Back to Journals » International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease » Volume 13
COPD uncovered: a cross-sectional study to assess the socioeconomic burden of COPD in Japan
Authors Igarashi A, Fukuchi Y, Hirata K, Ichinose M, Nagai A, Nishimura M , Yoshisue H, Ohara K, Gruenberger JB
Received 7 March 2018
Accepted for publication 16 May 2018
Published 28 August 2018 Volume 2018:13 Pages 2629—2641
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S167476
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Richard Russell
Ataru Igarashi,1 Yoshinosuke Fukuchi,2 Kazuto Hirata,3 Masakazu Ichinose,4 Atsushi Nagai,5 Masaharu Nishimura,6 Hajime Yoshisue,7 Kenichi Ohara,8 Jean-Bernard Gruenberger9
1Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan; 2Department of Respiratory Medicine, Graduate School of Medicine, Juntendo University, Tokyo, Japan; 3Department of Respiratory Medicine, Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka City University, Osaka, Japan; 4Department of Respiratory Medicine, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine, Sendai, Japan; 5Research Institute for Respiratory Diseases, Shin-Yurigaoka General Hospital, Kawasaki City, Japan; 6Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Faculty School of Medicine, Hokkaido University, Hokkaido, Japan; 7Medical Division, Novartis Pharma K.K., Tokyo, Japan; 8Market Access Division, Novartis Pharma K.K., Tokyo, Japan; 9Market Access Division, Novartis Pharma AG, Basel, Switzerland
Background: COPD remains a major health problem in Japan. Patients with COPD experience a reduced quality of life (QoL) and have a higher chance of work impairment and productivity loss. However, there is a lack of data on the impact of COPD in terms of QoL and work activity impairment in Japan. This study assessed the socioeconomic burden of COPD in Japan and the impact it may have on the working age population.
Patients and methods: This was a 2-year retrospective chart review in COPD patients aged ≥40 years, with at least one health care visit to clinic or hospital in the previous 12 months. Patients were required to have available medical charts for at least the previous 24 months. Symptoms were assessed using COPD assessment test score; EuroQoL Group 5 Dimension (EQ-5D-5L) and work productivity and activity impairment general health questionnaires were used to evaluate health-related QoL and work productivity, and health care resource utilization data were obtained from clinical charts.
Results: In total, 71 patients aged <65 years, and 151 patients aged ≥65 years were included; the majority of patients had moderate or severe airflow limitation. Exacerbations (moderate or severe) were reported by ~35% of patients in both age groups; 52.1% and 62.9% of patients in the <65-year and ≥65-year age groups had COPD assessment test scores ≥10. EQ-5D-5L index scores in the <65-year and ≥65-year age groups were 0.79 and 0.77, respectively. Work productivity and activity impairment scores were higher in <65-year age group. Annual costs of health care resource use per patient in the <65-year and ≥65-year age groups were ¥438,975 (US$4,389) and ¥467,871 (US$4,678), respectively. Costs due to productivity loss were estimated to be ¥5,287,024 (US$52,870) in the <65-year age group and ¥3,018,974 (US$30,187) in the ≥65-year age group.
Conclusion: COPD represents a significant socioeconomic burden in Japan. Patients with COPD report significant use of health care resources. Higher impact on work impairment and productivity loss was observed frequently in the working age population.
Keywords: health-realted quality of life, chart review, EQ-5D-5L questionnaire, health care resource utilization, productivity loss, work impairment WPAI-GH
Introduction
COPD is a common, preventable and treatable disease, characterized by persistent airflow limitation and respiratory symptoms, resulting in breathlessness and poor quality of life (QoL).1 COPD continues to be a leading cause of morbidity and mortality globally, contributing to a substantial social and economic burden. The Global Burden of Disease Study, in 2010, ranked COPD as the fourth leading cause of death worldwide.1–4 The global prevalence of COPD ranges from 7.6% to 8.9%.5 In Japan, the prevalence is 8.6% in patients aged ≥40 years6 and up to 10.3% in patients aged ≥60 years; the prevalence of COPD is 22% in patients with a history of smoking or respiratory symptoms.7,8
There is a significant difference in clinical features of COPD patients between Asian countries and the rest of the world.9 Higher age and low body mass index (BMI) are characteristic features of Japanese patients and have been reported as prognostic factors for various clinical outcomes of COPD.10–15 It has been reported that COPD patients in Japan have fewer exacerbation frequencies, compared with other countries.15,16 An aging population and lower BMI are independent risk factors for morbidity and mortality in patients with COPD,1,17,18 and these unique clinical features may emphasize the burden of COPD in Japan, compared with other countries.
COPD is generally perceived as a disease of old age; however, according to the cohort studies conducted in the USA, Europe and some Asian counties (other than Japan), it is estimated that approximately half of COPD patients are in the working age group (<65 years of age) and employed.19,20 Patients with COPD not only have higher disability but also have a reduced QoL. High resource utilization leads to high medical expenditure in the national health care budget.21 A study conducted by Polatli et al has reported higher medical costs associated with disease severity, higher COPD assessment test (CAT) score, COPD exacerbations and presence of comorbidities.22 COPD patients have a higher chance of working fewer hours, of absenteeism and of poorer work performance.23 The level of work impairment and productivity worsens with increasing age, disease severity and number of comorbidities.24
In Japan, the average annual cost per patient with moderate-to-severe COPD was estimated to be US$9,893 in the Continuing to Confront COPD survey.25 An earlier study by Katsura estimated the average annual cost per COPD patient in Japan to be US$5,189.21 The data from these studies, though different, highlight the high economic burden of COPD in Japan. Also, the information available on COPD burden in Japan is based mainly on the health care resource use. There is a paucity of data on the impact of COPD in terms of QoL, work activity impairment and productivity loss in Japan.23 In an effort to inform health care policies and improve resource allocation, we aimed to describe the socioeconomic burden of COPD in Japan and the impact it may have on the working-age population.
Patients and methods
Study design
This was a 2-year retrospective chart review with cross-sectional patient-reported outcomes (Figure 1). The study was conducted at 18 centers within Japan (9 clinics and 9 hospitals), where patients diagnosed with COPD are treated. The participating hospitals and clinics were selected based on geographical location, type of care (primary or secondary) and the population of the city/town where the site was located, in order to have a representative sample of COPD patients. Clinics were considered as primary care and hospitals as secondary.
This study was designed to capture the distribution of COPD severity among patients attending a physician’s office within the defined age group and not the distribution of the patients with COPD in general in Japan.
The study was conducted in line with the principles of Declaration of Helsinki and the Ethical Guidelines for Epidemiological Research and was approved by the individual institutional review board for each trial center (Supplementary materials). The study is reported in accordance with the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) recommendations.
Eligibility criteria
The study enrolled patients diagnosed with COPD patients who were aged ≥40 years, current or ex-smokers, with at least one health care visit in the previous 12 months. Patients were included if they had a confirmed COPD diagnosis through spirometry and met the guidelines of the Japanese Respiratory Society (3rd edition of Japanese Respiratory Society Guidelines) criteria of having a postbronchodilator forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1)/forced vital capacity (FVC) of <70%, and the absence of other diseases that may lead to airflow obstruction. Patients’ medical charts for a minimum of the previous 24 months, with information describing COPD treatment, consultations, hospitalizations and emergency hospital visits, were required to be available at the participating center.
Patients were excluded from the study if they had participated in any clinical trial at the time of study inclusion or in the previous 24 months, lack of reading and writing skills or severe cognitive impairment. As the study was retrospective, no patient withdrawal was expected. All patients who met the eligibility criteria and provided written informed consent were included in the study.
Data variables
Patient demographics and clinical characteristics were collected. Disease characteristics including COPD severity as per GOLD strategy;26 disease prognosis by the BMI, obstruction, dyspnea and exercise capacity (BODE) index; exacerbation history, including number and severity of exacerbations; COPD treatments received and degree of dyspnea as assessed by modified Medical Research Council (mMRC) dyspnea scale were also collected. Moderate exacerbations were defined as worsening of COPD symptoms that required consultation with primary care physician to provide change in treatment (eg, a prescription of steroid), and severe exacerbations were defined as worsening of symptoms resulting in hospitalization.
COPD symptoms were assessed by the CAT score that measured the impact of COPD on a patient’s life, with higher scores indicating a higher impact. Additionally, the COPD AM symptom questionnaire assessed symptoms that were worse in the morning, their duration and their impact on the rest of the day.
Health-related quality of life (HRQoL) was measured using the EuroQoL Group 5 Dimension (EQ-5D-5L) questionnaire, which has two parts: 1) descriptive system with five questions, assessing five components – “mobility”, “self-care”, “usual activities”, “pain/discomfort” and “anxiety/depression” and 2) a visual analogue scale (VAS), describing the patient’s health state on a scale from 0 (worst imaginable state) to 100 (best imaginable state) (EQ-5D-5L Questionnaire). The EQ-5D-5L health states, derived from the above descriptive system, can be converted to single index values and are presented in country-specific value sets. The index-based scores range from 0 to 1 in the Japanese population,27,28 where 0 indicates death and 1 indicates perfect health.
Impact on work productivity was assessed by the work productivity and activity impairment general health (WPAI-GH) questionnaire, which evaluates the effect of general health problems on productivity losses through six questions related to the working situation. For this study, the word “health problems” in the questionnaire was replaced with “COPD”. The questionnaire was administered to all enrolled patients aged ≤70 years to analyze work productivity in the group of working patients aged <65 years and 65–70 years. The outcomes from the WPAI-GH questionnaire were expressed as percentage of impairment, with higher numbers indicating greater impairment and lower productivity. These outcomes relate to 7 days prior to administration of questionnaire.29,30
Data on health care utilization due to COPD and comorbidities were collected during the 2-year review period and included hospitalization episodes, emergency services, consultations with health care providers and pulmonary rehabilitation. Total direct medical costs associated with COPD and comorbidities were calculated from the payer perspective at the national level. For hospitalization and other resources, unit costs were defined according to diagnosis-related group (DRG) listing. Unit costs for drugs were set at the price of the cheapest drug in the category, and unit costs were applied to the corresponding health care resources based on DRG list to obtain cost estimation.
Data collection and handling
The study was non-interventional; therefore, a therapy protocol, diagnostic/therapeutic procedure or a visit schedule was not imposed. Patients were treated as per routine medical practice according to the local prescribing information. The study was conducted in a cross-sectional fashion; the investigating physician collected the sociodemographic details (age, gender, BMI, smoking history and employment status), clinical data (duration of COPD, severity, comorbidities, ongoing COPD treatment and exacerbation history) and health care utilization data (hospitalization episodes, emergency services, consultation with health care providers and pulmonary rehabilitation) that were registered on each patient’s medical chart and recorded in an electronic Case Report Form (e-CRF) that had been especially designed for the study. At the time of routine visit, patients were asked to complete the paper-based questionnaires on patient-reported outcomes and work productivity (CAT questionnaire, EQ-5D questionnaire and WPAI-GH questionnaire) in their local language. The completed questionnaires were then transferred to the local contract research organization (CRO).
Statistical analysis
The study results were described according to age groups (<65 years and ≥65 years), and the study was not powered to compare the two age groups. The sample size was calculated to have a precise estimate of the mean percentage of time of absenteeism in patients aged <65 years and the burden of COPD in patients aged ≥65 years. Considering these, and based on the previous international survey on COPD,24 enrollment of a minimum of 154 patients in the <65 age group would allow estimation of the mean % time of absenteeism with a precision of 3.7 SD, and 151 patients in the older age group would allow estimation of the COPD burden with a precision of 0.16 SD. However, 71 patients were recruited in the <65-year age group, and the precision of study result was estimated to be between 5.4 and 5.5 points for this group.
Continuous variables were described by means of descriptive statistics, median and interquartile range and calculated for non-normally distributed data; categorical variables were described by frequencies and respective percentages. The study population was analyzed in terms of sociodemographic and clinical variables to describe the profile of COPD patients in Japan in each age subgroup. All costs were reported in Japanese yen (¥) and US dollars (US$), exchange rate as at 2015 ¥1 = US$0.01. Statistical analysis was performed using Statistical Analysis Software (SAS) ver. 9.3 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA).
Results
Patient demographics
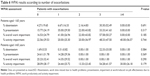
Based on the sample size calculation, it was expected that at least 305 patients would be enrolled in the study; however, in total, 222 patients were enrolled (71 patients aged <65 years; 151 aged ≥65 years, 151). Demographics and baseline characteristics are presented in Table 1. In both age subgroups, most patients were men, ex-smokers and had moderate or severe airflow limitation. The most frequently reported comorbidities in both age groups were hypertension, hyperdyslipidemia and other lung conditions. Asthma was the most frequent comorbidity among other lung conditions and was reported in 14 and 23 patients in the <65-year and ≥65-year age groups, respectively.
Disease and treatment characteristics
The risk of dying due to respiratory causes, as calculated by the BODE index, was greater in patients aged ≥65 years at the time of study visit (Table 2). During the 2-year reference period, long-acting muscarinic antagonists (LAMAs) were prescribed more frequently in patients aged ≥65 years, while patients aged <65 years were treated mostly with long-acting β2-agonist (LABA) combinations (Table 2). The annual number of exacerbations was comparable between the age groups, with most patients in both age groups experiencing moderate exacerbations. The number of patients experiencing severe exacerbations was slightly higher in the ≥65-year age group (Table 2).
At the time of study visit, the mean±SD CAT score for patients in the <65-year age group and the ≥65-year age group was 11.38±8.57 points and 13.66±8.26 points, respectively. A total of 37 patients (52.1%) in the <65-year age group and 95 patients (62.9%) in the ≥65-year age group had a CAT score of ≥10 points, indicating a high impact of COPD on patients’ lives. In patients aged <65 years, the most frequent symptoms reported in the morning were shortness of breath (35.2%) and cough and coughing up phlegm (19.7%), while for patients in the ≥65-year group, the most frequently observed symptoms were coughing up phlegm (37.1%) and shortness of breath (36.4%). Assessments based on the COPD AM symptom questionnaire are highlighted in Table 3.
  | Table 3 Responses in COPD AM symptom questionnaire according to age groups |
HRQoL
“Mobility” and “usual activities” were the most affected dimensions from the EQ-5D-5L questionnaire in the <65-year group, with 43.7% patients reporting problems in walking about and doing their usual activities; in the ≥65-year age group, “mobility” was most affected, with 56.3% of patients reporting problems in walking (Table 4). The mean VAS score was 70.51 (SD, 23.80) points for patients in the <65-year age group and 69.17 (SD, 18.72) points in the ≥65-year age group. The mean EQ-5D-5L index value for patients in the <65-year age group was 0.79 (SD, 0.22) and 0.77 (SD, 0.18) for patients in the ≥65-year age group.
  | Table 4 EQ-5D-5L dimensions in <65-year and ≥65-year age groups |
Health care utilization
During the 2-year retrospective period, 12.7% patients were hospitalized in the <65-year age group (mean±SD episodes 1.67±1.66); 8.4% patients had emergency room visits and 4.2% attended pulmonary rehabilitation programs (mean duration 72.00±25.63 weeks). In the ≥65-year age group, 12.6% were hospitalized during the 2-year study period (mean±SD hospitalization episodes 1.79±1.32); 6.6% patients had emergency room visits, and 10.6% attended pulmonary rehabilitation programs (mean duration 77.63±78.22 weeks). The mean±SD duration of hospital stay upon hospitalization (days per patient) was 16.67±13.84 and 18.03±12.40 in the <65-year and ≥65-year age groups, respectively. Estimated annual costs of health care resources associated with COPD are presented in Figure 2 for both age groups. The mean±SD annual costs per patient in the younger and older age groups were ¥438,975.8±534,379.0 (US$4,389.8±5,343.8) and ¥467,871.6±606,121.1 (US$4,678.7±6,061.2), respectively, with pharmacological treatment being the main driver of health care-related costs in both cohorts.
  | Figure 2 Distribution (%) of costs for health care resources due to COPD. |
According to the number of comorbidities, the estimated annual cost of health care resources related to COPD, in patients aged <65 years, with no comorbidities, was ¥379,060.8±414,781.5 (US$3,790.6±4,147.8); the respective cost in the ≥65-year age group (no comorbidity) was ¥159,799.2±121,764.7 (US$1,598.0±1,217.6). The corresponding costs were ¥481,686.3±419,062.0 (US$4,816.9±4,190.6) and ¥844,080.7±723,440.4 (US$8,440.8±7,234.4), respectively, for patients with three additional comorbidities. Health care resources not related to COPD, due to comorbidities, were also high and comparable in both age groups.
In the <65-year age group, eight patients (11.3%) were hospitalized due to comorbidities, with annual mean±SD number of hospitalization episodes of 0.94±0.73, and annual mean length of stay of 5.03±3.23 days; a total of four patients (5.6%) had emergency room visits with annual mean visits of 1.38±1.75. Sixteen patients (10.6%) in the ≥65-year age group were hospitalized due to comorbidities, the annual incidence of hospitalization was 0.81±0.54 times with a stay duration of 3.25±2.20 days; seven patients (4.6%) were treated in the emergency room with 0.64±0.38 mean annual visits. The annual costs of health care resources not related to COPD are presented in Table 5 for both the age groups.
  | Table 5 Health care resources utilization cost not related to COPD |
Work productivity
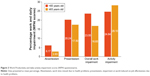
A total of 62.9% of patients in the younger age group and 23.3% in the ≥65-year age group were working for pay, according to the WPAI-GH questionnaire. Mean percentage of work and daily activity impairment in both age groups are highlighted in Figure 3. The mean ± SD cost of productivity loss was estimated to be ¥5,287,024.3±3,763,540.3 (US$52,870.2±37,635.4) in patients aged <65 years and ¥3,018,974.4±2,480,179.2 (US$30,187.4±24,799.8) in those aged ≥65 years. These data show a considerable impact of COPD on productivity loss in the working-age population. In both age groups, there was an increase in work impairment and in the number of exacerbations; however, none of the WPAI results achieved statistical significance (Table 6).
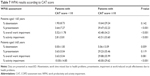
COPD symptoms also caused impairment during working hours, and overall and activity impairment. Work productivity, based on CAT score, was evaluated in both age groups with COPD. In patients aged <65 years, the impairment during working hours was significantly higher (P < 0.001) in patients with CAT score of ≥10 points versus those with CAT score <10 points. The overall work and activity impairment was also significantly higher (both P < 0.001) for patients with CAT scores ≥10 points (Table 7). In patients aged ≥65 years, the activity impairment due to COPD was significantly higher (P < 0.001), while other work productivity parameters were numerically higher in patients with CAT scores ≥10 points (Table 7).
Discussion
The objective of this observational study was to assess the socioeconomic burden of COPD in Japan and its impact on the working-age population (aged <65 years). The study also involved patients aged ≥65 years in order to understand the overall economic and societal impact of COPD. The study was not powered for comparison between the two age groups. The study was conducted through retrospective chart reviews of patient data, compared with another similar study conducted in six different countries through a subjective and retrospective survey,24 which may have had a greater risk of either under- or over-reporting of outcomes. Patients who attended the participant site during the study data collection period were invited to participate in the study and those who provided informed consent were included. It is possible that more severely affected patients in worse health condition chose to participate in the study in anticipation that it would result in better care from their treating physician. Selection bias could possibly have led to low recruitment in the younger population (aged <65 years) creating a vast imbalance in the ratio of patients enrolled in the two age groups, as patients in the ≥65-years age group are more prone to worsened health conditions.
Another possible reason for the lower-than-expected enrollment of <65-year-old patients in contrast to the elder (≥65 years of age) population might be that the average age of patients diagnosed with COPD in Japan is higher than in other countries, especially Western countries; the average age of patients with COPD in Japan is reported to be around 70 years, as revealed in several cohort studies conducted in Japan.13–15 This difference in age has also been observed in the demographic information in large clinical trials.31
In both age subgroups, the majority of patients were male, which, in line with other observational studies in Japan,8,32,33 reflects a higher prevalence of COPD in Japanese males. A higher proportion of patients had moderate or severe airflow limitation in both age groups; the number of patients with severe exacerbation was slightly higher in the ≥65-year age group. Most COPD patients experienced at least one comorbidity, with a higher proportion across both age groups suffering from diseases of the cardiovascular system and diabetes. Asthma was also reported as comorbidity in both age groups. It is well known that a differential diagnosis of asthma from COPD is clinically difficult at times, which may lead to an overlap of these disorders. In some patients with chronic asthma, a distinct diagnosis of COPD is not possible even using the current physiological testing and imaging techniques, and it is possible that asthma and COPD may coexist.1,34
More than half of patients (58%) in the <65-year age group were working for pay, compared with 18% in the ≥65-year age group. This is in contrast to the data from a patient survey conducted in several countries, which revealed that 45% of Japanese patients with COPD were working at the time of the survey.35 In each of the age cohorts, more than half of patients had a CAT score ≥10, indicating a high impact of COPD on patients’ HRQoL. This was in line with a population-based survey in Japan that revealed a mean CAT score of 16 points – similar to that observed in this study.35 Earlier studies have shown a strong correlation with the CAT questionnaire with severity of airflow obstruction, dyspnea and comorbidities in Japanese patients.13,36 Overall, these data show that COPD symptomatology remains an important factor on impairment of HRQoL.
In this study, EQ-5D-5L a preference-based generic questionnaire, was used to evaluate HRQoL in enrolled patients. A meta-analysis by Pickard et al37 showed that lower EQ-5D-5L index scores were associated with more severe GOLD stage. In our study, the index scores were comparable between the <65-year and the ≥65-year age groups (0.79 and 0.77, respectively), where a lower index score might have been expected in the older age group. The comparable index scores in both age groups in our study may be due to the lower proportion of very severe (GOLD grade IV) patients in the ≥65-year age group (9.8%), compared with the younger group (13.5%).
Work and activity impairment was found to be significantly higher in patients aged <65 years, with a greater impact on HRQoL (higher CAT score), while patients aged ≥65 years had greater activity impairment with a higher CAT score. To the best of our knowledge, this was the first study that correlated work activities to CAT scores, confirming that work activities are more affected in patients with reduced HRQoL. Almost 6% of patients in both age groups (four patients aged <65 years and nine patients aged ≥65 years) retired due to COPD. The proportion of patients retiring due to COPD observed in this study was lower when compared with that (18%) of a similar study conducted in six different countries,24 which may implicate the difference of COPD burden in Japan compared with other countries, although we cannot directly compare the two studies due to differences in demographic composition. There was a considerable impact of COPD on productivity loss in the working-age population, which was evident from the costs incurred due to productivity loss. Indirect costs associated with COPD are significant; in the US, the indirect costs for COPD patients accounted for 27%–61% of the total medical costs, depending on the population studied, while in Greece, it accounted for 37.5% of the annual medical cost for COPD patients.38,39 Although the indirect costs were estimated considering only the productivity loss, the number of patients retiring due to COPD highlights a considerable economic impact of the disease in Japan.
The annualized rate of hospitalizations was ~12% during the study, which was considerably higher than the 5% reported in the Continuing to Confront COPD International Patient Survey 2012–2013; however, emergency room visits in our study (8.4% in <65-year group and 6.6% in ≥65-year group) were comparable with the patient survey (9%). Differences in the study methodology should be considered when comparing results from the two studies. Another aspect to be considered is while the Continuing to Confront COPD International Patient Survey 2012–2013 survey included patients with physician-diagnosed COPD, emphysema or chronic bronchitis,35 our chart review study included only patients with physician-diagnosed COPD confirmed through spirometry. In our study, the mean hospitalization stay for COPD was 16.67 days in the <65-year and 18.03 days in the ≥65-year age groups. The annual mean direct medical cost per patient due to COPD was ¥349,080 as estimated in a model by Nishimura and Zaher;40 there was a small increase in mean annual costs in this study, ranging from ¥438,975.82 to ¥467,871.56. This Japan-based study not only confirmed the above findings but also showed that the annual cost of managing COPD patients (considering only the health care resources used due to COPD) increases when the number of comorbidities increases; however, the study was not powered to validate this association.
Limitations
Clinical-chart data had to be available for all patients at the participating sites. Despite follow-up of patients at participating sites, information on the clinical charts may have been incomplete. Another limitation was related to the sample size estimation as the study was not powered to allow for disease stratification or comparison between the age groups. Results from this non-interventional study can be extrapolated to the Japanese population with COPD within the age groups defined in the study, who were regularly attending their physician.
Conclusion
Overall, COPD presents a significant socioeconomic burden in Japan. It remains an important driver of HRQoL impairment and work and activity impairment among Japanese patients. The management of COPD contributes substantially to the cost of health care resources. A considerable impact was observed on patients of working age (<65 years), which augment the overall disease burden. These findings may inform future COPD health care initiatives in Japan.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge all the investigators and their patients for commitment to this study. Authors would like to thank Vatsal Vithlani and Santanu Sannigrahi (professional medical writers; Novartis) for assistance in the preparation of this article in accordance with the third edition of Good Publication Practice guidelines. Medical writing support was funded by study sponsors. The authors also acknowledge IMS Health for conducting data analysis. This study was presented at the American Thoracic Society International Conference 2016, San Francisco, CA, USA, May 13–18, 2016 (Figures 1 and 3 and Tables 1–2 and 4), and the International Society for Pharmacoeconomics and Outcomes Research Asia-Pacific Conference 2016, Singapore, September 3–6, 2016 (Figures 1 and 2 and Tables 1–2). The study was funded by Novartis Pharma AG and Novartis Pharma K.K.
Author contributions
All authors contributed toward data analysis, drafting and revising the paper and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Disclosure
The authors received no compensation related to the development of the manuscript. AI reports fees from Novartis, Chugai Pharmaceuticals Inc., Astellas Pharma Inc., CSL Behring Japan Inc., Fuji file Inc., Takeda Pharmaceuticals Inc., Sanofi Japan Inc. and grants from Gilead Sciences K.K., AbbVie GK, Abbott Japan Inc., Beckton Dickinson and Company, Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Milliman Inc., Creativ-Ceuticals Inc., Pfizer Inc., Intuitive Surgical G.K. and Terumo corporation. YF reports fees from Novartis and Boehringer Ingelheim. KH reports fees from Novartis, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co. Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceuticals Co. Ltd. and Astellas Pharma Inc. MI reports fees from Novartis, Boehringer Ingelheim and AstraZeneca. AN reports fees from Novartis, GlaxoSmithKline, Boehringer Ingelheim and AstraZeneca. MN reports fees from Novartis, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca and grants from Novartis Pharma K.K. HY, KO and JG are employees of study sponsor. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of COPD. Available from: https://goldcopd.org. Published 2017. Accessed December 12, 2017 | ||
Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380(9859):2095–2128. | ||
WHO [webpage on the Internet]. The Top 10 Causes of Death. Fact Sheet No. 310. 2017. Available from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs310/en/. Accessed March 5, 2018. | ||
Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380(9859):2163–2196. | ||
Halbert RJ, Natoli JL, Gano A, Badamgarav E, Buist AS, Mannino DM. Global burden of COPD: systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Respir J. 2006;28(3):523–532. | ||
Fukuchi Y, Nishimura M, Ichinose M, et al. COPD in Japan: the Nippon COPD Epidemiology study. Respirology. 2004;9(4):458–465. | ||
Minakata Y, Ichinose M. [Epidemiology of COPD in Japan]. Nihon Rinsho. 2011;69(10):1721–1726. | ||
Takemura H, Hida W, Sasaki T, Sugawara T, Sen T. Prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Japanese people on medical check-up. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2005;207(1):41–50. | ||
Zhong N, Moon HS, Lee KH, et al. TIOtropium Safety and Performance In Respimat(R) (TIOSPIRTM): analysis of Asian cohort of COPD patients. Respirology. 2016;21(8):1397–1403. | ||
Chubachi S, Sato M, Kameyama N, et al. Identification of five clusters of comorbidities in a longitudinal Japanese chronic obstructive pulmonary disease cohort. Respir Med. 2016;117:272–279. | ||
Haraguchi M, Nakamura H, Sasaki M, et al. Determinants of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease severity in the late-elderly differ from those in younger patients. BMC Res Notes. 2016;9:7. | ||
Makita H, Nasuhara Y, Nagai K, et al. Characterisation of phenotypes based on severity of emphysema in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax. 2007;62(11):932–937. | ||
Miyazaki M, Nakamura H, Chubachi S, et al. Analysis of comorbid factors that increase the COPD assessment test scores. Respir Res. 2014;15:13. | ||
Nishimura M, Makita H, Nagai K, et al. Annual change in pulmonary function and clinical phenotype in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;185(1):44–52. | ||
Suzuki M, Makita H, Ito YM, et al. Clinical features and determinants of COPD exacerbation in the Hokkaido COPD cohort study. Eur Respir J. 2014;43(5):1289–1297. | ||
Nishimura M. Similarities and differences between East and West in COPD. Respirology. 2016;21(8):1340–1341. | ||
Landbo C, Prescott E, Lange P, Vestbo J, Almdal TP. Prognostic value of nutritional status in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;160(6):1856–1861. | ||
Schols AM, Slangen J, Volovics L, Wouters EF. Weight loss is a reversible factor in the prognosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157(6 pt 1):1791–1797. | ||
Buist AS, McBurnie MA, Vollmer WM, et al. International variation in the prevalence of COPD (the BOLD Study): a population-based prevalence study. Lancet. 2007;370(9589):741–750. | ||
de Marco R, Accordini S, Cerveri I, et al. An international survey of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in young adults according to GOLD stages. Thorax. 2004;59(2):120–125. | ||
Katsura H. Economic burden of COPD in Japan. Jpn Med Assoc J. 2011;54(2):110–112. | ||
Polatli M, Ben Kheder A, Wali S, et al. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and associated healthcare resource consumption in the Middle East and North Africa: the BREATHE study. Respir Med. 2012;106(suppl 2):S75–S85. | ||
Chaker L, Falla A, van der Lee SJ, et al. The global impact of non-communicable diseases on macro-economic productivity: a systematic review. Eur J Epidemiol. 2015;30(5):357–395. | ||
Fletcher MJ, Upton J, Taylor-Fishwick J, et al. COPD uncovered: an international survey on the impact of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [COPD] on a working age population. BMC Public Health. 2011;11:612. | ||
Foo J, Landis SH, Maskell J, et al. Continuing to confront COPD international patient survey: economic impact of COPD in 12 countries. PLoS One. 2016;11(4):e0152618. | ||
Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of COPD. 2014. Available from: https://goldcopd.org. Accessed December 12, 2017. | ||
Ikeda T, Shiraiwa K, Igarashi A, et al. Developing a Japanese version of the EQ-5D-5L value set. J Natl Inst Publ Health. 2015;64(1):47–55. Japanese. | ||
EQ-5D-5L User Guide. Basic Information on How to Use the EQ-5D-5L Instrument. Version 2.1. 2015. Available from: https://euroqol.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/EQ-5D-5L_UserGuide_2015.pdf. Accessed May 7, 2018. | ||
Reilly MC, Zbrozek AS, Dukes EM. The validity and reproducibility of a work productivity and activity impairment instrument. Pharmacoeconomics. 1993;4(5):353–365. | ||
REILLY ASSOCIATES [webpage on the Internet]. WORK Productivity and Activity Impairment Questionnaire: General Health V2.0 (WPAI-GH). [updated October 20, 2004]. Available from: http://www.reillyassociates.net/WPAI_GH.html. Accessed May 7, 2018. | ||
Ichinose M, Taniguchi H, Takizawa A, et al. The efficacy and safety of combined tiotropium and olodaterol via the Respimat((R)) inhaler in patients with COPD: results from the Japanese sub-population of the Tonado((R)) studies. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016;11:2017–2027. | ||
Fukahori S, Matsuse H, Takamura N, et al. Prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases in general clinics in terms of FEV1/FVC. Int J Clin Pract. 2009;63(2):269–274. | ||
Matsumoto K, Seki N, Fukuyama S, et al. Prevalence of asthma with airflow limitation, COPD, and COPD with variable airflow limitation in older subjects in a general Japanese population: the Hisayama Study. Respir Investig. 2015;53(1):22–29. | ||
Woodruff PG, van den Berge M, Boucher RC, et al. American Thoracic Society/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Asthma-Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Overlap Workshop Report. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;196(3):375–381. | ||
Landis SH, Muellerova H, Mannino DM, et al. Continuing to confront COPD International Patient Survey: methods, COPD prevalence, and disease burden in 2012–2013. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2014;9:597–611. | ||
Horita N, Yomota M, Sasaki M, et al. Evaluation of the chronic obstructive pulmonary disease assessment test in Japanese outpatients. Clin Respir J. 2014;8(2):213–219. | ||
Pickard AS, Wilke C, Jung E, Patel S, Stavem K, Lee TA. Use of a preference-based measure of health (EQ-5D) in COPD and asthma. Respir Med. 2008;102(4):519–536. | ||
Patel JG, Nagar SP, Dalal AA. Indirect costs in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a review of the economic burden on employers and individuals in the United States. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2014;9:289–300. | ||
Souliotis K, Kousoulakou H, Hillas G, Tzanakis N, Toumbis M, Vassilakopoulos T. The direct and indirect costs of managing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Greece. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2017;12:1395–1400. | ||
Nishimura S, Zaher C. Cost impact of COPD in Japan: opportunities and challenges? Respirology. 2004;9(4):466–473. |
Supplementary materials
Institutional review board approval
The protocol for this study was approved by the individual institutional review board (IRB) for each trial center. These trial centers (all based in Japan) are the following:
  |
STROBE statement – checklist of items that should be included in reports of observational studies
  |
 © 2018 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2018 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.