Back to Journals » International Journal of Nanomedicine » Volume 10 » Issue 1
Nanoalumina induces apoptosis by impairing antioxidant enzyme systems in human hepatocarcinoma cells
Authors Alarifi S , Ali D , Alakahtani S
Received 2 February 2015
Accepted for publication 31 March 2015
Published 25 May 2015 Volume 2015:10(1) Pages 3751—3760
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S82050
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Thomas Webster
Saud Alarifi, Daoud Ali, Saad Alkahtani
Department of Zoology, College of Science, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Abstract: Alumina nanoparticles (Al2O3NPs) are gradually used in various areas, including nanomedicine, biosensors, and electronics. The current study aimed to explore the DNA damage and cytotoxicity due to Al2O3NPs on human hepatocarcinoma cells (HepG2). The MTT and neutral red uptake assays showed that Al2O3NPs induce significant cell death in a dose- and time-dependent manner. However, Al2O3NPs induced significant intracellular reactive oxygen species production and elevated lipid peroxidation and superoxide dismutase levels in the HepG2 cells. Al2O3NPs also induced significant decrease in reduced glutathione levels and increase caspase-3 activity in HepG2 cells. DNA fragmentation analysis using the alkaline single-cell gel electrophoresis showed that Al2O3NPs cause genotoxicity in dose- and time-dependent manner. However, they induce reactive oxygen species production and oxidative stress, leading to oxidative DNA damage, a probable mechanism of genotoxicity. This study warrants more careful assessment of Al2O3NPs before their industrial application.
Keywords: HepG2 cells, Al2O3NPs, oxidative stress, MTT assay, DNA damage
Introduction
Nanotechnology is one of the fastest growing areas of technology, thus being a source of hope for many branches of modern industry, as well as for medicine and pharmacy. It has been proven that metal nanoparticles, which are inhaled or come in contact with the skin, may penetrate into the bloodstream and may subsequently be transported to various organs of the animal and human body.1 Despite the toxicological studies conducted, it remains unclear which nanomaterials manufactured on an industrial scale pose a danger to living organisms. Among the nanoparticles, alumina nanoparticles (Al2O3NPs) have been used in industrial and biomedical applications.2 Yang and Watts3 found that Al2O3NPs show a minor inhibitory effect on seed germination and root elongation in plants such as maize, cabbage, and carrot, which is no longer seen after coating the nanoparticles with phenanthrene. Recently, toxicity of Al2O3NPs has been observed in nematodes.4 Aluminum is a vital etiopathogenic agent responsible for the incidence of neurodegenerative disease.5 The response of A549 cells after exposure to different nanoparticles showed that Al2O3NPs induce a minor cytotoxic effect compared to nanometric titanium dioxide and carbon nanotubes.6
Despite the existing studies on the toxicity of Al2O3NPs, the underlying mechanism leading to toxicity remains unclear. Moreover, none of the studies so far have explored the adverse effects of Al2O3NPs in the human liver, which is the primary organ of metabolism. The workers involved in the synthesis of Al2O3NPs may be exposed by unintentional hand-to-mouth transfer of nanomaterials. Their potential toxicological impacts are still a matter of investigation, and our actual knowledge on the effects of engineered nanosized contaminants on biological systems remains incomplete.7
Free oxygen radical generation and oxidative stress elicit a wide variety of cellular events, including DNA damage and apoptosis.8 The genotoxic potential of nanomaterials is of particular concern because the changes in the genetic material have potential for cell death, tissue malfunction, cancer development, and adverse reproductive effects. Recent studies reported nanoparticle-induced oxidative stress as determined by increasing membrane lipid peroxidation (LPO) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels and decreasing intracellular reduced glutathione (GSH) level.9 We evaluated the oxidative stress biomarkers, including GSH levels; ROS generation as a collective marker of superoxide anion, hydroxyl radical, and hydrogen peroxide levels; as well as LPO, in response to Al2O3NP exposure.
Therefore, the current study was designed to assess the cellular toxicity and genotoxic potential of Al2O3NPs in human hepatocarcinoma cells (HepG2) as well as to understand its possible mechanism.
Materials and methods
Chemicals and reagents
Al2O3NPs (product number 642991 and average particle size <30–60 nm), GSH, 5,5-dithio-bis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid) (DTNB), MTT, 2,7-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA), and propidium iodide were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St Louis, MO, USA). Fetal bovine serum (FBS), penicillin–streptomycin, and Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium: nutrient mixture F-12 (DMEM/F-12 medium) were purchased from Invitrogen Co (Carlsbad, CA, USA). All other chemicals were purchased from commercial sources.
Al2O3NP preparation and characterization
Al2O3NPs were suspended in Milli-Q water at a concentration of 10 mg/10 mL. Stock suspension was sonicated at 40 W for 15 minutes. Samples for transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis were prepared by drop coating Al2O3NPs solution on carbon-coated copper TEM grids. The films on the TEM grids were allowed to dry before measurement. TEM measurements were performed on a JEOL model 2100 F instrument operated at an accelerating voltage of 200 kV.
Cell culture and exposure of Al2O3NPs
The HepG2 cell line was procured from the American Type Culture Collection (Rockville, MD, USA) and it was subcultured and used to determine the cytotoxicity of Al2O3NPs. Cells were cultured in DMEM/F-12 medium supplemented with 10% FBS and 100 U/mL penicillin–streptomycin at 5% CO2 and 37°C. At 85% confluence, cells were harvested by using 0.25% trypsin and were subcultured into 75 c 2 flasks, six-well plates, or 96-well plates according to the experiments. Cells were allowed to attach to the surface for 24 hours before treatment. Al2O3NPs were suspended in cell culture medium and diluted to appropriate concentrations (0 μg/mL, 25 μg/mL, 50 μg/mL, 150 μg/mL, and 450 μg/mL). Appropriate dilutions of Al2O3NPs were then sonicated using a sonicator bath at room temperature for 10 minutes at 40 W to avoid nanoparticle agglomeration before exposure to the cells. Cells not exposed to Al2O3NPs served as control in each experiment.
Cell morphology
Morphology of the HepG2 cells was observed using an inverted microscope (Leica DM IL) after exposure to Al2O3NPs for 24 hours and 48 hours.
MTT assay
The MTT assay was used to investigate mitochondrial function, as described by Mossman.10 Briefly, 1×104 cells per well were seeded in 96-well plates and exposed to different concentrations (0 μg/mL, 25 μg/mL, 50 μg/mL, 150 μg/mL, and 450 μg/mL) of Al2O3NPs for 24 hours and 48 hours. At the end of the exposure, culture media were replaced with new media containing MTT solution (0.5 mg/mL) and incubated for 4 hours at 37°C. As a result, formazan crystals were formed and they were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). The plates were kept on a shaker for 10 minutes at room temperature and then analyzed at 530 nm using a multiwell microplate reader (FLUOstar Omega; BMG Labtech GmbH, Allmendgruen, Germany). Untreated sets were also run under identical conditions and these served as control.
Neutral red uptake assay
The neutral red uptake (NRU) assay was done according to the method of Borenfreund and Puerner.11 After treatment with Al2O3NPs, the medium was discarded and 100 μL of neutral red dye (50 μg/mL) dissolved in serum-free medium was added to each well. After incubation at 37°C for 3 hours, cells were washed with a solution of 0.5% formaldehyde and 1% CaCl2. The accumulated dye was extracted with 50% ethanol containing 1% (v/v) acetic acid and the plates were kept for 20 minutes on a shaker. The absorbance was recorded at 540 nm using a multiwall microplate reader (FLUOstar Omega). Subsequently, DMEM without Al2O3NP-treated sets were run under identical conditions and these served as controls.
Measurement of intracellular ROS
ROS generation was assessed in HepG2 cells after exposure of different concentrations (0 μg/mL, 25 μg/mL, 50 μg/mL, 150 μg/mL, and 450 μg/mL) of Al2O3NPs by using DCFH-DA dye as the fluorescence agent.12 For fluorometric analysis, 1×104 cells per well were seeded in 96-well black bottom culture plates and allowed to adhere to them for 24 hours in a CO2 incubator at 37°C. Then, the HepG2 cells were exposed to the above concentrations of Al2O3NPs for 24 hours and 48 hours. On completion of the respective exposure periods, cells were incubated with DCFH-DA (10 mM) for 30 minutes at 37°C. The reaction mixture was aspirated and replaced by 200 μL of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) in each well. The plates were kept on a shaker for 10 minutes at room temperature in the dark. Fluorescence intensity was measured using a multiwell microplate reader (FLUOstar Omega) at excitation wavelength (485 nm) and emission wavelength (528 nm), and the values were expressed as percentage of fluorescence intensity relative to control wells.
A parallel set of cells (5×104 cells per well) was analyzed for intracellular fluorescence using upright fluorescence microscope equipped with a charge-coupled device cool camera (Nikon Eclipse 80i equipped with Nikon DS-Ri1 12.7 mega pixel camera; Nikon Corporation, Tokyo, Japan).
Oxidative stress biomarkers
Cells at a final density of ~6×106 cells per well in a 75 cm2 culture flask were exposed to 0 μg/mL, 25 μg/mL, 50 μg/mL, 150 μg/mL, and 450 μg/mL of Al2O3NPs for 24 hours and 48 hours. After exposure, the cells were scraped and washed twice with chilled PBS (1×). The harvested cell pellets were lysed in cell lysis buffer (20 mM Tris–HCl [pH 7.5], 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, disodium salt (Na2EDTA), 1% Triton, and 2.5 mM sodium pyrophosphate). The cells were centrifuged at 15,000× g for 10 minutes at 4°C, and the supernatant (cell extract) was maintained on ice until assayed for oxidative stress biomarkers. Protein content was measured by the method of Bradford,13 using bovine serum albumin as the standard.
LPO assay
The extent of membrane LPO was estimated by measuring the formation of malondialdehyde (MDA) using the method of Ohkawa et al.14 MDA is one of the products of membrane LPO. A mixture of 0.1 mL cell extract and 1.9 mL of 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) was incubated at 37°C for 1 hour. The incubation mixture, after precipitation with 5% trichloroacetic acid, was centrifuged at 2,300× g for 15 minutes at room temperature, and the supernatant was collected. Then, 1.0 mL of 1% tert-Butyl alcohol was added to the supernatant and placed in boiling water for 15 minutes. After cooling to room temperature, the absorbance of the mixture was recorded at 532 nm and expressed in nanomoles of MDA per hour per milligram protein using a molar extinction coefficient of 1.56×105/M/cm.
GSH estimation
GSH level was quantified by using Ellman’s reagent (DTNB).15 The assay mixture contained phosphate buffer, DTNB, and cell extract. The reaction was monitored at 412 nm, and the amount of GSH was expressed in terms of nanomoles of GSH per milligram protein.
Measurement of superoxide dismutase
Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity was estimated using a method described by Alarifi et al.16 The assay mixture contained sodium pyrophosphate buffer, nitroblue tetrazolium, phenazine methosulfate, reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, and the required volume of cell extract. One unit of SOD enzyme activity is defined as the amount of enzyme required for inhibiting chromogen production (560 nm) by 50% in 1 minute under assay conditions and is expressed as the specific activity in units per minute per milligram protein.
4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindolestaining for chromosome condensation
Chromosome condensation in HepG2 cells due to Al2O3NP exposure was observed by 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining. DAPI solution was used to stain the exposed cells in eight-chamber slides, and the slides were incubated for 10 minutes in the dark at 37°C. Images of the nucleus were captured using a fluorescence microscope (Nikon).
Caspase-3 assay
The activity of caspase-3 was determined from the cleavage of the caspase-3 substrate N-acetyl-Asp-Glu-Val-Asp-p-nitroaniline; p-nitroaniline was used as the standard. Cleavage of the substrate was monitored at 405 nm, and the specific activity was expressed in picomoles of the product (nitroaniline) per minute per milligram of protein.
Single-cell gel test (comet assay)
The comet assay was performed as a three-layer procedure.17 In brief, 70,000 cells per well were seeded in a six-well plate. After 24 hours of seeding, cells were treated with different concentrations of Al2O3NPs for 24 hours and 48 hours. After treatment, the HepG2 cells were trypsinized and suspended in DMEM, and the cell suspension was centrifuged at 1,200 rpm at 4°C for 5 minutes. The cell pellet was finally suspended in chilled PBS for the comet assay. Viability of cells was evaluated by the trypan blue exclusion method.17 Samples showing cell viability >84% were further processed for the comet assay. In brief, approximately 15 μL of cell suspension was mixed with 85 μL of 0.5% low-melting-point agarose and layered on one end of a frosted plain glass slide, precoated with a layer of 200 μL normal agarose (1%). Thereafter, it was covered with a third layer of 100 μL low-melting-point agarose. After solidification of the gel, the slides were immersed in lysing solution (2.5 M NaCl, 100 mM Na2EDTA, 10 mM Tris [pH 10], with 10% DMSO and 1% Triton X-100 added fresh) overnight at 4°C. The slides were then placed in a horizontal gel electrophoresis unit. Fresh cold alkaline electrophoresis buffer (300 mM NaOH, 1 mM Na2EDTA, and 0.2% DMSO, pH 13.5) was poured into the chamber and left for 20 minutes at 4°C for DNA unwinding and conversion of alkali-labile sites to single-strand breaks. Electrophoresis was carried out using the same solution at 4°C for 20 minutes at 15 V (0.8 V/cm) and 300 mA. The slides were neutralized gently with 0.4 M Tris buffer at pH 7.5 and stained with 75 μL ethidium bromide (20 μg/mL). For positive control, the HepG2 cells were treated with 100 μM H2O2 for 10 minutes at 4°C. Two slides were prepared from each well (per concentration) and 50 cells per slide (100 cells per concentration) were scored randomly and analyzed using an image analysis system (Komet-5.0; Kinetic Imaging, Liverpool, UK) attached to a fluorescence microscope (DMLB; Leica, Germany) equipped with appropriate filters. The parameters, eg, percentage tail DNA (ie, % tail DNA =100 – % head DNA), were selected for quantification of DNA damage in HepG2 cells as determined by the software.
Statistical analysis
At least three independent experiments were carried out in duplicates for each evaluation. Data were expressed as mean (± standard error of the mean) and analyzed by one-way analysis of variance. P-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
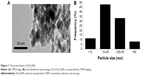
Morphology of Al2O3NPs
Figure 1A showed the typical TEM images of the Al2O3NPs. These figures exhibit that the majority of the Al2O3NPs were in spherical shape with smooth surfaces. Figure 1B shows the particle size distribution of the Al2O3NPs as determined by TEM.
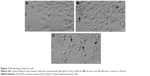
Morphological alterations of HepG2 cells
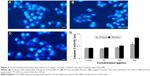
Figure 2 shows the comparative morphologies of untreated (Figure 2A) and Al2O3NP-treated HepG2 cells after 24 hours (Figure 2B) and 48 hours (Figure 2C). Cells treated with 450 μg/mL Al2O3NPs changed into spherical shape and detached from the surface (Figure 2B and C).
Al2O3NP-induced cytotoxicity in HepG2 cells
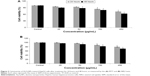
Al2O3NP-induced cytotoxicity in HepG2 cells was observed as mitochondrial function (MTT reduction) and NR uptake. MTT results are indicated as dose- and time-dependent cytotoxicity after exposure to Al2O3NPs in HepG2 cells (Figure 3A). NRU, a marker of lysosome damage, was estimated in HepG2 cells after exposure to Al2O3NPs. However, as the dose and time of Al2O3NPs exposure increased, significant cytotoxicity was recorded (Figure 3B).
Al2O3NP-induced ROS generation and oxidative stress
Induction of oxidative stress by Al2O3NPs was evaluated by determination of the ROS, LPO, GSH, and SOD levels in HepG2 cells. Results showed that Al2O3NPs induced intracellular ROS generation in a dose- and time-dependent manner (Figure 4). Al2O3NP-induced oxidative stress was further evidenced by depletion of GSH (Figure 5B) and elevation of LPO and SOD with dose and time of Al2O3NP exposure (Figure 5A and C).
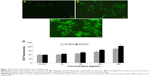
Induction of chromatin condensation and caspase-3 activity
Caspase-3 plays a key role in the apoptotic pathway of cells and it was induced after the treatment with Al2O3NPs (Figure 6D). When cells were treated with Al2O3NPs (0 μg/mL, 50 μg/mL, 150 μg/mL, and 450 μg/mL) for 24 hours and 48 hours, the activity of caspase-3 was increased in a dose- and time-dependent manner.
HepG2 cells treated with Al2O3NPs at the above-mentioned concentrations for 48 hours showed chromatin condensation (Figure 6A–C).
DNA damage
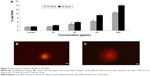
The DNA damage was measured as percentage tail DNA in control and Al2O3NP-exposed HepG2 cells. The HepG2 cells exposed to different doses of Al2O3NPs exhibited significantly higher DNA damage than control cells. The highest DNA damage in HepG2 cells was recorded at 450 μg/mL Al2O3NPs (Figure 7).
Discussion
In the current study, we have used the HepG2 cell line as it has been reported to be an excellent model to investigate mitochondrial toxicity because of its high content of organelle and mitochondrial DNA.18 Our results demonstrate that Al2O3NPs have cytotoxic and genotoxic effects on HepG2 cells. Results also revealed that the mode of cell death was apoptosis, which was mediated by the ROS-triggered mitochondrial pathway, as evidenced by cleavage of substrate by caspase-3. Before studying the genotoxicity and cytotoxicity potential of Al2O3NPs, we characterized their size range by TEM.
The size interference of nanoparticles in commonly used cytotoxicity test systems has been well reported in the literature. Monteiro-Riviere et al19 reported that cytotoxicity of nanoparticles should be assessed with two or more independent test systems for validating the findings. We have evaluated the cytotoxicity of Al2O3NPs with two different assays, namely, MTT and NRU assays, to increase the strength of our results. We found that Al2O3NPs induced cytotoxicity in a dose- and time-dependent manner.
LPO and oxidative stresses are key mechanisms of toxicity related to nanoparticles.20 Due to the small size and large surface area, nanoparticles produce ROS and oxidative stress.21 In our study, Al2O3NPs produced intracellular ROS when examined by the cell-permeable dye DCFH-DA. ROS consist of the superoxide radical, hydrogen peroxide, and hydroxyl radical, which cause damage to cellular components including DNA and ultimately lead to apoptotic cell death.22 We detected an increase in LPO and SOD, with decrease in the GSH level, which represents a marker of oxidative stress, in HepG2 cells after exposure to Al2O3NPs. LPO can give rise to more free radicals and further damage biomolecules in conjunction with ROS. Reduction of GSH in Al2O3NP-exposed cells, along with the increased level of LPO and SOD, indicates that oxidative stress may be the primary mechanism for the toxicity of Al2O3NPs in HepG2 cells. They can also lead to free radicals generation after their interaction with cells components, like mitochondrial damage. Another route by which ROS are generated is through the activation of the enzyme reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase, which is responsible for superoxide production in the membrane of phagocytic cells. When ROS generation increases or ROS defense mechanisms are compromised, cells and animals are said to be under oxidative stress.23 When free radicals come in close contact with the cellular organelles, they may oxidize macromolecules (DNA, lipids, and proteins), resulting in significant oxidative damage to cells.
SOD is one of the many antioxidant enzymes involved in protection against stress by converting superoxide to hydrogen peroxide in animals. As shown in Figure 5C, after 48-hour exposure, significant increase in SOD activity was detected in HepG2 cells exposed to 50 μg/mL–450 μg/mL of Al2O3NPs.
Nanoparticle-induced LPO and oxidative stress leads to DNA damage and apoptosis.24 Our results are reliable with our previous finding that cerium oxide nanoparticles have the potential to induce DNA damage.25 Some researchers reported that nanoparticles, due to their small size, are capable of reaching the nucleus and interacting with DNA.26 Nanoparticles may also exhibit an indirect effect on DNA through their ability to generate ROS. This DNA damage may induce carcinogenesis or cell death. We determined the genotoxic potential of Al2O3NPs in HepG2 cells by the single-cell gel test, which is capable of detecting single- as well as double-strand DNA breaks and alkali-labile sites even at low levels of DNA damage.25 ROS are involved in DNA damage, causing damage to purine and pyrimidine bases as well as the DNA backbone.27
Our results demonstrate that Al2O3NPs induce apoptosis and DNA damage in HepG2 cells, which may be mediated through ROS and oxidative stress.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their sincere appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for funding this research through the Research Group Project number RGP-180.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Sahoo SK, Parveen S, Panda JJ. The present and future of nanotechnology in human health care. Nanomedicine. 2007;3:20–31. | ||
Wagner AJ, Bleckmann CA, Murdock RC, Schrand AM, Schlager JJ, Hussain SM. Cellular interaction of different forms of aluminum nanoparticles in rat alveolar macrophages. J Phys Chem B. 2007;111: 7353–7359. | ||
Yang L, Watts DJ. Particle surface characteristics may play an important role in phytotoxicity of alumina nanoparticles. Toxicol Lett. 2005; 158:122–132. | ||
Wu S, Lu J-H, Rui Q, Yu S-H, Cai T, Wang D-Y. Aluminum nanoparticle exposure in L1 larvae results in more severe lethality toxicity than in L4 larvae or young adults by strengthening the formation of stress response and intestinal lipofuscin accumulation in nematodes. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2011;3:179–188. | ||
Halatek T, Sinczuk-Walczak H, Rydzynski K. Prognostic significance of low serum levels of Clara cell phospholipid-binding protein in occupational aluminium neurotoxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2005;99: 1904–1911. | ||
Simon-Deckers A, Gouget B, Mayne-L’Hermite M, Herlin-Boime N, Reynaud C, Carriere M. In Vitro investigation of oxide nanoparticle and carbon nanotube toxicity and intracellular accumulation in A549 human pneumocytes. Toxicology. 2008;253(1):137–146. | ||
Singh N, Manshian B, Jenkins GJ, et al. Nanogenotoxicology: the DNA damaging potential of engineered nanomaterials. Biomaterials. 2009; 30:3891–3914. | ||
Ostrovsky S, Kazimirsky G, Gedanken A, Brodie C. Selective cytotoxic effect of ZnO nanoparticles on glioma cells. Nano Res. 2009;2:882–890. | ||
Wang YG, Aker WG, Hwang HM, Yedjou CG, Yu HT, Tchounwou PB. A study of the mechanism of in vitro cytotoxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles using catfish primary hepatocytes and human HepG2 cells. Sci Total Environ. 2011;409:4753–4762. | ||
Mossman T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Meth. 1983;65:55–63. | ||
Borenfreund E, Puerner J. A simple quantitative procedure using monolayer cultures for cytotoxicity assays (HTD/NR-90). J Tissue Cult Methods. 1984;9(1):7–9. | ||
Wang H, Joseph JA. Quantifying cellular oxidative stress by dichlorofluorescein assay using microplate reader. Free Radic Biol Med. 1999; 27:612–616. | ||
Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. | ||
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem. 1979;95:351–358. | ||
Ellman G. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959;82: 70–77. | ||
Alarifi S, Ali D, Verma A, Alakhtani S, Ali BA. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of copper oxide nanoparticles in human skin keratinocytes cells. Int J Toxicol. 2013;32(4):296–307. | ||
Ali D, Ray RS, Hans RK. UVA-induced cyototoxicity and DNA damaging potential of Benz (e) acephenanthrylene in human skin cell line. Toxicol Lett. 2010;199(2):193–200. | ||
Pinti M, Troiano L, Nasi M, Ferraresi R, Dobrucki J, Cossarizza A. Hepatoma HepG2 cells as a model for in vitro studies on mitochondrial toxicity of antiviral drugs: which correlation with the patient. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2003;17:166–171. | ||
Monteiro-Riviere NA, Inman AO, Zhang LW. Limitations and relative utility of screening assays to assess engineered nanoparticle toxicity in a human cell line. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2009;234(2):222–235. | ||
Nel A, Xia T, Madler L, Li N. Toxic potential of materials at the nano level. Science. 2006;311(5761):622–627. | ||
Xia T, Kovochich M, Brant J, et al. Comparison of the abilities of ambient and manufactured nanoparticles to induce cellular toxicity according to an oxidative stress paradigm. Nano Lett. 2006;6(8):1794–1807. | ||
Ott M, Gogvadz V, Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B. Mitochondria, oxidative stress and cell death. Apoptosis. 2007;12:913–922. | ||
Huang J, Lemire BD. Mutations in the C. elegans succinate dehydrogenase iron sulfur subunit promote superoxide generation and premature aging. J Mol Biol. 2009;387:559–569. | ||
Kang SJ, Kim BM, Lee YJ, Chung H. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles trigger p53-mediated damage response in peripheral blood lymphocytes. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2008;49:399–405. | ||
Ali D, Alarifi S, Alkahtani S, AlKahtane AA, Almalik A. Cerium oxide anoparticles induce oxidative stress and genotoxicity in human skin melanoma cells. Cell Biochem Biophys. [Epub 2014 Nov 14]. | ||
Chen M, Mikecz A. Formation of nucleoplasmic protein aggregates impairs nuclear function in response to SiO2 nanoparticles. Exp Cell Res. 2005;305(1):51–62. | ||
Martinez GR, Loureiro AP, Marques SA, et al. Oxidative and alkylating damage in DNA. Mutat Res. 2003;544(2–3):115–127. |
 © 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.