Back to Journals » International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease » Volume 12
Community pharmacy-based case finding for COPD in urban and rural settings is feasible and effective
Authors Fathima M, Saini B , Foster JM , Armour CL
Received 28 June 2017
Accepted for publication 15 August 2017
Published 18 September 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 2753—2761
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S145073
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Richard Russell
Mariam Fathima,1 Bandana Saini,1,2 Juliet M Foster,1 Carol L Armour1,3
1Woolcock Institute of Medical Research, Sydney Medical School, 2Faculty of Pharmacy, The University of Sydney, 3Central Sydney Area Health Service, Sydney, NSW, Australia
Background and objective: Case finding of patients at risk of COPD by community pharmacists could identify a substantial number of people with undiagnosed COPD, but little is known about the feasibility and effectiveness of pharmacy-based COPD case finding using microspirometry. The objective of this study was to assess the feasibility and effectiveness of COPD case-finding service provided by community pharmacists, utilizing a combination of risk assessment questionnaire and microspirometry.
Methods: A 6-month service was conducted in 21 community pharmacies in Australia. Pharmacists trained in COPD case finding, including lung function test (LFT), invited their patients aged ≥35 years with a history of smoking and/or respiratory symptoms to participate. High-risk patients were identified via a COPD risk assessment questionnaire (Initial Screening Questionnaire [ISQ]) and underwent LFT. Pharmacists referred patients with a forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1)/forced expiratory volume in 6 seconds (FEV6) ratio <0.75 to their general practitioner (GP) for further assessment and diagnosis.
Results: In all, 91 of 167 (54%) patients had an ISQ score >3 indicating high COPD risk. Of the 157 patients who were able to complete LFT, 61 (39%) had an FEV1/FEV6 ratio of <0.75 and were referred to their GP. Patients with high ISQ symptoms scores (>3) were at a significantly higher risk of an FEV1/FEV6 ratio of <0.75, compared to patients with fewer COPD symptoms. A total of 15 (10%) patients were diagnosed with COPD by their GP. Another eight (5%) patients were diagnosed with other medical conditions and 87% of these were initiated on treatment. Although only half of all screened patients lived in regional areas, 93% of those diagnosed with COPD were from regional areas.
Conclusion: A brief community pharmacy-based COPD case-finding service utilizing the ISQ, LFT and GP referral is feasible and may lead to identification and diagnosis of a substantial number of people with COPD. This might be an important strategy for reducing the burden of COPD, particularly for those living in rural locations.
Keywords: COPD, community pharmacy, case finding, case detection, screening
Plain language summary
The underdiagnosis of COPD could be improved through screening using expiratory flow meter devices that are simpler than conventional spirometry in primary health care settings to reach a higher percentage of the at-risk population. A brief community pharmacy-based COPD case-finding service was conducted in Australia. It involved initial COPD risk assessment, microspirometry and general practitioner (GP) referral and had a diagnostic yield of 15% for COPD/other diseases. A higher symptom score corresponded with a significantly higher COPD risk. The COPD diagnostic yield was significantly higher in rural areas than in urban areas. Pharmacists’ confidence in providing the service and their fidelity to study processes was high.
Introduction
COPD causes ~3 million deaths annually.1 If successful strategies are not implemented, COPD is expected to be the third leading cause of death world-wide by 20301 and will lead to increasing and substantial economic and social burden.2 COPD prevalence, morbidity and mortality vary across different countries, and in Australia, it was the fifth leading cause of death in 2013 and the second leading cause of avoidable hospital admissions.3
COPD is usually not apparent until symptoms appear in the more advanced stages of the disease, and this has led to concerning rates of under- and misdiagnosis.4–7 Indeed, approximately half of those with symptomatic COPD in Australia and in other countries do not have a doctor’s diagnosis and are unable to take appropriate action to slow down the progression of COPD.8,9 Undiagnosed COPD patients typically present with breathlessness, cough and sputum production.10 As these patients have increased health care utilization before diagnosis, earlier diagnosis may allow a more rational and directed use of health care resources.11 Often the majority of COPD management is provided in primary care with the general practitioner (GP) responsible for screening, diagnosis and ongoing management, and hence, a greater awareness for early COPD diagnosis among primary care patients and their health care providers is required.12 The Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) guidelines recommend COPD diagnosis to be considered in any patient who has dyspnea, chronic cough or sputum production and a history of exposure to COPD risk factors.10 Diagnostic spirometry is the “gold standard” for fixed airway obstruction12,13 and is essential for the diagnosis and categorization of patients into the appropriate stage of COPD.14,15 However, spirometry remains underutilized in clinical practice16,17 and may not be cost-effective for routine COPD screening in primary care.18 In comparison to full spirometry, microspirometry is inexpensive and easy to use and requires minimal training to conduct the procedure and interpret results.19 It has been shown to have acceptable specificity and sensitivity compared to full spirometry for screening of COPD risk,20,21 prior to referral for confirmation with full spirometry and diagnosis.
On average, an Australian consumer visits a community pharmacy 14 times per year compared to a single visit to their GP.22 Pharmacists are comparatively accessible health professionals who have the appropriate skills and opportunity to identify and educate patients at risk of COPD and refer them to the GP for further assessment. The primary aims of this study were to assess the feasibility of a COPD case-finding service provided by community pharmacists for people at risk of COPD using microspirometry and refer them to their GP for potential diagnosis. The secondary aims were to assess the relationship between symptoms and COPD risk and to measure the proportion of people diagnosed with COPD by their GP and initiated on COPD treatment in urban and rural areas.
Methods
Study design
This was a pragmatic 6-month cross-sectional (patients), longitudinal (pharmacists) pilot study carried out in Australian community pharmacies from March 2016 to October 2016.
Ethics approval
The study received ethics approval from the University of Sydney’s Human Research Ethics Committee (HREC#2014/495).
Pharmacist recruitment and training
Community pharmacists from New South Wales (NSW) who were members of the Pharmacy Guild of Australia were invited to the COPD case-finding service, and interested pharmacists provided written informed consent for this study.
The inclusion criteria were:
- completion of an online COPD training module provided by the Lung Foundation of Australia with a pass mark of ≥80%,
- access to a suitable area to conduct lung function test (LFT) and
- willingness to screen at least 10 people at risk of COPD.
Enrolled pharmacists were provided a PiKo-6® microspirometer and received face-to-face training in LFT using the device. They were also provided access to online training videos developed specifically for the study, which incorporated PiKo-6 demonstration as well as information on the study protocol, study documentation, patient recruitment and communication strategies. The study coordinator telephoned each pharmacist fortnightly to provide suggestions on patient recruitment and to answer any questions on the case-finding processes.
Pharmacist confidence
Pharmacists were asked to report their confidence on five different aspects of the case-finding service at baseline and at study end. Their confidence was rated on a 5-point scale scored from 1 (not at all confident) to 5 (extremely confident).
Patient recruitment
Pharmacists were asked to promote the case-finding service in their pharmacy and to send introductory letters to their local GPs to inform them about the study. Pharmacists approached patients presenting to the pharmacy who
- requested smoking cessation products,
- had recurrent cough and requested cough suppressants or
- had a history of recurrent respiratory tract infections (more than two courses of antibiotics dispensed in the last 6 months).
Patient inclusion criteria
Patients were invited for screening if they were ≥35 years and had a history of smoking. Patients were ineligible if they were diagnosed with COPD, emphysema or chronic bronchitis; had a serious terminal illness (eg, cancer), cognitive impairment or any other comorbidity that hindered their participation or were not fluent in English.
Case-finding process
The COPD case-finding service involved three steps:
- risk assessment using the Initial Screening Questionnaire (ISQ; Table S1),
- LFT using the PiKo-6 device and
- patient referral to their GP and follow-up.
COPD risk assessment using the ISQ
The ISQ (Table S1) was developed in consultation with a COPD expert committee representing general practice, pulmonary specialists and community pharmacists and is based on the GOLD risk assessment criteria10 and COPD-X guidelines.23 The development of ISQ was based on questions within other validated instruments such as the COPD diagnosis questionnaire24 and the modified Medical Research Council (mMRC) dyspnea scale.25 The ISQ was effectively pilot tested in 125 pharmacy patients at risk of COPD,26 and small changes were made in response to their feedback for this study. It consisted of two sections: the first assessed risk exposure (eg, pollutants and tobacco smoke) and the second measured key symptoms of COPD, the impact of symptoms on activity and the history of respiratory infections. The patient was required to simply give a “yes” or “no” response to each question. All “yes” responses were scored 1 and “no” responses were scored 0. Patients were identified to be at risk if they scored ≥1 in section 1 and/or ≥1 in section 2. The Australian Lung Foundation has endorsed the ISQ and listed it as a screening checklist for use by trained pharmacists for COPD case finding.27
LFT
After obtaining the patient’s written informed consent for this study, the pharmacist checked for contraindications such as recent surgery, heart attack, pneumothorax and lung infections like pneumonia. Patients were also not eligible for LFT if they were coughing up blood, were feeling faint, had nausea or vomiting, had an intracranial aneurysm or were in the last trimester of pregnancy. The highest ratio of the three tests with reproducible results (forced expiratory volume in 1 second [FEV1] ≤0.2L of each other) was selected for interpretation. LFT results were categorized as high COPD risk (FEV1/forced expiratory volume in 6 seconds [FEV6] value <0.65; red zone), medium COPD risk (FEV1/FEV6 value 0.65–0.75; yellow zone) or low COPD risk (FEV1/FEV6 value >0.75; green zone).
Patient referral to their GP
Pharmacists referred patients at high or medium COPD risk by giving a completed GP referral form and asked them to consult their GP to discuss their LFT results. Pharmacists informed the patients that they would contact them in 14 days to collect the outcome of their GP appointment.
Patients who were judged to be at low risk of COPD but had reported at least one symptom were given information on risk factors for future development of COPD and lung disease and encouraged to see their GP.
Patient follow-up
A maximum of two follow-up telephone calls were made to each referred patient, by their pharmacist, 14 and 21 days after screening. If the patient had not visited their GP by the first call, the pharmacist advised them about the importance of early COPD diagnosis, reinforced that they go to their GP and informed them that they would call again in 7 days.
Data analysis
Data analysis was conducted using SPSS (V.24.0; IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Descriptive and relational analyses were conducted with reference to data normality. Descriptive statistics such as mean, standard deviation, median and range were calculated. Relational statistics such as paired sample t-test and chi-square test were used to compare differences between groups as appropriate. Statistical significance was determined by a P-value of <0.05.
Results
Of 27 pharmacies that initially consented, 21 pharmacies participated. In all, 55% of the pharmacists (mean age 40±10 years, 45% male) were pharmacy owners (Table 1). Four of the 21 participating pharmacies did not recruit any patients, and study documents were lost/not returned by two pharmacists, allowing us to analyze data from 15 pharmacies.
COPD risk assessment using the ISQ
A total of 181 patients were approached by the 15 pharmacies, and 167 (92%) patients (mean age 59±15.5 years, 49% male, 44% current smokers) agreed to participate (Table 1). Ten patients declined participation, and four patients were ineligible due to a preexisting respiratory condition or age <35 years.
In all, 91 of 167 (54%) participants had an ISQ score of >3 indicating high COPD risk. A total of 76 (46%) patients reported symptoms such as persistent cough, phlegm, wheeze or mucous production and 79 (47%) reported breathlessness causing prevention or limitation in activity and would get short of breath more easily than other people of their age. A family history of chronic bronchitis or emphysema was reported by 30 (18%) patients, and 78 (47%) patients linked breathlessness to aging or poor fitness. In all, 35 (21%) patients reported having a history of repeated episodes of bronchitis or respiratory tract infections.
LFT
A total of 157 of the 167 patients completed LFT. In all, 25 (16%) patients were at high COPD risk, 36 (23%) were at medium risk and 96 (61%) were at low risk. A total of 61 (38.8%) patients who were at high or medium risk were provided a GP referral; their overall mean FEV1/FEV6 was 0.66±0.11. Seven patients in the low-risk category were also referred to their GP based on the presence of symptoms or due to inconclusive LFT results (Figure 1).
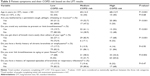
Patients at high COPD risk according to LFT had a significantly higher mean ISQ symptom score and significantly higher mean ISQ total scores than those at low COPD risk (Table 2). In all, 20 (80%) patients in the high COPD risk category reported symptoms on the ISQ, 17 (68%) reported getting short of breath more easily than others of their age and eight (32%) reported a history of repeated episodes of bronchitis or respiratory infections (Table 3). Patients with medium- to high-risk COPD were significantly older than those at low risk (mean age 65±14.3 years to 68±12.9 years versus 53±13.9 years, P<0.01), and there was a trend toward a greater likelihood of patients with medium- to high-risk COPD being female (56%–60% versus 46%, P=0.68; Table 3).
Case-finding duration
The time taken to conduct the case finding, recorded for all 157 patients, was 10±5 minutes (range 2–25 minutes).
Pharmacists’ confidence in delivering COPD case finding
Pharmacists’ confidence was high for all the five aspects of the study (ie, identifying patients at risk, conducting LFT, interpreting LFT results, referring to GPs and supporting patients’ COPD management) at baseline and at study end (Table S2). There was a trend in the patient screening rates being higher if the pharmacist had extra support staff (ie, an intern pharmacist or second pharmacist on duty) or if he or she processed a higher number of prescriptions/day or if they he or she screened their first patient soon after beginning the study.
Outcome of GP referral
Of the 68 patients referred to their GP, 15 (10%) were diagnosed with COPD. Eight (5%) further patients received other diagnoses (eg, uncontrolled asthma, lung cancer, bronchiectasis, allergic rhinitis). Eight (5%) patients received no diagnosis for COPD or any other condition (Figure 1). Of the 23 people who were diagnosed with COPD and different medical conditions, 20 (87%) were started on treatment (Figure 1).
Although only 56% (94/167) of screened patients were from regional NSW, 93% (14/15) of those diagnosed with COPD were from regional areas.
Pharmacists’ fidelity to the program
The fidelity of the participating pharmacists to the program was closely followed throughout the study. Pharmacists followed the program processes correctly, as indicated by the use of the ISQ prior to using LFT. Overall, 82% (14/17) of the pharmacists sent one or more GP introductory letters to their local GPs. Although 61 (39%) patients were categorized as being at high/medium COPD risk, pharmacists provided GP referrals to 68 (43%) patients for further assessment and diagnosis of COPD (Figure 1), based on their clinical judgment. Of the 68 patients referred to the GP for follow up, 47 (69%) GP referral letter copies were filed. Pharmacists attempted to follow-up 63 (93%) patients of whom 57 (84%) patients were successfully contacted to collect the outcome of their GP referral.
Discussion
This study demonstrates that a simple pharmacy-based case-finding service incorporating a brief risk assessment questionnaire and an LFT via an easy-to-use microspirometer can be successfully implemented in a community pharmacy setting, leading to a diagnostic yield as high as 15%, post GP referral. The study also showed that people who had a higher symptom score on the ISQ were at a significantly higher risk of COPD according to their LFT results, which is consistent with other studies.28,29 This indicates that if implemented, pharmacists could perhaps target only those with symptoms as this might be a more effective strategy. The rate of treatment initiation by the GPs, for the patients referred and diagnosed with COPD (100%) in this study, was much higher than that reported in comparable research (15%),30 highlighting the importance of informing local GPs about the case-finding program, along with follow-up reminder calls to the patients by pharmacists. These features had not been used together in previous COPD screening studies in pharmacy and may have increased both patient and GP “buy-in”.
Our study included a mixture of urban and rural pharmacies across NSW. This was important since we found higher case detection levels in rural versus urban areas. Although only half of all participants were from regional areas, the majority of those diagnosed with COPD were from regional areas indicating that case finding may be a particularly useful service in more remote locations. The higher rates of diagnosis in the regional areas could be due to a range of factors, including a level of disadvantage related to education; engaging in tobacco smoking; more occupation-related exposure to risk factors, such as farming or mining work; lower health awareness due to lower penetration of mass media coverage and comparatively poorer access and use of health services31 or simply due to a better relationship between the patients and the pharmacist, in that patients were more likely to agree to the screening and to follow up with the GP when prompted by the pharmacist.
Within the pharmacy-based model we applied, one in six individuals screened was identified to be at high risk for COPD and ~10 patients needed to be screened to diagnose one patient. This indicates that community pharmacy may be a useful setting for case-finding services. The COPD diagnostic yield of 10% was similar to the research by Castillo et al,30 which utilized full spirometry in pharmacies, indicating that our model (utilizing microspirometry) may be as useful but potentially more feasible for every day pharmacy settings.
Our diagnostic yield was only slightly lower than that obtained from screening programs utilized within Australian general practice settings (18%).32 Recent data in primary care reiterate systematic issues in the Australian primary care setting, such as a reactive and relatively delayed approach to diagnosis.33 Although cost-effectiveness analysis of the case-finding protocol was not attempted, our use of pharmacy-delivered microspirometry (instead of conventional spirometry), referring only those with high risk of COPD for onward GP review and diagnosis (instead of physicians undertaking the entire process from screening to diagnosis), the brevity of the case-finding protocol and the online modes (instead of face to face) of pharmacist training may render this model of COPD case detection more economic than conventional GP-based screening models where the onus of identifying, screening and testing potential COPD cases falls entirely upon the increasingly busy practices. In support of this, pharmacists’ confidence in providing the service, including microspirometry and their fidelity to the study protocol, was high. They followed key program processes such as correctly referring all at-risk patients to their GP and telephoning >90% of referred patients to encourage GP visits and to collect outcomes of GP referral. Indeed, this pharmacy-based model that supports more efficient diagnosis in general practice may be more readily adopted nationally to increase early recognition of COPD, especially in those people who do not go to their GP as often as visiting a pharmacy.
Limitations of the study include that 22% of pharmacists dropped out before initiating the case-finding service, and the reasons for this need to be addressed before implementing the service more widely. This pilot study had a small sample size, so changes in pharmacist confidence may have been underestimated, and future studies should measure confidence with LFT prior to provision of training. Although all the pharmacists followed the protocol and conducted three reproducible results, the PiKo-6 device, a screening tool, did not report the quality of the test. In addition, this was not a diagnostic accuracy study; hence, the case-finding protocols were not validated against standard criteria for COPD diagnosis, which is full spirometry and did not apply more stringent age-dependent lower limits of normal prediction equations (eg, GLI2012).34 Given the protocol is feasible and yielded results, further implementation should be considered. Prior to larger scale implementation, however, it may be useful to conduct a validation of the protocol (questionnaire, microspirometry and referral) against standard diagnostic methods in primary care. Furthermore, the study pharmacists were unable to confirm if all the people diagnosed with COPD after referral to the GP had undergone spirometry. Therefore, the clinical accuracy of GP’s diagnoses is assumed but not validated in our reported results.
Conclusion and future directions
Building on previous international research, this study demonstrates that case finding for COPD in community pharmacy is feasible and that there are substantial numbers of undiagnosed patients, particularly in rural settings, who might benefit from timely diagnosis.35–37 The study found that future implementation of the service would depend on pharmacists motivating patients to follow up with their GP. Perhaps, future research should consider the development of an online clinical decision support system that links community pharmacy with general practice to enhance collaboration and streamline case finding, GP referral and follow-up processes.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Pharmacy Guild of Australia and the Lung Foundation Australia for providing access to COPD online training and for providing the PiKo-6 devices to all the participating pharmacists. They thank Prof Christine Jenkins (Concord Clinical School) and Dr Brett Toelle (Woolcock Institute of Medical Research) for their advice and help with training videos. They also thank all the participating pharmacists and patients.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
World Health Organization [webpage on the Internet]. Burden of COPD. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017. Available from: http://www.who.int/respiratory/copd/burden/en/. Accessed January 23, 2017. | ||
Lopez AD, Shibuya K, Rao C, et al. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: current burden and future projections. Eur Respir J. 2006;27(2):397–412. | ||
Australian Institute of Health and Welfare [webpage on the Internet]. Australia’s Health 2016. 2016. Available from: http://www.aihw.gov.au/copd/. Accessed February 23, 2017. | ||
Hill K, Goldstein RS, Guyatt GH, et al. Prevalence and under-diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease among patients at risk in primary care. CMAJ. 2010;182(7):673–678. | ||
Bednarek M, Maciejewski J, Wozniak M, Kuca P, Zielinski J. Prevalence, severity and under-diagnosis of COPD in the primary care setting. Thorax. 2008;63(5):402–407. | ||
Vandevoorde J, Verbanck S, Gijssels L, et al. Early detection of COPD: a case finding study in general practice. Respir Med. 2007;101(3):525–530. | ||
Jordan RE, Lam KB, Cheng KK, et al. Case finding for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a model for optimising a targeted approach. Thorax. 2010;65(6):492–498. | ||
Xuan W, Toelle BG, Bird T, et al. Prevalence of respiratory symptoms, illnesses and spirometric diagnoses by age group and sex: the burden of lung disease (BOLD) study. A50. COPD Epidemiology. American Thoracic Society; 2011;183:A1734; Denver, Colorado. | ||
Lindberg A, Bjerg-Backlund A, Ronmark E, Larsson LG, Lundback B. Prevalence and underdiagnosis of COPD by disease severity and the attributable fraction of smoking report from the obstructive lung disease in Northern Sweden Studies. Respir Med. 2006;100(2):264–272. | ||
Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease [homepage on the Internet]. From the Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD, Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD). 2017. Available from: www.goldcopd.org. Accessed March 30, 2017. | ||
Akazawa M, Halpern R, Riedel AA, Stanford RH, Dalal A, Blanchette CM. Economic burden prior to COPD diagnosis: a matched case-control study in the United States. Respir Med. 2008;102(12):1744–1752. | ||
Vermeire P. The burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir Med. 2002;96(suppl C):S3–S10. | ||
Levy ML, Quanjer PH, Booker R, Cooper BG, Holmes S, Small I. Diagnostic spirometry in primary care: proposed standards for general practice compliant with American Thoracic Society and European Respiratory Society recommendations. Prim Care Respir J. 2009;18(3):130–147. | ||
Fabbri LM, Boschetto P, Mapp CE. COPD guidelines: the important thing is not to stop questioning. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;176(6):527–528. | ||
Soriano JB, Zielinski J, Price D. Screening for and early detection of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet. 2009;374(9691):721–732. | ||
Han MK, Kim MG, Mardon R, et al. Spirometry utilization for COPD: how do we measure up? Chest. 2007;132(2):403–409. | ||
Joo MJ, Lee TA, Weiss KB. Geographic variation of spirometry use in newly diagnosed COPD. Chest. 2008;134(1):38–45. | ||
Wilt TJ, Niewoehner D, Kim C, et al. Use of Spirometry for Case Finding, Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). Summary, Evidence Report/Technology Assessment No. 12. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (Prepared by the Minnesota Evidence-Based Practice Center); 2005. AHRQ Publication No: 05–E017–1, Contract No: 290–02–0009. | ||
Frith P, Crockett A, Beilby J, et al. Simplified COPD screening: validation of the PiKo-6® in primary care. Prim Care Respir J. 2011;20(2):190–198. | ||
Van den Bemt L, Wouters BC, Grootens J, Denis J, Poels PJ, Schermer TR. Diagnostic accuracy of pre-bronchodilator FEV1/FEV6 from microspirometry to detect airflow obstruction in primary care: a randomised cross-sectional study. NPJ Prim Care Respir Med. 2014;24:14033. | ||
Jing JY, Huang TC, Cui W, Xu F, Shen HH. Should FEV1/FEV6 replace FEV1/FVC ratio to detect airway obstruction? A meta-analysis. Chest. 2009;135(4):991–998. | ||
The Pharmacy Guild of Australia. Serving Australians: A system of community pharmacy. 2016. Available from: https://www.guild.org.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0020/5942/serving-australians-a-system-of-community-pharmacy.pdf. Accessed August 30, 2017. | ||
Yang IA, Dabscheck E, George J, et al. The COPD-X Plan: Australian and New Zealand Guidelines for the management of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 2017. Version 2.50, June 2017. Available from: http://copdx.org.au/copd-x-plan/. Accessed August 30, 2017. | ||
Sichletidis L, Spyratos D, Papaioannou M, et al. A combination of the IPAG questionnaire and PiKo-6® flow meter is a valuable screening tool for COPD in the primary care setting. Prim Care Respir J. 2011;20(2):184–189. | ||
Celli BR, Cote CG, Marin JM, et al. The body-mass index, airflow obstruction, dyspnea, and exercise capacity index in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(10):1005–1012. | ||
Allan H, Diamandis S, Saini B, Marshall D, Gavagna G, Peterson-Clark G. A Collaborative Screening, Referral and Management Process to Improve Health Outcomes in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). 2017. Available from: http://6cpa.com.au/wp-content/uploads/A-Collaborative-Screening-Referral-and-Management-Process-to-Improve-Health-Outcomes-in-Chronic-Obstructive-Pulmonary-Disease-COPD-Final-Report-Appendices-Part-Final-Report.pdf. Accessed August 4, 2017. | ||
Lung Foundation. The Results Record Form for COPD Case Finding – Pharmacy. 2017. Available from: http://lungfoundation.com.au/wp-content/uploads/2014/02/Results-Form-Pharmacy-20170314.pdf. Accessed August 8, 2017. | ||
Toelle BG, Xuan W, Bird TE, et al. Respiratory symptoms and illness in older Australians: the burden of obstructive lung disease (BOLD) study. Med J Aust. 2013;198(3):144–148. | ||
US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF), Siu AL, Bibbins-Domingo K, et al. Screening for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease US preventive services task force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2016;315(13):1372–1377. | ||
Castillo D, Burgos F, Guayta R, et al; FARMAEPOC group. Airflow obstruction case finding in community-pharmacies: a novel strategy to reduce COPD underdiagnosis. Respir Med. 2015;109(4):475–482. | ||
AIHW [webpage on the Internet]. Australia’s Health 2016. Australia’s Health No. 15. Cat. No. AUS 199. Canberra: AIHW; 2016. Available from: http://www.aihw.gov.au/rural-health/access-to-health-services/. Accessed May 14, 2017. | ||
Zwar N, Bunker JM, Reddel HK, et al. Early intervention for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by practice nurse and GP teams: a cluster randomized trial. Fam Pract. 2016;33(6):663–670. | ||
Bereznicki B, Walters H, Walters J, Peterson G, Bereznicki L. Initial diagnosis and management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Australia: views from the coal face. Intern Med J. 2017;47(7):807–813. doi:10.1111/imj.13418. | ||
Quanjer PH, Stanojevic S, Cole TJ, Baur X, Hall GL, Culver B. Multi-ethnic reference values for spirometry for the 3–95 year age range: the global lung function 2012 equations. Eur Respir J. 2012;40(6):1324–1343. | ||
Wright D, Twigg M, Thornley T. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease case finding by community pharmacists: a potential cost-effective public health intervention. Int J Pharm Pract. 2015;23(1):83–85. | ||
Castillo D, Guayta R, Giner J, et al; FARMAEPOC group. COPD case finding by spirometry in high-risk customers of urban community pharmacies: a pilot study. Respir Med. 2009;103(6):839–845. | ||
Fuller L, Conrad WF, Heaton PC, Panos R, Eschenbacher W, Frede SM. Pharmacist-managed chronic obstructive pulmonary disease screening in a community setting. J Am Pharm Assoc. 2012;52(5):e59–e66. |
Supplementary materials
  | Table S1 Initial COPD screening questionnaire |
 © 2017 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2017 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.