Back to Journals » Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management » Volume 11
The role of delamanid in the treatment of drug-resistant tuberculosis
Received 7 February 2015
Accepted for publication 31 March 2015
Published 13 May 2015 Volume 2015:11 Pages 779—791
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S71076
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Professor Garry Walsh
Joseph M Lewis,1 Derek J Sloan2,3
1Tropical and Infectious Disease Unit, Royal Liverpool University Hospital, Liverpool, UK; 2Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine, Pembroke Place, Liverpool, UK; 3Liverpool Heart and Chest Hospital, Liverpool, UK
Abstract: Tuberculosis (TB) remains a significant cause of death worldwide, and emergence of drug-resistant TB requires lengthy treatments with toxic drugs that are less effective than their first-line equivalents. New treatments are urgently needed. Delamanid, previously OPC-67863, is a novel drug of the dihydro-nitroimidazole class with potent anti-TB activity and great promise to be effective in the treatment of drug-resistant TB. This review examines the preclinical and clinical development of delamanid, reviews current guidance on its use and evaluates the opportunities and challenges for its future role in TB management.
Keywords: delamanid, OPC-67683, tuberculosis, drug resistance, MDR-TB
Introduction
Tuberculosis (TB) remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. In 2013, an estimated 9 million people developed TB, with 1.5 million deaths; this is second only to the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) as the leading infectious cause of death worldwide.1 The HIV epidemic continues to drive large numbers of new TB cases, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa.2 Combined HIV-TB management remains an important therapeutic challenge.
Effective 6-month combination treatment for TB using four first-line drugs (rifampicin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol) has been available since the 1980s.3 However, the magnitude of the global TB burden, particularly in low- and middle-income countries, continues to thwart effective disease control. Antibiotic resistance to Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) was identified in the 1940s4 and has expanded into a daunting clinical problem. Multidrug-resistant (MDR) TB is defined by resistance to both rifampicin and isoniazid. Although second-line drug regimens may be curative, treatment takes up to 2 years and medications are toxic and difficult to access.5 In 2013, 480,000 patients were diagnosed with MDR-TB but only 97,000 patients initiated therapy.1 MDR-TB treatment success rates are often <50%. Since 2006, extensively drug-resistant (XDR) TB, with additional resistance to injectable aminoglycosides and fluoroquinolones, has been described, with treatment success rates as low as 16%–22%.6–8 Since 2009, even more comprehensively resistant Mtb strains have been reported,9–12 generating fears that without new drugs, untreatable TB may reemerge in the 21st century.
The desired characteristics for new MDR-TB drugs and regimens have been clearly outlined; injectable agents should be replaced by all-oral regimens, therapy must be shorter, toxicity must be less, and drug-drug interactions (particularly with antiretroviral therapy [ART] for HIV) should be minimized.13,14
After a prolonged hiatus in the 1980s and 1990s, the last decade has seen the emergence of several new compounds from the drug development pipeline. In 2012, the diarylquinoline ATP-synthase inhibitor, bedaquiline, was the first new anti-TB agent to be licensed since rifampicin in 1967.15 Two members of the dihydro-nitroimidazole class (delamanid [formerly OPC-67863] and pretomanid [formerly PA-824]) are also undergoing advanced clinical assessment. Delamanid has already been approved by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the Japanese Ministry of Health, Welfare and Labor (MHWL) for the treatment of MDR-TB.16 This article describes the preclinical and clinical development of delamanid, reviews current guidance on its use, and evaluates the opportunities and challenges for its future role in TB management.
Preclinical data
The best known drug from the nitroimidazole class is metronidazole, which is widely used for the treatment of anaerobic and protozoan infections but has potency against Mtb. In 1989, a related compound, the bicyclic nitroimidazole CGI-17341, was found to possess more favorable in vitro and in vivo antimycobacterial activity. However, it could not be developed further because of mutagenic properties.17,18 Two different research groups later developed the related compounds PA-824 and OPC-67683 that were potent, orally bioavailable, and promising candidates for the treatment of TB. OPC-67683 was developed by Otsuka Pharmaceuticals and progressed to become delamanid. Table 1 summarizes the published preclinical studies for this compound.
Mechanism of action
Delamanid is thought to primarily inhibit synthesis of methoxy-mycolic and keto-mycolic acid, which are components of the mycobacterial cell wall; unlike isoniazid, the drug does not inhibit alpha-mycolic acid.19,20 It has no action against gram-negative or gram-positive bacteria,16 and this may be clinically advantageous as its restriction of use to mycobacterial infection may help prevent the generation of resistance. Like pretomanid, delamanid is a prodrug that requires metabolic activation for anti-TB activity to be exerted. Reactive intermediates in the metabolic pathway of the bicyclic nitroimidazoles may provide additional mechanisms of action, including interruption of cellular respiration.19,21 Activation of delamanid is thought to be mediated via the mycobacterial F420 coenzyme system.20,22
Antimycobacterial potency
Delamanid has potent in vitro activity against both standardized and clinical Mtb isolates, with no cross-resistance to rifampicin, isoniazid, ethambutol, or streptomycin, and no antagonistic activity to these drugs.19,23,24 The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) of delamanid ranges from 0.006 to 0.024 g/mL.19 Mtb may evade drug pressure by adopting intracellular sanctuary within macrophages. Delamanid’s intracellular bactericidal activity is similar to that of rifampicin.19 Among nontuberculous mycobacteria, delamanid has in vitro activity against M. kansasii and M. bovis but not M. avium, M. chelonae, M. abscessus, or M. fortuitum.19,25
In murine models of chronic TB, delamanid demonstrated a dose-dependent reduction in M. tuberculosis colony counts; it was equally effective in immunocompromised (nude BALB/c) mice, versus an inactive control. Drug doses associated with 95% reduction in colony-forming units (CFU) were 0.625 mg/kg for delamanid, 3.5 mg/kg for rifampicin, 5 mg/kg for isoniazid, 160 mg/kg for ethambutol, and 40 mg/kg for streptomycin.19 To assess the activity of delamanid in combination with standard antituberculous agents, a 6-month a regimen of delamanid, rifampicin, and isoniazid was compared with standard quadruple therapy (rifampicin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol) in a mouse model. After 6 months, 0/6 mice in the delamanid group had detectable M. tuberculosis colonies, versus 4/5 in the standard treatment group.19
Pharmacokinetic considerations
Mechanisms of interindividual pharmacokinetic variability and drug-drug interactions for anti-TB compounds include induction or inhibition of metabolism via hepatic cytochrome p450 enzymes, or transportation of drugs via P-glycoprotein (P-gp), an important efflux pump that can influence intracellular pharmacokinetics by transporting foreign substances out of cells. In preclinical studies, delamanid is highly (>97%) protein bound and its metabolism is mediated primarily by plasma albumin. The hepatic enzymes CYP3A4, CYP1A1, CYP2D6, and CYP2E1 may be implicated to a lesser extent.20 In animal models (dog, rat, mouse) it has an oral bioavailability of 35%–60%.26,27
The effect of delamanid on human cytochrome p450 enzymes has been studied in vitro with fresh human hepatocytes and human liver microsomes. At concentrations less than 100 μmol/L (thought to be higher than that attainable in human liver), there was no effect of delamanid on CYP1A1/2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C8/9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, and CYP3A4.19 Similarly, in a separate study, four delamanid metabolites had no effect on these CYP enzymes at in vitro concentrations believed to be higher than that attainable in human liver.28
There are no peer-reviewed published data on the potential for pharmacokinetic drug interactions at the level of P-gp. However, the EMA assessment of delamanid reports that, in vitro, delamanid at 5 μM is neither a substrate nor an inhibitor for P-gp mediated transport. However, this concentration is significantly lower than the estimated concentration of 74.8 μM in the intestinal lumen. Further post-authorization scrutiny of these studies is planned.20
Toxicity, mutagenicity, and teratogenicity
In animal studies, no toxic effects of delamanid on the central nervous or respiratory systems were found at concentrations 18.5- or 3.2-fold higher than the maximum serum concentrations expected in humans at a dose of 100 mg BD.20 Cardiac arrhythmias are of particular concern with second-line MDR-TB treatment as several key agents, including the fluoroquinolones (eg, moxifloxacin), clofazimine, and bedaquiline have ECG QTc-prolonging effects,29 raising concern about whether they can be coadministered. A degree of cardiac potassium channel (hERG channel) inhibition by delamanid was noted in vitro. In a canine model, there was no effect on ECG QTc interval in vivo after a single-dose but QTc interval prolongation was noted with repeated dosing.20 It is postulated that plasma metabolites of delamanid, in particular the human metabolite DM-6705, may be primarily responsible for prolongation of QTc. This hypothesis is supported by the in vitro effect of DM-6705 and other delamanid metabolites on HEK-293 and CHO-K1 cells that express hERG channels.20
Similarly, hepatotoxicity is a significant concern with TB treatment as three of the four first-line agents (rifampicin, isoniazid and pyrazinamide) show significant hepatotoxicity. There are no published preclinical data on the effect of delamanid on the liver – deleterious or otherwise – though there is a suggestion from clinical data that delamanid may rarely have the potential for hepatotoxicity (see Adverse events and toxicity in Clinical data section). In mouse, rabbit, and rat models, delamanid has been shown to reduce the levels of clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X by inhibiting vitamin K1 production, and increase prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT).20
Older bicyclic nitroimidazoles with antimycobacterial activity, including CGI-17341, were not further developed because of concerns about mutagenicity. Delamanid has been shown to have low rates of mutagenicity in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli bacteria by bacterial reverse mutation (BRM) testing;19 similarly, in animal models (mouse and rat), the administration of delamanid up to 104 weeks was not carcinogenic.20
Animal data suggests that delamanid administration has the potential to be teratogenic; delamanid metabolites in rat models produced fetal abnormalities, though only exposure to the drug at levels that were higher than would be expected clinically. Delamanid is also excreted in breast milk; in the rat, peak levels of delamanid in breast milk (Cmax) were fourfold higher than in the blood.20
Drug resistance
Like PA-824, delamanid is thought to require activation by mycobacterial F420-dependent deazaflavin-dependent nitroreductase (Ddn) coenzymes. Mutation in one of five coenzyme F420 genes, fgd, Rv3547 fbiA, fbiB, and fbiC has been proposed as the mechanism of resistance of delamanid.20,30 The in vitro spontaneous frequency of mutations conveying resistance to delamanid in one study was high and similar to that in isoniazid and pretomanid; rifampicin and moxifloxacin had lower rates.20 This suggests that delamanid monotherapy would rapidly result in resistance, though this is an area where published data are lacking and ongoing evaluation of the genetic barrier to resistance of delamanid is necessary. There is not thought to be cross-resistance between delamanid and other antituberculous agents.19
Clinical data
With favorable in vitro characteristics, delamanid progressed to clinical studies; Table 2 summarizes the published data from these studies, comprising Phase I pharmacokinetic and drug interaction studies, followed by Phase II clinical efficacy studies. The majority of Phase I data have not been published in peer-reviewed journals but are available in the EMA authorization report. The published trials were all carried out in accordance with the principles laid out in the declarations of Helsinki and national and local ethical guidelines.
Pharmacokinetics
Interindividual variability in the plasma concentrations of current first-line anti-TB drugs attained after standard weight-adjusted dosing is well described, and postulated to be responsible for some cases of treatment failure or generation of drug resistance.31,32 Debate about optimal dosing strategies in multidrug combinations are ongoing. Clinical information about the pharmacokinetic profile of new agents including delamanid is important.
The absolute oral bioavailability of delamanid has not been determined, but is thought to be 25%–47%.20 During dose escalation studies, administration of higher oral doses was associated with a less than proportional increase in plasma exposure.20,33 In contrast to some first-line anti-TB drugs (particularly rifampicin), delamanid exposure is increased by food, in particular by a high-fat meal. Exposure is approximately three times greater in a fed as opposed to fasted state.20,34 Differing absorption profiles between drugs may complicate coadministration in combination regimens. Delamanid is extremely (>99%) protein bound with a large apparent volume of distribution.20,34
Biotransformation and elimination
As stated above, delamanid is thought to be a prodrug that requires activation by mycobacterial F420-dependent Ddn coenzymes. Delamanid is eliminated directly from plasma with a half-life of 30–38 hours. It is not excreted in the urine.34 It is thought to be metabolized largely by plasma albumin; the full metabolic profile of delamanid has not been elucidated but the drug is thought to be largely converted to its primary metabolite, DM-6705 when amino groups in serum albumin react with the drug. DM-6705 is then broken down by hydrolysis and CYP3A4 to a number of other metabolites.20,34 Concentrations of these metabolites increase to steady-state over 6–10 weeks;34 they are thought to have poor anti-TB activity,20 but some metabolites may be primarily responsible for delamanid-associated toxicity. DM-6705, for example, is thought to be largely responsible for QTc prolongation. However, the full metabolic pathway of delamanid remains unknown.
Special populations
Hepatotoxicity is the most serious complication of current first-line anti-TB therapy, and the safety of new or alternative anti-TB drugs in patients with impaired liver function is an important clinical consideration.35 There are few data on the use of delamanid in patients with hepatic dysfunction and EMA advice is to avoid delamanid in patients with moderate to severe hepatic impairment. There is also a lack of data on the use of those over 65, in pediatric populations, and in HIV-infected individuals.20,34 This information will be important to establish the potential role of delamanid in vulnerable populations who run into difficulty with existing treatment options.
Dose adjustment for anti-TB drugs in renal impairment is also difficult and some second-line anti-TB drugs (particularly the injectable aminoglycosides) are associated with nephrotoxicity.36 Mild renal impairment (creatinine clearance 50–80 mL/min) is not thought to affect exposure to delamanid, and no dose adjustment is deemed necessary in mild-to-moderate renal impairment. It is not known if peritoneal or hemodialysis removes delamanid from plasma.20,34
There are no data on the use of delamanid in pregnant women, and it is unknown if delamanid is excreted in human breast milk. The use of delamanid in pregnant or breastfeeding women is therefore not recommended in the European license of delamanid.34
Potential for drug-drug interactions
The need for fewer drug-drug interactions has been noted as a desirable feature of new anti-TB agents. Table 3 shows available pharmacokinetic data from drug-drug interaction studies with delamanid. There is a clear interaction with the strong CYP3A4 inducer rifampicin, which reduced the exposure to delamanid by 47% in healthy volunteers.20 There are no data with other strong enzyme inducers but this interaction would be expected to be similar, leading the EMA to recommend that coadministration of delamanid with strong CYP3A4 enzyme inducers is contraindicated.34 This means that delamanid will only be suitable for future first-line regimens if rifampicin can be omitted. Given the established importance of rifampicin to prevent relapse in 6-month anti-TB treatment, this is unlikely to be achieved in the near future; hence, the key initial role of delamanid is likely to remain in the management of MDR-TB.
  | Table 3 Pharmacokinetic data on drug-drug interactions of delamanid |
Drug-drug interactions with ART are important when considering the role of delamanid for HIV-infected patients. In this regard, there was a modest increase in exposure to delamanid and its metabolites when coadministered with the protease inhibitor lopinavir/ritonavir in healthy volunteer studies.20,37,38 This has potential implications for increased toxicity (in particular QTc prolongation); see Adverse events and toxicity section.
Effectiveness in the treatment of MDR-TB
Definitive trials to ascertain the clinical efficacy of new anti-TB treatments are protracted and expensive because of the long duration of therapy and the need to incorporate posttreatment relapse rates into study endpoints.39 As MDR-TB treatment continues for up to 2 years, the problem is greatest with this form of the disease, and is compounded by inadequate surrogate markers to predict final outcome from shorter initial assessments.40 Furthermore, it is difficult to determine the effect of individual drugs during multidrug therapy. The standard approach is to begin by measuring the rate of decline in the bacterial load in sputum when single agents are administered for 7–14 days in Phase IIa studies (sometimes referred to as early bactericidal activity [EBA] studies). Preferred drug combinations are constructed for Phase IIb studies based on sputum culture conversion rates over a period of 8 weeks.41 Only regimens that perform well in Phase IIb studies should progress to Phase III clinical trials. Phase IIa and IIb data are available for delamanid but no Phase III studies have yet been reported.
The key Phase IIa study for delamanid was Trial 101 that evaluated four dosages of delamanid, administered orally for 14 consecutive days. It recruited 54 smear-positive pulmonary TB patients aged 18–64 at three centers in South Africa, and randomized them to a dose of 100 mg, 200 mg, 300 mg, or 400 mg of delamanid once daily, or standard quadruple therapy (rifampicin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, ethambutol); the primary outcome was the fall in log10 CFU of Mtb per mL of sputum per day. Exclusion criteria were: serious underlying medical conditions, electrocardiogram (ECG) abnormalities, HIV-infection with a CD4 count ≤350 cells/μL or use of ART, and patients with TB resistant to rifampicin on molecular testing.33
There was no statistically significant difference in the primary outcome between the four delamanid doses. The mean EBA across all delamanid groups was 0.04 log10 CFU/mL/day, similar to previous values for rifabutin,42 streptomycin,43 and amikacin,44 higher than pyrazinamide45 but lower than quinolones, isoniazid, ethambutol, linezolid, and rifampicin.46–48
Phase IIb data on the efficacy of delamanid comes from three related studies on the same cohort of MDR-TB patients: Trial 204, Trial 208, and Observational Study 116. Details of these will be described in sequence but the chronological flow and relationships between them are shown in Figure 1.
  | Figure 1 Summary of the design and results of Phase IIb and observational studies of delamanid therapy. |
Trial 204 provides the most robust data. It was a double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter, multinational trial to assess the effect of delamanid on sputum culture conversion at 2 months in patients with pulmonary MDR-TB, alongside a World Health Organization (WHO)-recommended MDR-TB background treatment regimen. It took place at 17 centers in nine countries: the Philippines, Peru, Latvia, Estonia, People’s Republic of China, Japan, Korea, Egypt, and the United States.49,50
Participants were aged 18–64 with sputum culture-positive MDR-TB and chest radiographic findings consistent with TB. Exclusion criteria included HIV-infection with a CD4 cell count ≤350 cells/μL or use of ART, ECG abnormalities, and co-therapy with antiarrhythmic agents or moxifloxacin. Patients were randomized to delamanid 100 mg or 200 mg twice daily or placebo, administered alongside an optimized background regimen (OBR) selected in accordance with WHO guidelines. The primary outcome was the proportion of patients with sputum culture conversion in Mycobacterial Growth Indicator Tube (MGIT) liquid broth media at 2 months. Secondary outcome measures included proportion of patients with sputum culture conversion on Lowenstein–Jensen (LJ) solid media and time to culture conversion on both media.49
A total of 611 patients were assessed for eligibility; 481 were randomized into the study. A large proportion (>90%) had received more than 30 days of TB therapy and almost 40% had received second- or third-line drugs. The median age was 35, and 68% were men and 54% were from Asia. HIV positive patients were poorly represented; only four HIV positive people were enrolled.49
Table 4 shows that there was significantly higher sputum culture conversion in both delamanid groups compared to the group receiving placebo, and time to sputum culture conversion was shorter in both groups receiving delamanid than in the group receiving placebo. These findings were consistent in both liquid and solid media.
  | Table 4 Primary and secondary outcomes of Trial 204 |
Trial 208 was an open-label extension to Trial 204, conducted at 14 of the 17 study sites. All Trial 204 participants were eligible to receive open-label delamanid 100 mg or 200 mg twice daily. The choice of dosage rested with the treating physician, who remained blind to treatment allocation from Trial 204. There was a variable delay between completion of Trial 204 and commencement of Trial 208, dependent on local regulatory and ethics approval for Trial 208 at each site. This gap varied from 4 weeks to greater than 4 months, but was greater than 4 months for a third of participants.51 Background MDR-TB treatment was continued during this time.
Observational Study 116 was conducted at all 17 sites participating in Trial 204; and patients were followed up for 2 years to assess final outcome. Data are available for 421 of the original 481 patients. Of these patients, 13.3% (56/421) had XDR-TB, and this subgroup is particularly interesting given the dearth of alternative treatment options for such patients. Participants in study 116 had received delamanid at a variable dose (100 mg or 200 mg or a combination of the two) for a variable length of time (between 0 and 8 months); some of this treatment was blinded, and some unblinded.51
Results of Trial 208 and Study 116 were published collectively.51 Patients who had been treated with either 8 months (n=126) or 6 months (n=66) of delamanid were combined into a “long-term” treatment group. Patients who had received either 2 months (n=156) or 0 months (n=73) of delamanid were combined into a “short-term” treatment group. The treatment outcomes for the two groups, defined as favorable (cured or completed treatment) or unfavorable (died, failed treatment, defaulted from treatment), are shown in Figure 2.
  | Figure 2 Long-term outcome data on delamanid use from Trial 208 and Observational Study 116. |
Among all MDR-TB and XDR-TB patients, there were more favorable outcomes in the “long-term” compared to the “short-term” delamanid treatment group (74.5% [143/192] vs 55.0% [116/229], P<0.001). There were also fewer deaths in the “long-term” group (1.0% [2/192] vs 8.3% [19/229], P<0.001).51 In the XDR-TB subgroup analysis, there was a significant difference in mortality between the “short-term” and “long-term” groups for mortality (0% [0/44] vs 25.0% [3/12], P<0.001).51
Adverse events and toxicity
In Trial 101, there were no serious adverse events and no patient discontinued the study drug due to toxicity. Minor QTc prolongation was thought to be related to delamanid in one patient; a detailed breakdown of adverse events is not presented in the published data.33
In Trial 204, over 90% of patients across all three treatment arms (delamanid 100 mg, delamanid 200 mg, or placebo) experienced an adverse event, as shown in Table 5. Only the rates of QTc prolongation differed statistically significantly between the three groups in pairwise comparisons; 4% of patients in the placebo group experienced QTc prolongation compared to 10% in the low-dose delamanid group, and 13% in the higher-dose delamanid group (P<0.004 for evaluation of the dose–response trend).49
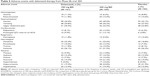  | Table 5 Adverse events with delamanid therapy from Phase IIb trial 204 |
Patients with QTc prolongation in Trial 204 experienced a progressive increase from day 1–56. All QTc prolongations greater than 60 ms were associated with concomitant fluoroquinolone use,20 illustrating the potential hazard of overlapping toxicities in multidrug therapy. No cases of prolonged QTc interval resulted in syncope or arrhythmia and no patient stopped delamanid due to QTc prolongation. Reassuringly, this suggests that few ECG abnormalities are likely to result in clinical consequences, but ongoing vigilance is clearly required.
Because delamanid metabolism involves serum albumin, administration of delamanid in the presence of hypoalbuminemia has been associated with an increased risk of QTc prolongation. Similarly, as the delamanid metabolite DM-6705 is metabolized by CYP3A4, CYP3A4 inhibitors may exacerbate prolongation of the QTc interval.34
The number of patients discontinuing Trial 204 because of adverse effects was low and evenly distributed across the three treatment groups; 4/161 (2.5%) for delamanid 100 mg BD (two due to psychiatric side effects, one due to dermatologic side effects, and one due to thrombocytopenia); 6/160 (3.8%) for delamanid 200 mg BD (one due to leukopenia, three due to psychiatric side effects, one due to respiratory failure, and one due to dermatologic side effects), and 4/160 (2.5%) for placebo, all due to dermatologic side effects.49
There were low rates of hepatotoxicity across all groups in Trial 204; 5/160 (3.1%) of patients in the placebo group, 4/161 (3.1%) in the delamanid 100 mg BD group and 5/160 (3.1%) reported a hepatobiliary disorder, and none stopped the trial.
Adverse events in Trial 208 have not been presented, but the EMA authorization report contains some details. There was only one death in Trial 208, of a 25-year old man taking delamanid 100 mg BD who developed drug-induced liver injury and right-sided cardiac failure on the 9th day of the trial thought to be possibly related to delamanid. His liver injury resolved by day 27 upon stopping delamanid but he subsequently experienced respiratory failure and died on day 72.20 This lack of robust long-term toxicity data makes it difficult to comment on the long-term safety of delamanid; certainly data from Trial 204 and the favorable outcomes in Study 116 are reassuring, but Phase III data are awaited (see Forthcoming trials).
Forthcoming trials
While the accumulative Phase II and observational data are encouraging, Phase III data will be required before definitive guidance on delamanid use is provided. A multicenter, double-blind Phase III placebo-controlled trial to assess the efficacy of 6 months of delamanid in addition to a background regimen for the treatment of MDR-TB is underway (NCT01424670).52 The trial protocol includes a subgroup of patients with HIV-infection, and results are expected in 2017.
Trials are also underway in a pediatric population; a Phase I open-label trial to assess the pharmacokinetics of delamanid over 10 days in children (NCT01856634)53 and a Phase II 6-month safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetic trial of delamanid in children with MDR-TB (NCT01859923).54 The inclusion criteria for the Phase II trial allows for the inclusion of children with “probable TB,” which may better reflect the reality of clinical practice than results from studies including only bacteriologically confirmed disease.
The United States AIDS clinical trial group (ACTG) is planning a trial of the safety and efficacy of coadministration of bedaquiline and delamanid (ACTG A5343).
The place of delamanid in MDR-TB treatment
Two key questions dominate attempts to synthesize the available data on delamanid into a critique of its place in TB treatment: is there enough information to currently recommend clinical prescription of this agent, and, if so, how should it be combined with other drugs for specific patient groups.
Assessment of when to license a new anti-TB drug is shaped by the tension between allowing sufficient time for thorough evaluation and providing potentially curative therapy to drug-resistant patients facing a poor prognosis with few other options. As with bedaquiline, the strength of Phase II and observational data has provisionally satisfied some regulators and, by January 2015, delamanid 100 mg BD had been cautiously approved for the treatment of MDR-TB by the EMA and Japanese MHWL.16 In 2014, the WHO also published interim guidance on delamanid for the treatment of drug-resistant TB.55
However, deficiencies in the available evidence must not be ignored. Although Trial 204 was well conducted, it was based on 2-month sputum culture conversion, which is at best an imperfect surrogate of long-term outcome56,57 and care is required when extrapolating from early microbiological response to final clinical endpoints. This issue was recently illustrated by reports of inferiority to standard treatment of shortened quinolone-based regimens (REMoxTB,58 OFLATUB,59 and RIFAQUIN60) in the management of drug-sensitive TB, despite promising rates of sputum culture conversion at 2 months.61 The longer-term studies of delamanid (Trial 208 and 116) used pragmatic designs with methodological limitations; doses and durations of administration of the study drug were variable, and there was no blinding or randomization. All of these factors may have confounded the analyses that should be interpreted with caution.
For these reasons, current EMA approval is conditional on the manufacturer providing data from the Phase III trials detailed above. The WHO currently classifies delamanid as a Group 5 agent (defined by “limited data on efficacy and/or long-term safety”)62 and at present only endorses its use within strict criteria. These include proper patient inclusion (ie, adults with highly drug-resistant disease including resistance to quinolones or injectables), incorporation of the new drug into recommended regimens,62 close monitoring, active pharmacovigilance, and informed patient consent.55 This WHO conditional recommendation for delamanid’s use is similar to that for bedaquiline; there are some subtle differences in that the WHO recommends that patients with QTc >500 ms should not receive delamanid (a restriction that is not present for bedaquiline) and suggests that the addition of delamanid to a regimen may not be warranted if an appropriate regimen can be constructed from conventional second-line drugs.
The question of how to combine delamanid with other drugs will require new clinical trials, especially as the only ongoing delamanid Phase III trial is designed to assess the efficacy of delamanid alongside a standard background regimen for MDR-TB, rather than in novel combination therapies or alongside novel drugs. There are several other promising anti-TB agents in advanced development, including new compounds, repurposed drugs, and existing agents at nonstandard doses.3 A strategy to shorten MDR-TB therapy by combining seven or more drugs (the “Bangladesh regimen”63) is currently being compared to the conventional WHO approach in the STREAM trial. Although a second Phase of the STREAM trail plans to incorporate 6- or 9-month all-oral regimens including bedaquiline, none of the proposed regimens include delamanid. As more data emerges, the contribution of individual drugs to a widening range of possible combinations needs to be systematically unraveled. Innovative study designs such as multiarm multistage trials may provide tools to rapidly compare multiple treatment regimens.64 Pharmacokinetic data on interactions between delamanid and other novel anti-TB agents are also needed.
In addition to selecting companion drugs, clinicians must decide whether new TB medicines are suitable for use in more complex patient groups. Despite case reports of successful use,65 data to guide the use of delamanid in children are lacking. This reflects a wider lack of trials of therapeutic studies in pediatric TB,66 driven by the difficulty in assessing TB in children.67 Full EMA approval of delamanid is also dependent on the manufacturer providing results of Phase I and II pediatric studies.
A further concern is the lack of data on delamanid in HIV-infected individuals. As Trial 204 only enrolled four individuals with HIV and excluded those on ART, there is no outcome or pharmacokinetic data yet on this specific population that represents a large proportion of TB cases in sub-Saharan Africa. There is also very limited data on drug-drug interactions with ART but preliminary data showing no interactions with tenofovir or efavirenz are reassuring.38
Finally, the place of delamanid in the programmatic management of MDR-TB will be driven by considerations of access and cost. Current licensing of delamanid is restricted to Europe and Japan and no licensing applications are in progress elsewhere, including countries with the highest MDR/XDR-TB burden. In the UK, a 40-tablet pack of 50 mg delamanid tablets costs £1,045.83,68 giving an approximate 6-month cost of £18,000. This can be prohibitively expensive even in settings where a licensing is in place.
Off-license access to delamanid is restricted to compassionate use programs but to date fewer than 20 patients have received the drug via this route, compared to several hundred patients who have received bedaquiline.69 Although bedaquiline is expensive, similar to delamanid in the UK, it has a differential pricing structure for low-income countries, and the manufacturer (Janssen), has recently announced a donation of 30,000 bedaquiline doses to low- and middle-income countries via the United States Agency for International Development (USAID). Innovative approaches to widening access to delamanid are also required to increase clinical knowledge and experience of this drug. This should occur within a careful framework of continuous efficacy and safety monitoring.
Conclusion
Delamanid is a promising agent that fulfills many target criteria for new TB drugs and may be particularly useful for the treatment of MDR-TB. It is administered orally and has bactericidal properties that may make it suitable in regimens designed to shorten treatment duration. Clinical efficacy data, while limited, are reassuring. It is well tolerated and, with the caveat of possible QTc prolongation, seems to have a favorable safety profile compared to existing second-line drugs. Long-term outcome data and greater experience of use in complex populations are required but there are considerable grounds to be optimistic that delamanid represents an important addition to the currently limited management options for drug-resistant TB.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
World Health Organisation. Global Tuberculosis Report 2014. Geneva: World Health Organisation; 2014. | ||
Corbett EL, Watt CJ, Walker N, et al. The growing burden of tuberculosis: global trends and interactions with the HIV epidemic. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163(9):1009–1021. | ||
Sloan DJ, Davies GR, Khoo SH. Recent advances in tuberculosis: new drugs and treatment regimens. Curr Respir Med Rev. 2013;9(3): 200–210. | ||
Streptomycin in Tuberculosis Trials Committee, Committee S in TT. Streptomycin treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis: a medical research council investigation. BMJ. 1948;2:769–782. | ||
Lange C, Abubakar I, Alffenaar JW, et al; TBNET. Management of patients with multidrug-resistant/extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis in Europe: a TBNET consensus statement. Eur Respir J. 2014;44: 23–63. | ||
Pietersen E, Ignatius E, Streicher EM, et al. Long-term outcomes of patients with extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis in South Africa: a cohort study. Lancet. 2014;383(9924):1230–1239. | ||
O’Donnell MR, Padayatchi N, Kvasnovsky C, Werner L, Master I, Horsburgh CR. Treatment outcomes for extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis and HIV co-infection. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;19(3):416–424. | ||
World Health Organisation. Drug-Resistant TB: Surveillance and Response. Supplement Global Tuberculosis Report. Geneva: World Health Organisation; 2014. | ||
Shah NS, Richardson J, Moodley P, et al. Increasing drug resistance in extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis, South Africa. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011;17:510–513. | ||
Udwadia ZF. Totally drug-resistant tuberculosis in India: who let the djinn out? Respirology. 2012;17:741–742. | ||
Velayati AA, Masjedi MR, Farnia P, et al. Emergence of new forms of totally drug-resistant tuberculosis bacilli: super extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis or totally drug-resistant strains in Iran. Chest. 2009;136:420–425. | ||
Migliori GB, De Iaco G, Besozzi G, Centis R, Cirillo DM. First tuberculosis cases in Italy resistant to all tested drugs. Euro Surveill. 2007;12(5):E070517.1. | ||
Ma Z, Lienhardt C, McIlleron H, Nunn AJ, Wang X. Global tuberculosis drug development pipeline: the need and the reality. Lancet. 2010;375:2100–2109. | ||
McIlleron H, Meintjes G, Burman WJ, Maartens G. Complications of antiretroviral therapy in patients with tuberculosis: drug interactions, toxicity, and immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. J Infect Dis. 2007;196(suppl):S63–S75. | ||
Cohen J. Approval of novel TB drug celebrated – with restraint. Science. 2013;339(6116):130. | ||
Ryan NJ, Lo JH. Delamanid: first global approval. Drugs. 2014;74(9): 1041–1045. | ||
Ashtekar DR, Costa-Perira R, Nagrajan K, Vishvanathan N, Bhatt AD, Rittel W. In vitro and in vivo activities of the nitroimidazole CGI 17341 against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993;37(2):183–186. | ||
Nagarajan K. Nitroimidazoles XXI 2,3-dihydro-6-nitroimidazo [2,1-b] oxazoles with antitubercular activity. Eur J Med Chem. 1989;24(6):631–633. | ||
Matsumoto M, Hashizume H, Tomishige T, et al. OPC-67683, a nitro-dihydro-imidazooxazole derivative with promising action against tuberculosis in vitro and in mice. PLoS Med. 2006;3(11):e466. | ||
European Medicines Agency. Assessment Report: Deltyba. London: European Medicines Agency; 2013. | ||
Mukherjee T, Boshoff H. Nitroimidazoles for the treatment of TB: past, present and future. Future Med Chem. 2011;3(11):1427–1454. | ||
Gurumurthy M, Mukherjee T, Dowd CS, et al. Substrate specificity of the deazaflavin-dependent nitroreductase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis responsible for the bioreductive activation of bicyclic nitroimidazoles. FEBS J. 2012;279(1):113–125. | ||
Saliu OY, Crismale C, Schwander SK, Wallis RS. Bactericidal activity of OPC-67683 against drug-tolerant Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007;60(5):994–998. | ||
Sasaki H, Haraguchi Y, Itotani M, et al. Synthesis and antituberculosis activity of a novel series of optically active 6-nitro-2,3-dihydroimidazo[2,1-b]oxazoles. J Med Chem. 2006;49(26):7854–7860. | ||
Doi N, Disratthakit A. Characteristic antimycobacterial spectra of the novel anti-TB drug candidates OPC-67683 and PA-824. Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (ICAAC). San Francisco, CA: 2006. Poster F1-F1377a. | ||
OPC-67683. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2008;88(2):132–133. | ||
Miyomoto G. Unique PK profile of OPC-67683, a new potent anti-tuberculous drug. Intersci Conf Antimicrob Agents Chemother. Washington, DC: 2005. Poster F-1466. | ||
Shimokawa Y, Sasahara K, Yoda N, Mizuno K, Umehara K. Delamanid does not inhibit or induce cytochrome p450 enzymes in vitro. Biol Pharm Bull. 2014;37(11):1727–1735. | ||
Nuermberger EL, Spigelman MK, Yew WW. Current development and future prospects in chemotherapy of tuberculosis. Respirology. 2010;15:764–778. | ||
Singh R, Manjunatha U, Boshoff HI, et al. PA-824 kills nonreplicating Mycobacterium tuberculosis by intracellular NO release. Science. 2008;322(5906):1392–1395. | ||
Chideya S, Winston CA, Peloquin CA, et al. Isoniazid, rifampin, ethambutol, and pyrazinamide pharmacokinetics and treatment outcomes among a predominantly HIV-infected cohort of adults with tuberculosis from Botswana. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;48:1685–1694. | ||
Pasipanodya JG, Srivastava S, Gumbo T. Meta-analysis of clinical studies supports the pharmacokinetic variability hypothesis for acquired drug resistance and failure of antituberculosis therapy. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;55:169–177. | ||
Diacon AH, Dawson R, Hanekom M, et al. Early bactericidal activity of delamanid (OPC-67683) in smear-positive pulmonary tuberculosis patients. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2011;15(7):949–954. | ||
European Medicines Agency. Deltyba: Summary of Product Characteristics. London: European Medicines Agency; 2014. | ||
Senousy BE, Belal SI, Draganov PV. Hepatotoxic effects of therapies for tuberculosis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;7:543–556. | ||
De Jager R, Van Altena R. Hearing loss and nephrotoxicity in long-term aminoglycoside treatment in patients with tuberculosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2002;6:622–627. | ||
Paccaly A, Petersen C, Patil S, et al. Absence of clinically relevant drug interaction between delamanid, a new drug for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) and tenofovir or lopinavir/ritonavir in healthy subjects. 19th International AIDS Conference. Washington, DC: 2012. Abstract No WEPE043. | ||
Petersen C. Delamanid, a new drug for multi-drug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB), and efavirenz do not show clinically relevant drug interactions in healthy subjects. 52nd ICAAC. San Francisco, CA: 2012. Poster abstract A-1255. | ||
Van Niekerk C, Ginsberg A. Assessment of global capacity to conduct tuberculosis drug development trials: do we have what it takes? Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2009;13:1367–1372. | ||
Sloan DJ, Corbett EL, Butterworth AE, et al. Optimizing outpatient serial sputum colony counting for studies of tuberculosis treatment in resource-poor settings. J Clin Microbiol. 2012;50:2315–2320. | ||
Burman WJ. Rip Van Winkle wakes up: development of tuberculosis treatment in the 21st century. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;50(suppl 3):S165–S172. | ||
Chan SL, Yew WW, Ma WK, et al. The early bactericidal activity of rifabutin measured by sputum viable counts in Hong Kong patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. Tuber Lung Dis. 1992;73(1):33–38. | ||
Donald PR, Sirgel FA, Venter A, et al. The early bactericidal activity of streptomycin. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2002;6(8):693–698. | ||
Donald PR, Sirgel FA, Venter A, et al. The early bactericidal activity of amikacin in pulmonary tuberculosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2001;5(6): 533–538. | ||
Botha FJ, Sirgel FA, Parkin DP, van de Wal BW, Donald PR, Mitchison DA. Early bactericidal activity of ethambutol, pyrazinamide and the fixed combination of isoniazid, rifampicin and pyrazinamide (Rifater) in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. S Afr Med J. 1996;86(2):155–158. | ||
Jindani A, Aber VR, Edwards EA, Mitchison DA. The early bactericidal activity of drugs in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980;121(6):939–949. | ||
Johnson JL, Hadad DJ, Boom WH, et al. Early and extended early bactericidal activity of levofloxacin, gatifloxacin and moxifloxacin in pulmonary tuberculosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2006;10(6):605–612. | ||
Dietze R, Hadad DJ, McGee B, et al. Early and extended early bactericidal activity of linezolid in pulmonary tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;178(11):1180–1185. | ||
Gler MT, Skripconoka V, Sanchez-Garavito E, et al. Delamanid for multidrug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(23): 2151–2160. | ||
Zhang Q, Liu Y, Tang S, Sha W, Xiao H. Clinical benefit of delamanid (OPC-67683) in the treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis patients in China. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2013;67(3):957–963. | ||
Skripconoka V, Danilovits M, Pehme L, et al. Delamanid improves outcomes and reduces mortality in multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. Eur Respir J. 2013;41(6):1393–1400. | ||
Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development and Commercialization, Inc. Safety and Efficacy Trial of Delamanid for 6 Months in Patients with Multidrug Resistant Tuberculosis. NLM identifier: NCT01424670. 2011. | ||
Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development and Commercialization, Inc. Pharmacokinetic and Safety Trial to Determine the Appropriate Dose for Pediatric Patients with Multidrug Resistant Tuberculosis. NLM identifier: NCT01856634. 2013. | ||
Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development and Commercialization, Inc. A 6-Month Safety, Efficacy, and Pharmacokinetic Trial of Delamanid in Pediatric Patients with Multidrug Resistant Tuberculosis. NLM identifier: NCT01859923. 2013. | ||
World Health Organisation. The Use of Delamanid in the Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis: Interim Policy Guidance. Geneva: World Health Organisation; 2014. | ||
Mitchison DA. Assessment of new sterilizing drugs for treating pulmonary tuberculosis by culture at 2 months. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993; 147(4):1062–1063. | ||
Davies GR. Early clinical development of anti-tuberculosis drugs: science, statistics and sterilizing activity. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2010; 90(3):171–176. | ||
Gillespie SH, Crook AM, McHugh TD, et al; REMoxTB Consortium. Four-month moxifloxacin-based regimens for drug-sensitive tuberculosis. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(17):140907080012008. | ||
Merle CS, Fielding K, Sow OB, et al; OFLOTUB/Gatifloxacin for Tuberculosis Project. A four-month gatifloxacin-containing regimen for treating tuberculosis. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(17):1588–1598. | ||
Jindani A, Harrison TS, Nunn AJ, et al; RIFAQUIN Trial Team. High-dose rifapentine with moxifloxacin for pulmonary tuberculosis. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(17):1599–1608. | ||
Rustomjee R, Lienhardt C, Kanyok T, et al; Gatifloxacin for TB (OFLOTUB) Study Team. A Phase II study of the sterilising activities of ofloxacin, gatifloxacin and moxifloxacin in pulmonary tuberculosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2008;12(2):128–138. | ||
World Health Organisation. Companion Handbook to the WHO Guidelines for the Programmatic Management of Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis. Geneva: World Health Organisation; 2014. | ||
Aung KJ, Van Deun A, Declercq E, et al. Successful “9-month Bangladesh regimen” for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among over 500 consecutive patients. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2014;18(10):1180–1187. | ||
Phillips PP, Gillespie SH, Boeree M, et al. Innovative trial designs are practical solutions for improving the treatment of tuberculosis. J Infect Dis. 2012;205(suppl):S250–S257. | ||
Esposito S, D’Ambrosio L, Tadolini M, et al. ERS/WHO tuberculosis consilium assistance with extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis management in a child: case study of compassionate delamanid use. Eur Respir J. 2014;44(3):811–815. | ||
Lienhardt C, Raviglione M, Spigelman M, et al. New drugs for the treatment of tuberculosis: needs, challenges, promise, and prospects for the future. J Infect Dis. 2012;205(suppl):S241–S249. | ||
Burman WJ, Cotton MF, Gibb DM, Walker AS, Vernon AA, Donald PR. Ensuring the involvement of children in the evaluation of new tuberculosis treatment regimens. PLoS Med. 2008;5(8):e176. | ||
Joint Formulary Commitee. British National Formulary. 68th ed. London: BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press; 2014. | ||
Gruber K. Access sought to tuberculosis drug from nutraceutical company. Nat Med. 2015;21(2):103. |
 © 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.


