, the membranes were visualized on an Odyssey CLx imaging system, model:Ody-3086 (LI-COR).
RNA isolation and real-time PCR
Total RNA was isolated from sample tissues or cell lines using the miRNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen NV, Venlo, the Netherlands). Ten microliters of the reaction mixture, including 1 μg of total RNA, 1 μL of 10× reaction buffer, 1 μL of 10 mM ATP, and 1 unit of Poly(A) polymerase, was incubated at 37°C for 30 minutes, followed by enzyme inactivation at 65°C for 5 minutes. After polyadenylation, reverse transcription was performed in 10 μL of the reaction mixture containing 1 μL of the polyadenylation reaction product, 1 μL of 0.5 μM RT primer, 0.5 μL of 10 mM dNTP, 1 μL of RT 10× reaction buffer, and 50 units of high-performance RT (Epicentre). The reaction mixture was incubated at 42°C for 60 minutes, and then terminated by heating at 85°C for 5 minutes. qPCR was performed with the MESA Green qPCR Master Mix Kit for SYBR Green (Eurogentic GmbH, Köln, Germany). In addition, qPCR reactions were performed on a CFX96 real-time PCR system (Bio-Rad Laboratories). In brief, we started with a 5-minute denaturation at 94°C followed by 40 cycles of 15 seconds at 95°C, and then 60 seconds at 60°C and, finally, 5 minutes at 72°C. Target gene expression was normalized to that of U6 and β-actin. Relative expression was calculated using the 2-ΔΔCt method.
Luciferase assay
The 3′-UTR sequence of PTEN and SMAD4 was amplified and subcloned into the pmirGLO luciferase reporter vector (Promega Corporation, Fitchburg, WI, USA). In addition, the predicted binding sequences were mutated by using the site-directed mutagenesis kit (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA, USA). Cells (3.5×104) were seeded in 24-well plates and cotransfected with wild-type or mutant 3′-UTR vectors and miR-214 mimics or scramble controlled using Lipofectamine 2000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific). After 48 hours, the firefly and Renilla luciferase activities were measured using the Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay System (Promega Corporation) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The firefly luciferase activities were normalized to the Renilla luciferase activity. All experiments were performed in triplicate.
Cell counting
The same amount of differently treated miR-214 cells was plated in six-well plates (5,000 cells per well) in SmGM-2, and adherent cells (viable cells) were detached by treatment with trypsin. Following this, they were counted using the TC10 automated cell counter (Bio-Rad Laboratories). All experiments were performed in triplicate.
BrdU incorporation assays
BrdU was added 2 hours prior to culture termination. At the end of culture, cells were immunoblocked with goat serum and incubated overnight at 4°C with the anti-BrdU antibody. Subsequently, they were incubated for 60 minutes with biotinylated Goat anti-Mouse IgG (1:200) and stained with DAB. The percentage of stained cells was determined by counting the number of positively stained cells within the microscopic vision field; this value was then divided by the total number of cells in the same field.
SMC culture and transfection
The human PASMCs (hPASMCs) used in this study were maintained in the SMC basal medium complemented with growth factors (including hEGF 0.5 mL, Insulin 0.5 mL, hFGF-B 1 mL, FBS 10 mL, GA-1000 0.5 mL, 10 U/mL penicillin, and 1 mg/mL streptomycin). This was done at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2. Cells were trypsinized and passaged at 95% confluence, and the studies were performed on cells at passages 4–6 and 60%–90% confluence. The cells were exposed to 1% hypoxia for 48 hours, and cells of the same passage were exposed to 20% oxygen (normoxia) for the same time periods that were used for controls. Cell counting, protein analysis, and ubiquitination assays were performed using these cells. Cell counting was performed using the Nucleo-Counter (New Brunswick Scientific).
Caspase 3 activity assay
Caspase 3 activity assay was performed using the Caspase-Glo 3 assay kit (Promega Corporation) following the manufacturer’s instructions.
Immunohistochemistry
All immunohistochemical experiments were performed on paraffin-embedded serial slides. Briefly, sample slides were deparaffinized and rehydrated and submerged into the EDTA antigenic retrieval buffer (pH 8.0) and microwaved for antigenic retrieval. After being blocked by normal goat serum for 30 minutes, the slides were incubated with the primary antibody (anti-TrkB, anti-BDNF, anti-NT-4/5, and anti-Egr-1; all from Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc. [Dallas, TX, USA] 1:100 diluted in ChemMate antibody diluent, Dako Denmark A/S [Glostrup, Denmark]) for 18 hours. Subsequently, slides were washed with Tris-buffered saline (pH 7.4–7.6) and incubated for 45 minutes with the corresponding secondary antibodies conjugated with alkaline phosphatase (Rockland, Gilbertsville, PA, USA) at 1:250 dilution. Negative controls were prepared with the omission of the primary antibody.
Statistical analysis
The data are expressed as mean ± SE (standard error) using the StatView software. Statistical comparisons between the two groups were performed by the unpaired Student's t-test. Comparisons among ≥3 groups were performed with one-way, two-way, or three-way ANOVA without repeated measures, as appropriate. Comparisons among ≥3 groups were carried out with one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's post hoc test. Comparisons among ≥3 groups were performed with two- or three-way ANOVA followed by a stratified independent t-test with Bonferroni corrections for multiple comparisons. Statistical significance was defined as P≤0.05.
Results
Dysregulation of miR-214 in the COPD patients with PH
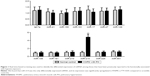
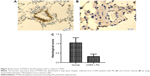
In order to identify the differentially expressed miRNAs between hPASMCs from COPD patients with PH and normal controls, we detected the expression levels of 13 candidate miRs, which, evidence suggested, were associated with hypoxia. As shown in Figure 1, only miR-214 was differentially expressed between the two groups; all others were comparable. The clinicopathological data of the participants is described in Table 1. No difference was noted between the cases and controls in relation to age, sex, height, weight, and body mass index. As expected from the recruitment criteria, the forced expiratory volume 1 in 1 second, diffusing capacity of lung for carbon monoxide, total lung capacity, and forced vital capacity were significantly lower in the case group than in the control group.
MiR-214 directly targets PTEN
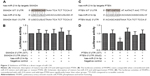
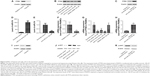
Using an online target prediction database (www.mirdb.org), we found that miR-214 was able to bind directly to the 3′UTR of two genes, PTEN and SMAD4. As shown in Figure 2, we compared the seed sequences in the 3′UTR of PTEN and SMAD4 and mature miR-214, and, following this, separately cloned the full-length 3′UTR of both genes into the pcDNA3.0 vector downstream of a luciferase gene (labeled pcDNA3-PTEN-WT-3′UTR and pcDNA3-SMAD4-WT-3′UTR, respectively; Figure 2A and C). In addition, seed sequences within the predicted miR-214 target site were mutated in the constructs respectively (labeled as pcDNA3-PTEN-Mut1-3′UTR and pcDNA3-SMAD4-Mut2-3′UTR; Figure 2A and C). We found that only the luciferase activity from the cells co-transfected with miR-214 mimics. Furthermore, wild-type PTEN 3′UTR was observed to decrease by ~50% (Figure 2D), and the others were comparable (Figure 2B). The results confirmed that wild-type PTEN was a validated target of miR-214 in hPASMCs.
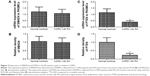
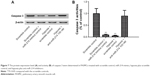
The next step was to examine the mRNA and protein expression levels of PTEN and SMAD4 in hPASMCs from COPD patients with PH in addition to the controls. The results indicated that the mRNA and protein expression of PTEN was decreased in hPASMCs from COPD patients with PH (Figure 3), while the protein and mRNA expression of SMAD4 was comparable between the groups (Figure 3A and B). This suggested that miR-214 may be involved in the development of PH in COPD via targeting PTEN instead of SMAD4. In order to verify the results further, we performed immunohistochemistry and found that the expression of PTEN was significantly downregulated in remodeled arteries (Figure 4A and B).
Effects of hypoxia and alteration of miR-214 on the expression of PTEN
We subsequently used real-time PCR and Western blotting in order to examine the effects that hypoxia and miR-214 mimics/inhibitors have on the mRNA and protein levels of PTEN and AKT in hPASMCs. As shown in Figure 5, the expression of PTEN of the cells exposed to hypoxia significantly decreased, while AKT was significantly increased in hPASMCs. At the same time, we found that anti-PTEN siRNA and miR-214 mimics (50 nM and 100 nM, respectively) could significantly downregulate the mRNA and protein expression of PTEN, while anti-PTEN siRNA had only a minimal effect on the expression of SMAD4 (Figure 5). Meanwhile, the expression of AKT of cells exposed to hypoxia significantly increased, while AKT was significantly increased in hPASMCs. At the same time, we found that anti-PTEN siRNA and miR-214 mimics (50 nM and 100 nM) could significantly upregulate the mRNA and protein expression of AKT (Figure 5). Furthermore, anti-miR-214 inhibitors significantly enhanced the expression of PTEN in hPASMCs exposed to hypoxia, while they decreased the expression of AKT (Figure 5).
Proliferation of PASMCs was suppressed by introduction of anti-miR-214
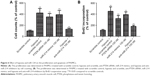
Proliferation of PASMCs is an essential part of vascular remodeling in PH, and so we transfected them with miR-214 mimics/inhibitor as well as the target gene-specific siRNA. This was carried out in order to assess the effects on proliferation by cell count and BrdU assay. As shown in Figure 6A and B, when the cells were exposed to hypoxia, proliferation was significantly enhanced; when transfected with anti-PTEN siRNA or miR-214 mimics, the result was similar. However, it should be noted that the introduction of anti-miR-214 inhibitors partially but significantly prevented the abnormally enhanced proliferation of hPASMCs induced by hypoxia.
Furthermore, caspase-3 activity was determined in order to explore the underlying molecular mechanism. The results revealed that transfection of miR-214 mimics or anti-PTEN siRNA similarly inhibited apoptosis. The results also indicated that transfection of anti-miR-214 inhibitors significantly suppressed the proliferation of PASMCs by introducing apoptosis (Figure 6A and B). Simultaneously, the expression level and activities of caspase 3 in PASMCs exposed to hypoxia or transfected with either miR-214 or anti-miR-214 mimics were measured. It was found that the protein levels and activities of caspase 3 were consistently downregulated in the cells that were exposed to hypoxia and transfected with miR-214 mimics. In addition, it was found that the hypoxic effect could be significantly attenuated by transfection with anti-miR-214 inhibitors (Figure 7A and B).
Discussion
Contemporary research into disease pathogenesis has revealed the fundamental role that miRNAs play. Distinct miRNA signatures in human diseases have been reported by many recent studies.14–16 MiRNAs are believed to be related to remodeling and the process of failure and hypertrophy in the vasculature and the heart.17 With reference to the lungs, a recent study highlighted the regulation of miRNAs after smoke inhalation injury.18 In this study, we determined the expression levels of 13 candidate miRs that are reportedly associated with hypoxia, but only miR-214 was differentially expressed.
Several studies have focused on comprehensive investigations into the biological functions of miR-214. A study based on the Human miRNA and Disease Database19 revealed that miR-214 has an increased expression level in many malignancies, including melanoma and cancer of the liver, stomach, breast, ovary, pancreas, and lungs.20 A number of target genes of miR-214, such as TP5321 and PTEN,16 have been confirmed by experiments, primarily as a result of searching the TarBase.22 Penna et al23 noted an overexpression of miR-214 in cancer tissues and metastatic melanoma cell lines, and found that metastasis was promoted by regulating two transcription factors: AP-2α and AP-2γ. In addition, it was found that a number of oncogenes, including JNK1 and MEK3, could be suppressed by miR-214 as well.24 Similarly, the complexity of miR-214 functioning in various diseases and tissue counts on different downstream signaling and targets provides a novel prospect for future investigations into the topic. In this study, we validated that PTEN was a direct target of miR-214 in hPASMCs by using in silico analysis and a luciferase reporter system. Furthermore, we demonstrated that the expression of PTEN of hypoxia tissues was significantly decreased in hPASMCs. Furthermore, it was shown that anti-PTEN siRNA and miR-214 mimics (50 nM and 100 nM, respectively) could significantly downregulate the mRNA and protein expression of PTEN, while anti-PTEN siRNA had only a minimal effect on the expression of SMAD4. MiR-214 is reportedly involved in the pathogenesis of PH in the patients with COPD.25–27 It is interesting to note that miR-214 targets the epithelial growth factor receptor, an oncogene that promotes the proliferation of cells. However, in our study we found that miR-214 was upregulated in PH samples and that it targeted PTEN, a well-known tumor suppressor. PTEN induces apoptosis and suppresses the proliferation of human cells. Such discrepancy could be attributed to the high heterogeneity of the disease.
PTEN is located on chromosome 10, considered to be a tumor suppressor gene and, at first, is a multifunctional lipid phosphatase.3 Active PTEN protein is involved in several cellular processes, including cell apoptosis, proliferation, migration, and survival.28–30 Recent studies have found that PTEN plays a critical role in the pulmonary and cardiovascular systems.31,32 Activated PTEN participated in the regulation of cardiomyocyte survival and hypertrophy, as well as the survival and proliferation of PASMCs.31,32 The activated PTEN leads to the constitutive activation of Akt when vascular injury occurs, and this plays an early and critical role in the activation of pulmonary SMCs and neointimal formation.33 Targeted deletion of PTEN in SMCs leads to PH and vascular remodeling.4 In contrast, it has been confirmed that the survival and proliferation of vascular SMCs are inhibited by the stabilization and overexpression of PTEN in vivo and vitro. This has been shown to result in PH and neointimal hyperplasia.3 The activation of PTEN targets the Akt pathway to regulate both survival genes and cell proliferation, which manipulate the progression of pulmonary and cardiovascular diseases.31,32 PTEN suppresses PI3K (phosphatidyl-inositol-3-kinase) and downstream functions such as cell proliferation, cell survival, and the activation of Akt in tumor cells with deletion or mutant-type PTEN.34 However, the function of PTEN in PH, particularly in the field of survival-signaling pathways, the proliferation of PASMCs, and their related mechanisms, has not yet been entirely figured out. One plausible explanation is that factors accelerating the development of PH, including hypoxia or those related to the remodeling process, might directly downregulate PTEN expression.35 The present study found that, when the cells were exposed to hypoxia, proliferation was significantly enhanced; when transfected with anti-PTEN siRNA or miR-214 mimics, the result was similar. At the same time, the introduction of anti-miR-214 inhibitors partially, but significantly, prevented the abnormally enhanced proliferation of hPASMCs induced by hypoxia. In addition, we also performed flow cytometry and Caspase-3 measurements to determine the apoptosis of differently treated PASMCs. We found that transfection of miR-214 mimics or anti-PTEN siRNA similarly inhibited apoptosis induced by incubation with H2O2. We were also able to conclude that transfection of anti-miR-214 inhibitors significantly suppressed the proliferation of PASMCs by introducing apoptosis.
Conclusion
We demonstrated that the aberrantly promoted proliferation of PASMCs induced by hypoxia was at least partially, but significantly, the result of the downregulation of PTEN. In turn, this was caused by the upregulation of miR-214 in response to hypoxia. It is expected that these findings will further our understanding of the underlying molecular mechanism of PH in patients with COPD, and they could serve to provide a possible therapeutic target for hypoxia induced PH.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by funds from the Natural Science Foundation of China (No 81170183).
Disclosure
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Rabinovitch M. Cellular and molecular pathobiology of pulmonary hypertension conference summary. Chest. 2005;128(6 suppl):642S–646S. | ||
Agarwal R, Gomberg-Maitland M. Current therapeutics and practical management strategies for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am Heart J. 2011;162(2):201–213. | ||
Huang J, Kontos CD. Inhibition of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, migration, and survival by the tumor suppressor protein PTEN. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002;22(5):745–751. | ||
Nemenoff RA, Simpson PA, Furgeson SB, et al. Targeted deletion of PTEN in smooth muscle cells results in vascular remodeling and recruitment of progenitor cells through induction of stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha. Circ Res. 2008;102(9):1036–1045. | ||
Nisbet RE, Bland JM, Kleinhenz DJ, et al. Rosiglitazone attenuates chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension in a mouse model. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2010;42(4):482–490. | ||
Rubin LJ. Cellular and molecular mechanisms responsible for the pathogenesis of primary pulmonary hypertension. Pediatr Pulmonol Suppl. 1999;18:194–197. | ||
Pietra GG, Capron F, Stewart S, et al. Pathologic assessment of vasculopathies in pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43(12 suppl S):25S–32S. | ||
Humbert M, Morrell NW, Archer SL, et al. Cellular and molecular pathobiology of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43(12 suppl S):13S–24S. | ||
Dorfmüller P, Perros F, Balabanian K, Humbert M. Inflammation in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur Respir J. 2003;22(2):358–363. | ||
Valencia-Sanchez MA, Liu J, Hannon GJ, Parker R. Control of translation and mRNA degradation by miRNAs and siRNAs. Genes Dev. 2006;20(5):515–524. | ||
Hobert O. Gene regulation by transcription factors and microRNAs. Science. 2008;319(5871):1785–1786. | ||
Chan SY, Loscalzo J. MicroRNA-210: a unique and pleiotropic hypoxamir. Cell Cycle. 2010;9(6):1072–1083. | ||
Hale AE, White K, Chan SY. Hypoxamirs in pulmonary hypertension: breathing new life into pulmonary vascular research. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2012;2(3):200–212. | ||
Lujambio A, Calin GA, Villanueva A, et al. A microRNA DNA methylation signature for human cancer metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(36):13556–13561. | ||
Ambs S, Prueitt RL, Yi M, et al. Genomic profiling of microRNA and messenger RNA reveals deregulated microRNA expression in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2008;68(15):6162–6170. | ||
Yang H, Kong W, He L, et al. MicroRNA expression profiling in human ovarian cancer: miR-214 induces cell survival and cisplatin resistance by targeting PTEN. Cancer Res. 2008;68(2):425–433. | ||
Cheng Y, Ji R, Yue J, et al. MicroRNAs are aberrantly expressed in hypertrophic heart: do they play a role in cardiac hypertrophy? Am J Pathol. 2007;170(6):1831–1840. | ||
Izzotti A, Calin GA, Arrigo P, Steele VE, Croce CM, De Flora S. Downregulation of microRNA expression in the lungs of rats exposed to cigarette smoke. FASEB J. 2009;23(3):806–812. | ||
Lu M, Zhang Q, Deng M, et al. An analysis of human microRNA and disease associations. PLoS One. 2008;3(10):e3420. | ||
Tuccari G, Barresi G. Lactoferrin in human tumours: immunohistochemical investigations during more than 25 years. Biometals. 2011;24(5):775–784. | ||
Kanaan Z, Rai SN, Eichenberger MR, et al. Differential microRNA expression tracks neoplastic progression in inflammatory bowel disease-associated colorectal cancer. Hum Mutat. 2012;33(3):551–560. | ||
Vergoulis T, Vlachos IS, Alexiou P, et al. TarBase 6.0: capturing the exponential growth of miRNA targets with experimental support. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(Database issue):D222–D229. | ||
Penna E, Orso F, Cimino D, et al. microRNA-214 contributes to melanoma tumour progression through suppression of TFAP2C. EMBO J. 2011;30(10):1990–2007. | ||
Yang Z, Chen S, Luan X, et al. MicroRNA-214 is aberrantly expressed in cervical cancers and inhibits the growth of HeLa cells. IUBMB Life. 2009;61(11):1075–1082. | ||
Zhou S, Li M, Zeng D, et al. A single nucleotide polymorphism in 3′ untranslated region of epithelial growth factor receptor confers risk for pulmonary hypertension in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36(1):166–178. | ||
Paulin R, Courboulin A, Barrier M, Bonnet S. From oncoproteins/tumor suppressors to microRNAs, the newest therapeutic targets for pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Mol Med (Berl). 2011;89(11):1089–1101. | ||
Boucherat O, Potus F, Bonnet S. microRNA and pulmonary hypertension. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;888:237–252. | ||
Moon SK, Kim HM, Kim CH. PTEN induces G1 cell cycle arrest and inhibits MMP-9 expression via the regulation of NF-kappaB and AP-1 in vascular smooth muscle cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2004;421(2):267–276. | ||
Tamguney T, Stokoe D. New insights into PTEN. J Cell Sci. 2007;120(pt 23):4071–4079. | ||
Van de Sande T, De Schrijver E, Heyns W, Verhoeven G, Swinnen JV. Role of the phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase/PTEN/Akt kinase pathway in the overexpression of fatty acid synthase in LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2002;62(3):642–646. | ||
Oudit GY, Penninger JM. Cardiac regulation by phosphoinositide 3-kinases and PTEN. Cardiovasc Res. 2009;82(2):250–260. | ||
Oudit GY, Sun H, Kerfant BG, Crackower MA, Penninger JM, Backx PH. The role of phosphoinositide-3 kinase and PTEN in cardiovascular physiology and disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2004;37(2):449–471. | ||
Noureddine H, Gary-Bobo G, Alifano M, et al. Pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell senescence is a pathogenic mechanism for pulmonary hypertension in chronic lung disease. Circ Res. 2011;109(5):543–553. | ||
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, et al. Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell. 1997;91(2):231–241. | ||
Voelkel NF, Tuder RM. Hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling: a model for what human disease? J Clin Invest. 2000;106(6):733–738. |
 © 2017 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2017 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.