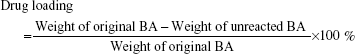Back to Journals » Drug Design, Development and Therapy » Volume 8
Characterization and in vitro studies of the anticancer effect of oxidized carbon nanotubes functionalized with betulinic acid
Authors Tan J , Karthivashan G, Arulselvan P , Fakurazi S, Hussein MZ
Received 4 July 2014
Accepted for publication 18 August 2014
Published 20 November 2014 Volume 2014:8 Pages 2333—2343
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S70650
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Professor Shu-Feng Zhou
Julia M Tan,1 Govindarajan Karthivashan,2 Palanisamy Arulselvan,2 Sharida Fakurazi,2,3 Mohd Zobir Hussein1
1Materials Synthesis and Characterization Laboratory, Institute of Advanced Technology (ITMA), Universiti Putra Malaysia, Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia; 2Laboratory of Vaccine and Immunotherapeutics, Institute of Bioscience (IBS), Universiti Putra Malaysia, Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia; 3Department of Human Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia
Abstract: Among the array of nanomaterials, carbon nanotubes have shown great potential as drug carriers in the field of nanomedicine, owing to their attractive physicochemical structure, which facilitates functionalization of therapeutic molecules onto their external walls or being encapsulated inside the tubes. The aim of this preliminary study was to formulate betulinic acid (BA), a poorly water-soluble drug, in oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT-COOH) for enhanced delivery efficiency into cancer cells with reduced cytotoxicity. The synthesized MWCNT-BA nanocomposite was characterized using ultraviolet-visible, Fourier transform infrared, thermogravimetric analysis, powder X-ray diffraction, and field emission scanning electron microscopy techniques. The loading of BA in MWCNT-COOH nanocarrier was estimated to be about 14.5%–14.8% (w/w), as determined by ultraviolet-visible and thermogravimetric analysis. Fourier transform infrared study shows that the peaks of the resulting MWCNT-BA nanocomposite correlate to the characteristic functional groups of BA and MWCNT-COOH. The powder X-ray diffraction results confirmed that the tubular structures of MWCNT-COOH were not affected by the drug loading mechanism of BA. The release profiles demonstrated that approximately 98% of BA could be released within 22 hours by phosphate-buffered saline solution at pH 7.4 compared with about 22% within 24 hours at pH 4.8. The biocompatibility studies revealed that MWCNT-BA at concentrations <50 µg/mL expressed no cytotoxicity effects for mouse embryo fibroblast cells after 72 hours of treatment. The anticancer activity of MWCNT-BA was observed to be more sensitive to human lung cancer cell line when compared with human liver cancer cell line, with half maximal inhibitory concentration values of 2.7 and 11.0 µg/mL, respectively. Our findings form a fundamental platform for further investigation of the MWCNT-BA formulation against different types of cancer cells.
Keywords: multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), drug delivery, controlled release, cytotoxicity, A549 cell line, HepG2 cell line
Introduction
Nanomedicine is the application of nanotechnology to the practice of health care and medicine.1 It has various applications in areas like drug delivery systems, in vivo imaging, in vitro diagnostics, biomaterials (eg, medical implants such as bone substitutes and dental restoratives), and tissue engineering.2 Among them, biocompatible nanomaterial-based drug delivery systems have emerged as one of the most prominent research areas in the application of nanomedicine. Nanomaterials such as carbon nanotubes (CNTs), liposomes, micelles, dendrimers, nanogels, inorganic nanoparticles, and quantum dots are a set of materials where at least one dimension is <100 nm, and they can be further engineered into novel formulations for the applications of both controlled and targeted drug delivery.3,4
Carbon-based nanoparticles such as CNTs are the most extensively studied nanomaterials due to their unique architectural properties. Multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) were first introduced by Iijima5 in 1991 via an arc-discharge method, and 2 years later he reported another form of nanotubes, a single-layered rolled-up graphene sheet known as single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs).6 In recent years, there has been a significant amount of work carried out in order to study the physicochemical properties (eg, electrical, mechanical, structural, chemical, and thermal) of CNTs7–9 and to explore various possible applications for these novel materials, including being employed as the drug delivery candidate in nanomedicine.10–14 The application of CNTs in nanomedicine is subject to their surface functionalization (eg, noncovalent or covalent modification), in which hydrophilic groups are introduced onto the hydrophobic surface of CNTs to improve their biocompatibility in a physiological environment.14–18 Many in vitro and in vivo studies using functionalized CNTs have been performed in recent years to enhance drug efficacy as well as solubility while reducing the side effects of the drug. For example, Zheng et al16 demonstrated that poly(amidoamine)-functionalized MWCNTs with a higher drug loading capacity increased the solubility of carvedilol (a poorly water-soluble drug used to treat hypertension) significantly. In another study, conducted by Ji et al18 using chitosan-functionalized SWCNTs for the delivery of anticancer drug doxorubicin, their results showed that the drug delivery system killed the liver cancer cells effectively and inhibited the growth of liver cancer in nude mice, while demonstrating negligible in vivo toxicity.
Betulinic acid (BA) (3β-hydroxyl-lup-20(29)-en-28-oic acid, Figure 1) is a pentacyclic triterpenoid extracted from a naturally occurring phytocompound called betulin. It is reported to possess a broad range of therapeutic properties, including antiviral, antioxidant, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, anti-HIV, antiangiogenic, and anticancer effects, against neuroectodermal origin and melanomas tumour.19–22 However, BA has a low solubility in water, and therefore commercially oxidized MWCNTs were used as the drug vehicle for efficient delivery. In this work, we report on the characterization of novel BA-loaded MWCNTs (MWCNT-BA) by ultraviolet-visible (UV/vis), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD), and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) techniques and investigate their release profiles. In addition, cell cytotoxicity properties of MWCNT-BA nanocomposite were evaluated using 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) proliferation assay in healthy mouse embryo fibroblast cells (3T3), human liver cancer cells (HepG2), and human lung cancer cells (A549) in order to determine the anticancer effects of the nanocomposite in vitro.
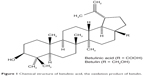  | Figure 1 Chemical structure of betulinic acid, the oxidation product of betulin. |
Materials and methods
Chemicals
BA (high-performance liquid chromatography grade) and phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) solution were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Saint Louis, MO, USA). Methanol obtained from HmbG Chemicals (Germany) was used to dissolve BA. MWCNT-COOH with a diameter of 20–30 nm, length of 0.5–2.0 μm, and purity of >95% from chemical vapour deposition production were supplied by Chengdu Organic Chemicals Co. Ltd, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Chengdu, People’s Republic of China). All other chemicals and solvents used in this work were of reagent grade and used as purchased without further purification.
Physicochemical characterization
To determine the drug loading and release, a UV/vis spectrophotometer (PerkinElmer, Lambda 35, Waltham, MA, USA) was used. FTIR spectra were recorded over the range of 500–4,000 cm−1 on an FTIR spectrometer (Thermo Nicolet Nexus, Smart Orbit, Vernon Hills, IL, USA) with 4 cm−1 resolution, fitted with attenuated total internal reflectance sampling accessory. Approximately 1% sample in 200 mg of spectroscopic grade potassium bromide was used and the pellet pressed at 10 tonnes. To determine the actual drug loading, TGA and differential TGA (DTGA) were performed using a TGA Q500 (TA Instruments, New Castle, DE, USA) with a heating rate of 10°C/min, from room temperature to 1,000°C, under a nitrogen atmosphere (nitrogen flow rate 40 mL/min). The drug content was determined from the weight loss between 200°C and 900°C. PXRD patterns were obtained with a PXRD-6000 diffractometer (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) with a dwell time of 0.5°/min. Data were recorded in the range of 4°–90° (diffraction angle 2θ) using CuKα radiation (λ=1.5418 Å) at 30 kV and 30 mA. The surface morphology of the samples was obtained with field emission scanning electron microscopes (JEOL, JSM-7600F, Tokyo, Japan).
Preparation of CNT-BA formulation
Briefly, 10 mg of MWCNT-COOH was added to 0.125 mg/mL of prepared BA solution and sonicated for 30 minutes at room temperature in an ultrasonic bath. The mixture was then magnetically stirred at room temperature to facilitate BA attachment onto the nanotubes. After stirring for 22 hours, the mixture was centrifuged at 4,000 rpm for 15 minutes, leaving a black precipitate (the product) at the bottom of the centrifuge tube and a clear supernatant, which was retained for further measurement. The product still contained an excessive amount of unreacted (not attached) BA, which was removed by washing with ethanol and deionized water. After three cycles of washing, centrifuging, and decanting, the product was finally dried at 60°C in an oven for 24 hours to yield a dry powder of MWCNT-BA nanocomposite. The resulting MWCNT-BA nanocomposite was stored in a desiccator at room temperature until further characterizations.
Drug loading evaluation
The amount of unreacted BA in the supernatant as described was measured at λ=209 nm by a UV/vis spectrophotometer. The loading of BA in MWCNT-COOH was calculated by the following equation:
| (1) |
In vitro release of drug at different pH levels
The drug release process was investigated according to the previous method.23 Briefly, suspensions of BA-loaded MWCNTs (1 mg) were prepared in 3.5 mL of PBS solution (pH 7.4 or pH 4.8) at a concentration of 0.01 mol/L. PBS solution contains a number of anions, like monobasic phosphate H2PO4−, dibasic phosphate HPO42−, and Cl−, which can affect the rate of the release. At predetermined time points, the accumulated release of BA in the release medium was measured by UV/vis spectrophotometer at λmax=209 nm due to the observed intense absorbance of BA at 209 nm. PBS solution of pH 7.4 or pH 4.8 was used as the blank solution in the drug release study. Data obtained from this in vitro release study were then fitted to three kinetic models, namely pseudo-first order, pseudo-second order, and parabolic equations to evaluate the release kinetic profiles. Relevant correlation coefficients were taken into consideration for the approach of best model selection.
Cell cultures: 3T3, HepG2, and A549 cell lines
Nontumorigenic normal mouse embryo fibroblast cells (3T3), human liver cancer cells (HepG2), and human lung cancer cells (A549) were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA). The cells were cultured in RPMI 1640 medium (Invitrogen, Auckland, New Zealand) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% antibiotics (100 μg /mL penicillin and 100 μg/mL streptomycin). The cells were maintained and incubated at 37°C in a humidified chamber (5% CO2, 95% room air) and grown to 80% confluence. The confluent cell layers were then harvested from T-75 flasks using trypsin-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and resuspended in fresh culture medium.
Preparation of CNT-BA formulation for cell viability assay
In the present study, all experiments were carried out in triplicate and a freshly prepared compound was used to treat the cells each time. MWCNT-COOH, BA, and MWCNT-BA compound were prepared separately in PBS solution. A stock concentration (10 mg/mL) of each compound was sonicated for 15 minutes with a Power Sonic 505 (HwaShin Technology Co., Seoul, Korea) and subsequently diluted to the required doses via serial dilutions. For further dispersion, the suspensions were vortex agitated for 2 minutes briefly prior to cell treatment. The suspensions of the test materials with different doses (0.78–50 μg/mL) were immediately added to the cells and incubated for 72 hours to assess cytotoxicity.
Cytotoxicity assay
MTT proliferation assay previously described by Mosmann24 was used to measure the cytotoxicity and anticancer effects of MWCNT-COOH nanocarrier, free drug BA, and MWCNT-BA formulation on the three cell lines. The MTT assay converts tetrazolium salt into a dark blue formazan product via mitochondrial dehydrogenases. The metabolic activity of cells is proportional to the color density formed. Considering that only active mitochondria contain these enzymes, this reaction only occurs in viable cells.
In brief, the cells were seeded into 96-well flat bottom microplates at a density of 1×105 cells/mL and kept in 5% CO2 humidified atmosphere at 37°C for 24 hours (cell attachment and cell recovery after trypsinization). Subsequently, the cells were treated with different doses ranging from 0.78 to 50 μg/mL. The untreated cell (control) was also included. Following incubation for 72 hours, 20 μL of MTT solution (5 mg/mL) was added to each well and further incubated at 37°C for 4 hours. Next, the supernatant from the wells was carefully removed and replaced with dimethyl sulfoxide (100 μL/well) to dissolve the dark blue formazan crystals formed due to the reduction of tetrazolium by living cells. The absorbance was measured at 570 nm and 630 nm (reference wavelength) using a microplate enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay reader (ELx800, BioTek Instruments, Winooski, VT, USA). The data obtained were averaged and fitted to Equation 2 to calculate the percentage of cell viability. The concentration that inhibits 50% of the cellular growth (IC50, half maximal inhibitory concentration) of the cell viability was then determined from the cell inhibitory growth curve by extrapolation:
Cell viability (%) = (Averagetest/Averagecontrol) ×100 | (2) |
Statistics
Results were analyzed using SPSS Version 20.0 software (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA). One-way analysis of variance was used to statistically evaluate the experimental data. All data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. The difference was considered significant at P-value <0.05.
Results and discussions
Physicochemical characterization
Drug loading
In the current work, the loading of BA in MWCNT-COOH was determined by a UV/vis spectrophotometer. After the centrifuge separation, the supernatant was collected and then measured at 209 nm, which is the characteristic absorption for BA (Figure 2). By comparing the absorbance of the unreacted BA in the supernatant with the original BA solution, the loading of BA was calculated to be around 14.8wt%. Figure 3 shows a schematic drawing of the possible interaction of BA noncovalently attached to MWCNT-COOH via π-π stacking and hydrogen bond between –OH and –COOH groups.
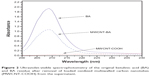  | Figure 2 Ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry of the original betulinic acid (BA) and BA residue after removal of loaded oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT-COOH) from the supernatant. |
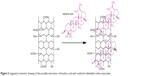  | Figure 3 Suggested schematic drawing of the possible interaction of betulinic acid with oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes. |
Fourier transform infrared
Apart from the supernatant, the product from the centrifuge separation was also characterized using the FTIR method. Figure 4 demonstrates the FTIR of the MWCNT-COOH before and after loading with BA. The bands at 2,915 and 1,383 cm−1 in the spectra of MWCNT-BA could be due to the asymmetric and symmetric C–H stretching vibrations from the methyl and methylene functional groups of BA.25 Another absorption peak observed at 1,630 cm−1 corresponding to the absorption peak of BA at 1,640 cm−1 could possibly be attributed to the typical stretching band of C=O vibrations of carboxylates. The MWCNT-BA nanocomposite was subjected to three cycles of washing after loading with BA, which means that these bands are from BA, indicating successful interaction of BA in the nanotubes.
  | Figure 4 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy of oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) before and after loading with betulinic acid (BA). |
Thermogravimetric and differential thermogravimetric analysis
TGA-DTGA was also performed on the product, and the weight loss profiles of MWCNTs before and after BA loading were used to determine the actual drug loading capacity. The TGA-DTGA curves of MWCNTs are shown in Figure 5. It is well known that the thermal degradation of MWCNTs is a multistep process. The first weight losses occurred in the range of 75°C–153°C and 100°C–185°C for both MWCNT-BA and MWCNT-COOH and are assigned to the elimination of surface physisorbed water.26 Subsequently, thermal degradation in the region between 150°C and 400°C may be due to the decarboxylation of the –COOH functional groups attached to the external walls of MWCNTs.27 The third stage, from 400°C to 600°C, could be explained by the removal of –OH functional groups present on the MWCNT walls.28 As presented in Figure 5B, MWCNT-BA lost about 33.6% by weight, whereas MWCNT-COOH exhibited a total weight loss of approximately 19.1% (Figure 5A). Therefore, the amount of drug loaded on MWCNT-COOH is calculated to be about 14.5wt%.
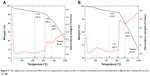  | Figure 5 Thermogravimetric analysis and differential thermogravimetric analysis profiles of oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes before (A) and after loading with betulinic acid (B). |
Powder X-ray diffraction
In the current work, PXRD was used to investigate whether a crystalline drug could be detected in the drug-loaded nanotubes. Figure 6 shows the PXRD patterns of free drug BA, MWCNT-COOH nanocarrier, and MWCNT-BA nanocomposite. Multiple sharp peaks were observed in the diffraction pattern of pure BA from 5° to 30°, indicating that BA is a highly crystalline drug. These peaks were not present in the diffraction pattern of MWCNT-BA in the range of 5°–30°, suggesting that BA could be loaded by MWCNTs in molecular form. In addition to that, the diffraction pattern of MWCNT-BA remained the same with the diffraction pattern of MWCNT-COOH. This indicates that the carbon graphitic crystallite structure of MWCNTs was not affected by the drug loading process. Similar XRD results were also obtained by Zheng et al16 and Jain et al29 on the biomolecule-loaded nanotubes.
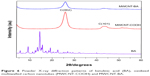  | Figure 6 Powder X-ray diffraction patterns of betulinic acid (BA), oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT-COOH) and MWCNT-BA. |
Field emission scanning electron microscope
The surface morphology of the MWCNTs before and after loading with BA was observed by FESEM (Figure 7). Figure 7A shows the typical image of the commercially obtained MWCNT-COOH with a smooth surface in an agglomerated state. Following the drug loading process (Figure 7B), the MWCNT-BA had a granular surface in a more dispersed form. This indicates that the surface of MWCNTs was coated with BA, and the coating was found to further reduce the van der Waals force that exists between the nanotubes.
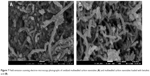  | Figure 7 Field emission scanning electron microscopy photographs of oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes (A) and multiwalled carbon nanotubes loaded with betulinic acid (B). |
In vitro release behavior of drug at different pH levels
CNTs tend to aggregate and form bundles due to van der Waals forces, which can significantly decrease their surface area accessible for adsorption. According to Foldvari and Bagonluri,30 there are four types of adsorption sites available for adsorption on CNTs, namely inner tubes, external surface, groove area, and interstitial pores. However, only the external surface of CNTs is generally available for adsorption.31 The inner tubes are not readily available for adsorption due to the dimensional limitation as a result of the presence of metals and amorphous carbon on both ends of the tube.32 Moreover, most organic molecules are too big to be adsorbed in the interstitial sites.33 Based on the molecular structure of BA with many aromatic rings, we conclude that the BA molecules are noncovalently adsorbed on the surface of the oxidized nanotubes through hydrogen bonds and by electrostatic as well as π-π stacking interaction.
pH value is one of the most important factors for studying the drug release process. In this work, the release profile of BA from MWCNT-COOH nanocarrier in PBS solution at pH 7.4 and 4.8 was investigated and is shown in Figure 8. The release of BA from its nanocarrier showed a relatively faster release of about 86% in the first 100 minutes (Figure 8A), followed by a slower step of sustained release of 98% in a later period (Figure 8B) when exposed to pH 7.4 buffer. When the pH of the buffer changed to pH 4.8, the release rate of BA decreased to the extent of 22% in 1,300 minutes. This indicates that the release of BA from BA-loaded MWCNTs is pH triggered. The different release rates observed could possibly be attributed to the increased solubility of MWCNT-COOH in aqueous solution of increasing pH values,34 which leads to weakening of the π-π stacking interaction and hydrogen bonding interaction between the –OH groups from BA and the –COOH groups from nanotube surface. In addition, the repulsive forces between the ionized MWCNT-COO− and BA− could be one of the reasons contributing to the different kinetics of BA released at different pH levels. Therefore, the release of BA would occur by an exchange process between the anions in the buffer and –COOH from the nanocarrier.
  | Figure 8 Release profiles of betulinic acid from oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes into phospate-buffered saline solution at pH 7.4 and 4.8 within (A) 100 minutes and (B) 1,300 minutes. |
In vitro release kinetics of drugs at different pH levels
To evaluate a drug delivery system, drug release kinetics is another crucial factor to take into consideration. In this study, pseudo-first order (Equation 3), pseudo-second order (Equation 4), and a parabolic diffusion kinetic model (Equation 5) were used35–37 to investigate the mechanism of BA release from MWCNT-COOH nanocarrier at pH 7.4 and 4.8. The equations used to fit the release profile data are as follows:
Pseudo-first order: |
In (qe – qt) = In qe – k1t |
(3) |
Pseudo-second order: |
t/qt = 1/k2qe2 + t/qe |
(4) |
Parabolic diffusion equation: |
(1 – Mt/M0)/t = kt−0.5 + b |
(5) |
In a pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order kinetic model, the qe and qt are the equilibrium release amount and the release amount at time t, respectively; k is the constant of the corresponding release amount in all three models; and M0 and Mt in parabolic equation are the drug content that remained in the MWCNT-COOH nanocarrier at release time 0 and t, respectively.
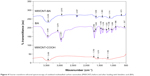
On the basis of these three models (Figure 9), it was found that for PBS solution at both pH values, the release profiles of MWCNT-BA formulation best fit to pseudo-second order kinetics (Figure 9B and E), with satisfactory correlation coefficients of 0.9994 (pH 7.4) and 0.9840 (pH 4.8). Table 1 shows the time taken for BA release to be half of accumulated release, t1/2 value, to be 58 minutes and 96 minutes for release in PBS solution at pH 7.4 and 4.8, respectively.
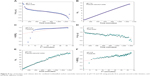  | Figure 9 Fits of betulinic acid release data for oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotube nanocarrier at pH 7.4 and 4.8 using pseudo-first, pseudo-second order kinetics, and parabolic diffusion model. |
The test results showed that the release rate of BA is significantly higher at pH 7.4 than at pH 4.8. This could possibly be due to the stronger electrostatic interaction and hydrogen bond38 at pH 4.8 compared with pH 7.4, which should reduce the amount of BA released from MWCNT-COOH. It has been reported that the intracellular pH of tumor tissues is slightly more alkaline than the extracellular fluid, which is acidosis due to the exportation of lactic acid and protons by acid base regulators from the tumor tissues.39–41 Therefore, the pH-dependent release behavior of the synthesized MWCNT-BA nanocomposite could benefit tumor treatment with controlled and sustained release properties.
Cytotoxicity assay
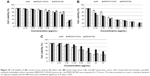
Prior to accessing drug delivery efficiency of MWCNT-BA, the biocompatibility of free drug, MWCNT-COOH, and MWCNT-BA was evaluated in advance. 3T3 normal strain fibroblasts were incubated with all of these compounds for 72 hours (Figure 10A) and the cell viabilities were tested by MTT assay. The obtained results indicated that incubation of MWCNT-BA formulation at concentration of 25 μg/mL did not cause any significant toxicity on the proliferation and viability of the 3T3 cells. However, high concentration of MWCNT-BA (50 μg/mL) resulted in a 64% loss of viable cells in 3T3 fibroblasts after 72 hours. The cause for this reduction of viable cells could possibly be associated with the effect of BA and also the functional groups (–C=O, –COOH, and/or –OH)42 present in MWCNT-COOH. On the other hand, the cell viability assay revealed that the MWCNT-COOH is concentration dependent with inhibitory response induced at the highest concentration of oxidized MWCNTs (50 μg/mL), causing a loss of >60% of the cells. This observation is in accordance with the cytotoxicity studies of Patlolla et al43 performed in normal human dermal fibroblast cells using oxidized MWCNTs at three concentrations (40, 200, and 400 μg/mL). Their findings suggested that an amount <40 μg/mL of oxidized MWCNTs could be utilized for a CNT drug delivery system in nanomedicine. Based on the MTT results in this study, the IC50 of BA, MWCNT-COOH, and MWCNT-BA was 38.0, 38.0, and 42.5 μg/mL, respectively. The results suggest that BA-loaded MWCNTs could further reduce cytotoxicity and drug-related side effects arising from the treatment with BA.
In order to evaluate the anticancer activity of the three compounds, in vitro cytotoxicity studies were also performed on two human cancer cell lines, namely A549 cells and HepG2 cells, for a treatment period of 72 hours, as shown in Figure 10B and C. It was observed that MWCNT-BA demonstrated significant cell growth inhibitory to A549 cells and moderate cell growth inhibitory activity to HepG2 in a concentration-dependent manner. The IC50 of MWCNT-BA in A549 and HepG2 cell lines was 2.7 and 11.0 μg/mL, respectively, and these values were far below those of free BA (IC50=3.5 and 15.0 μg/mL, respectively). On the other hand, MWCNT-COOH also exhibited significant cytotoxicity on A549 cells in comparison with HepG2 cells. However, cellular and molecular mechanisms of the nanocomposite were not known based on the present investigation. Other researchers have conducted a related experiment using MWCNT-OH at various concentrations (10, 20, 40, and 100 μg/mL) on A549 cell line. In their investigation, a concentration-dependent reduction in cell viability was detected after 24 hours of exposure to MWCNT-OH,44 and results showed that the viable cells were reduced by 40% at a concentration of 40 μg/mL. However, their lactate dehydrogenase results demonstrated that there was no significant cellular lactate dehydrogenase release, indicating that the membrane of the cells was not damaged. Hence, further experimental investigations are needed in order to elucidate the cellular uptake mechanism of BA in MWCNT-COOH.
Recently, another group of researchers reported the synthesis and characterization of BA prodrugs using multiarm polyethylene glycol linkers and investigated the in vitro effectiveness of the system on A549 cell line.45 Based on the cytotoxicity studies, the IC50 of BA prodrugs was 27.19–44.18 μg/mL with concentrations ranging from 2.5 to 500 μg/mL. At a concentration of 500 μg/mL, the cell viability of PEG-BA prodrugs was reduced by 90% after 72 hours of treatment. It was observed that our prepared MWCNT-BA nanocomposite demonstrated a much lower IC50, and when applied at a concentration of 50 μg/mL, the cell viability was reduced by about 80%.
Conclusion
In summary, we have designed an MWCNT formulation for the delivery of BA with enhanced delivery efficiency into cancer cells by using a simple preparation method. The characterization of the MWCNT-BA nanocomposite by FTIR and microscopic studies showed that BA molecules are loaded on the outer surface of MWCNT-COOH. This indicates that BA could be attached on the external walls of MWCNT-COOH via π-π stacking interaction due to the strong nonspecific adsorption of CNT, with a ~15% (w/w) loading of the active drug. As a result of the desorption process, BA was released from its nanocarrier in a controlled and sustained manner following pseudo-second order kinetic model. According to the in vitro MTT assay, it was observed that the MWCNT-BA nanocomposite demonstrated enhanced anticancer activity against A549 cell line in comparison with HepG2 cell line. The IC50 for MWCNT-BA in A549 and HepG2 cells was 2.7 and 11.0 μg/mL, respectively. By comparing the anticancer activity of BA alone (3.5 and 15.0 μg/mL for A549 and HepG2 cells), the studies clearly show that MWCNT-BA (about 15%wt of loaded BA) is more potent than the free drug (100% of BA), with the suggested range of concentrations <50 μg/mL. Based on these preliminary findings, our results indicate that a CNT-based delivery system could be utilized as a controlled release formulation for the delivery of drugs in cancer chemotherapies with improved therapeutic properties.
Acknowledgments
This research was sponsored by the Ministry of Education of Malaysia (MOE) under Grant No. GP-IPB/2013/9425800 and MyPhD scholarship under the MyBrain15 programme for author Julia M Tan. This financial support is gratefully acknowledged.
Disclosure
The authors declare that they have no financial or personal interests in the work described.
References
Boisseau P, Loubaton B. Nanomedicine, nanotechnology in medicine. C R Phys. 2011;12:620–636. | ||
Shi J, Votruba AR, Farokhzad OC, Langer R. Nanotechnology in drug delivery and tissue engineering: from discovery to applications. Nano Lett. 2010;10:3223–3230. | ||
Savolainen K, Pylkkänen L, Norppa H, et al. Nanotechnologies, engineered nanomaterials and occupational health and safety – a review. Safety Sci. 2010;48:957–963. | ||
Hughes GA. Nanostructure-mediated drug delivery. Nanomedicine. 2005;1:22–30. | ||
Iijima S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature. 1991;354:56–58. | ||
Iijima S, Ichihashi T. Single-shell carbon nanotubes of 1-nm diameter. Nature. 1993;363:603–605. | ||
Dai H. Carbon nanotubes: opportunities and challenges. Surf Sci. 2002;500:218–241. | ||
Tasis D, Tagmatarchis N, Bianco A, Prato M. Chemistry of carbon nanotubes. Chem Rev. 2006;106:1105–1136. | ||
Karousis N, Tagmatarchis N. Current progress on the chemical modification of carbon nanotubes. Chem Rev. 2010;110:5366–5397. | ||
Beg S, Rizwan M, Sheikh AM, Hasnain MS, Anwer K, Kohli K. Advancement in carbon nanotubes: basics, biomedical applications and toxicity. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2011;63:141–163. | ||
Bianco A, Kostarelos K, Prato M. Applications of carbon nanotubes in drug delivery. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2005;9:674–679. | ||
Lacerda L, Bianco A, Prato M, Kostarelos K. Carbon nanotubes as nanomedicines: from toxicology to pharmacology. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2006;58:1460–1470. | ||
Dinan NM, Atyabi F, Rouini M-R, Amini M, Golabchifar A-A, Dinarvand R. Doxorubicin loaded folate-targeted carbon nanotubes: preparation, cellular internalization, in vitro cytotoxicity and disposition kinetic study in the isolated perfused rat liver. Mater Sci Eng C. 2014;39:47–55. | ||
Tan JM, Arulselvan P, Fakurazi S, Ithinin H, Hussein MZ. A review on characterizations and biocompatibility of functionalized carbon nanotubes in drug delivery design. J Nanomater. 2014;Article ID 917024:20 pages. | ||
Yang F, Jin C, Yang D, et al. Magnetic functionalised carbon nanotubes as drug vehicles for cancer lymph node metastasis treatment. Eur J Cancer. 2011;47:1873–1882. | ||
Zheng X, Wang T, Jiang H, et al. Incorporation of carvedilol into PAMAM-functionalized MWNTs as a sustained drug delivery system for enhanced dissolution and drug-loading capacity. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2013;8:278–286. | ||
Modi CD, Patel SJ, Desai AB, Murthy RSR. Functionalization and evaluation of PEGylated carbon nanotubes as novel drug delivery for methotrexate. J Appl Pharm Sci. 2011;1:103–108. | ||
Ji Z, Lin G, Lu Q, et al. Targeted therapy of SMMC-7721 liver cancer in vitro and in vivo with carbon nanotubes based drug delivery system. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2012;365:143–149. | ||
Dehelean CA, Feflea S, Ganta S, Amiji M. Anti-angiogenic effects of betulinic acid administered in nanoemulsion formulation using chorioallantoic membrane assay. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2011;7:1–8. | ||
Sun YF, Song CK, Viernstein H, Unger F, Liang ZS. Apoptosis of human breast cancer cells induced by microencapsulated betulinic acid from sour jujube fruits through the mitochondria transduction pathway. Food Chem. 2013;138:1998–2007. | ||
Cichewicz RH, Kouzi SA. Chemistry, biological activity, and chemotherapeutic potential of betulinic acid for the prevention and treatment of cancer. Med Res Rev. 2004;24:90–114. | ||
Jung GR, Kim KJ, Choi CH, et al. Effect of betulinic acid on anticancer drug-resistant colon cancer cells. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2007;101:277–285. | ||
Tan JM, Karthivashan G, Arulselvan P, Fakurazi S, Hussein MZ. Characterization and in vitro sustained release of silibinin from pH responsive carbon nanotube-based drug delivery system. J Nanomater. 2014;Article ID 439873:10 pages. | ||
Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983;65:55–63. | ||
Cĭntă-Pĭnzaru S, Dehelean CA, Soica C, Culea M, Borcan F. Evaluation and differentiation of the Betulaceae birch bark species and their bioactive triterpene content using analytical FT-vibrational spectroscopy and GC-MS. Chem Cent J. 2012;6:67. | ||
Vuković G, Marinković A, Obradović M, et al. Synthesis, characterization and cytotoxicity of surface amino-functionalized water-dispersible multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Appl Surf Sci. 2009;255:8067–2075. | ||
Tang M, Dou H, Sun K. One-step synthesis of dextran based stable nanoparticles assisted by self-assembly. Polymer. 2006;47:728–734. | ||
Grandi S, Magistis A, Mustarelli P, Quartarone E, Tomasi C, Meda L. Synthesis and characterisation of SiO2-PEG hybrid materials. J Non-Cryst Solids. 2006;352:273–280. | ||
Jain AK, Dubey V, Mehra NK, et al. Carbohydrate-conjugated multiwalled carbon nanotubes: development and characterization. Nanomedicine. 2009;5:432–442. | ||
Foldvari M, Bagonluri M. Carbon nanotubes as functional excipients for nanomedicines: II. Drug delivery and biocompatibility issues. Nanomedicine. 2008;4:183–200. | ||
Gotovac S, Song L, Kanoh H, Kaneko K. Assembly structure control of single wall carbon nanotubes with liquid phase naphthalene adsorption. Colloids Surf A. 2007;300:117–121. | ||
Yang K, Zhu LZ, Xing BS. Adsorption of polycylic aromatic hydrocarbons by carbon nanomaterials. Environ Sci Technol. 2006;40:1855–1861. | ||
Hilding JM, Grulke EA. Heat of adsorption of butane on multiwalled carbon nanotubes. J Phys Chem B. 2004;108:13688–13695. | ||
Shieh YT, Liu GL, Wu HH, Lee CC. Effects of polarity and pH on the solubility of acid-treated carbon nanotubes in different media. Carbon. 2007;45:1880–1890. | ||
Kura AU, Hussein Al, Ali SH, Hussein MZ, Fakurazi S, Arulselvan P. Development of a controlled-release anti-parkinsonian nanodelivery system using levodopa as the active agent. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:1103–1110. | ||
Dong L, Yan L, Hou WG, Liu SJ. Synthesis and release behaviour of composites of camptothecin and layered double hydroxide. J Solid State Chem. 2010;183:1811–1816. | ||
Ho YS, Ofomaja AE. Pseudo-second-order model for lead ion sorption from aqueous solutions onto palm kernel fiber. J Hazard Mater. 2006;129:137–142. | ||
Kim J, Cote LJ, Kim F, Yuan W, Shull KR, Huang J. Graphene oxide sheets at interfaces. J Am Chem Soc. 2010;132:8180–8186. | ||
Griffiths JR. Are cancer cells acidic? Br J Cancer. 1991;64:425–427. | ||
Griffiths JR, Mcintyre DJ, Howe FA, Stubbs M. Why are cancers acidic? A carrier-mediated diffusion model for H+ transport in the interstitial fluid. Novartis Found Symp. 2001;240:46–62. | ||
Webb BA, Chimenti M, Jacobson MP, Barber DL. Dysregulated pH: a perfect storm for cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11:671–677. | ||
Magrez A, Kasas S, Salicio V, et al. Cellular toxicity of carbon-based nanomaterials. Nano Lett. 2006;6:1121–1125. | ||
Patlolla A, Knighten B, Tchounwou P. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes induce cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and apoptosis in normal human dermal fibroblast cells. Ethn Dis. 2010;20:S1–65–72. | ||
Ursini CL, Cavallo D, Fresegna AM, et al. Study of cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of hydroxyl-functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes on human pulmonary cells. J Nanomater. 2012;Article ID 815979, 9 pages. | ||
Dai L, Li D, Cheng J, Liu J, et al. Water soluble multiarm-polyethylene glycol-betulinic acid prodrugs: design, synthesis, and in vivo effectiveness. Polym Chem. 2014; DOI:10.1039/C4PY00648H. |
 © 2014 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2014 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.