Back to Journals » Drug Design, Development and Therapy » Volume 10
Design and characteristics of cytotoxic fibroblast growth factor 1 conjugate for fibroblast growth factor receptor-targeted cancer therapy
Authors Szlachcic A, Zakrzewska M, Lobocki M , Jakimowicz P, Otlewski J
Received 5 February 2016
Accepted for publication 31 March 2016
Published 9 August 2016 Volume 2016:10 Pages 2547—2560
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S105896
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Wei Duan
Anna Szlachcic, Malgorzata Zakrzewska, Michal Lobocki, Piotr Jakimowicz, Jacek Otlewski
Department of Protein Engineering, Faculty of Biotechnology, University of Wroclaw, Wroclaw, Poland
Abstract: Fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs) are attractive candidate cancer therapy targets as they are overexpressed in multiple types of tumors, such as breast, prostate, bladder, and lung cancer. In this study, a natural ligand of FGFR, an engineered variant of fibroblast growth factor 1 (FGF1V), was conjugated to a potent cytotoxic drug, monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE), and used as a targeting agent for cancer cells overexpressing FGFRs, similar to antibodies in antibody–drug conjugates. The FGF1V–valine–citrulline–MMAE conjugate showed a favorable stability profile, bound FGFRs on the cell surface specifically, and efficiently released the drug (MMAE) upon cleavage by the lysosomal protease cathepsin B. Importantly, the conjugate showed a prominent cytotoxic effect toward cell lines expressing FGFR. FGF1V–vcMMAE was highly cytotoxic at concentrations even an order of magnitude lower than those found for free MMAE. This effect was FGFR-specific as cells lacking FGFR did not show any increased mortality.
Keywords: fibroblast growth factor 1, FGF receptor, targeted cancer therapy, cytotoxic conjugates, FGFR-dependent cancer, MMAE, auristatin
Introduction
Targeted therapy is currently the most promising strategy in cancer treatment owing to its high specificity and minimal side effects. In this approach, malignant cells are distinguished from normal tissue by application of a targeting agent which recognizes precisely and selectively cell surface components that are upregulated only in the tumor cells. Antibodies are most frequently used to recognize specific macromolecules on cancer cells and deliver directly a potent cytotoxic drug attached covalently.1–4 Recent laboratory studies and clinical trials have demonstrated that such antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs) can be considered the next generation of targeted therapy, with two of them already approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for clinical use and 38 in different phases of clinical trials.5,6
While the main advantage of antibodies is their high specificity in recognizing cell surface markers, other molecules, such as natural ligands of upregulated receptors, exhibit a similar feature and could be considered as an alternative vehicle for directing anticancer drugs. For example, all four fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs) have been reported to be overexpressed in numerous human tumors, such as breast, lung, thyroid, and gastric cancers.7–12 Their natural ligands are 18 species of secreted fibroblast growth factors that bind to individual receptors with different affinities.
Among the fibroblast growth factors, only fibroblast growth factor 1 (FGF1) exhibits high affinity for all four receptors.13 Thus, it seems an attractive delivery molecule for specific targeting of FGFR-expressing cells and should be an effective targeting agent against diverse tumor types. Notably, FGF1 is efficiently internalized by cells in a receptor-dependent manner,14–16 which ensures effective drug delivery across the cell membrane. As FGF1 binding activates FGFRs and initiates downstream signaling pathways leading to cell proliferation, it should thereby sensitize cells to the action of an antiproliferative drug delivered with it.
Here, we present a strategy for destroying cancer cells overexpressing FGFRs by using an engineered variant of FGF1 fused with a highly cytotoxic agent, monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE). Our results show that the cytotoxic effect of auristatin E fused to the growth factor prevails over the FGF1 mitogenic activity, while FGF1 ensures highly selective delivery to FGFR-expressing cells only, leading to an excellent targeted toxicity of the growth factor conjugate.
Experimental procedures
Recombinant FGF1V expression and purification
The FGF1 variant described earlier designed for efficient chemical conjugation (FGF1V) was expressed and purified as described before.17 FGF1V is a truncated human FGF1 (residues 21–154) with three point mutations increasing its stability (Q40P, S47I, H93G) and an N-terminal four-amino-acid linker (CGGG).
FGF1V–vcMMAE conjugate preparation
FGF1V solution (30 μM) in 25 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, and 100 mM NaCl was reduced with 1 mM TCEP for 20 minutes at room temperature, desalted with a Zeba spin column (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), and added to a CH3CN solution of linker-functionalized MMAE (vcMMAE) containing a maleimide moiety, and the conjugation was carried out at 4°C. There was a two- to fivefold molar excess of the drug over the FGF1V N-terminal –SH group. The reaction was quenched after 16 hours with an excess of free cysteine. Different reaction conditions and durations were tested in order to achieve optimum conjugation efficiency with protein structure and function retained. Reaction progress was monitored by SDS-PAGE and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS).
To purify the conjugate, unmodified FGF1V was removed by hydrophobic interaction chromatography on phenyl-Sepharose (GE Healthcare, Chicago, IL, USA). The conjugation reaction mixture was loaded on a phenyl-Sepharose column equilibrated in 25 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, and 2 M NaCl, and FGF1V–vcMMAE was eluted with a linear gradient of decreasing salt concentration (from 0% to 100% of 25 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 0.1 M NaCl). Identity and purity of conjugated FGF1V–vcMMAE were confirmed by SDS-PAGE, Western blotting, and MALDI-TOF MS.
Proteolytic digestion of FGF1V–vcMMAE conjugate
Recombinant cathepsin B was purchased from Sino Biological (Beijing, People’s Republic of China). Digestion was carried out at 37°C, pH 5.2, and 1:200 protease-to-FGF1 ratio. Reaction products were separated by SDS-PAGE and visualized by Instant Blue staining.
Mass spectrometry
Single and multiple FGF1V modifications with vcMMAE were detected by MALDI-TOF MS using an Applied Biosystems AB 4800+ spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), with α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid as a matrix.
Biophysical characterization of FGF1V–vcMMAE conjugate
To determine the folded state of conjugated FGF1V, tryptophan fluorescence spectra were acquired using an FP-750 spectrofluorimeter (Jasco, Easton, MD, USA) with excitation at 280 nm and emission in the 300–450 nm range, at a protein concentration of 2×10−6 M in 25 mM sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7.3.
Thermal denaturation of FGF1V–vcMMAE conjugate was monitored by ellipticity changes at 227 nm using a Jasco J715 spectropolarimeter equipped with a Peltier cell holder. The denaturation measurements were performed in 25 mM sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7.3, with 0.7 M GdmCl and at a protein concentration of 2×10−6 M. The temperature increase rate was 0.25°C/minute. Thermodynamic data were analyzed using PeakFit software (Systat Sotfware, San Jose, CA, USA), assuming a two-state reversible equilibrium transition.
Cell culture
BJ cells (human fibroblasts, ATCC #CRL-2522) were grown in Quantum 333 medium (GE Healthcare), and NIH 3T3 cells (murine embryonic fibroblasts, ATCC #CRL-1658) were grown in Quantum 333 medium supplemented with 2% bovine serum (Thermo Fisher Scientific). MDA-MB-134-VI cells (human mammary gland ductal carcinoma, ATCC #HTB-23) were grown in L15 medium (Sigma-Aldrich Co., St Louis, MO, USA) with 20% fetal bovine serum (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and U2OS cells (human osteosarcoma, ATCC #HTB-96) in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific) containing 10% fetal bovine serum. All media were supplemented with 1% penicillin/streptomycin mix (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Cells were seeded into tissue culture plates the day preceding the start of experiments. BJ, NIH 3T3, and U2OS cells were cultured at 37°C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere, and MDA-MB-134-VI cells at 37°C in the absence of CO2. U2OS cells stably transfected with FGFR1 (U2OS FGFR1) were a kind gift of Dr Ellen M. Haugsten (Norwegian Radium Hospital, Oslo, Norway).
Cell viability assays
Cells grown on 96-well culture plates (5,000 cells/well) were treated in the presence of heparin (10 U/mL) with FGF1V, FGF1V–vcMMAE, or vcMMAE alone. After 24, 48, 72, or 96 hours of incubation, alamarBlue (Thermo Fisher Scientific) was added (1/10 of culture volume) and after 4 hours, formation of a fluorescent reduced form of the dye was measured on a Spectra Max Gemini XS (Molecular Devices LLC, Sunnyvale, CA, USA) fluorescence plate reader.
Activation of FGF1 signaling pathways
Serum-starved NIH 3T3 cells were stimulated for 15 minutes with 1, 10, or 100 ng/mL FGF1V or FGF1V–vcMMAE in the presence of heparin (10 U/mL). The cells were then washed with PBS, lysed with SDS sample buffer, and sonicated. Total cell lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE separation and Western blot analysis with anti-phospho-Erk1,2 kinase antibody (Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA), anti-phospho-FGFR antibody (Cell Signaling Technology), and anti-γ-tubulin antibody (Sigma-Aldrich) as a loading control. Horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies and a chemiluminescent substrate (Thermo Fisher Scientific) were used for visualization in a ChemiDoc station (Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc., Hercules, CA, USA). The intensities of detected bands were quantified based on Western blot densitometry, performed by ImageLab software (Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc.).
FGFR1 expression levels
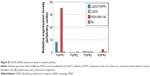
Cell lysates of BJ, MDA-MB-134-VI, U2OS, and U2OS FGFR1 were separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blot with anti-FGFR1 antibodies (Santa Cruz Biotechnology Biotechnology Inc., Dallas, TX, USA) and anti-γ-tubulin antibody (Sigma-Aldrich) as a loading control.
Annexin V staining and FACS analysis
MDA-MB-134-VI and U2OS R1 cells were stained with annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit (APOAF, Sigma-Aldrich) and analyzed on FACSCalibur flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA), in duplicates. Data analysis was performed with WinMDI 2.8 software (freeware by Joseph Trotter).
Quantitative real time PCR
Total RNA from each cell line was extracted using the Universal RNA Purification kit (EurX) and purified RNA was digested with DNase (Thermo Fisher Scientific) to remove any traces of genomic DNA contamination. RNA integrity was assessed using RNA 6000 Nano chip and Agilent 2100 BioAnalyzer and subjected to reverse transcription using RevertAid™ Premium cDNA Synthesis Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Oligo (dT)18 primer and random hexamer primer were used for first-strand cDNA synthesis. Gene-specific primer pairs for quantitative PCR were obtained from Real Time Primers LLC (Elkins Park, PA, USA). Quantitative real-time PCR was performed using Agilent Mx3005P QPCR System with Brilliant III SYBR Green Master mix (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Levels of target genes were normalized to HPRT1 gene. Experiments were carried out in duplicate for each experimental condition. Data were analyzed with Stratagene MX Pro software (Agilent Technologies).
Results
Design of the FGF1V–vcMMAE conjugate
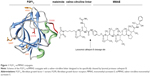
To test whether FGF1 can be effectively used as a targeting factor alternatively to the commonly applied antibodies, we conjugated a potent cytotoxic drug, MMAE, to a modified FGF1 molecule. As wild-type FGF1 suffers from relatively poor stability, is susceptible to protease degradation, and exhibits rather unfavorable pharmacological properties, we used the engineered human FGF1 multiple mutant (FGF1V) described earlier.17 FGF1V is a truncated human FGF1 devoid of 21 N-terminal residues and containing three point mutations (Q40P, S47I, and H93G) increasing its stability by ~20°C in terms of the denaturation temperature.18 In addition, FGF1V contains the C117S substitution eliminating a solvent-exposed cysteine (detailed below),19 and a four-amino acid linker at the N-terminus containing a free thiol group for conjugation (CGGG). This variant gives us the advantage of superior stability of the targeting protein coupled with the presence of a single solvent-accessible thiol group at the N-terminus allowing site-specific chemical conjugation (Figure 1).
The cytotoxic payload of our choice was a highly potent analog of auristatin (MMAE), a tubulin polymerization inhibitor. MMAE has been successfully used in many ADC approaches, with one (brentuximab vedotin, Adcetris®) already approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for clinical use.20 MMAE is a classical example of a cytotoxic drug so strong that it can only be used coupled to a targeting agent, with general side effects too severe to permit its administration as a classical single-agent chemotherapeutic.21–23 As in the case of brentuximab vedotin, in our study, specific release of the cytotoxic drug is additionally ensured by the presence of a cleavable dipeptide (valine–citrulline) linker between the targeting agent and the drug (Figure 1). The linker is designed to be stable in the plasma and only cleaved upon internalization of the ADC into the cell, thereby specifically releasing the drug inside tumor cells rather than into the circulation.24,25 The valine–citrulline–MMAE moiety is abbreviated henceforth as vcMMAE.
FGF1V–vcMMAE conjugation
We optimized the FGF1V–vcMMAE conjugation reaction toward a site-specific modification of the N-terminal cysteine to avoid undesired modification of the two remaining buried cysteines, which could lead to protein unfolding and a loss of receptor binding activity.
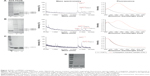
Among the initially tested conjugation conditions adapted from available ADC preparation protocols,25–27 none yielded a singly modified FGF1V. To evaluate the level of modification, number of vcMMAE molecules attached, and folded state of the protein, we applied electrophoretic separation, mass spectrometry, and fluorescence measurements, respectively (Figure 2). Tryptophan fluorescence is an elegant tool to monitor the FGF1V folded state, as its single tryptophan residue (Trp107) is quenched in the native protein, and upon unfolding its fluorescence increases strongly.28 According to these evaluations, most conjugation reactions yielded a mixture of singly, doubly, and triply coupled FGF1V (Figure 2A and B), which were difficult to separate from each other and showed spectral characteristics of a misfolded protein.
As heparin and heparan sulfates show protective effects for FGF1, we tested whether heparin use could help in developing successful conjugation conditions. The heparin binding site in FGF1 is distant from the N-terminal cysteine; thus, there should be no steric hindrance caused by vcMMAE attachment. Indeed, in the presence of heparin, singly modified FGF1 was obtained without any modification of the two buried cysteines (Figure 2C). Unfortunately, the reaction yield remained low even after several optimization attempts. Only ~15% of the protein could be modified with vcMMAE. We decided not to use the native-exposed Cys117 residue of FGF1 for vcMMAE conjugation, as it is not efficiently modified with auristatin E at low temperature (4°C) and we observed protein unfolding upon the reaction with vcMMAE at room temperature (Figure 2D).
We tested diverse chromatographic approaches to separate FGF1V–vcMMAE from unmodified FGF1V. As the molecular weights of FGF1V and FGF1V–vcMMAE differ by only 1.3 kDa (15.5 and 16.8 kDa), their separation with size exclusion chromatography is virtually impossible. Similarly, we failed to remove unmodified FGF1 using thiol-Sepharose, taking advantage of the free cysteine in the nonconjugated protein. However, we succeeded in separating unmodified FGF1 using hydrophobic interaction chromatography on phenyl-Sepharose, taking advantage of the higher hydrophobicity of the vcMMAE-containing protein. The obtained FGF1V–vcMMAE conjugate preparation was more than 95% pure and virtually free from unconjugated FGF1V.
Characterization of FGF1V–vcMMAE conjugate
To evaluate whether the attachment of vcMMAE to the N-terminus of FGF1V had any influence on the protein tertiary structure or stability, we obtained fluorescence spectra of purified FGF1V–vcMMAE. Due to the fact that the intrinsic vcMMAE fluorescence in the 300–450 nm range (with excitation at 280 nm) is negligible, the protein fluorescence in this range can be measured. FGF1V modified with one vcMMAE molecule remained folded, whereas attachment of two or three vcMMAE molecules led to protein unfolding, as evidenced by increased Trp107 fluorescence (Figure 2), suggesting that the internal cysteines could also be modified bringing about the unfolding.
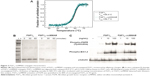
Similarly, we assessed whether the stability of FGF1V was affected by the conjugation. Thermal denaturation of the FGF1V–vcMMAE conjugate was monitored by circular dichroism (Figure 3A). The denaturation temperature of the conjugate was similar to that of FGF1V, 58.7°C compared to 59.4°C, respectively. The denaturation temperature for FGF1V estimated previously based on tryptophan fluorescence changes (60.9°C)17 was also similar to the one obtained in this study. Clearly, conjugation of vcMMAE with the introduced N-terminal cysteine in FGF1V does not impair proper protein folding, and the conjugate’s high stability enables its use in cell culture and in vivo assays.
The valine–citrulline linker used in this study was designed to be specifically cleaved by cathepsin B upon conjugate internalization into the lysosomal compartment.25 To check whether the linker behaves as expected, we subjected FGF1V–vcMMAE to proteolytic cleavage with cathepsin B in vitro, which confirmed that the linker is cleaved efficiently (Figure 3B). It can be noted that the minuscule molecular weight shift upon the valine–citrulline linker cleavage and vcMMAE removal could be detected by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). vcMMAE was released from the conjugate with a specific activity of cathepsin B ~430 nmol/min/mg, similar to the antibody conjugates with the valine–citrulline linker, suggesting that the drug release after internalization would be effective enough.25 Unconjugated FGF1V was not digested by cathepsin B within the time span studied (Figure 3B).
Finally, we evaluated the biological activity of the FGF1V–vcMMAE conjugate. The conjugate stimulated the same signaling pathways in NIH 3T3 cells (murine fibroblasts) as did unmodified FGF1V, as detected by Western blot analysis, although it showed slightly lower specific activity (Figure 3C). This indicates unimpaired FGFR binding of the conjugated proteins.
Effect of FGF1V–vcMMAE on FGFR-expressing cells
We evaluated the cytotoxic effect of the FGF1V–vcMMAE conjugate on FGFR-expressing cells, including a model human fibroblast cell line, BJ. In addition to BJ cells that express FGFR at a moderate level, corresponding to its physiological abundance on the cell surface, we used the breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-134-VI with FGFR overexpression.29 Furthermore, to test whether the cytotoxic effect is specific to FGFR-expressing cells, we employed a model system of U2OS and U2OS FGFR1 cells (stably transfected with the FGFR1) in which otherwise identical osteosarcoma cells lacking and expressing FGFRs can be compared. We have confirmed the FGFR expression levels in used cell lines on the protein level by anti-FGFR1 Western blot (Figure 4A) and on messenger RNA (mRNA) level by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) (Figure S1). As expected, FGFR1 levels were high in BJ, MDA-MB-134-VI, and U2OS FGFR1 cells, and very low in U2OS cells. For MDA-MB-134-VI cells, we observed a slight discrepancy regarding FGFR1 protein and mRNA level, but as mRNA amount does not correlate directly with protein level and may depend on mRNA stability, processing, translation efficiency, and receptor transport to the cell membrane, it is to be expected. Levels of other FGFRs (FGFR2, FGFR3, and FGFR4) were found to be below the detection limit of Western blot, in agreement with quantitative PCR, where mRNA levels for FGFRs other than FGFR1 were very low. In general, obtained results correlate well with cell line characteristics reported in the literature.
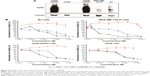
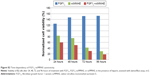
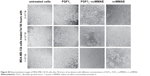
All the cell lines were treated with increasing concentrations of the conjugate, FGF1V, or vcMMAE for 96 hours, and then their viability was assessed by the alamarBlue assay or counting in trypan Blue stain (Figure 4B). As the maximum cytotoxic effect of both vcMMAE and FGF1V–MMAE was reached after 72–96 hours (Figure S2), the cytotoxicity assessment was performed after 96 hours of treatment. Together with these quantitative cell viability assays, we monitored cell apoptosis by annexin V staining and fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis (Figure S3). Cell morphology was also monitored by light microscopy, in particular looking for formation of apoptotic bodies and cell membrane budding, as well as decreased cell number in the field of vision (Figure S4).
The toxicity of free vcMMAE was very similar toward all the cell lines tested. Notably, once it was conjugated to FGF1V, its toxicity was distinctly different for different cell lines and correlated with the level of FGFR on their surface (Figure 4). FGF1V–vcMMAE conjugate decreased the viability of BJ and MDA-MB-134-VI cells markedly, and in concentrations higher than 1.0×10−7 M caused complete mortality of the latter. The IC50 (half maximal inhibitory concentration) of the conjugate toward MDA-MB-134-VI cells was almost tenfold lower than the IC50 of free vcMMAE (Table 1).
The U2OS–U2OS FGFR1 pair confirmed the specificity of this effect. For the FGFR-free U2OS cells, the toxicity of free vcMMAE and the conjugate was almost the same, whereas for U2OS FGFR1 cells the toxicity of free vcMMAE remained unchanged while that of the FGF1V–vcMMAE conjugate increased tenfold. This result is a strong indication that FGF1V–vcMMAE is internalized selectively by receptor-bearing cells and causes FGFR-dependent cell toxicity.
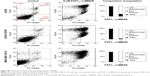
To confirm our results obtained in alamarBlue assay and further examine the effect of FGF1V–vcMMAE on cells, we performed annexin V and propidium iodide staining, allowing us to detect apoptotic and dead cells, respectively, followed by FACS analysis (Figure S3). For FGFR-expressing cells (MDA-MB-134-VI, U2OS FGFR1) subjected to treatment with 6 μM concentration of FGF1V–vcMMAE, almost all cells underwent apoptosis process and only <3% cells remained alive. For cells lacking FGFR (U2OS) treated with the same conjugate’s concentration, the observed cell viability was 40%. These data stay with agreement with results obtained in alamarBlue-based experiments and support our conclusion regarding specific cytotoxicity of FGF1V–vcMMAE conjugates on FGFR1-expressing cells.
Discussion
Targeted cancer therapies are being developed extensively as promising strategies for cancer treatment.30 Such therapies prove to be more effective than the nonspecific chemotherapeutic treatments and cause fewer side effects. For the development of a specific delivery system, the targeting molecule is key, antibodies being used most commonly for targeting cancer cells.5,31 As FGFRs are overexpressed in a wide variety of common cancers, we decided to test as the targeting molecule a natural FGFR ligand – FGF1 – instead of an antibody.
We synthesized an FGF1V-vcMMAE conjugate based on the ADC concept.1,4 In this entirely unexplored approach, in which an engineered FGF1 variant is conjugated to a highly cytotoxic drug, FGF1 was expected to act as a Trojan horse. After binding with high affinity and specificity to overexpressed FGFRs, the growth factor will first stimulate cell proliferation, but then, upon receptor-mediated internalization, will introduce a highly potent drug into the cell to destroy it. We linked MMAE to FGF1 via a commonly used valine–citrulline linker that can be specifically cleaved by endosomal proteases, such as cathepsin B,32–34 releasing a free drug that can then diffuse into the cytosol. This well established and thoroughly tested dipeptide linker is broadly used in ADC strategy and the release of cytotoxic drug was described in detail for both in vitro and in vivo conditions.34,35
Moreover, MMAE acts even more effectively on stimulated and dividing cells, as it binds tubulin to inhibit its polymerization crucial for cytoskeleton reorganization during cell division. Consequently, the FGF1–FGFR interaction would have a suicidal effect and the inherent proliferative activity of FGF1 could be beneficial in such an ADC analog. The summarized proposed mechanism of the conjugate action is presented in Figure 5.
Considering that FGF1 is a potent mitogen, we took care to obtain a pure FGF1V-vcMMAE conjugate of defined stoichiometry, in agreement with current trends in ADC development.5,36 We used an engineered FGF1 variant, called FGF1V, which shows improved stability. In this variant, the solvent-exposed Cys117 was substituted with serine, as its conjugation with vcMMAE is either ineffective or leads to protein unfolding. To create a convenient conjugation site, we added a fully exposed cysteine located in an N-terminal highly flexible linker. The remaining two cysteines present in FGF1 are buried, and their modification with MMAE was prevented effectively by addition of heparin during conjugation. To ensure complete separation of unmodified from modified FGF1V for obtaining a pure conjugate preparation suitable for cell cytotoxicity assessment, we optimized purification conditions of the reaction product.
FGFR-expressing cells treated with the FGF1V–vcMMAE conjugate showed remarkably decreased viability, and this effect correlated with the FGFR level on the cell surface: the cancer cell line with significant overexpression of FGFR (MDA-MB-134-VI) was twice as sensitive as the fibroblast cell line (BJ) with a physiological FGFR level. The FGFR-dependent conjugate toxicity in U2OS FGFR1/U2OS cell lines confirms the specificity of the drug delivery via the FGF1–FGFR interaction. The cell cytotoxicity was higher for the FGF1V–vcMMAE conjugate than for the free drug: the IC50 was about nine- and fourfold lower for the conjugate for the MDA-MB-134-VI and BJ cells, respectively. These results show that FGF1 exhibits a clear targeting potential toward cells expressing a specific receptor(s). One should note that, crucially for its prospective use in cancer therapy, there is a fairly broad range of concentrations in which FGF1V–vcMMAE is highly toxic to FGFR-expressing cells and has almost no effect on FGFR-free cells. In this proof-of-concept study, we attached a single MMAE molecule to a stabilized FGF1 via a Cys-containing linker on its N-terminus. Thus, the drug to protein ratio (in the case of ADCs called the DAR value) equals 1. The optimal DAR value for antibody conjugates is ~4.37–39 We expect that this value can be increased for FGF1 by rational design of multiple conjugation sites, although the solubility and stability of FGF1 loaded with many drug molecules could be compromised.
It has to be noted that FGF1 shows high affinity for heparin and heparan sulfate proteoglycans present on the surface of diverse cells and in the extracellular matrix. Consequently, it seems possible that upon systemic application a large fraction of the FGF1 conjugates will be captured far from the tumor site and their true concentration will be significantly lower than expected and needed for effective tumor eradication. Further development of FGF1-based conjugates may require elimination of the heparin-binding site. Luckily, it is well defined in FGF1 and can be disrupted by a previously described set of mutations.40,41 FGF1 is also the only growth factor in the fibroblast growth factor family that binds with high affinity to all four FGFR types and is effectively internalized13 and therefore is an excellent FGFR-targeting agent, especially for tumors expressing more than one type of FGFR.42 Additionally, it is a protein of fully human origin, and thus is advantageous over humanized or human sequence-derived antibodies that tend to induce some immunological response after prolonged treatment.43
Conclusion
This study shows that FGF can be effectively used as a specific delivery vehicle for a cytotoxic payload. The proliferative action of the growth factor can be overcome by the high cytotoxic potency of MMAE. Thus, FGF1 can be used as a targeting agent analogous to antibodies. The FGF1V–vcMMAE conjugate exhibits substantial toxicity toward FGFR-expressing cells, exceeding that of free MMAE, and the effect is dependent on the FGFR level on the cell surface.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Science Centre, Poland, grant number 2011/02/A/NZ1/00066 (NCN Maestro). We would like to thank Dr Agnieszka Kubiak for her skillful help with cell culture, Dr Ellen M Haugsten for the stably transfected U2OS FGFR1 cell line, and Dr Elzbieta Gocek for her help with performing FACS experiments.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Senter PD. Potent antibody drug conjugates for cancer therapy. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2009;13(3):235–244. | ||
Teicher BA, Chari RVJ. Antibody conjugate therapeutics: Challenges and potential. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(20):6389–6397. | ||
Casi G, Neri D. Antibody-drug conjugates: Basic concepts, examples and future perspectives. J Control Release. 2012;161(2):422–428. | ||
Sievers EL, Senter PD. Antibody-drug conjugates in cancer therapy. Annu Rev Med. 2013;64:15–29. | ||
Alley SC, Okeley NM, Senter PD. Antibody–drug conjugates: Targeted drug delivery for cancer. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2010;14(4):529–537. | ||
Sassoon I, Blanc V. Antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) clinical pipeline: A review. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1045:1–27. | ||
St Bernard R, Zheng L, Liu W, Winer D, Asa SL, Ezzat S. Fibroblast growth factor receptors as molecular targets in thyroid carcinoma. Endocrinology. 2005;146(3):1145–1153. | ||
Knights V, Cook SJ. De-regulated FGF receptors as therapeutic targets in cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 2010;125(1):105–117. | ||
Gavine PR, Mooney L, Kilgour E, et al. AZD4547: An orally bioavailable, potent, and selective inhibitor of the fibroblast growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase family. Cancer Res. 2012;72(8):2045–2056. | ||
Ho HK, Yeo AHL, Kang TS, Chua BT. Current strategies for inhibiting FGFR activities in clinical applications: Opportunities, challenges and toxicological considerations. Drug Discov Today. 2014;19(1):51–62. | ||
Kachel P, Trojanowicz B, Sekulla C, Prenzel H, Dralle H, Hoang-Vu C. Phosphorylation of pyruvate kinase M2 and lactate dehydrogenase A by fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 in benign and malignant thyroid tissue. BMC Cancer. 2015;15(1):1–13. | ||
Tiseo M, Gelsomino F, Alfieri R, et al. FGFR as potential target in the treatment of squamous non small cell lung cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2015;41(6):527–539. | ||
Zhang X, Ibrahimi OA, Olsen SK, Umemori H, Mohammadi M, Ornitz DM. Receptor specificity of the fibroblast growth factor family: The complete mammalian FGF family. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(23):15694–15700. | ||
Friesel R, Maciag T. Internalization and degradation of heparin binding growth factor-I by endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988;151(3):957–964. | ||
Grieb TA, Burgess WH. The mitogenic activity of fibroblast growth factor-1 correlates with its internalization and limited proteolytic processing. J Cell Physiol. 2000;184(2):171–182. | ||
Haugsten EM, Malecki J, Bjørklund SMS, Olsnes S, Wesche J. Ubiquitination of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 is required for its intracellular sorting but not for its endocytosis. Mol Biol Cell. 2008;19(8):3390–3403. | ||
Szlachcic A, Pala K, Zakrzewska M, Jakimowicz P, Wiedlocha A, Otlewski J. FGF1-gold nanoparticle conjugates targeting FGFR efficiently decrease cell viability upon NIR irradiation. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:5915–5927. | ||
Zakrzewska M, Krowarsch D, Wiedlocha A, Olsnes S, Otlewski J. Highly stable mutants of human fibroblast growth factor-1 exhibit prolonged biological action. J Mol Biol. 2005;352(4):860–875. | ||
Culajay JF, Blaber SI, Khurana A, Blaber M. Thermodynamic characterization of mutants of human fibroblast growth factor 1 with an increased physiological half-life. Biochemistry. 2000;39(24):7153–7158. | ||
Goozner M. Drug approvals 2011: Focus on companion diagnostics. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012;104(2):84–86. | ||
Patel S, Keohan ML, Saif MW, et al. Phase II study of intravenous TZT-1027 in patients with advanced or metastatic soft-tissue sarcomas with prior exposure to anthracycline-based chemotherapy. Cancer. 2006;107(12):2881–2887. | ||
Riely GJ, Gadgeel S, Rothman I, et al. A phase 2 study of TZT-1027, administered weekly to patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer following treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy. Lung Cancer. 2007;55(2):181–185. | ||
Banerjee S, Wang Z, Mohammad M, Sarkar FH, Mohammad RM. Efficacy of selected natural products as therapeutic agents against cancer. J Nat Prod. 2008;71(3):492–496. | ||
Francisco JA, Cerveny CG, Meyer DL, et al. cAC10-vcMMAE, an anti-CD30–monomethyl auristatin E conjugate with potent and selective antitumor activity. Blood. 2003;102(4):1458–1465. | ||
Doronina SO, Toki BE, Torgov MY, et al. Development of potent monoclonal antibody auristatin conjugates for cancer therapy. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21(7):778–784. | ||
Sutherland MSK, Sanderson RJ, Gordon KA, et al. Lysosomal trafficking and cysteine protease metabolism confer target-specific cytotoxicity by peptide-linked anti-CD30-auristatin conjugates. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(15):10540–10547. | ||
Gerber H, Kung-Sutherland M, Stone I, et al. Potent antitumor activity of the anti-CD19 auristatin antibody drug conjugate hBU12-vcMMAE against rituximab-sensitive and -resistant lymphomas. Blood. 2009;113(18):4352–4361. | ||
Copeland RA, Ji H, Halfpenny AJ, et al. The structure of human acidic fibroblast growth factor and its interaction with heparin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991;289(1):53–61. | ||
McLeskey SW, Ding IYF, Lippman ME, Kern FG. MDA-MB-134 breast carcinoma cells overexpress fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptors and are growth-inhibited by FGF ligands. Cancer Res. 1994;54(2):523–530. | ||
Sawyers C. Targeted cancer therapy. Nature. 2004;432(7015):294–297. | ||
Klute K, Nackos E, Tasaki S, Nguyen DP, Bander NH, Tagawa ST. Microtubule inhibitor-based antibody-drug conjugates for cancer therapy. Onco Targets Ther. 2014;7:2227–2236. | ||
Dubowchik GM, Firestone RA, Padilla L, et al. Cathepsin B-labile dipeptide linkers for lysosomal release of doxorubicin from internalizing immunoconjugates: model studies of enzymatic drug release and antigen-specific in vitro anticancer activity. Bioconjug Chem. 2002;13(4):855–869. | ||
Toki BE, Cerveny CG, Wahl AF, Senter PD. Protease-mediated fragmentation of p-amidobenzyl ethers: A new strategy for the activation of anticancer prodrugs. J Org Chem. 2002;67(6):1866–1872. | ||
Ducry L, Stump B. Antibody-drug conjugates: Linking cytotoxic payloads to monoclonal antibodies. Bioconjug Chem. 2010;21(1):5–13. | ||
Doronina SO, Mendelsohn BA, Bovee TD, et al. Enhanced activity of monomethylauristatin F through monoclonal antibody delivery: effects of linker technology on efficacy and toxicity. Bioconjug Chem. 2006;17(1):114–124. | ||
Goldmacher VS, Amphlett G, Wang L, Lazar AC. Statistics of the distribution of the abundance of molecules with various drug loads in maytansinoid antibody-drug conjugates. Mol Pharm. 2015;12(6):1738–1744. | ||
Hamblett KJ, Senter PD, Chace DF, et al. Effects of drug loading on the antitumor activity of a monoclonal antibody drug conjugate. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(20):7063–7070. | ||
Sievers EL, Senter PD. Antibody-drug conjugates in cancer therapy. Annu Rev Med. 2012;64:15–29. | ||
Sochaj AM, Świderska KW, Otlewski J. Current methods for the synthesis of homogeneous antibody–drug conjugates. Biotechnol Adv. 2015;33(6 Part 1):775–784. | ||
Burgess WH, Shaheen AM, Ravera M, Jaye M, Donohue PJ, Winkles JA. Possible dissociation of the heparin-binding and mitogenic activities of heparin-binding (acidic fibroblast) growth factor-1 from its receptor-binding activities by site-directed mutagenesis of a single lysine residue. J Cell Biol. 1990;111(5):2129–2138. | ||
Wong P, Hampton B, Szylobryt E, Gallagher AM, Jaye M, Burgess WH. Analysis of putative heparin-binding domains of fibroblast growth factor-1: Using site-directed mutagenesis and peptide analogues. J Biol Chem. 1995;270(43):25805–25811. | ||
Chandler LA, Sosnowski BA, Greenlees L, Aukerman SL, Baird A, Pierce GF. Prevalent expression of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptors and FGF2 in human tumor cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1999;81(3):451–458. | ||
Harding FA, Stickler MM, Razo J, DuBridge RB. The immunogenicity of humanized and fully human antibodies: Residual immunogenicity resides in the CDR regions. MAbs. 2010;2(3):256–265. |
Supplementary materials
 © 2016 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2016 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.