Back to Journals » Drug Design, Development and Therapy » Volume 11
Development of venetoclax for therapy of lymphoid malignancies
Received 1 January 2017
Accepted for publication 14 February 2017
Published 9 March 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 685—694
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S109325
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Anastasios Lymperopoulos
Huayuan Zhu,1,2 Alexandru Almasan1
1Department of Cancer Biology, Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA; 2Department of Hematology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Jiangsu Province Hospital, Nanjing, People’s Republic of China
Abstract: B-cell lymphoma-2 (BCL-2) family dysfunction and impairment of apoptosis are common in most B-cell lymphoid malignancies. Venetoclax (Venclexta™, formerly ABT-199, GDC-0199) is a highly selective BCL-2 inhibitor, which mimics its BCL-2 homology 3-domain to induce apoptosis. It was approved for treatment of previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients with 17p deletion early in 2016. It has also been in clinical trials for other B-cell lymphoid malignancies. Unlike the other recently approved targeted agents idelalisib and ibrutinib, so far there has been no relapse reported in some patients. Also, unlike the other targeted agents, it is effective against tumor cells that reside in the blood marrow. Despite its promising outcome in CLL, preclinical data have already uncovered mechanistic insights underlying venetoclax resistance, such as upregulation of MCL-1 or BCL-xL expression and protective signaling from the microenvironment. In this review, we describe the role of the BCL-2 family in the pathogenesis of B-cell lymphoid malignancies, the development of venetoclax, and its current clinical outcome in CLL and other B-cell malignancies. We also discuss the resistance mechanisms that develop following venetoclax therapy, potential strategies to overcome them, and how this knowledge can be translated into clinical applications.
Keywords: BCL-2, BCL-xL, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, MCL-1, venetoclax
Introduction
Apoptosis is an evolutionarily conserved process of cell death that plays a critical role in tissue homeostasis.1 There are two distinct apoptosis pathways: the “extrinsic (death receptor) pathway” and the “intrinsic (mitochondrial) pathway”. The intrinsic pathway is triggered by a range of signals, such as DNA damage or deprivation of growth factors and results in the release of apoptogenic proteins, including cytochrome c from the mitochondria to the cytoplasm and activation of caspases, eventually leading to cell death. Mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP) is the key point of “no return” in the intrinsic pathway, and it is regulated by the BCL-2 family proteins.
The B-cell lymphoma-2 (BCL-2) gene product was the first antiapoptosis protein discovered in 1980s as a consequence of t(14; 18) chromosomal translocation and the hallmark of follicular lymphoma (FL).2 Since then, more than 20 BCL-2 family members have been identified, and they have been classified into three groups based on their function and structure. The antiapoptotic proteins BCL-2, BCL-xL, BCL-W, BFL-1/A1, and MCL-1 have four BCL-2 homology (BH) domains and interact with other BCL-2 family proteins to prevent MOMP. The pro-apoptosis proteins, BIM, BID, BAD, NOXA, and PUMA, only share sequence homology with the BH3 domain and are therefore called BH3-only proteins. Finally, the cell death mediators BAX and BAK have three BH domains (BH1–3).3 Briefly, BAX and BAK are directly inhibited by the antiapoptotic proteins, such as BCL-2. Under cell stress signals, BH3-only proteins, such as BIM, can act as direct activators of BAX/BAK or as sensitizers, such as NOXA, by displacing BAX/BAK from their interaction with antiapoptotic proteins, resulting in BAX/BAK homo-oligomerization and MOMP. Antiapoptotic family members can also prevent BH3-only protein activation. Some of the BH3-only proteins, such as BIM, can bind to multiple antiapoptotic BCL-2 family proteins, while others, such as NOXA, are more restrictive, binding primarily to MCL-1.4 Also, some antiapoptotic BCL-2 proteins display a preference for BAX or BAK binding. Thus, BAK preferentially binds to MCL-1, but not BCL-2.5
Chemoimmunotherapy has been the standard treatment for patients with CLL and other B-cell lymphoid malignancies.6 The B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling inhibitors, such as idelalisib and ibrutinib, were proved to affect the survival of neoplastic B cells not only by destabilizing the multifactorial platform of microenvironment signals that commonly sustain the malignant clone but also by delocalizing a consistent fraction of the tumor B-cell clone from the protective tissue compartment.7 The outcome of relapsed CLL improved dramatically over the past 5 years with the advent of BCR signaling inhibitors, especially in the elderly and unfit.8–11 However, patients do relapse during treatment with ibrutinib or idelalisib, and some patients even fail to respond. The C481S mutation in the Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) domain was reported to be a major mechanism of resistance to ibrutinib. Therefore, novel therapies are needed to overcome resistance to ibrutinib and idelalisib. Second-generation BTK inhibitors, such as ACP-196, ONO/GS-4059, and BGB-3111, are being assessed in several clinical trials with promising outcome.12 Another alternative strategy is to target BCL-2, as dysfunction of apoptosis due to BCL-2 overexpression is one of the hallmarks in most B-cell malignancies.13 A series of BCL-2 inhibitors have been developed since the mid-2000s; among these, venetoclax (Venclexta™ [AbbVie Inc., North Chicago, IL, USA], formerly ABT-199, GDC-0199) is the first US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved drug for CLL patients with 17p deletion who received at least one prior therapy.14 Here, we review the clinical application and resistance mechanisms underlying venetoclax therapy and future directions for combination therapies with it, both in CLL and in other B-cell malignancies.
Aberrant expression of BCL-2 protein in B-cell malignancies
High levels of BCL-2 are universal in CLL, FL, mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia (WM), and one third of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCL). Most CLL primary cells present high BCL-2 levels not only due to the hypomethylation of the BCL-2 gene15 but also as a result of loss of microRNA (miR)-15 and miR-16 located at 13q14, a region deleted in more than half of CLL patients.16 Elevated BCL-2 protein levels were found as a result of the t(14; 18) translocation in 80%–90% of FL patients.2 About one third of DLBCL cases overexpress BCL-2 because of the t(14; 18) translocation or gene amplification.17 Aberrant expression of the BCL-2 protein is also found in MCL and multiple myeloma (MM), where it was associated with deregulation of cyclin D1 (CCND1) expression caused by its translocation.18,19 For all these reasons, targeting the BCL-2 protein to induce apoptosis is considered to be a promising therapeutic approach in B-cell lymphoid malignancies. While B-cell malignancies, such as CLL and FL, rely on BCL-2, and are therefore designated as BCL-2 dependent, there are others, such as MM, that are more dependent on MCL-1 or both MCL-1 and BCL-xL.
Development of BH3 mimetic drugs
BH3 mimetic drugs were designed on the basis of their structural similarity to the BH3 domain of the BH3-only proteins. The first such structure-based “bona fide” BCL-2 inhibitor acting as a synthetic BH3 mimetic was ABT-737, a small-molecule inhibitor that binds with a high affinity to BCL-2, BCL-xL, and BCL-W, but not MCL-1. In vitro, ABT-737 can induce apoptosis of primary CLL cells from patients at a concentration <100 nM.20 Later, its bioavailable derivative ABT-263 (navitoclax) was selected for clinical development.21 Navitoclax showed antitumor activity against CLL and FL in early phase clinical trials,22,23 but further studies were postponed because of its on target BCL-xL inhibition. As BCL-xL is a key survival factor for platelets,24 the patients administered navitoclax suffered from acute thrombocytopenia.22
Venetoclax was developed as a highly BCL-2-selective BH3-mimetic. It has a strong affinity only for BCL-2, with >100-fold less affinity for BCL-xL or BCL-W. As with navitoclax, in vitro cytotoxicity of venetoclax is dependent on the presence of BAX and BAK, which in turn leads to cell death by apoptosis.25 Other therapeutics that were initially considered as BH3 mimetics, later turned out not to represent “true” BH3 mimetics, as their mechanism of action was independent of BAX or BAK activation, even though they had clinical benefit.26 For example, gossypol increases expression of NOXA, most likely owing to endoplasmic reticulum stress. By binding to MCL-1, NOXA displaces BIM from the MCL-1/BIM complex, and then the freed BIM induces apoptosis through BAX activation.27 Other therapeutics, including proteasome inhibitors, may act similarly by activating the endoplasmic reticulum-specific transcription factors ATF3 and ATF4 that regulate NOXA expression.28,29
Determining the dependence on a particular antiapoptotic BCL-2 family protein has become critical for deciding a personalized therapy. The advent of “BH3 profiling” using specific peptides has led the way,30,31 although more recent availability of specific small-molecule inhibitors of BCL-xL (Wehi-539, A-1155463, A-1331852)32,33 and MCL-1 (A-1210477, S63845),34,35 in addition to inhibition of BCL-2 by venetoclax, has facilitated, at least in an ex vivo culture, a rapid determination of the BCL-2 family protein dependence. These tools make it possible to choose the most effective therapeutics to be used based on a functional output, their ability to induce tumor cell death.31 A panel of cell lines has been also engineered to facilitate this analysis by faithfully assessing the efficacy of BH3-mimetic small molecules in preclinical mouse models.36
The development of venetoclax as monochemotherapy
Venetoclax was first tested in relapsed or refractory CLL patients; it induced reduction of lymphocyte counts in a dose-dependent manner without provoking thrombocytopenia.25 The first clinical trial for venetoclax was a phase I dose-escalation study that enrolled 116 patients with relapsed or refractory CLL or small lymphocytic lymphoma, of which 92 (79%) had a response and 20% achieved complete remission (CR), including 5% with minimal residual disease (MRD) negative as assessed by flow cytometry. Objective responses were common among patients with resistance to fludarabine with del17p and unmutated IGHV. Progression-free survival (PFS) estimated for the 400-mg dose groups was 69% (Table 1).37 In the phase II, single-arm, multicenter study of venetoclax conducted exclusively in patients with del (17p) CLL, 107 patients were enrolled. Overall response rate (ORR) determined by an independent review was achieved in 85 (79.4%) patients with a median follow-up of 12.1 months.38 Response rates were similar regardless of whether the patients were refractory to prior fludarabine-based therapy. The clinical responses of CLL patients were also independent of del17p, TP53 mutation, and TP53 function.39
Recently, a phase II, open label, two-arm study reported the outcome of venetoclax monotherapy in 64 CLL patients who relapsed after, or were refractory to, ibrutinib or idelalisib, of whom 43 were on prior ibrutinib (Arm A) and 21 (Arm B) on prior idelalisib. ORR by an independent review for Arm A and Arm B was 70% and 48%, respectively. At the time of analysis, neither the PFS nor the overall survival has been reached. The estimated 12-month PFS was 72%, and overall survival was 90% for the overall group. This study demonstrated that venetoclax had robust activity in CLL patients who progressed during or after treatment with ibrutinib or idelalisib (Table 1).40
Venetoclax as monotherapy was investigated in a phase I study in patients with relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). The ORR varied in the different histologic subgroups, with the highest rates observed in WM (100%, all PR) and MCL (75%, including 21% CR). Responses were less frequent in FL (ORR: 34%, CR: 10%) and DLBCL (ORR: 15%, CR: 9%), and the median duration of response of DLBCL was only 3.3 months (Table 1).41 A pooled population pharmacokinetic analysis in CLL and NHL revealed that the concomitant administration of moderate and strong CYP3A inhibitors and rituximab, as well as food, were the main factors impacting venetoclax pharmacokinetics. Moderate and strong CYP3A inhibitors decreased venetoclax apparent clearance by 19% and 84%, respectively, while concomitant rituximab administration was estimated to increase venetoclax apparent clearance by 21%. Additionally, food increased venetoclax exposures by 3- to 4.2-fold relative to the fasting state. On the basis of these findings, moderate and strong CYP3A inhibitors should be avoided during venetoclax initiation.42 The most severe side effect in the phase I study in CLL patients was tumor lysis syndrome (TLS), with 3 of the 56 patients in the dose-escalation cohort experiencing TLS, with one sudden death. Following the adjustment of a slow ramp-up schedule subsequently, no additional clinical TLS was observed. Other toxicities were mild diarrhea, respiratory tract infection, and neutropenia.37,38 Overall, venetoclax had a manageable safety profile and was overall well tolerated in B-cell lymphoid malignances. Absorption, metabolism, and excretion of venetoclax in humans have recently been well defined.43
Resistance mechanism to venetoclax in B-cell lymphoid malignancies
Even though venetoclax as a single drug achieved a high response rate in CLL patients, CR was relatively low, and patients did progress under venetoclax treatment. In a phase I study in relapsed/refractory CLL, disease progression occurred in 41 patients (35%), including Richter’s transformation in 18 (16%), which was more common among patients with del (17p).37 Therefore, it is important to establish some prognostic index markers that can predict the sensitivity of venetoclax and also explore the ensuing resistance mechanism.
Retrospectively, reviewed data from a clinical trial revealed that fludarabine-refractoriness and a complex karyotype were the dominant risk factors for progression on venetoclax in CLL patients.44 Our previous study showed that the (MCL-1 + Bfl-1)/BCL-2 mRNA ratio predicts the response of CLL to ABT-737, as the ratio of (MCL-1 + Bfl-1)/BCL-2 is lower in the sensitive group as compared with the ABT-737-resistant group.45 The ratio of (MCL-1 + pBCL-2) to BCL-2 expression was also found to provide the most significant predictive marker for the cytotoxic potential of ABT-199 in CLL samples.46 In FL, sensitivity to venetoclax was found to be associated with the BCL-2/BIM ratio.47 The BCL-2/(BCL-XL + MCL-1) mRNA ratio is a strong predictor of sensitivity to venetoclax in MCL.48 Nevertheless, sensitivity to venetoclax correlated with high BCL-2 and low BCL-XL or MCL-1 expression in MM.49
The most likely resistance mechanism to venetoclax has been upregulation of alternative antiapoptotic BCL2 family members, such as MCL-1 and BCL-xL.50 Our previous study showed that acquired resistance could be obtained after chronic exposure to venetoclax in DLBCL cell lines, resulting in substantial AKT activation and upregulation of MCL-1 and BCL-xL levels that sequestered BIM (Figure 1).51 Importantly, genetic suppression of AKT, BCL-xL, or MCL-1 could restore sensitivity to venetoclax. Similarly, targeted agents that impact on MCL-1 expression through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) or mammalian target of rapamycin kinase (mTOR), such as idelalisib10 or NVP-BEZ235, were also effective.51
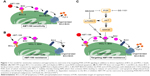  | Figure 1 Our model for venetoclax resistance and approaches to overcome it by targeting PI3K-mTOR signaling in addition to direct regulation of BCL-xL and MCL-1 levels. |
We found that increased BCL-xL expression was inversely correlated with that of miR-377 in ABT-199-resistant DLBCL cell lines and that high BCL-xL/low miR-377 expression conferred resistance to venetoclax in CLL patients.52 Using a hypomethylating agent, 5-azacytidine restored the response by increasing levels of miR-377 and, as a consequence, decreasing levels of BCL-xL. This finding opens up the possibility of extending the use of hypomethylating agents, alone or in combination, as currently explored clinically in myeloid diseases (eg, AML).53,54 This novel epigenetic regulation of BCL-xL may be unique to lymphoid malignancies. In contrast, in solid tumors, its expression is largely determined by gene copy number; BCL-2 and MCL-1 are some of the most highly amplified oncogenes.55
Levels of MCL-1 can be modulated by a large number of therapeutics at the transcriptional, posttranscriptional, or translational level. For example, a recent report revealed that Cyclin E/Cdk2 phosphorylates and stabilizes MCL-1, which in turn reduces cellular sensitivity to BH3-mimetics, including venetoclax.56 Site-specific mutagenesis has shown that specific residues in MCL-1 are responsible for either enhancing stability (Thr92 and Thr163) or BIM binding (Ser64) ability of MCL-1.56 Similarly, in vitro studies showed that BCL-xL plays a critical role in MM cell survival and that high levels of MCL-1 or BCL-xL may also be potential resistance factors to venetoclax treatment.49
Acquired BCL-2 mutation and posttranslational phosphorylation of BCL-2 were also associated with resistance to venetoclax. A missense mutation in the C-terminal transmembrane domain of BAX (G179E), generated after continuous exposure to venetoclax in resistant human lymphoma cells, abrogated BAX anchoring to mitochondria and thus blocked ABT-199-induced apoptosis, both in vitro and in vivo.57 BCL-2 phosphorylation prevented ABT-199 from displacing BAX and BIM from BCL-2, thereby blocking the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis.46
Other mechanisms reported were constitutive intracellular signaling (ie, downstream of BCR) and stroma-mediated treatment resistance due to pro-survival signals from the microenvironment. Stimulation of CLL cells with CD40L resulted in induction of the antiapoptotic proteins BCL-xL, BFL-1, and MCL-1, which in turn conferred reduction in venetoclax-induced apoptosis.58,59 Similarly, by mimicking the microenvironment through CD40 stimulation, ABT-199 sensitivity was compromised through activation of the NF-κB pathway and upregulation of BCL-xL in MCL.48,60 Moreover, the extracellular acid sensing G-protein coupled receptor, GPR65, is expressed in primary CLL cells, where its levels correlate strongly with those of antiapoptotic BCL-2 family members.61
Strategies to overcome resistance to venetoclax: preclinical and clinical data
Based on the resistance mechanisms discussed above, rational combinations of BCL-2 inhibitors with other agents are achieving a better clinical response. Thus, preclinical data suggested that distinct resistant mechanisms to venetoclax could be overcome by monoclonal antibodies, DNA damaging chemotherapy, proteasome inhibitors, BCR signaling inhibitors, such as ibrutinib and idelalisib, and MCL-1 inhibitors. Clinical trials were designed to evaluate the venetoclax as part of combination therapies in different B-cell lymphoid malignancies (Table 2).
In vitro, combination of GA101 or rituximab with ABT-199 demonstrated that CD40-induced resistance to ABT-199 could be counteracted in CLL.58 CD40-induced proliferation and mitochondrial priming loss in MCL can also be overcome by the second-generation anti-CD20 antibody obinutuzumab,60 which blocks induction of BCL-xL by inhibiting the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway. A series of clinical trials have begun to investigate the efficacy of venetoclax plus anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies and chemoimmunotherapy in patients with CLL and lymphoma (Table 2). Recently, a phase I study reported the promising outcome of venetoclax plus rituximab in 49 relapsed/refractory CLL. ORR was 86%, including 51% CR; estimated-2 year PFS and ongoing response were 82% and 89%, respectively. Notably, 80% (20/25) of the patients that were complete responders were MRD-negative in the blood marrow, with 11 of 13 responders remaining in ongoing remission after a median of 9.7 months off venetoclax; another 2 with MRD-positive CR progressed after 24 months off therapy and reattained response after reinitiation of venetoclax. The depth and durability of responses observed in this study offer an attractive potential treatment option for patients with relapsed/refractory CLL.62 Furthermore, interim data from a phase II study reported that venetoclax plus bendamustine and rituximab (BR) had a 68% ORR, including 50% CR in FL. ORR was 33% in the chemo-free group (venetoclax plus rituximab), but for nonrefractory patients in this group, ORR was 64%, with 27% CR.63
One appealing approach to overcome venetoclax resistance is to combine it with a BCR signaling inhibitor, as several laboratory studies provided support for this possibility. Basically, as BCR signaling pathway and BCL-2 overexpression interaction is complex, it is reasonable to suppress both pathways. In primary CLL cells, sustained stimulation of BCR results in significant ABT-199 resistance, dependent at least partly on induction of the antiapoptotic protein MCL-1. Different spleen tyrosine kinase (SYK), BTK, and PI3Kδ inhibitors can overcome the resistance to venetoclax by downregulating MCL-1.59 High-content screening further identified that venetoclax resistance in CLL might be induced by microenvironmental signals, resulting in overexpression of BCL-xl, MCL-1, and BFL-1/A1, which in turn could be counteracted by sunitinib, ibrutinib, and idelalisib.64 Another study showed that among the three BCL-2 family antiapoptotic proteins that were overexpressed in CLL, ibrutinib can decrease the levels of MCL-1 and BCL-xL, while ABT-199 selectively antagonizes BCL-2, suggesting that ibrutinib can synergize with venetoclax in the treatment of CLL.65 The synergistic effect of venetoclax plus ibrutinib was also confirmed in MCL cell lines48,66 and WM, irrespective of CXCR status (wild-type or mutated).67 As ibrutinib is very effective in dislocating CLL cells from the lymph node compartment, this combination may be particularly effective as venetoclax can then induce apoptosis of tumor cells that are released in circulation.
Addition of the dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 or idelalisib to venetoclax was able to overcome resistance in the DLBCL cell lines by reducing MCL-1 levels and leading to release of BIM from MCL-1 and BCL-XL, thus causing apoptosis by BAX activation (Figure 1).51 Another study also showed that BEZ235 could synergize with venetoclax by an alternative mechanism, by inducing the accumulation of BAD and BIM in DLBCL cells.68 In another study, cerdulatinib, a dual SYK/JAK inhibitor, was shown to induce apoptosis of CLL cells following inhibition of the BCR/IL-4 signaling pathways and could thus overcome nurse-like cell or anti-IgM/CD40L + IL-4-mediated protection in CLL primary cells from patients. Combination of cerdulatinib with venetoclax synergized to augment apoptosis in CLL samples induced by IL-4.69 Finally, CC-115, a novel inhibitor of mTOR and DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK), blocked cell proliferation induced by CD40+ interleukin-21 stimulation and reverted CD40-mediated resistance to venetoclax in CLL cell lines and primary CLL cells.70 Clinical trials are in progress to investigate the efficacy of kinase inhibitors plus venetoclax in B-cell lymphoid malignancies (Table 2). Recently, in a phase Ib/2 study of obinutuzmab, ibrutinib, and venetoclax in relapsed/refractory CLL, all six patients available for assessment achieved objective response: five PR, including one MRD-negative in peripheral blood (PB), one MRD-negative in both PB and bone marrow, and one CR with MRD-negative PB and bone marrow.71
With the understanding of the role of MCL-1 in the development of venetoclax resistance, another approach is to downregulate MCL-1 levels. In CLL, a shift toward lower pp38 and higher MCL-1 levels was uniquely found in ABT-737-resistant cells. Hypoxia induces p38 activation, which in turn downregulates MCL-1 expression and increases the sensitivity of CLL toward BH3 mimetics.72 Treatment with gossypol altered the splicing of MCL-1L to MCL-1s,27 which was reported to act as a pro-apoptotic protein. Similarly, the SF3B1 inhibitor spliceostatin A (SSA) altered the splicing of MCL-1L to MCL-1s, which was coincident with induction of apoptosis in CLL cells. Thus, combining spliceostatin A with venetoclax could overcome IL-4 and CD40L-induced pro-survival effect.73 In our previous study, we used the CDK inhibitor dinaciclib at low concentrations (which do not impact on its transcriptional control by CDK9 through DNA Pol II) to inhibit posttranslational regulation of MCL-1. Preventing CDK2/Cyclin E-mediated MCL-1 phosphorylation led to the release of BIM from MCL-1 and apoptosis in ABT-737-resistant cells. Dinaciclib in combination with ABT-199 resulted in robust synergistic cell death in DLBCL cell lines and primary CLL patient samples.56 Higher concentrations of dinaciclib (as those of flavoppridol [alvocibib] used earlier, but which have more severe unwanted side effects) decrease MCL-1 mRNA levels by blocking CDK9-mediated Pol II transcription.74,75 Thus, inhibition of MCL-1 by dinaciclib amplified apoptosis induced by venetoclax in DLBCL; potent antitumor activities of these combinations also were observed in xenografts and in a genetic murine model of Myc-BCL-2 double-hit lymphoma.76 Another study also showed that concurrent inhibition of BCL-2 and MCL-1 with ABT-199 and homoharringtonine, a plant alkaloid, could induce significant synthetic lethality in most BCL-2-expressing DLBCL cell lines.77 MCL-1 is widely and highly expressed in MM, and it is also an attractive therapeutic target.78 Recently, a novel MCL-1 inhibitor S63845 was reported to be tolerable and effective in diverse cancer models,35 making it possible to overcome venetoclax resistance in various types of B-cell lymphoid malignancies.
Several studies applied different drugs to increase the sensitivity of venetoclax. For example, co-treatment of human MM cell lines and primary patient samples with dexamethasone and venetoclax significantly increased cell death over venetoclax alone. Addition of dexamethasone increased the expression of both BCL-2 and BIM, resulting in increased sensitivity to venetoclax.79 Combination of venetoclax with acadesine, a nucleoside analog, could also achieve higher apoptosis in MCL.80 Combination of venetoclax with doxorubicin or cytarabine, bortezomib, and JQ1 produced synergistic cell kill against the double-hit lymphoma cell lines cultured in vitro.81 In vitro and in vivo results also supported that radiotherapy could synergize with venetoclax for treatment of DLBCL and MCL.82 All the above studies provide evidence for the feasibility of future combination therapy options.
Conclusion
Venetoclax has already provided promising results as monotherapy for treatment of relapsed/refractory CLL with del (17p). Unlike the other recently approved targeted agents idelalisib and ibrutinib, so far there has been no relapse reported in some patients.38 Also, unlike the other targeted agents, it is effective against tumor cells that reside in the blood marrow.37,65 However, the CR rate is still relatively low, and patients do progress under venetoclax treatment or may even be refractory. Moreover, the outcome of venetoclax as a single drug in FL and DLBCL so far has not been so satisfactory. With emerging knowledge of venetoclax resistance mechanisms, future studies should continue to define biomarkers that could predict the response of venetoclax in different B-cell malignancies. Moreover, the promising preclinical data from combination of BCL-2 inhibitors with other novel agents, such as MCL-1 inhibitors and ibrutinib, provide therapeutic benefit, which can be translated into early phase clinical trials. Results from the clinical application of venetoclax as monotherapy in a subset of patients for personalized therapy and more broadly in combination with first-line approved agents for treatment of B-cell lymphoid malignances are expected. Based on the experience with lymphoid malignancies, as has historically been seen with other novel FDA-approved therapeutics, the use of venetoclax will certainly see broader clinical applications in other liquid and solid tumors.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NCI) grant CA184137 to Alexandru Almasan and the National Natural Science Foundation-Youth Foundation from China (No 81400119) to Huayuan Zhu.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Hotchkiss RS, Strasser A, McDunn JE, Swanson PE. Cell death. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(16):1570–1583. | ||
Tsujimoto Y, Cossman J, Jaffe E, Croce CM. Involvement of the bcl-2 gene in human follicular lymphoma. Science. 1985;228(4706):1440–1443. | ||
Adams JM, Cory S. The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science. 1998;281(5381):1322–1326. | ||
Chen L, Willis SN, Wei A, et al. Differential targeting of prosurvival Bcl-2 proteins by their BH3-only ligands allows complementary apoptotic function. Mol Cell. 2005;17(3):393–403. | ||
Willis SN, Chen L, Dewson G, et al. Proapoptotic Bak is sequestered by Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL, but not Bcl-2, until displaced by BH3-only proteins. Genes Dev. 2005;19(11):1294–1305. | ||
Jain N, O’Brien S. Initial treatment of CLL: integrating biology and functional status. Blood. 2015;126(4):463–470. | ||
Maffei R, Fiorcari S, Martinelli S, Potenza L, Luppi M, Marasca R. Targeting neoplastic B cells and harnessing microenvironment: the “double face” of ibrutinib and idelalisib. J Hematol Oncol. 2015;8:60. | ||
Burger JA, Tedeschi A, Barr PM, et al. Ibrutinib as initial therapy for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(25):2425–2437. | ||
Furman RR, Sharman JP, Coutre SE, et al. Idelalisib and rituximab in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(11):997–1007. | ||
Madanat YF, Smith MR, Almasan A, Hill BT. Idelalisib therapy of indolent B-cell malignancies: chronic lymphocytic leukemia and small lymphocytic or follicular lymphomas. Blood Lymphat Cancer. 2016;6:1–6. | ||
Rai KR. Therapeutic potential of new B cell-targeted agents in the treatment of elderly and unfit patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Hematol Oncol. 2015;8:85. | ||
Wu J, Liu C, Tsui ST, Liu D. Second-generation inhibitors of Bruton tyrosine kinase. J Hematol Oncol. 2016;9(1):80. | ||
Reed JC. Bcl-2-family proteins and hematologic malignancies: history and future prospects. Blood. 2008;111(7):3322–3330. | ||
Cang S, Iragavarapu C, Savooji J, Song Y, Liu D. ABT-199 (venetoclax) and BCL-2 inhibitors in clinical development. J Hematol Oncol. 2015;8:129. | ||
Hanada M, Delia D, Aiello A, Stadtmauer E, Reed JC. bcl-2 gene hypomethylation and high-level expression in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1993;82(6):1820–1828. | ||
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, et al. miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(39):13944–13949. | ||
Friedberg JW. Using the pathology report in initial treatment decisions for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: time for a precision medicine approach. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2015;2015:618–624. | ||
Touzeau C, Dousset C, Bodet L, et al. ABT-737 induces apoptosis in mantle cell lymphoma cells with a Bcl-2high/Mcl-1low profile and synergizes with other antineoplastic agents. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(18):5973–5981. | ||
Touzeau C, Dousset C, Le Gouill S, et al. The Bcl-2 specific BH3 mimetic ABT-199: a promising targeted therapy for t(11;14) multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 2014;28(1):210–212. | ||
Oltersdorf T, Elmore SW, Shoemaker AR, et al. An inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins induces regression of solid tumours. Nature. 2005;435(7042):677–681. | ||
Tse C, Shoemaker AR, Adickes J, et al. ABT-263: a potent and orally bioavailable Bcl-2 family inhibitor. Cancer Res. 2008;68(9):3421–3428. | ||
Wilson WH, O’Connor OA, Czuczman MS, et al. Navitoclax, a targeted high-affinity inhibitor of BCL-2, in lymphoid malignancies: a phase 1 dose-escalation study of safety, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and antitumour activity. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11(12):1149–1159. | ||
Roberts AW, Seymour JF, Brown JR, et al. Substantial susceptibility of chronic lymphocytic leukemia to BCL2 inhibition: results of a phase I study of navitoclax in patients with relapsed or refractory disease. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(5):488–496. | ||
Zhang H, Nimmer PM, Tahir SK, et al. Bcl-2 family proteins are essential for platelet survival. Cell Death Differ. 2007;14(5):943–951. | ||
Souers AJ, Leverson JD, Boghaert ER, et al. ABT-199, a potent and selective BCL-2 inhibitor, achieves antitumor activity while sparing platelets. Nat Med. 2013;19(2):202–208. | ||
R Sonderquist R, Eastman A. BCL2 Inhibitors as anticancer drugs: a plethora of misleading BH3 mimetics. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016;15(9):2011–2017. | ||
Mazumder S, Choudhary GS, Al-Harbi S, Almasan A. Mcl-1 phosphorylation defines ABT-737 resistance that can be overcome by increased NOXA expression in leukemic B cells. Cancer Res. 2012;72(12):3069–3079. | ||
Wang Q, Mora-Jensen H, Weniger MA, et al. ERAD inhibitors integrate ER stress with an epigenetic mechanism to activate BH3-only protein NOXA in cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(7):2200–2205. | ||
Albershardt TC, Salerni BL, Soderquist RS, et al. Multiple BH3 mimetics antagonize antiapoptotic MCL1 protein by inducing the endoplasmic reticulum stress response and up-regulating BH3-only protein NOXA. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(28):24882–24895. | ||
Certo M, Del Gaizo Moore V, Nishino M, et al. Mitochondria primed by death signals determine cellular addiction to antiapoptotic BCL-2 family members. Cancer Cell. 2006;9(5):351–365. | ||
Touzeau C, Ryan J, Guerriero J, et al. BH3 profiling identifies heterogeneous dependency on Bcl-2 family members in multiple myeloma and predicts sensitivity to BH3 mimetics. Leukemia. 2016;30(3):761–764. | ||
Lessene G, Czabotar PE, Sleebs BE, et al. Structure-guided design of a selective BCL-X(L) inhibitor. Nat Chem Biol. 2013;9(6):390–397. | ||
Leverson JD, Phillips DC, Mitten MJ, et al. Exploiting selective BCL-2 family inhibitors to dissect cell survival dependencies and define improved strategies for cancer therapy. Sci Transl Med. 2015;7(279):279ra240. | ||
Bruncko M, Wang L, Sheppard GS, et al. Structure-guided design of a series of MCL-1 inhibitors with high affinity and selectivity. J Med Chem. 2015;58(5):2180–2194. | ||
Kotschy A, Szlavik Z, Murray J, et al. The MCL1 inhibitor S63845 is tolerable and effective in diverse cancer models. Nature. 2016;538(7626):477–482. | ||
Koss B, Ryan J, Budhraja A, et al. Defining specificity and on-target activity of BH3-mimetics using engineered B-ALL cell lines. Oncotarget. 2016;7(10):11500–11511. | ||
Roberts AW, Davids MS, Pagel JM, et al. Targeting BCL2 with venetoclax in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(4):311–322. | ||
Stilgenbauer S, Eichhorst B, Schetelig J, et al. Venetoclax in relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia with 17p deletion: a multicentre, open-label, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(6):768–778. | ||
Anderson MA, Deng J, Seymour JF, et al. The BCL2 selective inhibitor venetoclax induces rapid onset apoptosis of CLL cells in patients via a TP53-independent mechanism. Blood. 2016;127(25):3215–3224. | ||
Jones J, Choi MY, Mato AR, et al. Venetoclax (VEN) monotherapy for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who relapsed after or were refractory to ibrutinib or idelalisib. Blood. 2016;128(22):637. | ||
Gerecitano JF, Roberts AW, Seymour JF, et al. A Phase 1 Study of Venetoclax (ABT-199/GDC-0199) Monotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood. 2015;126(23):254. | ||
Jones AK, Freise KJ, Agarwal SK, Humerickhouse RA, Wong SL, Salem AH. Clinical predictors of venetoclax pharmacokinetics in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma patients: a pooled population pharmacokinetic analysis. AAPS J. 2016;18(5):1192–1202. | ||
Liu H, Michmerhuizen MJ, Lao Y, et al. Absorption, metabolism, and excretion of a Novel Bcl-2 Inhibitor venetoclax in humans. Drug Metab Dispos. 2016;45(3):294–305. | ||
Lew TE, Anderson MA, Tam CS, et al. Clinicopathological features and outcomes of progression for chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) treated with the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax. Blood. 2016;128(22):3223. | ||
Al-Harbi S, Hill BT, Mazumder S, et al. An antiapoptotic BCL-2 family expression index predicts the response of chronic lymphocytic leukemia to ABT-737. Blood. 2011;118(13):3579–3590. | ||
Song T, Chai G, Liu Y, Yu X, Wang Z, Zhang Z. Bcl-2 phosphorylation confers resistance on chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells to the BH3 mimetics ABT-737, ABT-263 and ABT-199 by impeding direct binding. Br J Pharmacol. 2016;173(3):471–483. | ||
Bodo J, Zhao X, Durkin L, et al. Acquired resistance to venetoclax (ABT-199) in t(14;18) positive lymphoma cells. Oncotarget. 2016;7(43):70000–70010. | ||
Chiron D, Dousset C, Brosseau C, et al. Biological rational for sequential targeting of Bruton tyrosine kinase and Bcl-2 to overcome CD40-induced ABT-199 resistance in mantle cell lymphoma. Oncotarget. 2015;6(11):8750–8759. | ||
Punnoose EA, Leverson JD, Peale F, et al. Expression profile of BCL-2, BCL-XL, and MCL-1 predicts pharmacological response to the BCL-2 selective antagonist venetoclax in multiple myeloma models. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016;15(5):1132–1144. | ||
Youle RJ, Strasser A. The BCL-2 protein family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9(1):47–59. | ||
Choudhary GS, Al-Harbi S, Mazumder S, et al. MCL-1 and BCL-xL-dependent resistance to the BCL-2 inhibitor ABT-199 can be overcome by preventing PI3K/AKT/mTOR activation in lymphoid malignancies. Cell Death Dis. 2015;6:e1593. | ||
Al-Harbi S, Choudhary GS, Ebron JS, et al. miR-377-dependent BCL-xL regulation drives chemotherapeutic resistance in B-cell lymphoid malignancies. Mol Cancer. 2015;14:185. | ||
Negrotto S, Ng KP, Jankowska AM, et al. CpG methylation patterns and decitabine treatment response in acute myeloid leukemia cells and normal hematopoietic precursors. Leukemia. 2012;26(2):244–254. | ||
Saunthararajah Y, Sekeres M, Advani A, et al. Evaluation of noncytotoxic DNMT1-depleting therapy in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Invest. 2015;125(3):1043–1055. | ||
Beroukhim R, Mermel CH, Porter D, et al. The landscape of somatic copy-number alteration across human cancers. Nature. 2010;463(7283):899–905. | ||
Choudhary GS, Tat TT, Misra S, et al. Cyclin E/Cdk2-dependent phosphorylation of Mcl-1 determines its stability and cellular sensitivity to BH3 mimetics. Oncotarget. 2015;6(19):16912–16925. | ||
Fresquet V, Rieger M, Carolis C, Garcia-Barchino MJ, Martinez-Climent JA. Acquired mutations in BCL2 family proteins conferring resistance to the BH3 mimetic ABT-199 in lymphoma. Blood. 2014;123(26):4111–4119. | ||
Thijssen R, Slinger E, Weller K, et al. Resistance to ABT-199 induced by microenvironmental signals in chronic lymphocytic leukemia can be counteracted by CD20 antibodies or kinase inhibitors. Haematologica. 2015;100(8):e302–e306. | ||
Bojarczuk K, Sasi BK, Gobessi S, et al. BCR signaling inhibitors differ in their ability to overcome Mcl-1-mediated resistance of CLL B cells to ABT-199. Blood. 2016;127(25):3192–3201. | ||
Chiron D, Bellanger C, Papin A, et al. Rational targeted therapies to overcome microenvironment-dependent expansion of mantle cell lymphoma. Blood. 2016;128(24):2808–2818. | ||
Rosko AE, McColl KS, Zhong F, et al. Acidosis sensing receptor GPR65 correlates with anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family member expression in CLL cells: potential implications for the CLL microenvironment. J Leuk (Los Angel). 2014;2(5):pii: 160. | ||
Seymour JF, Ma S, Brander DM, et al. Venetoclax plus rituximab in relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a phase 1b study. Lancet Oncol. Epub 2017 Jan 12. | ||
Zinzani PL, Topp MS, Yuen SL, et al. Phase 2 study of venetoclax plus rituximab or randomized ven plus bendamustine + rituximab (BR) versus BR in patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma: interim data. Blood. 2016;128(22):617. | ||
Oppermann S, Ylanko J, Shi Y, et al. High-content screening identifies kinase inhibitors that overcome venetoclax resistance in activated CLL cells. Blood. 2016;128(7):934–947. | ||
Cervantes-Gomez F, Lamothe B, Woyach JA, et al. Pharmacological and protein profiling suggests venetoclax (ABT-199) as optimal partner with ibrutinib in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21(16):3705–3715. | ||
Zhao X, Bodo J, Sun D, et al. Combination of ibrutinib with ABT-199: synergistic effects on proliferation inhibition and apoptosis in mantle cell lymphoma cells through perturbation of BTK, AKT and BCL2 pathways. Br J Haematol. 2015;168(5):765–768. | ||
Cao Y, Yang G, Hunter ZR, et al. The BCL2 antagonist ABT-199 triggers apoptosis, and augments ibrutinib and idelalisib mediated cytotoxicity in CXCR4 wild-type and CXCR4 WHIM mutated Waldenstrom macroglobulinaemia cells. Br J Haematol. 2015;170(1):134–138. | ||
Lee JS, Tang SS, Ortiz V, Vo TT, Fruman DA. MCL-1-independent mechanisms of synergy between dual PI3K/mTOR and BCL-2 inhibition in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Oncotarget. 2015;6(34):35202–35217. | ||
Blunt MD, Koehrer S, Dobson R, et al. The dual Syk/JAK inhibitor cerdulatinib antagonises B-cell receptor and microenvironmental signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. Epub 2016 Oct 3. | ||
Thijssen R, Ter Burg J, Garrick B, et al. Dual TORK/DNA-PK inhibition blocks critical signaling pathways in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2016;128(4):574–583. | ||
Jones JA, Woyach J, Awan FT, et al. Phase 1b results of a phase 1b/2 study of obinutuzmab, ibrutinib, and venetoclax in relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Blood. 2016;128(22):639. | ||
Huelsemann MF, Patz M, Beckmann L, et al. Hypoxia-induced p38 MAPK activation reduces Mcl-1 expression and facilitates sensitivity towards BH3 mimetics in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 2015;29(4):981–984. | ||
Larrayoz M, Blakemore SJ, Dobson RC, et al. The SF3B1 inhibitor spliceostatin A (SSA) elicits apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells through downregulation of Mcl-1. Leukemia. 2016;30(2):351–360. | ||
Flynn J, Jones J, Johnson AJ, et al. Dinaciclib is a novel cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor with significant clinical activity in relapsed and refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 2015;29(7):1524–1529. | ||
Blachly JS, Byrd JC, Grever M. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Semin Oncol. 2016;43(2):265–273. | ||
Li L, Pongtornpipat P, Tiutan T, et al. Synergistic induction of apoptosis in high-risk DLBCL by BCL2 inhibition with ABT-199 combined with pharmacologic loss of MCL1. Leukemia. 2015;29(8):1702–1712. | ||
Klanova M, Andera L, Brazina J, et al. Targeting of BCL2 Family Proteins with ABT-199 and Homoharringtonine Reveals BCL2- and MCL1-Dependent Subgroups of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22(5):1138–1149. | ||
Gong JN, Khong T, Segal D, et al. Hierarchy for targeting pro-survival BCL2 family proteins in multiple myeloma: pivotal role of MCL1. Blood. Epub 2016 Jul 27. | ||
Matulis SM, Gupta VA, Nooka AK, et al. Dexamethasone treatment promotes Bcl-2 dependence in multiple myeloma resulting in sensitivity to venetoclax. Leukemia. 2016;30(5):1086–1093. | ||
Montraveta A, Xargay-Torrent S, Rosich L, et al. Bcl-2high mantle cell lymphoma cells are sensitized to acadesine with ABT-199. Oncotarget. 2015;6(25):21159–21172. | ||
Johnson-Farley N, Veliz J, Bhagavathi S, Bertino JR. ABT-199, a BH3 mimetic that specifically targets Bcl-2, enhances the antitumor activity of chemotherapy, bortezomib and JQ1 in “double hit” lymphoma cells. Leuk Lymphoma. 2015;56(7):2146–2152. | ||
O’Steen S, Waltman A, Booth G, Kenoyer AL, Nartea M. Venetoclax synergizes with radiation therapy for treatment of B-cell lymphomas. Blood. 2016;128(22):467. |
 © 2017 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2017 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.


