Back to Journals » Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management » Volume 15
Risk of immune-related adverse events associated with ipilimumab-plus-nivolumab and nivolumab therapy in cancer patients
Authors Zhou S, Khanal S, Zhang H
Received 3 November 2018
Accepted for publication 28 December 2018
Published 31 January 2019 Volume 2019:15 Pages 211—221
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S193338
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Deyun Wang
Shi Zhou,* Samrat Khanal,* Haijun Zhang
Department of Oncology, Zhongda Hospital, Medical School of Southeast University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, People’s Republic of China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Purpose: The aim of this study was to evaluate the risk of immune-related adverse events (irAEs) among cancer patients receiving nivolumab-plus-ipilimumab therapy and nivolumab monotherapy.
Patients and methods: PubMed and Web of Science were searched for related studies from inception to June 2018. Eligible studies included randomized controlled trials comparing nivolumab-plus-ipilimumab with nivolumab alone in cancer patients reporting on all-grade (grade 1–4) and high-grade (grade 3/4) irAEs. Paired reviewers selected studies for inclusion and extracted data. The odds risk and 95% CI were calculated.
Results: A total of 2,946 patients from four studies were included in the meta-analysis. The underlying malignancies included lung cancer (two trials) and melanoma (two trials). Compared with nivolumab monotherapy, the nivolumab-plus-ipilimumab therapy was associated with a significantly higher risk of all- and high-grade irAEs such as pruritus, rash, diarrhea, colitis, alanine aminotransferase elevation, and pneumonitis.
Conclusion: The combination therapy of nivolumab and ipilimumab increased the incidence of irAEs in patients with advanced cancer.
Keywords: immune-related adverse events, immune checkpoint inhibitors, nivolumab, ipilimumab, lung cancer, melanoma
Introduction
The recent advancement regarding immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) represents a major breakthrough in the management of cancer.1 Furthermore, immunotherapy has made great progress in cancer treatment recently, besides the advancements in surgery, chemotherapy, molecularly targeted therapy, and radiation. On certain aberrant circumstances, it is understood that T-cell activation plays a significant role in adaptive immunity resulting in autoimmunity.2 Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4), which was represented as the first immune checkpoint receptor, was introduced for the immune-associated targeted therapy. CTLA-4 is recruited on the surface of regulatory T cells and interacts with B7 receptors present on antigen-presenting cells, resulting in the downregulation of any further T-cell activation and immune response expansion.3 The abovementioned mechanism shows the significant role played by CTLA-4 in maintaining normal immunologic homeostasis, which was further proven by the death of mice deficient in CTLA-4 due to fatal lymphoproliferation.4–7 The CTLA-4 inhibitor (ipilimumab) was the first agent to be associated with an obvious improvement in overall survival (OS) in a Phase III study (MDX 010–020) that enrolled 676 patients pretreated for metastatic melanoma.8 As a result, ipilimumab was approved in 2011 for the management of advanced melanoma. Programmed death 1 (PD-1), a well-known immune checkpoint molecule, is expressed on a variety of immune cells.9 PD-1 is an inhibitory receptor expressed on activated lymphocytes and is associated with regulation of immune tolerance and autoimmunity. The ligands of PD1, which can be divided into PD-L1 and PD-L2, have distinct patterns of expression and can be induced, or essentially expressed, on an array of cells including a number of tumor cells.10 Eventually, in December 2014, nivolumab was approved for the management of unresectable melanoma that was unresponsive to other drugs.11
The disordered expression of CTLA-4 and PD-1 is suspected to play an important role in tumor immune evasion and has become an appealing target for intervention in therapy.12 Therefore, application of immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) with anti-CTLA4 and anti-PD1 has gained significant attention in tumor immunology. In patients diagnosed with metastatic melanoma, the combination of ipilimumab and nivolumab showed an enhanced activity relative to either monotherapy, although the median OS was not reached after conducting a follow-up study for a minimum of 2 years. Among advanced stage lung cancer patients, tumor mutational burden or 3 years of OS was strikingly higher among patients receiving combination therapy as compared with nivolumab alone. Now, the combination treatment has been approved in the Europe and the US for patients with melanoma.13,14
Immunotherapy, which involves reactivation of the immune system, has led to the occurrence of new toxicity profiles, also called immune-related adverse events (irAEs), which can be fatal in some cases.15 Most frequently, these irAEs affect a wide range of organs like skin, colon, liver, pituitary, thyroid, and lungs, although uncommon events involving the heart, nervous system, and other organs do occur.16,17 Previous research revealed that ipilimumab could increase the risk of mortality by 130% in cancer patients, with an overall incidence of fatal adverse events of 1.13%.18 The combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab was superior as compared to the single agents alone for the treatment of metastatic melanoma.19,20 However, combined PD-1 plus CTLA-4 blockade substantially triggered more toxic events as compared with anti-PD-1 alone (55%–60% vs 10%–20% high-grade events).21 These irAEs remain a major challenge in clinical care and are significant barriers for developing more effective combination therapies.
Currently, the combination of ipilimumab and nivolumab has been proven to enhance objective response rate and progression-free survival as compared with single agent (monotherapy) among patients with advanced tumor. However, there are no evident studies evaluating the risk of irAEs in nivolumab-plus ipilimumab as compared with nivolumab group alone.22 This meta-analysis was performed to evaluate the incidence of irAEs in patients receiving nivolumab-plus-ipilimumab therapy and nivolumab monotherapy. We expect that the pooled studies would be more helpful in detecting significant association than single study alone.
Patients and methods
This meta-analysis was reported according to the PRISMA statement.23
Search strategy
A literature search was carried out using PubMed and Web of Science to identify clinical study from inception to June 2018. The keywords included CTLA-4, PD-1, nivolumab, ipilimumab, clinical trials, immune checkpoint, and immune-related adverse events. The search was conducted in June 2018. Only those studies published in English were included. The retrieved studies were scrutinized and examined for title and abstracts by two reviewers. Further exploration of full texts was conducted in order to check the studies’ eligibility for inclusion in accordance with the inclusion criteria. The literature search was supplemented with manual searches for references of the included studies and for related citations.
Study selection
We included all published studies comparing the irAEs of nivolumab-plus-ipilimumab to nivolumab in patients with advanced malignancy. Case and animal-based studies were excluded. Any trial with incomplete data was excluded from this meta-analysis. Any disagreements with regard to the protocol were to be resolved by the third author, but none occurred.
Outcome measures
The irAEs that were commonly observed were pruritus, rash, diarrhea, colitis, alanine aminotransferase (ALT) elevation, aspartate aminotransferase elevation, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, hypophysitis, hepatitis, and pneumonitis. The immune-related toxicity estimated by adverse events was categorized into two gradings (grade 1–4 and grade 3/4). The severity of adverse events was graded and evaluated according to the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 5.0.24
Data extraction
Two reviewers (SZ and SK) collected the data independently using a predefined data extraction form. We compiled the following information from each study: 1) year of publication, 2) first author’s name, 3) participant characteristics, 4) therapies and number of groups, and 5) number of adverse effects.
Quality assessment
Studies fulfilling the review inclusion criteria were assessed for methodological quality by two reviewers. The Cochrane Collaboration Tool was used to evaluate the risk of bias in the included studies.25
Statistical methods
The data extracted from the included studies were entered into Review Manager software version 5.3 (http://ims.cochrane.org/revman/download) for statistical analysis. The odds ratio (OR) was applied for comparing dichotomous variables. All the results were reported with 95% CI. For dichotomous data, Mantel–Haenszel method was applied for pooled OR and 95% CI estimation. I2 test was used to assess the impact of study heterogeneity. According to the Cochrane review guidelines, if the heterogeneity (I2) ≤50%, then pooled OR is calculated by the fixed-effect model (Mantel–Haenszel), otherwise the OR is calculated by random-effect model (Der Simonian-Laird). The significance of OR is determined by Z-test.
Results
Search results and patient characteristics
A total of four reports were included in this review. The search provided a total of 1,207 publications at the beginning. Of these, 1,118 studies were discarded after reading the title, abstract, and, if necessary, after reading the manuscript. Eighty-five reports were further excluded after assessing the full text of articles. More detailed information is given in Figure 1.26–29 A total of 2,946 patients (nivolumab:1,589; nivolumab-plus-ipilimumab:1,357) were included in the analysis from the four included studies. The underlying malignancies were lung cancer (two trials) and melanoma (two trials). The baseline characteristics of each study are presented in Table 1.
  | Figure 1 The flow diagram of literature search and selection. |
Immunotherapy-related adverse events
As compared with nivolumab monotherapy, the combined therapy was associated with a significantly higher risk of all- and high-grade irAEs such as pruritus, rash, diarrhea, colitis, ALT elevation, hyperthyroidism, hypophysitis, and pneumonitis. However, there was no statistical difference with regard to the risk of vitiligo (P>0.05). The analysis results are summarized in Table 2.
Meta-analysis of the risk of pruritus and rash
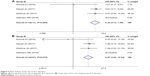
The incidence of pruritus was reported among four studies where patients were divided into nivolumab-plus-ipilimumab group and nivolumab group. The selected studies included cases of melanoma, small-cell lung cancer (SCLC), and non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The pooled ORs of all-grade (grade 1–4) pruritus and high-grade (grade 3/4) pruritus were 2.104 (95% CI: 1.739–2.546, P<0.05, I2=0.0%) and 7.585 (95% CI: 2.220–25.919, P<0.05, I2=0.0%), respectively (Figure 2).
  | Figure 2 Meta-analysis of the risk of pruritus. |
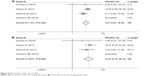
Similarly, the result for rash also showed significantly higher risk among nivolumab-plus-ipilimumab group than the nivolumab group. The pooled ORs for all-grade rash and high-grade rash were 2.046 (95% CI: 1.488–2.814, P<0.05, I2=56.5%) and 4.957 (95% CI: 2.443–10.061, P<0.05, I2=0.0%), respectively (Figure 3).
  | Figure 3 Meta-analysis of the risk of rash. |
Meta-analysis of the risk of diarrhea and colitis
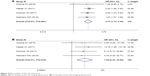
Among the four included studies, patients treated with nivolumab-plus-ipilimumab group had a higher risk of diarrhea. The pooled ORs of all-grade rash and high-grade rash were 2.715 (95% CI: 1.759–4.192, P<0.05, I2=77.7%) and 4.738 (95% CI: 2.943–7.628, P<0.05, I2=28.9%), respectively (Figure 4).
  | Figure 4 Meta-analysis of the risk of diarrhea. |
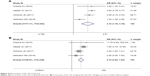
Three studies reporting the incidence of colitis included patients with melanoma and SCLC. The observed pooled OR for all-grade colitis was 9.909 (95% CI 5.833–16.833, P<0.05) with a low heterogeneity (I2=1.5%). The pooled OR for high-grade colitis was 12.671 (95% CI: 6.148–26.118, P<0.05) with a low heterogeneity (I2=0.0%) (Figure 5).
  | Figure 5 Meta-analysis of the risk of colitis. |
Meta-analysis of the risk of ALT elevation
Among the four studies included, a higher risk of ALT elevation was observed for nivolumab-plus-ipilimumab group than the nivolumab group. The pooled OR for all-grade increase in ALT was 5.322 (95% CI: 3.732–7.589, P<0.05, I2=36.1%). The pooled OR for high-grade increase in ALT was 6.866 (95% CI: 3.819–12.344, P<0.05, I2=22.6%) (Figure 6).
Meta-analysis of the risk of pneumonitis
When nivolumab-plus-ipilimumab group was compared with nivolumab alone group, the risk of pneumonitis was higher with combined treatment over nivolumab monotherapy. The pooled ORs of all-grade pneumonitis and high-grade pneumonitis were 3.825 (95% CI: 2.286–6.399, P<0.05, I2=3.2%) and 4.445 (95% CI: 1.206–16.379, P<0.05, I2=0.0%), respectively (Figure 7).
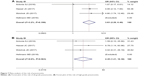  | Figure 7 Meta-analysis of the risk of pneumonitis. |
Study quality and publication bias
Funnel plots were used to evaluate the potential publication bias. We used Begg’s and Egger’s tests to evaluate the asymmetry of the funnel plot.30 Furthermore, the forest plots of irAEs (Figures 2–7), and Begg’s and Egger’s tests (P>0.05) show that there was no publication bias.
Discussion
ICB therapy is increasingly being recognized in patients with lung cancer and advanced melanoma and is further being evaluated for various other cancers. However, irAEs can limit their use due to serious adverse outcomes including death. It has been reported that combined therapy is more frequently associated with multiorgan involvement, with nearly one-third of all deaths resulting from myocarditis, myositis, and neurologic events.31 In the present study, we performed a meta-analysis to evaluate the incidence of irAEs in patients receiving nivolumab-plus-ipilimumab and nivolumab therapy alone.
Previously, Komaki et al published a meta-analysis of irAEs with CTLA-4 blockade and PD-1 therapy, which included nivolumab, ipilimumab, and tremelimumab (non-approved).32 They pooled 11,144 patients’ data from clinical trials. However, their search strategy was limited and included cases only up to December 2016. Anti-CTLA4 therapy was associated with a higher risk of overall irAEs. Anti-PD1 therapy was associated with a higher risk of pruritus in comparison to other adverse events. In our study, we included studies from inception to June 2018. The majority of irAEs included in our analysis were from recent trials, which could be due to the fact that researchers were more aware and aggressive in their management of irAEs. Furthermore, we evaluated all-grade and high-grade irAEs in patients receiving nivolumab-plus-ipilimumab and nivolumab therapy.
Immune-mediated pneumonitis during treatment with ICIs was rare (considering all grades of severity, <10% of patients).33 A previous report demonstrated that 4% of patients on ipilimumab developed pneumonitis, whereas the percentage was 11% among patients treated with ipilimumab plus nivolumab in a comparative metastatic melanoma study.14 So, there was an increase in the prevalence of pneumonitis on combined therapy with PD-1 and CTLA-4 inhibitors. Moreover, the pooled incidences of all-grade and high-grade pneumonitis in patients treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors were 3.2% and 1.1%, respectively,34 while our data showed that the risk of pneumonitis was 4.445 times higher in nivolumab-plus-ipilimumab than in nivolumab group. Therefore, clinicians should pay enough attention to patients manifesting pulmonary symptoms including dry cough, hypoxia, and shortness of breath.35 Furthermore, comorbidities such as chronic obstructive airways disease and prior therapies including lung irradiation in patients with NSCLC would have influenced the observed higher risks of pneumonitis when treated with PD-1 inhibitors.15 Given the occurrence of pneumonia, the management of pneumonitis primarily consisted of administering rapid and high-dose corticosteroid treatment.
One of the common irAEs was diarrhea caused by immune-related colitis.36 A previous report showed that the incidence of severe diarrhea/colitis with anti-PD1 therapy was much lower than with anti-CTLA4 therapy (8%–19% vs 23%–33%).37 Combined therapy had a striking 44% increase in the risk of diarrhea and immune-related colitis.38 It is reported that diarrhea and colitis could also be associated with autoimmune diseases, long-term use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, elevated plasma IL-17, and elevated expression of carcinoembryonic antigen-related cellular adhesion molecule 1, but it was noticed that these risk factors could not be detected in most laboratory centers. Therefore, the clinical application of detecting the risk factors associated with diarrhea and colitis is still lagging.
The analysis of nivolumab-plus-ipilimumab and nivolumab monotherapy for the immune-mediated hypophysitis (IMH) revealed that the incidence increased to 8%, with high-grade hypophysitis occurring in 2% of cases.13 The results indicated that the risk of hypophysis was 18.487 times higher in ipilimumab-plus-nivolumab therapy in comparison to nivolumab therapy. These pituitary adverse events often occurred between 6 and 13 weeks, as well as 19 months after the completion of treatment.39 This condition is usually associated with atypical symptoms, such as mild fatigue, joint pain, and decreased sexual interest caused by hormonal changes. Severe symptoms included headache due to gravitational effects caused by glandular edema. Due to these atypical symptoms, pituitary inflammation was easily missed. With no standard management protocol for IMH, it is important to be cognizant of the fact that adrenocortical failure caused by hypophysitis may be life threatening, and further management studies are required on this premise.33
Since ICIs are associated with distinctive toxicity, many oncologists are not acquainted with the optimal principle management of irAEs, which requires early recognition and appropriate treatment. Further, clinicians are required to identify the risk factors and assess the severity of irAEs accurately. Fortunately, it is inspiring to know that most of the irAEs are sensitive to glucocorticoid therapy and can be well controlled within 6–12 weeks. Our study could be important in considering the benefit/risk trade-off by providing the odds risks for irAEs in patients treated with combination therapy.
There are certain limitations in our meta-analysis, which should be mentioned. First, our results were based on unadjusted analysis, and more accurate outcomes would result from making adjustments for other confounders such as gender, age, dosage of drugs, PD-L1 status, prior systemic therapy, and so on. Second, the small number of included studies would make the outcomes more prone to be influenced by a potential publication bias. As a result, we could not confidently assess the publication bias. Third, language of studies was limited to English, which may result in missing data from studies published in other languages.
Conclusion
In summary, our study indicated that the combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab increased the risk of all- and high-grade irAEs in patients with advanced cancer. In spite of its considerable benefit in patients, ICB can be limited by the occurrence of irAEs, which can be life threatening. Therefore, additional drug intervention to prevent or treat these adverse events should be considered when standardizing an anti-PD-1 combined with anti-CTLA-4 therapy for metastatic tumors.
Acknowledgment
We would like to thank Mr Zhang, Southeast University, for excellent technical assistance.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Harris TJ, Drake CG. Primer on tumor immunology and cancer immunotherapy. J Immunother Cancer. 2013;1:12. | ||
Kumar P, Bhattacharya P, Prabhakar BS. A comprehensive review on the role of co-signaling receptors and Treg homeostasis in autoimmunity and tumor immunity. J Autoimmun. 2018;95:77–99. | ||
Mellman I, Coukos G, Dranoff G. Cancer immunotherapy comes of age. Nature. 2011;480(7378):480–489. | ||
Linsley PS, Brady W, Urnes M, Grosmaire LS, Damle NK, Ledbetter JA. CTLA-4 is a second receptor for the B cell activation antigen B7. J Exp Med. 1991;174(3):561–569. | ||
Qureshi OS, Zheng Y, Nakamura K, et al. Trans-endocytosis of CD80 and CD86: a molecular basis for the cell-extrinsic function of CTLA-4. Science. 2011;332(6029):600–603. | ||
Riley JL, Mao M, Kobayashi S, et al. Modulation of TCR-induced transcriptional profiles by ligation of CD28, ICOS, and CTLA-4 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(18):11790–11795. | ||
Schneider H, Downey J, Smith A, et al. Reversal of the TCR stop signal by CTLA-4. Science. 2006;313(5795):1972–1975. | ||
Hodi FS, O’Day SJ, Mcdermott DF, et al. Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(8):711–723. | ||
Bardhan K, Anagnostou T, Boussiotis VA. The PD1:PD-L1/2 Pathway from Discovery to Clinical Implementation. Front Immunol. 2016;7(1):550. | ||
Keir ME, Liang SC, Guleria I, et al. Tissue expression of PD-L1 mediates peripheral T cell tolerance. J Exp Med. 2006;203(4):883–895. | ||
Faghfuri E, Faramarzi MA, Nikfar S, Abdollahi M. Nivolumab and pembrolizumab as immune-modulating monoclonal antibodies targeting the PD-1 receptor to treat melanoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2015;15(9):981–993. | ||
Okazaki T, Chikuma S, Iwai Y, Fagarasan S, Honjo T. A rheostat for immune responses: the unique properties of PD-1 and their advantages for clinical application. Nat Immunol. 2013;14(12):1212–1218. | ||
Larkin J, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, et al. Combined nivolumab and ipilimumab or monotherapy in untreated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(1):23–34. | ||
Postow MA, Chesney J, Pavlick AC, et al. Nivolumab and ipilimumab versus ipilimumab in untreated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(21):2006–2017. | ||
Khoja L, Day D, Wei-Wu Chen T, Siu LL, Hansen AR. Tumour- and class-specific patterns of immune-related adverse events of immune checkpoint inhibitors: a systematic review. Ann Oncol. 2017;28(10):2377–2385. | ||
Hassel JC, Heinzerling L, Aberle J, et al. Combined immune checkpoint blockade (anti-PD-1/anti-CTLA-4): evaluation and management of adverse drug reactions. Cancer Treat Rev. 2017;57:36–49. | ||
Girotra M, Hansen A, Farooki A, et al; Task Force collaboration. The current understanding of the endocrine effects from immune checkpoint inhibitors and recommendations for management. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2018;2(3):pky021. | ||
Zhang S, Liang F, Li W, Wang Q. Risk of treatment-related mortality in cancer patients treated with ipilimumab: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer. 2017;83:71–79. | ||
Hryniewicki AT, Wang C, Shatsky RA, Coyne CJ. Management of immune checkpoint inhibitor toxicities: a review and clinical guideline for emergency physicians. J Emerg Med. 2018;55(4):489–502. | ||
Grimaldi AM, Marincola FM, Ascierto PA. Single versus combination immunotherapy drug treatment in melanoma. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2016;16(4):433–441. | ||
Shoushtari AN, Friedman CF, Navid-Azarbaijani P, et al. Measuring toxic effects and time to treatment failure for nivolumab plus ipilimumab in melanoma. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4(1):98–101. | ||
Nagai H, Muto M. Optimal management of immune-related adverse events resulting from treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a review and update. Int J Clin Oncol. 2018;23(3):410–420. | ||
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000097. | ||
National Cancer Institute [webpage on the Internet]. Common terminology criteria for adverse events (CTCAE) version 5.0. 2018. Available from: https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocolDevelopment/electronic_applications/ctc.htm. Accessed January 23, 2019. | ||
Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, et al; Cochrane Bias Methods Group. The Cochrane collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2011;343:d5928. | ||
Antonia SJ, López-Martin JA, Bendell J, et al. Nivolumab alone and nivolumab plus ipilimumab in recurrent small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 032): a multicentre, open-label, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(7):883–895. | ||
Hellmann MD, Ciuleanu TE, Pluzanski A, et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in lung cancer with a high tumor mutational burden. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(22):2093–2104. | ||
Wolchok JD, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, et al. Overall survival with combined nivolumab and ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(14):1345–1356. | ||
Hassel JC, Heinzerling L, Aberle J, et al. Combined immune checkpoint blockade (anti-PD-1/anti-CTLA-4): evaluation and management of adverse drug reactions. Cancer Treat Rev. 2017;57:36–49. | ||
Sterne JA, Gavaghan D, Egger M. Publication and related bias in meta-analysis: power of statistical tests and prevalence in the literature. J Clin Epidemiol. 2000;53(11):1119–1129. | ||
Wang DY, Salem JE, Cohen JV. Fatal toxic effects associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4(12):1721–1728. | ||
Komaki Y, Komaki F, Yamada A, Micic D, Ido A, Sakuraba A. Meta-analysis of the risk of immune-related adverse events with Anticytotoxic T-Lymphocyte-Associated antigen 4 and Antiprogrammed death 1 therapies. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2018;103(2):318–331. | ||
Abdel-Wahab N, Shah M, Suarez-Almazor ME. Adverse events associated with immune checkpoint blockade in patients with cancer: a systematic review of case reports. PLoS One. 2016;11(7):e0160221. | ||
Zhang S, Liang F, Zhu J, Chen Q. Risk of pneumonitis associated with programmed cell death 1 inhibitors in cancer patients: a meta-analysis. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017;16(8):1588–1595. | ||
Zhao B, Zhao H, Zhao J. Serious adverse events and fatal adverse events associated with nivolumab treatment in cancer patients: nivolumab-related serious/fatal adverse events. J Immunother Cancer. 2018;6(1):101. | ||
Weber JS, Dummer R, de Pril V, Lebbé C, Hodi FS; MDX010-20 Investigators. Patterns of onset and resolution of immune-related adverse events of special interest with ipilimumab: detailed safety analysis from a phase 3 trial in patients with advanced melanoma. Cancer. 2013;119(9):1675–1682. | ||
Verschuren EC, van den Eertwegh AJ, Wonders J, et al. Clinical, endoscopic, and histologic characteristics of Ipilimumab-Associated colitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14(6):836–842. | ||
Emens LA, Braiteh FS, Cassier P, et al. Abstract 2859: inhibition of PD-L1 by MPDL3280A leads to clinical activity in patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). Cancer Res. 2015;75(15 Supplement):2859. | ||
Sangro B, Gomez-Martin C, de La Mata M, et al. A clinical trial of CTLA-4 blockade with tremelimumab in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 2013;59(1):81–88. |
 © 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2019 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.