Back to Journals » Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology » Volume 13
Use of a Topical Film-Forming Medical Device Containing Repairsomes® in a Patient with Xeroderma Pigmentosum to Avoid Progression to Skin Cancerization
Authors González-Morán A, Piquero-Casals J
Received 28 July 2020
Accepted for publication 1 September 2020
Published 15 September 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 677—681
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CCID.S274423
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jeffrey Weinberg
Alfonso González-Morán,1 Jaime Piquero-Casals2
1Sección de Dermatología del Hospital de Nuestra Señora de Sonsoles, Ávila, Spain; 2Dermik, Multidisciplinary Dermatological Clinic, Barcelona, Spain
Correspondence: Jaime Piquero-Casals
Dermik, Multidisciplinary Dermatological Clinic, Barcelona, Spain
Tel +34 935464710
Email [email protected]
Abstract: This paper reports a case of xeroderma pigmentosum in a 78-year-old woman with a 17-year history of multiple basal cell carcinomas, keratoacanthoma, and lentigo maligna melanoma, in different photoexposed facial regions. To prevent aggravation of these medical conditions, for five years, the patient had been applying a film-forming topical medical device (MD) containing the DNA-repair enzyme photolyase in liposomes and high-protection UV filters (Repairsomes) twice a day. During this time, the patient had no clinical or dermatoscopic evidence of new skin cancer lesions. However, at her last visit, the patient had a new basal cell carcinoma on the face, in the right supramaxillary area. After questioning, the patient recognized that she had not been applying the product on a regular basis during the last year. This may have been a coincidence; however, there is clinical evidence of the preventive effect of this MD in reducing the cancerization field and consequently the development of skin cancer. This product contains a light-activated flavoenzyme called photolyase which creates the condition to revert cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer. In the discussion of this case, we review recent publications and stress some important aspects on the role of photoprotection and photorepair as a strategy to more effectively reduce the risk of UV-induced premalignant and malignant skin lesions compared to traditional photoprotection strategies.
Keywords: xeroderma pigmentosum, lentigo maligna melanoma, skin cancer, cancerization field, sunscreen, photolyase, non-melanoma skin cancer, melanoma
Introduction
Xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) is a rare, autosomal-recessive genodermatosis characterized by defective DNA repair leading to increased propensity for solar skin damage and predisposition to skin cancer. Different genes can be mutated, resulting in at least eight different clinical entities recognizable by clinical presentation and the characteristics of the molecular defect.1
About 50% of XP patients present in the first weeks of life with sunburn and extreme sensitivity to sunlight. This onset incidental finding offers the opportunity for early diagnosis and treatment. Poikilodermatous changes develop on sun-exposed areas, and first skin cancer occurs at a median of 9 years of age.2 Patients younger than 20 years with XP have a 2000-fold increase in melanoma, a 10,000-fold increase in the frequency of nonmelanoma skin cancer, and a 12-fold increased risk of internal malignancy, particularly brain neoplasms.1,3
The clinical features include xerosis, poikiloderma, actinic keratosis, hyperpigmented lentigines, acute burning with minimal sun exposure and development of malignant lesions in sun-exposed areas, such as basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma. Many patients also develop cataracts and other ocular manifestations and neurodegeneration with frequent involvement of peripheral nerves and progressive cognitive impairment, hearing loss and ataxia. The worldwide prevalence is 2.3 per million.2
The current management of XP mostly focuses on prevention of sun exposure with sunscreens, appropriate clothes, sunglasses, hats and plastic UVR filters to avoid the development of skin cancer.4
Oral vitamin D supplementation, imiquimod, Hedgehog inhibitors and anti-PD1 monoclonal antibodies could be used for improving survival and for prevention and treatment of lesions.4,5
Conventional photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a suitable and useful treatment for multiple actinic keratoses (AK) and superficial carcinomas in XP patients.6 A recent publication of a case series with 13 XP patients showed the utility of daylight PDT as an effective treatment to improve AK lesions in black skin with XP.7
The major progress in the management of xeroderma pigmentosum and other nucleotide excision repair disorders has been the development of a topical medical device which combines two basic principles for the prevention of skin cancer: a very high SPF (at least 50+ or even 100+) and DNA repair enzymes encapsulated in liposomes (Photosome®); both elements work together facilitating the protection and the repair of UVB radiation-induced DNA photoproducts involved in mutagenesis and photo-immunosuppression.8 Giustini et al, in 2014,4 reported data from a retrospective analysis of the use of this film-forming medical device combination in eight patients diagnosed with xeroderma pigmentosum who as a result of a genetic defect of the DNA repair system had increased rates of AK and other premalignant and malignant skin lesions. Treatment with this medical device was associated with a 65% reduction in the appearance of new AK lesions and with 56% and 100% reduction in the incidence of new BCC and SCC lesions respectively.9–11 Various other photoprotection options containing DNA-repairing enzymes are available on the market, but very few have been studied their use in patients with XP.
Herein, we present a patient with XP and successful skin cancer prevention with the continuous use of this topical film-forming medical device. The patient signed forms giving their consent for the use of case details and images for scientific purposes.
Case Report
We report a 78-year-old Mediterranean woman with xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) who had been under follow-up in the dermatology department of Hospital de Nuestra Señora de Sonsoles (Ávila, Spain) for 20 years. The patient first attended with a lentigo maligna melanoma on the left cheek (Figure 1) and had a lifetime history of several non-melanoma skin cancers (NMSC) on the face (frontal region, malar, supraciliary, submandibular, preauricular, among others). There was no history of other family members having XP. The patient did not have any neurodegenerative abnormalities or cognitive impairment. By 2014, she had undergone surgical treatment for 18 facial and neck tumors, 17 basal cell carcinomas (BCC) and one keratoacanthoma, prompting a search for measures to prevent tumor formation in this area (Figure 2).
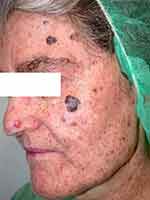 |
Figure 1 Lentigo maligna melanoma on the cheek and several non-melanoma skin cancers (NMSC) on the frontal region and nasal area. |
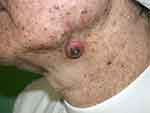 |
Figure 2 Keratoacanthoma. A solitary and well-circumscribed, erythematous dome-shaped nodule with central crateriform keratin plug over the submandibular area. |
The patient used the product topically twice daily (in the morning and at noon) in a sun-exposed skin area. After starting this treatment, she was followed up at the dermatology department for the following four years. Clinical assessment and dermoscopy evaluation confirmed the absence of new skin cancer lesions and clinical improvement in AK lesions after treatment with Eryfotona® AK-NMSC in a fluid vehicle during this period.
Over the past year, the patient used the product intermittently and irregularly, not on a daily basis. This could be a classic case of lack of compliance as there were no new tumors for several years, so vigilance may have dropped. During this year she developed a 5mm facial BCC on the left cheek.
Discussion
XP is a genetic disorder with defective DNA repair or with chromosomal instability. It is included in a group of skin conditions associated with an abnormal reaction to ultraviolet (UV) radiation also called photodermatoses. These photodermatoses are classified into four groups: immune-mediated photodermatoses, chemical and drug-induced photosensitivity, photoaggravated dermatoses and genetic disorders.3 A systematic approach including clinical features, family history, phototesting and laboratory testing is important to ensure the correct diagnosis and management. Photoprotection with specific and high SPF sunscreens, appropriate clothing, and the use of hats and sunglasses are essential in the management. There are also promising emerging photoprotective agents.9
A film-forming medical device with sun filters together with a DNA repair enzyme photolyase entrapped in liposomes (Repairsomes) is one such emerging topical photoprotective and photorepair agent.10 Photolyase is a flavoenzyme derived from an algae Anacystis nidulans which utilizes the energy from visible blue light to revert cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPD).8–11
The major features of XP result from a buildup of unrepaired DNA damage. If sufficient DNA damage occurs, there will be cellular transformation and the development of cutaneous field cancerization and, eventually, malignancies.3,6
Cutaneous field cancerization (CFC) is associated with genomic alterations due to the carcinogenic effect of sun exposure. Sunlight radiation induces the production of CPD and 6–4 photoproducts (6–4PPs) interfering with biological processes critically for cell viability.8,9 There is an endogenous nucleotide excision repair system (NER) to remove this DNA damage. Many organisms have an additional repair mechanism named photoreactivation which is carried out by photolyases which specifically recognize and repair CPD.8
Many of the genes related to xeroderma pigmentosum (DDB2 ERCC2 ERCC3 ERCC4 ERCC5 XPA XPC) are part of this nucleotide excision repair (NER). The proteins produced from these genes play a variety of roles in this process. They recognize DNA damage, unwind regions of DNA where the damage has occurred, snip out (excise) the abnormal sections, and replace the damaged areas with the correct DNA. The POLH gene also plays a role in protecting cells from UV-induced DNA damage, although it is not involved in NER; mutations in this gene cause the variant type of xeroderma pigmentosum.1,3
Finally, the topical use of this film-forming medical device with SPF 100+ and photolyase entrapped in liposomes results in an easy-to-apply, low-cost, essential part of the global therapy of this genetical photodermatosis.4,9
In this case report, we present a 78-year-old patient with XP and a 17-year history of multiple skin cancers. Five years previously, when the patient started twice-daily application of this medical device there was no clinical or dermatoscopic evidence of new skin cancer lesions. However, in the past year, the patient had reduced adherence to the treatment and a BCC lesion appeared. This may be causal; from our history-taking from the patient, we determined that there were few other significant changes in her lifestyle, although the effect of other factors cannot be ruled out definitively in a single patient.
While the most effective method of decreasing the number of malignant tumors in patients with XP is strict sun avoidance and protection, this can be insufficient to prevent such progression, and other measures to improve skin cancer prevention should also be considered. Other additional topical therapies are chemoprevention with 5-fluorouracil or imiquimod, and systemic retinoids such as acitretin could be used as adjuvant therapy.9,12
Oral supplements with polypodium leucotomos, green tea extract, Vitis vinifera, vitamins C, E, and D and carotenoids allow better tolerance to sun exposure. Nutricosmetics can be an excellent option as an adjuvant to topical photoprotection in susceptible populations, as they restore the intracellular redox status and increase the MED, inducing photoadaptation and photo-immunoprotection.12,13
XP patients are also at increased risk for internal neoplasms, and it is important to advise them to avoid smoking and exposure to other carcinogens whenever possible.
Conclusions
This case highlights the importance of the continued use of a film-forming DNA-repair topical medical device containing the DNA-repair enzyme photolyase in liposomes and high-protection UV filters (Repairsomes) containing photolyase and UVB-UVA filters (very high SPF) as an essential part of the treatment to avoid the development of skin cancer lesions in patients with XP.
A protocol for regular follow-ups which increases the chances for better overall survival rates is required and recommended.
Acknowledgment
Jesus Delgado MD and Corinne Granger MD supported the writing of the manuscript. Special thanks to Jane Marshall (freelance) for editing assistance.
Declaration of Patient Consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent forms. In the form the patient has given her consent for her images and other clinical information to be reported in the journal. Institutional approval is not required for this case study. Patient gave written consent for publication of photographs.
Disclosure
Sponsorship for this paper was funded by ISDIN® (Barcelona, Spain). As part of the compassionate use program Isdin® provides this MD for free to XP patients in Spain. JPC is an external consultant for ISDIN who manufactures the product studied and reports grants from ISDIN® (Barcelona, Spain), during the conduct of the study; grants from ISDIN® (Barcelona, Spain), outside the submitted work, and report no other potential conflicts of interest for this work. AGM declares no conflicts of interest for this work.
References
1. Bradford PT, Goldstein AM, Tamura D, et al. Cancer and neurologic degeneration in xeroderma pigmentosum: long term follow-up characterizes the role of DNA repair. J Med Genet. 2011;48(3):168–176. doi:10.1136/jmg.2010.083022
2. Abeti R, Zeitlberger A, Peelo C, et al. Xeroderma pigmentosum: overview of pharmacology and novel therapeutic strategies for neurological symptoms. Br J Pharmacol. 2019;176(22):4293–4301.
3. Lehmann J, Seebode C, Martens MC, et al. Xeroderma pigmentosum – facts and perspectives. Anticancer Res. 2018;38:1159–1164.
4. Giustini S, Miraglia E, Berardesca E, Milani M, Calvieri S. Preventive long-term effects of a topical film-forming medical device with ultra-high UV protection filters and DNA repair enzyme in xeroderma pigmentosum: a retrospective study of eight cases. Case Rep Dermatol. 2014;6(3):222–226. doi:10.1159/000368182
5. Weon JL, Glass DA. Novel therapeutic approaches to xeroderma pigmentosum. Br J Dermatol. 2019;181(2):249–255. doi:10.1111/bjd.17253
6. Wolf P, Kerl H. Photodynamic therapy in patient with xeroderma pigmentosum. Lancet. 1991;337(8757):1613–1614. doi:10.1016/0140-6736(91)93315-Z
7. Fernández-Guarino M, Mavura D, Fernández-González P, et al. Daylight photodynamic therapy is an option for the treatment of actinic keratosis in patients with xeroderma pigmentosum in Africa. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2020;29:101631. doi:10.1016/j.pdpdt.2019.101631
8. Puig S, Granger C, Garre A, Trullàs C, Sanmartin O, Argenziano G. Review of clinical evidence over 10 years on prevention and treatment of a film-forming medical device containing photolyase in the management of field cancerization in actinic keratosis. Dermatol Ther. 2019;9(2):259–270. doi:10.1007/s13555-019-0294-1
9. Leccia MT, Lebbe C, Claudel JP, Narda M, Basset-Seguin N. New vision in photoprotection and photorepair. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2019;9(1):103–115. doi:10.1007/s13555-019-0282-5
10. Krutmann J, Berking C, Berneburg M, Diepgen TL, Dirschka T, Szeimies M. New strategies in the prevention of actinic keratosis: a critical review. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2015;28(6):281–289. doi:10.1159/000437272
11. Laino L, Elia F, Desiderio F, et al. The efficacy of a photolyase-based device on the cancerization field: a clinical and thermographic study. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2015;34(1):84. doi:10.1186/s13046-015-0203-0
12. Piquero-Casals J, Morgado-Carrasco D, Gilaberte Y, et al. Management pearls on the treatment of actinic keratoses and field cancerization. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2020;10(5):903–915. doi:10.1007/s13555-020-00425-4
13. Granger C, Aladren S, Delgado J, Garre A, Trullas C, Gilaberte Y. Prospective evaluation of the efficacy of a food supplement in increasing photoprotection and improving selective markers related to skin photo-ageing. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2020;10(1):163–178. doi:10.1007/s13555-019-00345-y
 © 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
