Back to Journals » Clinical Ophthalmology » Volume 14
Relation of Corneal Astigmatism with Various Corneal Image Quality Parameters in a Large Cohort of Naïve Corneas
Authors Omar Yousif M , Elkitkat RS , Abdelsadek Alaarag N, Shams A , Gharieb HM
Received 27 May 2020
Accepted for publication 16 July 2020
Published 4 August 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 2203—2210
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OPTH.S264706
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Scott Fraser
Mohamed Omar Yousif,1,2 Rania Serag Elkitkat,1,3 Noha Abdelsadek Alaarag,1 Abdelrhman Shams,1 Hesham Mohamed Gharieb1,4
1Faculty of Medicine, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt; 2Maadi Eye Subspecialty Center, Cairo, Egypt; 3Al Watani Eye Hospitals, Cairo, Egypt; 4Research and Development Department, Eye World Hospital, Giza, Egypt
Correspondence: Abdelrhman Shams Cairo, Egypt
Tel +201222131012
Email [email protected]
Purpose: To investigate the relationship between corneal astigmatism and corneal image quality parameters (i.e., root mean square [RMS] of some major corneal higher order aberrations [HOAs] “namely RMS of coma aberrations, RMS of trefoil aberrations, and RMS of spherical aberration [RMS-SA]” and Strehl ratio [SR] of point spread function [PSF]) by using the Sirius topographer (CSO Italia, Florence, Italy).
Patients and Methods: This cross-sectional study used the Sirius topographer to evaluate the naïve corneas of right eyes (n = 1,356). The study included three groups which were based on the mean anterior corneal astigmatism value (group 1, < 1 D; group 2, 1– 2 D; and group 3, > 2 D).
Results: The corneal astigmatism showed statistically significant (yet narrow clinical) differences among the groups regarding all the examined parameters (P< 0.001), except for the RMS-SA (which was statistically insignificant among the three groups). Correlation coefficients were weak between the corneal astigmatism and HOAs (correlation coefficient “r” not reaching 0.2 with any of the evaluated HOAs).
Conclusion: Significant differences existed among the astigmatic groups regarding corneal HOAs, but the mean values were very close. The deduced relations between corneal astigmatism and corneal image quality parameters had limited clinical relevance. Thus, the corneal astigmatism should be evaluated separately from corneal image quality parameters, either when deciding between refractive correction modalities (customized versus optimized ablation techniques) or when evaluating corneal image quality of a naïve cornea.
Keywords: Sirius topographer, corneal astigmatism, corneal image quality, higher order aberrations (HOAs), customized versus optimized laser corneal ablation
Introduction
In the ophthalmic field, the assessment of visual performance is a cornerstone for proper ocular evaluation and for plotting research methodologies.1 Furthermore, comprehensive analysis of visual function before refractive surgeries is pivotal for attaining the desired outcomes. Visual acuity assessment is the most commonly used parameter for evaluating the overall visual function of the human eye. However, under conditions of dim light or low contrast sensitivity, visual acuity does not truly reflect a person’s subjective visual function.2 Moreover, subjective visual tests, which primarily include visual acuity and contrast sensitivity, do not objectively reflect the true visual performance of the eye. For this reason, objective modalities for visual quality assessment are increasingly being adopted to “more truly” deduce the potential visual performance, especially for refractive candidates.3
Proper visual performance requires intact optical system of the eye. A major optically active surface is the cornea, which contributes roughly to 70% of the total refractive power.4 Hence, studying the cornea’s optical and refractive properties is mandatory for objective visual analysis. The corneal wavefront technology is a robust benchmark for the objective evaluation of corneal image quality.1 It is considered as one of the major determinants of the overall optical quality of the eye.5
Corneal wavefront technology is conveniently described by using Zernike polynomials.6,7 These polynomials represent corneal aberrations, which are focusing errors due to imperfections of the corneal shape that prevent light rays from converging into a single image point.8 Corneal aberrations substantially contribute to decreased visual performance.9 The most significant corneal aberrations are the sphere and cylinder, which constitute the lower order aberrations (LOAs [i.e., defocus of the eye]). Higher order aberrations (HOAs) can also alter visual quality, even in normal eyes.10
Objective descriptors of corneal aberrations have been derived from wavefront information. Optical quality metrics (e.g., root mean square [RMS] error) quantify the optical quality of the cornea, whereas image quality metrics (e.g., point spread function [PSF]) predict the optical image quality at the fovea.1,3 The Strehl ratio (SR) is a robust parameter that is calculated from the PSF of the eye’s optical system and has been incorporated in topography equipment. The SR can express and quantify corneal aberrations, which are objectively used to assess image quality.1,11
Corneal topography/tomography has been developing along the previous decades. Placido based corneal topography relies on the data available from the anterior corneal surface only. Afterwards, the Scheimpflug principle emanated, where data is obtained from both the anterior and posterior corneal surfaces, with possible detection of corneal elevations and pachymetric data.12 The Sirius topographer (CSO Italia, Florence Italy) is a recently developed device that includes a comprehensive corneal wavefront analysis. It is a corneal topography/tomography device that utilizes both a Scheimpflug camera and Placido disc for anterior segment examination.13
During the past 2 decades, much research has led to dramatic advances in the refractive surgical corrections, which include newer excimer laser platforms for faster eye tracking or customized ablation techniques with wavefront-guided or topography-guided profiles. Recent studies have addressed the postoperative outcomes of these various modalities with regard to subjective visual quality (i.e., visual acuity and contrast sensitivity). Controversial results have been deduced as per the proper choice of the refractive correction modality, especially in the presence of a significant corneal cylinder, by using an optimized profile with cyclotorsion control or a customized profile. The corneal HOAs are the major determinants of the need for customized rather than optimized corneal ablation with cyclotorsion control.14,15
The primary goal of this study was to investigate the corneal astigmatism with regard to the possibly existing relationships between it and the corneal image quality parameters (mainly HOAs) by using the Sirius topographer. We aimed to determine whether they should be regarded as related or separate entities in preoperative evaluations of refractive surgery candidates and in planning for the proper choice of the better suited ablation profile.
Patients and Methods
This cross sectional, noncomparative, noncontrolled, observational study was conducted at Maadi Eye Subspecialty Center in Cairo, Egypt. All recruited participants sought medical advice for refractive surgical correction or for medical consultation between May 2017 and April 2019. All included subjects had normal (i.e., nonectatic) corneas. We excluded candidates who had worn contact lens within the previous 2 weeks, who had previous ocular trauma or surgeries, or who had any evident anterior segment pathology on slit lamp examination (including corneal scars). Furthermore, narrow palpebral fissures affecting proper scanning and any topographic evidence of keratoconus or other ectatic conditions (as detected by the Sirius topographer) were other exclusion criteria. The study adhered to the Tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethical Committee of Ain Shams University.
Right eyes were enrolled in the study. Refractive errors (using the spherical equivalent [SE]) and corrected distance visual acuity were recorded. The recruited cohort underwent slit lamp examinations. The participants’ corneas were evaluated using the Sirius topographer (CSO Italia) with software version Phoenix 3.2.1.60. The scanning process acquires a series of 25 Scheimpflug images (i.e., meridians) and 1 Placido top-view image to analyze the anterior segment by obtaining 25 radial sections of the cornea and anterior chamber. Then the device merges the anterior surface data from the Placido and Scheimpflug images using a proprietary method. Corneal aberrometry was obtained using the ray-tracing technique.
One optometrist conducted all measurements using the Sirius topographer. The participant’s eye was aligned along the visual axis using a central fixation light. Participants were instructed to blink between shots to keep eyes moist. The images were captured under mesopic lighting conditions and were obtained using the automatic mode. The system constantly monitored the patient’s eye movement. The quality factor was automatically evaluated and the best scans were chosen for evaluation (valid fixation check, and the best acquisition quality for the Scheimpflug images “coverage, data not edited, and clearness” and also for the Keratoscopy “centration and coverage”). The acquisition qualities of these various parameters are color coded within the device to facilitate their interpretation.
The recruited cohort was subdivided into three groups based on the mean values of corneal astigmatism for the anterior corneal surface: group 1 (637 eyes) had corneal astigmatism of <1 D; group 2 (476 eyes), 1–2 D; and group 3 (243 eyes), >2 D. The corneal astigmatism was deduced by subtracting the keratometric power of the flattest meridian (K1) from the keratometric power of the steepest meridian (K2), which were both obtained from the Sirius topographer.
The following values of the total corneal image quality parameters were obtained from the Sirius topographer (at 6 mm optical zone):
- Root mean square (RMS) of the total aberrations (RMS-total)
- RMS of lower order aberrations (RMS-LOAs)
- RMS of higher order aberrations (RMS-HOAs)
- RMS of coma aberrations
- RMS of trefoil aberrations
- RMS of spherical aberration (RMS-SA)
- Strehl ratio of the point spread function (PSF-SR)
The differences among the three groups were detected with regard to the relationships between the corneal astigmatism and the evaluated corneal image quality parameters.
Statistical Analysis
Data were collected, revised, coded and entered to the Statistical Package for Social Science, version 23 (IBM SPSS). The quantitative data were presented as the mean, standard deviation, and range. The comparisons among more than two groups regarding the quantitative data with parametric distribution was conducted by using the one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) test, followed by post hoc analysis using the least significant difference (LSD) test when significant, whereas data with nonparametric distribution were compared among the three groups by using the Kruskal–Wallis test, followed by post hoc analysis using the Mann–Whitney test. Spearman correlation coefficients were used to assess the correlation between two quantitative parameters in the same group. The confidence interval was set to 95% and the accepted margin of error was set to 5%. Therefore, the value of P < 0.05 was significant.
Results
This cross-sectional study included 1356 right eyes of 1356 participants with naïve corneas. The female to male ratio was 62.90% to 37.10%. The age range of the enrolled participants was 15–69 years with a mean ± standard deviation of 29.49 ± 8.89 years.
The mean SE for the study group was −4.25 ± 1.27 D, with an average best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) of 20/25. Slit lamp examination for the enrolled cohort was unremarkable. The mean corneal astigmatism was 1.28 ± 0.89 D with a range of 0.03–6.65 D.
Besides, we recorded the aforementioned data for each of the three enrolled groups, including the female to male ratio (group 1: 38.70% to 61.30%, group 2: 34.50% to 65.50%, group 3: 46.20% to 53.80%), SE (group 1: −2.75 ± 1.5 D, group 2: −4.00 ± 1.00 D, group 3: −6.00 ± 1.5 D), BCVA (group 1: 20/25, group 2: 20/25, group 3: 20/20), and corneal astigmatism (group 1: 0.59 ± 0.25, group 2: 1.68 ±0.51, group 3: 3.66 ± 0.65).
Data analyses revealed the existence of statistically significant differences among the three studied groups (P < 0.001; one way ANOVA or the Kruskal–Wallis test) with regard to all the assessed parameters of image quality, except for the RMS-SA, as shown in Table 1. Table 2 highlights the post hoc test results, declaring statistically significant differences between any of the three groups and the other for all the evaluated indices, except for the RMS-SA.
 |
Table 1 The Mean ± Standard Deviation and/Or the Median of the Studied Parameters, and the P Values of Significance Within the Three Astigmatic Groups |
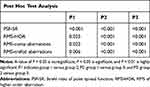 |
Table 2 Differences Between the Astigmatic Groups, Based on Post Hoc Test Analysis |
The mean and ranges for some of the examined corneal aberrations (RMS-total, RMS of coma aberrations, and RMS-SA) for each group were also displayed in the form of boxes and whisker graphs (Figures 1–3).
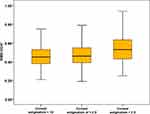 |
Figure 1 Boxes and Whiskers for mean and range of root mean square-higher order aberrations among the three studied groups. Abbreviation: RMS-HOA, root mean square-higher order aberrations. |
 |
Figure 2 Boxes and Whiskers for mean and range of root mean square-coma aberrations among the three studied groups. Abbreviation: RMS-coma, root mean square coma aberrations. |
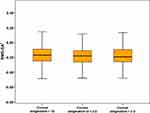 |
Figure 3 Boxes and Whiskers for mean and range of root mean square-spherical aberrations among the three studies groups. Abbreviation: RMS-SA, root mean square-spherical aberrations. |
The correlation coefficients were calculated to detect correlations between the evaluated corneal image quality parameters and corneal astigmatism (Table 3). This analysis revealed some existing, yet weak, correlations (the correlation coefficient “r” did not exceed 0.2), except for an intuitive strong correlation between corneal astigmatism and PSF-SR (r= −0.873).
 |
Table 3 Correlation Coefficients Between Corneal Astigmatism and Corneal Image Quality Parameters |
The same correlations were plotted, after conducting partial correlation analysis, which was controlled for age. The correlations with the mean corneal astigmatism showed nearly the same results as the correlations conducted without controlling for age (Table 4), where the highest correlation that existed between the corneal astigmatism and any of the examined corneal aberrations did not exceed 0.3 (the r value of correlation between corneal astigmatism and RMS-HOA =0.251).
 |
Table 4 Correlation Coefficients and P values of Significance Between Corneal Astigmatism and the Corneal Image Quality Parameters, After Controlling for Age |
Discussion
In this study, a large cohort of naïve corneas was enrolled for evaluating a possible relation between corneal astigmatism and corneal image quality parameters. This study was novel in recruiting a large sample (1,356 eyes) for studying the effect of corneal astigmatism on various corneal image quality parameters (i.e., corneal HOAs, coma, trefoil, spherical aberration, and PSF-SR), as a proposed theoretical model to aid in the decisions of refractive surgical corrections.
Despite the recent availability of many refractive correction alternatives, gaining familiarity with newer platforms and the consequent need for reliable nomogram adjustments mandate the availability of clear scientific-based evidence regarding the superiority of one system over another. This has been controversial in the related literature.16 Some studies reported better visual outcomes with the customized laser platforms rather than with the standard and optimized correction,15,17 owing to the ability of the customized ablation to reduce the corneal HOAs and thereby improve the visual performance. By contrast, other studies18,19 failed to demonstrate a significant, clinically relevant, benefit of customized corneal ablation techniques over the traditional optimized procedures with cyclotorsion control. Some investigators consider customized corneal ablation as beneficial but only if substantial corneal HOAs exist, which was given an average magnitude of 0.30–0.35 um, regardless of the amount of corneal astigmatism.20,21
Based on the conflicting results of the aforementioned studies, we aimed to investigate whether the corneal astigmatism could influence a surgeon’s choice between optimized ablation with cyclotorsion control and customized laser ablation techniques. The latter is primarily indicated for high corneal HOAs.
The results of our study showed statistically significant (yet clinically irrelevant, narrow) differences and also statistically significant (yet weak) correlations between the corneal astigmatism and the corneal HOAs. As the corneal astigmatism increased from one group to another, the aberrations increased and the SR (as a measure for the PSF) decreased, which may have caused the poorer image quality. With regard to the relation between the PSF and the corneal astigmatism, the findings of Gao et al22 agreed with ours: the value of PSF decreased as the corneal astigmatism increased. Thus, the image quality reduced with increasing astigmatism values. Corneal astigmatism and HOAs have a direct major effect on the PSF, and are both components used to deduce its value. Therefore, the finding that the PSF changed in parallel with their changes seems intuitive.
A previous study by Mohammadpour et al highlighted a relationship between corneal astigmatism and HOAs; they deduced that HOA values increase with increasing corneal astigmatism.23 This finding is in accordance with our study results from the statistical point of view. Nevertheless, this study did not discuss the clinical aspect of the presumed theory.
Furthermore, on analyzing the differences among the astigmatic groups with regard to the major HOA components (i.e., coma, trefoil, and SA), our study results showed that RMS-SA was the only HOA with no statistically significant differences among the groups. This finding agrees with those of Hu et al,24 which showed a significant correlation between corneal astigmatism and coma aberrations rather than spherical aberrations.
We need to mention that the aforementioned studies that demonstrated an association between the corneal astigmatism and the various corneal image quality parameters were not conducted using the Sirius topographer, but were rather conducted using aberrometers utilizing the Hartmann–Shack technique. Hence, comparing our study results to the results of these studies may be partially erroneous.
A recent study by Anbar et al was conducted to report the characteristics of corneal HOAs in patients with different refractive errors using the Sirius topographer. The study results showed that the most significant differences were detected between the hypermetropic group and the other groups, mainly in the RMS- total and coma aberrations. In our study, we did not enroll either hypermetropic or mixed astigmatism eyes. This may partially explain the absence of clinically significant differences in our study, in contradiction to Anbar et al.25
It has been postulated that statistically significant data should be read in concordance with its clinical meanings, especially in studies with large sample sizes where the data could be statistically significant yet irrelevant from the clinical point of view,26 so the authors believe that the differences among the astigmatic groups may not be proven if implemented in clinical practice. The numerical values did not show a robust difference that would attract a surgeon’s attention, and the existing correlations were weak ones. Thus, the differences in corneal image quality parameters among the study groups may not be of concern for refractive surgeons when choosing the proper refractive surgical correction modality (optimized with cyclotorsion control or customized corneal ablation profile) for refractive candidates. Hence, from a clinical point of view, the corneal astigmatism should be regarded as a separate entity from the corneal image quality parameters within the ranges of corneal astigmatism in our recruited cohort. Surgeons should base their choice of refractive correction modality on a separate evaluation of corneal image quality parameters, primarily the corneal HOAs, while disregarding any influential effect of corneal astigmatism, which contradicts the concept adopted by some refractive surgeons in their routine performance of customized ablation profiles based only on the presence of a high cylinder. The use of an optimized profile with cyclotorsion control may be the optimum choice for these patients if no significant HOAs are detected.
Our proposed weak clinical relevance of the relations between corneal astigmatism and HOAs were recently validated by de Ortueta et al,27 who evaluated the outcomes of transepithelial photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) in moderate to high astigmatism with a non-wavefront-guided aberration-neutral ablation profile. Based on the results of de Ortueta et al study, no clinically relevant changes were seen among the astigmatic groups in HOAs. This result is in accordance with our proposed study result. More future longitudinal studies on refractive surgery candidates can be based on our proposed theory and the results of de Ortueta et al study.
Enrollment of the right eyes rather than bilateral eye enrollment in this study aimed to avoid inter-eye correlation bias that may lead to inaccurate results or erroneous augmentations of the deduced conclusions.
We recommend that future studies should be directed towards combining objective and subjective image quality parameters to validate whether any statistically significant differences in values would have a true impact on the subjective quality of vision (primarily contrast sensitivity), especially in cases of narrow ranges among groups, as detected in our study.
In conclusion, this study demonstrated a statistical rather than a clinical relationship between corneal astigmatism and corneal image quality parameters (mainly HOAs), and included a large cohort of naïve corneas. Hence, the corneal astigmatism and the corneal image quality parameters can be regarded separately when deciding between refractive correction modalities and also when evaluating the image quality of the corneas. We should mention that this conclusion should be applied to the ranges of corneal astigmatism in our studied cohort (0.03–6.65 D), and the results should not be implemented on the extremes of values outside this range.
Ethical Approval
The study adhered to the Tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethical Committee of Ain Shams University.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Editage for English language editing.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Marsack JD, Thibos LN, Applegate RA. Metrics of optical quality derived from wave aberrations predict visual performance. J Vis. 2004;4(4):8. doi:10.1167/4.4.8
2. Li L, Cheng GP, Ng AL, Chan TC, Jhanji V, Wang Y. Influence of refractive status on the higher-order aberration pattern after small incision lenticule extraction surgery. Cornea. 2017;36(8):967–972. doi:10.1097/ICO.0000000000001264
3. Cheng X, Thibos LN, Bradley A. Estimating visual quality from wavefront aberration measurements. J Refract Surg. 2003;19(5):S579–S584. doi:10.3928/1081-597X-20030901-14
4. Zheng S, Ying J, Wang B, Xie Z, Huang X, Shi M. Three-dimensional model for human anterior corneal surface. J Biomed Opt. 2013;18(6):065002. doi:10.1117/1.JBO.18.6.065002
5. Guirao A, Artal P. Corneal wave aberration from videokeratography: accuracy and limitations of the procedure. JOSA A. 2000;17(6):955–965. doi:10.1364/JOSAA.17.000955
6. Gobbe M, Guillon M. Corneal wavefront aberration measurements to detect keratoconus patients. Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2005;28(2):57–66. doi:10.1016/j.clae.2004.12.001
7. Perez-Straziota CE, Randleman JB, Stulting RD. Visual acuity and higher-order aberrations with wavefront-guided and wavefront-optimized laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010;36(3):437–441. doi:10.1016/j.jcrs.2009.09.031
8. Williams D, Yoon GY, Porter J, Guirao A, Hofer H, Cox I. Visual benefit of correcting higher order aberrations of the eye. J Refract Surg. 2000;16(5):S554–S559.
9. Guirao A, Porter J, Williams DR, Cox IG. Calculated impact of higher-order monochromatic aberrations on retinal image quality in a population of human eyes: erratum. JOSA A. 2002;19(3):620–628. doi:10.1364/JOSAA.19.000620
10. Rocha KM, Vabre L, Chateau N, Krueger RR. Enhanced visual acuity and image perception following correction of highly aberrated eyes using an adaptive optics visual simulator. J Refract Surg. 2010;26(1):52–56. doi:10.3928/1081597X-20101215-08
11. Applegate RA, Hilmantel G, Howland HC, Tu EY, Starck T, Zayac EJ. Corneal first surface optical aberrations and visual performance. J Refract Surg. 2000;16(5):507–514.
12. Wilson SE, Ambrosio R. Computerized corneal topography and its importance to wavefront technology. Cornea. 2001;20(5):441–454. doi:10.1097/00003226-200107000-00001
13. Savini G, Barboni P, Carbonelli M, Hoffer KJ. Repeatability of automatic measurements by a new Scheimpflug camera combined with Placido topography. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011;37(10):1809–1816. doi:10.1016/j.jcrs.2011.04.033
14. Smadja D, Reggiani-Mello G, Santhiago MR, Krueger RR. Wavefront ablation profiles in refractive surgery: description, results, and limitations. J Refract Surg. 2012;28(3):224–232. doi:10.3928/1081597X-20120217-01
15. Lee HK, Choe CM, Ma KT, Kim EK. Measurement of contrast sensitivity and glare under mesopic and photopic conditions following wavefront-guided and conventional LASIK surgery. J Refract Surg. 2006;22(7):647–655. doi:10.3928/1081-597X-20060901-05
16. Lee K, Ahn JM, Kim EK. Comparison of optical quality parameters and ocular aberrations after wavefront-guided laser in-situ keratomileusis versus wavefront-guided laser epithelial keratomileusis for myopia. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2013;251(9):2163–2169. doi:10.1007/s00417-013-2356-x
17. Tuan K-M, Liang J. Improved contrast sensitivity and visual acuity after wavefront-guided laser in situ keratomileusis: in-depth statistical analysis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006;32(2):215–220. doi:10.1016/j.jcrs.2005.07.045
18. Dougherty PJ, Bains HS. A retrospective comparison of LASIK outcomes for myopia and myopic astigmatism with conventional NIDEK versus wavefront-guided VISX and Alcon platforms. J Refract Surg. 2008;24(9):891–896. doi:10.3928/1081597X-20081101-07
19. Tiwari NN, Sachdev GS, Ramamurthy S, Dandapani R. Comparative analysis of visual outcomes and ocular aberrations following wavefront optimized and topography-guided customized femtosecond laser in situ keratomileusis for myopia and myopic astigmatism: a contralateral eye study. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2018;66(11):1558. doi:10.4103/ijo.IJO_507_18
20. Hantera M. Comparison of postoperative wavefront aberrations after NIDEK CXIII optimized aspheric transition zone treatment and OPD-guided custom aspheric treatment. J Refract Surg. 2009;25(10):S922–S926. doi:10.3928/1081597X-20090915-04
21. Feng Y, Yu J, Wang Q. Meta-analysis of wavefront-guided vs. wavefront-optimized LASIK for myopia. Optom Vis Sci. 2011;88(12):1463–1469. doi:10.1097/OPX.0b013e3182333a50
22. Gao J, Wang X-X, Wang L, Sun Y, Liu R-F, Zhao Q. The effect of the degree of astigmatism on optical quality in children. J Ophthalmol. 2017;2017:1–4. doi:10.1155/2017/5786265
23. Mohammadpour M, Heidari Z, Mohammad-Rabei H, et al. Correlation of higher order aberrations and components of astigmatism in myopic refractive surgery candidates. J Curr Ophthalmol. 2016;28(3):112–116. doi:10.1016/j.joco.2016.04.007
24. Hu J, Yan Z, Liu C, Huang L. Higher-order aberrations in myopic and astigmatism eyes. [Zhonghua yan Ke Za Zhi] Chin J Ophthalmol. 2004;40(1):13–16.
25. Anbar M, Mohamed Mostafa E, Elhawary AM, Awny I, Farouk MM, Mounir A. Evaluation of corneal higher-order aberrations by scheimpflug–placido topography in patients with different refractive errors: a retrospective observational study. J Ophthalmol. 2019;2019.
26. Ranganathan P, Pramesh C, Buyse M. Common pitfalls in statistical analysis: clinical versus statistical significance. Perspect Clin Res. 2015;6(3):169. doi:10.4103/2229-3485.159943
27. de Ortueta D, von Rüden D, Verma S, Magnago T, Arba-Mosquera S. Transepithelial photorefractive keratectomy in moderate to high astigmatism with a non-wavefront–guided aberration-neutral ablation profile. J Refract Surg. 2018;34(7):466–474. doi:10.3928/1081597X-20180402-04
 © 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2020 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
