Back to Journals » Clinical Ophthalmology » Volume 15
One-Handed Rotational Phacoemulsification Technique
Authors Gigliola S , Sborgia G, Niro A , Palmisano C, Puzo P , Giuliani G , Sborgia L, Pastore V, Sborgia A, Alessio G
Received 16 September 2020
Accepted for publication 23 November 2020
Published 5 February 2021 Volume 2021:15 Pages 431—435
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OPTH.S281857
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Scott Fraser
Supplementary video of "One-handed rotational phacoemulsification technique" [ID 281857].
Views: 1664
Samuele Gigliola,1 Giancarlo Sborgia,1 Alfredo Niro,2 Carmela Palmisano,1 Pasquale Puzo,1 Gianluigi Giuliani,1 Luigi Sborgia,1 Valentina Pastore,1 Alessandra Sborgia,2 Giovanni Alessio1
1Eye Clinic, Depatment of Medical Science, Neuroscience and Sense Organs, University of Bari, Bari, Italy; 2Eye Clinic, Hospital “S. G. MOSCATI”, ASL TA, Taranto, Italy
Correspondence: Alfredo Niro
Eye Clinic, Hospital “S. G. MOSCATI,” ASL TA, Via per Martina Franca, Statte, Taranto, 74010, Italy
Email [email protected]
Introduction: We described a one-handed rotational phacoemulsification technique to decrease phaco time and power, and surgical stress on the cornea in eyes with different types of cataract.
Methods: In this technique a single sutureless corneal incision was made without any side-port incision. After hydrodissection and hydrodelamination were performed, a phaco tip was positioned in contact with the nucleus beside the capsulorhexis edge. By using a peristaltic pump, phacoemulsification was started with high levels of vacuum to keep the probe tip on the edge of the lens and to ensure the rotation of the nucleus, and with low ultrasound energy. The torsional mode used required less occlusion time and volume of fluid. The inclination of the tip was modified to 45-degree, directing it toward the lens center. So the nucleus was aspirated from the periphery toward the center by a rotational movement.
Results: The eye in the technical video had a NC4-NO4 cataract. The preoperative vision in this eye was 20/100 with no improvement with refraction. On postoperative day 1, visual acuity had improved to 20/20. We recorded low intraoperative parameters including ultrasound time (21.4 sec), phacoemulsification power (73%), balanced salt solution used (31 mL) and cumulative dissipated energy (7.27) at the conclusion of the case. After 1 month, Central Corneal Thickness changed from 504 μm to 516 μm, and Endothelial Cell Loss was 1.15%.
Conclusion: This technique uses a single clear corneal incision, high vacuum and low ultrasound power to reduce the exposition to excessive surgical maneuvers, fluid turbulence and ultrasound energy.
Keywords: cataract surgery, single corneal incision, one-handed phacoemulsification, phaco-rolling
Introduction
Phacoemulsification technique has become a common and effective surgical method for small-incision cataract surgery since Kelman’s invention of phacoemulsification in 1967. Different variations of surgical technique and innovations in technology made surgery safer in term of endothelial damage and more efficient in term of functional outcomes.
In the nineties, different techniques were designed including the “divide-and-conquer”1,2 and phaco-chop with its variations.3–5
Subsequently, an innovative bimanual approach called “phaco-rolling technique” for soft and medium-hard nuclear cataracts, firstly described by Gϋell et al, was defined to reduce phacoemulsification time and energy, maintaining a constant irrigation/aspiration, minimizing instrument movement within the eye and decreasing corneal distortion.6 Recently, Jardine et al described a bimanual cataract extraction using the carousel technique in the posterior chamber.7 However, this technique was dependent on the newly designed tip with a 3-port irrigation system.
These techniques used also a chopper through a corneal side port; however, the chopper can tear the anterior or posterior capsule, causing zonulysis or lens drop,8 and the creation of a corneal side port can rotate the axis of astigmatism.9
In order to avoid a side-port incision, reduce surgical manipulations and minimize ultrasound energy, we describe a one-handed rotational technique to perform phacoemulsification in the bag through a single incision for different types of cataracts.
Methods
We reported a single patient case report to describe a surgical approach for different types of cataract using a single corneal incision without any side-port access, high vacuum and low ultrasound power. We recorded machine setting for different surgical steps, intraoperative technical parameters as ultrasound time (sec), phacoemulsification power (%), balanced salt solution used (mL) and cumulative dissipated energy [total phacoemulsification time (min)×average phacoemulsification power] + [torsional time (sec)×0.4×avarage torsional amplitude (%)].
This report contains no unique identifiers and was approved by the local institutional review board. Surgical consent was obtained from the patient.
Surgical Technique
Preoperatively, the patient is treated with topical ofloxacin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID, bromfenac) three times a day for 2 days prior to surgery.
Before starting surgery, the eyelid and periorbital skin are prepared with 10% povidone-iodine. Mydriasert ophthalmic insert (combination of phenylephrine hydrochloride (5.4 mg) and Tropicamide (0.28 mg)) are preoperatively used to achieve pupil dilation. Surgery is performed under topical anesthesia. Topical 5% povidone-iodine solution is instilled before surgery and at the end of surgery. No additional equipment is required for this technique compared with traditional phaco, as the Ocular Viscoelastic Device (OVD, IAL-F® (Bausch & Lomb, Rochester, NY)) and the phacoemulsification machine (INFINITI® Vision System Alcon Laboratories, Inc, Fort Worth, Tex, US).
After surgery, a treatment consisting of corticosteroid–antibiotic combination eye drops and NSAID eye drops with tapered frequency is administered.
Steps
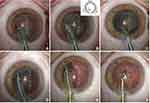
A clear corneal sutureless 2.4 mm incision is made by a precalibrated knife. No paracentesis is performed. The anterior chamber is filled with OVD. A continuous curvilinear capsulorhexis (CCC) of 5.5 mm is created with a capsulorhexis forceps. After the hydrodissection, surgeon performs the hydrodelineation with balanced salt solution (BSS®) using a flat-tip cannula. A complete rotation of the lens within the capsular bag is realized. Subsequently, a 15-degree phaco-tip is angled steeply posterior in the mid-periphery of the nucleus beside the capsulorhexis edge and in contact with the nucleus-epinucleus surface, so the nucleus is turned on its horizontal axis within the capsular bag.
High levels of aspiration (machine setting: power, 0%; vacuum, 450 mmHg; aspiration, 37 cc/min; Ozil, 100%; bottle height, 110 cm) are used to keep the probe tip occluded on the edge of the lens and to ensure the rotation of the nucleus. The surgeon modifies the inclination of the tip to 45-degree, directing it toward the lens center. During this phase, a short series of ultrasound is used to allow moving emulsified nucleus through the aspiration line. The nucleus is aspirated starting from the periphery toward the center with a rotational movement.
At the end of this phase, the endo-nucleus is aspirated in the center of the bag, far from the capsular bag. Also, the epi-nucleus is emulsified and aspirated.
At the end of phacoemulsification, the irrigation/aspiration of residual cortex is performed (machine setting: vacuum, 350 mmHg; aspiration, 30 cc/min; bottle height, 85 cm) followed by the posterior capsule polishing (machine setting: vacuum, 20 mmHg; aspiration, 10 cc/min, bottle height, 80 cm) (Figure 1). The intraocular lens (IOL) is then inserted into the capsular bag using the corresponding injector. At the end of surgery the OVD is removed (machine setting: vacuum, 600 mmHg; aspiration, 40 cc/min; bottle height, 80 cm) (Supplementary Video 1)
A solution of 0.1 mL Cefuroxime (Aprokam®) is introduced into the anterior chamber and finally the corneal incision is hydro-sutured.
Results
The patient in the Figure 1 and technical Supplementary Video 1 had a NC4-NO4 cataract (according to the Lens Opacities Classification System III). The preoperative vision in this eye was 20/100 with no improvement with refraction. Using the one-handed rotational technique, we recorded an ultrasound time of 21.4 sec, a phacoemulsification power of 73%, a quantitative of balanced salt solution used of 31 mL and a cumulative dissipated energy of 7.27 at the conclusion of the case. On postoperative day 1, visual acuity had improved to 20/20. After 1 month, Central Corneal Thickness changed from 504 µm to 516 µm, and Endothelial Cell Loss was 1.15%. No complications were reported.
Discussion
We present the one-handed rotational phacoemulsification technique that uses a single clear corneal incision, high vacuum and low ultrasound power to perform phacoemulsification.
Previously, phaco-rolling technique was tailored to reduce the excessive and repetitive surgical movements in the anterior chamber and the exposition of endothelial cells to the ultrasound energy compared with conventional technique.6,7 This technique uses a bimanual approach, the phaco-tip in one hand and the manipulator to keep the lens in a correct position during rotational movement in the other one. Moreover, in “Phaco-rolling Technique” by Guell et al6 and carouseling approach by Jardine et al7 a side-port incision was performed. To date, small incision cataract surgery is considered a refractive surgery, targeting early visual rehabilitation and emmetropia. Any incision will affect the corneal structure and alter the astigmatism. So, if side-port instrumentation could provide stability for the eye, permits greater efficiency and less turbulence, the side-port incision could influence the post-surgical astigmatism.9,10 Moreover, the side-port incision also must be well constructed and protected from damage during surgery. Inserting instruments or performing excessive manipulation through these incisions can favourite potential leakage and increase the risk of endophthalmitis.11–13 So, we designed a single-handly approach realized through a single corneal incision without any side-port incision to further reduce surgical stress on the cornea and the risk of incision-related infection without any increase of surgical manipulations in the eye. The complete hydrodissection and hydrodelamination, the correct position and inclination of the phaco-tip and the high aspiration can allow to perform surgery using a single hand. The rotation or rolling is a crucial step of this technique and care should be taken to avoid nucleus dislocation in the anterior chamber. So, the occlusion of the phaco tip should not be interrupted during the whole emulsification phase of the nucleus. A combination of phacosuction and emulsification is performed with this technique. This reduces the use of ultrasound and fluid. As reported in the above-mentioned case, phaco-rolling approach takes low intraoperative parameters as ultrasound time and power, and cumulative dissipated energy. Also, the quantitative of BSS® used was low, reducing the turbulence in the anterior chamber. It is well known that ultrasound time, ultrasound power, cumulative dissipated energy and volume of fluid used are important risk factors for endothelial cell loss after phacoemulsification.14 The fluidics control on phaco machine used prevents the collapse of the anterior chamber, so we can use high levels of vacuum and flow, and little ultrasound power. The high vacuum and flow rate increase the rotational movement and, therefore, allow the aspiration of the nucleus in a shorter time than conventional surgery. Also, the risk of capsular rupture can be limited by the continuous occlusion of the tip. Differently from previous reports by Gϋell and Jardine, we use the torsional mode combined to the Ozil IP software of the Infiniti Vision System (Alcon Laboratories, Inc.) that requires less occlusion time and BSS®, improving the efficiency and safety of the procedure.15 In the paper by Gϋell, the use of a Venturi phaco pump was strongly recommended, although it is possible to use a peristaltic pump.6 We usually work with our phaco unit (INFINITI, Alcon Surgical) using a peristaltic pump without any technical problems. Different IOLs with different design including multipiece or monobloc, plate or open-loop style, angulated or planar haptics, different optic geometry, could be placed in the capsular bag in all the eyes underwent this surgical technique. The surgeon experience and well-performed surgical maneuvers including hydrodissection and hydrodelamination, nucleus rotation and phaco-tip occlusion could limit intraoperative and postoperative complications reducing the stress on the posterior capsule, the zonule and corneal endothelium. So, we speculate that this technique could be useful for experienced surgeon to treat soft and medium-hard uncomplicated cataracts but also complex cataract due to compromised endothelium or weak zonule, myopic condition and previous vitrectomy.
Declaration of Patient Consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent forms. In the form, the patients have given their consent for images and other clinical information to be reported in the journal. The patients understand that their name and initials will not be published and due efforts will be made to conceal their identity, but anonymity cannot be guaranteed.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Gimbel HV. Divide and conquer nucleofractis phacoemulsification: development and variations. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1991;17(3):281–291. doi:10.1016/S0886-3350(13)80824-3
2. Shepherd JR. In situ fracture. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1990;16:436–440. doi:10.1016/S0886-3350(13)80796-1
3. Gimbel HV. Nuclear phacoemulsification; alternative lens in a horizontal position during rotational move methods. In: Steinert RF, editor. Cataract Surgery. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders; 1995:148–181.
4. Koch PS, Katzen LE. Stop and chop phacoemulsification. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1994;20:566–570. doi:10.1016/S0886-3350(13)80239-8
5. Linebarger EJ, Hardten DR, Shah GK, Lindstrom RL. Phacoemulsification and modern cataract surgery. Surv Ophthalmol. 1999;44:123–147.
6. Güell JL, Vázquez M, Lucena J, Velasco F, Manero F. Phaco rolling technique. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004;30(10):2043–2045. doi:10.1016/j.jcrs.2004.05.005
7. Jardine GJ, Wong GC, Elsnab JR, Gale BK, Ambati BK. Endocapsular carousel technique phacoemulsification. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011;37(3):433–437. doi:10.1016/j.jcrs.2010.12.013
8. Kamoi K, Mochizuki M. Phaco forward-chop technique for managing posterior nuclear plate of hard cataract. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010;36(1):9–12.5. doi:10.1016/j.jcrs.2009.07.047
9. Kawahara A, Kurosaka D, Yoshida A. Comparison of surgically induced astigmatism between one-handed and two-handed cataract surgery techniques. Clin Ophthalmol. 2013;7:1967–1972. doi:10.2147/OPTH.S52415
10. Theodoulidou S, Asproudis I, Kalogeropoulos C, Athanasiadis A, Aspiotis M. The role of sideport incision in astigmatism change after cataract surgery. Clin Ophthalmol. 2015;9:1421–1428. doi:10.2147/OPTH.S86213
11. Alió y Sanz JL, Fine IH. Minimizing Incisions and Maximizing Outcomes in Cataract Surgery. Springer Verlag; 2009.
12. Daoud YJ, Khan YA, Kashiwabuchi RT, et al. Prospective analysis of side port incision morphology in the early postoperative period: examining the relationship between axial length and wound gaping. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52:6236.
13. Devesh V, Iqbal IKA. Chopper and side-port incision leakage. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010;36(2):362.
14. Mahdy MA, Eid MZ, Mohammed MA, Hafez A, Bhatia J. Relationship between endothelial cell loss and microcoaxial phacoemulsification parameters in noncomplicated cataract surgery. Clin Ophthalmol. 2012;6:503–510. doi:10.2147/OPTH.S29865
15. Liu Y, Zeng M, Liu X, et al. Torsional mode versus conventional ultrasound mode phacoemulsification: randomized comparative clinical study. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007;33:287–292. doi:10.1016/j.jcrs.2006.10.044
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.