Back to Journals » Cancer Management and Research » Volume 12
Analyses of DNA Methylation Involved in the Activation of Nuclear Karyopherin Alpha 2 Leading to Identify the Progression and Prognostic Significance Across Human Breast Cancer
Authors Cui X , Jing X, Wu X, Xu J, Liu Z, Huo K, Wang H
Received 15 May 2020
Accepted for publication 13 July 2020
Published 3 August 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 6665—6677
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S261290
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Bilikere Dwarakanath
Xiangrong Cui,1,* Xuan Jing,2,* Xueqing Wu,1 Jing Xu,3 Zhuang Liu,3 Kai Huo,4 Hongwei Wang3
1Reproductive Medicine Center, Children’s Hospital of Shanxi and Women Health Center of Shanxi, Affiliated of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, People’s Republic of China; 2Clinical Laboratory, Shanxi Province People’s Hospital, Affiliated of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, People’s Republic of China; 3Department of Hematology, 2nd Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan, Shanxi 030001, People’s Republic of China; 4Department of Breast Surgery, Shanxi Cancer Hospital, Taiyuan 030000, People’s Republic of China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Correspondence: Hongwei Wang Tel +86-351-3360725
Email [email protected]
Background: Karyopherin alpha 2 (KPNA2) is a nuclear import factor that plays a crucial role in nucleocytoplasmic transport, as well as cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in several cancers. However, the roles of KPNA2 in breast cancer as well as the underlying molecular mechanisms have not been elucidated.
Materials and Methods: To evaluate gene expression alterations during breast carcinogenesis, KPNA2 expression was analyzed using the Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis and Oncomine analyses. The correlation between methylation and expression was analyzed using the MEXPRESS tool, UALCAN cancer database, and cBioPortal browser. Then, the expression and prognostic value of KPNA2 were investigated by our own breast cancer samples using RT-PCR. KPNA2 methylation level was detected by methylation-specific PCR.
Results: We obtained the following important results. (1) KPNA2 expression was significantly higher in breast cancer than normal samples and regulated by aberrant DNA hypomethylation of promoter region. (2) Among patients with breast cancer, those with higher KPNA2 expression had a lower survival rate. (3) The major mutation type of KPNA2 in breast cancer samples was missense mutation. (4) Homer1 was able to promote breast cancer progression may be through upregulating TPX2 expression.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that aberrant DNA hypomethylation of promoter regions contributes to the aberrant expression of KPNA2 in breast cancer, which might be a potential indicator of poor prognosis.
Keywords: KPNA2, breast cancer, prognosis, methylation, TPX2
Introduction
Breast cancer (BC) is the most frequent malignant tumor in women and accounts for 24.2% of female new cases worldwide (8.6 million new cases), with about 15.0% associated deaths globally (4.2 million deaths) in 2018 according to Global Cancer Statistics 2018.1 Although the progression of modern medical technology has advanced the therapeutic effect of breast cancer, it remains the main cancer-related cause of female deaths.2–5 Therefore, the progress in molecular diagnostic and recognition of prognostic value biomarkers in patients are desired in the medical field.
Karyopherin alpha 2 (KPNA2; also known as importinα1 or RAG cohort 1) is one of the seven members of karyopherin alpha family, which plays a crucial role in nucleocytoplasmic transport.5–9 KPNA2 cooperates with nuclear receptor importin-β and mediates numerous nuclear translocations of target proteins guided cargo proteins through the nuclear pore complex.9,10 Previous studies have reported a significant amount of KPNA2 protein expressed is observed in various types of cancer, including breast cancer, gastric cancer, lung cancer, and prostate cancer, suggesting that KPNA2 may play some roles in these tumors.10–13 Further analysis also demonstrated an independent negative correlation between nuclear KPNA2 protein expression in the primary tumor and overall survival (OS) of breast cancer patients.14,15 However, the precise role of KPNA2 in breast cancer and the molecular mechanisms underlying its effects have not been elucidated.
In the current study, we hypothesized that KPNA2 might be a promising candidate as diagnostic and prognostic marker for breast cancer. To test this hypothesis, we performed a bioinformatics method to determine the expression and prognostic value of KPNA2 in breast cancer overall and its subtypes. Furthermore, we identified the mutation and methylation status of KPNA2 in breast cancer to investigate the molecular mechanisms for the effect of increased KPNA2 expression on breast cancer. Our results demonstrated that relative expression of KPNA2 was upregulated and KPNA2 was hypomethylated in breast cancer tissues and cells, which will contribute to the development and optimization of novel diagnosis and therapeutics for breast cancer.
Methods
Clinical Samples
This study enrolled a consecutive series of 33 patients with breast cancer from the middle area of China. As a control, we used 20 non-tumoral-adjacent tissues. Frozen tissues were collected at the Department of Breast Surgery from Shanxi Tumour Hospital (China). The patients ranged in age from 34 to 75 years with a mean age of 48.62 years. Fresh tissues were frozen in liquid nitrogen within 5 mins after excision and transferred to a −80°C freezer. Informed written consent was obtained from each patient and the study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Shanxi Medical University (Ethical code: 201922021). We declare that the guidelines outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki were met.
Cell Culture
Human breast cancer cell line (MCF7) was obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Rockville, MD, USA). MCF7 cells were maintained in DMEM/F12 medium supplemented 10% FBS (fetal bovine serum) (both from Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA), 100 U/mL penicillin and 100 mg/mL streptomycin. Culture plates were maintained at 37°C in a 5% CO2 humidified atmosphere.
DNA Methylation Inhibitor Treatment
The same numbers of cells MCF7 cells were cultured in 6-well plates and incubated at 37°C overnight. Cells were treated with 1, 5, or 10 μM Decitabine (Selleck, Houston, TX, USA) or vehicle (DMSO) and incubated for 72 with the purpose of mRNA extraction. The cell culture medium was refreshed daily.
Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
RNA extraction kit (BioTeke Corporation, Beijing, China) was employed to extract total RNAs. Prime ScriptTM RT Master Mix kit (Takara Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Dalian, China) was conducted to reverse transcribe the extracted RNA into complementary DNA. The qRT-PCR was carried out following SYBR® Premix Ex Taq Kit (Takara Bio, Inc., Tokyo, Japan). For PCR amplification, glyceraldehyde –phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was employed as a suitable internal control. The results were recorded when the cycle was finished. The primers used were as follows: KPNA2, forward, 5′-ATTGCAGGTGATGGCTCAGT-3′ and reverse, 5′-CTGCTCAACAGCATC TATCG-3′; GAPDH, forward, 5ʹ-ACCACAGTCCATGCCATCAC-3ʹ; and reverse, 5ʹ-TCCACCA CCCTGTTGCTGTA-3ʹ. Relative gene expression was calculated with the 2−ΔΔCt method, and Step One Software v2.1 was used to evaluate the results.
Methylation-Specific PCR
The extraction of genomic DNA from cells was performed by the use of a DNeasy Tissue Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. DNA samples were PCR-amplified and fragmented in a volume of 20 μL comprised 0.25 μL of Hot-StarTaq Master Mix, 0.5 μM of paired primer, and 2μg of bisulfite-treated DNA template. The agarose gel (3%) containing GelRedTM Nucleic Acid Gel Stain (10,000×; Biotium, CA) was used to separate MSP products in a 20μL volume after amplification. DNA-free water was served as negative control. The primers used were as follows: forward M primer, 5′-AAATACGAACGGTTTAGGGAATC-3′ and reverse M primer, 5′-ACATCGCGAAATAAAAAAACG-3′; forward U primer, 5′-GGAAATATGAATGGTTTAGGGAATT-3′, reverse U primer, 5′-ATAACATCACAAAATAAAAAAACAAC-3′.
Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis
Differential expressions of KPNA2 in breast invasive carcinoma tissues were assessed by GEPIA2 (Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis; http://gepia2.cancer-pku.cn), an online database with fast and customizable features based on TCGA (The Cancer Genome Atlas).16 Here, GEPIA database containing 1085 breast invasive carcinoma tissues and 112 normal mammary tissues was downloaded for analyses. Gene expression data of the RNA-seq datasets were transformed to log2 (transcript count per million [TPM] + 1).
Oncomine Database Analysis
KPNA2 gene expression levels in normal or malignant human tissues were obtained from the Oncomine Cancer Microarray database (http://www.oncomine.org), a web-based data mining platform for collecting, standardizing, analyzing, and providing cancer microarray information.17
cBio Portal Database Analysis
cBioPortal (The cBio Cancer Genomics Portal) database is a publicly accessible online database (http://www.cbioportal.org/),18,19 which provides visualization and analysis tool for more than 715 datasets and 86,733 samples. The term “KPNA2” was used to search the cBioPortal database and The Breast Invasive Carcinoma (TCGA, Cell 2015, n = 818) cohort was utilized. The search parameters included mutations, putative copy-number, and methylation alterations from GISTIC. Furthermore, the correlations between KNPA2 and the TPX2 were also analyzed using cBioPortal.
COSMIC Analysis
The COSMIC (Catalogue of Somatic Mutations in Cancer) database (http://cancer.sanger.ac.uk), an online accessible network tool was performed to analyze mutations in KPNA2. An overview of the distribution of mutations and substitution types on the codogenic strand in breast cancer specimens was performed, and the results are drawn in a pie chart.20
Kaplan–Meier Plotter Analysis
Kaplan–Meier Plotter (http://kmplot.com/analysis/) is an online database of published microarray datasets that assess the effect of 54,675 genes on survival using 10,461 cancer samples (6,234 breast, 2,190 ovarian, 3,452 lung, and 1,440 gastric cancer).21 We used the Kaplan–Meier plotter to assess the correlation between overall survival, relapse-free survival, distant metastasis-free survival, post-progression survival, and KPNA2 mRNA expression in patients with breast cancer. The hazard ratio (HR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) and log-rank p-value were also computed.
MEXPRESS Tool
The MEXPRESS tool (http://mexpress.be/), a web tool for the visualization and interpretation of TCGA data, offers clinical researchers an easy way to access TCGA expression (normalized RNASeqV2 value), DNA methylation, and clinical data, as well as the relationship between them for one signale in the specific tumor type. In MEXPRESS tool, it executed the Pearson correlation to evaluate the difference between expression value and methylation level. In our research, the KNPA2 expression and methylation status in breast cancer were assessed using the MEXPRESS tool.
UALCAN Cancer Database
UALCAN (http://ualcan.path.uab.edu/) is a comprehensive, user-friendly, and interactive online portal for analyzing cancer OMICS data, which provides protein expression analysis option using data from TCGA dataset.22–24 We evaluated the expression and methylation level of KPNA2 in breast cancer by UALCAN analysis.
Cell Viability Assay
Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay (Chongqing ATGene Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd., Chongqing, China) was performed to test cell viability. Briefly, MCF7 cells received different treatments were harvested and were incubated with CCK-8 reagent 10 μL for 1 h at 37°C. Cell viability was analyzed by recording the optical density at 450 nm using a microplate reader (BioTek Instruments, Inc., Winooski, VT, USA).
Results
KPNA2 Transcript Expression Status in Human Breast Cancer
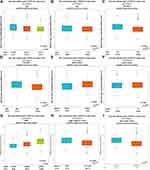
The expression profile of KPNA2 was identified using Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis. GEPIA data showed that the expression level of KPNA2 was significantly higher in BLCA (bladder urothelial carcinoma), BRCA (breast cancer), CESC (cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endocervical adenocarcinoma), COAD (colon adenocarcinoma), DLBC (lymphoid neoplasm diffuse large B-cell lymphoma), ESCA (esophageal carcinoma), GBM (glioblastoma multiforme), HNSC (head and neck squamous cell carcinoma), LIHC (liver hepatocellular carcinoma), LUAD (lung adenocarcinoma), LUSC (lung squamous cell carcinoma), OV (ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma), PAAD (pancreatic adenocarcinoma), READ (rectum adenocarcinoma), SKCM (skin cutaneous melanoma), STAD (stomach adenocarcinoma), THYM (thymoma), UCEC (uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma), UCS (uterine carcinosarcoma) (Figure 1). To further confirm this result, the Oncomine database was performed to analyze the expression profile of KPNA2. Elevated mRNA expression of KPNA2 was identified in various human tumors, including bladder cancer, brain and CNS cancer, breast cancer, cervical cancer, colorectal cancer, esophageal cancer, gastric cancer, head and neck cancer, kidney cancer, liver cancer, lung cancer, melanoma, myeloma, ovarian cancer, pancreatic cancer, and sarcoma (Figure 2A). KPNA2 expression was significantly higher in ductal breast carcinoma, male breast carcinoma, invasive ductal breast carcinoma, invasive breast carcinoma, invasive lobular breast carcinoma, ductal breast carcinoma in situ, and medullary breast carcinoma than in normal samples (Table 1, Figure 2B).
 |
Table 1 KPNA2 Expression in Breast Cancer |
KPNA2 Mutations in Breast Cancer
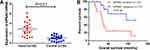
The pie chart in Figure 3A generated using COSMIC summarizes the observed mutation types, including nonsense substitutions, missense substitutions, synonymous substitutions, in-frame insertions, frameshift insertions, in-frame deletions, frameshift deletions, and complex mutations. Mutation of in breast cancer samples mainly is missense substitution (30.00%). Furthermore, KPNA2 mutations in breast cancer samples were 16.67% A > G, 33.33% C > T, 33.33% G > A, and 16.67% G > T. As determined using cBioPortal, the KPNA2 mutation frequency was less than 1.5% in patients with breast cancer (Figure 3B).
Genetic Alterations in KPNA2 and Clinicopathological Parameters
We analyzed the expression profile of KPNA2 across PAM50 breast cancer subtypes in 5861 patients using bcGenExMiner v4.4 web-tool based on clinical-pathological parameters. Regarding age, KPNA2 mRNA expression was remarkably higher in patients ≤ 51 years old than in patients > 51 years old. Furthermore, the expression of KNPA2 decreased significantly with age (Table 2, Figure 4A and B). ER (estrogen receptor) and PR (progesterone receptor) status were negatively correlated with KPNA2 expression, while HER-2 (human epidermal growth factor receptor-2) and nodal status were positively correlated with KPNA2 expression (Table 2, Figure 4C–F). Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is negative for ER, PR, and HER-2. KPNA2 mRNA expression was significantly upregulated in patients with TBNC (p < 0.0001) compared with that in the group without TBNC (p < 0.0001) (Table 2, Figure 4H). Furthermore, patients with positive basal-like characteristics and mutated P53 status exhibited significantly higher KPNA2 expression than that in patients without basal-like characteristics (p < 0.0001) (Table 2, Figure 4I). A more advanced Scarff Bloom & Richardson grade status (SBR) and Nottingham Prognostic Index grade status (NPI) grades were associated with higher KPNA2 expression (Table 2, Figure 4G).
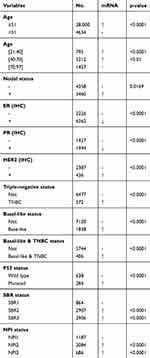 |
Table 2 The Relationship Between mRNA Expression of KPNA2 and Clinicopathological Parameters of Breast Carcinoma |
Co-Expression of KPNA2 Gene
To investigate the regulatory mechanisms underlying the role of KPNA2 in breast cancer, data mining was performed for a breast cancer cohort using cBioPortal. TPX2 (Targeting protein for Xenopus kinesin-like protein 2) is a highly correlated gene (Figure 5A); it drives proliferation, tumorigenicity, and metastasis of various tumors through regulating cell cycle and multiple signaling pathways that promote tumor proliferation. A regression analysis using cBioPortal revealed that KPNA2 and TPX2 levels are highly correlated, which demonstrated that KPNA2 may be related to TPX2 pathway in breast cancer (Figure 5B).
 |
Figure 5 (A) Co-expression of the KPNA2 gene as determined by cBioPortal. (B) Regression analysis between KPNA2 and TPX2 in breast cancer performed by cBioPortal. |
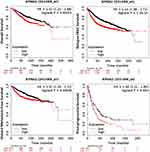
Relationship of KPNA2 Expression and Prognosis in Breast Cancers
To explore whether the expression level of KPNA2 has predictive value for breast cancer prognosis, we used the online survival analysis software Kaplan–Meier plotter (Figure 6). It was determined that a high expression of KPNA2 mRNA was significantly related to OS (overall survival), RFS (relapse-free survival), DMFS (distant metastasis-free survival), and PPS (post-progression survival). Our own results demonstrated the upregulation of KPNA2 mRNA expression and worse probabilities of survival in breast cancer (Figure 7)
KPNA2 Expression is Upregulated by Hypomethylation in Breast Tumors
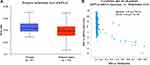
Using the MEXPRESS browser, we generated the methylation of KPNA2 using 13 probes distributed in different regions of the gene (the localization of each probe is presented in the figure, and those localized in the promoter region are highlighted in dark blue). All regions analyzed revealed a negative correlation with respect to KPNA2 gene expression (Pearson’s correlation coefficients for each probe are indicated on the right in Figure 8, suggesting that KPNA2 methylation silences gene expression.). Furthermore, we analyzed the expression and promoter methylation level of KPNA2 using UALCAN tool from TCGA dataset. We found the methylation level of KPNA2 in breast cancer was significantly lower than normal samples (p = 3.49E-12). Subsequently, we evaluated the expression and methylation level of KPNA2 in breast cancer by cBioPortal tool. We further confirmed a negative correlation with respect to KPNA2 gene expression, suggesting that KPNA2 methylation silences gene expression (Figure 9).
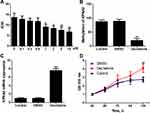
Decitabine Caused Demethylation and the Activation of KPNA2 in Breast Cancer
The effects of epigenetic agents on breast cancer progression were investigated using the minimum effective dose which was 1 μM for decitabine (Figure 10A). After decitabine treatment, the degree of demethylation was lower in the MCF7 cell line than that in untreated cells (Figure 10B). The result of the relative mRNA expression showed the upregulated by the treatment of decitabine against its expression in control cells (Figure 10C). Furthermore, cell proliferation was promoted by the decitabine treatment (Figure 10D).
Discussion
KPNA2, an adaptor protein for nuclear receptor importin-β, mediates numerous nuclear translocations of macromolecules by classical nuclear localization signal through the nuclear pore complex.25–27 KPNA2 has been first described in matched ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and invasive lesions of the breast.28 Furthermore, KPNA2 may be the primary determinant for transcription factors transporting and transcriptional activity in various cancers including breast cancer, melanoma, liver cancer, and lung cancer, and therefore is probably related to the cancer cell growth and invasion.15,29–31 These findings suggest that high KPNA2 expression in patients with breast may be related with worse prognosis.
To further investigate the role of KPNA2 in the development and proliferation of breast cancer, we analyzed extensive gene expression data with well-defined parameters in breast cancer and normal samples. Using GEPIA and Oncomine, we found that the expression level of KPNA2 is significantly higher in breast cancer tissues than in normal samples. Using Oncomine, we further determined that KPNA2 is in ductal breast carcinoma, male breast carcinoma, invasive ductal breast carcinoma, invasive breast carcinoma, invasive lobular breast carcinoma, ductal breast carcinoma in situ, and medullary breast carcinoma than in normal samples. Furthermore, we analyzed the expression profile of KPNA2 across PAM50 breast cancer using bcGenExMiner v4.4 web-too, we demonstrated that age, ER and PR status were negatively correlated with KPNA2 expression, while basal-like, mutated P53, HER-2, SBR, NPI, and nodal status were positively correlated with KPNA2 expression. Subsequently, we further found that upregulation of KPNA2 mRNA expression is closely related to worse probabilities of survival in breast cancer. And KPNA2 was able to promote breast cancer progression may be through upregulating TPX2 expression. Tony et al have demonstrated that release of TPX2 from a complex with KPNA2 at the nuclear envelope is increased,32 which is largely in agreement with the observations of our study. Somatically acquired inherited, epigenetic, transcriptomic, and proteomic alterations are the major alterations that occur in specific genomic regions, which could lead to inhibitory or carcinogenic roles.33–35 Therefore, the frequencies of alterations and mutations in KPNA2 were analyzed using the COSMIC and cBioPortal databases. The major mutation type in KPNA2 was missense substitution. However, a low KPNA2 alteration frequency was observed in breast cancer. We investigated the mechanisms underlying KPNA2 dysregulation.
DNA methylation is an early event in the process of tumorigenesis and gradually enhances during tumor progression.36 Therefore, DNA methylation of precancerous lesions or early tumors is the most promising method for early diagnosis and prognosis of cancer. By examining its DNA methylation status through MEXPRESS web-tool, we observed that aberrant DAN hypomethylation of promoter regions is one of the mechanisms underlying the aberrant expression of KPNA2 in breast cancer. By UALCAN and cBioPortal analyses further indicated that the methylation level of KPNA2 in breast cancer was significantly lower than normal samples and negative correlation with respect to KPNA2 gene expression. Interestingly, when methylation was inhibited, the expression of KPNA2 was significantly increased and the proliferation ability was significantly enhanced. Moreover, hypomethylation of the KPNA2 promoter was reported in hepatocellular carcinoma,37 and KPNA2 upregulation induced by lower promoter methylation has been suggested to be important for the pathogenesis of HCC,37 which is largely in agreement with the observations of our study.
Conclusions
In summary, KPNA2 is highly expressed in breast cancer and is independent risk factor for poor prognosis in breast cancer patients. Furthermore, KPNA2 has a role in malignancy mainly through the TPX2 signaling pathway, which is a potential therapeutic target for breast cancer. Finally, our results suggest that aberrant DNA hypomethylation of promoter regions contributes to the aberrant expression of KPNA2 in breast cancer and may be an indicator of poor prognosis.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Informed consent was obtained from each participant. The entire experiments have already obtained the approval of the Ethics Committee of Shanxi Medical University (Ethical code: 201922021).
Data Sharing Statement
The datasets generated for this study are available on request to the corresponding author.
Disclosure
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
1. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. doi:10.3322/caac.21492
2. Qin Y, Liu Y, Zhang X, et al. Contrast-enhanced spectral mammography: a potential exclusion diagnosis modality in dense breast patients. Cancer Med. 2020;9(8):2653–2659. doi:10.1002/cam4.2877
3. Khosrow-Khavar F, Filion KB, Bouganim N, Suissa S, Azoulay L. Aromatase inhibitors and the risk of cardiovascular outcomes in women with breast cancer: a population-based cohort study. Circulation. 2020;141(7):549–559. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.044750
4. Hassett MJ, Somerfield MR, Baker ER, et al. Management of male breast cancer: ASCO guideline. J clin oncol. 2020;JCO1903120.
5. Huang JX, Wu YC, Cheng YY, Wang CL, Yu CJ. IRF1 negatively regulates oncogenic KPNA2 expression under growth stimulation and hypoxia in lung cancer cells. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:11475–11486. doi:10.2147/OTT.S221832
6. Han Y, Wang X. The emerging roles of KPNA2 in cancer. Life Sci. 2020;241:117140. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117140
7. Lin F, Gao L, Su Z, et al. Knockdown of KPNA2 inhibits autophagy in oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines by blocking p53 nuclear translocation. Oncol Rep. 2018;40(1):179–194. doi:10.3892/or.2018.6451
8. Ma S, Zhao X. KPNA2 is a promising biomarker candidate for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and correlates with cell proliferation. Oncol Rep. 2014;32(4):1631–1637. doi:10.3892/or.2014.3381
9. Tachita T, Kinoshita S, Ri M, et al. Expression, mutation, and methylation of crbn-pathway genes at pre- and post-lenalidomide treatment in multiple myeloma. Cancer Sci. 2020;111(4):1333–1343. doi:10.1111/cas.14352
10. Song KH, Jung SY, Park JI, et al. Inhibition of Karyopherin-alpha2 augments radiation-induced cell death by perturbing BRCA1-mediated DNA repair. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(11):11. doi:10.3390/ijms20112843
11. Wang CI, Chen YY, Wang CL, Yu JS, Chang YS, Yu CJ. mTOR regulates proteasomal degradation and Dp1/E2F1- mediated transcription of KPNA2 in lung cancer cells. Oncotarget. 2016;7(18):25432–25442. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.8170
12. Tsai MM, Huang HW, Wang CS, et al. MicroRNA-26b inhibits tumor metastasis by targeting the KPNA2/c-jun pathway in human gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7(26):39511–39526. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.8629
13. Grupp K, Boumesli R, Tsourlakis MC, et al. The prognostic impact of high Nijmegen breakage syndrome (NBS1) gene expression in ERG-negative prostate cancers lacking PTEN deletion is driven by KPNA2 expression. Int J Cancer. 2014;135(6):1399–1407. doi:10.1002/ijc.28778
14. Lu Y, Xiao L, Liu Y, et al. MIR517C inhibits autophagy and the epithelial-to-mesenchymal (-like) transition phenotype in human glioblastoma through KPNA2-dependent disruption of TP53 nuclear translocation. Autophagy. 2015;11(12):2213–2232. doi:10.1080/15548627.2015.1108507
15. Drucker E, Holzer K, Pusch S, et al. Karyopherin alpha2-dependent import of E2F1 and TFDP1 maintains protumorigenic stathmin expression in liver cancer. Cell Commun Signal. 2019;17(1):159. doi:10.1186/s12964-019-0456-x
16. Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C, Zhang Z. GEPIA: a web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(W1):W98–W102. doi:10.1093/nar/gkx247
17. Rhodes DR, Yu J, Shanker K, et al. ONCOMINE: a cancer microarray database and integrated data-mining platform. Neoplasia. 2004;6(1):1–6. doi:10.1016/S1476-5586(04)80047-2
18. Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012;2(5):401–404. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0095
19. Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, et al. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal. 2013;6(269):pl1. doi:10.1126/scisignal.2004088
20. Tate JG, Bamford S, Jubb HC, et al. COSMIC: the catalogue of somatic mutations in cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(D1):D941–D947. doi:10.1093/nar/gky1015
21. Jezequel P, Frenel JS, Campion L, et al. bc-GenExMiner 3.0: new mining module computes breast cancer gene expression correlation analyses. Database. 2013;2013:bas060. doi:10.1093/database/bas060
22. Men C, Chai H, Song X, Li Y, Du H, Ren Q. Identification of DNA methylation associated gene signatures in endometrial cancer via integrated analysis of DNA methylation and gene expression systematically. J Gynecol Oncol. 2017;28(6):e83. doi:10.3802/jgo.2017.28.e83
23. Shinawi T, Hill VK, Krex D, et al. DNA methylation profiles of long- and short-term glioblastoma survivors. Epigenetics. 2013;8(2):149–156. doi:10.4161/epi.23398
24. Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya SAH, et al. UALCAN: a portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia. 2017;19(8):649–658. doi:10.1016/j.neo.2017.05.002
25. Ye J, Zhong L, Xiong L, et al. Nuclear import of NLS- RARalpha is mediated by importin alpha/beta. Cell Signal. 2020;69:109567. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109567
26. Fan X, Li Z, Wang X, Wang J, Hao Z. Silencing of KPNA2 inhibits high glucose-induced podocyte injury via inactivation of mTORC1/p70S6K signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;521(4):1017–1023. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.10.200
27. Song H, Song J, Lu L, Li S. SNHG8 is upregulated in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and directly sponges microRNA-411 to increase oncogenicity by upregulating KPNA2. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:6991–7004. doi:10.2147/OTT.S214881
28. Klein A, Wessel R, Graessmann M, et al. Comparison of gene expression data from human and mouse breast cancers: identification of a conserved breast tumor gene set. Int J Cancer. 2007;121(3):683–688. doi:10.1002/ijc.22630
29. Wang JJ, Huang YQ, Song W, et al. Comprehensive analysis of the lncRNA associated competing endogenous RNA network in breast cancer. Oncol Rep. 2019;42(6):2572–2582. doi:10.3892/or.2019.7374
30. Winnepenninckx V, Lazar V, Michiels S, et al. Gene expression profiling of primary cutaneous melanoma and clinical outcome. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98(7):472–482. doi:10.1093/jnci/djj103
31. Wang CI, Wang CL, Wang CW, et al. Importin subunit alpha-2 is identified as a potential biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer by integration of the cancer cell secretome and tissue transcriptome. Int J Cancer. 2011;128(10):2364–2372. doi:10.1002/ijc.25568
32. Chu TLH, Connell M, Zhou L, et al. Cell cycle-dependent tumor engraftment and migration are enabled by Aurora-A. Mol Cancer Res. 2018;16(1):16–31. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-17-0417
33. Krawczyk M, Liebe R, Lammert F. Towards genetic prediction of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease trajectories: PNPLA3 and beyond. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(7):1865–1880.e1. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.01.053
34. Della Corte CM, Sen T, Gay CM, et al. STING pathway expression identifies non-small cell lung cancers with an immune-responsive phenotype. J Thorac Oncol. 2020;15(5):777–791. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2020.01.009
35. Rehman SU, Rizwan M, Khan S, Mehmood A, Munir A. Proteomic analysis of medicinal plant calotropis gigantea by insilico peptide mass fingerprinting. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2020;16. doi:10.2174/1573409916666200219114531
36. Povedano E, Ruiz-Valdepenas Montiel V, Gamella M, et al. Amperometric bioplatforms to detect regional DNA methylation with single-base sensitivity. Anal Chem. 2020. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.0c00628
37. Hua S, Ji Z, Quan Y, et al. Identification of hub genes in hepatocellular carcinoma using integrated bioinformatic analysis. Aging. 2020;12(6):5439–5468. doi:10.18632/aging.102969
38. Richardson AL, Wang ZC, De Nicolo A, et al. X chromosomal abnormalities in basal-like human breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 2006;9(2):121–132. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2006.01.013
39. Ma XJ, Dahiya S, Richardson E, Erlander M, Sgroi DC. Gene expression profiling of the tumor microenvironment during breast cancer progression. Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(1):R7. doi:10.1186/bcr2222
40. Curtis C, Shah SP, Chin SF, et al. The genomic and transcriptomic architecture of 2000 breast tumours reveals novel subgroups. Nature. 2012;486(7403):346–352. doi:10.1038/nature10983
 © 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.