Back to Journals » International Journal of Nanomedicine » Volume 14
Capping gold nanoparticles with albumin to improve their biomedical properties
Authors Bolaños K, Kogan MJ , Araya E
Received 9 April 2019
Accepted for publication 18 June 2019
Published 9 August 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 6387—6406
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S210992
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Anderson Oliveira Lobo
Karen Bolaños,1–3 Marcelo J Kogan,2,3 Eyleen Araya1,2
1Departamento de Ciencias Quimicas, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas, Universidad Andres Bello, Santiago, Chile; 2Departamento de Quimica Farmacologica y Toxicologica, Facultad de Ciencias Químicas y Farmacéuticas, Universidad de Chile, Santiago, Chile; 3Advanced Center of Chronic Diseases, Santiago, Chile
Abstract: Nanotechnology is an emerging field which has created great opportunities either through the creation of new materials or by improving the properties of existing ones. Nanoscale materials with a wide range of applications in areas ranging from engineering to biomedicine have been produced. Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) have emerged as a therapeutic agent, and are useful for imaging, drug delivery, and photodynamic and photothermal therapy. AuNPs have the advantage of ease of functionalization with therapeutic agents through covalent and ionic binding. Combining AuNPs and other materials can result in nanoplatforms, which can be useful for biomedical applications. Biomaterials such as biomolecules, polymers and proteins can improve the therapeutic properties of nanoparticles, such as their biocompatibility, biodistribution, stability and half-life. Serum albumin is a versatile, non-toxic, stable, and biodegradable protein, in which structural domains and functional groups allow the binding and capping of inorganic nanoparticles. AuNPs coated with albumin have improved properties such as greater compatibility, bioavailability, longer circulation times, lower toxicity, and selective bioaccumulation. In the current article, we review the features of albumin, as well as its interaction with AuNPs, focusing on its biomedical applications.
Keywords: albumin, drug delivery, photothermal therapy, theranostics
Introduction
Nanotechnology is an emerging field which has provided a wide range of opportunities in applied sciences such as materials science and medicine.1 Novel therapies for chronic diseases, including cancer, aim to overcome the adverse effects caused by the lack of specificity of conventional treatments, thereby improving drug administration.2 In this context, a new and interesting branch of nanotechnology has recently emerged which involves the use of noble metal nanoparticles covered by albumin.3
Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs), of different geometric shapes, can be used for spatially and temporally controlled drug release, thereby taking advantage of their biocompatibility, size and ease of functionalization, in addition to their optic, plasmonic and photothermal properties.4 Optic properties in AuNPs can be modulated by controlling their shape, size, and surface modification through synthetic approaches. A wide variety of AuNP shapes have been reported, including gold nanospheres (AuNSs), nanorods (AuNRs), nanoprisms (AuNPrs), nanoclusters (AuNCs), nanoflowers and core-shells.5–7 Irradiation of AuNPs in their plasmonic band, allows them to absorb and dissipate the energy as local heat, which can be exploited in biomedical applications, including photothermal therapy and drug release.8
Localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) on AuNPs is highly dependent on their shape, size, and the surrounding medium, and in this context they are useful for biosensing and detection.9 However, their unique optical properties allow not only transport and release of molecules with therapeutic properties, but also theranostic applications.10 The term “theranostic” was coined in 2002 and is defined as a material that combines the modalities of therapy and diagnostic imaging. Therefore, theranostics deliver therapeutic drugs and diagnostic imaging agents at the same time.11 Small nanoparticles can easily scatter light and be detected through techniques as simple as dark field microscopy to more complex methods such as computerized tomography.9
In a complementary way, AuNP functionalization and coating with endogenous proteins can increase the circulation time, biocompatibility, selective uptake and biodistribution of AuNP-based nanosystems.12,13 Serum albumin (SA) is the most abundant protein in plasma. SA includes a lot of amino acids with charged functional groups, such as carboxyl, amino and sulfhydryl,14 which allow it to have several binding sites for attachment to therapeutic systems, including polyconjugated dyes, drugs, and nanoparticles.2 In addition, SA can undergo cell uptake through specific receptors in tumor cells15,16 as a nutrient and amino acid source, thereby increasing the bioavailability of loaded agents.17–20
AuNPs can be capped with SA molecules or encapsulated into SA nanocapsules, thereby giving rise to multifunctional nanoplatforms, which can transport drugs and deliver them to target sites.21,22 Furthermore, the AuNP-SA system can be used in other biomedical applications, as described in the current review, including drug delivery, photothermal therapy, diagnostics and theranostics.
Recently, numerous studies concerning AuNP-SA-based systems have been reported, which represent the beginning of a promising nanoplatform for biomedical applications. Albumin has been employed extensively for pharmaceutical applications and also in clinical trials. For a more extensive discussion of the applications of albumin the reader can consult illustrative literature.2,15,16,23–28 With regard to AuNPs-SA, we believe that further developments are possible, and in the future these systems will be trialed clinically.
In the current review, we present a description of SA, a conventional but promising material in nanocarrier design, in addition to discussing AuNPs as a new and versatile material with fascinating properties, as well as forefront approaches for the creation of hybrid AuNP-SA systems.
AuNP properties for biomedical applications
Nanoparticles are defined as particles with sizes that lie between 1 and 100 nm, and which are formed in two or three dimensions. AuNPs exhibit a single structure, consisting of a highly symmetric face center cubic crystalline network.29 AuNPs are characterized by specific geometrically dependent surface properties, as well as susceptibility to several environmental stimuli, such as light or heat.30 Existing methodologies allow for AuNPs of diverse geometries, and the most common in biomedical applications are nanospheres, nanorods, nanoshells, nanocages and nanoprisms. Figure 1 shows a pictorial representation of the above-mentioned systems.
 |
Figure 1 Different shapes of gold nanoparticles used in biomedical applications. Reprinted from Journal of Experimental & Clinical Medicine, 6, Ajnai G, Chiu A, Kan T, Cheng C-C, Tsai T-H, Chang J, Trends of gold nanoparticle-based drug delivery system in cancer therapy, pages 172-178, Copyright (2014) with permission from Elsevier.47 |
For noble metal particles, where the particle size is smaller than the incident wavelength, the properties of the surface of the material influence interactions with electromagnetic radiation, and such interactions usually occur in visible (Vis) and near infrared (NIR) wavelengths.31 Interestingly, AuNPs can absorb electromagnetic radiation and convert it to thermal energy through photoexcitation mechanisms, thereby releasing heat efficiently. The energy emission and absorption properties depend on the particle shape and size.
Optical properties of AuNPs
The unique properties of AuNPs are caused by the electromagnetic effect of the collective oscillation of the surface of the electrons (conduction electrons). When conduction electrons interact with light (Figure 2), the restoring force, ie Coulombic attraction, from the electrons to the nuclei in the crystalline network, establishes a resonating condition in a relatively tight spectral band, the so-called LSPR, or surface plasmon.32 In nanoparticles that possess this property, the excitation of the surface plasmon results in substantial electromagnetic fields at the surface of the nanoparticles, which strongly outweigh the intensity of the incident light field.4
The electron density at the surface of the nanoparticle depends on its size, shape, metal structure and the surroundings, which directly affects the location of the surface plasmon in the electromagnetic spectrum (ES). In spherical AuNPs (AuNS), for example, a strong absorption band centered in the visible region (approximately 520 nm) occurs because the frequency of the electromagnetic wave of the incident light is resonant with the collective oscillation of the conduction electrons, creating the reddish tones observed in spherical AuNPs in solution. In contrast, for anisotropic AuNPs, such as rod and prism shaped (AuNRs and AuNPrs) nanoparticles, more than one band appears in the ES. AuNRs have two bands of surface plasmon resonance, which correspond to the resonant electrons in the transverse and longitudinal bands (less and more intense, respectively).33–35 Figure 3 shows a comparison between the spectra of AuNSs and AuNRs.
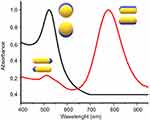 |
Figure 3 UV-Vis absorption spectrum AUNSs (black line), AUNRs (red line) and the oscillation modes on AuNPs. |
The LSPR produces unique effects in metallic nanoparticles, such as the photothermal effect through phonons, in which energy is transformed into the vibration of crystalline structures. Absorbed photons are converted into phonons, in a process that involves a rapid relaxation of electrons and phonons, followed by phonon-phonon relaxation, which results in an increase in the system temperature and conduction to its surroundings, thereby producing an increase in local temperature (Figure 4).36–39 The temperature increase produced at the AuNP surface can be used in diverse therapeutic applications, and in particular, photothermal therapy.
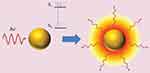 |
Figure 4 Photothermal effect on gold nanoparticles. After irradiation AuNPs absorbs light, which leads to an electronic transition of the surface electrons from a ground state (S0) to an excited state (S1). The energy is released in the environment of the nanostructure as local heat. Republished with permission of Future Medicine Ltd, from Gold nanoparticles for photothermally controlled drug release, Guerrero AR, Hassan N, Escobar CA, Albericio F, Kogan MJ, Araya E, 9, 2014; permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.32 |
It is important to mention that for biomedical applications the system should have the least possible toxicity, which requires that the absorption of the plasmon be in the so-called biological window (700–1,100 nm). In this region of the spectrum, none of the radiation is absorbed by the molecules present in human tissue, allowing the irradiation to penetrate tissues and generate a photothermal effect, without causing secondary damage.40
The development of multimodal functional nanoparticles has gained attention as a way to produce promising nanomaterials for biomedical applications.41,42 AuNPs have been one of the most used building blocks, not only for their optical properties, but also because of their load capacity, low toxicity and modifiable surface.43 AuNPs in combination with biomaterials have shown significant efficacy in the treatment of various diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease13,44,45 and several types of cancer.43,46,47
An important issue that should be considered for the pharmaceutical use of nanoparticles is that when nanoparticles are intravenously administered, several plasma proteins bind to their surface, forming the so-called protein corona.48 These capped nanoparticles can then be recognized by the macrophage cell surface and be internalized,49 leading to a significant loss of the nanoparticles from circulation. A portion of the serum proteins that bind and cap the nanoparticles are termed opsonins. Nanoparticles capped with these proteins can be recognized and captured by macrophages, contributing to the loss of the majority of the administrated dose because of retention by the reticuloendothelial system (RES).50
It is important to mention that the protein corona can change over time to create different protein profiles.51,52 Modification of colloidal particles with polymers such as polyethyleneglycol (PEG) can increase their half-life in the blood47 and also enhance the selective delivery of nanoparticles. For example, capping nanoparticles with endogenous serum proteins, such as apolipoprotein-B and/or ApoE, could support blood brain barrier penetration through transcytosis via a low-density lipoprotein receptor.53,54 Considering the importance of the protein corona for targeting purposes, it is important to reduce non-specific protein adsorption and favor the recruiting of specific proteins.
Serum albumin
SA is of great interest because it is the most abundant protein in plasma, and it has many important functions, including the regulation of blood pH and osmotic pressure.55 Albumin is a globular protein, and is non-toxic, water soluble, stable from pH 4–9 and in organic solvents,24 and exhibits several binding sites.14 Albumin acts as a solubilizing agent for fatty acids and detoxifies blood plasma, thereby reducing the levels of harmful substances such as heavy metals, reactive oxygen species and ions.25 Furthermore, SA can transport and release many compounds, such as drugs, through the plasma.55
Albumin sources
Albumin can be obtained from diverse sources, such as egg (ovalbumin, OVA), bovine serum (bovine serum albumin, BSA), human serum (human serum albumin, HSA), rat serum, soy, milk and grains.24,56 OVA, BSA and HSA are most commonly used for biophysical and biochemical studies, and all are commercially available. They have the advantages of great stability, biocompatibility, and pH and low temperature sensitivity.57 Albumin is chemically attractive because of its disulfide bonds and sulfhydryl groups, which allow interaction with organic and inorganic ligands. Table 1 presents some properties and advantages of OVA, BSA and HSA.
 |
Table 1 Properties of OVA, BSA and HSA |
Structural considerations
OVA, BSA and HSA demonstrate similarities, whereby all three are formed mainly of an α-helix with a globular formation, contain hydrophilic and hydrophobic sites, and demonstrate an acid nature. There are, however, numerous differences. Structurally, OVA consists of a single polypeptide chain of 385 amino acids, with a serpin-like structure58 and a helical reactive loop arrangement.24 OVA is widely used in the food industry because of its ability to foam and form gels.59
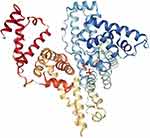 |
Figure 5 Crystal structure of BSA. Reprinted from Elsevier, 52(3-4) , Majorek KA, Porebski PJ, Dayal A, et al. Structural and immunologic characterization of bovine, horse, and rabbit serum albumins, 174-182, Copyright 2012, with permission from Elsevier.55 |
BSA (Figure 5) has 583 amino acids,60 and this protein is made up of three homologous domains, which themselves are the product of two subdomains, and their structure is 67% α-helical. BSA is attractive because of its availability, binding affinity in the formation of ligand-protein complexes, intrinsic fluorescence through its two tryptophan residues (Trp-134 in the first domain and Trp-212 in the second domain),61 and structural and functional similarities to HSA.62
Similar to BSA, HSA consists of 585 amino acids in a globular conformation, which contains three homologous domains in an α-helical ellipsoid shape.15,24,55 The amino acids in HSA can be dissimilated and used as a source of nutrition for peripheral tissues and preferentially undergo uptake by tumors and inflamed tissue.15,16 Moreover, HSA possesses different binding sites, which gives it the ability to transport drugs, hormones, fatty acids and ions through the body.24,63 These characteristics make it a good candidate for a drug delivery vehicle,57 and for use in pharmaceutical preparations.
BSA and HSA
BSA and HSA are homologous in structure, conformation and properties. In fact, BSA and HSA share 76% sequential identity,27 and the major difference lies in tryptophan (Trp) residue location. In HSA there is just one Trp, located at position 214, whilst BSA has a Trp-212 at subdomain IIA, and additionally a Trp-134 exposed in solvent at subdomain IB.64
The important differences between OVA and the other two albumins are shown in Figure 5 and Table 1. The molecular weight, size, structure, S-S bridges and SH groups differ significantly between OVA and BSA/HSA. These properties are related to binding abilities, surface modifications2 and the formation of nanostructures, which will be the core issue in the current review. For this reason, we will focus only on BSA and HSA for biomedical applications.
Compared with other albumins, BSA and HSA are less immunogenic and they are considered to be well tolerated by humans15 and are used as a protein carrier in different delivery systems.64 BSA and HSA are currently used in drug delivery approaches in which drugs are conjugated to the binding sites of the protein,65 thereby improving water solubility, therapeutic efficiency, bioavailability, biocompatibility,66 biodistribution67 and reducing drug side effects,68–70 including for anti-inflammatory, chemotherapeutic19 and hypoglycemic drugs.18,28
Capping AuNPs with albumin to increase their colloidal stability and to reduce their interaction with plasma proteins
Surface modification of nanoparticles generally provides better water solubility, increases colloidal stability, increases biocompatibility, modifies cell uptake and intracellular traficking71 and improves blood circulation time compared with bare nanoparticles. Nanoparticles can be stabilized using a wide variety of molecules, such as peptides, proteins, DNA and polymers.72–74 Functionalization of AuNPs using PEG helps to diminish interactions with plasma proteins, reduces nanoparticle phagocytosis by the reticuloendothelial system with consequent accumulation in the liver and spleen, increases the half-life in circulation and allows selective delivery to tumors.74,75 Stabilization can also be achieved by capping AuNPs with albumin.75 Capping is produced through electrostatic or hydrophobic interactions between nanoparticles and albumin or through chemisorption of the thiols to the gold surface.76 For capping, it is possible to incubate AuNPs in a solution of the protein, taking into account various parameters, such as concentration, ionic strength and pH. Controlling the pH is necessary to regulate the degree of ionization of the species, considering the isoelectric point of albumin (approximately 5) and the zeta potential of the nanoparticles to allow electrostatic interactions. Albumin-capped nanoparticles can be stabilized through steric stabilization. BSA-encapsulated AuNPs (Au-BSA) have been used to load large amounts of methotrexate, which was useful for the delivery of this drug to breast cancer cells.77
Albumin to favor the selective delivery of AuNPs
One of the exploitable features of cancer cells, in terms of increasing the selectivity of anticancer treatments, is their accelerated rate of proliferation, resulting in a higher demand for energy and nutrients.17 This demand can be supplied by increasing the protein consumption and metabolism rate. Since albumin is the predominant plasmatic protein, it is the primary nutrition source for tumor cells.18–20 This can be seen by the fact that advanced cancer patients have a low level of serum albumin (hypoalbuminemia), as a result of the widespread need for tumors to be supplied with amino acids.25
For drug delivery, there are two predominant ways in which nanosystems can reach a tumor site; these are active targeting and passive targeting. The first involves the interaction of a nanosystem with overexpressed or specific receptors in a tumor, thereby resulting in capture and further internalization at the tumor site or inside cancer cells. In this manner, albumin interacts with several specific receptors, including glycoproteins (Gp18, Gp30 and Gp60) and Secreted Protein Acidic Rich in Cysteine (SPARC), which is responsible for its recycling and transcytosis.78
Because of the active targeting demonstrated by albumin, in addition to its excellent biocompatibility, several albumin-based formulations have been proposed to overcome the drawbacks of unmodified drugs, such as rapid clearance from the body, poor solubility, and a short-half life. As a result, the FDA has approved several albumin-based drugs, including Abraxane, Levimir and Victoza, which are currently used in medical treatments for cancer and diabetes. It has been shown that these albumin-conjugated drugs can accumulate in inflamed tumors and tissues modulated by GP60 and SPARC receptors, as shown in Figure 6.15,16 Moreover, through BSA conjugation, drug biodistribution can be increased,67 and release can be promoted through protein digestion.66 In the case of albumin nanoparticles conjugated to paclitaxel, as is the case with Abraxane (clinically probed), the selective effect on tumor cells is achieved by using the endogenous mechanism for delivering proteins to cells. Albumin binding to the glycoprotein receptor gp60 on endothelial cells results in activation of caveolin-1 and the transcytosis of intact nanoparticles across the cell membrane. In addition to the active albumin-mediated transport of drugs into tumor cells, a degree of tumor-selective targeting is provided by SPARC, a protein which modulates the interaction of cells with the extracellular matrix and is over-expressed in many cancer types.79,80 Although associated with tumors, SPARC is not tumor-specific since it is found in healthy tissues, especially during embryonic development.81 Increased levels of SPARC are associated with tissue and bone remodeling and hyperproliferation, but a pronounced increase in expression is seen with malignant transformation. SPARC is present on the surface of MX-1 human mammary carcinoma cells.81 It is thought that the SPARC-mediated concentration of paclitaxel-carrying albumin molecules in the vicinity of tumor cells could lead to locally high levels of drug release.
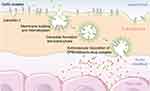 |
Figure 6 Albumin uptake in tumor interstitial mediated by transcytosis with GP60 and subsequent binding to SPARC in the extracellular tumor matrix. Reprinted from Journal of Controlled Release, 157, Elsadek B, Kratz F, Impact of albumin on drug delivery - New applications on the horizon, Pages 4-28, Copyright (2012), with permission from Elsevier. 99 |
In contrast, passive targeting refers to the accumulation of macromolecules through the enhanced permeability and retention effect (EPR), which in summary, refers to angiogenesis-generated anatomic defects in tumor blood vessels. Tumors demonstrate increased permeability, because of intercellular gaps in blood vessels, which can reach up to 4 μm (in healthy tissues such gaps are typically less than 5 nm),82–84 and which allow for the extravasation of macromolecules and nanoparticles of more than 10 nm, including viruses and bacteria.
The EPR effect depends on the size of drugs.83,85 Small drugs can freely diffuse in/out of the tumor blood vessels without accumulating, while objects between 20 and 200 nm1 can enter the tumor interstitial space without returning to the bloodstream, because of their large size.
Albumin, in addition to being used to load therapeutic and imaging agents, is also useful for surface modification of numerous types of nanoparticle, as shown in Figure 7. Surface modification of nanoparticles generally provides greater water solubility, and increased biocompatibility and blood circulation time, compared with uncoated nanoparticles.2
 |
Figure 7 Nanoparticles surface modification with albumin. Copyright © 2016. John Wiley and Sons. Reproduced from Chen Q, Liu Z. Albumin carriers for cancer theranostics: a conventionalplatform with new promise. Adv Mater. 2016;28:10557–10566.2 |
Interesting functional drug delivery systems can be obtained from AuNPs, which possess numerous useful properties such as a high surface area, protection of cargo molecules from degradation, and energy absorption and emission dependent on their size, shape and surface modification, which will be subsequently described.32,70,86 However, nanoparticles with a suitable size to allow for accumulation through passive targeting, if combined with SA, may demonstrate a dual ability to be captured through passive and active targeting, and therefore represent useful nanoplatforms for drug delivery with significant physiological stability and enhanced half-life compared with albumin or AuNPs alone.87
AuNPs and albumin
Nanotransporters have provided a wide range of opportunities in the area of drug administration.88 AuNPs offer the possibility of trapping and transporting poorly soluble or minimally biocompatible drugs, thereby improving circulation time, biocompatibility and, most importantly, preferential accumulation at a disease site.89 Metallic nanoparticles, such as magnetic nanoparticles, plasmonics and quantum dots, have various properties that make them useful for biomedical applications.
SA interaction with AuNPs induces structural changes in SA, which are dependent on the size, shape and surface modification of the AuNPs. AuNP size is an important aspect to consider in AuNP-SA interactions, and small nanoparticles have a more efficient interaction with SA compared with larger nanoparticles.90–93 However, nanoparticle shape also has a strong influence on protein adsorption in AuNPs, as demonstrated by Moustaoui et al,94 who assessed protein interaction in AuNSs and branched-shaped nanoparticles (AuNU). AuNSs showed an increase in the hydrodynamic radius, indicating that each type of protein binds on the gold nanoparticle in a specific orientation, and AuNUs showed different protein orientations because of their multi-oriented surfaces (tips) with a higher surface to volume area.
In another study, Chakraborty6 et al showed that AuNRs and AuNSs induce variations in the stability, structure and function of SA. In this work, a spectroscopic analysis comparing the interaction between SA and two nanoparticle geometries, namely that of AuNRs and AuNS with either Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) or PEG, was performed. Variation in the HSA structure was found to be higher in the order HSA-CTAB-AuNRs > HSA-CTAB-AuNSs > HSA-PEG-AuNRs > HSA-PEG-AuNSs. Accordingly, a rod shaped structure showed greater levels of denaturation than a spherical counterpart. However, the presence of CTAB on the surface resulted in a higher aggregation level, and was correlated with a positive charge, whereas PEGylated AuNPs have a near zero charge because of the neutral charge of PEG.39,95
Interestingly, shapes with planar surfaces have reduced accessibility and therefore less interaction with SA, as demonstrated by Carnovale et al96. In this novel study, the interaction between SA and AuNPs with different geometries was compared, namely AuNSs, AuNRs, AuNPrs and AuNCs. It was found that AuNRs have higher adsorption constant values, while geometric shapes with large flat planar surfaces, such as prisms and cubes, presented lower adsorption values.
Strategies for AuNP conjugation with albumin
The characteristics of its structural domains allow SA to bind to different photothermal agents, including AuNPs. The resulting structures can be observed as AuNPs with a protein “halo” or take the form of nanocapsules in which AuNPs are confined in a cavity surrounded by albumin.67
The first case, in which AuNPs present a halo, is attributable to SA attaching to AuNPs through physical or chemical adsorption, as summarized in Figure 8. This can be achieved in several ways:
- Passive adsorption: in which SA charged functional groups, or specific atoms are attached to the gold surface through covalent or non-covalent interactions. An example of this is the interaction between SH groups in the SA cysteine residues and Au atoms on the AuNP surface, giving rise to Au-S covalent bonds.68 As a result of the binding abilities of SA, direct adsorption is usually achieved through simple incubation of an AuNP solution in the presence of SA. This adsorption strategy is remarkable because of its methodological simplicity and economy, avoiding the use of additional reagents and drastic conditions.
- Active adsorption: this process is a bit more complicated because it involves the use of modified SA, with the aim to increase the amount or quality of interactions between SA-Au or SA-surface molecules on the AuNPs. Modification of SA can be achieved through functionalization, giving rise to carboxylated or thiolated SA or changes in the total charge, resulting in cationic or anionic SA.27,97 This is a convenient strategy when the AuNP surface is functionalized to other molecules or polymers, and an SA coating is required; for example, for an AuNP-PEG coating, cationic BSA can improve the covering.67
- In situ: this strategy refers to the use of albumin, either as a synthesis reagent (eg as a reducing agent) or as a building block for AuNP synthesis, where SA is added during the synthesis procedure resulting in AuNPs with an SA coating.2,98 Several studies report the use of SA as a foaming and stabilizing agent or even as a template for AuNC synthesis. As a result, AuNC-SA hybrids can be obtained through one-pot synthesis.2,98 However, SA nanocapsules are also useful as a drug delivery platform. The use of SA encapsulation methods offers some benefits, including the loading of poorly soluble agents and the protection of cargo from natural degradation.2,23,69,99 Some of the most common procedures for SA nanocapsule creation are shown in Figure 9 and are detailed below:
- Desolvation cross-linking: This method, also known as a coacervation process, is mainly used to produce core-shell SA-AuNPs, as shown in Figure 9A. In practice, AuNPs are added to an SA solution as nuclei for capsule formation, after organic solvent (usually methanol, ethanol or acetone) is added dropwise until a turbid solution is observed, in which SA is desolvated. Therefore, water solubility decreases considerably, giving rise to phase separation, and resulting in albumin aggregates. The desolvated albumin has exposed amine groups, which can be cross-linked by crosslinking agents, such as glutaraldehyde. Advantageously, this strategy allows chemical agents (including nanoparticles, drugs and diagnostic agents) to be physically entrapped inside SA capsules. SA nanocapsules are highly stable and protect entrapped agents against degradation.24,63,100
- Emulsification: Albumin has a wide variety of amino acids, some of which are hydrophobic. In a conventional emulsification procedure, a SA solution is mixed with a non-aqueous phase (oil), for shearing and high-pressure homogenization, giving rise to an emulsion. AuNPs functionalized with hydrophobic molecules can be used as seeds for interactions with hydrophobic amino acids in albumin in this procedure, generating a core-shell. For nanocapsule stabilization, either crosslinking agents or stirring at high temperatures can be used. Finally, the solvent is removed through low pressure evaporation.23,27 This is a methodology mainly used for the encapsulation of lipophilic drugs, and increases biocompatibility and water solubility.101
- Thermal gelation: Protein structure is susceptible to temperature changes. In thermal gelation, a SA aqueous solution is heated to produce protein unfolding, which induces protein-protein interactions through hydrophobic, electrostatic, disulfide and hydrogen bonding. Unfolding also gives rise to SA interactions with AuNPs, resulting in self-assembly on the AuNP surface and protein coating.101
Biomedical applications of albumin-AuNPs
Nanotransporters have provided a wide range of opportunities in the area of drug administration.88 Metallic nanoparticles, such as magnetic nanoparticles, plasmonics and quantum dots, have interesting optic properties that make them useful for biomedical applications.102 AuNPs offer the possibility of trapping and transporting poorly soluble or minimally biocompatible drugs, thereby improving circulation time, biocompatibility and, most importantly, preferential accumulation at a disease site.89 An SA coating on the surface of AuNPs increases stability, targeting and biocompatibility.
The biomedical applications discussed in the current review are summarized in Table 2 and are detailed in the following sections.
 |
Table 2 Biomedical applications of gold nanoparticles |
Albumin-AuNPs for photothermal therapy
Photothermal therapy involves the use of photoactive metals, which can convert light into heat through a previously described photothermal effect. The released heat kills malignant cells, resulting in weakening or removal of a treated tumor. Several studies have been conducted on photothermal therapy, and include the use of spherical AuNPs,76,103 nanorods, nanoshells104 and nanostars105 bound to SA. These nanobioconjugates achieved high stability, selective accumulation in malignant tissue, and selective photothermal ablation through laser irradiation.
An example of an AuNP photothermal system was reported by AL-Jawad et al,6 where AuNPs (size <5 nm) covered with BSA were synthesized and administered to rhabdomyosarcoma murine fibroblasts (L20B) and RAW 264.7 monocyte-macrophage cells. A drastic concentration-dependent photothermal ablation was achieved after a 532 nm and 800 nm irradiation, reaching more than 74% cytotoxicity for all tested cell lines. In another study, Mocan et al76 developed an original model of liver hepatocellular carcinoma, and tested the effect of AuNPs-BSA. The study showed selective accumulation of the nanosystem in tumor cells, as well as apoptosis induced by laser irradiation at 808 nm. Zhang et al106 synthesized highly stable AuNRs functionalized with BSA and administered them to fibroblast L929 and gastric adenocarcinoma YCC-2 cells in vitro, resulting in significant anticancer efficacy through NIR hyperthermia.
The inclusion of targeting agents in nanosystems results in improved properties, and increased selectivity and uptake by malignant cells. Folic acid (FA) is a widely used cancer targeting agent, since cancer cells overexpress FA receptors. This strategy was demonstrated in a study by Li et al100 in which AuNSs were synthesized and conjugated with BSA-FA, resulting in a highly stable BSA–FA–AuNS system with low toxicity. The system underwent cell uptake in HeLa cells because of overexpressed FA receptors, and cell ablation was possible after laser irradiation, reaching 70% and 75% toxicity after NIR and green laser irradiation, respectively.
Aside from FA, other molecular systems can be used to promote the cell uptake of nanocapsules, including AuNR-BSA encapsulated in ssPalmM:DOPE:cholesterol lipid, as described by Paraiso et al.107 In vitro assays with this nanosystem were performed in 4T1 breast cancer cells, in which cell viability decreased from 100% in the absence of irradiation to 11% after NIR irradiation, and an increase in dosage killed all the cells. Cell uptake played a key role in these results, since without lipid encapsulation, the AuNR-BSA system showed a plateau in killing efficiency (30% cell viability after irradiation), showing the suitability of the system for hyperthermia.
However, nanoparticle-based photothermal therapy must be carefully assessed before conducting pre-clinical trials, since it is necessary to consider the impact and harm caused by laser irradiation; this is particularly relevant for systems in which irradiation is performed at wavelengths outside the biological window.6,108,109 In such cases, the risk of radiation-induced damage makes it difficult to discern if cell death is caused by hyperthermia through the photothermal effect or by the laser itself. However, even though photothermal therapy works by killing a high percentage of malignant cells by itself, combined approaches including drug delivery and photodynamic therapy controlled by external stimuli provide added value to photothermal systems.36,110
Albumin-AuNPs for drug delivery
One of the issues that nanotechnology addresses is the lack of selectivity of existing drugs, since this problem is one of the major causes of poor efficacy, besides the undesirable secondary effects associated with current treatments.
Biomedical applications involving AuNPs are mainly based on nanoparticles with spherical,22,39,44,111–113 nanorod,12,68,107,114–118 nanoprism5,119,120 and nanocluster geometry;6,121–125 however, current synthetic methods allow for the development of nanoparticles with different morphologies. Morphological changes can also modulate the physicochemical properties of AuNPs, which in combination with SA may be improved and exploited for therapeutic applications.
Because of its bioaccumulation, targeting, biocompatibility and surface properties, albumin can transport diverse therapeutic systems in a localized way, which is denoted “spatially controlled release”. The interesting optical properties of AuNPs allow them to be monitored using imaging tools, and the photothermal effect can release adsorbed molecules on the AuNP surface, thereby temporally controlling drug release. Therefore, albumin-AuNPs are a promising system for drug delivery.
The photothermal effect is frequently used for controlled drug release, as in Peralta et al,10 where AuNRs were synthesized, conjugated to the commercial anticancer drug paclitaxel (PAC) and encapsulated in HSA, and 3 μg of PAC/mg could be loaded into the system. The nanoplatform accumulated in 4T1 mouse breast cells through the EPR effect. After irradiation, the system generated approximately 94% cell death, through a combined photothermal effect and PAC release, as shown in Figure 10, which demonstrates that the system reached its highest toxicity only after irradiation, as an external stimulus, and is therefore temporally controlled.
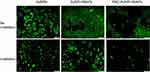 |
Figure 10 Fluorescence microscopy images of the cytotoxic effects on 4T1 breast cancer cells when treated with free AuNRs, AuNR-HSAPs or PAC-AuNR-HSAPs. (White scale bar denotes 100 μm). Reprinted with permission from Peralta DV, Heidari Z, Dash S, Tarr MA. Hybrid paclitaxel and 1030 gold nanorod-loaded human serum albumin nanoparticles for simultaneous chemotherapeutic and photothermal therapy on 4T1 breast cancer cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7:7101–7111.10 Copyright 2015 American Chemical Society. |
Callaghan et al126 reported a controlled drug delivery system based on HSAP-AuNRs, for the tyrosine kinase inhibitor sorafenib (SRF). In cytotoxicity and uptake trials in renal carcinoma cells (RCCs), this system demonstrated a dual therapeutic action, with drug release and induction of photothermal ablation by hyperthermia. HSAP-AuNR-SRFs have potential for the treatment of advanced RCC. In an additional study by Liu et al,127 AuNRs-HSA were used to encapsulate SRF and deliver it in a human metastatic cell carcinoma mouse model. The HSA-AuNR-SRF system produced 11.1% necrosis, while SRF alone produced only 4.2%; in contrast, after irradiation HSA-AuNR produced 62% necrosis and HSA-AuNR-SRF killed 100% of the cells, showing that AuNRs-HSA improved drug delivery compared with SRF alone. In addition to the ablation created by the photothermal effect, the drug load produced complementary effects, causing enhanced cell toxicity.
In another study, Wang et al128 developed a delivery system for gemcitabine (Gem) based on AuNP@BSA. The system was synthesized in a facile one-pot reaction via the reduction of HAuCl4 with BSA as a stabilizer, which was subsequently conjugated to Gem through electrostatic interaction to give rise to the AuNP@BSA-Gem system. In vitro assays in pulmonary carcinoma cells showed that the AuNP@BSA system demonstrated high biocompatibility and, as expected, a high cell death rate was produced by Au@BSA-Gem, even in comparison with free Gem.
Precise control of drug release is required to achieve optimal delivery of therapeutic agents; with this aim, Chiu et al129 developed a one-step synthesis for a doxorubicin (DOX) loaded gold nanorod/BSA core-shell (NR@DOX:BSA), which acted as an improved macrophage-mediated delivery system, with photothermal/chemotherapeutic drug distribution and retention abilities. The nanoconstruct showed low toxicity, but after irradiation, DOX was released, causing a drastic increase in cell death. In vivo studies showed that DOX exhibited limited antitumor effects because of its rapid clearance; in contrast, the synthesized nanosystem was delivered through tumor-tropic migration to tumor tissues.
Gold nanoflowers (AuNFs) represent an interesting and novel nanoparticle shape; in a recent study by Uppal and Bose,7 AuNFs were successfully capped with HSA through either electrostatic or covalent attachment, resulting in a stable system that was non-toxic in a cancer cell line (human squamous carcinoma, Nt8e). This study demonstrates the promise of AuNF-BSA for biomedical applications, such as drug delivery or theranostics.
In another study, non-conventional gold nanocube-protein hybrids (PGHNs) were constructed by Ding et al,123 using AuNCs, BSA and Trp as building blocks. The PGHNs demonstrated blue emission, high biocompatibility and cell internalization in S. ceresiviae cells. The PGHNs were loaded with rhodamine 6G and DOX separately and administered to the cells, resulting in internalization and release in the nucleus, demonstrating that they are a promising vehicle for drug delivery.
Scientific advances in nanotechnology have resulted in new nanoplatforms to treat diseases other than cancer; for example, the systems described in the current review may have applications ranging from the treatment of dermatological diseases to bacterial infections. Examples of this are included in the works of Lademann et al130 and Rastogi et al.112
Lademann et al130 focused on dermatotherapy, resulting in photoactivated fluorescein isothiocyanate release from an AuNP-doped BSA system. In an ex vivo porcine skin model, the system selectively targeted follicular ducts, because of the suitable size and biocompatibility properties of the particles. The plasmonic release of the encapsulated drug after irradiation demonstrates that this system is feasible as a plasmonic nanocarrier for the treatment of dermatological diseases.
AuNPs have also been used as antibiotic delivery systems, as demonstrated in a study by Rastogi et al,112 in which highly stable albumin-capped AuNSs were synthesized using sodium borohydride as a reducing agent. The system was functionalized for amino-glycosidic antibiotic delivery (streptomycin, neomycin, gentamicin and kanamycin), and the resulting nanoconstruct showed increased antibacterial activity against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial strains, compared with free antibiotic; therefore, this system has considerable potential for infection prevention and therapeutics.
Albumin AuNPs for diagnostic devices
One of the objectives of nanomedicine is to improve the capabilities of current medicine and make it more selective and sensitive. In this context, it is important to develop diagnostic devices to identify diseased tissue in a non-invasive way.
AuNPs have emerged as a promising diagnostic system, because of their optic properties. Moreover, they can be functionalized; for example, they can be selectively delivered to a malignant site and therefore this site can be detected by the presence of the AuNPs. One of the techniques used to detect AuNPs is photoacoustic (PA) imaging, as it is a highly sensitive nonionizing imaging modality, in which a pulsed laser can penetrate deep tissue (up to 5 cm), thereby causing rapid heating and thermal expansion, which generates an acoustic pressure wave.105 PA combined with computed tomography (CT) provides 3D visual images with high spatial resolution. For example, in Zu et al,105 BSA-capped gold nanostars (AuNS-BSA) were synthesized, and demonstrated an average size of 85 nm, excellent biocompatibility in HepG2 cells and PA contrast enhancement, which improves CT accuracy, thereby giving rise to a dual-modal CT/PA imaging contrast agent.
In addition to PA/CT, there are other techniques to detect AuNPs and their derivates. Chen et al131 synthesized AuNSs conjugated to indocyanine green (ICG) and stabilized using albumin (AuNS-ICG-BSA), which demonstrated good biocompatibility and low cytotoxicity, together with a superior photothermal ablation effect in U87 glioma cells. This represents a spatially controlled antitumor agent, and it caused cell damage only after light irradiation. However, this nanoconstruct is useful for surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) imaging-based real-time sensitive monitoring of intracellular temperature in phototh photothermal therapy (PTT). Interestingly, this system allows for the detection of small temperature variations within a cell during PTT, and this can be monitored through SERS, as a nanothermometer. A simpler system was demonstrated in a study by Florina et al132 in which highly stable and biocompatible PEG-AuNP and BSA-PEG-AuNP systems, with good internalization in A549 cells and SERS activity, were demonstrated to be promising candidates for intracellular sensing applications.
Albumin AuNP theranostic devices
In recent years, a new strategy called theranostics has become increasingly important in nanomedicine. The acronym “theranostics” derives from the words therapy and diagnosis, and a theranostic agent can detect the signs of a pathology (including tumors, infections, damaged tissue, and overexpressed receptors) and generate treatment.133 This field involves the use of systems with therapeutic action for the treatment of diseases, and which in turn, allow for non-invasive diagnosis and monitoring in real time,27 providing an efficient treatment, and early (non-invasive) detection of the disease, in addition to personalized therapy.133
To date, a great variety of theranostic platforms have been reported, including polymers, liposomes, micelles, dendrimers,134 organic materials,135,136 inorganic nanoparticles,137–139 and proteins,24,140 of which, the latter have been used as nanotransporters. Surface modifications, changes in particle size and functionalization of nanomaterials can improve biocompatibility, retention and therapeutic efficacy.
An AuNP-BSA system has shown therapeutic effectiveness in chronic diseases such as cancer, as demonstrated in a recent study by Chiu et al.138 The study demonstrated a simple one-step fabrication of a biomimetic nanomaterial (AuNR@SA) from a synthetic source. AuNRs were synthesized and encapsulated with SA, giving rise to core-shell gold nanorods-albumin, AuNR@SA. The SA capping was achieved through either glutaraldehyde crosslinking (GTA), or a denaturing method using methanol/ethanol (EM). GTA showed less interaction with endogenous proteins (SA, transferrin and fibrinogen), thereby leading to reduced protein corona formation, compared to the EM system. Moreover, GTA crosslinking resulted in a higher photothermal efficiency and temperature increase. The system was tested for DOX delivery, and produced in vivo tumor growth inhibition through NIR laser exposure, through a combination of photothermal therapy and chemotherapy. Moreover, the GTA system has proven to be useful for diagnosis with PA, showing a 3.5-fold higher signal than AuNR-CTAB in tramp C1 cells and in vivo mouse models (Figure 11A and B), as well as accumulation in tumor cells.
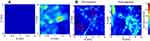 |
Figure 11 Capability of NR@SA nanoplatform for PA imaging. (A) 2 × 2 mm area of projected C-scan PA images of nontreated and NR@SA treated tramp C1 tumor cells. (B) in vivo photoacoustic imaging from tumor-bearing mice during and after local delivery of NR@SA. Reprinted with permission from Chiu HT, Chen CH, Li ML, et al. Bioprosthesis of core-shell gold nanorod/serum albumin nanoimitation: a half-native and half-artificial nanohybrid for cancer theranostics. Chem Mater. 2018;30:729–747.138 Copyright (2018) American Chemical Society. |
Another interesting system is that described by Sashidaran et al,110 where gold nanostars (AuNSs) were synthesized through a simple wet chemistry route and subsequently BSA-functionalized, yielding a stable monodispersed solution, with an average particle size of 120 nm. AuNS-BSA did not exhibit any inherent cytotoxic activity towards healthy (L929) and cancerous (KB) cells, but it showed significant photothermal ablation properties after laser exposure, thereby working as a therapeutic agent. Interestingly, the system also showed good CT imaging properties. AuNS-BSAs were loaded with rhodamine 6G, allowing the system to exhibit SERS and it is considered to be promising for Raman imaging.
AuNCs are prominent nanosystems because of their ease of functionalization and small size, which allows them to be easily cleared by the kidneys.141 Cui et al121 synthesized BSA stabilized AuNCs, which were subsequently cross-linked to create a well-defined gold cluster nanoassembly (AuCNA). The AuCNA showed high biocompatibility and precise tumor targeting to 4T1 breast cancer cells, as seen through NIR fluorescence images. However, laser irradiation (660 nm) generated reactive oxygen species (ROS), which caused significant cell death in vitro, and this effect resulted in tumor death in an in vivo assay.
In a study by Fu et al,137 curcumin, a hydrophobic, but promising therapeutic agent, was encapsulated in BSA functionalized gold nanoclusters (BSA-AuNCs), and showed enhanced internalization in human neuroblastoma (SH-SY5Y) cells, followed by strong fluorescence within the cells and the inhibition of proliferation via the induction of apoptosis. This research is ongoing, but highlights that the system has significant potential as a candidate for theranostic applications, by taking advantage of such fluorescence signals.
The AuNCs-BSA system has also been used for the delivery of approved anticancer drugs, such as in Ding et al,125 where constructed BSA@AuNCs were modified using cyclic arginine-glycine-aspartate (cRGD) and loaded with DOX (DOX/RGD-BSA@AuNCs). This nanosystem produced growth inhibition in cancer cells, including Hela, MCF-7, U251 and CAL-27 cells. Remarkably, the DOX/RGD-BSA@AuNCs system proved to be useful not only for drug delivery, but also for localized in vivo imaging, as shown in Figure 12, where a decrease in tumor size and specific detection of the tumor site is notable after treatment using the nanosystem and laser irradiation.
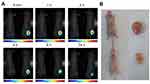 |
Figure 12 (A) In vivo targeted cancer fluorescence images of Hela tumor-bearing mice exposed to the laser (488 nm, 425 mW cm2, 25 min) after injection of the DOX/RGD-BSA@AuNCs system. (B) The images of tumor excised from mice after injection of PBS solution or DOX/RGD-BSA@AuNCs solutions at 19 day. Reprinted with permission from Ding C, Xu Y, Zhao Y, Zhong H, Luo X. Fabrication of BSA@AuNC-based nanostructures for cell fluoresce imaging 1435 and target drug delivery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10:8947-8954.125 Copyright (2018) American Chemical Society. |
Nanosystems offer a wide variety of possibilities because of their versatility and functionalization potential, and they can present enhanced and special characteristics, such as sensitivity to external stimuli (such as light, laser radiation, heat and pH). By means of pH sensitivity, Huang et al98 used BSA as a template for the creation of an Au-BSA core/shell, which was subsequently functionalized with DOX and FA (Au–BSA–DOX–FA). The nanocomposite showed in vitro non-toxicity in MGC-803 and GES-1 cells, pH-sensitive drug release properties, and superior antitumor activity compared with free DOX. In vivo CT imaging showed that the nanocomposite had selective antitumor activity by targeting overexpressed folate receptors in gastric cancer.
AuNPs can be combined with other metallic nanoparticles, such as Gd2O3 nanoparticles, which can improve the properties of the system for theranostic applications. An example is reported in a study by Han et al,142 in which gadolinium oxide-gold nanocluster hybrids (Gd2O3−AuNCs), stabilized in BSA were synthesized, showing high biocompatibility, in vivo and in vitro uptake, as well as signal enhancement for magnetic resonance and X-ray CT imaging. This system, besides enhancing imaging, can be used to kill tumor cells through the production of singlet oxygen species (1O2) after NIR irradiation (808 nm). However, this nanosystem also proved to be useful for loading and delivering the fluorescent dye ICG, improving photodynamic properties. Similarly, You et al143 designed a multifunctional delivery platform for Gd based on hollow gold nanoshells coated with BSA (Au@BSA-Gd), in which gold conferred photothermal properties, and the construct exhibited properties that are useful for CT and PA. The incorporation of ICG into the system provided photodynamic/photothermal properties and near-infrared fluorescence (NIRF)/PA imaging capabilities, thereby achieving an ideal theranostic agent for NIRF/PA/CT/MR quadmodal imaging.
Other non-conventional AuNP geometries also offer interesting properties, which in addition to SA enhanced biocompatibility, can be useful for theranostic applications. An example is branched gold nanoshells (BAuNSHs), as synthesized by Topete et al144 through a seeded-growth, and which were loaded with DOX. The system was also coated with a BSA-ICG-FA complex. This is a multifunctional system useful for fluorescence imaging because of the inherent fluorescence of the internalized dye and the presence of FA. The system also has the potential to deliver chemotherapy through its loaded drug, and photothermal and photodynamic therapy upon NIR irradiation. The synergistic effect of the nanoconstruct was observed in terms of an increase in internalization and toxicity in HeLa cells, and bioaccumulation at tumor sites in a tumor-bearing mouse model, observed through fluorescence imaging.
Conclusion
Albumin is a promising biomaterial for new approaches, and its biocompatibility and transport properties allow for the creation of new materials and the improvement of existing materials. The special characteristics of malignant tissues, such as an accelerated rate of proliferation and increased cellular stress and cell growth, resulting in a higher demand for energy and nutrients, can be exploited for controlled drug delivery.
The synergy between SA and AuNPs results in interesting properties, such as an increase in stability, a reduction in the interaction with plasma proteins, passive and active targeting of malignant cells, and an increase in selectivity. The photothermal properties and the NIR absorption of light of AuNPs are suitable for local hyperthermia, photothermal ablation and photothermal release. The system demonstrates significant potential in terms of spatial and temporally controlled release, in addition to its applications in theranostics, using simple detection techniques such as PA, CT or a combination of both, as previously described. Coating AuNPs with SA decreases the interaction of the nanosytem with endogenous proteins in the body, protecting the cargo against degradation.
Future perspectives
Although, a limited number of clinical trials are now in progress, with promising results145–147 the use of AuNPs for clinical applications has been delayed due to the inherent potential toxicity of metal nanoparticles. As mentioned previously, the capping of AuNPs with SA allows for an improvement in their biological properties, which may encourage the scientific community to investigate AuNP-SA-based nanosystems for clinical trials, as well as other types of SA-coated NIR-plasmonic nanoparticles for biomedical applications.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by FONDAP 15130011, FONDECYT 1170929 and 1190623, and CONICYT 21180258. The abstract of this paper was presented at the as a poster presentation with interim findings. The poster’s abstract was published in “Poster Abstracts” in the 11th Workshop on Computational Chemistry and Molecular Spectroscopy in October 2018 (11thWCCMS): http://www.wccms.cl/downloads/wccms_2018_proceedings.pdf.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Danhier F. To exploit the tumor microenvironment: since the EPR effect fails in the clinic, what is the future of nanomedicine? J Control Release. 2016;244:108–121. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.11.015
2. Chen Q, Liu Z. Albumin carriers for cancer theranostics: a conventional platform with new promise. Adv Mater. 2016;28:10557–10566. doi:10.1002/adma.v28.47
3. Mariam J, Sivakami S, Dongre PM. Elucidation of structural and functional properties of albumin bound to gold nanoparticles. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2017;35:368–379. doi:10.1080/07391102.2016.1144223
4. Eustis S, El-Sayed MA. Why gold nanoparticles are more precious than pretty gold: noble metal surface plasmon resonance and its enhancement of the radiative and nonradiative properties of nanocrystals of different shapes. Chem Soc Rev. 2006;35:209–217. doi:10.1039/B514191E
5. Alfranca, G, Artiga A, Stepien G, et al. Gold nanoprism – nanorod face off : comparing the heating efficiency, cellular internalization and thermoablation capacity. Nanomedicine (Lond.). 2016;11:2903–2916. doi:10.2217/nnm-2016-0233
6. AL-Jawad SMH, Taha AA, Al-Halbosiy MMF, AL-Barram LFA. Synthesis and characterization of small-sized gold nanoparticles coated by bovine serum albumin (BSA) for cancer photothermal therapy. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2018;21:201–210. doi:10.1016/j.pdpdt.2017.12.004
7. Uppal A, Bose B. Synthesis, stability, and in vitro oral cancer cell toxicity of human serum albumin stabilised gold nanoflowers. IEE. 2018. doi:10.1049/iet-nbt.2017.0002
8. Kuo W-S, Chang Y-T, Cho K-C, et al. Gold nanomaterials conjugated with indocyanine green for dual-modality photodynamic and photothermal therapy. Biomaterials. 2012;33:3270–3278. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.01.035
9. Santos NC, Domingues MM, Felício MR, Gonçalves S, Carvalho PM. Application of light scattering techniques to nanoparticle characterization and development. Front Chem. 2018;6:1–17.
10. Peralta DV, Heidari Z, Dash S, Tarr MA. Hybrid paclitaxel and gold nanorod-loaded human serum albumin nanoparticles for simultaneous chemotherapeutic and photothermal therapy on 4T1 breast cancer cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7:7101–7111. doi:10.1021/acsami.5b00858
11. Kelkar SS, Reineke TM. Theranostics : combining imaging and therapy. Bioconjug Chem. 2011;22:1879–1903. doi:10.1021/bc200151q
12. Adura C, Guerrero S, Salas E, et al. Stable conjugates of peptides with gold nanorods for biomedical applications with reduced effects on cell viability. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5:4076–4085. doi:10.1021/am401486h
13. Olmedo I, Araya E, Sanz F, et al. How changes in the sequence of the peptide CLPFFD-NH 2 can modify the conjugation and stability of gold nanoparticles and their affinity for -amyloid fibrils. Bioconjug Chem. 2008;19:1154–1163. doi:10.1021/bc800016y
14. Cheema MA, Taboada P, Barbosa S, et al. Human serum albumin unfolding pathway upon drug binding: A thermodynamic and spectroscopic description. J Chem Thermodyn. 2009;41:439–447. doi:10.1016/j.jct.2008.11.011
15. Lee ES, Youn YS. Albumin-based potential drugs: focus on half-life extension and nanoparticle preparation. J Pharm Investig. 2016;46:305–315. doi:10.1007/s40005-016-0250-3
16. Bairagi U, Mittal P, Albumin MB. A versatile drug carrier. Austin Ther. 2015;2:1–6.
17. Cantor JR, Sabatini DM. Cancer cell metabolism: one hallmark, many faces. Cancer Discov. 2013;2:881–898. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0345
18. Swiercz R, Mo M, Khare P, et al. Loss of expression of the recycling receptor, FcRn, promotes tumor cell growth by increasing albumin consumption. Oncotarget. 2017;8:3528–3541. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.13869
19. Commisso C,Davison S, Soydaner-Azeloglu R, et al. Macropinocytosis of protein is an amino acid supply route in Ras-transformed cells. Nature. 2013;497:633–637. doi:10.1038/nature12138
20. Merlot AM, Kalinowski DS, Richardson DR. Unraveling the mysteries of serum albumin-more than just a serum protein. Front Physiol. 2014;5:1–7. doi:10.3389/fphys.2014.00268
21. Nguyen VH, Lee BJ. Protein corona: A new approach for nanomedicine design. Int J Nanomed. 2017;12:3137–3151. doi:10.2147/IJN.S129300
22. Yu Z, Yu M, Zhang Z, Hong G, Xiong Q. Bovine serum albumin nanoparticles as controlled release carrier for local drug delivery to the inner ear. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2014;9:1–7. doi:10.1186/1556-276X-9-343
23. Bhushan B, Khanadeev V, Khlebtsov B, Khlebtsov N, Gopinath P. Impact of albumin based approaches in nanomedicine: imaging, targeting and drug delivery. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2017;246:13–39. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2017.06.012
24. Karimi M, Bahrami S, Ravari SB, et al. Albumin nanostructures as advanced drug delivery systems. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2016;13:1609–1623. doi:10.1080/17425247.2016.1193149
25. Kratz F. A clinical update of using albumin as a drug vehicle - a commentary. J Control Release. 2014;190:331–336. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.03.013
26. Kratz F. Albumin as a drug carrier: design of prodrugs, drug conjugates and nanoparticles. J Control Release. 2008;132:171–183. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2008.05.010
27. Kudarha RR, Sawant KK. Albumin based versatile multifunctional nanocarriers for cancer therapy: fabrication, surface modification, multimodal therapeutics and imaging approaches. Mater Sci Eng C. 2017;81:607–626. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2017.08.004
28. Min Y, Caster JM, Eblan MJ, Wang AZ. Clinical translation of nanomedicine. Chem Rev. 2015;115:11147−11190. doi:10.1021/cr5004419
29. Saverot S-E, Reese LM, Cimini D, Vikesland PJ, Bickford LR. Characterization of conventional one-step sodium thiosulfate facilitated gold nanoparticle synthesis. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2015;10:241. doi:10.1186/s11671-015-0940-1
30. Jeremic B, Aguerri AR, Filipovic N. Radiosensitization by gold nanoparticles. Clin Transl Oncol. 2013;15:593–601. doi:10.1007/s12094-013-1034-0
31. Pastoriza-Santos I, Liz-Marzan LM. Colloidal silver nanoplates. State of the art and future challenges. J Mater Chem. 2008;18:1724–1737. doi:10.1039/b716538b
32. Guerrero AR, Hassan N, Escobar CA, Albericio F, Kogan MJ, Araya E. Gold nanoparticles for photothermally controlled drug release. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2014;9:2023–2039. doi:10.2217/nnm.14.126
33. Kelly KL, Coronado E, Zhao LL, Schatz GC. The optical properties of metal nanoparticles: the influence of size, shape, and dielectric environment. J Phys Chem. 2003;B668–B677. doi:10.1021/jp026731y
34. Link S, El-Sayed MA. Shape and size dependence of radiative, non-radiative and photothermal properties of gold nanocrystals. Int Rev Phys Chem. 2000;19:409–453. doi:10.1080/01442350050034180
35. Link S, El-Sayed MA. Optical properties and ultrafast d ynamics of metallic nanocrystals. Annu Rev Phys Chem. 2003;54:331–366. doi:10.1146/annurev.physchem.54.011002.103759
36. Huang X, El-Sayed MA. Gold nanoparticles: optical properties and implementations in cancer diagnosis and photothermal therapy. J Adv Res. 2010;1:13–28. doi:10.1016/j.jare.2010.02.002
37. Wicki A, Witzigmann D, Balasubramanian V, Huwyler J. Nanomedicine in cancer therapy : challenges, opportunities, and clinical applications. J Control Release. 2015;200:138–157. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.12.030
38. Vetterlein C, Vasquez R, Bolaños K, et al. Exploring the influence of Diels-Alder linker length on photothermal molecule release from gold nanorods. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018;166:323–329. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.03.021
39. Alex SA, Chakraborty D, Chandrasekaran N, Mukherjee A. A comprehensive investigation of the differential interaction of human serum albumin with gold nanoparticles based on the variation in morphology and surface functionalization. RSC Adv. 2016;6:52683–52694. doi:10.1039/C6RA10506H
40. Bayazitoglu Y, Kheradmand S, Tullius TK. An overview of nanoparticle assisted laser therapy. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2013;67:469–486. doi:10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2013.08.018
41. Schleich N, Danhier F, Préat V. Iron oxide-loaded nanotheranostics: major obstacles to in vivo studies and clinical translation. J Control Release. 2015;198:35–54. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.11.024
42. Sahu A, Lee JH, Lee HG, Jeong YY, Tae G. Prussian blue/serum albumin/indocyanine green as a multifunctional nanotheranostic agent for bimodal imaging guided laser mediated combinatorial phototherapy. J Control Release. 2016;236:90–99. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.06.031
43. Qiu Y, Liu Y, Wang L, et al. Surface chemistry and aspect ratio mediated cellular uptake of Au nanorods. Biomaterials. 2010;31:7606–7619. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.01.042
44. Prades R, Guerrero S, Araya E, et al. Delivery of gold nanoparticles to the brain by conjugation with a peptide that recognizes the transferrin receptor. Biomaterials. 2012;33:7194–7205. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.06.063
45. Kogan MJ, Bastus NG, Amigo R, et al. Nanoparticle-mediated local and remote manipulation of protein aggregation. Nano Lett. 2006;6:110–115. doi:10.1021/nl052110f
46. Stone J, Jackson S, Wright D. Biological applications of gold nanorods. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2011;3:100–109. doi:10.1002/wnan.120
47. Ajnai G, Chiu A, Kan T, Cheng C-C, Tsai T-H, Chang J. Trends of gold nanoparticle-based drug delivery system in cancer therapy. J Exp Clin Med. 2014;6:172–178. doi:10.1016/j.jecm.2014.10.015
48. Velasco-Aguirre C, Morales F, Gallardo-Toledo E, et al. Peptides and proteins used to enhance gold nanoparticle delivery to the brain: preclinical approaches. Int J Nanomed. 2015;10:4919–4936.
49. Walkey CD, Olsen JB, Guo H, Emili A, Chan WCW. Nanoparticle size and surface chemistry determine serum protein adsorption and macrophage uptake. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134:2139–2147. doi:10.1021/ja2084338
50. Dobrovolskaia MA, Aggarwal P, Hall JB, Mcneil SE. Preclinical studies to understand nanoparticle interaction with the immune system and its potential effects on nanoparticle biodistribution. Mol Pharm. 2008;5:487–495. doi:10.1021/mp800032f
51. Xiao W, Gao H. The impact of protein corona on the behavior and targeting capability of nanoparticle-based delivery system. Int J Pharm. 2018;552:328–339. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.10.011
52. Charbgoo F, Nejabat M, Abnous K, et al. Gold nanoparticle should understand protein corona for being a clinical nanomaterial. J Control Release. 2018;272:39–53. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.01.002
53. Kreuter J. Influence of the surface properties on nanoparticle-mediated transport of drugs to the brain. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2004;4:484–488. doi:10.1166/jnn.2003.077
54. Reddy JS, Vobalaboina V. novel delivery systems for drug targeting to the brain. Drugs Future. 2004;29:63–83. doi:10.1358/dof.2004.029.01.872585
55. Majorek KA, Porebski PJ, Dayal A, et al. Structural and immunologic characterization of bovine, horse, and rabbit serum albumins. Mol Immunol. 2012;52(3-4):174-82. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2012.05.011
56. Bhatty RS. Albumin proteins of eight edible grain legume species: electrophoretic patterns and amino acid composition. J Agric Food Chem. 1982;30:620–622. doi:10.1021/jf00111a057
57. Elzoghby AO, Samy WM, Elgindy NA. Albumin-based nanoparticles as potential controlled release drug delivery systems. J Control Release. 2012;157:168–182. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.07.031
58. Majorek KA, Porebski PJ, Dayal A, Zimmerman MD, Jablonska K, Stewart AJ, Chruszcz M, Minor W. PDB ID: 3V03. Mol Immunol 52, 174–182 (2012).
59. Lv L, Chi Y, Chen C, Xu W. Structural and functional properties of ovalbumin glycated by dry-heating in the presence of maltodextrin. Int J Food Prop. 2015;18:1326–1333. doi:10.1080/10942912.2011.620204
60. Wang Y, Yu H, Shi X, Luo Z, Lin D, Huang M. PDB ID: 4K2C. J Biol Chem 288, 15980–15987 (2013).
61. Binaymotlagh R, Hadadzadeh H, Farrokhpour H, et al. In situ generation of the gold nanoparticles-bovine serum albumin (AuNPs-BSA) bioconjugated system using pulsed-laser ablation (PLA). Mater Chem Phys. 2016;177:360–370.
62. Apadopoulou ATP, Reen REJG, Razier RIAF. Interaction of flavonoids with bovine serum albumin : a fluorescence quenching study. Agric Food Chem. 2005;53:158–163. doi:10.1021/jf048693g
63. Nosrati H, Salehiabar M, Manjili HK, Danafar H, Davaran S. Preparation of magnetic albumin nanoparticles via a simple and one-pot desolvation and co-precipitation method for medical and pharmaceutical applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;108:909–915. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.10.180
64. Peters TJ. All About Albumin. San Diego: Academic Press; 1995.
65. Pragna Lakshmi T, Mondal M, Ramadas K, Natarajan S. Molecular interaction of 2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol (DAPG) with human serum albumin (HSA): the spectroscopic, calorimetric and computational investigation. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2017;183:90–102. doi:10.1016/j.saa.2017.04.012
66. Li C, Xing L, Che S. Coordination bonding based pH-responsive albumin nanoparticles for anticancer drug delivery. Dalt Trans. 2012;41:3714. doi:10.1039/c2dt30226h
67. Mariam J, Sivakami S, Dongre PM. Albumin corona on nanoparticles – a strategic approach in drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 2015;1–9. doi:10.3109/10717544.2015.1048488
68. Zhiya MA, Xia H, Liu Y, Liu B, Chen W, Zhao Y. Applications of gold nanorods in biomedical imaging and related fields. Chin Sci Bull. 2013;58:2530–2536. doi:10.1007/s11434-013-5720-7
69. Tarhini M, Greige-Gerges H, Elaissari A. Protein-based nanoparticles: from preparation to encapsulation of active molecules. Int J Pharm. 2017;522:172–197. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.01.067
70. Blanco E, Shen H, Ferrari M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat Biotechnol. 2015;33:941–951. doi:10.1038/nbt.3330
71. Zhao F, Zhao Y, Liu Y, Chang X, Chen C, Zhao Y. Cellular uptake, intracellular trafficking, and cytotoxicity of nanomaterials. Small. 2011;7(10):1322–1337. doi:10.1002/smll.201100001
72. Connor EE, Mwamuka J, Gole A, Murphy CJ, Wyatt MD. Toxicity of nanoparticles gold nanoparticles are taken up by human cells but do not cause acute cytotoxicity. Small. 2005;3:325–327. doi:10.1002/smll.200400093
73. Hussain I, Nichols RJ, Schiffrin DJ, Brust M, Fernig DG. Rational and combinatorial design of peptide capping ligands for gold nanoparticles. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2004;126:10076–10084.
74. Liu Y, Shipton MK, Ryan J, Kaufman ED, Franzen S, Feldheim DL. Synthesis, stability, and cellular internalization of gold nanoparticles containing mixed peptide - poly (ethylene glycol) monolayers. Anal Chem. 2007;79:2221–2229. doi:10.1021/ac061578f
75. Pissuwan D, Cortie CH, Valenzuela SM, Cortie MB. Gold nanosphere-antibody conjugates for hyperthermal therapeutic applications. Gold Bull. 2007;40:121–129. doi:10.1007/BF03215568
76. Mocan L, Matea C, Tabaran FA, et al. Selective ex vivo photothermal nano-therapy of solid liver tumors mediated by albumin conjugated gold nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2017;119:33–42. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.12.009
77. Murawala P, Tirmale A, Shiras A, Prasad BLV. In situ synthesized BSA capped gold nanoparticles : effective carrier of anticancer drug Methotrexate to MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Mater Sci Eng C. 2014;34:158–167. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2013.09.004
78. Larsen MT, Kuhlmann M, Hvam ML, Howard KA. Albumin-based drug delivery: harnessing nature to cure disease. Mol Cell Ther. 2016;4:3. doi:10.1186/s40591-016-0048-8
79. Brekken RA, Sage EH, Brekken RA. Mini review SPARC, a matricellular protein: at the crossroads of cell matrix SPARC, a matricellular protein : at the crossroads of cell matrix communication. Matrix Biol. 2001;19:815–827.
80. Kouros M. SPARC (osteonectin/BM-40). Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1999;31:1363–1366. doi:10.1016/S1357-2725(99)00090-4
81. Podhajcer OL, Benedetti LG, Girotti MR, Prada F, Salvatierra E, Llera AS. The role of the matricellular protein SPARC in the dynamic interaction between the tumor and the host. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008;27:53. doi:10.1007/s10555-008-9146-7
82. Maeda H. The link between infection and cancer: tumor vasculature, free radicals, and drug delivery to tumors via the EPR effect. Cancer Sci. 2013;104:779–789. doi:10.1111/cas.12152
83. Iyer AK, Khaled G, Fang J, Maeda H. Exploiting the enhanced permeability and retention effect for tumor targeting. Drug Discov Today. 2006;11:812–818. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2006.07.005
84. Yuan F, Dellian M, Fukumura D, et al. Vascular permeability in a human tumor xenograft : molecular size dependence and cutoff size advances in brief vascular permeability in a human tumor xenograft: molecular size dependence and cutoff size. Cancer Res. 1995;55:3752–3756.
85. Grobmyer SR, Moudgil B. What is cancer nanotechnology? Methods Mol Biol. 2010;624:1–9. doi:10.1007/978-1-60761-609-2_1
86. Bhamidipati M, Fabris L. Multiparametric assessment of gold nanoparticle cytotoxicity in cancerous and healthy cells: the role of size, shape, and surface chemistry. Bioconjug Chem. 2016;28:449–460. doi:10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.6b00627
87. Sanchez-Iglesias A, Grzelczak M, Altantzis T, et al. Hydrophobic interactions modulate self-assembly of nanoparticles. ACS Nano. 2012;6:11059–11065. doi:10.1021/nn3047605
88. Ahmad R, Fu J, He N, Li S. Advanced gold nanomaterials for photothermal therapy of cancer. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2016;16:67–80. doi:10.1166/jnn.2016.10770
89. Elzoghby AO, Hemasa AL, Freag MS. Hybrid protein-inorganic nanoparticles: from tumor-targeted drug delivery to cancer imaging. J Control Release. 2016;243:303–322. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.10.023
90. Pramanik S, Banerjee P, Sarkar A, Bhattacharya SC. Size-dependent interaction of gold nanoparticles with transport protein: a spectroscopic study. J Lumin. 2008;128:1969–1974. doi:10.1016/j.jlumin.2008.06.008
91. Boulos SP, Davis TA, Yang JA, et al. Nanoparticle − protein interactions: a thermodynamic and kinetic study of the adsorption of bovine serum albumin to gold nanoparticle surfaces. Langmuir. 2013;29(48):14984–14996. doi:10.1021/la402920f
92. Rafaela G-Á, Marilena H, Ana S-I, Luis -ML-M, Kostas K. In vivo formation of protein corona on gold nanoparticles. The effect of their size and shape. Nanoscale. 2018;10:1256–1264. doi:10.1039/C7NR08322J
93. Chakraborty S, Joshi P, Shanker V, et al. Contrasting effect of gold nanoparticles and nanorods with different surface modifications on the structure and activity of bovine serum albumin. Langmuir. 2011;27(12):7722–7731. doi:10.1021/la200787t
94. Moustaoui H, Saber J, Djeddi I, et al. A protein corona study by scattering correlation spectroscopy: a comparative study between spherical and urchin-shaped gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale. 2019;11:3665–3673. doi:10.1039/C8NR09891C
95. Online VA, Chandrasekaran N, Mukherjee A. A comprehensive investigation of the differential interaction of Human Serum Albumin with Gold nanoparticles based on the variation in morphology and surface functionalization. RSC Adv. 2016;58:52683–52694.
96. Carnovale C, Bryant G. Impact of nanogold morphology on interactions with human serum. Phys Chem Phys. 2018;30:29558–29565. doi:10.1039/C8CP05938A
97. Maleki MS, Moradi O, Tahmasebi S. Adsorption of albumin by gold nanoparticles: equilibrium and thermodynamics studies. Arab J Chem. 2017;10:S491–S502. doi:10.1016/j.arabjc.2012.10.009
98. Liu M. pH-sensitive Au – BSA – DOX – FA nanocomposites for combined CT imaging and targeted drug delivery. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12:2829–2843. doi:10.2147/IJN.S128270
99. Elsadek B, Kratz F. Impact of albumin on drug delivery - New applications on the horizon. J Control Release. 2012;157:4–28. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.09.069
100. Li J, Cai R, Kawazoe N, Chen G. Facile preparation of albumin-stabilized gold nanostars for the targeted photothermal ablation of cancer cells. J Mater Chem B. 2015;3:5806–5814. doi:10.1039/C4TB02051K
101. Loureiro A, Azoia NG, Gomes AC, Cavaco-Paulo A. Albumin-based nanodevices as drug carriers. Curr Pharm Des. 2016;22:1371–1390. doi:10.2174/1381612822666160125114900
102. Chen L, Feng W, Zhou X, et al. Facile synthesis of novel albumin-functionalized flower-like MoS 2 nanoparticles for in vitro chemo-photothermal synergistic therapy. RSC Adv. 2016;6:13040–13049. doi:10.1039/C5RA27822H
103. Lademann J, Richter H, Knorr F, et al. Acta Biomaterialia Triggered release of model drug from AuNP-doped BSA nanocarriers in hair follicles using IRA radiation. Acta Biomater. 2016;30:388–396. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2015.11.052
104. Peralta DV, He J, Wheeler DA, Zhang JZ, Tarr MA. Encapsulating gold nanomaterials into size-controlled human serum albumin nanoparticles for cancer therapy platforms. J Microencapsul. 2014;31:824–831. doi:10.3109/02652048.2014.940012
105. Zu L, Liu L, Qin Y, Liu H, Yang H. Multifunctional BSA-Au nanostars for photoacoustic imaging and X-ray computed tomography. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med. 2016;12:1805–1813. doi:10.1016/j.nano.2016.05.003
106. Zhang L, Xia K, Bai YY, et al. Synthesis of gold nanorods and their functionalization with bovine serum albumin for optical hyperthermia. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2014;10:1440–1449.
107. Paraiso WKD, Tanaka H, Sato Y, et al. Preparation of envelope-type lipid nanoparticles containing gold nanorods for photothermal cancer therapy. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017;160:715–723. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.10.009
108. Sun J, Guo Y, Xing R, et al. Synergistic in vivo photodynamic and photothermal antitumor therapy based on collagen-gold hybrid hydrogels with inclusion of photosensitive drugs. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp. 2017;514:155–160. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2016.11.062
109. Liu P, Zheng H, Yang Z, et al. Facile preparation of versatile gadolinium-chelated protein nanocomposite for T1magnetic resonance imaging-guided photodynamic and photothermal synergetic therapy. J Mater Chem. 2018;B 6:1688–1698. doi:10.1039/C8TB00148K
110. Sasidharan S, Bahadur D, Srivastava R. Albumin stabilized gold nanostars: A biocompatible nanoplatform for SERS, CT imaging and photothermal therapy of cancer. RSC Adv. 2016;6:84025–84034. doi:10.1039/C6RA11405A
111. Liu J, Peng Q. Protein-gold nanoparticle interactions and their possible impact on biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 2017;55:13–27. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2017.03.055
112. Rastogi L, Kora AJ, Arunachalam J. Highly stable, protein capped gold nanoparticles as effective drug delivery vehicles for amino-glycosidic antibiotics. Mater Sci Eng C. 2012;32:1571–1577. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2012.04.044
113. Klebowski B, Depciuch J, Parlinska-Wojtan M, Baran J. Applications of noble metal-based nanoparticles in medicine. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19. doi:10.3390/ijms19124031
114. Li D, Zhang M, Xu F, et al. Biomimetic albumin-modified gold nanorods for photothermo-chemotherapy and macrophage polarization modulation. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2018;8:74–84. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2018.04.006
115. Jokerst JV, Cole AJ, Van de Sompel D, Gambhir SS. Gold nanorods for ovarian cancer detection with photoacoustic imaging and resection guidance via raman imaging in living mice. ACS Nano. 2012;6:10366–10377. doi:10.1021/nn304347g
116. Almada M, Leal-Martínez BH, Hassan N, et al. Photothermal conversion ef fi ciency and cytotoxic effect of gold nanorods stabilized with chitosan, alginate and poly (vinyl alcohol). Mater Sci Eng C. 2017;77:583–593. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2017.03.218
117. Zhang Z, Wang J, Nie X, et al. Near infrared laser-induced targeted cancer therapy using thermoresponsive polymer encapsulated gold nanorods. J Am Chem Soc. 2014;136:7317–7326. doi:10.1021/ja412735p
118. Encinas-Basurto D, Ibarra J, Juarez J, et al. Hybrid folic acid-conjugated gold nanorods-loaded human serum albumin nanoparticles for simultaneous photothermal and chemotherapeutic therapy. Mater Sci Eng C. 2018;91:669–678. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2018.06.002
119. Pelaz B, Grazu V, Ibarra A, et al. Tailoring the synthesis and heating ability of gold nanoprisms for bioapplications. Langmuir. 2012;28:8965–8970. doi:10.1021/la204712u
120. Bao C, Beziere N, del Pino P, et al. Gold nanoprisms as optoacoustic signal nanoamplifiers for in vivo bioimaging of gastrointestinal cancers. Small. 2013;9:68–74. doi:10.1002/smll.201201779
121. Cui H-D, Hu D-H, Zhang J-N, et al. Theranostic gold cluster nanoassembly for simultaneous enhanced cancer imaging and photodynamic therapy. Chin Chem Lett. 2017;28:1391–1398. doi:10.1016/j.cclet.2016.12.038
122. Santhosh M, Chinnadayyala SR, Singh NK, Goswami P. Human serum albumin-stabilized gold nanoclusters act as an electron transfer bridge supporting specific electrocatalysis of bilirubin useful for biosensing applications. Bioelectrochemistry. 2016;111:7–14. doi:10.1016/j.bioelechem.2016.04.003
123. Ding H, Yang D, Zhao C, et al. Protein-gold hybrid nanocubes for cell imaging and drug delivery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7:4713–4719. doi:10.1021/am5083733
124. Yu X, Liu W, Deng X, Yan S, Su Z. Gold nanocluster embedded bovine serum albumin nanofibers-graphene hybrid membranes for the efficient detection and separation of mercury ion. Chem Eng J. 2018;335:176–184. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.148
125. Ding C, Xu Y, Zhao Y, Zhong H, Luo X. Fabrication of BSA@AuNC-based nanostructures for cell fluoresce imaging and target drug delivery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10:8947–8954. doi:10.1021/acsami.7b18493
126. Callaghan C, Peralta D, Liu J, et al. Combined treatment of tyrosine kinase inhibitor-labeled gold nanorod encapsulated albumin with laser thermal ablation in a renal cell carcinoma model. J Pharm Sci. 2016;105:284–292. doi:10.1016/j.xphs.2015.11.017
127. Liu J, Abshire C, Carry C, et al. Nanotechnology combined therapy: tyrosine kinase-bound gold nanorod and laser thermal ablation produce a synergistic higher treatment response of renal cell carcinoma in a murine model. BJU Int. 2017;119:342–348. doi:10.1111/bju.2017.119.issue-2
128. Wang Z, Chen L, Chu Z, Huang C, Huang Y, Jia N. Gemcitabine-loaded gold nanospheres mediated by albumin for enhanced anti-tumor activity combining with CT imaging. Mater Sci Eng C. 2018;89:106–118. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2018.03.025
129. Chiu HT, Su CK, Sun YC, Chiang CS, Huang YF. Albumin-gold nanorod nanoplatform for cell-mediated tumoritropic delivery with homogenous chemodrug distribution and enhanced retention ability. Theranostics. 2017;7:3034–3052. doi:10.7150/thno.19279
130. Lademann J, Richter H, Knorr F, et al. Triggered release of model drug from AuNP-doped BSA nanocarriers in hair follicles using IRA radiation. Acta Biomater. 2016;30:388–396. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2015.11.052
131. Chen J, Sheng Z, Li P, et al. Indocyanine green-loaded gold nanostars for sensitive SERS imaging and subcellular monitoring of photothermal therapy. Nanoscale. 2017;9:11888–11901. doi:10.1039/C7NR02798B
132. Leopold LF, Tódor IS, Diaconeasa Z, et al. Assessment of PEG and BSA-PEG gold nanoparticles cellular interaction. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng Asp. 2017;532:70–76. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2017.06.061
133. Baum RP, Kulkarni HR. Theranostics: from molecular imaging using Ga-68 labeled tracers and PET/CT to personalized radionuclide therapy - the bad berka experience. Theranostics. 2012;2:437–447. doi:10.7150/thno.3645
134. Ganta S, Devalapally H, Shahiwala A, Amiji M. A review of stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug and gene delivery. J Control Release. 2008;126:187–204. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2007.12.010
135. Fernandez-Fernandez A, Manchanda R, McGoron AJ. Theranostic applications of nanomaterials in cancer: drug delivery, image-guided therapy, and multifunctional platforms. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2011;165:1628–1651. doi:10.1007/s12010-011-9383-z
136. Fiegel V, Harlepp S, Begin-Colin S, Begin D, Mertz D. Design of protein-coated carbon nanotubes loaded with hydrophobic drugs through sacrificial templating of mesoporous silica shells. Chem Eur J. 2018. doi:10.1002/chem.201705845
137. Fu C, Ding C, Sun X, Fu A. Curcumin nanocapsules stabilized by bovine serum albumin-capped gold nanoclusters (BSA-AuNCs) for drug delivery and theranosis. Mater Sci Eng C. 2018. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2017.12.028
138. Chiu HT, Chen CH, Li ML, et al. Bioprosthesis of core-shell gold nanorod/serum albumin nanoimitation: a half-native and half-artificial nanohybrid for cancer theranostics. Chem Mater. 2018;30:729–747. doi:10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b04127
139. Quan Q, Xie J, Gao H, et al. HSA coated iron oxide nanoparticles as drug delivery vehicles for cancer therapy. Mol Pharm. 2011;8:1669–1676. doi:10.1021/mp200125j
140. Abbas M, Zou Q, Li S, Yan X. Self-assembled peptide- and protein-based nanomaterials for antitumor photodynamic and photothermal therapy. Adv Mater. 2017;29. doi:10.1002/adma.201700681
141. Khlebtsov B, Prilepskii A, Lomova M, Khlebtsov N. Au-nanocluster-loaded human serum albumin nanoparticles with enhanced cellular uptake for fluorescent imaging. J Innov Opt Health Sci. 2015;9:1650004. doi:10.1142/S1793545816500048
142. Han L, Xia J-M, Hai X, Shu Y, Chen X-W, Wang J-H. Protein-stabilized gadolinium oxide-gold nanoclusters hybrid for multimodal imaging and drug delivery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9:6941–6949. doi:10.1021/acsami.7b00246
143. You Q, Sun Q, Yu M, et al. BSA-bioinspired gadolinium hybrid-functionalized hollow gold nanoshells for NIRF/PA/CT/MR quadmodal diagnostic imaging-guided photothermal/photodynamic cancer therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9:40017–40030. doi:10.1021/acsami.7b11926
144. Topete A, Alatorre-Meda M, Iglesias P, et al. Fluorescent drug-loaded, polymeric-based, branched gold nanoshells for localized multimodal therapy and imaging of tumoral cells. ACS Nano. 2014;8:2725–2738. doi:10.1021/nn406425h
145. Aaron C, Mitragotri AS. Nanoparticles in the clinic. Bioeng Transl Med. 2016;1:10–29. doi:10.1002/btm2.10003
146. Ali MRK, Rahman MA, Wu Y, et al. Efficacy, long-term toxicity, and mechanistic studies of gold nanorods photothermal therapy of cancer in xenograft mice. Proc National Acad Sci. 2017;114:E3110–E3118. doi:10.1073/pnas.1619302114
147. Kharlamov AN, Tyurnina AE, Veselova VS, Kovtun OP, Shur VY, Gabinsky JL. Silica-gold nanoparticles for atheroprotective management of plaques: results of the NANOM-FIM trial. Nanoscale. 2015;7:8003–8015. doi:10.1039/C5NR01050K
 © 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.