Back to Journals » Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment » Volume 16
Association Analysis Between SNPs in the Promoter Region of RGS4 and Schizophrenia in the Northern Chinese Han Population
Authors Xu F, Yao J , Wu X, Xia X, Xing J, Xuan J, Liu Y, Wang B
Received 18 February 2020
Accepted for publication 30 March 2020
Published 16 April 2020 Volume 2020:16 Pages 985—992
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S250282
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yuping Ning
Feng-ling Xu, Jun Yao, Xue Wu, Xi Xia, Jia-xin Xing, Jin-feng Xuan, Yong-ping Liu, Bao-jie Wang
School of Forensic Medicine, China Medical University, Shenyang 110122, People’s Republic of China
Correspondence: Bao-jie Wang
School of Forensic Medicine, China Medical University, No. 77 Puhe Road, Shenbei New District, Shenyang 110122, People’s Republic of China
Email [email protected]
Background: Abnormal RGS4 gene expression may cause neurotransmitter disorders, resulting in schizophrenia. The association between RGS4 and the risk of schizophrenia is controversial, and there has been little research on the SNPs in the promoter region of RGS4.
Purpose: The present study was performed to detect the association between SNPs in the promoter region of the RGS4 gene and the risk of schizophrenia.
Materials and Methods: In this study, the 1757-bp fragment (− 1119–+600, TSS+1) of RGS4 was amplified and sequenced in 198 schizophrenia patients and 264 healthy controls of the northern Chinese Han population. Allele, genotype and haplotype frequencies were analyzed by chi‐square test.
Results: Four SNPs were detected in the region. LD analysis determined that rs7515900 was linked to rs10917671 (D’ = 1, r2 = 1). Therefore, the data for rs10917671 were eliminated from further analysis. Genotype TT of rs12041948 (P = 0.009, OR = 1.829, and 95% CI = 0.038– 0.766) was significantly different between the two groups in the northern Chinese Han population. In males, genotype GG of rs6678136 (P = 0.009, OR = 2.292, and 95% CI = 1.256– 4.18) and CC of rs7515900 (P = 0.003, OR = 2.523, and 95% CI = 1.332– 4.778) were significantly different.
Conclusion: The results of this study suggested that genotype TT of rs12041948 in the pooled male and female samples and GG of rs6678136 and CC of rs7515900 in the male samples could be risk factors for schizophrenia. The present study is the first to detect an association between SNPs in the promoter region of the RGS4 gene and the risk of schizophrenia in the northern Chinese Han population. Functional studies are required to confirm these findings.
Keywords: RGS4, schizophrenia, promoter region, SNPs
Introduction
Schizophrenia is a chronic mental disorder characterized by fantasies, delusions, altered emotional responses, behavioral disorders, social isolation, and cognitive impairment.1,2 The clinical manifestations of this disease in different patients are divergent, and the pathogenesis remains unknown.3 Studies of schizophrenic twins found that the incidence in monozygotic twins was four to six times higher than that in dizygotic twins.4 Studies on the relationship between twins and adoptees and schizophrenia suggested that both genetic and environmental factors could influence the onset of schizophrenia.5 Associations between genes and the risk of schizophrenia are controversial.6–8 Regulators of G-protein signaling (RGS) negatively modulate G-protein signaling by acting as GTPase-activating proteins that shorten, sharpen, or otherwise attenuate signals transduced by heterotrimeric G-protein-coupled receptors.9,10 The RGS gene has been associated with many disorders, including schizophrenia11 and neuroglioma.12 RGS4 has attracted more attention than other RGS. The RGS4 gene is highly expressed in the brain, especially in the cerebral cortex. RGS4 is expressed in a highly regulated manner in subclasses of developing neurons.13 RGS4 plays an important role in pre- and post-synaptic neurotransmitter transmission, such as opioid, serotoninergic dopaminergic, and acetylcholine signaling.10,14 The relationship between RGS4 and the risk of schizophrenia is controversial based on epidemiological surveys and meta-analyses.15,16 One hypothesis is that abnormal RGS4 expression would cause neurotransmitter disorders, resulting in schizophrenia.17,18 The current study is the first to investigate the association between SNPs in the promoter region of the RGS4 gene and the risk of schizophrenia in the northern Chinese Han population.
Materials and Methods
Samples
The study included venous blood specimens from 198 schizophrenia patients (case group, 87 males and 111 females) and 264 healthy subjects of the northern Chinese Han population (control group, 133 males and 131 females). The inclusion criteria for the case group were as follows: (1) recruited from the Third People’s Hospital of Liaoning Province; (2) northern Chinese Han population; (3) fully met DSM-IV criteria. The inclusion criteria for the control group were as follows: (1) recruited from blood donors; (2) northern Chinese Han population; (3) unaffected by mental disorder through at least three generations. Participants were excluded if they had other mental diseases or serious physiological diseases or were relatives of other participants. The case group (mean age ± standard deviation [SD], 43.1 ± 6.1 years; range 21–65 years) and control group (mean age ± SD, 40.7 ± 6.4 years; range 24–65 years) were matched for ethnicity, age, gender, and geographical region.
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. All participants provided written consent after being informed of the study procedures and implications. Sample collection and analysis were approved by the Ethics Committee of China Medical University.
DNA Extraction, Amplification, and Sequencing
Genomic DNA was extracted using the phenol-chloroform method previously described.19 The primers for amplification (F and R) and sequencing (CXF and CXR) were designed using the Premier 5 Design Program (www.premierbiosoft.com) (Table 1). The 1757-bp fragment (−1119–+600, TSS+1) was amplified using primers F and R. The 20 µL PCR reaction contained 2.0 µL 10×buffer, 2 µL 2.5 mM dNTP mix, 0.2 µL of LA Taq (5.0 U/µL), 1.5 µL each primer (5 pM), and 20 ng of template DNA. PCR was conducted according to the following cycle conditions: initial denaturation of 94°C for 5 min; 30 cycles of 94°C denaturation for 30 s, 64°C annealing for 30 s, and 72°C elongation for 60 s; final extension at 72°C for 10 min.
 |
Table 1 Primers in the Study |
Sequencing was performed with an ABI 377 DNA automatic sequencer by the Taihe Biotechnology Co. (Beijing, China).
Data Analysis
The generated sequences were aligned with reference sequences in the National Center for Biotechnology Information database to identify polymorphisms. Allele, genotype and haplotype frequencies were calculated using Microsoft Excel. The Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) test, haplotype verification, and linkage disequilibrium (LD) were performed using Haploview 4.1 software (Broad Institute, Cambridge, MA, USA).19 The differences between case and control groups were determined by the chi‐square test using SPSS PASW Statistics v. 20.0 (IBM, Chicago, IL). A p < 0.05 was statistically significant. The Bonferroni correction was conducted for multiple independent tests (p < 0.05/4 as statistically significant).20
Results
Genotype TT of Rs12041948 Was a Risk Factor in the Northern Chinese Han Population
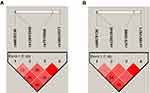
There were four SNPs (rs6678136, rs12041948, rs7515900, and rs10917671) detected in the 1757-bp fragment of the RGS4 gene. The frequencies of the alleles and genotypes of the four SNPs are shown in Table 2. The LD block is presented in Figure 1 (rs6678136 and rs12041948 D’ = 0.722, r2 = 0.167; rs12041948 and rs7515900 D’ = 0.806, r2 = 0.166; rs7515900 and rs10917671 D’ = 1, r2 = 1). LD analysis determined that rs7515900 was linked to rs10917671. Therefore, the data for rs10917671 were excluded from further analysis. In the control group, the four SNPs satisfied the HWE for the northern Chinese Han population (Table 2).
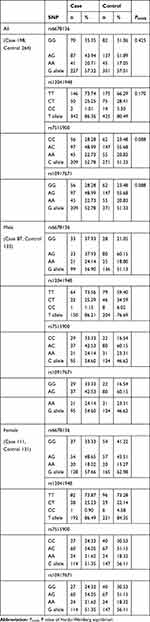 |
Table 2 Genotype and Allele Distributions of the RGS4 Gene in Patients and Controls |
No association was observed between rs6678136 or rs7515900 and the risk of schizophrenia (Table 3). However, the T allele of rs12041948 was associated with the risk of schizophrenia (P = 0.021, odds ratio (OR) = 1.535, and 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.072–2.197). In the homozygous codominant model, genotype TT (P = 0.009, OR = 5.840, and 95% CI = 1.306–26.115) was significantly different between the two groups. In the dominant model, the genotype TT+TC was significantly different (P = 0.018, OR = 1.818, and 95% CI = 0.041–0.811); however, this difference disappeared following the Bonferroni correction.
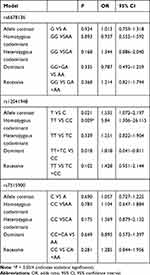 |
Table 3 Analysis of RGS4 Polymorphisms and Schizophrenia in Cases and Controls |
Genotype GG of Rs6678136 and CC of Rs7515900 Were Risk Factors in the Male Northern Chinese Han Population
Relationships between the three SNPs and the risk of schizophrenia were detected in the male population (Table 4). Genotype GG of rs6678136 was significantly different between case and control groups in the heterozygous codominant model (P = 0.002, OR = 2.857, and 95% CI = 1.497–5.454) and recessive model (P = 0.009, OR = 2.292, and 95% CI = 1.256–4.18). The differences were also significant after the Bonferroni correction. In the recessive model, genotype TT of rs12041948 (P = 0.043, OR = 1.902, and 95% CI = 1.056–3.427) was significantly different between the two groups; however, the difference was not significant after the Bonferroni correction. In the heterozygous codominant and recessive models, genotype CC of rs7515900 was associated with the risk of schizophrenia (P = 0.003, OR = 2.850, and 95% CI = 1.448–5.611; P = 0.003, OR = 2.523, and 95% CI = 1.332–4.778, respectively). These differences remained after the Bonferroni correction.
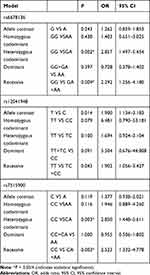 |
Table 4 Analysis of RGS4 Polymorphisms and Schizophrenia in Male Cases and Controls |
No Association Was Detected Between RGS4 and the Risk of Schizophrenia in the Female Northern Chinese Han Population
No significant differences were found between rs6678136, rs12041948, and rs7515900 and the risk of schizophrenia in the female northern Chinese Han population (Table 5).
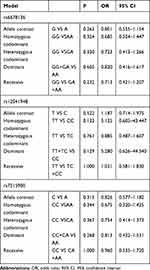 |
Table 5 Analysis of RGS4 Polymorphisms and Schizophrenia in Female Cases and Controls |
No Associations Were Detected Between Haplotypes and the Risk of Schizophrenia
Eight haplotypes composed of the three SNPs (rs6678136, rs12041948, and rs7515900) were found in the northern Chinese Han population. Three haplotypes (ATC, GCA, GCC) were only detected in the control group (Table 6). Haplotype GTC was the most frequent haplotype. No significant differences were detected between any of the haplotypes and the risk of schizophrenia.
 |
Table 6 Haplotype Distribution of Rs6678136, Rs12041948, and Rs7515900 of the RGS4 Gene |
Discussion
In previous studies, five target SNPs (rs10917670, rs951436, rs951439, rs2661319, and rs10759) in the RGS4 gene were intensively studied to determine the association between the RGS4 gene and the risk of schizophrenia.21–23 However, there has been little study of the 1757-bp fragment (−1119–+600, TSS+1) analyzed in the current study. Moreover, the relationships between the three SNPs (rs6678136, rs12041948, and rs7515900) and the risk of schizophrenia were not previously studied in the northern Chinese Han population. In the present study, there was no association between rs6678136 or rs7515900 and the risk of schizophrenia in the northern Chinese Han population. These findings were consistent with a previous study of a population in the United States.24 Furthermore, in male subgroup analysis, both genotype GG of rs6678136 and genotype CC of rs7515900 were identified as risk factors for schizophrenia. It was previously shown that gender might affect the outcome of schizophrenia and influence the correlation between candidate genes and schizophrenia.25 The genotype TT of rs12041948 was a risk factor for schizophrenia in the northern Chinese Han population; however, a significant difference was not detected by gender subgroup analysis. Finally, the haplotypes composed of the three SNPs were not associated with the risk of schizophrenia.
The association between RGS4 and the risk of schizophrenia was controversial in different ethnic groups,15,26 geographical locations,27 and sample number.16 It was reported that some marker SNPs within the RGS4 gene were associated with a more severe baseline for the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) total score.28 RGS4 gene variants were associated with risperidone antipsychotic treatment response in schizophrenia.29 The clinical manifestation of schizophrenia and treatment response can be influenced by the SNPs in the RGS4 gene, suggesting that the RGS4 gene might play a role in the fundamental process of disease pathophysiology.30 In addition, RGS4 mRNA expression was decreased in the prefrontal region of post-mortem brains from schizophrenic patients.31
Transcription factors acting as critical activators or repressors regulate transcription by targeting cis-acting elements in the promoter region of genes.32 RGS4 expression was regulated by some transcription factors,33,34 such as C/EBP, Bcl6,35 and GATA-6.34 The SNPs identified in this study might affect the binding of specific transcription factors, leading to altered gene expression. Functional assays are needed to address these possibilities. The transcription factors that could bind to the RGS4 promoter region were predicted in JASPAR (http://jaspar.genereg.net/). Rs6678136 might be located at the binding site of activating transcription factor 2 (ATF2), which was associated with depression and schizophrenia.36,37 ATF2 overexpression in the nucleus accumbens caused an increase in emotional reactivity and antidepressant-like responses.38 Rs12041948 might be located at the binding site for aristaless-like homeobox 3 (ALX3). Garcia-Sanz et al found that ALX3 caused congenital craniofacial and neural tube defects.39 Rs7515900 might be located at the androgen receptor (AR) binding site. One SNP, which was functional for AR binding and transcription, represented a risk-associated allele for schizophrenia.40
The present study is the first to detect an association between SNPs in the promoter region of the RGS4 gene and the risk of schizophrenia in the northern Chinese Han population. The association we observed should be viewed with caution. First, the sample number was not large enough to represent the northern Chinese Han population. Second, only SNPs in the RGS4 promoter region were analyzed. Third, interaction of gene-gene, which might influence the occurrence of schizophrenia, was not detected.41,42 In addition, functional assays are needed to confirm the results. The findings of this study have implications for future molecular genetic studies and personalized medicine.
Acknowledgment
All authors of the study were worthy of appreciation.
Disclosure
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Ide M, Ohnishi T, Toyoshima M, et al. Excess hydrogen sulfide and polysulfides production underlies a schizophrenia pathophysiology. EMBO Mol Med. 2019;11(12):e10695. doi:10.15252/emmm.201910695
2. Kim SJ, Jung D, Shim JC, et al. The effect of anticholinergic burden on cognitive and daily living functions in patients with schizophrenia. Asian J Psychiatr. 2019;46:111–117. doi:10.1016/j.ajp.2019.10.013
3. Yung AR, Wood SJ, Malla A, Nelson B, McGorry P, Shah J. The reality of at risk mental state services: a response to recent criticisms. Psychol Med. 2019;1–7. doi:10.1017/S003329171900299X
4. McGue M, Gottesman II. A single dominant gene still cannot account for the transmission of schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1989;46(5):478–480. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.1989.01810050092016
5. Jitoku D, Yoshikawa T. [Genetics of schizophrenia]. Nihon Rinsho. 2013;71(4):599–604. Japanese.
6. Munoz-Negro JE, Cuadrado L, Cervilla JA. Current Evidences on Psychopharmacology of Schizoaffective Disorder. Actas Esp Psiquiatr. 2019;47(5):190–201.
7. Wood LS, Pickering EH, Dechairo BM. Significant support for DAO as a schizophrenia susceptibility locus: examination of five genes putatively associated with schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 2007;61(10):1195–1199. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.07.005
8. Nicodemus KK, Kolachana BS, Vakkalanka R, et al. Evidence for statistical epistasis between catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) and polymorphisms in RGS4, G72 (DAOA), GRM3, and DISC1: influence on risk of schizophrenia. Hum Genet. 2007;120(6):889–906. doi:10.1007/s00439-006-0257-3
9. Mohammadi M, Mohammadiarani H, Shaw VS, Neubig RR, Vashisth H. Interplay of cysteine exposure and global protein dynamics in small-molecule recognition by a regulator of G-protein signaling protein. Proteins. 2019;87(2):146–156. doi:10.1002/prot.25642
10. Ross EM, Wilkie TM. GTPase-activating proteins for heterotrimeric G proteins: regulators of G protein signaling (RGS) and RGS-like proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 2000;69(1):795–827. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.69.1.795
11. Huang MW, Lin YJ, Chang CW, et al. RGS4 deficit in prefrontal cortex contributes to the behaviors related to schizophrenia via system xc(-)-mediated glutamatergic dysfunction in mice. Theranostics. 2018;8(17):4781–4794. doi:10.7150/thno.25189
12. Bao MH, Lv QL, Szeto V, et al. TRPM2-AS inhibits the growth, migration, and invasion of gliomas through JNK, c-Jun, and RGS4. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(5):4594–4604. doi:10.1002/jcp.29336
13. Grillet N, Dubreuil V, Dufour HD, Brunet JF. Dynamic expression of RGS4 in the developing nervous system and regulation by the neural type-specific transcription factor Phox2b. J Neurosci. 2003;23(33):10613–10621. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-33-10613.2003
14. De Vries L, Zheng B, Fischer T, Elenko E, Farquhar MG. The regulator of G protein signaling family. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2000;40(1):235–271. doi:10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.40.1.235
15. Zhang F, St Clair D, Liu X, et al. Association analysis of the RGS4 gene in Han Chinese and Scottish populations with schizophrenia. Genes Brain Behav. 2005;4(7):444–448. doi:10.1111/j.1601-183X.2005.00167.x
16. Talkowski ME, Seltman H, Bassett AS, et al. Evaluation of a susceptibility gene for schizophrenia: genotype based meta-analysis of RGS4 polymorphisms from thirteen independent samples. Biol Psychiatry. 2006;60(2):152–162. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.02.015
17. Cheng YC, Scotting PJ, Hsu LS, et al. Zebrafish rgs4 is essential for motility and axonogenesis mediated by Akt signaling. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013;70(5):935–950. doi:10.1007/s00018-012-1178-z
18. Ding L, Hegde AN. Expression of RGS4 splice variants in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of schizophrenic and bipolar disorder patients. Biol Psychiatry. 2009;65(6):541–545. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.10.026
19. Zhang XC, Ding M, Adnan A, et al. No association between polymorphisms in the promoter region of dopamine receptor D2 gene and schizophrenia in the northern Chinese Han population: a case-control study. Brain Behav. 2019;9(2):e01193. doi:10.1002/brb3.1193
20. Armstrong RA. When to use the Bonferroni correction. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2014;34(5):502–508. doi:10.1111/opo.12131
21. Rethelyi JM, Bakker SC, Polgar P, et al. Association study of NRG1, DTNBP1, RGS4, G72/G30, and PIP5K2A with schizophrenia and symptom severity in a Hungarian sample. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2010;153B(3):792–801. doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.31049
22. Jonsson EG, Saetre P, Nyholm H, et al. Lack of association between the regulator of G-protein signaling 4 (RGS4) rs951436 polymorphism and schizophrenia. Psychiatr Genet. 2012;22(5):263–264. doi:10.1097/YPG.0b013e32834f3558
23. So HC, Chen RY, Chen EY, Cheung EF, Li T, Sham PC. An association study of RGS4 polymorphisms with clinical phenotypes of schizophrenia in a Chinese population. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2008;147B(1):77–85. doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.30577
24. Sanders AR, Duan J, Levinson DF, et al. No significant association of 14 candidate genes with schizophrenia in a large European ancestry sample: implications for psychiatric genetics. Am J Psychiatry. 2008;165(4):497–506. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2007.07101573
25. Seeman MV. Does Gender Influence Outcome in Schizophrenia? Psychiatr Q. 2019;90(1):173–184. doi:10.1007/s11126-018-9619-y
26. Sobell JL, Richard C, Wirshing DA, Heston LL. Failure to confirm association between RGS4 haplotypes and schizophrenia in Caucasians. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2005;139B(1):23–27. doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.30221
27. Li D, He L. Association study of the G-protein signaling 4 (RGS4) and proline dehydrogenase (PRODH) genes with schizophrenia: a meta-analysis. Eur J Hum Genet. 2006;14(10):1130–1135. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201680
28. Campbell DB, Ebert PJ, Skelly T, et al. Ethnic stratification of the association of RGS4 variants with antipsychotic treatment response in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 2008;63(1):32–41. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.04.018
29. Kaur H, Jajodia A, Grover S, et al. Genetic variations of PIP4K2A confer vulnerability to poor antipsychotic response in severely ill schizophrenia patients. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e102556. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0102556
30. Lane HY, Liu YC, Huang CL, et al. RGS4 polymorphisms predict clinical manifestations and responses to risperidone treatment in patients with schizophrenia. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2008;28(1):64–68. doi:10.1097/jcp.0b013e3181603f5a
31. Mirnics K, Middleton FA, Stanwood GD, Lewis DA, Levitt P. Disease-specific changes in regulator of G-protein signaling 4 (RGS4) expression in schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry. 2001;6(3):293–301. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4000866
32. Scalia P, Williams SJ, Giordano A. Core Element Cloning, Cis-Element Mapping and Serum Regulation of the Human EphB4 Promoter: a Novel TATA-Less Inr/MTE/DPE-Like Regulated Gene. Genes (Basel). 2019;10(12):997. doi:10.3390/genes10120997
33. Yang J, Huang J, Chatterjee TK, Twait E, Fisher RA. A novel mechanism involving coordinated regulation of nuclear levels and acetylation of NF-YA and Bcl6 activates RGS4 transcription. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(39):29760–29769. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.121459
34. Zhang Y, Li F, Xiao X, et al. Regulator of G protein signaling 4 is a novel target of GATA-6 transcription factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;483(3):923–929. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.10.024
35. Chowdari KV, Bamne M, Wood J, et al. Linkage disequilibrium patterns and functional analysis of RGS4 polymorphisms in relation to schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 2008;34(1):118–126. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbm042
36. Laifenfeld D, Karry R, Grauer E, Klein E, Ben-Shachar D. ATF2, a member of the CREB/ATF family of transcription factors, in chronic stress and consequent to antidepressant treatment: animal models and human post-mortem brains. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2004;29(3):589–597. doi:10.1038/sj.npp.1300357
37. Lencz T, Lambert C, DeRosse P, et al. Runs of homozygosity reveal highly penetrant recessive loci in schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(50):19942–19947. doi:10.1073/pnas.0710021104
38. Green TA, Alibhai IN, Unterberg S, et al. Induction of activating transcription factors (ATFs) ATF2, ATF3, and ATF4 in the nucleus accumbens and their regulation of emotional behavior. J Neurosci. 2008;28(9):2025–2032. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5273-07.2008
39. Garcia-Sanz P, Mirasierra M, Moratalla R, Vallejo M. Embryonic defence mechanisms against glucose-dependent oxidative stress require enhanced expression of Alx3 to prevent malformations during diabetic pregnancy. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):389. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-00334-1
40. Hashimoto R, Ohi K, Yasuda Y, et al. Variants of the RELA gene are associated with schizophrenia and their startle responses. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011;36(9):1921–1931. doi:10.1038/npp.2011.78
41. Mohamed ZI, Tee SF, Tang PY. Association of functional polymorphisms in 3ʹ-untranslated regions of COMT, DISC1, and DTNBP1 with schizophrenia: a meta-analysis. Psychiatr Genet. 2018;28(6):110–119. doi:10.1097/YPG.0000000000000210
42. Edwards TL, Wang X, Chen Q, et al. Interaction between interleukin 3 and dystrobrevin-binding protein 1 in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2008;106(2–3):208–217. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2008.07.022
 © 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.