Back to Journals » Clinical Interventions in Aging » Volume 12
Yogurt supplemented with probiotics can protect the healthy elderly from respiratory infections: A randomized controlled open-label trial
Authors Pu F, Guo Y, Li M, Zhu H , Wang S, Shen X, He M, Huang C, He F
Received 10 May 2017
Accepted for publication 25 June 2017
Published 8 August 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 1223—1231
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S141518
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Zhi-Ying Wu
Fangfang Pu,1,* Yue Guo,1,2,* Ming Li,1 Hong Zhu,3 Shijie Wang,3 Xi Shen,1 Miao He,1 Chengyu Huang,1 Fang He1
1Department of Nutrition, Food Safety and Toxicology, West China School of Public Health, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, People’s Republic of China; 2Microbiology laboratory, Chengdu Center for Disease Control & Prevention, Chengdu, Sichuan, People’s Republic of China; 3R&D center, Shijiazhuang Junlebao Dairy Co. Ltd., Shijiazhuang, Hebei, People’s Republic of China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Purpose: To evaluate whether yogurt supplemented with a probiotic strain could protect middle-aged and elderly people from acute upper respiratory tract infections (URTI) using a randomized, blank-controlled, parallel-group design.
Patients and methods: Two hundred and five volunteers aged ≥45 years were randomly divided into two groups. The subjects in the intervention group were orally administered 300 mL/d of yogurt supplemented with a probiotic strain, Lactobacillus paracasei N1115 (N1115), 3.6×107 CFU/mL for 12 weeks, while those in the control group retained their normal diet without any probiotic supplementation. The primary outcome was the incidence of URTI, and changes in serum protein, immunoglobulins, and the profiles of the T-lymphocyte subsets (total T-cells [CD3+], T-helper cells [CD4+], and T-cytotoxic-suppressor cells [CD8+]) during the intervention were the secondary outcomes.
Results: Compared to the control group, the number of persons diagnosed with an acute URTI and the number of URTI events significantly decreased in the intervention group (P=0.038, P=0.030, respectively). The risk of URTI in the intervention group was evaluated as 55% of that in the control group (relative risk =0.55, 95% CI: 0.307–0.969). The change in the percentage of CD3+ cells in the intervention group was significantly higher than in the control group (P=0.038). However, no significant differences were observed in the total protein, albumin, globulin, and prealbumin levels in both groups (P>0.05).
Conclusion: The study suggested that yogurt with selected probiotic strains such as N1115 may reduce the risk of acute upper tract infections in the elderly. The enhancement of the T-cell-mediated natural immune defense might be one of the important underlying mechanisms for probiotics to express their anti-infective effects.
Keywords: yogurt, probiotics, Lactobacillus paracasei N1115, immunosenescence, acute upper respiratory tract infection, elderly
Introduction
Acute respiratory infection is an infection that may interfere with normal breathing. It usually begins as a viral infection in the nose, trachea (windpipe), or lungs. If the infection is not treated, it can spread to the entire respiratory system. One of these acute respiratory infections is influenza. In the past, influenza has spread around the world during seasonal epidemics, resulting in the deaths of hundreds of thousands annually and in the death of millions during pandemic years. The management of influenza has been given the highest priority consideration in terms of public health in many countries including China. Vaccinations against influenza are usually given to people as a practical, protective technique. However, a vaccine formulated for a given year may be ineffective in the following year as pathogenic viruses evolve rapidly and different strains become dominant year after year.1 Therefore, the enhancement of natural defenses by triggering nonspecific cell-mediated immunity in a host animal might be a practical, effective method for the management of flu infections.2
Yogurt was a kind of traditional fermented milks which contained Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus bulgaricus.3 Yogurt has been used for a long time and has been known to maintain human health by its excellent nutrition profile. Recent studies have also suggested that supplementation with probiotics can significantly enhance the health-promoting effects of traditional yogurt such as the immunomodulatory effect,4,5 because probiotic lactobacilli, particularly certain selected strains, can modify the innate and acquired host immune responses and thus protect against respiratory infections.6–9 Furthermore, several recent animal and human studies have found that probiotics can enhance immunity in senescence-accelerated mice and elderly humans.8,10 However, there have been very few well-designed human interventional studies conducted to evaluate the clinical effects of yogurt, especially for those yogurts supplemented with selected probiotics against acute upper respiratory tract infection (URTI).11–14 The related underlying mechanisms remain unclear.
In the present study, a randomized, blank-controlled, parallel-group clinical trial was conducted to evaluate whether yogurt supplemented with a selected strain of L. paracasei N1115 (N1115) could protect middle-aged and elderly people from acute URTI. The physiology, nutrition, and immunology changes of the tested subjects were also analyzed in detail to explore the underlying mechanisms of the protective effects of the tested yogurt during the intervention.
Materials and methods
Study design
The study was conducted between March 31 and June 30 in 2013 in a randomized, open-label manner with healthy middle-aged and elderly volunteers. Subjects were assigned sequentially in a 1:1 ratio to the intervention and control groups based on a computer-generated random sequence. Volunteers in the experimental group were given the test fermented product (tested yogurt), while those in control group were asked to maintain their normal diet without using any probiotic supplements during the study. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. All subjects were fully informed regarding its purpose, and a detailed study procedure was provided. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants. The study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Sichuan University on March 13, 2013 (2014002-03) and registered in the International Standard Randomized Controlled Trial Number Register (registration identification number: ChiCTR-IOR-16010164; URL: http://www.chictr.org.cn).
Subjects
Volunteers were recruited from the healthy male or female adults aged ≥45 years who lived around the West China School of Public Health, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China, and had similar living environments and standards of living. Volunteers had to be able to physically adapt to the long-term daily consumption of 300 mL of yogurt and would be finally be selected through a three-step screening test. The first step was a baseline survey which primarily included patient characteristics and details of bowel conditions, diseases, and drug (especially antibiotic) usage. People who were unable to communicate, had been hospitalized in the previous 3 months, were suffering from any severe acute and chronic diseases, or were using long-term antibiotics before study entry were excluded. The second step was an adaptive test which included drinking 100 mL of yogurt during the first day, 200 mL during the second day, and 300 mL during the third day. The occurrence of any responses was recorded during these 3 days; those who exhibited intolerance or an allergy to milk were excluded. The third step was a blood test for immunity and nutrition-related parameters. People who had markedly abnormal results in any of these blood tests were excluded.
All subjects were asked to maintain the same diet and lifestyle as before the study. The intake of probiotic/prebiotic supplements or some fermented dairy products and the use of antibiotic treatments or any other drug treatment that could influence the immune response were not recommended during the whole phase study.
Procedures
For 12 weeks, volunteers in the intervention group were given 100-mL bottles of test yogurt produced by Shijiazhuang Junlebao Dairy Co., Ltd. (Shijiazhuang, People’s Republic of China) which contained living N1115 3.6×109 CFU. The tested yogurt was delivered every 2 weeks to WCSPH, Sichuan University, Chengdu by cold-chain transportation and then stored at 0°C–4°C. Participants were given the tested yogurt once a week (21 bottles for three bottles per day) and asked to store them in the refrigerator before drinking. The control group did not receive this yogurt.
Baseline data and blood samples were collected during the three-step screening test. During the intervention period, all participants filled the monitoring table including the occurrence of acute upper respiratory tract symptoms, defecation, antibiotic usage, and details about diet and exercise. Volunteers in the test group also had to record the actual daily consumption of the yogurt. Staff that received integrated training would contact each participant biweekly to access the data survey. If there were questions, the staff communicated with the participants in a timely manner. A second blood sample was collected at the end of the study (12 weeks). The drinks were consumed throughout the entire study period and were usually taken during or after meals (breakfast and dinner). If any of the doses were missed, subjects were instructed to take the yogurt at any other time during the day to make sure that the amount of yogurt taken per day was 300 mL.
Observations and measurements
The primary clinical outcome measurement of the study was the comparison of the incidence of all acute URTIs in the groups during the 12 weeks of the study. According to previous research and guidelines,15–18 the diagnostic criteria for acute URTI were as follows: 1) symptoms of acute rhinitis or acute pharyngitis such as nasal congestion, sneezing, or runny nose that appeared in a short time and with rapidly increasing severity, 2) the duration of the above symptoms for ≥1 day, and 3) symptoms that occurred ≥7 days after the end of the last acute URTI episode, which were considered to be a new episode. Moreover, each infection event would be scored using six items: 1) nasal congestion, sneezing, and runny nose, 2) conjunctival hyperemia and lacrimation, 3) sore throats, 4) cough and sputum, 5) headache and muscle soreness, and 6) fever. Each item would be scored as follows: 0 (none), 1 (occurring but did not hinder daily life), or 2 (seriously affecting work, life, and sleep).
The secondary outcome parameters were changes in a series of blood indicators during the intervention. Immune functions were assessed by the profiles of the lymphocyte subsets (total T-cells [CD3+], T-helper cells [CD4+], and T-cytotoxic-suppressor cells [CD8+]) and of immunoglobulin (Ig)A, IgG, and IgM. Nutritional status was reflected by total protein, albumin, globin, prealbumin, glucose, total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), high-density lipoproteins (HDL-C), low-density lipoproteins (LDL-C) and very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL-C). All analyses were conducted by the West China Medical Detection Institute, Sichuan University, Chengdu, People’s Republic of China, by using standard procedures.
Sample size calculation
First, a sample size calculation was performed based on published data. To determine the appropriate sample size, the primary parameter to consider was the prevalence of acute URTI in people aged ≥45 years in Chengdu. However, since the prevalence of acute URTI varied with regions, ages, and seasons, it was difficult to get accurate information from the place and specific population to estimate the sample size. At the same time, the most obvious immune system change in the elderly was the change of T-cells with aging; therefore, we choose a 95% normal reference range and the SD of CD3+ cells which represented mature T-cells when calculating the sample size. Finally, 112 subjects per group were required with a power of 90%, a significance level of 0.05, and a potential dropout of 20%.
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were calculated using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS 17.0, SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Comparisons between the intervention group and the control group were performed using two-sided statistical tests with a significance level of 5% (P<0.05). Baseline characteristics were analyzed selecting an independent samples t-test, a χ2 test, or a nonparametric test based on the specific indicators. For the qualitative data, a χ2 test or a univariate logistic regression was used. Comparisons of continuous data were made using a one-way analysis of variance model or an appropriate nonparametric analysis. The blood parameters were analyzed with the changes from baseline (week 12–baseline) between the two groups.
Results
Volunteer demographics
A total of 395 volunteers were enrolled in this study. One hundred sixty-two volunteers who could not meet the requirements were excluded after the screening test. The remaining 233 volunteers were randomly assigned to the intervention group (n=115) and the control group (n=118), respectively. During the experiment, 12 people in the probiotic group and 16 in the control group quit the study for various reasons (eg, worked in or traveled to another city, lost to follow-up, and refused to have a second blood test). The dietary and exercise survey showed that all subjects maintained their lifestyle during the intervention period. Therefore, the final analysis included 103 participants in the intervention group and 102 in the control group (Figure 1). No significant difference in the distribution of subjects leaving the study was observed. Furthermore, no adverse events associated with the consumption of the tested yogurt were reported. Table 1 provides details about the characteristics of the subjects before treatment, which were balanced across the intervention and control groups, regarding age, BMI, sex ratio, occupations, levels of education, drinking, or smoking, current diseases, diet, and exercise. The current diseases were divided by different systems, mainly included cardiovascular diseases, kidney diseases, respiratory diseases, and digestive diseases, which have been diagnosed in the past and not the present occurred illness, which did not need drug to control, were mild, and did not influence the life quality of elderly during the study period. During the previous 3 months, the prevalence of URTI in the intervention group was similar to that in the control group. The results of the initial clinical examination were normal for all volunteers.
  | Figure 1 Volunteer flow in the study. |
Incidence of acute URTIs
The duration of study and the style of information collection for the control group were similar to those for the intervention group. Withdrawals from the study were lower than 20% in each group (10.4% of intervention group, 13.6% of control group, and 12% of all volunteers), and the basic information was not statistically different between the lost volunteers and the subjects that completed the study. Thus, the loss bias was small.
During the study period, all subjects retained their habits and lifestyle from prior to the intervention, and all baseline characteristics were consistent between the two groups, particularly the prevalence of URTI 3 months prior to the study, which could reduce susceptibility to URTI and the influence of other confounding factors on the results. Furthermore, four participants in the control group had taken antibiotics for 1–2 days to cure a cold, which was so short that these data were not excluded. There was no severe disease occurring in either group during the study.
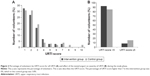
During the study period, 205 volunteers experienced a total of 89 episodes of URTI (Table 2). One hundred three volunteers reported 37 URTI events in the fermented product group, compared with 102 volunteers who reported 52 URTI events in the control group (35.9% vs 51.0%, P=0.030). The number of persons diagnosed with an acute URTI in the intervention group was lower than in the control group (30.1% vs 44.1%, P=0.038). The risk of URTI in the experimental group was 55% of the control group, which was evaluated using univariate logistic regression (RR=0.55, 95% CI: 0.307–0.969). The mean of URTI episodes of intervention group was 0.4, and it was 0.5 in the control group (P=0.043). In addition, number of volunteer experiencing 2 or more URTI episodes in the intervention was smaller than that of control group. For the URTI score, although there was no significant difference between the intervention group and the control group (2.5±1.5 vs 2.7±2.0, P=0.913), the percentage of volunteers whose URTI score was 5 or more in the intervention group had a tendency to decline compared with that of the control group (Figure 2A and B).
Biochemical and immune parameters
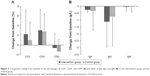
For percentage of CD3+ cells, the intervention group showed significantly greater changes from baseline compared with the control group (P=0.037). No significant differences were detected in the plasma percentage of CD4+ and CD8+ cells. Furthermore, no relevant differences were seen in IgA, IgG, and IgM levels (Figure 3). There were no significant changes in the serum total protein, albumin, globin, prealbumin, glucose, TC, TG, HDL-C, LDL-C, and VLDL-C levels between groups (P>0.05 for all comparisons) (Table 3).
Discussion
Acute respiratory infection, including influenza, is particularly dangerous for older adults as well as children and people with immune system disorders. One of the possible reasons might be immunosenescene in the elderly. Immunosenescene has been defined as the gradual deterioration of the immune system with aging, and it involves alterations in the immune organs, immune cells, and immune-related molecules and increases susceptibility to various diseases such as cardiovascular disease, autoimmune disease, and infections.19,20 The most obvious alteration in the immune organs occurs in the thymus where the T-lymphocytes mature. Mature T-lymphocytes express CD3 on their surfaces; at the same time, they also selectively express CD4 or CD8.21,22 Thymus involution leads to an absence of new T-lymphocyte generation.19 Some studies have found that the lymphocyte numbers in the peripheral blood decreased with age.23,24 It has also been reported that the percentages of CD3+ T-cells and CD8+ T-cells decreased in the elderly.25 In a mouse study, the proportion of CD8+ T-cell decreased with age.26 Another important immune cell, the B lymphocyte, might not decline in the elderly.23 Furthermore, several recent animal and human studies have found that probiotics can enhance immunity in senescence-accelerated mice and elderly humans.8,10
Besides immunosenescence, age-related physiologic alterations in combination with organic processes can contribute to the development of malnutrition in older adults,27 which is characterized by the deficiencies of protein-energy, vitamins, and minerals,28–30 which can have consequences on immunity characterized by a decrease in cell-mediated immunity.31 Even a slight reduction in serum albumin levels below the normal range has been associated with age-related alterations in the T-cell subsets.24 Shimizu indicated that lower serum albumin levels were observed in patients with severe urinary tract infections compared to patients with mild urinary tract infection and healthy people.32 Considering these previous studies, we hypothesized that yogurt supplemented with selected probiotic strains could protect the elderly from acute respiratory infections by enhancing immunosenescence and improving the nutritional status of the elderly population.
In the present study, 12 weeks of oral administration of the yogurt supplemented with N1115 significantly reduced the risk of URTI and the frequency of URTI in the subjects compared with the control group. Although the severity of URTI between the two groups was not significantly different, the cumulative number of participants who scored more than 5 slightly decreased in the intervention group that has yogurt supplemented with N1115. These results had good agreement with the previous study conducted by Makino et al33 in which yogurt containing L. delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus OLL1073R-1 also reduced the risk of catching a common cold in the elderly population compared with simple milk intake. However, the results from the present study were different from other studies along the same lines. For example, Guillemard et al11 found that a fermented dairy drink containing L. casei DN-114 001 did not improve the incidence and severity of URTI but significantly reduced the duration of URTI in elderly people. Sugimura et al12 observed that fermented milk containing Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis JCM5805 did not influence the incidence of colds but did reduce the duration of cough and fever in adults. Fujita et al14 showed that fermented product containing L. casei strain Shirota reduced the mean infection duration per infection event but not the number of persons diagnosed with an acute URTI in a healthy elderly population. The differences observed among the tested yogurts may be attributed to the diagnostic criteria of URTI and the specific probiotic strains used in the different yogurts. Currently, there is no gold standard (clinical or laboratorial) for the diagnosis of an URTI, especially in the middle-aged and elderly populations. Many researchers made this diagnosis based on respiratory and other related clinical symptoms.12,14,33 In the present study, the diagnosis criteria of URTI was made based on URTI related symptoms, guidelines, scale, and researches (criteria defined in the “Materials and methods” section).15–18 Interestingly, the prevalence of colds in our study was similar to that in Makino et al33 (14.7%/4 weeks vs 14.3%/4 weeks) in the same season and race (URTI equals the common cold). Therefore, the diagnostic method for URTI used in the present study was feasible. Another possible reason behind the different protective effects among tested yogurts may have resulted from the strain-specific action of each probiotic strain on URTI. Therefore, the results from the present study have indicated that probiotics could determine or shape the protective effects of yogurt against URTI.
Immunosenescence has been attributed to the loss of lymphoid tissue during aging,34–36 which has been implicated in the increased susceptibility of aged people to variety diseases.20,37,38 The percentages of different lymphoid subsets such as CD3+, CD4+, and CD8+ T-cells and the immunoglobins are some of the main immunological parameters that reflect the immune reactive states. A significant negative correlation between the percentage of CD3 and the risk of URTI was observed in the present study. Furthermore, higher CD3 levels and a lower incidence of URTI were also found in the subjects exposed to N1115 in the yogurt compared to those subjects in the control group. These results suggested that an increased percentage of CD3 could be one of the underlying mechanisms behind the protective effects of N1115-containing yogurt. The change in the concentration of IgA, IgG, and IgM with aging remains controversial,23,39,40 which might be the reason that we did not see significant difference in the change of IgA, IgG, and IgM levels between groups. Also, the results from the present study were also consistent with those reported by Nermes et al,41 who demonstrated that L. rhamnosus GG could increase the proportions of CD19+CD27+ B cells but had no influence on IgA, IgG, or IgM levels in infants with atopic dermatitis.
In addition, it is generally accepted that nutrition is an important determinant of immune function.42 We hypothesized that the immune function of yogurt was generated via not only the immunomodulatory pathway of probiotics but also by the improvement in nutritional status from macro-/micronutrients. However, there was no significant change from the baseline in all nutrition-related blood indicators such as total protein, albumin, prealbumin, glucose, TC, TG, HDL-C, LDL-C, or VLDL-C between the two groups. However, prior to the intervention, the subjects in the groups had no serious organic diseases and were healthy with normal blood protein, glucose, and lipid levels. Perhaps the yogurt did not influence the nutritional status of the healthy elderly population.
In this study, we used a yogurt with selected strain L. paracasei N1115, which is a new strain with probiotic properties that has been isolated from traditional homemade dairy products in Inner Mongolia, China. This bacterium has been taxonomically identified, and its complete genomic sequence shows high similarity to the well-studied probiotic L. rhamnosus GG; however, three structures were found to be inversions.43 N1115 has a strong tolerance to gastric acid and bile acid in vitro and can express a characteristic adhesion to human epidermal cells in the cell line test. Oral administration of this bacterium can promote intestinal epithelial cell proliferation and differentiation, and strengthen the intestinal mucosal barrier in neonatal mice.44 The previous study also has found that N1115 could activate macrophages in a strain-dependent manner to produce interleukin-10 (IL-10), IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α).45 However, milk could also stimulate T-lymphocyte proliferation and natural killer cell activity in a clinical trial.33 As a blank control study, it is difficult to know whether the role of this yogurt was caused by milk, N1115, or both.
Conclusion
In all, the intake of yogurt containing N1115 could protect against the risk of acute URTI in the mid-aged and elderly, one of the underlying mechanisms of which might be that N1115 stimulated the T-cell immunity. Dietary intervention using a yogurt containing the probiotic strain N1115 might be considered as a means to improve immune system function and health status in the middle-aged and elderly, which could have important clinical, public health, and economic consequences. But as this study was limited to a blank control trial, a better designed, placebo-controlled trial is needed to clearly clarify the immune effect of the strain N1115 in the future.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank Enago for the English language review.
Author contributions
FH and ML designed this study. FP, YG, XS, and MH conducted the study. HZ, SW, ML, and FH provided technical support and prepared the tested yogurt. FP and YG analyzed the data. FP and YG wrote and revised the manuscript. FH and CH reviewed the manuscript. All authors contributed toward data analysis, drafting and critically revising the paper and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Disclosure
This work was supported by Shijiazhuang Junlebao Dairy Co. Ltd. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Girard MP, Cherian T, Pervikov Y, Kieny MP. A review of vaccine research and development: human acute respiratory infections. Vaccine. 2006;24(15):2732–2750. | ||
Borchers AT, Selmi C, Meyers FJ, Keen CL, Gershwin ME. Probiotics and immunity. J Gastroenterol. 2009;44(1):26–46. | ||
Bourlioux P, Pochart P. Nutritional and health properties of yogurt. World Rev Nutr Diet. 1988;56:217–258. | ||
Nova E, Wärnberg J, Gómez-Martínez S, Díaz LE, Romeo J, Marcos A. Immunomodulatory effects of probiotics in different stages of life. Br J Nutr. 2007;98(Suppl 1):90–95. | ||
Dong H, Rowland I, Thomas LV, Yaqoob P. Immunomodulatory effects of a probiotic drink containing Lactobacillus casei Shirota in healthy older volunteers. Eur J Nutr. 2013;52(8):1853–1863. | ||
Harata G, He F, Hiruta N, et al. Intranasal administration of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG protects mice from H1N1 influenza virus infection by regulating respiratory immune responses. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2010;50(6):597–602. | ||
Kawase M, He F, Kubota A, Harata G, Hiramatsu M. Oral administration of lactobacilli from human intestinal tract protects mice against influenza virus infection. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2010;51(1):6–10. | ||
Kawase M, He F, Kubota A, Yoda K, Miyazawa K, Hiramatsu M. Heat-killed Lactobacillus gasseri TMC0356 protects mice against influenza virus infection by stimulating gut and respiratory immune responses. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2012;64(2):280–288. | ||
Yoda K, He F, Miyazawa K, Kawase M, Kubota A, Hiramatsu M. Orally administered heat-killed Lactobacillus gasseri TMC0356 alters respiratory immune responses and intestinal microbiota of diet-induced obese mice. J Appl Microbiol. 2012;113(1):155–162. | ||
Miyazawa K, Kawase M, Kubota A, et al. Heat-killed Lactobacillus gasseri can enhance immunity in the elderly in a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study. Benef Microbes. 2015;6(4):441–449. | ||
Guillemard E, Tondu F, Lacoin F, Schrezenmeir J. Consumption of a fermented dairy product containing the probiotic Lactobacillus casei DN-114001 reduces the duration of respiratory infections in the elderly in a randomised controlled trial. Br J Nutr. 2010;103(1):58–68. | ||
Sugimura T, Takahashi H, Jounai K, et al. Effects of oral intake of plasmacytoid dendritic cells-stimulative lactic acid bacterial strain on pathogenesis of influenza-like illness and immunological response to influenza virus. Br J Nutr. 2015;114(5):727–733. | ||
Boge T, Rémigy M, Vaudaine S, Tanguy J, Bourdetsicard R, Van der Werf S. A probiotic fermented dairy drink improves antibody response to influenza vaccination in the elderly in two randomised controlled trials. Vaccine. 2009;27(41):5677–5684. | ||
Fujita R, Iimuro S, Shinozaki T, et al. Decreased duration of acute upper respiratory tract infections with daily intake of fermented milk: a multicenter, double-blinded, randomized comparative study in users of day care facilities for the elderly population. Am J Infect Control. 2013;41(12):1231–1235. | ||
Barrett B, Brown R, Mundt M, et al. The Wisconsin Upper Respiratory Symptom Survey is responsive, reliable, and valid. J Clin Epidemiol. 2005;58(6):609–617. | ||
Respiratory Physicians CMDA, Emergency Physicians CMDA. Experts’ consensus on the criteria for the diagnosis and treatment of common cold in China. Chin J Intern Med. 2012;51(4):330–333. | ||
Van Puyenbroeck K, Hens N, Coenen S, et al. Efficacy of daily intake of Lactobacillus casei Shirota on respiratory symptoms and influenza vaccination immune response: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in healthy elderly nursing home residents. Am J Clin Nutr. 2012;95(5):1165–1171. | ||
Smith TJ, Rigassio-Radler D, Denmark R, Haley T, Touger-Decker R. Effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus LGG® and Bifidobacterium animalis ssp. lactis BB-12® on health-related quality of life in college students affected by upper respiratory infections. Br J Nutr. 2013;109(11):1999–2007. | ||
Dunnwalters DWD. The ageing immune system and its clinical implications. Rev Clin Gerontol. 2011;21(2):110–124. | ||
Mcelhaney JE, Effros RB. Immunosenescence: what does it mean to health outcomes in older adults? Curr Opin Immunol. 2009;21(21):418–424. | ||
Lanier LL, Ruitenberg JJ, Phillips JH. Human CD3+ T lymphocytes that express neither CD4 nor CD8 antigens. J Exp Med. 1986;164(1):339–344. | ||
Reinherz EL, Schlossman SF. Discrete stages of human intrathymic differentiation: analysis of normal thymocytes and leukemic lymphoblasts of T-cell lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980;77(3):1588–1592. | ||
Lesourd BM. Nutrition and immunity in the elderly: modification of immune responses with nutritional treatments. Am J Clin Nutr. 1997;66(2):478S–484S. | ||
Lesourd B, Mazari L. Nutrition and immunity in the elderly. Proc Nutr Soc. 1999;58(58):685–695. | ||
Valiathan R, Ashman M, Asthana D. Effects of aging on the immune system: infants to elderly. Scand J Immunol. 2016;83(4):255–266. | ||
Chen J, Flurkey K, Harrison DE. A reduced peripheral blood CD4(+) lymphocyte proportion is a consistent ageing phenotype. Mech Ageing Dev. 2002;123(2–3):145–153. | ||
Hajjar R, Kamel H, Denson K. Malnutrition in aging. Internet J Geriatr Gerontol. 2003;1(1). | ||
Calvo MS, Whiting SJ, Barton CN. Vitamin D fortification in the United States and Canada: current status and data needs. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;80(Suppl 6):1710S–1716S. | ||
Offord EA, Karagounis LG, Vidal K, Fielding R, Meydani S, Penninger JM. Nutrition and the biology of human ageing: Bone health & osteoporosis/sarcopenia /immune deficiency. J Nutr Health Aging. 2013;17(8):712–716. | ||
Lesourd B. Nutrition: a major factor influencing immunity in the elderly. J Nutr Health Aging. 2004;8(1):28–37. | ||
Moulias S. [Nutrition and immunity in the elderly]. Annales De Médecine Interne. 2002;153(7):446–449. | ||
Shimizu T, Namikawa T, Jyoko C, et al. PP150-SUN: immunity and nutritional evaluation in the elderly with chronic urinary tract infection. Clin Nutr. 2014;33:S76–S76. | ||
Makino S, Ikegami S, Kume A, Horiuchi H, Sasaki H, Orii N. Reducing the risk of infection in the elderly by dietary intake of yoghurt fermented with Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus OLL1073R-1. Br J Nutr. 2010;104(7):998–1006. | ||
Pan WR, Suami H, Taylor GI. Senile changes in human lymph nodes. Lymphat Res Biol. 2008;6(2):77–83. | ||
Linton PJ, Dorshkind K. Age-related changes in lymphocyte development and function. Nat Immunol. 2004;5(2):133–139. | ||
Miller RA. Aging and immune function. Int Rev Cytol. 1991;124(10):187–215. | ||
Aw D, Silva AB, Palmer DB. Immunosenescence: emerging challenges for an ageing population. Immunology. 2007;120(4):435–446. | ||
Grubeckloebenstein B, Della BS, Iorio AM, Michel JP, Pawelec G, Solana R. Immunosenescence and vaccine failure in the elderly. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2009;21(3):201–209. | ||
Moulias R, Proust J, Wang A, et al. Age-related increase in autoantibodies. Lancet. 1984;1(8386):1128–1129. | ||
Bátory G, Jancsó Á, Puskás É, Rédei A, Lengyel É. Antibody and immunoglobulin levels in aged humans. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 1984;3(2):175–188. | ||
Nermes M, Kantele JM, Atosuo TJ, Salminen S, Isolauri E. Interaction of orally administered Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG with skin and gut microbiota and humoral immunity in infants with atopic dermatitis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2011;41(3):370–377. | ||
Chandra RK. Nutrition and the immune system: an introduction. Am J Clin Nutr. 1997;66(2):460s–463s. | ||
Wang S, Zhu H, He F, et al. Whole genome sequence of the probiotic strain Lactobacillus paracasei N1115, isolated from traditional Chinese fermented milk. Genome Announc. 2014;2(2). | ||
Wang S, Yan F, He F, Zhu H. Effects of Lactobacillus paracasei N1115 on intestinal development in neonatal mice, Acta Nutrimenta Sinica. 2016;38(1):71–74. | ||
Zhu H, Wang S, Lu C, et al. Inventors. Lactobacillus casei N1115, its immunoregulation effect and application. 2011. |
 © 2017 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2017 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.