Back to Journals » Chronic Wound Care Management and Research » Volume 2
Local management of deep cavity wounds – current and emerging therapies
Authors Smith N, Overland J, Greenwood J
Received 5 June 2015
Accepted for publication 15 July 2015
Published 29 October 2015 Volume 2015:2 Pages 159—170
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CWCMR.S62553
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Marco Romanelli
Nicholas Smith*, Joseph Overland*, John E Greenwood
Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Royal Adelaide Hospital, Adelaide, SA, Australia
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Abstract: Cavity wounds, defined as a loss of continuity of the skin or mucous membrane with associated tissue loss, represent a complex management issue for health care providers. The successful management of a deep cavity wound centers on assessment of the patient, assessment of the wound, and treating the underlying etiology. Adequate debridement and an appropriate dressings plan aim to create the optimum conditions that promote healing. Regular follow-up and serial examinations are essential to ensure progress and address any complication in a timely manner. Finally, continued patient education and the management of patient concerns are important to encourage compliance with management goals. In this review, we discuss the main management issues surrounding deep cavity wounds, review the current and emerging therapies available in the treatment of deep cavity wounds, discuss options for the management of pain, and discuss the impacts on quality of life for these patients.
Keywords: pressure sore, pain management, debridement
Introduction to the management issues in the treatment of deep cavity wounds
Definition of a cavity wound
A wound is defined as a loss of continuity of the skin or mucous membrane with associated tissue loss, which involves the epidermal layer of the skin.1 If these wound types extend below the subdermal layers of the skin and expose underlying structures such as tendons, muscle, and bone, they are referred to as “cavity wounds”.
Management aims for successfully addressing a deep cavity wound
The management aims for the successful treatment of a deep cavity wound should include:
- Determination of the underlying etiology
- Assessment of the patient including past medical history
- Assessment of the cavity wound
- Developing and implementing a management plan including:
- Debridement and regular dressing
- Pain management
- Ongoing regular review
- Management of both predisposing factors and risk factors for poor healing in the future
- Patient education and follow-up.
Etiology of cavity wounds
Cavity wounds are caused and influenced by many factors. Mechanisms of injury include ischemia, abnormal healing, malnutrition, smoking, pressure, immunosuppression, and infection. These mechanisms, alone or in combination, lead to different types of cavity wounds. They can be either acute or chronic in nature.
Acute causes of cavity wounds
Surgical cavity wounds
Surgical cavity wounds are created from acute surgically inflicted wounds, where the risk of infection from closing the wound primarily is high. The wound is therefore debrided and left to heal via secondary intention. Surgical cavity wounds are generally uniform in dimension and boat/saucer shaped, and allow free drainage of the wound.2 Examples of these wounds include pilonidal sinuses and subcutaneous abscesses.
Surgical dehiscence wounds
Surgical dehiscence wounds are a result of wound breakdown after primary closure. The main factors that lead to wound dehiscence are related to impaired microvasculature to the wound edges and impaired healing. They can be divided into wound-related factors, including high wound tension, concurrent infection, wound edema, tight sutures, and poor blood supply to the area, and patient-related factors, including systemic disease, steroid therapy, immune suppression, smoking, impaired vascular supply/venous drainage, and noncompliance. Surgical dehiscence wounds are often transformed into surgical cavity wounds following debridement and left to heal by secondary intention.
Traumatic cavity wounds
Traumatic cavity wounds may be caused by motor vehicle accidents, falls, gunshot wounds, and stabbings. They may result in loss of a large volume of tissue and can often be very difficult to treat.2 Tissue that has been exposed to trauma is commonly not viable for surgical closure, and healing by secondary intention can be used to progress the wound to a condition in which it may be closed primarily. It is important to surgically debride devascularized tissue within these wounds to prevent infection.
Chronic causes of cavity wounds
Diabetic foot ulcers
Diabetic foot ulcers are caused by diabetic neuropathy leading to trauma of the feet, coupled with impaired healing from immunosuppression and vascular disease, leading to chronic ulcer formation. Early identification of an at-risk foot is crucial in the management of diabetic foot ulcers. At risk feet may be identified by the features present in Table 1.3 Diabetic foot ulcers can lead to infection of underlying bone and subsequent amputation.4
  | Table 1 Features of at risk foot3 |
Pressure ulcers
Pressure ulcers are lesions caused by unrelieved pressure or shear resulting in microvascular ischemia causing damage to the underlying tissue.5 They are very common in the health care setting, especially in bedbound, elderly, and paraplegic patients. A Canadian study found the prevalence of pressure ulcers to be 25% in acute care settings.6 Pressure ulcers can be graded using the National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel (NPUAP) system (Table 2), developed in 1989.7
  | Table 2 NPUAP Staging System for Pressure Ulcers |
Venous leg ulcers
Both venous reflux and obstruction contribute to the pathophysiology of chronic venous disease. Venous reflux has a much higher prevalence; however, obstruction will lead to venous ulceration over a much shorter time span.8 Whatever the route cause of chronic venous disease, the underlying pathology is increased pressure and decreased capillary microperfusion.9 These hemodynamic changes within the large vessels of the leg are transferred into the microcirculation and lead to the development of venous microangiopathy.10 Microangiopathy in turn leads to increased capillary permeability, which, when coupled with the increased venous pressures, causes significant edema to be forced into the extracellular space. These changes to the microvasculature in chronic venous disease contribute significantly to the formation of venous ulcers.11
Venous ulcers make up 80% to 95% of vascular lesions and affect between 10% and 35% of the population.4 They can be very difficult to treat, with recurrence rates ranging from 54% to 78%.12 Venous ulcers can have a huge societal burden, costing France and Belgium approximately 2.5% of their health budget in 1995.12 Furthermore, it is estimated that approximately 6 million workdays per year are lost to chronic venous insufficiency complications in the USA.13
Surgical cavity wounds
Surgical cavity wounds can also be chronic. A deep surgical space infection is one that occurs 30 days after the operation and involves deep soft tissues of the incision and at least one of 1) purulent drainage; 2) spontaneous dehiscence of the deep incision; 3) an abscess or other evidence of infection; or 4) diagnosis of a surgical space infection by a surgeon.14
Assessment of a cavity wound
Patient assessment
Thorough patient assessment is paramount in forming an appropriate management plan for a deep cavity wound. It is important to treat the patient as a whole, and not just treat the wound.
Past medical history
Past medical history may elicit concurrent systemic illnesses (Table 3), such as diabetes or vascular disease, which may impact on healing.15 Other comorbidities that do not affect healing, but may affect other aspects of the management plan, for example, movement disorders or paraplegia, may also predispose patients to cavity wound formation. Medications such as steroids and chemotherapeutic agents may also impact on wound healing, along with the well-established risk factors of smoking,16 alcohol,17 and poor nutrition.18 Halim et al state that diabetic control, elimination of immunosuppressive medications, correction of anemia, and cessation of smoking are among the most important determinants of cavity wound healing.19
  | Table 3 Risk factors for poor healing of cavity wounds |
A poor nutritional state can contribute to poor wound healing and the development of chronic cavity wounds. The impairment of wound healing is related to the percentage of lean body weight that a patient has lost.20 Early recognition of poor nutrition and its immediate reversal results in increased wound healing and better outcomes for the patient.21
Allergies are important because they can limit treatment options and affect compliance with treatment.2 Social history can play a role in assessing the likelihood of engagement with sometimes burdensome therapy. Baseline functioning, living arrangements, family support, access to community-based services, and mental state are all useful in identifying those patients who may need increased levels of social support to overcome their injury.
Physical examination
Physical examination and serial documentation of the patient and the wound is vital to assess progress and management potential complications in a timely manner. Evidence of the main risk factors for cavity wounds (Table 3) should be sought. Examination should then move to the wound. Cavity wounds should be assessed for the following:2,22,23
- Size: measure the longest length and the longest width from wound edge to wound edge.
- Shape: important to assess for any sinuses, tunneling, or undermining of the cavity under the skin edge.
- Depth: from the visible skin edge to the deepest surface of the wound. Can be difficult to accurately establish.
- Tissue at wound bed: assess tissue color, propensity to bleed, and tissue type (muscle, tendon, bone, and fascia). Any necrotic tissue needs to be debrided.
- Exudate: assess color, consistency, and volume. Moderate to heavy serous may indicate high bacterial colonization. Thick exudate that has changed in color may indicate clinical infection.
- Edema: assess for swelling and firmness at wound edges.
- Contamination: assess the wound for foreign material. The mechanism of injury can lead to suspicion of specific contaminants, eg, sutures in surgical wound, metal in industrial accident.
- Wound infection: recognition of local and systemic signs and symptoms is important. Local signs include new/increasing pain, erythema, warmth, swelling, purulent exudate, delayed healing/wound breakdown, discoloration, friable tissue, and malodor. Systemic signs can range from malaise and poor appetite to fever, sepsis, and shock.
- Surrounding environment: inspect the periwound environment for aforementioned signs of infection, scar tissue formation, bruising, ecchymosis, or rashes.
It is important to note that cavity wounds should be inspected as frequently as possible. At every dressing change, they should be observed and proper documentation of their progress should be kept.
Clinical tools for wound assessment
Two valuable and easy-to-use scales are the TIME71 (Table 4) and Applied Wound Management scales72 (Table 5).
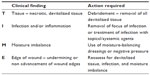  | Table 4 TIME assessment tool |
  | Table 5 Applied Wound Management (AWM) assessment tool |
Review of the current and emerging treatment therapies for deep cavity wounds
Wound bed management
The key to the commencement of proper treatment of cavity wounds is good wound bed preparation. Initially introduced by Falanga24 and Sibbald et al25 for chronic wounds, and subsequently updated to incorporate the TIME acronym, wound bed management provides the underpinning principles for treatment of deep cavity wounds.
Tissue debridement
Nonviable tissue overlying a cavity wound should be removed as a potential source of infection and to fully assess the size and shape of the wound. There are several options for debridement technique, including surgical, mechanical, autolytic, enzymatic, and biological methods.19 The method of debridement should be chosen based on individual patient conditions, availability of resources, and condition of the wound.
Surgical debridement is quick and effective, but is nonselective in that it removes healthy tissue with devitalized tissue. One emerging technique for surgical wound bed debridement is high-pressure parallel waterjets. Similar to the older mechanical method of pulse lavage, which involves a pulsatile stream of irrigation fluid being pumped into the wound whilst concurrent suction removes necrotic debris and foreign material, a high-pressure parallel waterjet device uses the flow of fluid through the device to generate a partial vacuum that can remove debris. This has been shown to decrease absolute bacterial count in open surgical and traumatic wounds by an average of 90.8%.26
Mechanical debridement involves methods such as pressure irrigation and wet-to-dry dressings.19 Wet-to-dry dressings involve packing wet gauze into a wound and allowing it to dry before removal. It is effective but can be very painful. Like surgical debridement, it can remove healthy tissue alongside necrotic debris. Pressure irrigation describes a wide array of irrigation fluids delivered with varying pressures and has long been used as an effective method of wound bed preparation.27 Studies have shown that higher-pressure irrigation is more effective at reducing bacterial load and removing devitalized tissue than lower-pressure irrigation.28,29
Autolytic debridement describes the body’s natural method of wound bed cleansing.30 It involves using a moist wound packing to create an environment to painlessly remove necrotic debris using the body’s natural immune measures. It is relatively easy to perform and is selective for devitalized tissue, but is time-consuming and can increase the risk of wound infection.31
Enzymatic debridement involves the use of manufactured enzymes to dissolve devitalized tissue. There are a number of products available, including collagenase-based products, papain-based products, and papain–urea–chlorophyllin copper complex. Further research is required to confirm the efficacy and effectiveness of these enzymatic agents.32
Biological debridement is a relatively new and emerging trend in wound management. It involves placing larvae of Lucilia sericata within the wound itself. In Europe, approximately 15,000 people receive this type of treatment annually.33 Larval secretions contribute to the removal of devitalized tissue, reduce the bacterial load, and promote granulation tissue formation.33 Mudge et al have shown larval therapy to be quicker at debridement for leg ulcers when compared to hydrogel.34
Infection and inflammation
Cavity wounds remain open for an extended period of time, exposing them to an increased risk of colonization by both bacteria and fungi. It has been shown that a bacterial burden of 106 organisms or greater per gram of tissue impairs healing.35 Thus, prevention of infection is key to the treatment of cavity wounds.
It is important to recognize the distinction between colonization and infection of a wound, and the implications of both. Colonization represents the presence of bacteria within the wound, but the wound tissue itself is not damaged.36 Colonization of a cavity wound can still lead to delayed healing through the formation of biofilms and the subsequent stimulation of a chronic inflammatory response.36 Infection occurs when the bacteria multiply beyond the host immune system’s capability and cause damage to local and surrounding tissue, which can lead to systemic illness. Chronic wounds which may be colonized, and acute or chronic wounds showing signs of infection, should have appropriate specimens including swabs and/or debrided tissue sent for microscopy, culture and antibiotic sensitivities collected in order to guide targeted antibiotic/antimicrobial therapy.
The options for treating wound colonization and infection can be broken into two types of therapy: topical and systemic. In their 2011 update on wound bed preparation, Sibbald et al provided a framework for choosing which therapy to use on a particular wound (Table 6).25
  | Table 6 Treatment of wound colonization and infection |
There are now at least four main classes of antimicrobial dressings – silver-based, honey-based, iodine-based, and chlorhexidine-based.37 The greatest literary support is for silver-based dressings. In a meta-analysis, they were shown to improve wound healing, reduce odor and pain symptoms, and decrease the amount of wound exudate when compared with alternative wound management techniques.37 Silver is effective against gram-negative, gram-positive, and anaerobic and aerobic bacteria; methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus, and can accelerate wound healing by stimulation of growth factors and cytokines.38 Silver dressings can be combined with alginates (nonwoven absorbent dressings derived from seaweed), foams, hydrofibers, and hydrogels, and can be left in situ for up to 1 week.
Should a wound exhibit three of the features outlined in STONEES (Table 6), which are increased size, increased temperature, bone exposure, new breakdown, increasing exudate, increasing erythema/edema, or smell, then systemic antibiotics should be used as per local therapeutic guidelines.25
Moisture balance
The moisture content within a deep cavity wound is an important balancing act. There is strong evidence that keeping a wound moist does not increase infection rates.35,39,40 Moreover, moisture may actually accelerate reepithelialization of the wound bed.35 A moist environment is required for optimization of growth factors and cytokines contained within wound exudate and to encourage proliferation of new cells.19 However, excessive wound fluids can contribute to “trapping” and improper distribution of cytokines and growth factors crucial in wound healing.35 Furthermore, certain bacteria thrive in moist environments, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Edge of wound – epithelial advancement
Advancement of the epithelial surface of a wound is an important clinical marker of healing. Failure of advancement, or wound stalling, should direct the clinician to reassess earlier elements of the TIME acronym. A “cliff-like edge” in between epithelium and granulation tissue may be observed in a stalled wound; whereas a healing wound will have tapered edges.41 Cavity wounds that have stalled may be particularly responsive to negative-pressure wound therapy (NPWT).
Pressure care management
Pressure care management involves recognizing those patients who are at risk for developing pressure sores and managing them with appropriate pressure care equipment. Pressure care equipment options are numerous; wheelchairs, cushions, mattresses, commodes, shower chairs, toilet seats, car seats, and lounge chairs can all be provided to patients to prevent pressure wound development.42 They will also require regular repositioning, without which pressure care equipment is ineffective.43 Factors exposing patients to an increased risk of pressure sore development include immobility, sensory loss, altered consciousness, moisture, shear/friction, increasing age, altered vascular supply, and infection.42,44
Selecting which material to use for cavity wounds
Historically, management of a cavity wound has involved packing it with ribbon gauze soaked in an antiseptic solution. This method results in adherence of the gauze to the wound bed when it dries out and subsequent trauma to the wound on removal of the dressing.22 More recently, many new products have been placed on the market, all of which have use for different types of wounds. Table 7 is a summary of available materials for dressing a cavity wound and the specific advantages and disadvantages of each. The decision of which material to use for dressing a cavity wound must also consider the type of wound (Table 8).
  | Table 7 Types of dressings for cavity wounds |
  | Table 8 Matching wound characteristics with dressing types |
NPWT
NPWT is a critical tool in the management of cavity wounds. Using a noninvasive system, it creates a subatmospheric environment around a wound.4,22,45 NPWT expedites wound healing by a number of mechanisms. It has been shown that NPWT causes strain-induced production of growth factors and cytokines, contributing to a shift toward an anti-inflammatory cytokine profile in cavity wounds.46,47 This is the result of dilatation of the arterioles, increased granulation tissue, greater wound retraction, and increased removal of exudate. NPWT also decreases interstitial edema.4,22,48 Some studies49,50 have noted a reduction of bacterial load using NPWT, but it must also be noted that others have found a clinically insignificant rise in bacterial burden.
While there are differences between NPWT products, they all have three essential components:22,48
- A comfortable and easily compressed wound filler
- An airtight wound covering
- A suction device: administration pressures may vary between –5 mmHg and –200 mmHg depending on patient comfort and device used.
As of 2009, there were 22 NPWT products listed with the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA); however, there are currently only two systems widely used in Australia, namely vacuum assisted closure (VAC) (KCI Medical Incorporated, NSW, Australia) and Vista (Smith and Nephew, Smith & Nephew Pty Ltd Healthcare Division, Victoria, Australia). Different devices use different types of wound filler. For the purposes of this article, we will focus on the devices available within Australia. The VAC system uses a foam dressing, while Vista employs the Chariker-Jeter technique and uses gauze as the wound filler.48 In a recent comparison of the two products at our own institution, Panicker found that the foam dressing of the VAC system had the propensity to adhere to the granulation tissue, especially when left in the wound for longer than the recommended duration. Conversely, Panicker found that the gauze-based system did not adhere to the wound bed even when left on the wound for more than 2 days. Moreover, this comparison estimated a 30% cost saving achieved by using the gauze-based system.48
NPWT is the treatment of choice for large and difficult-to-treat cavity wounds at our institution. The indications and contraindications for NPWT are listed in Table 9.
  | Table 9 Indications and contraindications of negative-pressure wound therapy |
Cell-based therapy and tissue engineering: an emerging field
Advanced treatment of chronic skin wounds in the future will be a derivative of our development of regenerative medicine with tissue bioengineering. In recent times, significant enhancements have been made in our understanding of stem cell biology as a clinical tool and treatment for difficult-to-heal wounds. Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapy has emerged as a promising potential treatment for nonhealing wounds,51 with the US National Institutes of Health (NIH) currently registering 521 studies being undertaken into MSCs.52 MSCs are multipotent adult stem cells, which possess the ability to differentiate into several mesenchymal lineages including tendon, bone, cartilage, and adipose tissue.53 Due to the fact that they do not express class II major histocompatibility complexes (MHCs) on their cell surfaces, they are immune-privileged cells, making them suitable for allogenic transplantation.53
There is growing evidence that endogenous stem cells play a cell role in normal tissue repair of almost all tissue types,51 but this endogenous function can sometimes be overwhelmed by severe injury, old age, hostile microenvironment, and immunosuppression.54 There is a growing body of work investigating the ability of MSCs to secrete a multitude of bioactive molecules, including SDF-1, VEGF, and TGF-beta, and the effect of these molecules on endogenous stem cell recruitment.55
Clinical utilization has thus far been limited for three reasons. First, because of the small percentage of bone marrow-derived stem cells that can be isolated and the large volumes of tissue required to do so.56 Second, there is a possibility that these cells may undergo unfavorable changes51,53,56 and have a potential carcinogenic effect.53,56 Finally, there remain significant ethical problems behind the use of such cells. While further research is certainly needed into this field, the possible implications for the treatment of cavity wounds are exciting.
Efficacy and tolerance of conventional and modern management of cavity wounds
As detailed earlier, cavity wounds comprise a vast array of varying wound types. Different dressings are more or less efficacious for specific types of cavity wounds. It should be remembered that dressing choice should be influenced by the specific characteristics of each cavity wound. Below is a discussion of informing features of three main groups of dressings: conventional, modern, and NPWT.
Conventional dressings
Gauze
Conventional dressings such as wet-to-dry gauze can be incredibly effective at debriding necrotic tissue, but perform this action at an increased risk to surrounding granulation tissue. They are sometimes allergenic. Frequent dressing changes are required, and these can often be very painful for the patient due to adherence of the dressing to the wound bed. When used in heavily exuding wounds, conventional dressings can cause maceration of periwound skin.57 Gauze dressings can still be very useful in treating cavity wounds involving bone and tendon.57
Modern dressings
Alginates
Alginates are nontoxic and nonallergenic. They have hemostatic properties. They can cause maceration of periwound skin if exudate spreads past the wound edges, and may cause irritation of a dry wound. The ability to remain moist decreases pain on removal of dressing. Current evidence does not suggest that they are more or less effective than hydrocolloid or nonadherent dressings in treating cavity wounds such as leg ulcers.58
Hydrocolloids
Hydrocolloids retain moisture well, contributing to decreased pain on removal.59 They have clearly been shown to be less painful to remove than paraffin gauze dressings.60 They are only required to be changed every 3–5 days. Evidence has shown that they cause a statistically significant decrease in time to heal when compared to conventional dressings, when used for pressure ulcers.61 Hydrocolloids have been shown to be allergenic, causing contact dermatitis.62
Conventional versus modern dressings
In a review of 31 randomized controlled trials to compare conventional and modern wound dressings for leg ulcers, Bouza et al found that there was no statistically significant difference in the outcomes or safety profiles of ulcers treated by either conventional or modern dressing types, nor did they find any statistically significant difference in tolerance rates between the two groups.63 Research like this indicates the dearth of evidence available when selecting a dressing type for cavity wounds and highlights the importance of clinical examination and assessment to obtain a wound profile and select an appropriate dressing for its features.
NPWT
Based on clinical experience within our own center, NPWT is the most efficacious treatment of large cavity wounds. This is especially true of wounds that have failed to respond to treatment with conventional or modern dressings. Evidence within the literature is beginning to support this view. Argenta and Morykwas found that, of 300 wounds that were treated with negative-pressure dressings, 296 responded favorably with an increased rate of granulation tissue formation.63 Moreover, in a multicenter, randomized controlled trial involving 342 patients with a mean age of 58 years, Blume et al analyzed the safety and clinical efficacy of vacuum-assisted closure dressings versus advanced moist wound therapy.45 They showed that 43.2% of diabetic foot ulcers treated achieved complete closure (defined as 100% reepithelialization without drainage or further dressing requirements) versus 28.9% treated with traditional measures such as hydrogels and alginates. They also found that the negative-pressure group experienced significantly (P=0.035) fewer secondary amputations. They found no significant difference in safety between groups in complications such as infection, cellulitis, and osteomyelitis at 6 months posttreatment.
Generally, NPWT dressings only require changing every 2–4 days.63 This is significantly less than some conventional and modern dressings, which can often require daily changes, and sometimes even more frequent changes. When used with gauze, NPWT has been shown to be painless in 80% of removals.64 It gains good control of exudate, resulting in decreased soiling of bedsheets and clothing, and does not prevent mobility for rehabilitation.7 While these characteristics do contribute to good patient tolerance, NPWT is not without risk. According to the FDA, there were more than 100 adverse events associated with NPWT reported between January 1, 2000 and June 29, 2006.6 These included leaving foam within a healed wound, damage to underlying organs, cellulitis, amputation, and wound infection.6
Management therapies to reduce surface area and pain
Systemic
Pain assessment and relief
It is important to be able to quantify the amount of pain a cavity wound may be causing a patient. Pain should be quantified in terms of nature, intensity, location, duration, onset/offset, concurrent symptoms, and aggravating/relieving factors. The cause of pain should also be identified. Incident pain can occur from debridement or trauma. Episodic or procedural pain may occur due to cleaning and dressing changes.65 Continuous or background pain may be due to the wound itself or infection and irritation.65 It may be useful for the clinician to use validated pain scales such as the Numerical Rating Scale.66
Pain relief in cavity wounds should be a mixture of treatment and prevention. Analgesics should be used in accordance with the World Health Organization (WHO)’s Pain Ladder (Table 10)67 and its underpinning principles.68
  | Table 10 Principles of the World Health Organization (WHO) Pain Ladder |
Prevention of pain is achieved by selecting the appropriate dressing type for the particular wound and by recognizing and successfully treating infection, both of which are discussed in detail earlier.
Local options
Topical anesthesia
Alone or in combination with systemic analgesia, topical anesthetics can be useful in managing the pain caused by a cavity wound. Numerous options are available and local guidelines should be consulted.
Soaking dressings before removal
Soaking dressings before removal can reduce the amount of viable and innervated tissue that is removed along with the dressing. This can significantly reduce the patient’s pain and contributes to wound healing by ensuring minimal healthy, healing tissue is removed during dressing changes.
Implications for patients, such as quality of life
Cavity wounds, especially those that are unresponsive to traditional therapy, are extremely burdensome and impact negatively on a patient’s quality of life. This negative impact manifests as physical, financial, social, and psychological impairment.
The physical burden of a wound is influenced by its size, location, and duration. Cavity wounds can impact on a patient’s ability to function independently. Pain can impact on mobility, which in turn limits social contact and contributes to a less healthy lifestyle. It can also disrupt a patient’s sleep, and embarrassment over increasing exudate or unsightly appearance can cause social withdrawal.69
Cavity wounds have a huge financial burden for both health care systems as a whole and for the patients they treat. In the USA, the attributable cost to the health care system for a 40- to 65-year-old male with a new foot ulcer is $27,987 for the 2 years after diagnosis.70 At a patient level, chronic leg ulcers have been shown to be associated with lost time at work, loss of employment, and adverse effects on finances.71
The psychological impact of a cavity wound is one area that is sometimes overlooked. Patients living with a cavity wound can experience anxiety/depression, fear, altered/poor body image, low self-esteem, feelings of uncleanliness, anger/frustration, stigma from others, loneliness, and guilt. Up to 68% of patients with chronic leg ulcers report a negative emotional impact on their lives.71
Effective management of cavity wounds using the materials and devices laid out in this article can significantly improve the quality of life for patients. Successful treatment of these wounds assists patients to keep gainful employment, to mobilize and socialize independently. Prompt resolution of cavity wounds diminishes the financial burden of disease, limits the associated negative emotions, and reduces noncompliance with therapy.
Discussion and conclusion
The approach to the patient with a cavity wound should be systematic. In determining the etiology, it is important to consider the different contributing factors that will be influenced by the patient’s specific circumstances and background and to treat the underlying cause concurrent with the treatment of the wound itself. Thorough assessment of the patient should be undertaken and should include history and physical examination. Wound bed management, summarized by the TIME acronym, is the backbone of this assessment and plays an important role in the subsequent management of these wounds. Local and systemic factors should be taken into account when formulating and instigating these management plans, and regular follow-up is essential. Physical and mental pain are common among this patient subset, and excessive pain or psychosocial dysfunction are to be monitored for and actively treated. Finally, our article outlines the multitude of options available for dressing cavity wounds. These are all useful in specific situations, and their use is based on the clinical appearance and characteristics of the wound.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Leaper DJ, Harding KG, editors. Wounds: Biology and Management. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1998. | |
Timmons J, Cooper P. How to systematically assess a patient with a cavity wound. Wounds UK. 2008;4(2):4–18. | |
Department of Health, Western Australia. High Risk Foot Model of Care. Perth: Health Networks Branch, Department of Health, Western Australia; 2010. Available from http://www.healthnetworks.health.wa.gov.au/modelsofcare/docs/High_Risk_Foot_Model_of_Care.pdf. Accessed July 30, 2015. | |
Sullivan N, Snyder DL, Tipton K, Uhl S, Schoelles KM. Negative Pressure Wound Therapy Devices. Rockville: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. 2009. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK253229/pdf/Bookshelf_NBK253229.pdf. Accessed April 15, 2015. | |
de Leon J. Negative pressure wound therapy in pressure ulcer management. Ostomy Wound Manage. 2005;51(2A Suppl): 3S–8S. | |
Health Quality Ontario. Negative pressure wound therapy: an evidence-based analysis. Negative pressure wound therapy: an evidence-based analysis. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006;6(14):1–38. | |
Spear M. Pressure ulcer staging-revisited. Plast Surg Nurs. 2013;33(4):192–194. | |
O’Donnell TF Jr, Passman MA, Marston WA, et al; Society for Vascular Surgery; American Venous Forum. Management of venous leg ulcers: clinical practice guidelines of the Society for Vascular Surgery® and the American Venous Forum. J Vasc Surg. 2014;60(2 Suppl):3S–59S. | |
Eberhardt RT, Raffetto JD. Chronic venous insufficiency. Circulation. 2014;130(4):333–346. | |
Franzeck UK, Haselbach P, Speiser D, Bollinger A. Microangiopathy of cutaneous blood and lymphatic capillaries in chronic venous insufficiency (CVI). The Yale Journal of Biology and Medicine. 1993;66(1):37–46. | |
Gschwandtner ME, Ehringer H. Microcirculation in chronic venous insufficiency. Vasc Med. 2001;6(3):169–179. | |
Abbade LP, Lastória S. Venous ulcer: epidemiology, physiopathology, diagnosis and treatment. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44(6):449–456. | |
Weiss RA, Heagle CR, Raymond-Martimbeau P. The Bulletin of the North American Society of Phlebology. Insurance Advisory Committee Report. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1992;18(7):609–616. | |
Horan TC, Gaynes RP, Martone WJ, Jarvis WR, Emori TG. CDC Definitions of Nosocomial Surgical Site Infections, 1992: A Modification of CDC Definitions of Surgical Wound Infections. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 1992; 13: 606–608” Available from: http://www.jstor.org/stable/30148464?&seq=1#page_scan_tab_contents. Accessed July 30, 2015. | |
Thorne CH, Beasley RW, Aston SJ, Bartlett SP, Gurtner GC, Spear SL, editors. Grabb and Smith’s Plastic Surgery. 6th ed. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2007. | |
Babayan RK. Wound healing and infection in surgery: the pathophysiological impact of smoking, smoking cessation, and nicotine replacement therapy: a systematic review. J Urol. 2012;188(6):2243–2244. | |
Guo S, Dipietro LA. Factors affecting wound healing. J Dent Res. 2010;89(3):219–229. | |
Kavalukas SL, Barbul A. Nutrition and wound healing: an update. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011;127 Suppl 1:38S–43S. | |
Halim AS, Khoo TL, Saad AZ. Wound bed preparation from a clinical perspective. Indian J Plast Surg. 2012;45(2):193–202. | |
al WMe. Nutrition and Wound Healing. Expert Guide for Healthcare Professionals. Australian Wound Management Association; 2009. Available from: http://www.awma.com.au/publications/2009_vic_expert_guide_nutrition_wound_healing.pdf. Accessed April 17, 2015. | |
Johnston E. The role of nutrition in tissue viability. Wound Essentials. 2007;2:10–21. | |
Pudner R. Managing cavity wounds. Journal of Community Nursing. 1998;12(3):22–24. | |
Gethin G. The importance of continuous wound measuring. Wounds UK. 2006;2(2):60–68. | |
Falanga V. Classifications for wound bed preparation and stimulation of chronic wounds. Wound Repair Regen. 2000;8(5):347–352. | |
Sibbald RG, Williamson D, Orsted HL, et al. Preparing the wound bed – debridement, bacterial balance, and moisture balance. Ostomy Wound Manage. 2000;46(11):14–22, 24–28, 30–35; quiz 36–37. | |
Granick MS, Tenenhaus M, Knox KR, Ulm JP. Comparison of wound irrigation and tangential hydrodissection in bacterial clearance of contaminated wounds: results of a randomized, controlled clinical study. Ostomy Wound Manage. 2007;53(4):64–66, 68–70, 72. | |
Bhandari M, Thompson K, Adili A, Shaughnessy SG. High and low pressure irrigation in contaminated wounds with exposed bone. Int J Surg Investig. 2000;2(3):179–182. | |
Gross A, Cutright DE, Bhaskar SN. Effectiveness of pulsating water jet lavage in treatment of contaminated crushed wounds. Am J Surg. 1972;124(3):373–377. | |
Brown LL, Shelton HT, Bornside GH, Cohn I Jr. Evaluation of wound irrigation by pulsatile jet and conventional methods. Ann Surg. 1978;187(2):170–173. | |
Atkin L. Understanding methods of wound debridement. Br J Nurs. 2014;23(12):S10–S12, S14–S15. | |
Madhok BM, Vowden K, Vowden P. New techniques for wound debridement. Int Wound J. 2013;10(3):247–251. | |
Smith RG. Enzymatic debriding agents: an evaluation of the medical literature. Ostomy Wound Manage. 2008;54(8):16–34. | |
Cazander G, Pritchard DI, Nigam Y, Jung W, Nibbering PH. Multiple actions of Lucilia sericata larvae in hard-to-heal wounds: larval secretions contain molecules that accelerate wound healing, reduce chronic inflammation and inhibit bacterial infection. Bioessays. 2013;35(12):1083–1092. | |
Mudge E, Price P, Walkley N, Harding KG. A randomized controlled trial of larval therapy for the debridement of leg ulcers: results of a multicenter, randomized, controlled, open, observer blind, parallel group study. Wound Repair Regen . 2014;22(1):43–51. | |
al CSe. Wound Bed Preparation in Practice: Position Document. European Wound Management Association; 2004. Available from: http://ewma.org/fileadmin/user_upload/EWMA/pdf/Position_Documents/2004/pos_doc_English_final_04.pdf. Accessed April 16, 2015. | |
Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 6th ed. Elsevier Churchill Livingstone; 2005. | |
Lo SF, Chang CJ, Hu WY, Hayter M, Chang YT. The effectiveness of silver-releasing dressings in the management of non-healing chronic wounds: a meta-analysis. J Clin Nurs. 2009;18(5):716–728. | |
Cartlidge-Gann L. Consider the whole patient, not just the hole: healing a wound cavity by secondary intention. Wound Practice and Research. 2008;16(4):176–180. | |
Hutchinson JJ. Infection under occlusion. Ostomy Wound Manage. 1994;40(3):28–30, 32–33. | |
Hutchinson JJ, Lawrence JC. Wound infection under occlusive dressings. J Hosp Infect. 1991;17(2):83–94. | |
Sibbald RG, Goodman L, Woo KY, et al. Special considerations in wound bed preparation 2011: an update ©. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2011; 24(9):415–436; quiz 437–438. | |
Statewide Spinal Cord Injury Service Skin Management Taskforce Committee. An Overview of Skin and Pressure Area Management in Adults with Spinal Cord Injuries. Rural Spinal Cord Injury Project; 2005. Available from: http://www.aci.health.nsw.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0004/155209/skin.pdf. Accessed April 12, 2015. | |
Beldon P. Pressure ulcer prevention and management: using mattresses and cushions. Wound Essentials. 2007;2:92–100. | |
Woodward M. Risk factors for pressure ulcers – can they withstand the pressure? Primary Intention. 1999;52–61. | |
Blume PA, Walters J, Payne W, Ayala J, Lantis J. Comparison of negative pressure wound therapy using vacuum-assisted closure with advanced moist wound therapy in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care. 2008;31(4):631–636. | |
Yang SL, Han R, Liu Y, Hu LY, Li XL, Zhu LY. Negative pressure wound therapy is associated with up-regulation of bFGF and ERK1/2 in human diabetic foot wounds. Wound Repair Regen. 2014;22(4):548–554. | |
Glass GE, Murphy GF, Esmaeili A, Lai LM, Nanchahal J. Systematic review of molecular mechanism of action of negative-pressure wound therapy. Br J Surg. 2014;101(13):1627–1636. | |
Panicker VN. A pilot study evaluating topical negative pressure using V1STA® technology. Wound Practice and Research. 2009;17(4):194–200. | |
Morykwas M, Argenta L, Shelton-Brown E et al. Vacuum-assisted closure: a new method for wound control and treatment: animal studies and basic foundation. Ann Plast Surg, 1997;38(6):553–562. | |
Morykwas M, Simpson J, Punger K et al. Vacuum-assisted closure: state of basic research and physiologic foundation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006:117(suppl 7):121S–126S. | |
Li M, Zhao Y, Hao H, Han W, Fu X. Mesenchymal stem cell based therapy for non-healing wounds: today and tomorrow. Wound Repair Regen. Epub 2015 Apr 15. | |
Clinical Trials.gov [homepage on the Internet]. US National Institutues of Health; 2015. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=mesenchymal+stem+cells&Search=Search. Accessed July 14, 2015. | |
Mundra V, Gerling IC, Mahato RI. Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy. Mol Pharm. 2013;10(1):77–89. | |
Dong F, Caplan AI. Cell transplantation as an initiator of endogenous stem cell-based tissue repair. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2012;17(6):670–674. | |
Caplan AI, Correa D. The MSC: an injury drugstore. Cell Stem Cell. 2011;9(1):11–15. | |
Castilla DM, Liu ZJ, Tian R, Li Y, Livingstone AS, Velazquez OC. A novel autologous cell-based therapy to promote diabetic wound healing. Ann Surg. 2012;256(4):560–572. | |
DM. Moist Wound Dressings and Pressure Relieving Surfaces: Mechanisms, Materials and a Review of Some Cost-Effectiveness FIndings. Centre for Health Program Evaluation; 1997. Available from: http://arrow.monash.edu.au/vital/access/%20/services/Download/monash:2594/DOC. Accessed on June 12, 2015. | |
O’Meara S, Martyn-St James M. Alginate dressings for venous leg ulcers. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;4:CD010182. | |
Wound Dressings – Acute Traumatic Wounds [webpage on the Internet]. Parkville: The Royal Children’s Hospital Melbourne; 2015. Available from: http://www.rch.org.au/clinicalguide/guideline_index/Wound_dressings_acute_traumatic_wounds/. Accessed June 25, 2015. | |
Cadier MA, Clarke JA. Dermasorb versus Jelonet in patients with burns skin graft donor sites. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1996;17(3):246–251. | |
Bouza C, Saz Z, Muñoz A, Amate JM. Efficacy of advanced dressings in the treatment of pressure ulcers: a systematic review. J Wound Care. 2005;14(5):193–199. | |
Grange-Prunier A, Couilliet D, Grange F, Guillaume JC. [Allergic contact dermatitis to the Comfeel hydrocolloid dressing]. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2002;129(5 Pt 1):725–727. French. | |
Argenta LC, Morykwas MJ. Vacuum-assisted closure: a new method for wound control and treatment: clinical experience. Ann Plast Surg. 1997;38(6):563–576; discussion 577. | |
Henderson V, Timmons J, Hurd, T, Deroo K, Maloney S, Sabo S. NPWT in everyday practice made easy. Wounds International. 2010;1(5):1–6. | |
Svoboda SJ, Bice TG, Gooden HA, Brooks DE, Thomas DB, Wenke JC. Comparison of bulb syringe and pulsed lavage irrigation with use of a bioluminescent musculoskeletal wound model. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(10):2167–2174. | |
Ferreira-Valente MA, Pais-Ribeiro JL, Jensen MP. Validity of four pain intensity rating scales. Pain. 2011;152(10):2399–2404. | |
WHO’s cancer pain ladder for adults [webpage on the Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2015. Available from: http://www.who.int/cancer/palliative/painladder/en/. Accessed June 12, 2015. | |
Vargas-Schaffer G. Is the WHO analgesic ladder still valid? Twenty-four years of experience. Can Fam Physician. 2010;56(6):514–517, e202–e205. English, French. | |
International consensus. Optimising wellbeing in people living with a wound. An expert working group review. London: Wounds International, 2012. Available from: http://www. woundsinternational.com. Accessed on June 19. | |
Ramsey SD, Newton K, Blough D, et al. Incidence, outcomes, and cost of foot ulcers in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1999;22(3):382–387. | |
Phillips T, Stanton B, Provan A, Lew R. A study of the impact of leg ulcers on quality of life: financial, social, and psychologic implications. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;31(1):49–53. | |
Thomas Hess C. Checklist for factors affecting wound healing. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2011;24(4):192. | |
Dowsett C. Using the TIME framework in wound bed preparation. Br J Community Nurs. 2008;13(6):S15–S16, S18, S20. | |
Gray D, White R, Cooper P, Kingsley A. The Wound Healing Continuum, An Aid To Clinical Decision Making And Clinical Audit, Wounds UK Applied Wound Management Supplement. 9-12. 2005. Available from: http://www.wounds-uk.com/pdf/content_8975.pdf. Accessed on June 3 2015. | |
Morgan, N. What you need to know about hydrocolloid dressings. Wound Care Advisor. May/June 2013;2(3):28–30. | |
KCI Medical: VAC Therapy Clinical Guidlines, 2012. Available from: http://www.kci1.com/cs/Satellite?blobcol=urldata&blobheadername1=Content-type&blobheadername2=Content-disposition&blobheadername3=MDT-Type&blobheadervalue1=application%2Fpdf&blobheadervalue2=inline%3B+filename%3D283%252F927%252F2-B-128b_Clinical%2BGuidelines_WEB.pdf&blobheadervalue3=abinary%3B+charset%3DUTF-8&blobkey=id& blobtable=MungoBlobs&blobwhere=1226642516226&ssbinary=true. Accessed April 04, 2015. |
 © 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2015 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
