Back to Journals » Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity » Volume 14
Attitudes and Awareness Towards Diabetic Retinopathy Among Patients with Diabetes in Amman, Jordan
Authors Al-latayfeh M , Shatnawi R , Al Shdaifat AA
Received 19 January 2021
Accepted for publication 9 March 2021
Published 26 March 2021 Volume 2021:14 Pages 1425—1430
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S302554
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Juei-Tang Cheng
Motasem Al-latayfeh,1 Raed Shatnawi,1 Amjad A Al Shdaifat2
1Department of General and Special Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, The Hashemite University, Zarqa, Jordan; 2Department of Medicine and Family Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, The Hashemite University, Zarqa, Jordan
Correspondence: Motasem Al-latayfeh
The Hashemite University, P.O. Box 1134, Amman, 11947, Jordan
Email [email protected]
Purpose: This study aimed to investigate the attitudes and awareness about the development of retinopathy among the patients suffering from diabetes in Amman, Jordan.
Methods: A questionnaire was distributed among patients with diabetes visiting internal medicine and endocrinology clinics in a tertiary hospital, in addition to a primary health care center in Amman. The questionnaire inquired about retinopathy awareness, history of screening for retinopathy, and awareness about retinopathy treatment. The patients were also asked about risk factors and preventive measures for diabetic retinopathy management.
Results: A total of 303 patients were recruited in the study. Majority of the patients (77%) had their HbA1c levels tested at least once since diagnosis, and most of them (60%) do it regularly. However, 86% of patients reported an A1c > 6.5%. Two thirds of patients are not aware about retinopathy being a recognized complication of diabetes. Lower level of education, female sex, younger age, and shorter duration of diabetes mellitus were associated with less awareness.
Conclusion: The study concluded that majority of patients with diabetes were aware of diabetes management. However, the sample population indicated less awareness of diabetic retinopathy. Hence, more educational efforts are needed to further boost patients’ awareness about diabetic retinopathy.
Keywords: awareness, diabetes mellitus, diabetic retinopathy, Jordan
Introduction
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is considered as a major public health concern globally. It is estimated that around 600 million individuals worldwide will be affected by DM in 2030. In 2019, diabetes-related health expenditure in the Middle-East and North Africa (MENA) region totaled USD 24.9 billion, and is expected to increase by 30.3% to USD 32.5 billion by 2030.1 In Jordan, a study conducted by Ajlouni et al stated that diabetes prevalence increased from 13% in 1994 to 23.7% in 2017.2 According to World Health Organization statistics, the prevalence of DM in Jordan is estimated to be 13% of population.3 Poor management of diabetes may lead to several serious complications, including end-stage renal disease, diabetic retinopathy (DR), diabetic neuropathy, and cardiovascular complications.4,5
DR is considered as a serious potential complication of DM, and occurs due to damaged neurons and small blood vessels of the retina.6,7 The worldwide prevalence of DR has been estimated to be 34%-40%, with visually threatening DR at approximately 6–7%.8,9 Al-Amer et al reported that the prevalence of DR among Jordanians with DM is about 34%.10 Rabiu et al also reported DR to be the second leading cause of blindness in the Jordanian population.11
The ability of an individual to perform self-management activities is critical, and significantly affects their health status. Patients with diabetes need to maintain their health status through proper monitoring of blood glucose levels, an effective exercise program, medication, and foot care.12 The visual impairment that develops as a result of DR can be controlled through early diagnosis and retinopathy treatment. Furthermore, patients with diabetes need to control their blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and lipid levels to prevent the progression of eye complications.13,14
There is a need for timely interventions and periodic eye examinations in order to delay the development of eye complications. Therefore, the attitudes and awareness regarding eye care among patients with diabetes are crucial. Currently, patients with diabetes survive longer due to improved health services and access to affordable facilities for renal dialysis. However, eye complications, including visual impairment, usually occur among patients with longer disease duration.1 Previous studies have measured awareness about DR among the Jordanian population. Bakkar et al reported DR awareness to be about 88%,15 whereas Haddad et al reported a much lower awareness level, at 37%.16 Moreover, Jammal et al reported a high incidence of diabetic macular edema among patients in Jordan with DM type II who present to the eye clinic for first time.17 Hence, we need further studies to assess disease awareness about DR among patients with DM. Therefore, this study has investigated the attitudes and awareness of DR among patients with diabetes in Amman, Jordan, particularly with respect to the development of eye complications.
Materials and Methods
A questionnaire has been designed and randomly distributed among patients with diabetes visiting internal medicine and endocrinology clinics in a tertiary hospital and primary health care center in Amman, Jordan. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Hashemite University. All participants were informed of the purpose of the study, which was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Consent forms were signed by all the recruited participants, and parental or legal guardian informed consent was obtained for participants under the age of 18 years. Patients with DM were first selected randomly from clinics and a short interview with them was conducted to explain the purpose of the study and obtain consent. Inclusion criteria included patients with DM type I or II, who can interact and intellectually react to our questionnaire as judged by the initial interview. Patients who are unable to respond to our questions or refuse to sign the consent form were excluded. The required sample size was calculated using Sample size calculator (https://www.calculator.net/sample-size-calculator.html) based on Jordan’s population of 10 million, as per the official statistics,18 as well as a 95% confidence interval and 5% margin of error. The percentage of patients with DM ranges between 13%3 to 23.7%.2 Accordingly, the resultant sample size ranged from 174 to 278 patients.
Patients were asked about their personal details, medical information, and knowledge about diabetes and DR. The questionnaire also gathered information regarding age, gender, education, economic status, and duration of diabetes. The answers were collected directly through face-to-face interviews. The second part of the questionnaire was about retinopathy awareness, history of screening for retinopathy, and awareness about retinopathy treatment. The patients were also asked about risk factors and preventive measures for the effective management of DR. The obtained data were analyzed using Microsoft Excel 365 v.16 (Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA) and statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 26.0 (IBM corporation, CA, USA). Student’s t-test was used to test for significance in continuous variables, and chi-square was used in categorical variables, considering the significance level at a p-value of 0.05 and confidence interval of 95%.
Results
A total of 303 patients were recruited and interviewed in the present study, out of which 49% were males and 51% were females. The average age of recruited patients was 61 years (range: 15–84 years). Most of the patients (more than 85%) were from Amman and had DM type II (97%) (Table 1).
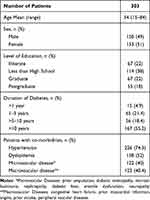 |
Table 1 Patients’ Demographics |
Furthermore, 54.35% of patients stated that they have been suffering from diabetes for 10 years; nevertheless, their knowledge about normal serum glucose level was only satisfactory, with 56.18% aware of the normal serum glucose levels. The last HbA1c value reported among 37.71% patients was 6.5–8; on the other hand, 31.57% patients had HbA1c levels >8. Moreover, 51.18% of the patients visited internists for disease management, and 80.55% visited the clinics regularly for checkup.
Regarding retinal exams, 61.6% of respondents said they have undergone a retinal exam at least once in their life. By contrast, 53% of them used to undergo a retinal exam on an irregular basis. Furthermore, in the majority of patients, retinal exam was performed one year after being diagnosed with diabetes (76.40%) (Table 2).
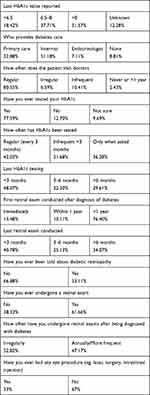 |
Table 2 Patients’ Response to Different Questions Related to Awareness About Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic Retinopathy |
Regarding patient awareness about DR, 66.88% of the patients stated that they have not been told about DR, with only 33.11% of the patients talked about the risk of developing DR initially. Based on the univariate analysis, the rate of being unaware of DR was significantly correlated with lower level of education (p<0.0001), female sex (p=0.039), younger age (p=0.03) and shorter duration of DM (p<0.0001) (Table 3). However, the multivariate analysis showed that only the level of education (p<0.0001) and duration of DM (p=0.001) retained statistical significance.
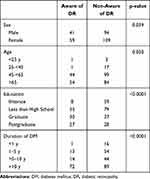 |
Table 3 Factors Predicting Level of Diabetic Retinopathy Awareness Among Patients with Diabetes Mellitus |
Discussion
Educating patients about their chronic illnesses is crucial for their understanding of the nature of their disease, as well as for their compliance to the recommended treatment.19,20 Currently, patients get educated mostly via the internet, through different media, or to a lesser extent, through their caregivers.21 With continuously increasing patient volume, doctors may not allocate enough time for each patient to discuss different aspects of their illness as well as to answer questions. At the same time, patients may not understand all of the instructions and information given by their doctors.20 Patients who are aware of their diseases are more likely to comply with physician instructions, taking preventive measures and administering the prescribed treatments.
In Jordan, the awareness and attitudes of patients towards their DM and DR is of crucial importance due to the high prevalence of DM in our community. Rabiu et al have mentioned that there is an increased rate of prevalence related to blindness and DR in the Northern region of Jordan.11
In this cohort, the majority of the patients were well aware of the significance of good glycemic control, as shown by their metabolic control. About 80% of patients were regularly visiting their caregiver. This may indicate that patients are taking good care of their DM. The presence of other macro-and micro-vascular DM complications, which were observed in 40% of patients, may have also contributed to the high percentage of compliance. However, the self-reported HbA1c indicated poor disease control. Better glycemic control is reportedly associated with better awareness about eye complications, as demonstrated by other studies.22 This association could be explained by the fact that patients with DM take better care of themselves when driven by their knowledge about its complications, especially DR.
Two-thirds of study sample were not aware of DR being a complication of DM. Similar findings in Jordan have been shown by Haddad et al.16 However, Bakkar et al reported a higher percentage of awareness among patients with diabetes in Jordan.15 Moreover, a study conducted in Saudi Arabia revealed that awareness about retinopathy was high (61%) among patients suffering from DM.23 Similar results were obtained among patients from Myanmar and Nigeria, where 86% and 84.3% patients were aware about the complications of DR, respectively.24,25 These differences may be attributed to the different populations selected in the surveys. In this study, we interviewed patients visiting mostly primary health care systems in the public sector, which had a higher percentage of low educational levels compared to the population surveyed in the study by Bakkar et al. In both studies, higher educational level has been demonstrated to be associated with better DR awareness. The other predictive factor of awareness in this study was the duration of DM, which is consistent with findings from other studies.15,16,26,27 Patients with DM tend to have more cumulative knowledge about their disease, making them more aware of its complications. Younger age and female sex were associated with lower levels of awareness, as per univariate analysis. However, they lost their statistical significance during the multivariate analysis. Previous studies also did not find any correlation between age and sex and the level of DR awareness.15,26,27 The majority of patients were from urban areas in Amman, where it is expected to have higher level of health awareness. Given this fact and study findings, it is speculated that lower levels of awareness will be observed in the more rural areas of Jordan.
DR treatment is most effective during the early stage before the development of vision-threatening retinopathy. Regular screening is of paramount importance in early detection of retinopathy and its subsequent treatment.28 The diabetic condition is a self-managed disease, which needs intrinsic motivation for successful and optimal self-management. Patients with diabetes need to be regularly screened for the early diagnosis of retinopathy, which also requires proper awareness about this disease among the affected individuals. In this cohort, although the majority had undergone retinal exams (62%), most of them had it on an irregular basis. In addition, the vast majority had their first retinal exam more than one year after diagnosis (76%). Bakkar et al also reported that 32% of patients have never had their retina examined. Compliance with regular eye exam remains a global issue, as demonstrated by several other studies.22,29,30 In Jordan, this lack of compliance can be attributed to poorly distributed secondary and tertiary medical services across the country, which makes it difficult for patients with DM to reach proper facilities for screening within their geographic area.
This study has several limitations. It is a qualitative study where results depend mainly on respondents’ answers, which may not be accurate. Moreover, the selected sample of patients may not be representative of the true study population, since patients were recruited from a health facility in an urban setting, rather than a random community selection involving rural areas.
Conclusion
The study concluded that diabetes, being an epidemic problem worldwide, needs attention from patients, health care providers, and the government. Moreover, the study has revealed that the majority of patients suffering from diabetes are well aware of the importance of diabetic management and control of blood sugar. However, most of them also demonstrate poorly controlled disease, based on self-reported A1c levels. Moreover, the majority of patients recruited in this study were unaware of serious complications associated with the development of DR. Regular routine examination of diabetic complications as well as the management of patients with diabetes may help in decreasing the complications associated with the disease. Therefore, there is a need to conduct more studies to create awareness among the patients suffering from diabetes. There is also a need to re-evaluate non-governmental and governmental efforts to educate people about the complications associated with diabetes.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the great efforts of the medical students at the Hashemite University: Ayman Abu-Qub’a, Sara Otom, and Othman Odeh who helped greatly in data collection and patients’ interviews.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. International Diabetes Federation, Belgium. IDF Diabetes Atlas. 9th edition; 2019. Available from: https://www.diabetesatlas.org/en/. Accessed July 27, 2020.
2. Ajlouni K, Batieha A, Jaddou H, et al. Time trends in diabetes mellitus in Jordan between 1994 and 2017. Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t. Diabet Med. 2019;36(9):1176–1182. doi:10.1111/dme.13894
3. World Health Organization. Country profile-Jordan; 2021. Available from: https://www.who.int/diabetes/country-profiles/jor_en.pdf.
4. Harding JL, Pavkov ME, Magliano DJ, Shaw JE, Gregg EW. Global trends in diabetes complications: a review of current evidence. Review. Diabetologia. 2019;62(1):3–16. doi:10.1007/s00125-018-4711-2
5. Paneni F, Beckman JA, Creager MA, Cosentino F. Diabetes and vascular disease: pathophysiology, clinical consequences, and medical therapy: part I. Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t Review. Eur Heart J. 2013;34(31):2436–2443. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/eht149
6. Klein R, Klein BE, Moss SE, Davis MD, DeMets DL. The Wisconsin epidemiologic study of diabetic retinopathy. III. Prevalence and risk of diabetic retinopathy when age at diagnosis is 30 or more years. Research Support, U.S. Gov’t, P.H.S. Arch Ophthalmol. 1984;102(4):527–532. doi:10.1001/archopht.1984.01040030405011
7. Klein R, Klein BE, Moss SE, Davis MD, DeMets DL. The Wisconsin epidemiologic study of diabetic retinopathy. II. Prevalence and risk of diabetic retinopathy when age at diagnosis is less than 30 years. Research Support, U.S. Gov’t, P.H.S. Arch Ophthalmol. 1984;102(4):520–526. doi:10.1001/archopht.1984.01040030398010
8. Yau JW, Rogers SL, Kawasaki R, et al. Global prevalence and major risk factors of diabetic retinopathy. Research Support, N.I.H., Extramural Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t Review Systematic Review. Diabetes Care. 2012;35(3):556–564. doi:10.2337/dc11-1909
9. Kempen JH, O’Colmain BJ, Leske MC, et al. The prevalence of diabetic retinopathy among adults in the United States. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004;122(4):552–563. doi:10.1001/archopht.122.4.552
10. Al-Amer RM, Khader Y, Malas S, Abu-Yaghi N, Al-Bdour M, Ajlouni K. Prevalence and risk factors of diabetic retinopathy among Jordanian patients with type 2 diabetes. Digit J Ophthalmol. 2008;14:42–49. doi:10.5693/djo.01.2008.013
11. Rabiu MM, Al Bdour MD, Abu Ameerh MA, Jadoon MZ. Prevalence of blindness and diabetic retinopathy in northern Jordan. Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2015;25(4):320–327. doi:10.5301/ejo.5000557
12. Arcury TA, Grzywacz JG, Ip EH, et al. Social integration and diabetes management among rural older adults. Research Support, N.I.H., Extramural. J Aging Health. 2012;24(6):899–922. doi:10.1177/0898264312449186
13. Kohner EM. Microvascular disease: what does the UKPDS tell us about diabetic retinopathy? Diabet Med. 2008;25(Suppl 2):20–24. doi:10.1111/j.1464-5491.2008.02505.x
14. Hainsworth DP, Bebu I, Aiello LP, et al. Risk factors for retinopathy in type 1 diabetes: the DCCT/EDIC study. Observational Study Research Support, N.I.H., Extramural Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(5):875–882. doi:10.2337/dc18-2308
15. Bakkar MM, Haddad MF, Gammoh YS. Awareness of diabetic retinopathy among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Jordan. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2017;10:435–441. doi:10.2147/DMSO.S140841
16. Haddad MF, Bakkar MM, Abdo N. Public awareness of common eye diseases in Jordan. BMC Ophthalmol. 2017;17(1):177. doi:10.1186/s12886-017-0575-3
17. Jammal H, Khader Y, Alkhatib S, Abujbara M, Alomari M, Ajlouni K. Diabetic retinopathy in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus in Jordan: prevalence and associated factors. J Diabetes. 2013;5(2):172–179. doi:10.1111/1753-0407.12015
18. Statistics Do. Estimated population of 2020 and some selected data; 2021. Available from: http://dosweb.dos.gov.jo/DataBank/Population_Estimares/PopulationEstimates.pdf.
19. Wald HS, Dube CE, Anthony DC. Untangling the Web – the impact of Internet use on health care and the physician-patient relationship. Review. Patient Educ Couns. 2007;68(3):218–224. doi:10.1016/j.pec.2007.05.016
20. Austin Boren S, Gunlock TL, Krishna S, Kramer TC. Computer-aided diabetes education: a synthesis of randomized controlled trials. Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t Review. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2006;51–55.
21. Glasgow RE. Interactive media for diabetes self-management: issues in maximizing public health impact. Research Support, N.I.H., Extramural Review. Med Decis Making. 2010;30(6):745–758. doi:10.1177/0272989X10385845
22. Katibeh M, Ahmadieh H, Beiranvand R, Soleimanizad R, Javadi MA. Awareness of the necessity of regular eye examinations among diabetics: the Yazd Eye Study. Int J Prev Med. 2017;8:49. doi:10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_218_15
23. Alasiri RA, Bafaraj AG. Awareness of diabetic retinopathy among diabetic patients in King Abdulaziz University Hospital, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Ann Int Med Dent Res. 2016;2(6). doi:10.21276/aimdr.2016.2.6.ME10
24. Muecke JS, Newland HS, Ryan P, et al. Awareness of diabetic eye disease among general practitioners and diabetic patients in Yangon, Myanmar. Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2008;36(3):265–273. doi:10.1111/j.1442-9071.2008.01724.x
25. Mohammed AW. Awareness of diabetic retinopathy amongst diabetic patients at the murtala mohammed hospital, Kano, Nigeria. Niger Med J. 2009;50(2):38–41.
26. Mian LS, Moin M, Khan IH, Manzoor A. Awareness of diabetic retinopathy among diabetic patients. Pak J Ophthalmol. 2017;33(3):7.
27. Addoor KR, Bhandary SV, Khanna R, et al. Assessment of awareness of diabetic retinopathy among the diabetics attending the peripheral diabetic clinics in Melaka, Malaysia. Med J Malaysia. 2011;66(1):48–52.
28. Ferris FL. How effective are treatments for diabetic retinopathy? JAMA. 1993;269(10):1290–1291. doi:10.1001/jama.1993.03500100088034
29. Hussain R, Rajesh B, Giridhar A, et al. Knowledge and awareness about diabetes mellitus and diabetic retinopathy in suburban population of a South Indian state and its practice among the patients with diabetes mellitus: a population-based study. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2016;64(4):272–276. doi:10.4103/0301-4738.182937
30. Cetin EN, Zencir M, Fenkci S, Akin F, Yildirim C. Assessment of awareness of diabetic retinopathy and utilization of eye care services among Turkish diabetic patients. Prim Care Diabetes. 2013;7(4):297–302. doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2013.04.002
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
