Back to Archived Journals » Reports in Medical Imaging » Volume 10
Molecular imaging of integrins in oncology
Received 22 July 2016
Accepted for publication 3 November 2016
Published 31 January 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 17—30
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/RMI.S96767
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Professor Tarik Massoud
Carsten Höltke,1 Andreas Faust2
1Department of Clinical Radiology, University Hospital Münster, and 2European Institute for Molecular Imaging, University of Münster, Münster, Germany
Abstract: Integrins are a class of heterodimeric cell surface receptors with a variety of essential contributions to cell–cell and cell–extracellular matrix interactions. In particular, integrin αvβ3 plays an important role in the regulation of normal and tumor cell migration and survival, as well as in tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Its overexpression has been proved for a number of malignancies, and the level of αvβ3 expression has been recognized as a potential surrogate marker of angiogenic activity. Therefore, αvβ3 represents an important target structure in noninvasive cancer diagnosis and the evaluation of antiangiogenic therapies. One common feature of many integrins is high-affinity binding to proteins containing an Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) peptide motif, which can be found in their endogenous ligands, for example, fibronectin, vitronectin, and fibrinogen. Consequently, not only small synthetic peptides containing the RGD motif but also peptidomimetic structures based on RGD have been designed, and appropriate labeling strategies utilized them for molecular imaging approaches. This review focuses on recent advances of integrin molecular imaging in cancer diagnosis. First, clinical applications are highlighted, and then experimental approaches in preclinical research and multimodal setups are discussed.
Keywords: integrins, angiogenesis, RGD, cancer diagnostics
Introduction
Integrins are a large family of heterodimeric transmembrane proteins mediating cell–cell and cell–extracellular matrix (ECM) interactions. In mammals, there are 18 different α- and eight β-subunits that combine to form 24 different integrin subtypes, for example, fibronectin receptor α5β1, vitronectin receptor αvβ3, or lymphocyte Peyer patch adhesion molecule α4β7.1–3 Integrins regulate a number of cellular functions like cell adhesion, proliferation, and migration. Therefore, integrin activation contributes to many pathophysiological processes like tumor invasion, metastasis, and angiogenesis, the process of blood vessel formation from existing vasculature, which in cancer is up- or dysregulated.4 This is achieved by complex manipulation of signaling cascades, for example, vascular endothelial growth factor and chemokine receptor CXCR4 communication pathways, which trigger vascular sprouting and tumor dissemination. While integrins expressed on endothelial cells are responsible for the regulation of cell motility and survival, those integrins on carcinoma cells increase the metastatic potential of the tumor by facilitating invasion and tumor cell infiltration. The effects of different expression levels of integrin subtypes on clinical parameters have been described, for example, for breast, prostate, pancreatic, and cervical cancers; a recent overview summarizes the biological background and therapeutic options.5–9
Several integrins have been demonstrated to bind the Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) motif, an arginine-glycine-aspartic acid-based peptide sequence, which is typically found in a number of ECM proteins like fibronectin or vitronectin. Especially, integrins known to be highly active in tumor neoangiogenesis, such as αvβ3 and α5β1, display a high affinity to RGD.10,11 In this context, most approaches toward the evaluation of integrin expression in cancer imaging imply labeled RGD-based peptides. Of the possible imaging modalities especially scintigraphic techniques like positron emission tomography (PET) and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) have been used for the delineation of integrin expression, and also optical imaging is very frequently used, especially in preclinical settings. In addition, nanoconstructs for magnetic resonance (MR) imaging or even for multimodal techniques have been developed.12–16 First, clinical studies employing novel RGD-based scintigraphic probes focus on safety issues, comparability to standard-of-care diagnostics, and the possibility to monitor antiangiogenic therapies. Figure 1 shows the number of publications dealing with integrin imaging in different contexts in the last few decades. Interestingly, it shows stagnation or even a decline during the last 5 years. This trend could be observed for most molecular imaging topics and might display a typical example of the Gartner hype cycle.17 It probably reflects that after a first run for the development of new tracer entities, a more thorough evaluation of the most promising compounds is presently underway, with a clear focus on future clinical applications.
  | Figure 1 Number of papers per year as extracted from PubMed/Medline using the query terms displayed (date of inquiry: June 15, 2016). Abbreviation: RGD, Arg-Gly-Asp. |
During the last years, a number of comprehensive review articles have been published.12,18–20 This review focuses on recent advances of integrin molecular imaging for cancer diagnosis. First, clinical applications are highlighted, and experimental approaches in preclinical research and multimodal setups are also discussed.
Preclinical laboratory applications
MR imaging
MR imaging of pathophysiological integrin expression was first reported in 1998. The authors analyzed syngeneic V2 carcinomas in New Zealand White rabbits and FaDu human squamous cell carcinoma xenografts in mice by using antibody-conjugated paramagnetic liposomes. Data were acquired from a human 3T MR scanner; the reported signal enhancement in rabbits was very promising (twofold for isotype-matched controls and tenfold for avidin-labeled control liposomes) and the authors speculated that in future applications the “use of Fab fragments or of peptide or small molecule ligands” may be the method of choice.15 Since then, only few examples of molecular imaging approaches not using RGD-based peptides as the targeting vector have been described. In a report from 2008, a non-peptidic RGD mimetic probe coupled to diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid (DTPA) as Gd-chelator is presented. This compound was able to delineate vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques in ApoE-deficient mice and was suggested for potential future use in other pathologies like cancer.21 However, the majority of achievements among the recently published examples deal with peptidic RGD compounds. Kazmierczak et al22 present an MR relaxometry study with an RGD-peptide-decorated ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle (USPIO) to monitor bevacizumab therapy of breast cancer xenografts (MDA-MB 231) in nude mice. They found a significantly reduced ΔR2 value in the therapy group, indicating that RGD-USPIO magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be applicable for the in vivo monitoring of early antiangiogenic therapy effects in cancer stratification.22 Recent literature describes (nano)constructs that are designed to serve more than one imaging modality or target more than one molecular structure. Xin et al synthesized a single-domain antibody Gd-DTPA construct targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor fused with an RGD peptide and imaged BGC823 tumor xenografts in mice.23 Li et al developed a synthetic dendrimer nanoprobe decorated with RGD peptides, a Gd-chelator for MR imaging, and a fluorescent dye for optical imaging and employed the probe for the visualization of liver fibrosis in thioacetamide-treated mice. A significant enhancement of MR signal could be observed in fibrotic tissue at 24 h postinjection and fluorescent imaging of hepatic sections showed good co-localization of the probe with β3 integrin (CD61), α-SMA, and CD31 on vascular structures.24 Elaborate synthetic work has been put into the fabrication of dedicated gold nanoparticles (AuNPs), since these possess unique physical and chemical properties, making them ideal tools for a variety of biomedical applications.25 For example, their use in computer tomography has been reported.26 Chen et al reported the synthesis of dendrimer-coated AuNPs decorated with RGD peptides and Gd-chelators for computed tomography (CT) and MR imaging applications.27 Human U87MG glioblastoma cells showed good tolerance up to 100 µM AuNPs and competition studies with free RGD peptide and receptor-negative cells proved specificity. In vivo, the probe enabled targeted dual-modality CT/MR imaging of a U87MG xenograft tumor model. Recent effort has also shown the potential of AuNPs as radiosensitizers in tumor therapy. Yang et al developed a number of differently sized particles and targeted them to αvβ3 integrin-expressing tumor xenografts in mice by conjugating RGD peptides to the surface. Additional functional modifications enabled 99mTc- and Gd-labeling, and thus SPECT- and MR-based imaging.28 So far, clinical applications of integrin-targeted MR imaging for cancer diagnosis have not been reported. This is because the clinical use of nanoparticles is considered rather skeptical and numerous challenges have to be faced to introduce new nanoparticle-based compounds to the market and into routine clinical practice.29 However, novel functional MR imaging methods serve as a valuable tool for the evaluation of antiangiogenic therapy effects on tumor blood volume, vascularization, and vessel size.30,31
Scintigraphic imaging
Several reviews have been published in the last few years focusing on RGD-based strategies to target αvβ3 integrin in radionuclide-based tumor imaging. Tracer development for SPECT and PET mainly yielded various derivatives of RGD peptides to optimize their biological characteristics, including affinity, targeting efficacy, and pharmacokinetics.20,32,33 Also, special compounds like multivalent RGD-based PET tracers or multimodality probes and labeling with a number of diagnostic or therapeutic nuclides show that αvβ3 is in fact one of the best evaluated diagnostic targets in molecular imaging.34 One impressive example is an approach combining targeted alpha particle therapy with Cerenkov luminescence imaging (CLI) using the theranostic probe [225Ac]DOTA-c(RGDyK). In vivo biodistribution studies confirmed the ability of the compound to target αvβ3 integrin with high specificity. Also, results confirm that CLI with certain α-emitting radiopharmaceuticals is possible in live animals for the evaluation of tracer distribution.35 Until now, the most promising SPECT tracer seems to be [99mTc]3PRGD2, which is extensively used in tumor imaging studies and is well evaluated by different groups with a clear clinical perspective (see Clinical applications).36 Nowadays, one main focus of investigations lies on the biodistribution of compounds, and a study by Yan et al demonstrated that [99mTc]3PRGD2 is predominantly renally excreted but only rarely hepatobiliary.37 The high activity in the kidneys could make it difficult to detect metastases within or close to these organs, as reported by [18F]FDG imaging.38 An expected improvement by trimerization of the peptide ([99mTc]4PRGD3) showed almost identical tumor uptake and similar biodistribution patterns, but with better metabolic stability compared to [99mTc]3PRGD2.39
Guo et al developed a simultaneous dual-isotope SPECT/CT imaging method to assist diagnosis of hepatic tumor and liver fibrosis. Achieving sufficiently low background, it was possible to use the radioiodinated liver-specific probe [131I]NGA for liver function and [99mTc]3PRGD2 for tumor lesions and fibrotic liver tissues in one measurement with a clear discrimination as shown in Figure 2.40
  | Figure 2 In the 99mTc-window, for tumorous mice (B), activity is found in tumor and kidney. While for normal mice (A), no tumor lesion was found. In the 131I-window, high accumulation of [131I]NGA in residual normal liver parenchyma was achieved. Copyright © Guo Z, Gao M, Zhang D, et al. Simultaneous SPECT imaging of multitargets to assist in identifying hepatic lesions. Sci Rep. 2016;6:28812. Creative Commons license and disclaimer available from: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/legalcode. Abbreviations: max, maximum; min, minimum. |
PET radiopharmaceuticals for imaging integrin expression were extensively reviewed by Haubner and Liu.12,19 First clinical studies described in the second part of this review already show very promising results. A strategy to improve tracer kinetics is the utilization of homodimeric or -trimeric RGD-based compounds, thereby enhancing the local RGD concentration and hence the target affinity. This concept was introduced by Maheshwari in 2000 concerning RGD ligand clustering approaches in vitro.41 The translation of this strategy toward imaging applications has been described by Tumshirn and Kessler in 2003.42 During the last 2 years, some modifications in the molecular architecture of the RGD-based tracers have been described. One evaluated compound is the symmetric, homodimeric peptide PEG2-β-Glu-RGD2, labeled with fluorine-18 via conjugation with 4-nitrophenyl-2-18F-fluoropropionate. Hu et al found a high tumor uptake and good tumor-to-background contrast in murine PC-3, A549, and C6 tumor models.43 However, the compound did not show any improvement compared to a similar, established tracer ([18F]FPPRGD2, see Clinical applications) concerning metabolic behavior or background signal.43 This study shows that minor structural modifications can easily be applied to successful compounds, yielding similar imaging results but no improvement or progress in the field.
One novel peptidic tracer was introduced by He et al based on tumstatin (T7 and T7-6H), an antiangiogenic and proapoptotic peptide fragment from collagen IV, which binds integrin αvβ3 independent from an RGD sequence. They labeled the peptide T7 and its derivative T7-6H with 99mTc and evaluated their biological distribution in vivo in a subcutaneous NCI-H157 lung cancer model, which again yielded reasonable tumor-to-background ratios in SPECT experiments. Unfortunately, they neither identified the precise binding mode of the radiometal, nor did they show any animal images; so it is hard to compare the potency of the method with the existing SPECT tracers.44
The fibronectin receptor, integrin α5β1, has also been the subject of a number of recent studies and might become a promising prognostic biomarker for cancer patients. Jin et al functionalized an α5β1-specific fibronectin-mimetic peptide and radiolabeled it with fluorine-18 based on the chelation of 18F-aluminum fluoride.45 Imaging and biodistribution studies suggested higher uptake of the tracer in α5β1-positive than in α5β1-negative tumors. Notni et al46 recently introduced [68Ga]aquibeprin, a multimeric RGD mimetic, as an α5β1-specific PET-imaging probe. Together with the RGD peptide-based [68Ga]avebetrin, it constitutes a perfectly matched pair of α5β1/αvβ3 integrin ligands for in vivo quantification of the different expression patterns of these target structures.46 Furthermore, they hypothesize that high uptake in small tissue compartments requires radiopharmaceuticals possessing both high target affinity and high specific activity as a key for molecular imaging and effective radionuclide therapy of small-sized tumor lesions, such as micrometastases.47
Optical imaging
Optical imaging developments targeting integrins produced a huge variety of imaging probes during the last decade. Ye and Chen published an extensive review in 2011.16 Since then, one main focus was to enforce the optical probes to human application. Besides optimization of pharmacokinetic behavior by changing the structural properties of dyes, different hybrid techniques were developed for intraoperative identification of tumor lesions in image-guided surgery. One example is the intraoperative delineation of microfoci of hepatocellular carcinoma with RGD-conjugated mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with indocyanine green that could accurately visualize liver lesions and provide high tumor-to-muscle contrast.48 Liu et al recently performed an in vivo toxicology study on an IRDye800cw-conjugated cyclic RGD peptide. The blood test and the histological analysis demonstrated that no obvious toxicity was found for mice treated with the compound for 2 weeks.49 Another interesting RGD-based approach was introduced by Yao et al. It is known that lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) is an effective biomarker for early stage ovarian carcinoma (cutoff values ≥1.5 μM).50 For early diagnosis, the authors combined a near-infrared (NIR) fluorescent probe, that can selectively respond to LPA based on polarity-sensitive emission, with two RGD units targeting the αvβ3 integrin receptor. The probe has high biocompatibility and pH stability and its NIR turn-on fluorescence can be used to effectively monitor LPA imaging in a SKOV-3 tumor-bearing mouse model (Figure 3).51
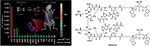  | Figure 3 The fluorescence response of G4RGDSq2 (10 μM) at 720 nm upon the addition of various species underlines the high specificity and corresponding in vivo measurements of xenograft tumor mice without inhibitor treatment show a nice turn on fluorescence monitoring LPA (A). Copyright © American Chemical Society. Reproduced with permission from Near-infrared fluorogenic probes with polaritysensitive emission for in vivo imaging of an ovarian cancer biomarker. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(9):5847–5856.51 The chemical structure of G4RGDSq2 is displayed (B). Reproduced from Yao D, Lin Z, Wu J. Near-infrared fluorogenic probes with polaritysensitive emission for in vivo imaging of an ovarian cancer biomarker. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(9):5847–5856.51 Abbreviation: LPA, lysophosphatidic acid. |
Also, novel peptidomimetic optical probes were successfully developed. Alsibai et al introduced a non-peptidic fluorescent tracer with high affinity to αvβ3 integrin and high selectivity with respect to platelet fibrinogen receptor αIIbβ3. In vivo experiments with murine xenograft models of high αvβ3 integrin expression showed a clear accumulation in the tumor region with very good tumor-to-muscle contrast.52 For deep tissue vasculature imaging in angiogenesis, RGD-labeled probes can also be excited via two-photon absorption for the enhancement of tissue image quality. Yue et al synthesized RGD conjugates with new NIR-emitting pyranyl fluorophore derivatives enabling two-photon fluorescence microscopy. Detection of fluorescence emission was observed as deep as 350 μm, with good resolution of tumor vasculature.53
In terms of imaging depth and resolution, photoacoustic imaging becomes more appealing. Very recently, Zhang et al reported photoacoustic molecular imaging of integrin αvβ6-positive xenografts. The Atto740-labeled cysteine knot peptide probe A740-R01 enabled imaging of integrin αvβ6-positive tumors by both photoacoustic and fluorescence imaging and showed a good tumor uptake.54 Since most of the RGD-based imaging probes yield reasonable tumor-to-background ratios with a clear demarcation of tumor tissue, a combination with therapeutic approaches seems conceivable. One recent example by Luan et al demonstrates that a phthalocyanine-conjugated RGD peptide exhibits significantly high cellular uptake in αvβ3-positive DU145 prostate cancer cells along with efficient photocytotoxicity after irradiation with NIR light (photodynamic therapy).55 Due to extensive knowledge about RGD-based probes and integrin expression in preclinical animal models, the RGD motif has also been used as a tool for improving fluorescent probes. To reduce the dye-related background signal, Choi et al developed new NIR dyes for optimized optical imaging.56 The new zwitterionic dye ZW800-1 was conjugated to cyclic RGD and tested in different murine tumor models and showed a clear improvement of the signal-to-background ratio. Also, recently, Bunschoten et al extensively tested different new dyes on a hybrid RGD tracer for optical and PET or SPECT imaging and got comparable results.57
Ultrasound (US) imaging
US is a noninvasive and inexpensive imaging methodology and can be used to examine preclinical models of tumor angiogenesis very easily. In addition, Doppler US can be used to estimate blood flow and blood volume and contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) employing microbubbles can provide additional information about tumor vascularity. Microbubbles labeled with agents that bind to angiogenic markers such as αvβ3 are useful tools for the molecular imaging of tumor angiogenesis. Targeting of microbubbles can be accomplished by conjugation of ligands, antibodies, or peptides to the microbubble surface. Targeted US imaging of integrin αvβ3 for the evaluation of tumor angiogenesis has been successfully demonstrated by Ellegala et al.58 Rats with orthotopically implanted U87MG human glioma tumors were imaged with CEUS using microbubbles coated with echistatin, an RGD-based disintegrin from the viper Echis carinatus.59 The highest signal was observed after 4 weeks of tumor growth at the margin of the lesions where integrin expression was enhanced as confirmed by immunohistochemistry. Recently, Hu et al showed that RGD-coated microbubbles can be used to delineate αvβ3 integrin expression in a murine model of tumor angiogenesis.
The authors labeled microbubbles with RGD peptides via biotin–avidin conjugation to quantify dynamic changes in αvβ3 integrin expression at different stages of tumor growth in human laryngeal carcinoma xenografts. Interestingly, the intensities of the targeted CEUS signals decreased as tumor size increased (Figure 4). The authors argue that the secretion of pro-angiogenic growth factors and proteolytic enzymes in early fast growing tumors highly upregulates both sprouting and intussusceptive angiogenesis, while in larger stabilized tumors intussusceptive angiogenesis predominates.60
  | Figure 4 Transverse color-coded ultrasonography after intravenous administration of RGD microbubbles obtained at three different tumor stages of subcutaneous Hep-2 tumor xenografts. (A) Small tumor (50–150 mm3). (B) Medium tumor (151–250 mm3). (C) Large tumor (>250 mm3). Green represents targeted ultrasound signals from adherent RGD-microbubbles. Reproduced from Hu Q, Wang XY, Kang LK, Wei HM, Xu CM, Wang T, Wen ZI. RGD targeted ultrasound contrast agent for longitudinal assessment of Hep-2 tumor angiogenesis in vivo. PLoS One. 2016;11(2):e0149075. Creative Commons license and disclaimer available from: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/legalcode. Abbreviation: RGD, Arg-Gly-Asp. |
All molecular imaging modalities used for the presented examinations have both advantages and disadvantages. Since there are already dedicated imaging devices for small animals covering the whole modality portfolio, there has to be a substantial initial investment. MRI technology is by far the most expensive equipment acquisition, followed by PET, SPECT, and CT devices. Albeit, one has to keep in mind that the latter techniques demand diverse radiation protection measures, which are also costly. In comparison, US and optical imaging devices are rather inexpensive and do not entail costly safety measures. More details about advantages and disadvantages of the different modalities are summarized in Table 1; a summary of compounds and constructs used in diverse preclinical imaging approaches in recent years can be found in Figure 5.
Clinical applications
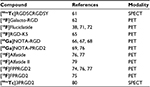
In recent years, a number of integrin-targeted probes have been applied for initial human studies. All of them are RGD-based constructs and many are focusing oncological issues. A short summary is listed in Table 2.
  | Table 2 Compounds applied in human studies Abbreviations: PET, positron emission tomography; SPECT, single-photon emission computed tomography. |
The first integrin-targeting scintigraphic tracer used in clinical studies was a 99mTc-labeled synthetic RGD peptide, which was used for the visualization of metastatic melanoma. Sivolapenko et al were able to identify 77.3% of neoplastic sites in a cohort of 14 patients with a number of differently localized metastases.61
Haubner et al introduced [18F]galacto-RGD as an integrin-targeting PET tracer with improved pharmacokinetic properties and presented first data from eight cancer patients with metastatic melanoma and sarcoma. Their study revealed high interindividual and intraindividual variances in tracer accumulation in the different lesions, indicating profound heterogeneity in target expression. Also, in some lesions, no [18F]galacto-RGD signal indicated αvβ3 expression, although [18F]FDG uptake in tumor cells was detected.62 This was confirmed in a later study with 18 patients with metastatic lesions, suggesting that αvβ3 expression and tumor viability are not closely linked in malignant tumors (Figure 6).63
  | Figure 6 Comparison between [18F]galacto-RGD and [18F]FDG in two patients, emphasizing the high interindividual and intraindividual variances in tracer accumulation. (A) Patient with NSCLC of left upper lobe (arrow, closed tip) and multiple metastases to bone (arrow, open tip), liver, lymph nodes, and adrenal glands. Note intense uptake in all lesions in MIPs of [18F]FDG PET, whereas uptake in lesions in MIPs of [18F]galacto-RGD PET is substantially lower. (B) Patient with neuroendocrine tumor of bronchus in right lower lobe (arrow, closed tip) and multiple metastases to bone (arrows, open tip), liver, spleen, and lymph nodes. This patient shows more intense uptake in lesions on [18F]galacto-RGD PET compared with that of [18F]FDG PET. This research was originally published in JNM. Beer AJ, Lorenzen S, Metz S, et al. Comparison of integrin alphaVbeta3 expression and glucose metabolism in primary and metastatic lesions in cancer patients: a PET study using 18F-galacto-RGD and 18F-FDG. J Nucl Med. 2008;49(1):22–29. © by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, Inc.63 Abbreviations: PET, positron emission tomography; MIP, maximum intensity projection; NSCLC, non-small-cell lung cancer. |
In a later study with patients suffering from metastatic prostate cancer (n=12), Beer et al discovered that [18F]galacto-RGD uptake in bone metastases was also very heterogeneous with high intra- and inter-patient variability, suggesting highly varying differences in target expression in the examined lesions. They concluded that [18F]galacto-RGD is therefore inferior to conventional bone scintigraphy, at least in the selected patient cohorts.64
A number of other tracers for especially PET imaging of αvβ3 expression have since been used in first clinical applications (Figure 7), including 18F- and 68Ga-labeled compounds ([18F]fluciclatide, [18F]RGD-K5,65 [68Ga]NOTA-RGD,66–68 [68Ga]NOTA-PRGD2,69 [18F]FPPRGD2, and [18F]alfatide).
[18F]Fluciclatide is a cyclic RGD-based peptide with two small polyethylene glycol modifiers for the improvement of pharmacokinetic properties. It was first described by Indrevoll et al in 2006.70 In 2008, a phase I clinical trial in seven patients with metastatic breast cancer proved the safety of the compound, its metabolic stability, and the retention of radioactivity in all anatomical lesions.38 Recently, Mena et al71 showed that melanoma and renal cell carcinoma can be very well visualized by this PET agent (Figure 8). They evaluated 18 patients with solid tumors ≥2.0 cm. Additionally, all patients underwent surgery and tumor tissue immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis for αvβ3 and αvβ5 integrins showed a rather moderate correlation between PET/CT and IHC with r values between 0.40 and 0.63.71
  | Figure 8 [18F]Fluciclatide PET/CT images of a right kidney tumor (arrows) in a patient. Axial (A), sagittal (B), and coronal (C) images show abnormally increased uptake of [18F]fluciclatide within the tumor (SUV80% max 8.9). A renal tumor with a chromophobe component was confirmed by pathology. © Springer-Verlay Berlin Heidelberg 2014. Reproduced from Mena E, Owenius R, Turkbey B, et al. [(18)F]fluciclatide in the in vivo evaluation of human melanoma and renal tumors expressing alphavbeta 3 and alpha vbeta 5 integrins. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014;41(10):1879–1888. With permission of Springer.71 Abbreviations: PET, positron emission tomography; CT, computed tomography. |
The test–retest reproducibility of [18F]fluciclatide imaging of solid tumors, including breast and colorectal cancer lesions, was investigated in a multicenter study on 39 lesions from 26 patients. A well tolerable repeatability was described, but it was also emphasized that not all tumors could be visualized on [18F]fluciclatide PET scans compared with standard-of-care imaging.72 Very recently, Kim et al68 presented a study with [68Ga]NOTA-RGD, in which they looked for the comparability of PET/CT with dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) MRI in 44 breast cancer patients. The patients were prospectively enrolled and underwent [68Ga]NOTA-RGD PET/CT and DCE-MRI imaging before neoadjuvant chemotherapy and surgery. Ten patients experienced recurrent disease after a median time of 1.5 years. The authors found that pretreatment [68Ga]NOTA-RGD PET/CT as well as DCE-MRI offered significant prognostic values for the prediction of disease free survival in these patients. Among the studied parameters, regional maximum standardized uptake values (SUVmax) values showed significance, and it had a complementary value with the enhancement index (EImax) from DCE-MRI. The authors therefore concluded that [68Ga]NOTA-RGD PET/CT provided additional value compared with conventional DCE-MRI parameters.68 Already as in 2003, Thumshirn et al showed that by using constructs containing multimeric RGD peptides, the affinity toward integrins could be markedly improved (see section Preclinical laboratory applications/Scintigraphic imaging).42 The first developed tracers, for example, [18F]FPPRGD2, however, demanded multistep, time-consuming synthetic procedures, which made routine clinical investigations rather limited.73 In a pilot study, six patients suffering from cervix and ovarian carcinoma were monitored with [18F]FPPRGD2 and [18F]FDG before and after therapy containing bevacizumab, an antiangiogenic drug.74 Of these six patients, only four could finally be completely analyzed, bearing a total of 33 lesions. In this study, it could be shown that bevacizumab-containing therapy did not influence [18F]FPPRGD2 uptake in normal organs, but did alter tracer uptake in the lesions. Furthermore, changes in [18F]FPPRGD2 uptake at 1 week after treatment could be linked to therapy prognosis. Additionally, the authors could prove the independence of [18F]FPPRGD2 and [18F]FDG imaging outcome in these cancer patients, as has been shown by others also.63 A very similar tracer, [18F]FPRGD2, in combination with [18F]FDG, has been employed in a study to monitor the effect of combined chemo-radiotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer patients. After evaluating 32 enrolled patients, the investigators found that although all the lesions were visualized, the intensity of [18F]FPRGD2 uptake was significantly lower than that of [18F]FDG and concluded that the specificity of the tracer was too low for further evaluation as a routine clinical tracer.75 Novel and faster synthetic procedures applied chelation chemistry and allowed radiotracer preparation without the need of high-performance liquid chromatography purification. These resulted in the development of 68Ga-labeled multimeric RGD derivatives, for example, [68Ga]NOTA-PRGD2,69 and, especially, of 18F-fluoride-aluminum complexes for the labeling of peptides.76,77 The corresponding multimeric RGD tracers, denoted [18F]alfatide and [18F]alfatide II, have both been applied in first clinical studies. [18F]Alfatide has been used in 26 patients with suspected lung cancer and was able to recognize lesions in 17 patients, four patients were found true negative, and five patients were false positive.78 Mi et al reported an investigation of 30 patients suspected of different types of bone metastases including osteolytic, osteoblastic, mixed, and bone marrow metastases, in comparison with [18F]FDG PET. Of these, 25 patients were diagnosed to have malignancies. Eleven of them were confirmed to have metastatic bone lesions. The results demonstrated that [18F]alfatide II PET/CT had comparable detection efficiency as [18F]FDG for osteolytic and mixed bone metastases, whereas it was superior to [18F]FDG PET/CT in the detection of especially osteoblastic lesions.79 In another study, the authors used [99mTc]3PRGD2 as the tracer for SPECT imaging of bone metastases in patients with lung cancer and compared the imaging accuracy to imaging with the conventional [99mTc]MDP tracer (Figure 9). It showed that although [99mTc]MDP imaging had better contrast in most lesions, the [99mTc]3PRGD2 tracer was more effective to exclude pseudo-positive lesions and detect bone metastases without osteogenesis. This resulted in better positive and negative predictive values (97.6% vs 89.7% ppv [positive predictive values] and 75% vs 56% npv [negative predictive values]) for the integrin imaging agent.80 These findings are in contrast to those from Beer et al described earlier, using the monomeric [18F]galacto-RGD tracer in comparison with [18F]FDG.64
  | Figure 9 Comparison of [99mTc]3PRGD2 with [99mTc]MDP imaging in a patient with multiple bone metastases. (A) [99mTc]3PRGD2 imaging showed the primary lesion (green arrow), lymph node metastases (blue arrow), and bone metastases (red arrow) at the same time. One hour images showed better results than 4 h images because of the lower background in bone marrow, liver, kidneys, and spleen. (B) [99mTc]MDP bone scan demonstrated better contrast, facilitating the detection of small bone lesions. However, [99mTc]MDP accumulated with lower specificity. Reproduced from Miao W, Zheng S, Dai H, et al. Comparison of 99mTc-3PRGD2 integrin receptor imaging with 99mTc-MDP bone can in diagnosis of bone metastasis in patients with lung cancer: a multicenter study. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e111221. Creative Commons license and disclaimer available from: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/legalcode. |
Conclusion
The concept of imaging integrin expression in the angiogenic context of tumor progression came into focus a number of years ago. First attempts used antibodies targeted at diverse integrins, but soon RGD-based peptides replaced these antibodies and the main interest focused on integrin αvβ3. All the probes applied in human investigations are RGD-based peptides labeled with radionuclides for PET or SPECT imaging. They are rather small (<3 kD) and therefore rapidly distributed and excreted, which is an advantage for this kind of imaging. In addition, a large number of nanoconstructs have been designed and developed, mainly for multimodal approaches (eg, MR and optical imaging) and thus are dedicated only to preclinical settings. The clinical translation of such probes, however, is limited by mendable pharmacokinetic behavior and unclear long-term toxicity.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from the Deutsche Forschungs-gemeinschaft, DFG SFB 656 “Cardiovascular Molecular Imaging,” projects A04, A09, and A10 and the Excellence Cluster “Cells in Motion” (CiM), project B5 (FF-2013-10).
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Pierschbacher MD, Ruoslahti E. Cell attachment activity of fibronectin can be duplicated by small synthetic fragments of the molecule. Nature. 1984;309(5963):30–33. | ||
Ruoslahti E, Pierschbacher MD. New perspectives in cell adhesion: RGD and integrins. Science. 1987;238(4826):491–497. | ||
Hynes RO. Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell. 2002;110(6):673–687. | ||
Brooks PC, Clark RA, Cheresh DA. Requirement of vascular integrin alpha v beta 3 for angiogenesis. Science. 1994;264(5158):569–571. | ||
Sloan EK, Pouliot N, Stanley KL, Chia J, Moseley JM, Hards DK, Anderson RL. Tumor-specific expression of alphavbeta3 integrin promotes spontaneous metastasis of breast cancer to bone. Breast Cancer Res. 2006;8(2):R20. | ||
McCabe NP, De S, Vasanji A, Brainard J, Byzova TV. Prostate cancer specific integrin alphavbeta3 modulates bone metastatic growth and tissue remodeling. Oncogene. 2007;26(42):6238–6243. | ||
Hosotani R, Kawaguchi M, Masui T, et al. Expression of integrin alphaVbeta3 in pancreatic carcinoma: relation to MMP-2 activation and lymph node metastasis. Pancreas. 2002;25(2):e30–e35. | ||
Gruber G, Hess J, Stiefel C, et al. Correlation between the tumoral expression of beta3-integrin and outcome in cervical cancer patients who had undergone radiotherapy. Br J Cancer. 2005;92(1):41–46. | ||
Desgrosellier JS, Cheresh DA. Integrins in cancer: biological implications and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10(1):9–22. | ||
Mahabeleshwar GH, Feng W, Phillips DR, Byzova TV. Integrin signaling is critical for pathological angiogenesis. J Exp Med. 2006;203(11):2495–2507. | ||
Garmy-Susini B, Varner JA. Roles of integrins in tumor angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Lymphat Res Biol. 2008;6(3–4):155–163. | ||
Haubner R, Maschauer S, Prante O. PET radiopharmaceuticals for imaging integrin expression: tracers in clinical studies and recent developments. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:871609. | ||
Bolley J, Lalatonne Y, Haddad O, Letourneur D, Soussan M, Pérard-Viret J, Motte L. Optimized multimodal nanoplatforms for targeting alpha(v)beta3 integrins. Nanoscale. 2013;5(23):11478–11489. | ||
Melemenidis S, Jefferson A, Ruparelia N, et al. Molecular magnetic resonance imaging of angiogenesis in vivo using polyvalent cyclic RGD-iron oxide microparticle conjugates. Theranostics. 2015;5(5):515–529. | ||
Sipkins DA, Cheresh DA, Kazemi MR, Nevin LM, Bednarski MD, Li KC. Detection of tumor angiogenesis in vivo by alphaVbeta3-targeted magnetic resonance imaging. Nat Med. 1998;4(5):623–626. | ||
Ye Y, Chen X. Integrin targeting for tumor optical imaging. Theranostics. 2011;1:102–126. | ||
Fenn J, Raskino M. Mastering the Hype Cycle. Boston, MA: Harvard Business Press; 2008. | ||
Chen H, Niu G, Wu H, Chen X. Clinical Application of radiolabeled RGD peptides for PET imaging of integrin alphavbeta3. Theranostics. 2016;6(1):78–92. | ||
Liu S. Radiolabeled cyclic RGD peptide bioconjugates as radiotracers targeting multiple integrins. Bioconjug Chem. 2015;26(8):1413–1438. | ||
Zhou Y, Chakraborty S, Liu S. Radiolabeled cyclic RGD peptides as radiotracers for imaging tumors and thrombosis by SPECT. Theranostics. 2011;1:58–82. | ||
Burtea C, Laurent S, Murariu O, et al. Molecular imaging of alpha v beta3 integrin expression in atherosclerotic plaques with a mimetic of RGD peptide grafted to Gd-DTPA. Cardiovasc Res. 2008;78(1):148–157. | ||
Kazmierczak PM, Schneider M, Habereder T, et al. Alpha(v)beta(3-Integrin-targeted magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of early antiangiogenic therapy effects in orthotopic breast cancer xenografts. Invest Radiol. 2016;51(11):746–755. | ||
Xin X, Sha H, Shen J, Zhang B, Zhu B, Liu B. Coupling GdDTPA with a bispecific, recombinant protein antiEGFRiRGD complex improves tumor targeting in MRI. Oncol Rep. 2016;35(6):3227–3235. | ||
Li F, Yan H, Wang J, et al. Non-invasively differentiating extent of liver fibrosis by visualizing hepatic integrin alphavbeta3 expression with an MRI modality in mice. Biomaterials. 2016;102:162–174. | ||
Dykman L, Khlebtsov N. Gold nanoparticles in biomedical applications: recent advances and perspectives. Chem Soc Rev. 2012;41(6):2256–2282. | ||
Ahn S, Jung SY, Lee SJ. Gold nanoparticle contrast agents in advanced X-ray imaging technologies. Molecules. 2013;18(5):5858–5890. | ||
Chen Q, Wang H, Liu H, et al. Multifunctional dendrimer-entrapped gold nanoparticles modified with RGD peptide for targeted computed tomography/magnetic resonance dual-modal imaging of tumors. Anal Chem. 2015;87(7):3949–3956. | ||
Yang Y, Zhang L, Cai J, et al. Tumor angiogenesis targeted radiosensitization therapy using gold nanoprobes guided by MRI/SPECT imaging. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(3):1718–1732. | ||
Skotland T, Iversen TG, Sandvig K. Development of nanoparticles for clinical use. Nanomedicine. 2014;9(9):1295–1299. | ||
Persigehl T, Wall A, Kellert J, et al. Tumor blood volume determination by using susceptibility-corrected DeltaR2 multiecho MR. Radiology. 2010;255(3):781–789. | ||
Ring J, Persigehl T, Remmele S, Heindel W, Dahnke H, Bremer C. Monitoring of bevacizumab-induced antiangiogenic treatment effects by “steady state” ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide particles magnetic resonance imaging using robust multiecho DeltaR2 relaxometry. Invest Radiol. 2011;46(5):326–330. | ||
Lu X, Wang RF. A concise review of current radiopharmaceuticals in tumor angiogenesis imaging. Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(8):1032–1040. | ||
Tateishi U, Oka T, Inoue T. Radiolabeled RGD peptides as integrin alpha(v)beta3-targeted PET tracers. Curr Med Chem. 2012;19(20):3301–3309. | ||
Cai H, Conti PS. RGD-based PET tracers for imaging receptor integrin alphav beta3 expression. J Labelled Comp Radiopharm. 2013;56(5):264–279. | ||
Pandya DN, Hantgan R, Budzevich MM, et al. Preliminary therapy evaluation of (225)Ac-DOTA-c(RGDyK) demonstrates that cerenkov radiation derived from (225)Ac daughter decay can be detected by optical imaging for in vivo tumor visualization. Theranostics. 2016;6(5):698–709. | ||
Zhu Z, Miao W, Li Q, et al. 99mTc-3PRGD2 for integrin receptor imaging of lung cancer: a multicenter study. J Nucl Med. 2012;53(5):716–722. | ||
Yan B, Qiu F, Ren L, et al. 99mTc-3P-RGD2 molecular imaging targeting integrin alpha v beta 3 in head and neck squamous cancer xenograft. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. 2015;304(3):1171–1177. | ||
Kenny LM, Coombes RC, Oulie I, et al. Phase I trial of the positron-emitting Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) peptide radioligand 18F-AH111585 in breast cancer patients. J Nucl Med. 2008;49(6):879–886. | ||
Zhao Z-Q, Yang Y, Fang W, Liu S. Comparison of biological properties of 99mTc-labeled cyclic RGD peptide trimer and dimer useful as SPECT radiotracers for tumor imaging. Nucl Med Biol. 2016;43(11):661–669. | ||
Guo Z, Gao M, Zhang D, et al. Simultaneous SPECT imaging of multi-targets to assist in identifying hepatic lesions. Sci Rep. 2016;6:28812. | ||
Maheshwari G, Brown G, Lauffenburger DA, Wells A, Griffith LG. Cell adhesion and motility depend on nanoscale RGD clustering. J Cell Sci. 2000;113(Pt 10):1677–1686. | ||
Thumshirn G, Hersel U, Goodman SL, Kessler H. Multimeric cyclic RGD peptides as potential tools for tumor targeting: solid-phase peptide synthesis and chemoselective oxime ligation. Chemistry. 2003;9(12):2717–2725. | ||
Hu K, Tang X, Tang G, et al. 18F-FP-PEG2-beta-Glu-RGD2: a symmetric integrin alphavbeta3-targeting radiotracer for tumor PET imaging. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0138675. | ||
He X, Hao Y, Long W, Song N, Fan S, Meng A. Exploration of peptide T7 and its derivative as integrin alphavbeta3-targeted imaging agents. Onco Targets Ther. 2015;8:1483–1491. | ||
Jin ZH, Furukawa T, Kumata K, et al. Development of the fibronectin-mimetic peptide KSSPHSRN(SG)5RGDSP as a novel radioprobe for molecular imaging of the cancer biomarker alpha5beta1 integrin. Biol Pharm Bull. 2015;38(11):1722–1731. | ||
Notni J, Steiger K, Hoffmann F, et al. Complementary, selective PET imaging of integrin subtypes alpha5beta1 and alphavbeta3 using 68Ga-aquibeprin and 68Ga-avebetrin. J Nucl Med. 2016;57(3):460–466. | ||
Notni J, Steiger K, Hoffmann F, Reich D, Schwaiger M, Kessler H, Wester HJ. Variation of specific activities of Ga-68-aquibeprin and Ga-68-avebetrin enables selective PET-imaging of different expression levels of integrins alpha5beta1 and alphavbeta3. J Nucl Med. 2016;57(10):1618–1624. | ||
Zeng C, Shang W, Wang K, et al. Intraoperative identification of liver cancer microfoci using a targeted near-infrared fluorescent probe for imaging-guided surgery. Sci Rep. 2016;6:21959. | ||
Liu L, Lin G, Yin F, Law WC, Yong KT. Near-infrared fluorescent peptide probes for imaging of tumor in vivo and their biotoxicity evaluation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(4):910–916. | ||
Sutphen R, Xu Y, Wilbanks GD, et al. Lysophospholipids are potential biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2004;13(7):1185–1191. | ||
Yao D, Lin Z, Wu J. Near-infrared fluorogenic probes with polarity-sensitive emission for in vivo imaging of an ovarian cancer biomarker. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(9):5847–5856. | ||
Alsibai W, Hahnenkamp A, Eisenblaetter M, et al. Fluorescent non-peptidic RGD mimetics with high selectivity for alpha(V)beta(3) vs alpha(IIb)beta(3) integrin receptor: novel probes for in vivo optical imaging. J Med Chem. 2014;57(23):9971–9982. | ||
Yue X, Morales AR, Githaiga GW, et al. RGD-conjugated two-photon absorbing near-IR emitting fluorescent probes for tumor vasculature imaging. Org Biomol Chem. 2015;13(43):10716–10725. | ||
Zhang C, Kimura R, Abou-Elkacem L, Levi J, Xu L, Gambhir SS. A cystine knot peptide targeting integrin alphavbeta6 for photoacoustic and fluorescence imaging of tumors in living subjects. J Nucl Med. 2016;57(10):1629–1634. | ||
Luan L, Fang W, Liu W, Tian M, Ni Y, Chen X, Yu X. Phthalocyanine-cRGD conjugate: synthesis, photophysical properties and in vitro biological activity for targeting photodynamic therapy. Org Biomol Chem. 2016;14(10):2985–2992. | ||
Choi HS, Gibbs SL, Lee JH, et al. Targeted zwitterionic near-infrared fluorophores for improved optical imaging. Nat Biotechnol. 2013;31(2):148–153. | ||
Bunschoten A, van Willigen DM, Buckle T, et al. Tailoring fluorescent dyes to optimize a hybrid RGD-tracer. Bioconjug Chem. 2016;27(5):1253–1258. | ||
Ellegala DB, Leong-Poi H, Carpenter JE, et al. Imaging tumor angiogenesis with contrast ultrasound and microbubbles targeted to alpha(v)beta3. Circulation. 2003;108(3):336–341. | ||
Gan ZR, Gould RJ, Jacobs JW, Friedman PA, Polokoff MA. Echistatin. A potent platelet aggregation inhibitor from the venom of the viper, Echis carinatus. J Biol Chem. 1988;263(36):19827–19832. | ||
Hu Q, Wang XY, Kang LK, Wei HM, Xu CM, Wang T, Wen ZI. RGD-targeted ultrasound contrast agent for longitudinal assessment of Hep-2 tumor angiogenesis in vivo. PLoS One. 2016;11(2):e0149075. | ||
Sivolapenko GB, Skarlos D, Pectasides D, et al. Imaging of metastatic melanoma utilising a technetium-99m labelled RGD-containing synthetic peptide. Eur J Nucl Med. 1998;25(10):1383–1389. | ||
Haubner R, Weber WA, Beer AJ, et al. Noninvasive visualization of the activated alphavbeta3 integrin in cancer patients by positron emission tomography and [18F]Galacto-RGD. PLoS Med. 2005;2(3):e70. | ||
Beer AJ, Lorenzen S, Metz S, et al. Comparison of integrin alphaVbeta3 expression and glucose metabolism in primary and metastatic lesions in cancer patients: a PET study using 18F-galacto-RGD and 18F-FDG. J Nucl Med. 2008;49(1):22–29. | ||
Beer AJ, Schwarzenbock SM, Zantl N, et al. Non-invasive assessment of inter-and intrapatient variability of integrin expression in metastasized prostate cancer by PET. Oncotarget. 2016;7(19):28151–28155. | ||
Chen SH, Wang HM, Lin CY, et al. RGD-K5 PET/CT in patients with advanced head and neck cancer treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy: results from a pilot study non-invasive assessment of inter-and intrapatient variability of integrin expression in metastasized prostate cancer by PET In situ validation of VEGFR-2 and alpha v ss 3 integrin as targets for breast lesion characterization. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016;19(2):245–254. | ||
Israel I, Richter D, Stritzker J, van Ooschot M, Donat U, Buck AK, Samnick S. PET imaging with [68Ga]NOTA-RGD for prostate cancer: a comparative study with [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose and [18F]fluoroethylcholine. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2014;14(4):371–379. | ||
Kim JH, Lee JS, Kang KW, et al. Whole-body distribution and radiation dosimetry of (68)Ga-NOTA-RGD, a positron emission tomography agent for angiogenesis imaging. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2012;27(1):65–71. | ||
Kim YI, Yoon HJ, Paeng JC, et al. Prognostic value of 68Ga-NOTA-RGD PET/CT for predicting disease-free survival for patients with breast cancer undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy and surgery: a comparison study with dynamic contrast enhanced MRI. Clin Nucl Med. 2016;41(8):614–620. | ||
Zheng K, Liang N, Zhang J, et al. 68Ga-NOTA-PRGD2 PET/CT for integrin imaging in patients with lung cancer. J Nucl Med. 2015;56(12):1823–1827. | ||
Indrevoll B, Kindberg GM, Solbakken M, et al. NC-100717: a versatile RGD peptide scaffold for angiogenesis imaging. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006;16(24):6190–6193. | ||
Mena E, Owenius R, Turkbey B, et al. [(18)F]fluciclatide in the in vivo evaluation of human melanoma and renal tumors expressing alphavbeta 3 and alpha vbeta 5 integrins. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014;41(10):1879–1888. | ||
Sharma R, Kallur KG, Ryu JS, et al. Multicenter reproducibility of 18F-fluciclatide PET imaging in subjects with solid tumors. J Nucl Med. 2015;56(12):1855–1861. | ||
Liu S, Liu Z, Chen K, et al. 18F-labeled galacto and PEGylated RGD dimers for PET imaging of alphavbeta3 integrin expression. Mol Imaging Biol. 2010;12(5):530–538. | ||
Minamimoto R, Karam A, Jamali M, et al. Pilot prospective evaluation of (18)F-FPPRGD2 PET/CT in patients with cervical and ovarian cancer RGD-K5 PET/CT in patients with advanced head and neck cancer treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy: results from a pilot study non-invasive assessment of inter-and intrapatient variability of integrin expression in metastasized prostate cancer by PET in situ validation of VEGFR-2 and alpha v ss 3 integrin as targets for breast lesion characterization. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016;43(6):1047–1055. | ||
Withofs N, Martinive P, Vanderick J, et al. [(18)F]FPRGD2 PET/CT imaging of integrin alphavbeta3 levels in patients with locally advanced rectal carcinoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016;43(4):654–662. | ||
Guo N, Lang L, Li W, et al. Quantitative analysis and comparison study of [18F]AlF-NOTA-PRGD2, [18F]FPPRGD2 and [68Ga]Ga-NOTA-PRGD2 using a reference tissue model. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37506. | ||
Lang L, Li W, Guo N, et al. Comparison study of [18F]FAl-NOTA-PRGD2, [18F]FPPRGD2, and [68Ga]Ga-NOTA-PRGD2 for PET imaging of U87MG tumors in mice. Bioconjug Chem. 2011;22(12):2415–2422. | ||
Gao S, Wu H, Li W, et al. A pilot study imaging integrin alphavbeta3 with RGD PET/CT in suspected lung cancer patients. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015;42(13):2029–2037. | ||
Mi B, Yu C, Pan D, et al. Pilot prospective evaluation of (18)F-alfatide II for detection of skeletal metastases. Theranostics. 2015;5(10):1115–1121. | ||
Miao W, Zheng S, Dai H, et al. Comparison of 99mTc-3PRGD2 integrin receptor imaging with 99mTc-MDP bone scan in diagnosis of bone metastasis in patients with lung cancer: a multicenter study. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e111221. |
 © 2017 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2017 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.



