Back to Journals » International Journal of Nanomedicine » Volume 10 » Issue 1
An efficient method for in vitro gene delivery via regulation of cellular endocytosis pathway
Authors Luo J, Li C, Chen J, Wang G, Gao R , Gu Z
Received 14 November 2014
Accepted for publication 28 December 2014
Published 2 March 2015 Volume 2015:10(1) Pages 1667—1678
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S77527
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Lei Yang
Jing Luo,1,2,* Caixia Li,3,* Jianlin Chen,1,2 Gang Wang,2 Rong Gao,1 Zhongwei Gu2
1Key Laboratory for Bio-Resource and Eco-Environment of Ministry of Education, Key Laboratory for Animal Disease Prevention and Food Safety of Sichuan Province, College of Life Science, Sichuan University, Chengdu, People’s Republic of China; 2National Engineering Research Center for Biomaterials, Sichuan University, Chengdu, People’s Republic of China; 3Chengdu Institute of Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu, People’s Republic of China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Abstract: Transfection efficiency was the primary goal for in vitro gene delivery mediated by nonviral gene carriers. Here, we report a modified gene transfection method that could greatly increase the efficiency of, and accelerate the process mediated by, 25 kDa branched polyethyleneimine and Lipofectamine™ 2000 in a broad range of cell strains, including tumor, normal, primary, and embryonic stem cells. In this method, the combination of transfection procedure with optimized complexation volume had a determinant effect on gene delivery result. The superiorities of the method were found to be related to the change of cellular endocytosis pathway and decrease of particle size. The efficient and simple method established in this study can be widely used for in vitro gene delivery into cultured cells. We think it may also be applicable for many more nonviral gene delivery materials than polyethyleneimine and liposome.
Keywords: gene delivery, gene expression, endocytosis, polyethyleneimine, Lipofectamine™ 2000
Introduction
Delivery of exogenous gene into cells has great importance in gene function research, genetic modification of cells, and gene therapy.1–4 Viral vector owns the highest gene transfection efficiency, but its wide application has been limited by safety issues.5,6 Nonviral gene carriers such as cationic lipids and polymers have been potential alternatives for safe and efficient gene delivery due to their good biocompatibility, versatility, and controllable molecule size.7–9 However, their gene transfection efficiencies are much lower than those of viral vectors.10 Therefore, increasing gene delivery efficiency has been the primary challenge for nonviral material-mediated gene transfer trials.11
The gene delivery efficiency of nonviral materials is usually influenced by many factors, such as the quantity and quality of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), ratio of DNA to material, serum, antibiotics, solvent for DNA and material, incubation time, and mixing order.12–18 Therefore, the readily available off-the-shelf gene carriers usually provide standard transfection procedures that have been considered to generate the highest gene transfection efficiency for cultured cells.19,20 Branched polyethyleneimine (PEI, Mw~=25 kDa), a typical cationic polymer, has been commonly used as the ‘gold standard’ for in vitro gene delivery.21 Lipofectamine™ 2000 (Lipo2000) is one of the most widely used commercial cationic lipids with high efficiency for in vitro gene transfer.22 Both materials have their recommended optimal transfection procedures that have been used for many years.
In this study, we will present a modified method applicable for improving the efficiency of PEI- and Lipo2000-mediated gene delivery into a wide range of cell strains. Exploration of the mechanism underlying this method may also give us innovative insights into transgene delivery procedure.
Materials and methods
Materials
The plasmids pEGFP-C1 (Clontech, Takara Biotechnology Co. Ltd, Dalian, People’s Republic of China) encoding enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) and pGL3-control (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) containing the modified coding region for firefly (Photinus pyralis) luciferase (Luc) were amplified in Escherichia coli DH5α and extracted using the PureLink® Hipure Plasmid Filter Maxiprep Kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Branched PEI (25 kDa), methyl-β-cyclodextrin (MβCD), amiloride hydrochloride, and chlorpromazine hydrochloride were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St Louis, MO, USA) and used without further treatment. Lipo2000, fetal bovine serum (FBS), Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM), RPMI-1640, Minimum Essential Medium (MEM with Earle’s Balanced Salt Solution), and Opti-MEM® I Medium were purchased from Invitrogen.
Cell culture
Hep G2 (human hepatocellular carcinoma; American Type Culture Collection [ATCC] No HB-8065™), SMMC-7721 (human hepatocellular carcinoma), MCF-7 (human breast adenocarcinoma; ATCC No HTB-22™), AGS (human gastric adenocarcinoma; ATCC No CRL-1739™), Hela (human cervix adenocarcinoma; ATCC No CCL-2™), 4T1 (mouse breast cancer; ATCC No CRL-2539™), NIH/3T3 (mouse embryo fibroblast; ATCC No CRL-1568™), C2C12 (mouse muscle myoblast; ATCC No CRL-1772™), R1 (mouse embryonic stem cell; ATCC No CRL-11114™), and L6 (rat skeletal muscle myoblast; ATCC No CRL-1458™) cell lines were purchased from the cell bank of the Chinese Academy of Science (Shanghai, People’s Republic of China) and the China Center for Type Culture Collection (Wuhan, People’s Republic of China). Cells were cultured according to the recommended procedures by ATCC. For primary fibroblast isolation, a piece of sterile neonatal foreskin was separated, washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), minced thoroughly, and transferred into a 0.1 mM trypsin/1 mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid solution. After trypsinization at 37°C for ~30 minutes, an equal volume of DMEM/FBS (10%) was added and the tissue/medium mixture was pipetted up and down a few times for tissue dissociation. After 5-minutes’ incubation at room temperature, the supernatant was transferred into a new tube and centrifuged at 2,000 g for 5 minutes at 4°C. Cells were resuspended in fresh DMEM containing 15% FBS and 1% penicillin–streptomycin. All cells were cultured as adherent monolayer in a CO2 incubator at 37°C under saturated humidity.
Cell transfection
One day before transfection, cells were seeded in six-well or 24-well plates and cultured in growth medium without antibiotics. For PEI-mediated transfection cases, the suitable cell confluency was 70%–80% at the time of transfection, while for Lipo2000, it was 90%–95%. Plasmids 4 μg/well were used for transfection in six-well and 0.8 μg/well for 24-well format. PEI, Lipo2000, and pDNA were freshly diluted to equal volumes with Opti-MEM® I medium prior to use. The polyplexes were prepared by adding PEI into pDNA using an N/P ratio of 10. The lipoplexes were prepared by adding pDNA into Lipo2000 using a DNA (μg) to Lipo2000 (μL) ratio of 1:2.5. The polyplexes and lipoplexes were incubated for 20 minutes at room temperature. In standard PEI and Lipo2000 transfection cases, the growth medium was replaced by fresh FBS−/antibiotics− medium (2 mL for six-well and 0.5 mL for 24-well plate) and then the complexes (500 μL for six-well and 100 μL for 24-well plate) were added. In the modified transfection procedures for PEI or Lipo2000, the growth medium was completely removed and different volumes of polyplexes or lipoplexes were gently added to the corresponding cells. After incubation at 37°C for a certain time (4 hours for standard or 0.5–4 hours for modified method), the growth medium was replaced with fresh FBS+/antibiotics+ media and cultured for 1–3 days for detections.
Gene transfection efficiency assays
To qualitatively evaluate the transfection efficiency, cells transfected with pEGFP-C1 were observed and imaged using an inverted fluorescent microscope (Leica DMI 4000B; Wetzlar, Germany) for EGFP expression at days 1 and 2 after transfection.
The transfection efficiency was quantitatively analyzed by detecting and comparing the luciferase activity between the standard and modified transfection groups. Two days after transfection, cells treated with pGL3-control were washed with PBS, digested with 0.25% (w/v) trypsin, harvested in 1 mL PBS, and lysed by adding 200 μL 1× lysis reporter buffer (Promega). The cell lysates were centrifuged at 12,000 g for 5 minutes at 4°C. Total protein concentrations in the supernatants were determined using the BCA Protein Assay Kit (Pierce, Rockford, IL, USA) with bovine serum albumin as the standard. To detect the luciferase activity, 20 μL of supernatant was added in a 96-well plate and mixed with 100 μL luciferase substrate (Promega), and the light emission was measured for 10 seconds in a multifunctional microplate reader (Varioskan Flash; Thermo Fisher). The gene transfection efficiency was represented by luciferase activity, which was normalized to total protein concentration and calculated as relative light units per milligram of total protein.
The transfection efficiency was also quantitatively detected at cellular level. In brief, by using fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS; Calibur; Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA), the proportion of EGFP-expressing cells in 1×104 cells was analyzed. Data were treated by CellQuest software (Becton Dickinson).
Cytotoxicity assay
Cytotoxicity was presented as the percentage of cell viability, which was evaluated by a cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8; Dojindo Laboratories, Kumamoto, Japan) method. In 300 μL antibiotics-free medium, 5.0×103 or 1.0×104 cells/well were seeded in 24-well plates and cultured to 70%–80% confluence for PEI or ~90% for Lipo2000 at the time of transfection. The PEI/pDNA or Lipo2000/pDNA complexes containing 0.8 μg pEGFP-C1 were added to corresponding wells according to the transfection procedures. To each well 30 μL of CCK-8 was added and the plates were incubated at 37°C for an additional 2 hours. Absorbance values were measured at a wavelength of 490 nm and a reference wavelength of 630 nm using a multifunctional microplate reader (Varioskan Flash; Thermo Fisher). The cell viability was calculated according to the formula: cell viability (%) = [(Asample–Ablank)/(Acontrol–Ablank)] ×100%. Here, Asample, Acontrol, and Ablank are the absorbance values of transfected cells, untransfected cells, and the medium, respectively.
DNA labeling and intracellular traffic analysis
The plasmid pGL3-control was labeled with TOTO®-3 iodide (Molecular Probes, Inc. Eugene, OR, USA) according to previously described protocol.23 Cells were treated with PEI/ TOTO®-3-pDNA polyplexes using the standard and modified methods for 4 hours and 1.5 hours, respectively. To observe the intracellular traffic of labeled pDNA, cells were washed with PBS twice and analyzed using confocal laser scanning microscopy (Leica TCP SP5) with the excitation wavelength at 642 nm and emission wavelength at 660 nm.
Particle size and zeta potential analysis
For the standard method, 4 μg pDNA (pGL3-control) and 5 μL PEI (1 mg/mL) or 4 μg pDNA and 10 μL Lipo2000 were diluted, respectively, in 250 μL H2O, mixed, incubated for 20 minutes at room temperature, and then diluted to 2 mL with H2O. For the modified method, 6 μg pDNA and 7.5 μL PEI or 6 μg pDNA and 15 μL Lipo2000 were diluted, respectively, in 525 μL H2O, mixed, and incubated for 20 minutes at room temperature. One milliliter of the complexes was used for size and zeta potential measurements using a Malvern Zetasizer Nano ZS90 (Malvern Instruments Ltd, Malvern, UK) at 25°C.
Endocytosis inhibition assay
Hep G2 cells were pretreated with 5 mM mβCD, 1 mM amiloride hydrochloride, or 10 μg/mL chlorpromazine hydrochloride for 1 hour at 37°C, respectively. The subsequent transfection of pEGFP-C1 was performed as described and cells were analyzed 48 hours later for EGFP expression by FACS.
Statistical analysis
Each experiment was performed in triplicate and repeated three times unless stated otherwise. Data were statistically analyzed using the software SPSS 11.5 and presented as mean ± standard deviation. The value of P<0.05 was considered as a significant difference, while P<0.01 was highly significant.
Results
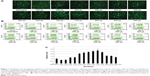
The influence of polyplex volume on transfection efficiency
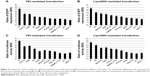
The transfection efficiencies were qualitatively evaluated by observing the expression of EGFP in Hep G2 cells. In the transfection cases using the modified method, the efficiencies were higher than those of the PEI standard method when the volumes of PEI/pEGFP-C1 polyplexes were above 400 μL (Figure 1A). The results were further quantitatively analyzed by FACS (Figure 1B). The efficiencies increased gradually in the cases from 300 μL to 700 μL of polyplexes and then decreased. At the volume of 700 μL, the peak value was significantly higher than others and approximately 2.8-fold that of PEI standard transfection (Figure 1C). The results indicated that the modified transfection method significantly improved the gene transfection efficiency in a volume-dependent manner.
The influence of transfection procedure on transfection efficiency
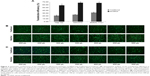
For the modified transfection procedure, the optimal volume was 700 μL in the six-well plate; for standard transfection, it was 2,500 μL (500 μL complex + 2,000 μL medium). Therefore, we wondered whether the increase of transfection efficiency was due only to the decrease of complexation volume. To address this question, we compared the efficiencies of modified and traditional procedures at a fixed volume of 700 μL using three different cell strains. In the modified transfection, the medium was discarded and 700 μL polyplex was added to the cells; in traditional trials that mimic the standard procedure, the medium was exchanged with 200 μL of fresh medium and then the 500 μL polyplex was added in. The data showed that the modified method presented significantly higher transfection efficiencies than those of the traditional procedure in Hep G2, NIH/3T3, and SMMC-7721 cell strains (Figure 2A; P<0.01). To further investigate the results, we systematically compared the efficiencies of the two methods among a series of complexation volumes from 200 μL to 500 μL in a 24-well format using both Lipo2000/pEGFP-C1 lipoplexes (Figure 2B) and PEI/pEGFP-C1 polyplexes (Figure 2C). The results indicated that 1) at each volume, the modified method presented obviously higher transfection efficiency than the traditional method; 2) in the modified cases, the transfection efficiencies varied in a volume-dependent manner and 300 μL was the optimal volume; and 3) changing the complexation volume only had a slight influence on transfection efficiency in traditional cases. Altogether, the results confirmed that the improved efficiency was due to the combination of decreased complexation volume with transfection procedure. The best modified transfection method was to add a suitable volume (700 μL for the six-well plate and 300 μL for the 24-well plate) of transfection complex to cells without medium.
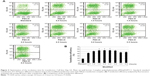
Optimization of the incubation time of polyplex with cells
In the modified procedure, a shorter incubation time of polyplex with cells can also result in high transgene expression level when compared with that in the standard procedure (Figure 3A). The peak values of transfection were acquired after 1.5–2.5 hours’ incubation, which were significantly higher than those of others except in the case of 3.0 hours (P<0.05) (Figure 3B). The results indicated that the modified procedure presented a faster transfection process and the suitable incubation time was reduced to 1.5–2.5 hours.
The influence of transfection methods on cell viability
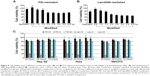
In traditional transfection cases, a longer incubation time usually generates higher transfection efficiency but stronger cytotoxicity.24 In the modified method, removal of cell medium followed with direct addition of transfection complex onto cells might also exert certain influence on cellular physiological state. Therefore, a suitable incubation time should be identified to balance transfection efficiency and cytotoxicity. In both PEI- (Figure 4A) and Lipo2000-mediated (Figure 4B) transfection trials, the 0.5 hours’ incubation had the minimum cytotoxicity, but its transfection efficiency was too low (Figure 3B). In comparison, the 1 hour and 1.5 hours of incubation showed similar cytotoxicity as that of the standard method (Figure 4A, B; P>0.05). Considering that the 1.5 hours of incubation generated high transfection efficiency (Figure 3B), we selected it as the optimal parameter. It was further verified by transfecting other cell lines. Using the modified method with 1.5 hours’ incubation time in both PEI- and Lipo2000-mediated transfection, Hep G2 and NIH/3T3 cells showed equal viability to those in the standard method; Hela cells in modified trials even had higher cell viability than those in the standard cases (Figure 4C).
The concentration of PEI/pDNA or Lipo2000/pDNA complex in the modified method was about 3.57 times that in the standard method. We wondered whether the standard transfection with the same complex concentration as that in modified method can also provide higher transfection efficiency. However, most of the cells died in these cases (Figure 4C; PEI-S2 and Lipo-S2). It demonstrated that the simple increase of complex concentration brought higher cytotoxicity instead of higher transfection efficiency.
Application of the modified method on the transfection of different cell strains
Based on the aforementioned outcomes, we concluded that the optimal procedure for the modified transfection method contained four steps (Table 1).
  | Table 1 Optimal procedure for the modified transfection method |
Further, we wanted to know whether the modified method can be widely used to transfect different cell strains. As confirmed by both FACS (Figure 5A and B) and luciferase activity assay (Figure 5C and D), for each cell strain, the modified method greatly improved the transfection efficiency mediated by PEI (Figure 5A and C) and Lipo2000 (Figure 5B and D). The cell strains included different cancer cells (AGS, Hela, Hep G2, SMMC-7721, MCF-7, and 4T1), normal cells (C2C12, L6, and NIH/3T3), embryonic stem cells (R1), and even primary skin fibroblasts (primary). The cell strains can also be divided into human (AGS, Hela, Hep G2, MCF-7, and primary), rat (L6), and mice (C2C12, NIH/3T3, and R1) cells. The results indicated that the modified method was suitable, at least, for PEI and Lipo2000 in gene transfer into a wide range of cell strains.
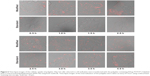
Internalization course of PEI/pDNA polyplex
By monitoring the internalization course of PEI/pDNA polyplex, we hope to find some clues to explore the reason why the modified method had better performance on gene delivery. As shown in Figure 6, in the modified procedure, the polyplexes attached to cell membranes from 0.5 hour penetrated into the cells from 1.0 hour to 1.5 hours and dispersed within the cytoplasm/nucleus from 1.5 hours to 2.5 hours after transfection. In the standard procedure, the attachment/penetration was a slower kinetics process within 2.5 hours, and the dispersion of the polyplexes in the cells took place 2 hours after transfection. The results indicated that the modified method provided a more active kinetics process for the polyplex internalization than that in the standard method. Meanwhile, the proportion of fluorescent cells in the modified transfection was higher than that in the standard method. This may be the reason why the modified method provided higher transgene expression than the standard.
Endocytosis pathways in different transfection methods
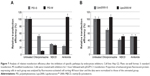
The difference of internalization kinetics of the polyplex between the two methods may be related to their different endocytosis pathways. So we investigated the cellular endocytosis by excluding specific pathways with endocytosis inhibitors. When Hep G2 cells were, respectively, treated with chlorpromazine, MβCD, and amiloride, the cellular transfection efficiencies mediated by PEI and Lipo2000 standard methods were all significantly decreased, indicating that the uptake of polyplexes and lipoplexes were, simultaneously, through clathrin-, caveolae-, and macropinocytosis-mediated endocytosis pathways (Figure 7). However, when macropinocytosis-mediated endocytosis in the PEI-modified method (Figure 7A) and clathrin-mediated endocytosis in the Lipo2000-modified method (Figure 7B) were inhibited, respectively, the gene transfection efficiencies were not decreased. The results revealed that macropinocytosis-mediated endocytosis in the PEI-modified method and clathrin-mediated endocytosis in the Lipo2000-modified method were excluded. We further found that for both PEI and Lipo2000 transfection, the particle size prepared in the modified method was much smaller than that in the standard method, while the zeta potentials were not changed (Table 2).
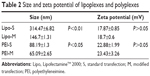  | Table 2 Size and zeta potential of lipoplexes and polyplexes |
Discussion
For nonviral gene delivery material, the optimal transfection procedure represented the balance between high efficiency and low cytotoxicity, which was commonly acquired by optimizing a lot of parameters.10 For this reason, the commercially available gene carriers such as PEI, cationic lipids, and polymers usually have their specific standard protocols, which have been considered as the optimal procedures in gene delivery cases. However, the standard procedure can also be empirically improved in some cases, and compared with the complicated and time-consuming modifications on gene delivery carriers, optimization of transfection method sometimes seems to be more simple and efficient. In a reported case, the authors showed an optimized protocol for more efficient transfection of adherent primary mammalian cells using 25 kDa branched PEI.12 In this study, the modified method was applicable for, at least, PEI and liposome to deliver genes into a wider range of cell lines.
The determinant point in the modified method is the combination of transfection procedure with optimized complexation volume. The complexation volume can greatly affect the transfection efficiency: the smaller the volume, the higher the efficiency. Although the smaller volume possesses a higher complex concentration, a simple increase of complex concentration only brought higher cytotoxicity instead of higher transfection efficiency (Figure 4C; PEI-S2 and Lipo-S2). Therefore, the decrease of complexation volume should be combined with the new transfection procedure in which the DNA/material complex was added to the cells immediately after the removal of cell culture medium. In fact, when the volume was reduced to 300 μL, cells located at the margin of the well had the highest transfection efficiency, but cells in the middle of the well were rarely transfected because this area was only slightly covered by the transfection mixture due to the surface tension (data not shown). So the global efficiency in the 300 μL system was less than that in the 700 μL system (Figure 1), because cells in the latter were well covered by the transfection mixture. If the transfection procedure was similar to the standard procedure, the reduction of complexation volume only had a very limited increase on the transfection efficiency. More interestingly, in the equal volume, the modified procedure had higher transfection efficiency than that of the standard procedure (Figure 2). The results implied that the transfection procedure had a more important role than complexation volume in gene delivery.
The additional superiority of the modified method was the faster transfection process (Figure 3). Usually, shorter incubation time results in lower cytotoxicity, but higher transfection efficiency needs longer incubation time.25 To resolve this paradox, an optimal incubation time should be experimentally determined to balance transfection efficiency and cytotoxicity. If the biocompatibility of a material was not good enough but its gene transfection ability was excellent, an alternative solution was to reduce the incubation time to control its cytotoxicity using the modified method. In addition, it is well known that some cell lines, such as stem cells and primarily cultured cells, are difficult to transfect and sensitive to toxic reagent.26 The modified method offered significantly increased efficiency for all the tested cell strains (Figure 5).
There are multiple pathways for cellular uptake of particles and solutes.27,28 The endocytosis pathways of DNA/material particles were commonly classified as clathrin-dependent, caveolae-mediated, caveolae- and clathrin-independent, and macropinocytosis.29–31 Endocytosis inhibitors were usually applied to analyze the endocytosis pathways of cells, but their concentrations and treatment time should be well determined to minimize cytotoxicity.32,33 Meanwhile, inhibition of certain endocytosis pathways may artificially upregulate other internalization routes that are not originally involved in the uptake of transfection particles because many chemical inhibitors are not specific to a single internalization pathway.27 Therefore, inhibition experiments should be rationally designed to observe effects at a suitable time in referable parallel treatments.34 In the standard transfection, both PEI- and Lipo2000-mediated endocytosis involved clathrin-dependent, caveolae-mediated, and macropinocytosis pathways. In the modified transfection, however, the endocytosis pathways were changed: clathrin-dependent and caveolae-mediated for PEI while caveolae-mediated and macropinocytosis for Lipo2000 (Figure 7). We think that the regulation is mainly due to the change of transfection procedure. When the transfection mixture was added, cells suffered a sudden stimulation. In the modified transfection, the culture medium was already removed and the concentration of complexes was increased, making the stimulation so great that the cellular endocytosis pathways were changed. In the standard or traditional transfection, the stimulation was buffered by the culture medium. The decreased size and increased concentration of pDNA/material particles in the modified method may also influence the endocytosis pathway and kinetics of internalization (Figure 6). In general, complexes may undergo physicochemical changes when mixed at different concentrations, and the aggregation of particles may also be influenced by the different ionic strength in the medium.12,35 The complexation of pDNA/material particle was formed in 700 μL solution for the modified transfection while in 500 μL and then diluted to 2,500 μL system for standard transfection, leading to a different particle concentration and size. Altogether, the change of cellular endocytosis pathway, decrease of particle size, and increase of particle concentration made the modified transfection method a potent tool for nonviral material-mediated gene delivery into a wide range of cell strains.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No 31370972, 51133004, 81361140343), National Basic Research Program of China (973 program, No 2011CB606206), National Support Program of Science and Technology (No 2012BAI17B06), and National International Cooperation Program (No 2011DFA10101103).
Disclosure
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Reference
Boussif O, Lezoualc’h F, Zanta MA, et al. A versatile vector for gene and oligonucleotide transfer into cells in culture and in vivo: polyethylenimine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92(16):7297–7301. | ||
Zhang S, Zhao B, Jiang H, Wang B, Ma B. Cationic lipids and polymers mediated vectors for delivery of siRNA. J Control Release. 2007;123(1):1–10. | ||
Colosimo A, Goncz KK, Holmes AR, et al. Transfer and expression of foreign genes in mammalian cells. Biotechniques. 2000;29(2):314–318, 320–322, 324 passim. | ||
Sun NF, Liu ZA, Huang WB, Tian AL, Hu SY. The research of nanoparticles as gene vector for tumor gene therapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2014;89(3):352–357. | ||
Kay MA. State-of-the-art gene-based therapies: the road ahead. Nat Rev Genet. 2011;12(5):316–328. | ||
Ibraheem D, Elaissari A, Fessi H. Gene therapy and DNA delivery systems. Int J Pharm. 2014;459(1–2):70–83. | ||
Patnaik S, Gupta KC. Novel polyethylenimine-derived nanoparticles for in vivo gene delivery. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2013;10(2):215–228. | ||
Mohit E, Rafati S. Biological delivery approaches for gene therapy: strategies to potentiate efficacy and enhance specificity. Mol Immunol. 2013;56(4):599–611. | ||
Basarkar A, Singh J. Nanoparticulate systems for polynucleotide delivery. Int J Nanomed. 2007;2(3):353–360. | ||
Mintzer MA, Simanek EE. Nonviral vectors for gene delivery. Chem Rev. 2009;109(2):259–302. | ||
Wang W, Li W, Ma N, Steinhoff G. Non-viral gene delivery methods. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2013;14(1):46–60. | ||
Hsu CY, Uludağ H. A simple and rapid nonviral approach to efficiently transfect primary tissue-derived cells using polyethylenimine. Nat Protoc. 2012;7(5):935–945. | ||
Zhang S, Xu Y, Wang B, Qiao W, Liu D, Li Z. Cationic compounds used in lipoplexes and polyplexes for gene delivery. J Control Release. 2004;100(2):165–180. | ||
Huh SH, Do HJ, Lim HY, et al. Optimization of 25 kDa linear polyethylenimine for efficient gene delivery. Biologicals. 2007;35(3):165–171. | ||
Zhou J, Liu J, Cheng CJ, et al. Biodegradable poly(amine-co-ester) terpolymers for targeted gene delivery. Nat Mater. 2011;11(1):82–90. | ||
Audouy S, Molema G, de Leij L, Hoekstra D. Serum as a modulator of lipoplex-mediated gene transfection: dependence of amphiphile, cell type and complex stability. J Gene Med. 2000;2(6):465–476. | ||
Chen JL, Wang H, Gao JQ, Chen HL, Liang WQ. Liposomes modified with polycation used for gene delivery: preparation, characterization and transfection in vitro. Int J Pharm. 2007;343(1–2):255–261. | ||
Zhao QQ, Chen JL, Lv TF, et al. N/P ratio significantly influences the transfection efficiency and cytotoxicity of a polyethylenimine/chitosan/DNA complex. Biol Pharm Bull. 2009;32(4):706–710. | ||
Dalby B, Cates S, Harris A, et al. Advanced transfection with Lipofectamine 2000 reagent: primary neurons, siRNA, and high-throughput applications. Methods. 2004;33(2):95–103. | ||
Yamano S, Dai J, Moursi AM. Comparison of transfection efficiency of nonviral gene transfer reagents. Mol Biotechnol. 2010;46(3):287–300. | ||
Zhong D, Jiao Y, Zhang Y, et al. Effects of the gene carrier polyethyleneimines on structure and function of blood components. Biomaterials. 2013;34(1):294–305. | ||
Huang SL. Liposomes in ultrasonic drug and gene delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008;60(10):1167–1176. | ||
Liu S, Ma L, et al. Safe and efficient local gene delivery into skeletal muscle via a combination of Pluronic L64 and modified electrotransfer. Gene Ther. 2014;21(6):558–565. | ||
Gao X, Kim KS, Liu D. Nonviral gene delivery: what we know and what is next. AAPS J. 2007;9(1):E92–E104. | ||
Davis ME, Chen ZG, Shin DM. Nanoparticle therapeutics: an emerging treatment modality for cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7(9):771–782. | ||
Pack DM, Hoffman AS, Pun S, Stayton PS. Design and development of polymers for gene delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4(7):581–593. | ||
Adil MM, Erdman ZS, Kokkoli E. Transfection mechanisms of polyplexes, lipoplexes, and stealth liposomes in α5β1 integrin bearing DLD-1 colorectal cancer cells. Langmuir. 2014;30(13):3802-3810. | ||
El-Sayed A, Harashima H. Endocytosis of gene delivery vectors: from clathrin-dependent to lipid raft-mediated endocytosis. Mol Ther. 2013;21(6):1118–1130. | ||
Sahay G, Alakhova DY, Kabanov AV. Endocytosis of nanomedicines. J Control Release. 2010;145(3):182–195. | ||
Rejman J, Bragonzi A, Conese M. Role of clathrin- and caveolae-mediated endocytosis in gene transfer mediated by lipo- and polyplexes. Mol Ther. 2005;12(3):468-474. | ||
Rehman Zu, Zuhorn IS, Hoekstra D. How cationic lipids transfer nucleic acids into cells and across cellular membranes: recent advances. J Control Release. 2013;166(1):46-56. | ||
Cao D, Qin L, Huang H, Feng M, Pan S, Chen J. Transfection activity and the mechanism of pDNA-complexes based on the hybrid of low-generation PAMAM and branched PEI-1.8k. Mol Biosyst. 2013;9(12):3175-3186. | ||
Cao J, Xie X, Lu A, et al. Cellular internalization of doxorubicin loaded star-shaped micelles with hydrophilic zwitterionic sulfobetaine segments. Biomaterials. 2014;35(15):4517-4524. | ||
Ivanov AI. Pharmacological inhibition of endocytic pathways: is it specific enough to be useful? Methods Mol Biol. 2008;440:15-33. | ||
Ikonen M, Murtomäki L, Kontturi K. Controlled complexation of plasmid DNA with cationic polymers: effect of surfactant on the complexation and stability of the complexes. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2008;66(1):77-83. |
 © 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.