Back to Journals » Cancer Management and Research » Volume 13
Circ_0035483 Functions as a Tumor Promoter in Renal Cell Carcinoma via the miR-31-5p-Mediated HMGA1 Upregulation
Received 18 September 2020
Accepted for publication 15 December 2020
Published 25 January 2021 Volume 2021:13 Pages 693—706
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S282806
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Xueqiong Zhu
Zheng Liu,1,* Ronghai Wang,2,* Guangze Zhu3
1Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Acupuncture, Central Hospital of Baoji, Baoji City, Shaanxi Province, People’s Republic of China; 2Department of Urology, Linzi District People’s Hospital, Zibo City, Shandong Province, People’s Republic of China; 3Department of Clinical Laboratory Medicine, The Affiliated Hospital to Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, Changchun City, Jilin Province, People’s Republic of China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Correspondence: Guangze Zhu
Department of Clinical Laboratory Medicine, The Affiliated Hospital to Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, No. 1478 Gongnong Road, Chaoyang District, Changchun, Jilin Province 130021, People’s Republic of China
Tel/Fax +86 431-86177939
Email [email protected]
Background: Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) that originates from the proximal renal tubules is the most common cancer of the human kidney. Increasing circRNA/miRNA/mRNA networks have been found in RCC regulation. This study will explore the regulatory relation of circular RNA (circRNA) circ_0035483, microRNA-31-5p (miR-31-5p) and high mobility group A1 (HMGA1).
Methods: The levels of circ_0035483, miR-31-5p and HMGA1 were measured by real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) or Western blot. Cell proliferation was determined using Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) and colony formation assays. Cell migration and invasion were assessed by transwell assay. HMGA1 and epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related protein levels were quantified using Western blot. Glycolytic metabolism was evaluated by glucose consumption and lactate production. The interaction between targets was confirmed via dual-luciferase reporter, RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) and RNA pull-down assays. In vivo experiment was performed through the establishment of xenograft models in mice.
Results: Circ_0035483 expression was upregulated in RCC tissues and cells. The inhibitory effects on RCC cell proliferation, migration, invasion, EMT and glycolysis were induced after circ_0035483 was downregulated. MiR-31-5p was identified as a target of circ_0035483 and miR-31-5p upregulation was related to the function of circ_0035483 knockdown in RCC cells. Additionally, miR-31-5p targeted HMGA1 and inhibited the malignant behaviors of RCC cells by negatively regulating HMGA1. Moreover, HMGA1 expression was regulated by circ_0035483 via targeting miR-31-5p. Circ_0035483 also affected tumor growth in vivo by relying on the miR-31-5p/HMGA1 axis.
Conclusion: These findings clarified that the tumor-promoting function of circ_0035483 in RCC was partly achieved by regulating the miR-31-5p/HMGA1 axis.
Keywords: circ_0035483, renal cell carcinoma; RCC, miR-31-5p, HMGA1
Introduction
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) accounts for more than 90% of cancers occurred in the genitourinary system, and it is a heterogeneous disease containing different kinds of histological subtypes.1 Due to the asymptomatic property in the early phase, the targeted diagnosis has been emerging as an effective strategy for RCC screening.2 Tumor metastasis of RCC is commonly found in human anatomical sites, such as lung, bone, liver, and brain.3 The current management for RCC therapy has been rapidly developed, especially the targeted therapy.4 The molecular biomarkers are pivotal for improving the clinical diagnosis and optimizing the therapeutic outcomes.5
Noncoding circular RNAs (circRNAs) can serve as the molecular sponges of microRNAs (miRNAs) in cancer cells.6 MiRNAs also can control the expression of downstream targets by binding to the 3ʹ-untranslated regions (3ʹ-UTRs) of messenger RNAs (mRNAs).7 Moreover, circRNAs regulate the gene expression through sponging miRNAs to play their regulatory roles in various kinds of cancers.8 For example, Mao et al have reported that circRNA_000554 blocked the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of breast cancer cells via targeting miR-182 to regulate the ZFP36 level.9 Yin et al reported that circ_0046263 facilitated the malignant behaviors of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by upregulating the expression of IGFBP3 via binding to miR-133a-5p.10 Knockdown of circ_0109320 was shown to repress cell proliferation and invasion by the miR-595/E2F7 axis in non-small cell lung cancer.11
A recent RCC research indicated that circ_0035483 was upregulated in RCC and its promoting effect on tumor growth was associated with the miR-335/CCNB1 axis.12 The roles of circ_0035483 in cell migration, invasion and metabolic process of RCC are unreported, and its other molecular mechanisms need to be investigated. MicroRNA-31-5p (miR-31-5p) was downregulated in RCC and played as a suppressive role by targeting FLOT1 or CDK1.13,14 Dong et al found that high mobility group A1 (HMGA1) was overexpressed in RCC and generated the oncogenic function in cell progression of RCC.15
This study hypothesizes that circ_0035483 targets miR-31-5p and miR-31-5p targets HMGA1, and further explores the regulatory potential of circ_0035483 on HMGA1 by targeting miR-31-5p. The key point of this study is to discover the circ_0035483/miR-31-5p/HMGA1 axis in the development of RCC.
Materials and Methods
Tissue Collection
60 patients with RCC have participated in the current study and no therapy was performed for them before the surgical resection at Central Hospital of Baoji. RCC tissues (n=60) and coterminous normal tissues (n=60, more than 3 cm from RCC tissues) were carefully collected during the surgery. Instantly, these fresh tissues were immerged in RNAlater® RNA Stabilization Agent (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) for stabilizing RNA and then saved in liquid nitrogen. 60 patients have provided the written informed consent forms for this research. Moreover, all operating procedures followed the Declaration of Helsinki involving human subjects and got ratification from the Ethics Committee of Central Hospital of Baoji.
Cell Culture
Human RCC cell lines 786-O and CaKi-1 were chosen for RCC research in our study, using human kidney tube cell line HK-2 as the normal control. Three cell lines were all purchased from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA). Cell medium was prepared by mixing Roswell Park Memorial Institute-1640 (RPMI-1640; Gibco, Carlsbad, CA, USA), fetal bovine serum (FBS; 10%, Gibco) and penicillin/streptomycin solution (1%, Gibco). Cells were cultured using the nutrient medium in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2 at 37°C, using.
Cell Transfection
Small interfering RNAs (si-circ_0035483#1, si-circ_0035483#2, and negative control si-NC), miRNA mimics (miR-31-5p and miR-NC), miRNA inhibitors (anti-miR-31-5p and anti-miR-NC), and lentiviral short hairpin RNA (shRNA) vectors (sh-circ_0035483 and sh-NC) were bought from GenePharma (Shanghai, China). In addition, an empty pcDNA expression vector was acquired from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA, USA) and the recombinant pcDNA-HMGA1 vector was constructed for HMGA1 overexpression. After 786-O and CaKi-1 cell density reached 60%, the mixture of oligonucleotides or vectors, Lipofectamine™ 3000 Reagent (Invitrogen) and Opti-MEM™ I Reduced Serum Medium (Gibco) was added following the operating instruction for users.
RNA Acquisition and Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
Total RNA was extracted from the tissues samples and cells using TRIzol™ Reagent (Invitrogen), and the reverse transcription was performed via QuantiTect Reverse Transcription Kit (Qiagen) according to the manufacturers’ guidelines. Then QuantiTect SYBR® Green PCR Kit (Qiagen) was used for RNA quantification on ABI 7500 Real-Time PCR system (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). The sequences for primers were shown as below: forward, 5ʹ-TCATCCTTCTAAGGTAGCAGCAG-3ʹ and reverse, 5ʹ-CTTCGACGCTGTAGCCTTGT-3ʹ (circ_0035483); forward, 5ʹ-ACACTCCAGCTGGGAGGCAAGATGCTGGC-3ʹ and reverse, 5ʹ-TGGTGTCGTGGAGTCG-3ʹ (miR-31-5p); forward, 5ʹ-CATCCGCATTTGCTACCAGC-3ʹ and reverse, 5ʹ-GGGCTCCTTCTGACTCCCTA-3ʹ (HMGA1); forward: 5ʹ-CGGGAAATCGTGCGTGACAT-3ʹ and reverse: 5ʹ-AACCGCTCATTGCCAATGGT-3ʹ (β-actin); forward: 5ʹ-CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA-3ʹ and reverse: 5ʹ-ACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT-3ʹ (U6). β-actin and U6 acted as the housekeeping genes for circ_0035483 or HMGA1 and miR-31-5p. The comparative cycle threshold (2−∆∆Ct) method was applied for the analysis of the relative expression.
Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) Assay
The absorbance (450 nm) was measured at 0 h, 24 h, 48 h and 72 h to assess the proliferative ability of transfected 786-O and CaKi-1 cells. After cell transfection, 10 μL CCK-8 solution (Dojindo, Kumamoto, Japan) was respectively added into each well in the 96-well plates, followed by 4 h-incubation at 37°C and the detection under the microplate reader (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA).
Colony Formation Assay
Colony formation assay was also used for cell proliferation analysis. 786-O and CaKi-1 cells (200 cells/well) were transplanted into a 6-well plate after transfection for 48 h. Two weeks later, these cell colonies were fastened in 4% paraformaldehyde (Invitrogen) and dyed in 0.1% crystal violet (Solarbio, Beijing, China). Then the staining fluid was discarded and the colonies were washed in Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS; Gibco), followed by counting the colonies manually.
Transwell Assay
The transwell chamber (Corning Inc., Corning, NY, USA) was applied to perform the migration assay and transwell chamber pre-coated with matrigel (Corning Inc.) was used in the invasion assay. Briefly, 786-O and CaKi-1 cells in serum-free RPMI-1640 medium were respectively seeded into the top chamber and 10% FBS+RPMI-1640 medium was pipetted into the bottom chamber. After cell culture for 24 h in the normal condition, cells in the top chamber passed into the bottom chamber were considered as the migratory and invasive cells. 4% paraformaldehyde (Invitrogen) and 0.1% crystal violet (Solarbio) were used for cell fixation and staining. Eventually, cell images were acquired with 100 × magnification under the inverted microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan), and cell number of each group was counted.
Western Blot
Protein extraction was conducted by Radioimmunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) Lysis Buffer for tissues and cells (Solarbio). Protein products were electrophoresed on sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel (Invitrogen) and transferred onto the Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) membranes (Invitrogen), then the membranes were soaked in 5% nonfat dry milk (Cell Signaling Technology, CST; Boston, MA, USA) for protein blocking. After the incubation of primary antibodies at 4°C overnight and secondary antibody (CST, #7074, 1:3000) at room temperature for 1 h, the protein blots were discerned using ECL Chemiluminescent Substrate Reagent Kit (Invitrogen) and the expression analysis was performed by Image Lab software (Bio-Rad). Primary antibodies used in this study were listed as follows: E-cadherin (CST, #3195, 1:1000), Vimentin (CST, #5741, 1:1000), Snail (CST, #3879, 1:1000), HMGA1 (CST, #7777, 1:1000), β-actin (CST, #4970, 1:1000).
Detection of Glucose Consumption and Lactate Production
Glucose Assay Kit-WST® and Lactate Assay Kit-WST® (Dojindo) were respectively applied for detecting the consumption of glucose and the production of lactate. At 48 h post-transfection, cell supernatant was pipetted into a new tube and diluted with ultrapure water. After cell seeding into the 96-well plates, the levels of glucose and lactate were determined as per the users’ manuals.
Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay
The sequence of circ_0035483 (wild-type, WT) containing the binding sites for miR-31-5p was inserted into the pmirGLO vector (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) to construct the recombinant luciferase plasmidscirc_0035483-WT. These binding sites of miR-31-5p were mutated in the circ_0035483 sequence, and the mutant-type (MUT) sequence was used for the construction of circ_0035483-MUT. HMGA1 3ʹUTR WT and MUT sequences were also cloned into the pmirGLO vector to obtain the luciferase plasmids HMGA1 3ʹUTR-WT and HMGA1 3ʹUTR-MUT. 786-O and CaKi-1 cells were plated into the well-plates, then co-transfected with the above each plasmid and miR-31-5p or miR-NC. The firefly luciferase activity (normalized by the renilla luciferase activity) was detected using the Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay System (Promega), referring to the producer’s specification.
RNA Immunoprecipitation (RIP) Assay
786-O and CaKi-1 cells were harvested and incubated with antibody-conjugated magnetic beads according to the Dynabeads™ Protein A Immunoprecipitation Kit (Invitrogen). Total RNA was isolated from the magnetic beads of Anti-Argonaute-2 (Anti-Ago2) or Anti-immunoglobulin G (Anti-IgG) group, then the qRT-PCR was carried out for the examination of circ_0035483, miR-31-5p and HMGA1 levels.
Biotin-Coupled miR-31-5p Capture
786-O and CaKi-1 cells were transfected with the biotin-miR-31-5p mimic (Bio-miR-31-5p) or Bio-miR-NC, and cell lysates were incubated with the magnetic beads in Pierce™ Magnetic RNA-Protein Pull-Down Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The enrichment of circ_0035483 was quantified by qRT-PCR after the extraction of total RNA.
In vivo Assay
Twelve five-week-old male BALB/c nude mice were provided by Vital River Laboratory Animal Technology Co. Ltd (Beijing, China) and randomly divided into two groups. Circ_0035483 was stably knocked down by the construction of 786-O cell strain with stable expression of sh-circ_0035483, with sh-NC as the negative control group. 5 × 106 cells were subcutaneously injected into the right flank of mice back. Tumor volume (length × width2 × 0.5) was measured weekly and all those mice were euthanatized by CO2 asphyxia method (displacing 30% air in the cage each minute) after 35 days. Tumors were excised from mice and weighed on the electronic scale. Then the expression levels of circ_0035483, miR-31-5p and HMGA1 in tumor tissues were assayed by qRT-PCR or Western blot. This animal assay was performed at Central Hospital of Baoji in accordance with the Guidelines of Laboratory Animals of National Institutes of Health (NIH) and approved by Animal Ethical Committee of Central Hospital of Baoji.
Statistical Analysis
Our data were revealed as the mean ± standard error of mean (SEM). The linear relationship was analyzed using Pearson’s correlation coefficient. SPSS 24.0 was used for the statistical analysis in this study. Student’s t-test or one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s test were performed for analyzing the difference of two groups or multiple groups. P<0.05 was in the presence of significant difference.
Results
Circ_0035483 Level Was Overexpressed in RCC Tissues and Cells
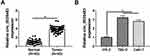
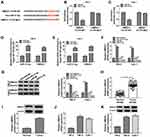
The expression detection of circ_0035483 was performed by qRT-PCR in tissues and cells. Contrasted with normal tissues, circ_0035483 expression was significantly upregulated in RCC tissues (Figure 1A). Also, the level of circ_0035483 was higher in 786-O and CaKi-1 cells than that in normal HK-2 cells (Figure 1B). The dysregulation of circ_0035483 implied its potential association with the cellular regulation of RCC.
Silencing Circ_0035483 Retarded Proliferation, Migration, Invasion and Glycolysis of RCC Cells
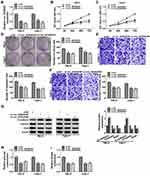
After transfection of si-circ_0035483#1 or si-circ_0035483#2 in 786-O and CaKi-1 cells, we observed the prominent downregulation of circ_0035483 expression relative to transfection of si-NC (Figure 2A). As the consequences of circ_0035483 knockdown, the inhibitory effects were found on cell proliferation by performing CCK-8 (Figure 2B–C) and colony formation (Figure 2D) assays, as well as cell migration and invasion by transwell assay (Figure 2E–F). Inhibition of E-cadherin and upregulation of Vimentin or Snail are the common indications for EMT.16 E-cadherin protein expression was increased but Vimentin and Snail protein levels were reduced in the si-circ_0035483#1 and si-circ_0035483#2 groups compared to si-NC group (Figure 2G), showing that EMT process was blocked by knockdown of circ_0035483. In addition, the low circ_0035483 expression induced the repression of glucose consumption (Figure 2H) and lactate production (Figure 2I) in 786-O and CaKi-1 cells. These experimental results indicated that the silence of circ_0035483 suppressed the malignant behaviors in RCC cells.
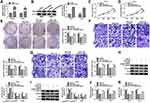
MiR-31-5p Was a miRNA Target of Circ_0035483
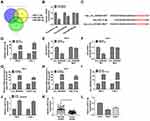
The miRNA targets of circ_0035483 were predicted by bioinformatic softwares circinteractome, circBank and Starbase3.0. Venn diagram was used for the further screening of miRNAs. As depicted in Figure 3A, three miRNAs (miR-31-5p, miR-432-5p, miR-582-5p) were mutually predicted by three softwares and considered as the candidate targets of circ_0035483. The qRT-PCR exhibited miR-31-5p and miR-432-5p were downregulated in RCC tissues compared to normal tissues while miR-582-3p expression was unchanged in RCC tissues contrasted with normal tissues (Figure 3B). The expression change of miR-31-5p was more significant than miR-432-5p, and we then further explored the target relation between circ_0035483 and miR-31-5p. Circinteractome has shown the binding sites between the sequences of circ_0035483 and miR-31-5p as the presentation in Figure 3C. Overexpression of miR-31-5p by miR-31-5p mimic (Figure 3D) resulted in the inhibition of the luciferase activity of circ_0035483-WT group, while luciferase activity of circ_0035483-MUT group was unaffected in 786-O and CaKi-1 cells (Figure 3E–F). In RIP assay, the higher enrichment of circ_0035483 and miR-31-5p was also observed in Anti-Ago group than those in Anti-IgG group (Figure 3G–H). Moreover, RNA pull-down assay indicated that circ_0035483 was largely pulled down by miR-31-5p (Figure 3I). Also, miR-31-5p level was obviously promoted after the introduction of si-circ_0035483#2 in 786-O and CaKi-1 cells in contrast with si-NC group (Figure 3J). There was a downregulating level of miR-31-5p in RCC tissues and cells compared to the normal tissues and cells (Figure 3K–L). The above data identified miR-31-5p as a miRNA target of circ_0035483.
Circ_0035483 Affected the Malignant Behaviors of RCC Cells via Negatively Regulating miR-31-5p
The expression inhibition for miR-31-5p was achieved by anti-miR-31-5p transfection in 786-O and CaKi-1 cells (Figure 4A). The relation of miR-31-5p and circ_0035483 was explored in regulating RCC cellular processes. As expected, si-circ_0035483#2-induced suppressive influences on cell proliferation (Figure 4B–D), migration and invasion (Figure 4E–F) were countervailed by the transfection of anti-miR-31-5p. The alleviative phenomenons mediated by anti-miR-31-5p for si-circ_0035483#2 were also found in EMT process (Figure 4G–H) and glycolytic metabolism (Figure 4I–J) of 786-O and CaKi-1 cells. Therefore, the effects of circ_0035483 on RCC cells were associated with the negative regulation of miR-31-5p.
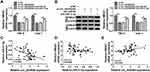
HMGA1 Was a Downstream Target of miR-31-5p
Starbase3.0 has manifested that HMGA1 3ʹUTR sequence contained the miR-31-5p-binding sites (Figure 5A). Subsequently, the dual-luciferase reporter assay (Figure 5B–C) and RIP assay (Figure 5D–E) validated the combination between HMGA1 and miR-31-5p in 786-O and CaKi-1 cells. Our qRT-PCR and Western blot results further suggested the negative modulation of HMGA1 by miR-31-5p because of the HMGA1 upregulation by miR-31-5p inhibition and HMGA1 downregulation by miR-31-5p overexpression (Figure 5F–G). HMGA1 mRNA and protein levels were found to be evidently enhanced in RCC tissues (Figure 5H–I) and cells (Figure 5J–K). Taken together, HMGA1 was a target in the downstream of miR-31-5p.
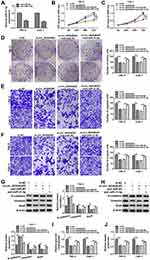
MiR-31-5p Downregulated HMGA1 to Impede the Progression of RCC
The qRT-PCR and Western blot showed that the mRNA and protein levels of HMGA1 were increased in 786-O and CaKi-1 cells transfected with pcDNA-HMGA1 compared to cells transfected with pcDNA (Figure 6A–B). Functional analysis revealed that miR-31-5p overexpression led to the distinct inhibition in cell proliferation (Figure 6C-E), migration (Figure 6F) and invasion (Figure 6G), which was ameliorated following the transfection of pcDNA-HMGA1. In the EMT process, the overexpression of HMGA1 also rescued the miR-31-5p-induced upregulation of E-cadherin and reduction of Vimentin or Snail (Figure 6H–I). Similarly, the inhibitory influences of miR-31-5p on glucose consumption and lactate production were reversed after HMGA1 expression was promoted (Figure 6J–K). MiR-31-5p acted as a repressor in RCC via targeting HMGA1.
Circ_0035483 Could Regulate HMGA1 by Serving as a Sponge of miR-31-5p
To analyze the potential association of circ_0035483 and HMGA1 via miR-31-5p, HMGA1 expression was detected after 786-O and CaKi-1 cells were transfected with si-circ_0035483#2, si-circ_0035483#2+anti-miR-31-5p or the matched controls. As illustrated in Figure 7A–B, anti-miR-31-5p transfection evidently abolished the HMGA1 expression inhibition caused by knockdown of circ_0035483. Pearson’s correlation coefficient has shown the negative relation between miR-31-5p and circ_0035483 (r=−0.465, P=0.0002) or HMGA1 (r=−0.331, P=0.0099), as well as the positive correlation between circ_0035483 and HMGA1 (r=0.313, P=0.0148) (Figure 7C–E). Collectively, HMGA1 could be regulated by circ_0035483 via targeting miR-31-5p.
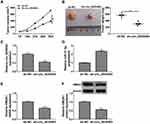
RCC Tumor Growth in vivo Was Reduced by Downregulation of Circ_0035483 via the miR-31-5p/HMGA1 Axis
Xenograft tumor assay demonstrated that tumor volume (Figure 8A) and weight (Figure 8B) were decreased in mice of sh-circ_0035483 group by comparison to that of sh-NC group. After the RNA isolation and qRT-PCR analysis, we noticed that sh-circ_0035483 triggered the repression of circ_0035483 expression (Figure 8C) and an opposite effect on miR-31-5p level (Figure 8D) in contrast with sh-NC group. In addition, HMGA1 mRNA and protein levels were reduced by the downregulation of circ_0035483 in mice (Figure 8E-F). In vivo, downregulating circ_0035483 could inhibit tumor growth of RCC via regulating the miR-31-5p/HMGA1 axis.
Discussion
RCC is one of the most lethal urological malignancies with high incidence and mortality rates.17 It is important to know the pathological mechanisms and discover biomolecules for RCC. Circ_0035483 was found to inhibit the malignant development of RCC by targeting the miR-31-5p/HMGA1 axis, which disclosed a specific functional mechanism of circ_0035483 and the potential of circ_0035483 as a biological target in RCC.
CircRNAs have been reported as crucial regulators in diverse human cancers, such as breast cancer, gastric cancer, lung cancer, and colorectal cancer.18–21 Cellular processes of RCC were reported to be affected by different circRNAs. For instance, overexpression of circ_0001368 inhibited RCC cell growth and invasion by regulating the levels of miR-492 and LATS2;22 hsa-circ-0072309 acted as an anti-tumor molecule via targeting miR-100 to inactivate the downstream signal pathways;23 circ-AKT3 inhibited the migratory and invasive abilities of RCC cells via acting on the miR-296-3p/E-cadherin network.24 In addition to the tumor-inhibitory roles, circRNAs also can exert the tumor-promoting effect on RCC. Li et al discovered that hsa_circ_0054537 contributed to the proliferation and migration in RCC cells by sponging miR-130a-3p to downregulate the cMet expression.25 Downregulation of circ_001895 or circ_000926 impeded cell growth and invasion through targeting the miR-296-5p/SOX12 or miR-411/CDH2 axis in RCC cells.26,27 In this report, the experimental results denoted that RCC cell proliferation, migration, invasion and EMT process were all suppressed with the inhibition of circ_0035483 expression.
Glycolysis is a frequent metabolic pathway in the developing process of tumor cells, accompanied by the heavy consumption of glucose and production of lactate under aerobic condition.28 Glycolytic activity is increased in proliferating cells and glycolysis is also used as a target site in the therapy of kidney cancer.29 Carcinogenic circRNAs have been found to promote glycolysis in cancer cells, such as circMAGI3 in non-small cell lung cancer,30 circMAT2B in gastric cancer31 and circDENND4C in colorectal cancer.32 However, the association of circRNAs and glycolysis in RCC is not fully explicit. The downregulation of circ_0035483 suppressed the glucose consumption and lactate production in RCC cells here, showing that circ_0035483 overexpression facilitated the glycolytic metabolism in RCC.
Regarding the researches of circRNAs as the sponges of miRNAs, Jin et al have declared that circ_0000523 retarded the evolution of colorectal cancer via miR-3133 and circ_0001564 served for a miR-29c-3p sponge to mediate the tumorigenicity in osteosarcoma.34 After the online prediction for the miRNA targets of circ_0035483 and Veen diagram analysis, three miRNAs were selected as the candidates and miR-31-5p was used for the final research subject after the expression analysis in RCC. Our data validated the combination between circ_0035483 and miR-31-5p, and the negative regulation of circ_0035483 on miR-31-5p in RCC cells. Moreover, the revert experiments manifested that the regulation of circ_0035483 in RCC cells was achieved by targeting miR-31-5p at least in part. Meanwhile, HMGA1 was demonstrated to be a target of miR-31-5p in RCC. The anti-cancer effects of miR-31-5p in RCC cell proliferation, migration, invasion and glycolysis were dependent on inhibiting the expression of HMGA1. More interestingly, circ_0035483 could regulate the level of HMGA1 by targeting miR-31-5p. The previous studies have identified the circRNA/miRNA/mRNA networks in many cancers.35–37 Not only in vitro, the circ_0035483/miR-31-5p/HMGA1 axis was also found in regulating RCC tumor growth in vivo.
Conclusion
Altogether, circ_0035483 contributed to the cellular malignant behaviors in RCC via the action on the miR-31-5p/HMGA1 axis. These findings indicated that circ_0035483 might have great clinical values as a useful biomarker for the early diagnosis and treatment of RCC patients.
Highlights
- Silence of circ_0035483 suppresses RCC cell proliferation, migration, invasion and glycolytic metabolism.
- Circ_0035483/miR-31-5p and miR-31-5p/HMGA1 axes are identified in the regulation of RCC cell malignant behaviors.
- RCC tumor growth in vivo was regulated by circ_0035483/miR-31-5p/HMGA1 axis.
Ethics Approval and Consent Participate
Written informed consent was obtained from patients with approval by the Institutional Review Board in Central Hospital of Baoji.
Disclosure
The authors declare that they have no financial conflicts of interest.
References
1. Hsieh JJ, Purdue MP, Signoretti S, et al. Renal cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17009. doi:10.1038/nrdp.2017.9
2. Usher-Smith J, Simmons RK, Rossi SH, et al. Current evidence on screening for renal cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 2020;17(11):637–642. doi:10.1038/s41585-020-0363-3
3. Dabestani S, Marconi L, Hofmann F, et al. Local treatments for metastases of renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(12):e549–561. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70235-9
4. Posadas EM, Limvorasak S, Figlin RA. Targeted therapies for renal cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017;13(8):496–511. doi:10.1038/nrneph.2017.82
5. Kotecha RR, Motzer RJ, Voss MH. Towards individualized therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2019;16(10):621–633. doi:10.1038/s41571-019-0209-1
6. Panda AC. Circular RNAs act as miRNA sponges. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1087:67–79. doi:10.1007/978-981-13-1426-1_6
7. Schuster SL, Hsieh AC. The untranslated regions of mRNAs in cancer. Trends Cancer. 2019;5(4):245–262. doi:10.1016/j.trecan.2019.02.011
8. Qu S, Yang X, Li X, et al. Circular RNA: a new star of noncoding RNAs. Cancer Lett. 2015;365(2):141–148. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2015.06.003
9. Mao Y, Lv M, Cao W, et al. Circular RNA 000554 represses epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer by regulating microRNA-182/ZFP36 axis. FASEB J. 2020;34(9):11405–11420. doi:10.1096/fj.201903047R
10. Yin L, Chen J, Ma C, et al. Hsa_circ_0046263 functions as a ceRNA to promote nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression by upregulating IGFBP3. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:562. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-02785-3
11. Bai Q, Li L, Chen F, et al. Suppression of circular RNA Hsa_circ_0109320 attenuates non-small cell lung cancer progression via MiR-595/E2F7 axis. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e921200. doi:10.12659/MSM.921200
12. Yan L, Liu G, Cao H, et al. Hsa_circ_0035483 sponges hsa-miR-335 to promote the gemcitabine-resistance of human renal cancer cells by autophagy regulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;519:172–178. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.08.093
13. Lv D, Xiang Y, Yang Q, et al. Long non-coding RNA TUG1 promotes cell proliferation and inhibits cell apoptosis, Autophagy in clear cell renal cell carcinoma via MiR-31-5p/FLOT1 axis. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:5857–5868. doi:10.2147/OTT.S254634
14. Li Y, Quan J, Chen F, et al. MiR-31-5p acts as a tumor suppressor in renal cell carcinoma by targeting cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1). Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;111:517–526. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.102
15. Dong H, Sun S, Yan T, et al. MicroRNA-195 inhibits proliferation and metastasis in renal cell carcinoma via regulating HMGA1. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12:2781–2792.
16. Odero-Marah V, Hawsawi O, Henderson V, et al. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) and prostate cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1095:101–110. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-95693-0_6
17. Capitanio U, Bensalah K, Bex A, et al. Epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2019;75(1):74–84. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2018.08.036
18. Li Z, Chen Z, Hu G, et al. Roles of circular RNA in breast cancer: present and future. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(7):3945–3954.
19. Ruan Y, Li Z, Shen Y, et al. Functions of circular RNAs and their potential applications in gastric cancer. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;14(2):85–92. doi:10.1080/17474124.2020.1715211
20. Chen Y, Wei S, Wang X, et al. Progress in research on the role of circular RNAs in lung cancer. World J Surg Oncol. 2018;16(1):215. doi:10.1186/s12957-018-1515-2
21. Wang P, He X. Current research on circular RNAs associated with colorectal cancer. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2017;52(11):1203–1210. doi:10.1080/00365521.2017.1365168
22. Chen L, Wu D, Ding T. Circular RNA circ_0001368 inhibited growth and invasion in renal cell carcinoma by sponging miR-492 and targeting LATS2. Gene. 2020;753:144781. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2020.144781
23. Chen T, Shao S, Li W, et al. The circular RNA hsa-circ-0072309 plays anti-tumour roles by sponging miR-100 through the deactivation of PI3K/AKT and mTOR pathways in the renal carcinoma cell lines. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47(1):3638–3648. doi:10.1080/21691401.2019.1657873
24. Xue D, Wang H, Chen Y, et al. Circ-AKT3 inhibits clear cell renal cell carcinoma metastasis via altering miR-296-3p/E-cadherin signals. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:151. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1072-5
25. Li R, Luo S, Zhang D. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0054537 sponges miR-130a-3p to promote the progression of renal cell carcinoma through regulating cMet pathway. Gene. 2020;754:144811. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2020.144811
26. Chen Z, Xiao K, Chen S, et al. Circular RNA hsa_circ_001895 serves as a sponge of microRNA-296-5p to promote clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression by regulating SOX12. Cancer Science. 2020;111(2):713–726. doi:10.1111/cas.14261
27. Zhang D, Yang XJ, Luo QD, et al. Down-regulation of circular RNA_000926 attenuates renal cell carcinoma progression through miRNA-411-dependent CDH2 inhibition. Am J Pathol. 2019;189:2469–2486. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2019.06.016
28. Ganapathy-Kanniappan S. Molecular intricacies of aerobic glycolysis in cancer: current insights into the classic metabolic phenotype. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2018;53:667–682. doi:10.1080/10409238.2018.1556578
29. Ghazi S, Polesel M, Hall AM. Targeting glycolysis in proliferative kidney diseases. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019;317:F1531–F1535. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00460.2019
30. Guo F, Li S, Guo C, et al. Circular RNA circMAGI3 accelerates the glycolysis of non-small cell lung cancer through miR-515-5p/HDGF. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(7):3953–3963.
31. Liu J, Liu H, Zeng Q, et al. Circular RNA circ-MAT2B facilitates glycolysis and growth of gastric cancer through regulating the miR-515-5p/HIF-1alpha axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20(1):171. doi:10.1186/s12935-020-01256-1
32. Zhang ZJ, Zhang YH, Qin XJ, et al. Circular RNA circDENND4C facilitates proliferation, migration and glycolysis of colorectal cancer cells through miR-760/GLUT1 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(5):2387–2400. doi:10.26355/eurrev_202003_20506
33. Jin Y, Yu LL, Zhang B, et al. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0000523 regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells as miRNA sponge. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2018;51(12):e7811. doi:10.1590/1414-431X20187811
34. Song YZ, Li JF. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0001564 regulates osteosarcoma proliferation and apoptosis by acting miRNA sponge. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;495(3):2369–2375. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.12.050
35. Yang G, Zhang Y, Yang J. Identification of potentially functional CircRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network in gastric carcinoma using bioinformatics analysis. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:8777–8796. doi:10.12659/MSM.916902
36. Bai S, Wu Y, Yan Y, et al. Construct a circRNA/miRNA/mRNA regulatory network to explore potential pathogenesis and therapy options of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):13659. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-70484-2
37. Liu Z, Yang Y, Yang Z, et al. Novel circRNA_0071196/miRNA19b3p/CIT axis is associated with proliferation and migration of bladder cancer. Int J Oncol. 2020;57(3):767–779. doi:10.3892/ijo.2020.5093
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.