Back to Journals » Infection and Drug Resistance » Volume 14
Therapeutic Options for Metallo-β-Lactamase-Producing Enterobacterales
Authors Tan X, Kim HS, Baugh K , Huang Y, Kadiyala N , Wences M, Singh N , Wenzler E, Bulman ZP
Received 2 November 2020
Accepted for publication 22 December 2020
Published 18 January 2021 Volume 2021:14 Pages 125—142
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S246174
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Suresh Antony
Xing Tan, 1 Hwan Seung Kim, 1 Kimberly Baugh, 2 Yanqin Huang, 1 Neeraja Kadiyala, 1 Marisol Wences, 1 Nidhi Singh, 1 Eric Wenzler, 1 Zackery P Bulman 1
1Department of Pharmacy Practice, University of Illinois at Chicago College of Pharmacy, Chicago, IL, USA; 2Franciscan Health Hammond/Dyer, Hammond, IN, USA
Correspondence: Zackery P Bulman Department of Pharmacy Practice
College of Pharmacy, University of Illinois at Chicago, 833 South Wood Street, Room 164 (M/C 886), Chicago, IL 60612, USA
Tel +1 312-996-1415
Fax +1 312-413-1797
Email [email protected]
Abstract: The spread of metallo-β-lactamase (MBL)-producing Enterobacterales worldwide without the simultaneous increase in active antibiotics makes these organisms an urgent public health threat. This review summarizes recent advancements in diagnostic and treatment strategies for infections caused by MBL-producing Enterobacterales. Adequate treatment of patients infected with MBL-producing Enterobacterales relies on detection of the β-lactamase in the clinic. There are several molecular platforms that are currently available to identify clinically relevant MBLs as well as other important serine-β-lactamases. Once detected, there are several antibiotics that have historically been used for the treatment of MBL-producing Enterobacterales. Antimicrobials such as aminoglycosides, tetracyclines, fosfomycin, and polymyxins often show promising in vitro activity though clinical data are currently lacking to support their widespread use. Ceftazidime-avibactam combined with aztreonam is promising for treatment of infections caused by MBL-producing Enterobacterales and currently has the most clinical data of any available antibiotic to support its use. While cefiderocol has displayed promising activity against MBL-producing Enterobacterales in vitro and in preliminary clinical studies, further clinical studies will better shed light on its place in treatment. Lastly, there are several promising MBL inhibitors in the pipeline, which may further improve the treatment of MBL-producing Enterobacterales.
Keywords: metallo-β-lactamase, Enterobacterales, carbapenemase, ceftazidime-avibactam, aztreonam, rapid diagnostics
Corrigendum for this paper has been published
Introduction
β-Lactams have been widely used in the treatment of bacterial infections since the 1940s, accounting for more than half of all parenterally administered antibiotic prescriptions in the United States.1 β-Lactam antibiotics are efficacious and have been shown to be superior to other antibiotic classes for a variety of infections including those caused by carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales (CRE) and methicillin susceptible Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA).2–4 They also display favorable safety profiles.2,4 However, the reliance on β-lactams in the clinical setting has driven bacteria to develop resistance. From the first identification of penicillin resistance in 1940, bacteria in the clinical setting have continued to acquire mechanisms to overcome the wide range of β-lactam antibiotics.5 β-Lactam resistance can be caused by expression of efflux pumps, mutations in the PBP enzymes, alterations to membrane permeability, or through the production of β-lactamase enzymes, which is the most prevalent mechanism of β-lactam resistance in Enterobacterales. Bacteria can either intrinsically harbor a gene on the chromosome that encodes a β-lactamase or they can gain the ability to produce β-lactamases through the acquisition of genes on plasmids. The β-lactamases that are produced from these genes are most commonly categorized into Ambler class A, B, C, and D, based on amino acid sequence similarity.6
An especially troubling group of β-lactamases are carbapenemases, which confer resistance to nearly all of the β-lactams, including the penicillins, cephalosporins, and carbapenems.7 Carbapenems are a critically important class of β-lactams often reserved as a last-line treatment option for infections that are resistant to more narrow spectrum β-lactams. Carbapenemases are categorized as either a metallo-β-lactamase (MBL) in Ambler class B or a serine β-lactamase in one of the functional subgroups of classes A or D.6 Class A and D β-lactamases each utilize serine whereas Class B MBL enzymes utilize a Zn2+ metal cofactor in their active site to catalyze the inactivation of β-lactams. β-lactamase enzyme classification has been thoroughly discussed previously.8 Class B β-lactamases are metallo-β-lactamases (MBLs), which have spread globally within Enterobacterales, and can inactivate virtually all clinically used bicyclic β-lactams and serine β-lactamase-inhibiting drugs such as sulbactam, tazobactam, clavulanic acid, and avibactam.2 These class B β-lactamases are further divided into Ambler subclasses with the most clinically important in Enterobacterales being subclass B1. Subclass B1 falls under the functional β-lactamase group 3a since these enzymes can be inhibited in vitro by EDTA and produce broad spectrum hydrolysis against penicillins, cephalosporins, and carbapenems but not monobactams.8 Class B1 enzymes include Verona integron-encoded MBLs (VIM), imipenemases (IMP), and New Delhi MBLs (NDM).
Detection of bacterial isolates that harbor MBL genes is increasing globally at an alarming speed, in part due to an increased use of carbapenems clinically.9 Continued spread of MBLs may have dire consequences to patients since the clinically relevant variants of MBLs possess a broad β-lactam substrate profile and the isolates often simultaneously harbor other antibiotic resistance genes.10,11 There is substantial geographic variability in the prevalence of MBL enzymes among CRE. For example, in some portions of Southeast Asia, MBLs are the most common carbapenemase detected whereas in other regions of the world where serine carbapenemases are more common, MBLs are only a minor cause of carbapenem resistance.12,13 In the United States, MBL enzymes account for <5% of detected carbapenemases.14 IMP enzymes, originally identified in Japan in 1990, were the first MBL identified and remain an important cause of carbapenem resistance in Enterobacterales across Japan and Southeast Asia.15,16 VIM MBL enzymes were first detected in P. aeruginosa isolates in Europe in the mid 1990s and have remained predominant in southern Europe.17,18 NDM enzymes were the most recently discovered of the B1 MBLs and were first identified in a K. pneumoniae isolate from India in 2006.10,19 Although NDM enzymes were initially confined to the Indian subcontinent, they have since disseminated globally in fewer than 5 years and become a prevalent MBL.10,20 The rapid spread of blaNDM may in part be due to the limited fitness cost conferred by this enzyme to its bacterial hosts.21,22 Among MBL enzymes NDM is the most common in Enterobacterales; a study conducted using isolates from 40 countries between 2012 and 2014 revealed that 44.2% of all MBL-producing Enterobacterales possessed blaNDM, 39.3% harbored blaVIM, and 16.5% contained blaIMP.11 K. pneumoniae, followed by E. coli, are the most common hosts of blaNDM across global surveillance studies.23 All three B1 β-lactamases, IMP, VIM, and NDM, have now spread worldwide with multitudes of clinical variants and represent an urgent health threat.
Factors that put patients at risk for becoming infected with MBL-producing Enterobacterales are largely the same as the risk factors for infections caused by other carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. These risk factors often include prior antibiotic use, presence of indwelling catheters, healthcare exposure, or comorbidities.13,24 One study comparing patients infected with MBL-producing Enterobacterales versus those infected with other multidrug-resistant isolates found that prior carbapenem use and central venous catheterization were strongest predictors of MBL infections.25 Once infected, these patients are at considerable risk of mortality. Two studies conducted in patients with bloodstream infections in Athens, Greece found that 23.9–32.1% of patients died within 14 days following infection with VIM-producing K. pneumoniae.26,27 Another study conducted in a hospital in Southern India looked at 101 patients with bloodstream infections caused by NDM-producing Enterobacterales and found a mortality rate of 33.7%.25 de Jager et al examined just hospital-associated infections (detected >48 hours after admission) caused by NDM-producers in an ICU in South Africa and observed mortality rates of 55.3%.28 More recently, a study conducted in Italy and Greece included 102 patients with bloodstream infections caused by NDM- or VIM-producing Enterobacterales and found an overall mortality rate of 31.4%.29 Importantly though, the authors found that there was a significant difference in mortality rates based on the antimicrobial regimen administered suggesting that optimizing antimicrobial therapy is a top priority for infections caused by MBL-producing Enterobacterales.
Detection of MBLs Using Rapid Diagnostic Tests
Rapid diagnostics involving organism identification and genotypic resistance mechanism detection have been shown to decrease mortality among Gram-negative blood stream infections with the coordinated efforts of an antimicrobial stewardship team.30 Since antibiotic recommendations vary substantially based on the cause of carbapenem resistance in Enterobacterales (ie, serine carbapenemases vs MBLs) and traditional phenotypic susceptibility testing cannot determine the underlying mechanism, it is critical to rapidly detect MBL-producing Enterobacterales as the pathogen causing infection. Fortunately, there are several FDA-approved molecular and biochemical rapid diagnostic methods in the market that can detect MBL-producing organisms (Table 1). Of the molecular assays, there are several platforms that identify multiple bacterial species and their resistance mechanisms including Nanosphere Verigene BC-GN, Biofire BCID2 Panel, GenMark Diagnostics ePlex BCID-GN, Biofire FilmArray Pneumonia Panel, and Unyvero Lower Respiratory Tract (LRT) Application.31–36 These allow for direct sampling from a positive blood culture bottle or respiratory sample, detection of polymicrobial infections, and resistance marker detection. Conversely, there are several molecular assays approved for the detection of various carbapenemase enzymes from rectal swab samples or from a pure colony that are only intended for infection control purposes rather than for guidance of treatment (Cepheid Xpert Carba-R, BD MAX Check-Points CPO, GenePOC Carba).37–39 There are also biochemical assays that detect the presence of carbapenemases including the NG-Test CARBA 5 and Rapidec Carba NP tests.40,41 However, these are only intended for infection control purposes. The NG-Test CARBA 5 test is able to distinguish between the type of carbapenemase enzyme while the Rapidec Carba NP test qualitatively indicates hydrolysis of imipenem but the type of resistance mechanism is not characterized. Similar to the Rapidec Carba NP assay, the MBT STAR-Carba IVD Kit is a MALDI-TOF-MS-based assay that detects carbapenem hydrolysis products but cannot distinguish between the type of carbapenemase enzyme.42 Lastly, the Accelerate PhenoTest BC Kit allows for rapid susceptibility testing through morphokinetic cellular analysis; however, no resistant determinant identification is performed.43
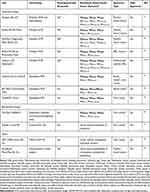 |
Table 1 Rapid Diagnostic Tests Relevant to MBL-Producing Enterobacterales |
Despite the strengths of available technologies, results from these rapid diagnostic tests come with several caveats. Each test has specific organisms or target resistance genes it is testing for, and therefore a negative result does not rule out the presence of bacteria or definitively indicate carbapenem susceptibility. Further, a positive result indicating presence of a resistance gene such as an MBL does not always indicate carbapenem resistance, as the level of conferred resistance will depend on the expression level of the gene and other non-carbapenemase related factors such as the function of the outer membrane porin channels. However, in the case a rapid diagnostic test detects the presence of an MBL it is prudent to assume carbapenem resistance and select therapy accordingly. Rapidly identifying MBL-producing Enterobacterales as the cause of infection will guide selection of appropriate antibiotic therapy and may improve patient outcomes.
Treatment
MBL-producing Enterobacterales is becoming a more prevalent cause of infection globally over the last decade; however, limited treatment options exist. Herein we review the current and pipeline treatment options and available supporting data.
Aztreonam/Avibactam
MBLs can hydrolyze all beta-lactams, except for the monobactam aztreonam (ATM). However, due to the frequent co-production of serine β-lactamases within MBL-producing Enterobacterales, which can hydrolyze aztreonam, aztreonam only remains active against about 30% of these isolates.44 Thus, a combination between ATM and a β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor such as ceftazidime-avibactam (CAZ-AVI) has become an attractive combination with synergistic in vitro activity, even against pathogens co-producing metallo- and serine β-lactamases.45–50 This in vitro synergy has also been observed against NDM producing K. pneumoniae in the murine neutropenic thigh infection model.46 Avibactam’s spectrum of activity includes Class A, C, and some D β-lactamases, including clinically important enzymes CTX-M, KPC-2, AmpC, and OXA-48.51 Ceftazidime cannot be hydrolyzed by OXA-48-like carbapenemases.52 Other β-lactamase inhibitors such as vaborbactam and relebactam could also be useful in combination with aztreonam given their increased activity against class A serine β-lactamases (ie, KPC-3) compared to avibactam.53,54 However, avibactam offers broader spectrum of activity inhibiting class D serine β-lactamases (eg, OXA-48) while vaborbactam and relebactam do not.53,55,56 Further, clinical data against MBL-producing Enterobacterales are only available for ATM and CAZ-AVI, thus this combination will be the focus of this review.
The promising synergy of CAZ-AVI plus ATM against MBL-producing pathogens demonstrated in numerous studies has led to the clinical use of this combination regimen. The current available clinical data are limited to observational studies including various case reports and one prospective study to support its efficacy.29,49,57–61 In the lone prospective observational study, Falcone et al compared outcomes for 102 patients with bloodstream infections caused by MBL-producing Enterobacterales receiving either CAZ-AVI plus ATM or another active antibiotic. The most common causative organism was K. pneumoniae (91.2%) and only NDM (80.4%) and VIM (19.6%) were detected among all patients enrolled in the study. The study found that the 30-day mortality rate was lower in the CAZ-AVI plus ATM group compared to the other active antibiotics group (19.2% [n=52] vs 44% [n=50]; p=0.007). A majority of patients in the best available therapy group received a colistin-containing regimen (n=27). Although the study was nonrandomized and observational, there was little difference in severity of illness between groups and a matched propensity score analysis confirmed that treatment with CAZ-AVI plus ATM was associated with lower mortality. Therefore, this study supports CAZ-AVI plus ATM as a promising treatment option for MBL-producing Enterobacterales. However, additional clinical studies evaluating this combination, especially for other types of infection are warranted.
Although the preliminary clinical data are promising, there remain some questions about the use of CAZ-AVI and ATM for the treatment of Enterobacterales. For example, the optimal dosing strategy for the combination of CAZ-AVI and ATM has not yet been fully defined. A recent hollow-fiber infection model study found that human-simulated dosing of CAZ-AVI 2–0.5 g every 8 h plus ATM 2 g every 6 h over 2 h, or both agents administered as continuous infusions yielded the greatest bacterial killing without emergence of resistance over 7 days.62 This in vitro study may provide guidance for use clinically while awaiting further studies. Furthermore, the pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) target parameters of this combination against MBL-producing Enterobacterales has yet to be fully elucidated. As these agents are two separate FDA-approved agents, automated susceptibility testing for this combination is not available and testing for synergy poses a challenge for many institutional microbiology labs.63
To streamline the CAZ-AVI plus ATM combination, a single product formulation of ATM-AVI is currently under development in Phase III studies for the treatment of serious infections (ie, complicated intra-abdominal infections, nosocomial pneumonia including hospital-acquired pneumonia and ventilator-associated pneumonia, complicated urinary tract infections, or bloodstream infections) caused by MBL-producing gram-negative bacteria.64 Given similar spectrum of microbiologic activity profiles between CAZ-AVI plus ATM and ATM-AVI, the single product ATM-AVI will address many issues encountered with CAZ-AVI plus ATM use, including epidemiological surveillance data (Table 2), susceptibility testing and identifying target exposures predictive of bacterial killing.63,65 Against MBL-producing Enterobacterales, the addition of avibactam at 4 mg/L yielded significant reductions in ATM MICs to 1–2 mg/L across several surveillance studies.44,66,67 The addition of AVI to ATM yielded significant bacterial density reductions in a neutropenic-mouse thigh infection model against 14 MBL-producing Enterobacterales isolates (ATM-AVI MIC ≤16 mg/L) compared to ATM alone, which caused bacterial reductions against only 2 isolates (ATM MIC ≤32 mg/L).65 Unfortunately, decreased susceptibility to ATM-AVI among MBL-producing Escherichia coli has already been observed and determined to be at least in part attributed to a small insertion into PBP3 that impacts binding of aztreonam, ceftazidime, among other β-lactams.68,69 MBL-producing Enterobacterales that co-harbor an AmpC, such as blaCMY, may be particularly prone to developing ATM-AVI resistance as mutations in the gene encoding for this enzyme have also been shown to cause ATM-AVI resistance.70,71 The insertion is not associated with MBL β-lactamases and appears limited to E. coli isolates.
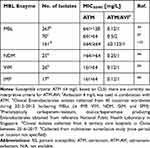 |
Table 2 Aztreonam and Aztreonam-Avibactam Susceptibilities Among MBL-Producing Enterobacterales |
Recently published PK data for ATM-AVI (REJUVENATE study) suggests that a maintenance dose of 1500–500 mg every 6 hours (3-hour infusion) with a 500–167 mg loading dose (30-minute infusion) displays >90% probability of target attainment at an MIC of 8 mg/L with a target of 60% fT>MIC.72 With MIC90 values ≤2 mg/L for most clinical isolates, ATM-AVI appears promising (Table 2). Importantly, the ATM-AVI adverse events were comparable to those reported for ATM monotherapy.
Despite the limitations of using CAZ-AVI plus ATM, this combination still has the most supporting clinical data of any treatment available for MBL-producing Enterobacterales and therefore remains a preferred option while awaiting market availability of ATM-AVI. Optimal dosing can be extrapolated from ATM-AVI PK study as well as available in vitro data. The combination of CAZ-AVI plus ATM was also considered a preferred regimen for MBL-producing Enterobacterales by a recent IDSA guidance document.73
Cefiderocol
Cefiderocol is a novel siderophore cephalosporin that enters the bacterial cell through iron transporters, circumventing the need for porin channels thereby evading resistance caused by porin channel mutations and efflux pump overproduction. Additionally, cefiderocol has other chemical structure attributes that confer increased activity against difficult to treat Gram-negative pathogens and stability to hydrolysis by various beta-lactamases in vitro, including MBLs.74 The chemical modifications include a: pyrrolidinium group on the C-3 side chain that confers stability against β-lactamases (similar to cefepime), a carboxypropanoxyimino group on the C-7 side chain to improve permeability across the outer membrane (similar to ceftazidime), as well as a chlorocatechol group on the C-3 side chain that facilitates the siderophore activity. These modifications translate to a lower catalytic efficiency of cefiderocol by MBL enzymes compared to meropenem (260-fold lower against IMP-1 and VIM-2 among P. aeruginosa isolates, and 3-fold lower against NDM-1 among Enterobacterales isolates).75 The percentage of Enterobacterales exhibiting a cefiderocol MIC ≤ 2mg/L (FDA susceptible breakpoint) was 41% (n=61) to 85.7% (n=49) among NDM-positive isolates, 80.9% (n=47) to 91.7% (n=12) among VIM-positive isolates, and 87.5% (n=8) to 93.3% (n=15) among IMP-positive isolates.76,77 The percentage of Enterobacterales exhibiting a cefiderocol MIC ≤ 4 mg/L (CLSI susceptible breakpoint) was 72.1% (n=61) to 89.8% (n=49) among NDM-positive isolates, 91.7% (n=12) to 95.7% (n=47) among VIM-positive isolates, and 87.5% (n=8) to 100% (n=15) among IMP-positive isolates (Table 3).76,77 In a multinational surveillance study (SIDERO-WT-2014 study), mechanisms of resistance were categorized for cefiderocol non-susceptible isolates and among 5 NDM-producing Enterobacterales isolates, it was found that elevated MICs were most likely due to a co-production of metallo- and serine-beta-lactamases and not impacted by porin protein truncation or loss.76,78 The PK/PD index of cefiderocol for Enterobacterales was determined to be 73.3% and 64.4% fT>MIC in the thigh and lung murine infection models, respectively, including isolates producing MBLs.79 This target appears attainable for organisms up to MIC 4 mg/L.80 However, considering a target fT>MIC of 75%, the probability of target attainment falls quickly to <70% when the cefiderocol MIC is 8 mg/L and is 0% for MICs ≥16 mg/L.81 Thus, there is a relatively narrow window between high probability of target attainment and predicted treatment failure. This narrow window is particularly concerning for MBL-producing Enterobacterales since they often have MICs closer to the susceptibility breakpoint (Table 3) and are also vulnerable to MIC discrepancies due to variations between testing modalities.77,82–84
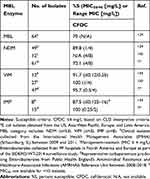 |
Table 3 Cefiderocol Susceptibilities Among MBL-Producing Enterobacterales |
There is limited clinical data evaluating the use of cefiderocol against MBL-producing Enterobacterales.85–87 In cefiderocol’s Phase II study for the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections (APEKS-cUTI study) and phase III study for the treatment of nosocomial pneumonia (APEKS-NP), carbapenem-resistant organisms were excluded as the comparator agent was imipenem-cilastatin.86,88 However, a separate pathogen-focused study (CREDIBLE-CR) was also conducted.87 CREDIBLE-CR was a phase III, open-label study comparing cefiderocol with the best available therapy against carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria causing pneumonia, bloodstream infections/sepsis, or complicated urinary tract infections. Overall, there was a numerically higher all-cause mortality rate observed in the cefiderocol group compared to a best available therapy arm (34% vs 18%), which primarily comprised of colistin-containing regimens (61%). No definitive conclusions have been drawn regarding the cause of increased mortality seen in the cefiderocol group, though it appears to have been driven by higher treatment failure rates among patients infected with carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii. Yet, this finding is still concerning and led to a warning in the cefiderocol prescribing information.89 Within the CREDIBLE-CR study, 23 patients had MBL-producing pathogens of which 16 received cefiderocol and 7 received best available therapy. The most common MBL enzyme was NDM (n=15) followed by IMP (n=5) and VIM (n=4); some isolates contained >1 MBL enzyme. Clinical cure rates were 75% in the cefiderocol group at the test of cure compared to 29% in the best available therapy groups, though none of the patients in the best available therapy group received CAZ-AVI plus ATM.
Despite these promising preliminary findings, there remain some concerns for cefiderocol’s use against MBL-producing Enterobacterales, including the increased mortality rate in the CREDIBLE-CR study, logistical issues with susceptibility testing and interpretation (discordance between FDA [MIC ≤2 mg/L] vs CLSI [MIC ≤4 mg/L] susceptible breakpoints), and PK/PD concerns for isolates with higher MICs.83,84,90–92 The recent IDSA guidance update considers cefiderocol as another preferred antibiotic for the treatment of MBL-producing Enterobacterales with CAZ-AVI plus ATM.73 Although there are some promising data to support the use of cefiderocol against MBL-producing Enterobacterales, there is still less clinical evidence to support its use than there is for the combination of CAZ-AVI plus ATM. Thus, based on the currently available data, we would suggest considering cefiderocol an alternative for when CAZ-AVI plus ATM is not an option.
Carbapenems
MBL enzymes can readily hydrolyze carbapenems in vitro, yet some data suggests that their ability to cause carbapenem resistance is an artifact of the current testing modalities that utilize media with supraphysiologic zinc concentrations.93 Since zinc is required at the active site of the enzyme, the quantity of zinc at the site of infection could impact the function of the enzyme and also the rate of antibiotic hydrolysis. However, the data are inconclusive. Asempa et al found that meropenem against a panel of NDM-, VIM-, and IMP-producing Enterobacterales appeared resistant in vitro but generated >1 log bacterial killing in murine infection models.93 They showed that the meropenem in vivo activity better correlated with MICs performed in zinc-depleted media, where the isolates appeared susceptible to carbapenems, than in traditional cation adjusted Mueller Hinton broth.
Roujansky et al also report in vivo efficacy of ertapenem and imipenem against a carbapenem-resistant NDM-1 producing E. coli isolate.94 However, they proposed an alternative hypothesis to this paradoxical activity, suggesting that subinhibitory antibiotic concentrations are affecting bacterial fitness and the host’s immune response. Another recent study did not find the same discordance between in vitro and in vivo meropenem activity in all MBL-producing isolates, though they did suggest that enzyme variations may be driving the inter-isolate variability observed for in vivo meropenem response.95 MBL-enzymes may also be evolving to retain their catalytic activity under low zinc concentrations.96 Zinc chelators have also been proposed as adjuvants to carbapenems for MBL-producing Enterobacterales as they may reduce the zinc available to the MBL active site, thereby impairing the enzyme’s ability to hydrolyze carbapenems.97 One in vivo study showed that a zinc chelator (DMSA) used in combination with a carbapenem significantly reduced bacterial counts in an MBL-producing E. coli murine peritonitis model compared to carbapenems alone.98
The clinical implications of these findings remain uncertain. While some case reports have shown mostly positive outcomes with carbapenem-based regimens for infections caused by MBL-producing Enterobacterales,99 Falcone et al noted that among 6 patients who received meropenem-containing combinations, 3 of them died, though none of them were receiving carbapenem monotherapy.29 Given the conflicting preclinical data and the very limited clinical data, the risks of using a carbapenem to treat an MBL-producing Enterobacterales isolate seem to outweigh the potential benefit given that alternative treatment strategies are available.100 Of note, the newer carbapenem-β-lactamase inhibitor combinations (meropenem-vaborbactam and imipenem-relebactam) do not display additional activity against MBL-producing Enterobacterales compared to their carbapenem counterparts alone. This is due to the inability of both vaborbactam and relebactam to inhibit MBLs, as has been discussed previously.53,101
Aminoglycosides
Aminoglycosides are rapidly bactericidal and exert antibacterial activity through protein synthesis inhibition by binding to the 30S ribosome. However, aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes (AMEs) can confer resistance to some of the aminoglycosides and are common among MBL-producing Enterobacterales.102–106 Plazomicin is the newest semi-synthetic aminoglycoside and is able to evade the most common AMEs in Enterobacterales.107−109 Though, plazomicin is still liable to the aminoglycoside resistance conferred by the 16S rRNA methyltransferases (16S-RMTases) that prevent all clinically available aminoglycosides from binding to the ribosome.108,110 16S-RMTases are commonly co-harbored by MBL-producing Enterobacterales. Across several surveillance studies, plazomicin was the most active aminoglycoside compared to amikacin, tobramycin, and gentamicin (Table 4).108,111–113 Although amikacin susceptibility rates were similar to those of plazomicin in several studies, this should be interpreted with caution due to the high amikacin MIC breakpoint set by CLSI relative to other organizations such as EUCAST or USCAST.114 A surveillance study in 26 European countries revealed that among 37 MBL-producing Enterobacterales isolates (blaVIM and blaNDM-1), only 40.5% were susceptible to plazomicin and 16S rRNA methyltransferases (primarily rmtB and armA) were detected in 60% of isolates.108 In isolates only harboring an AME, plazomicin retained susceptibility in 99%. In the largest reported study of MBL-producing Enterobacterales (n=488), plazomicin was active against >75% of all isolates however the difference in activities between NDM, VIM, and IMP are noted, with all aminoglycosides being the least active against NDM-producers.115 Similar susceptibilities were noted in other studies (Table 4).111–113 Taken together, plazomicin susceptibility rates were low for NDM-producing isolates (22.7% to 52.7%) but were much higher for VIM- and IMP-producing isolates (89.6% to 95% for VIM, and 100% for IMP). This suggests that 16S-RMTases may be more commonly co-harbored in NDM-producing isolates, though future studies are warranted. Apramycin, which is in Phase I clinical trials, has been shown to be active against Enterobacterales that produce 16S-RMTases, which confer resistance to all other currently available aminoglycosides.116,117 Although limited data about apramycin against MBL-producing Enterobacterales is currently available, it holds potential to become a therapeutic option for MBL-producing Enterobacterales based on its spectrum of activity.
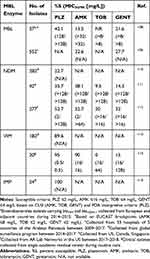 |
Table 4 Aminoglycoside Susceptibilities Among MBL-Producing Enterobacterales |
Beyond susceptibility studies, very limited data exists that evaluates plazomicin against MBL-producing Enterobacterales. One in vitro time-kill study found synergy with plazomicin plus meropenem, colistin, or fosfomycin against two K. pneumoniae isolates with blaVIM.118 A phase III, randomized, open-label, pathogen-directed study was performed assessing plazomicin plus meropenem or tigecycline compared with colistin plus meropenem or tigecycline for bloodstream infection or hospital-acquired or ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia caused by a carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales (CARE trial).119 The most common carbapenemase gene detected was blaKPC but it is not reported if any patients were infected with MBL-producing isolates. The study was stopped early due to slow enrollment; however, 24% (4/17) in the plazomicin group versus 50% (10/20) of patients in the colistin group had a composite of death from any cause at 28 days or significant disease-related complications. In summary, the high resistance rates preclude the use of aminoglycosides as empiric therapy for NDM-type MBLs. If the isolate is susceptible an aminoglycoside, such as plazomicin, may be a possible adjuvant to other active agents for MBL-producing Enterobacterales, though additional data is required in order to make a reliable recommendation.
Tetracyclines
The tetracyclines exert antibacterial activity by binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit and preventing the docking of amino-acyl-transfer RNA (tRNA).120 Resistance to tetracyclines emerge by efflux, ribosomal protection, and enzymatic inactivation of drug. With two recent additions (eravacycline and omadacycline) to join tigecycline and minocycline among the crucial tetracyclines to combat MDR Enterobacterales, their activity against MBL-producers is an important question. Investigations into tetracycline resistance among MBL-producing Enterobacterales are scarce. One study reports tigecycline resistance among 5 NDM-positive E. coli isolates to be attributed to a single nucleotide substitution in the 30S ribosome.121 Another study showed high transferability and stability of plasmids carrying tet(X4) in NDM-positive E. coli isolates conferring resistance to tigecycline and eravacycline.122 In a large surveillance study of MBL-producing Enterobacterales isolates collected in the US between 2017 and 2018, tetracycline susceptibilities are illustrated.112 Among 275 Enterobacterales isolates harboring blaNDM tigecycline was the most active tetracycline agent followed by eravacycline (Table 5). In another susceptibility study, tigecycline, eravacycline, and minocycline susceptibilities were evaluated against NDM (n=42), VIM (n=44), and IMP-producing (n=15) Enterobacterales isolates.91,123 Similarly, tigecycline was the most active agent followed by eravacycline and susceptibilities between the different types of MBL enzymes were similar. Tigecycline and eravacycline were also highly active (>95% rates of susceptibility) against another collection of MBL-producing E. coli isolates from around the world.124 In a murine lung infection model, tigecycline was evaluated as monotherapy and in combination with ceftazidime-avibactam and aztreonam.125 Two humanized doses simulating tigecycline 50 mg every 12 h and 100 mg every 12 h were used. As monotherapy, both tigecycline groups resulted in bacterial regrowth while all combinations resulted in ≥2 log10 reduction in CFU, supporting tigecycline’s potential role in combination therapy against MBL-producing Enterobacterales.
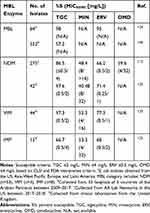 |
Table 5 Tetracycline Susceptibilities Among MBL-Producing Enterobacterales |
Clinical data evaluating any of the tetracycline analogues against MBL-producing Enterobacterales is limited to one observational study in which tigecycline monotherapy or combination therapy was used in 15 septic patients with various infection types caused by VIM-1 producing K. pneumoniae.126 The overall 30-day mortality rate was 25% and mortality was associated with underlying severity of disease. Although, due to the small sample size and variability of infection types, general conclusions are difficult to draw from this study. Based on the available data, tigecycline followed by eravacycline are the most active tetracycline analogues in vitro. There are important pharmacokinetic properties to note for minocycline, tigecycline, eravacycline, and omadacycline. Generally, all four tetracyclines have higher tissue concentrations than serum, concentration-dependent plasma protein binding ranging from 70% to 90% (except eravacycline is 21%), and exhibit minimal renal clearance. Although incompletely understood, the higher tissue concentrations relative to serum of the tetracyclines make them an important class of antibiotics for infections located in various tissues. The organism’s MIC along with the pharmacokinetics of these agents considering the infection site should be taken into consideration when selecting therapy. More in vitro, in vivo, and clinical studies are needed to determine the tetracyclines’ place in therapy.
Fosfomycin
Fosfomycin inhibits the MurA enzyme that disrupts peptidoglycan synthesis in bacteria.127 The major mechanisms of resistance are conferred through chromosomal mutations leading to decreased uptake, decreased binding to target MurA, and enzymatic inactivation (FosA). There are only a few studies that have evaluated the activity of fosfomycin against MBL-producing Enterobacterales (Table 6) with limited data on the mechanisms of fosfomycin resistance among MBL-producing Enterobacterales.128 One study found that 76.2% (n=48/63) of VIM-1-producing K. pneumoniae isolates were susceptible (MIC ≤64 mg/L) to fosfomycin; however, this data is only applicable to urinary isolates.91,129 In a neutropenic murine thigh infection model, the fosfomycin AUC/MIC ratio to achieve stasis and 1-log kill was 11 and 22, respectively, against a K. pneumoniae isolate harboring NDM-1 (fosfomycin MIC 4 mg/L).130
 |
Table 6 Fosfomycin Susceptibilities Among MBL-Producing Enterobacterales |
There are no clinical studies examining the use of fosfomycin against MBL-producing Enterobacterales directly; thus, the discussion here focuses on available pharmacokinetic studies for Enterobacterales generally. A phase III study for intravenous fosfomycin utilized a dose of 6 g IV every 8 h in the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections or acute pyelonephritis and met its primary end point for non-inferiority compared with piperacillin-tazobactam.131 Based on the pharmacokinetic study of intravenous fosfomycin, a 6 g IV every 8 h dose would yield an exposure ~715 μg·h/mL, suggesting that AUC/MIC ratios required for 1-log kill can be achieved with fosfomycin MIC 8 mg/L among Enterobacterales, irrespective of strain and β-lactamase.130–132 The high exposures achieved also suggest its potential use in systemic infections, such as has been done in countries who have had access to intravenous fosfomycin.133 However, in vitro pharmacodynamic studies also need to be taken into consideration as they suggest that monotherapy fosfomycin may not be useful due to baseline heteroresistant subpopulations and rapid regrowth, despite fosfomycin MICs of 0.5–8 mg/L.134–136 Susceptibility testing issues also remain a challenge and are another limitation to the widespread clinical use of fosfomycin.137 Larger surveillance and clinical studies are needed to determine fosfomycin’s place in therapy against contemporary MBL-producing Enterobacterales and in various infection types.138,139
Polymyxins
The polymyxin antibiotics (colistin and polymyxin B) were originally discovered in the 1940s and retain high rates of in vitro activity against many carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. The polymyxins bind to the lipid A portion of the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) molecule, thereby destabilizing the bacterial outer membrane which causes increased permeability and cell death. Resistance to polymyxins mostly involves the addition of 4-amino-4-deoxy-1-arabinose or phosphoethanolamine to the LPS, which decreases binding of polymyxins to lipid A. These chemical modifications are caused by chromosomal mutations in two-component regulatory systems or acquired phosphoethanolamine transferase genes harboured by plasmids (eg, mcr-1).140 Several studies have investigated prevalence of polymyxin resistance among MBL-producing Enterobacterales isolates (Table 7). In a global surveillance program that aimed to determine polymyxin activity in β-lactamase producing isolates, it was found that among Enterobacterales that harbored an MBL (n=81), 92.6% of isolates were susceptible to colistin, which was higher than in KPC-positive (87.9%) or OXA-48-positive isolates (84.2%) using EUCAST breakpoints (MIC ≤2 mg/L).141 The prevalence of MBL-producing Enterobacterales among colistin-resistant isolates (1.6%, 309/19,719) was also low (6 isolates). Despite high susceptibility among MBL-producing Enterobacterales, colistin-containing regimens were associated with higher mortality rates than CAZ-AVI plus ATM (59.3% vs 19.2%, respectively) for MBL-producing CRE in the study by Falcone et al.29 Extrapolating from previous studies that assessed polymyxins against other carbapenem-resistant organisms (non-MBL) further suggests that polymyxins are no longer a preferred agent for MBL-producing Enterobacterales. Furthermore, dose-limiting nephrotoxicity is common with polymyxin use.142 Thus, the data suggests that polymyxins should be considered a backup to β-lactam-based regimens, such as CAZ-AVI plus ATM or cefiderocol, when they are available.2,143 If polymyxins are used, combination therapy is recommended for treatment of CRE.144 Some in vitro data shows promise for combinations between polymyxin and aztreonam against Enterobacterales harboring blaNDM or blaVIM, which represents a potential area for future research and may revitalize the utility of the polymyxins for MBL-producing Enterobacterales.145,146
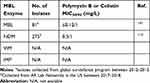 |
Table 7 Polymyxin Susceptibilities Among MBL-Producing Enterobacterales |
Pipeline Agents
All of the recently approved β-lactamase inhibitors are only active against serine β-lactamases in class A or D; MBL inhibitors are urgently needed. There are several MBL inhibitors in the pipeline that may address the growing global threat of MBL-producing bacteria (Table 8).147 Taniborbactam (formerly VNRX-5133) is a cyclic boronate β-lactamase inhibitor in phase III clinical trials and the first to display activity against class A-D β-lactamases (including MBLs with the exception of IMP) and is currently being co-developed with cefepime.148,149 LYS228 is a novel monobactam currently in phase II development as a stand-alone agent with stability against MBLs and a broad spectrum of serine β-lactamases while retaining antibacterial activity through inhibition of penicillin-binding protein 3.150,151 LYS228 has been shown to be less stable to PER and VEB β-lactamases, as well as other non-β-lactamase-mediated resistance mechanisms. QPX7728 is another cyclic boronate β-lactamase inhibitor with an expanded spectrum of inhibition compared to taniborbactam, including against class A (CTX-M, SHV, TEM, VEB, PER and carbapenemases KPC, SME, NMC-A, BKC-1), B (NDM, VIM, CcrA, IMP, and GIM), C (CMY, FOX, MIR, DHA, P99, PDC, ADC), and D (OXA-48, OXA-23/24/72/58).152 QPX7728 is currently undergoing a Phase I study. Thiazole carboxylate derivative, ANT2681, inhibits MBLs through interaction with the dinuclear zinc ion cluster and is being co-developed with meropenem.95 It is currently ready to enter phase I clinical development with positive in vitro and in vivo results where it potentiated meropenem activity (decreasing meropenem MIC from >32 mg/L to 8 mg/L). The MBL inhibitor pipeline holds much potential to address a global unmet need.
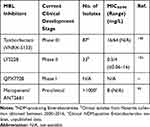 |
Table 8 MICs for Pipeline Agents Against MBL-Producing CRE |
Conclusions
MBL-producing Enterobacterales are an urgent global public health threat that have rapidly disseminated worldwide and cause infections that are associated with mortality rates of ~30-50%. Rapid diagnostic tests are important to detect MBLs and guide early treatment since the mechanism of carbapenem resistance in CRE dictates the preferred treatment option. Fortunately, there are many available FDA-approved instruments that can detect MBLs and are able to help meet the challenges associated with increasing MBL prevalence. Although many antibiotics display in vitro activity, there is little clinical data to clearly define their place in treatment. However, newer data generally support the use of ceftazidime-avibactam in combination with aztreonam as a primary treatment option for MBL-producing Enterobacterales. Cefiderocol may be a reasonable alternative if isolates are found to be susceptible, though additional clinical studies are necessary. Various agents in the pipeline are active against MBL-producing Enterobacterales and may eventually add to our treatment armamentarium. Future studies are warranted and can be used to refine the treatment approach for treating MBL-producing Enterobacterales infections and improve patient outcomes.
Funding
Z.P.B. was supported by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number R01AI148560.
Disclosure
E.W. reports personal fees from GenMark Diagnostics, outside the submitted work, and serves on the speaker’s bureau for Melinta Therapeutics, Astellas Pharma, and Allergan Plc. and on the advisory board for Shionogi and Genmark Diagnostics. Zackery P Bulman reports grants from the National Institutes of Health under Award Number R01AI148560, during the conduct of the study. The authors report no other potential conflicts of interest for this work.
References
1. Bush K, Bradford PA. β-Lactams and β-lactamase inhibitors: an overview. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2016;6:8. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a025247
2. van Duin D, Lok JJ, Earley M, et al. Colistin versus ceftazidime-avibactam in the treatment of infections due to carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Clin Infect Dis. 2018;66(2):163–171. doi:10.1093/cid/cix783
3. McDanel JS, Perencevich EN, Diekema DJ, et al. Comparative effectiveness of beta-lactams versus vancomycin for treatment of methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections among 122 hospitals. Clin Infect Dis. 2015;61(3):361–367. doi:10.1093/cid/civ308
4. Wunderink RG, Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ, Rahav G, et al. Effect and safety of meropenem-vaborbactam versus best-available therapy in patients with carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae infections: the TANGO II randomized clinical trial. Infect Dis Ther. 2018;7(4):439–455. doi:10.1007/s40121-018-0214-1
5. Abraham EP, Chain E. An enzyme from bacteria able to destroy penicillin. Nature. 1940;146(3713):837. doi:10.1038/146837a0
6. Ambler RP. The structure of beta-lactamases. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980;289(1036):321–331.
7. Hammoudi Halat D, Ayoub Moubareck C. The current burden of carbapenemases: review of significant properties and dissemination among gram-negative bacteria. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020;9:4.
8. Bush K, Jacoby GA. Updated functional classification of beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010;54(3):969–976. doi:10.1128/AAC.01009-09
9. McLaughlin M, Advincula MR, Malczynski M, Qi C, Bolon M, Scheetz MH. Correlations of antibiotic use and carbapenem resistance in enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57(10):5131–5133. doi:10.1128/AAC.00607-13
10. Bush K, Bradford PA. Epidemiology of β-lactamase-producing pathogens. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2020;33:2.
11. Kazmierczak KM, Rabine S, Hackel M, et al. Multiyear, multinational survey of the incidence and global distribution of metallo-β-lactamase-producing enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016;60(2):1067–1078. doi:10.1128/AAC.02379-15
12. Kazi M, Drego L, Nikam C, et al. Molecular characterization of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae at a tertiary care laboratory in Mumbai. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015;34(3):467–472. doi:10.1007/s10096-014-2249-x
13. van Duin D. The global epidemiology of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Virulence. 2017;8(4):460–469.
14. van Duin D, Arias CA, Komarow L, et al. Molecular and clinical epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales in the USA (CRACKLE-2): a prospective cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020;20(6):731–741. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(19)30755-8
15. Watanabe M, Iyobe S, Inoue M, Mitsuhashi S. Transferable imipenem resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991;35(1):147–151. doi:10.1128/AAC.35.1.147
16. Walsh TR, Toleman MA, Poirel L, Nordmann P. Metallo-beta-lactamases: the quiet before the storm? Clin Microbiol Rev. 2005;18(2):306–325. doi:10.1128/CMR.18.2.306-325.2005
17. Poirel L, Naas T, Nicolas D, et al. Characterization of VIM-2, a carbapenem-hydrolyzing metallo-beta-lactamase and its plasmid- and integron-borne gene from a Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolate in France. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000;44(4):891–897. doi:10.1128/AAC.44.4.891-897.2000
18. Lauretti L, Riccio ML, Mazzariol A, et al. Cloning and characterization of blaVIM, a new integron-borne metallo-beta-lactamase gene from a Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999;43(7):1584–1590. doi:10.1128/AAC.43.7.1584
19. Yong D, Toleman MA, Giske CG, et al. Characterization of a new metallo-beta-lactamase gene, bla(NDM-1), and a novel erythromycin esterase gene carried on a unique genetic structure in Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 14 from India. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53(12):5046–5054. doi:10.1128/AAC.00774-09
20. Moellering RC
21. López C, Ayala JA, Bonomo RA, González LJ, Vila AJ. Protein determinants of dissemination and host specificity of metallo-β-lactamases. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):3617. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-11615-w
22. Ma T, Fu J, Xie N, et al. Fitness cost of bla(NDM-5)-carrying p3R-IncX3 plasmids in wild-type NDM-free Enterobacteriaceae. Microorganisms. 2020;8:3. doi:10.3390/microorganisms8030377
23. Wu W, Feng Y, Tang G, Qiao F, McNally A, Zong Z. NDM Metallo-β-lactamases and their bacterial producers in health care settings. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2019;32:2.
24. Falagas ME, Rafailidis PI, Kofteridis D, et al. Risk factors of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infections: a matched case control study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007;60(5):1124–1130. doi:10.1093/jac/dkm356
25. Snyder BM, Montague BT, Anandan S, et al. Risk factors and epidemiologic predictors of blood stream infections with New Delhi Metallo-b-lactamase (NDM-1) producing Enterobacteriaceae. Epidemiol Infect. 2019;147:e137. doi:10.1017/S0950268819000256
26. Daikos GL, Petrikkos P, Psichogiou M, et al. Prospective observational study of the impact of VIM-1 metallo-beta-lactamase on the outcome of patients with Klebsiella pneumoniae bloodstream infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53(5):1868–1873. doi:10.1128/AAC.00782-08
27. Daikos GL, Karabinis A, Paramythiotou E, et al. VIM-1-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae bloodstream infections: analysis of 28 cases. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2007;29(4):471–473. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2006.11.006
28. de Jager P, Chirwa T, Naidoo S, Perovic O, Thomas J. Nosocomial outbreak of New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase-1-producing gram-negative bacteria in South Africa: a case-control study. PLoS One. 2015;10(4):e0123337. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0123337
29. Falcone M, Daikos GL, Tiseo G, et al. Efficacy of ceftazidime-avibactam plus aztreonam in patients with bloodstream infections caused by MBL-producing Enterobacterales. Clin Infect Dis. 2020. doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa586
30. Timbrook TT, Morton JB, McConeghy KW, Caffrey AR, Mylonakis E, LaPlante KL. The effect of molecular rapid diagnostic testing on clinical outcomes in bloodstream infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;64(1):15–23. doi:10.1093/cid/ciw649
31. Nanosphere, Inc. Verigene Gram Negative Blood Culture Nucleic Acid Test (BC-GN). 2014; Available from:https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/reviews/K132843.pdf.
32. BioFire Diagnostics, LLC. BioFire Blood Culture Identification 2 (BCID2) Panel. 2020; Available from:https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/reviews/K193519.pdf.
33. BioFire Diagnostics, LLC. FilmArray Pneumonia Panel. 2018. Available from:https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/reviews/K180966.pdf.
34. Curetis GmbH. Unyvero Lower Respiratory Tract (LRT) Application. 2018; Available from:https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/reviews/DEN170047.pdf.
35. Curetis GmbH. Unyvero LRT BAL Application. 2019; Available from:https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/reviews/K191967.pdf.
36. GenMark Diagnostics, Inc. EPlex Blood Culture Identification Gram Negative (BCID-GN) Panel. 2019; Available from:https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/reviews/K182619.pdf.
37. Cepheid. Xpert Carba-R. 2018; Available from:https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/reviews/K173263.pdf.
38. Check-Points Health B.V. BD MAX Check-Points CPO. 2019; Available from:https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/reviews/K190613.pdf.
39. GenePOC Inc. GenePOC Carba. 2019; Available from:https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/reviews/K190275.pdf.
40. NG Biotech. NG-Test CARBA 5. 2019; Available from:https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/reviews/K191889.pdf.
41. bioMérieux SA. Rapidec Carba NP. 2017; Available from:https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/reviews/K162385.pdf.
42. Dortet L, Tandé D, de Briel D, et al. MALDI-TOF for the rapid detection of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae: comparison of the commercialized MBT STAR®-Carba IVD Kit with two in-house MALDI-TOF techniques and the RAPIDEC® CARBA NP. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2018;73(9):2352–2359. doi:10.1093/jac/dky209
43. Accelerate Diagnostics. Accelerate Pheno System, Accelerate Phenotest BC Kit. 2017; Available from:https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/reviews/DEN160032.pdf.
44. Karlowsky JA, Kazmierczak KM, de Jonge BLM, Hackel MA, Sahm DF, Bradford PA. In vitro activity of aztreonam-avibactam against enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated by clinical laboratories in 40 Countries from 2012 to 2015. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61:9. doi:10.1128/AAC.00472-17
45. Falcone M, Paterson D. Spotlight on ceftazidime/avibactam: a new option for MDR Gram-negative infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016;71(10):2713–2722. doi:10.1093/jac/dkw239
46. Marshall S, Hujer AM, Rojas LJ, et al. Can ceftazidime-avibactam and aztreonam overcome beta-lactam resistance conferred by metallo-beta-lactamases in Enterobacteriaceae? Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61:4. doi:10.1128/AAC.02243-16
47. Wenzler E, Deraedt MF, Harrington AT, Danizger LH. Synergistic activity of ceftazidime-avibactam and aztreonam against serine and metallo-beta-lactamase-producing gram-negative pathogens. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2017;88(4):352–354. doi:10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2017.05.009
48. Biagi M, Wu T, Lee M, Patel S, Butler D, Wenzler E. Searching for the optimal treatment for metallo- and serine-beta-lactamase producing enterobacteriaceae: aztreonam in combination with ceftazidime-avibactam or Meropenem-vaborbactam. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019. doi:10.1128/AAC.01426-19
49. Davido B, Fellous L, Lawrence C, Maxime V, Rottman M, Dinh A. Ceftazidime-avibactam and aztreonam, an interesting strategy to overcome beta-lactam resistance conferred by metallo-beta-lactamases in Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61:9. doi:10.1128/AAC.01008-17
50. Avery LM, Nicolau DP. Assessing the in vitro activity of ceftazidime/avibactam and aztreonam among carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae: defining the zone of hope. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2018;52(5):688–691. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2018.07.011
51. Ehmann DE, Jahic H, Ross PL, et al. Kinetics of avibactam inhibition against Class A, C, and D β-lactamases. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(39):27960–27971. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.485979
52. Stojanoski V, Chow DC, Fryszczyn B, et al. Structural basis for different substrate profiles of two closely related Class D β-Lactamases and their inhibition by Halogens. Biochemistry. 2015;54(21):3370–3380. doi:10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00298
53. Lomovskaya O, Sun D, Rubio-Aparicio D, et al. Vaborbactam: spectrum of beta-lactamase inhibition and impact of resistance mechanisms on activity in Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61:11. doi:10.1128/AAC.01443-17
54. Haidar G, Clancy CJ, Chen L, et al. Identifying spectra of activity and therapeutic niches for ceftazidime-avibactam and imipenem-relebactam against carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61:9. doi:10.1128/AAC.00642-17
55. Li H, Estabrook M, Jacoby GA, Nichols WW, Testa RT, Bush K. In vitro susceptibility of characterized beta-lactamase-producing strains tested with avibactam combinations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59(3):1789–1793. doi:10.1128/AAC.04191-14
56. Canver MC, Satlin MJ, Westblade LF, et al. Activity of imipenem-relebactam and comparator agents against genetically characterized isolates of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019;63:9. doi:10.1128/AAC.00672-19
57. Hobson CA, Bonacorsi S, Fahd M, et al. Successful treatment of bacteremia due to NDM-1-producing morganella morganii with aztreonam and ceftazidime-avibactam combination in a pediatric patient with hematologic malignancy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019;63:2.
58. Yasmin M, Fouts DE, Jacobs MR, et al. Monitoring ceftazidime-avibactam and aztreonam concentrations in the treatment of a bloodstream infection caused by a multidrug-resistant Enterobacter sp. Carrying Both Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase-4 and New Delhi Metallo-beta-Lactamase-1. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71(4):1095–1098. doi:10.1093/cid/ciz1155
59. Benchetrit L, Mathy V, Armand-Lefevre L, Bouadma L, Timsit JF. Successful treatment of septic shock due to NDM-1-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae using ceftazidime/avibactam combined with aztreonam in solid organ transplant recipients: report of two cases. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020;55(1):105842. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2019.10.023
60. Shah PJ, Tran T, Emelogu F, Tariq F. Aztreonam, Ceftazidime/ Avibactam, and colistin combination for the management of carbapenemase-producing klebsiella pneumoniae bacteremia: a case report. J Pharm Pract. 2019;897190019882262.
61. Shaw E, Rombauts A, Tubau F, et al. Clinical outcomes after combination treatment with ceftazidime/avibactam and aztreonam for NDM-1/OXA-48/CTX-M-15-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae infection. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2018;73(4):1104–1106. doi:10.1093/jac/dkx496
62. Lodise TP, Smith NM, O’Donnell N, et al. Determining the optimal dosing of a novel combination regimen of ceftazidime/avibactam with aztreonam against NDM-1-producing Enterobacteriaceae using a hollow-fibre infection model. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2020;75(9):2622–2632. doi:10.1093/jac/dkaa197
63. Ransom E, Bhatnagar A, Patel JB, et al. Validation of aztreonam-avibactam susceptibility testing using digitally dispensed custom panels. J Clin Microbiol. 2020;58:4. doi:10.1128/JCM.01944-19
64. Clinicaltrials.gov. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of ATM-AVI in the treatment of serious infection due to MBL-producing gram-negative bacteria. 2018; Available from:https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03580044?cond=aztreonam+avibactam&draw=2&rank=5.
65. Crandon JL, Nicolau DP. Human simulated studies of aztreonam and aztreonam-avibactam to evaluate activity against challenging gram-negative organisms, including metallo-beta-lactamase producers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57(7):3299–3306. doi:10.1128/AAC.01989-12
66. Castanheira M, Sader HS, Flamm RK, Jones RN, Huband MD Activity of aztreonam combined with the beta-lactamase inhibitor avibactam tested against metallo beta-lactamase-producing organisms. P1615. ECCMID 2013; Berlin, Germany. 2013; Available from:https://www.escmid.org/escmid_publications/escmid_elibrary/?q=Activity+of+Aztreonam+Combined+with+the+Beta-lactamase+Inhibitor+Avibactam+Tested+against+Metallo-%CE%B2-lactamase-producing+Organisms&id=2173&L=0&x=28&y=17.
67. Chew KL, Tay MKL, Cheng B, Lin RTP, Octavia S, Teo JWP. Aztreonam-avibactam combination restores susceptibility of aztreonam in dual-carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018;62:8. doi:10.1128/AAC.00414-18
68. Alm RA, Johnstone MR, Lahiri SD. Characterization of Escherichia coli NDM isolates with decreased susceptibility to aztreonam/avibactam: role of a novel insertion in PBP3. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2015;70(5):1420–1428. doi:10.1093/jac/dku568
69. Sadek M, Juhas M, Poirel L, Nordmann P. Genetic features leading to reduced susceptibility to aztreonam-avibactam among metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. doi:10.1128/AAC.01659-20
70. Ma K, Feng Y, McNally A, Zong Z. Struggle to survive: the choir of target alteration, hydrolyzing enzyme, and plasmid expression as a novel Aztreonam-Avibactam resistance mechanism. mSystems. 2020;5:6. doi:10.1128/mSystems.00821-20
71. Niu S, Wei J, Zou C, et al. In vitro selection of aztreonam/avibactam resistance in dual-carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2020;75(3):559–565. doi:10.1093/jac/dkz468
72. Cornely OA, Cisneros JM, Torre-Cisneros J, et al. Pharmacokinetics and safety of aztreonam/avibactam for the treatment of complicated intra-abdominal infections in hospitalized adults: results from the REJUVENATE study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2020;75(3):618–627. doi:10.1093/jac/dkz497
73. Tamma PD, Aitken SL, Bonomo RA. Infectious Diseases Society of America antimicrobial resistant treatment guidance: gram-negative. Bacterial Infections. 2020.
74. Sato T, Yamawaki K. Cefiderocol: discovery, chemistry, and in vivo profiles of a novel siderophore Cephalosporin. Clin Infect Dis. 2019;69(Suppl 7):S538–S543. doi:10.1093/cid/ciz826
75. Ito-Horiyama T, Ishii Y, Ito A, et al. Stability of novel siderophore cephalosporin S-649266 against clinically relevant carbapenemases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016;60(7):4384–4386. doi:10.1128/AAC.03098-15
76. Kohira N, Hackel MA, Ishioka Y, et al. Reduced susceptibility mechanism to cefiderocol, a siderophore cephalosporin, among clinical isolates from a global surveillance programme (SIDERO-WT-2014). J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2020;22:738–741. doi:10.1016/j.jgar.2020.07.009
77. Mushtaq S, Sadouki Z, Vickers A, Livermore DM, Woodford N. In vitro activity of cefiderocol, a siderophore cephalosporin, against multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020;64(12). doi:10.1128/AAC.01582-20
78. Kazmierczak KM, Bradford PA, Stone GG, de Jonge BLM, Sahm DF. In vitro activity of ceftazidime-Avibactam and Aztreonam-Avibactam against OXA-48-carrying enterobacteriaceae isolated as part of the International Network for Optimal Resistance Monitoring (INFORM) Global Surveillance Program from 2012 to 2015. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018;62:12. doi:10.1128/AAC.00592-18
79. Nakamura R, Ito-Horiyama T, Takemura M, et al. In vivo pharmacodynamic study of cefiderocol, a novel parenteral siderophore cephalosporin, in murine thigh and lung infection models. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019;63:9. doi:10.1128/AAC.02031-18
80. Katsube T, Echols R, Wajima T. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles of cefiderocol, a novel siderophore cephalosporin. Clin Infect Dis. 2019;69(Suppl 7):S552–S558. doi:10.1093/cid/ciz828
81. Katsube T, Wajima T, Ishibashi T, Arjona Ferreira JC, Echols R. Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic modeling and simulation of cefiderocol, a parenteral siderophore cephalosporin, for dose adjustment based on renal function. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61:1. doi:10.1128/AAC.01381-16
82. Delgado-Valverde M, Conejo MDC, Serrano L, Fernández-Cuenca F, Pascual Á. Activity of cefiderocol against high-risk clones of multidrug-resistant Enterobacterales, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2020;75(7):1840–1849. doi:10.1093/jac/dkaa117
83. Morris CP, Bergman Y, Tekle T, Fissel J, Tamma PD, Simner PJ. Cefiderocol antimicrobial susceptibility testing against multidrug-resistant gram-negative Bacilli: a comparison of disk diffusion to broth microdilution. J Clin Microbiol. 2020.
84. Albano M, Karau MJ, Schuetz AN, Patel R. Comparison of agar dilution to broth microdilution for testing in vitro activity of cefiderocol against gram-negative bacilli. J Clin Microbiol. 2020. doi:10.1128/JCM.00966-20
85. Contreras DA, Fitzwater SP, Nanayakkara DD, et al. Coinfections of two strains of NDM-1- and OXA-232-coproducing Klebsiella pneumoniae in a kidney transplant patient. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020;64:4. doi:10.1128/AAC.00948-19
86. Wunderink RG, Matsunaga Y, Ariyasu M, et al. Cefiderocol versus high-dose, extended-infusion meropenem for the treatment of Gram-negative nosocomial pneumonia (APEKS-NP): a randomised, double-blind, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020.
87. Bassetti M, Echols R, Matsunaga Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of cefiderocol or best available therapy for the treatment of serious infections caused by carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria (CREDIBLE-CR): a randomised, open-label, multicentre, pathogen-focused, descriptive, phase 3 trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30796-9
88. Portsmouth S, van Veenhuyzen D, Echols R, et al. Cefiderocol versus imipenem-cilastatin for the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections caused by Gram-negative uropathogens: a phase 2, randomised, double-blind, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018;18(12):1319–1328. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30554-1
89. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Antimicrobial Drugs Advisory Committee. 2019. Cefiderocol briefing document. NDA 2094445. Shionogi I, Florham Park, NJ.
90. Fetroja (cefiderocol). Package Insert. Shionogi FP, NJ; 2019.
91. CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. CLSI Supplement M100-30.
92. Simner PJ, Patel R. Cefiderocol antimicrobial susceptibility testing considerations: the Achilles Heel of the Trojan Horse? J Clin Microbiol. 2020;59(1):e00951–20. doi:10.1128/JCM.00951-20
93. Asempa TE, Abdelraouf K, Nicolau DP. Metallo-beta-lactamase resistance in Enterobacteriaceae is an artefact of currently utilized antimicrobial susceptibility testing methods. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2020;75(4):997–1005. doi:10.1093/jac/dkz532
94. Roujansky A, de Lastours V, Guérin F, et al. Analysis of paradoxical efficacy of carbapenems against carbapenemase-producing Escherichia coli in a Murine model of lethal peritonitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020;64:8. doi:10.1128/AAC.00853-20
95. Das S, Johnson A, McEntee L, et al. Pharmacodynamics of the Novel Metallo-β-Lactamase inhibitor ANT2681 in combination with meropenem for the treatment of infections caused by NDM-producing enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020;64(11). doi:10.1128/AAC.01076-20.
96. Cheng Z, Shurina BA, Bethel CR, et al. A single salt bridge in VIM-20 increases protein stability and antibiotic resistance under low-zinc conditions. mBio. 2019;10:6. doi:10.1128/mBio.02412-19
97. Principe L, Vecchio G, Sheehan G, et al. Zinc chelators as Carbapenem adjuvants for Metallo-β-lactamase-producing bacteria: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Microb Drug Resist. 2020;26(10):1133–1143. doi:10.1089/mdr.2020.0037
98. Cheminet G, de Lastours V, Poirel L, et al. Dimercaptosuccinic acid in combination with carbapenems against isogenic strains of Escherichia coli producing or not producing a metallo-β-lactamase in vitro and in murine peritonitis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2020;75(12):3593–3600. doi:10.1093/jac/dkaa347
99. Chibabhai V, Nana T, Bosman N, Thomas T, Lowman W. Were all carbapenemases created equal? Treatment of NDM-producing extensively drug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae: a case report and literature review. Infection. 2018;46(1):1–13. doi:10.1007/s15010-017-1070-8
100. Daikos GL, Markogiannakis A. Carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae: (when) might we still consider treating with carbapenems? Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011;17(8):1135–1141. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03553.x
101. Livermore DM, Warner M, Mushtaq S. Activity of MK-7655 combined with imipenem against Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013;68(10):2286–2290. doi:10.1093/jac/dkt178
102. Cross AS, Opal S, Kopecko DJ. Progressive increase in antibiotic resistance of gram-negative bacterial isolates. Walter Reed Hospital, 1976 to 1980: specific analysis of gentamicin, tobramycin, and amikacin resistance. Arch Intern Med. 1983;143(11):2075–2080. doi:10.1001/archinte.1983.00350110053015
103. Ramirez MS, Tolmasky ME. Aminoglycoside modifying enzymes. Drug Resist Updat. 2010;13(6):151–171. doi:10.1016/j.drup.2010.08.003
104. Miro E, Grunbaum F, Gomez L, et al. Characterization of aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes in enterobacteriaceae clinical strains and characterization of the plasmids implicated in their diffusion. Microb Drug Resist. 2013;19(2):94–99. doi:10.1089/mdr.2012.0125
105. Galani I, Nafplioti K, Adamou P, et al. Nationwide epidemiology of carbapenem resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from Greek hospitals, with regards to plazomicin and aminoglycoside resistance. BMC Infect Dis. 2019;19(1):167. doi:10.1186/s12879-019-3801-1
106. Firmo EF, Beltrao EMB, Silva F, et al. Association of blaNDM-1 with blaKPC-2 and aminoglycoside-modifying enzyme genes among Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis and Serratia marcescens clinical isolates in Brazil. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2020;21:255–261. doi:10.1016/j.jgar.2019.08.026
107. Aggen JB, Armstrong ES, Goldblum AA, et al. Synthesis and spectrum of the neoglycoside ACHN-490. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010;54(11):4636–4642. doi:10.1128/AAC.00572-10
108. Castanheira M, Deshpande LM, Woosley LN, Serio AW, Krause KM, Flamm RK. Activity of plazomicin compared with other aminoglycosides against isolates from European and adjacent countries, including Enterobacteriaceae molecularly characterized for aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes and other resistance mechanisms. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2018;73(12):3346–3354. doi:10.1093/jac/dky344
109. Castanheira M, Davis AP, Serio AW, Krause KM, Mendes RE. In vitro activity of Plazomicin against Enterobacteriaceae isolates carrying genes encoding aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes most common in US Census divisions. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019;94(1):73–77. doi:10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2018.10.023
110. Doi Y, Arakawa Y. 16S ribosomal RNA methylation: emerging resistance mechanism against aminoglycosides. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45(1):88–94. doi:10.1086/518605
111. Fleischmann WA, Greenwood-Quaintance KE, Patel R. In vitro activity of plazomicin compared to amikacin, gentamicin, and tobramycin against multidrug-resistant aerobic Gram-Negative Bacilli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020;64:2. doi:10.1128/AAC.01711-19
112. Lutgring JD, Balbuena R, Reese N, et al. Antibiotic susceptibility of NDM-producing enterobacterales collected in the United States in 2017 and 2018. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020;64:9. doi:10.1128/AAC.00499-20
113. Clark JA, Kulengowski B, Burgess DS. In vitro activity of plazomicin compared to other clinically relevant aminoglycosides in carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020;98(2):115117. doi:10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2020.115117
114. Bhavnani SM, Onufrak NJ, Hammel JP, et al. Re-Appraisal of Aminoglycoside (AG) susceptibility testing breakpoints based on the application of Pharmacokinetics–Pharmacodynamics (PK-PD) and contemporary microbiology surveillance data. Open Forum Infectious Dis. 2018;5(suppl_1). doi:10.1093/ofid/ofy209.170.
115. Serio AW, Keepers T, Krause KM. Plazomicin is active against metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2019;6(4):ofz123. doi:10.1093/ofid/ofz123
116. Sou T, Hansen J, Liepinsh E, et al. Model-informed drug development for antimicrobials: translational PK and PK/PD modeling to predict an efficacious human dose for Apramycin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2020. doi:10.1002/cpt.2104
117. Hao M, Shi X, Lv J, et al. In vitro activity of apramycin against Carbapenem-resistant and Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates. Front Microbiol. 2020;11:425. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.00425
118. Rodriguez-Avial I, Pena I, Picazo JJ, Rodriguez-Avial C, Culebras E. In vitro activity of the next-generation aminoglycoside plazomicin alone and in combination with colistin, meropenem, fosfomycin or tigecycline against carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae strains. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2015;46(6):616–621. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2015.07.021
119. McKinnell JA, Dwyer JP, Talbot GH, et al. Plazomicin for infections caused by carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(8):791–793. doi:10.1056/NEJMc1807634
120. Grossman TH. Tetracycline antibiotics and resistance. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2016;6(4):a025387. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a025387
121. Li X, Mu X, Yang Y, et al. Rapid emergence of high-level tigecycline resistance in Escherichia coli strains harbouring blaNDM-5 in vivo. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2016;47(4):324–327. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2016.01.005
122. Sun J, Chen C, Cui CY, et al. Plasmid-encoded tet(X) genes that confer high-level tigecycline resistance in Escherichia coli. Nat Microbiol. 2019;4(9):1457–1464. doi:10.1038/s41564-019-0496-4
123. Livermore DM, Mushtaq S, Warner M, Woodford N. In vitro activity of eravacycline against Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae and Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016;60(6):3840–3844. doi:10.1128/AAC.00436-16
124. Johnston BD, Thuras P, Porter SB, et al. Activity of Cefiderocol, Ceftazidime-Avibactam, and Eravacycline against Carbapenem-Resistant Escherichia coli Isolates from the United States and International Sites in Relation to Clonal Background, Resistance Genes, Coresistance, and Region. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020;64:10.
125. Monogue ML, Abbo LM, Rosa R, et al. In vitro discordance with in vivo activity: humanized exposures of Ceftazidime-Avibactam, Aztreonam, and Tigecycline Alone and in Combination against New Delhi Metallo-beta-Lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Murine Lung Infection Model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61:7. doi:10.1128/AAC.00486-17
126. Balandin Moreno B, Fernandez Simon I, Pintado Garcia V, et al. Tigecycline therapy for infections due to carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in critically ill patients. Scand J Infect Dis. 2014;46(3):175–180. doi:10.3109/00365548.2013.861608
127. Silver LL. Fosfomycin: mechanism and resistance. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2017;7:2. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a025262
128. Vardakas KZ, Legakis NJ, Triarides N, Falagas ME. Susceptibility of contemporary isolates to fosfomycin: a systematic review of the literature. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2016;47(4):269–285. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2016.02.001
129. Pena I, Picazo JJ, Rodriguez-Avial C, Rodriguez-Avial I. Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in a tertiary hospital in Madrid, Spain: high percentage of colistin resistance among VIM-1-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST11 isolates. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2014;43(5):460–464. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2014.01.021
130. Lepak AJ, Zhao M, VanScoy B, et al. In Vivo Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of ZTI-01 (Fosfomycin for injection) in the Neutropenic Murine Thigh Infection Model against Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61:6.
131. Kaye KS, Rice LB, Dane AL, et al. Fosfomycin for Injection (ZTI-01) versus piperacillin-tazobactam for the treatment of complicated urinary tract infection including acute pyelonephritis: ZEUS, a Phase 2/3 randomized trial. Clin Infect Dis. 2019;69(12):2045–2056. doi:10.1093/cid/ciz181
132. Wenzler E, Ellis-Grosse EJ, Rodvold KA. Pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of single-dose Intravenous (ZTI-01) and oral fosfomycin in healthy volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61:9. doi:10.1128/AAC.00775-17
133. Grabein B, Graninger W, Rodriguez Bano J, Dinh A, Liesenfeld DB. Intravenous fosfomycin-back to the future. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the clinical literature. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2017;23(6):363–372. doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2016.12.005
134. Lim TP, Teo JQ, Goh AW, et al. In vitro pharmacodynamics of Fosfomycin against Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacter cloacae and Klebsiella aerogenes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020;64:9. doi:10.1128/AAC.00536-20
135. Bulman ZP, Zhao M, Satlin MJ, et al. Polymyxin B and fosfomycin thwart KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in the hollow-fibre infection model. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2018;52(1):114–118. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2018.02.010
136. Zhao M, Bulman ZP, Lenhard JR, et al. Pharmacodynamics of colistin and fosfomycin: a ‘treasure trove’ combination combats KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017;72(7):1985–1990. doi:10.1093/jac/dkx070
137. Elliott ZS, Barry KE, Cox HL, et al. The role of fosA in challenges with fosfomycin susceptibility testing of multispecies klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase-producing clinical isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 2019;57:10. doi:10.1128/JCM.00634-19
138. van den Bijllaardt W, Schijffelen MJ, Bosboom RW, et al. Susceptibility of ESBL Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae to fosfomycin in the Netherlands and comparison of several testing methods including Etest, MIC test strip, Vitek2, Phoenix and disc diffusion. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2018;73(9):2380–2387. doi:10.1093/jac/dky214
139. Camarlinghi G, Parisio EM, Antonelli A, et al. Discrepancies in fosfomycin susceptibility testing of KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae with various commercial methods. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019;93(1):74–76. doi:10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2018.07.014
140. Moffatt JH, Harper M, Boyce JD. Mechanisms of polymyxin resistance. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1145:55–71.
141. Bradford PA, Kazmierczak KM, Biedenbach DJ, Wise MG, Hackel M, Sahm DF. Correlation of beta-lactamase production and colistin resistance among Enterobacteriaceae isolates from a global surveillance program. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;60(3):1385–1392. doi:10.1128/AAC.01870-15
142. Kubin CJ, Ellman TM, Phadke V, Haynes LJ, Calfee DP, Yin MT. Incidence and predictors of acute kidney injury associated with intravenous polymyxin B therapy. J Infect. 2012;65(1):80–87. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2012.01.015
143. Shields RK, Nguyen MH, Chen L, et al. Ceftazidime-avibactam is superior to other treatment regimens against Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Bacteremia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61(8):e00883–00817. doi:10.1128/AAC.00883-17
144. Tsuji BT, Pogue JM, Zavascki AP, et al. International Consensus Guidelines for the Optimal Use of the Polymyxins: endorsed by the American College of Clinical Pharmacy (ACCP), European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID), Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), International Society for Anti-infective Pharmacology (ISAP), Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM), and Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists (SIDP). Pharmacotherapy. 2019;39(1):10–39. doi:10.1002/phar.2209
145. Bulman ZP, Chen L, Walsh TJ, et al. Polymyxin combinations combat Escherichia coli harboring mcr-1 and blaNDM-5: preparation for a Postantibiotic Era. mBio. 2017;8(4):e00540–00517. doi:10.1128/mBio.00540-17
146. Tangden T, Hickman RA, Forsberg P, Lagerback P, Giske CG, Cars O. Evaluation of double- and triple-antibiotic combinations for VIM- and NDM-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae by in vitro time-kill experiments. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58(3):1757–1762. doi:10.1128/AAC.00741-13
147. Castanheira M, Deshpande LM, Mendes RE, Canton R, Sader HS, Jones RN. Variations in the occurrence of resistance phenotypes and carbapenemase genes among enterobacteriaceae isolates in 20 Years of the SENTRY Antimicrobial surveillance program. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2019;6(Suppl 1):S23–S33. doi:10.1093/ofid/ofy347
148. Wang X, Zhao C, Wang Q, et al. In vitro activity of the novel beta-lactamase inhibitor taniborbactam (VNRX-5133), in combination with cefepime or meropenem, against MDR Gram-negative bacterial isolates from China. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2020;75(7):1850–1858. doi:10.1093/jac/dkaa053
149. Hamrick JC, Docquier JD, Uehara T, et al. VNRX-5133 (Taniborbactam), a broad-spectrum inhibitor of serine- and metallo-beta-lactamases, restores activity of cefepime in enterobacterales and pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020;64:3. doi:10.1128/AAC.01963-19
150. Blais J, Lopez S, Li C, et al. In vitro activity of LYS228, a novel monobactam antibiotic, against multidrug-resistant enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018;62:10. doi:10.1128/AAC.00552-18
151. Dean CR, Barkan DT, Bermingham A, et al. Mode of action of the monobactam LYS228 and mechanisms decreasing in vitro susceptibility in escherichia coli and klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018;62:10. doi:10.1128/AAC.01200-18
152. Lomovskaya O, Tsivkovski R, Nelson K, et al. Spectrum of Beta-lactamase inhibition by the cyclic boronate QPX7728, an ultrabroad-spectrum beta-lactamase inhibitor of serine and metallo-beta-lactamases: enhancement of activity of multiple antibiotics against isogenic strains expressing single beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020;64:6.
153. Zhang B, Zhu Z, Jia W, et al. In vitro activity of aztreonam-avibactam against metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae – a multicenter study in China. Int J Infect Dis. 2020;97:11–18. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.05.075
154. Kohira N, West J, Ito A, et al. In vitro antimicrobial activity of a siderophore cephalosporin, S-649266, against Enterobacteriaceae clinical isolates, including carbapenem-resistant strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016;60(2):729–734. doi:10.1128/AAC.01695-15
155. Kazmierczak KM, Tsuji M, Wise MG, et al. In vitro activity of cefiderocol, a siderophore cephalosporin, against a recent collection of clinically relevant carbapenem-non-susceptible Gram-negative bacilli, including serine carbapenemase- and metallo-beta-lactamase-producing isolates (SIDERO-WT-2014 Study). Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2019;53(2):177–184. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2018.10.007
156. Sonnevend Á, Ghazawi A, Darwish D, et al. In vitro efficacy of ceftazidime-avibactam, aztreonam-avibactam and other rescue antibiotics against carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales from the Arabian Peninsula. Int J Infect Dis. 2020;99:253–259. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.07.050
157. Livermore DM, Warner M, Mushtaq S, Doumith M, Zhang J, Woodford N. What remains against carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae? Evaluation of chloramphenicol, ciprofloxacin, colistin, fosfomycin, minocycline, nitrofurantoin, temocillin and tigecycline. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2011;37(5):415–419. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2011.01.012
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
