Back to Journals » International Medical Case Reports Journal » Volume 14
Keratitis by Scopulariopsis brevicaulis Fungus After LASIK – A Case Report
Authors Baptista PM , Vieira R , Monteiro S , Abreu AC , Gomes M , Pinto Snr MDC
Received 7 January 2021
Accepted for publication 4 February 2021
Published 17 February 2021 Volume 2021:14 Pages 107—110
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IMCRJ.S299454
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Scott Fraser
Pedro Manuel Baptista,1,2 Rita Vieira,1 Sílvia Monteiro,1 Ana Carolina Abreu,1 Miguel Gomes,1,2 Maria do Céu Pinto Snr1
1Ophthalmology Department, Centro Hospitalar Universitário do Porto, Porto, Portugal; 2Instituto de Ciências Biomédicas Abel Salazar, Porto, Portugal
Correspondence: Pedro Manuel Baptista
Centro Hospitalar Universitário do Porto, Largo Prof. Abel Salazar, Porto, 4099-001, Portugal
Tel +35-1917868372
Email [email protected]
Purpose: To describe a rare case of an interface filamentous fungal keratitis and its successful clinical approach and management.
Patients and Methods: Retrospective case report. Analysis of the patient’s clinical records.
Results: A healthy 30-year-old woman presenting with complaints of blurred vision, photophobia and intense pain, was previously diagnosed with a suspected unilateral diffuse lamellar keratitis after laser in situ keratomileusis surgery, and accordingly treated with a scheme of oral and subconjunctival corticosteroids. Due to worsening of symptoms, the patient was later referred to our ophthalmology department. Upon examination, a corneal infiltration was observed and a fungal infection was suspected. Treatment with fortified Voriconazole (1%) was initiated and both topical and oral corticosteroids were tapered. The infiltrate resolved after 6 weeks of antifungal topical treatment. Scopulariopsis brevicaulis was isolated on culture media. At the end of follow-up, the uncorrected distance visual acuity was 20/20 with mild scarring.
Conclusion: Scopulariopsis brevicaulis can be associated with post-laser in situ keratomileusis interface infection. A quick intervention may dictate a good outcome, when combining early suspicion and microbiological diagnosis, and an appropriate conservative management. Furthermore, Voriconazole seems to be effective and safe in the treatment of such cases.
Keywords: fungus, keratitis, laser in situ keratomileusis, Scopulariopsis brevicaulis, laser vision correction
Introduction
Laser in situ keratomileusis (LASIK) is an effective and safe procedure applied to correct low to moderate ametropia, commonly used worldwide. Despite being very rare, any infection after the procedure, mainly those related to flap interface, can be a sight-threatening complication in previously otherwise healthy eyes, in young individuals.1
Over time, the main cause of non-viral infectious keratitis after LASIK has changed from the atypical Mycobacterium to gram-positive organisms, particularly Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Additionally, the postoperative intensive steroid use increases host susceptibility to opportunistic agents, including fungi.2 Only a few cases3–6 of Scopulariopsis spp. fungal keratitis have been reported in the literature, with only one case describing infection after laser refractive surgery.
In this report, we present a rare case of post-LASIK interface filamentous fungal keratitis and its successful clinical management.
Patients and Methods
Retrospective case-report. Data were collected from the patient’s clinical records.
Results
A healthy 30-year-old woman underwent uncomplicated bilateral LASIK surgery for myopia at a private medical center (day 1). In the postoperative period, she was medicated with topical ofloxacin 5id (Floxedol®), dexamethasone phosphate 5id (Ronic®) and artificial tears.
Two weeks after surgery (day 14), the patient presented complaints of blurred vision, photophobia and intense pain on her left eye (LE). As diffuse lamellar keratitis (DLK) diagnosis was postulated, in addition to the previously established medication, oral prednisolone (Lepicortinolo®) 60mg/day was initiated and two injections of subconjunctival triamcinolone (Kenalog A-40®) were applied in two consecutive days (day 15 and 16). Despite only mild clinical improvement, a third subconjunctival injection of triamcinolone was applied to the patient (day 18) and a flap lift was proposed.
Due to worsening of symptoms and clinical deterioration, seven days after the third subconjunctival corticosteroid injection, the patient came to our department, seeking second medical opinion (day 25). A complete medical history was then carried out, highlighting close contact to cereal seeds for a short period of time, when cooking, and jogging in a natural park, 4 and 10 days after surgery, respectively. Uncorrected distance visual acuity (UDVA) of the LE was 20/100. Slit-lamp examination revealed diffuse corneal edema, a central and irregular white nodular infiltrate with corneal ulceration and the presence of numerous inflammatory cells on the flap’s interface [Figure 1] [e-Figures 1–3]. As infectious etiology (namely fungal or acanthamoeba) was suspected, corneal scrapings were taken from the ulcer and the treatment scheme was altered to fortified voriconazole (1%) drops applied hourly and moxifloxacin (Vigamox®) drops 5id. Dexamethasone phosphate drops were tapered by one drop per day and oral prednisolone was tapered from 60mg/day, by steps of 20mg, every 3 days. The flap lift approach was postponed.
 |
Figure 1 Slit-lamp examination, day 25. |
After three days (day 28), clinical improvement was perceived [e-Figures 4 and 5] and the treatment plan was maintained. Continued gradual progress was observed in the following days (day 33), with a visual recovery to 20/40 [e-Figure 6]. One week later (day 40), after oral and topical corticosteroid withdrawal, improvement was sustained, with a residual mild to moderate central double-ring shaped opacity with defined edges [e-Figures 7 and 8]. The morphologic analysis of the cultural media from the initial ulcer scraping by an experienced microbiologist revealed the presence of Scopulariopsis brevicaulis fungus. The fungus was sensible to Voriconazole. After confirmation of the suspected diagnosis, moxifloxacin was suspended, and only topical Voriconazole 1% 5id was maintained.
After 50 days of treatment (day 75), the corneal infiltrate had resolved with mild scarring and the topical fortified voriconazole was stopped. There were no side effects reported from medication. More than one year after the infection, the patient maintains a mild density leucoma, with 20/20 of UCVA [Figure 2].
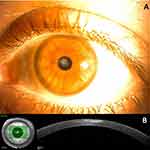 |
Figure 2 (A) Slit-lamp examination, one year and a half after the infection; (B) anterior segment OCT, one year and a half after the infection. |
Discussion
The authors present a very rare case of unilateral fungal infection by Scopulariopsis brevicaulis. As these species are soil saprophytes,7 the authors hypothesize that the contact with cereal seeds and jogging activity in the park, 4 and 10 days after the surgery, respectively, might have played a role as risk factors; however, intraoperative contamination from adjacent structures like the conjunctiva, eyelids and eyelashes, or even from surgical gloves, operative drapes and room air during the procedure should not be neglected.8 Additionally, the risk can be increased by other factors, such as an epithelial break after LASIK, allowing the penetration of pathogens,9 or the long-term use of steroids, decreasing the host immune response. Moreover, these pathogens are usually associated to mild onychomycosis in humans,7 so a possible source of infection could be the hands of both healthcare professionals or the patient.
Only few cases3–6 of Scopulariopsis spp. keratitis have been reported, of which only one case described after laser refractive surgery. In the present case, hypopyon was never observed and the infection was initially misdiagnosed as a DLK, justified by the presence of a pattern of diffuse inflammatory infiltrates, rather than satellite lesions. Thus, the initial treatment with a large dose of local corticosteroids, could have allowed the fungus to spread, as reported in the literature.10
The rapid progression and the difficulties in the treatment of corneal fungal infections make a timely microbiological workup, including sensitivity tests, of utmost importance when post-LASIK infection is suspected; however, it is crucial to be aware of the time-consuming cultural exams and its high rate of false negative results, which may contribute to a challenging diagnosis and delayed directed treatment. A careful clinical biomicroscopic examination is helpful towards reaching a diagnosis and the subsequent decision of antifungal treatment. In this case, considering the initial suspicion of a possible fungal etiology, broad spectrum fortified topical antifungal agent was promptly initiated and corticotherapy was tapered, in order to decrease the risk of rebound inflammation due to complete withdrawal.
Flap lifting for culturing and irrigation with directed antimicrobial solution is recommended by the American Society of Cataract and Refractive Surgery.11 In this case, the central infiltrate almost occupying the complete flap thickness and its communication with the corneal ulcer raised the risk of flap break during surgical lift, with subsequent amputation and its severe visual function implications. Therefore, a conservative approach with close monitoring was preferred, and ulcer scraps were collected for culture.
In fact, usually, fungal keratitis requires long-term administration of antifungal treatment and the possibility of clinical relapse, even after complete clinical improvement, should not be neglected. In this case, we experienced a good and fast clinical response based on topical, fortified Voriconazole, which was maintained for fifty days. Plus, more than one year after antifungal discontinuation and without chemoprophylaxis, the patient did not present any sign of relapse and conserved a very good visual function after the keratorefractive procedure.
The strengths of the present case-report are the rarity of the etiological agent and the good clinical response and outcome to medical treatment, without the need for a more invasive intervention, such as flap lifting. The main limitation is the absence of photographic data from ophthalmological examination before the first evaluation in our department.
Conclusions
Despite being an extremely rare complication, post-LASIK fungal keratitis is a severe complication that can lead to poor visual outcomes. This report shows that despite the initial difficulty in the differential diagnosis with DLK, an early diagnostic suspicion, combined with early microbiological diagnosis and appropriate conservative management can result in good clinical outcomes. Furthermore, voriconazole seems to be effective and safe to treat such cases.
Data Sharing Statement
The data used in the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. The abstract of this paper was presented at the European Society of Cataract and Refractive Surgeons as a poster presentation with interim findings.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
The ethics committee of the Centro Hospitalar e Universitário do Porto approved the study (nr. 2020.167 (130-DEFI/132-CE)). Consent to participate was signed by the patient.
Consent for Publication
Consent to publish the case report with anonymized data, including images, was signed by the patient.
Acknowledgments
We want to express our gratitude to the chief of the Ophthalmology department from the Centro Hospitalar e Universitário do Porto, Prof. Dr. Pedro Menéres, for his vision and enthusiasm with new technologies and resources to improve the ophthalmic care of the population.
Funding
This study received no funding. There is no financial disclosure regarding any of the authors, their families or direct business associates.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Schallhorn SC, Amesbury EC, Tanzer DJ. Avoidance, recognition, and management of LASIK complications. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006;141:733–739. doi:10.1016/j.ajo.2005.11.036
2. Randleman JB, Shah RD. LASIK interface complications: etiology, management, and outcomes. J Refract Surg. 2012;28:575–586. doi:10.3928/1081597X-20120722-01
3. Del Prete A, Sepe G, Ferrante M, Loffredo C, Masciello M, Sebastiani A. Fungal keratitis due to Scopulariopsis brevicaulis in an eye previously suffering from herpetic keratitis. Ophthalmol J Int. 1994;208:333–335. doi:10.1159/000310533
4. Kouyoumdjian GA, Forstot SL, Durairaj VD, Damiano RE. Infectious keratitis after laser refractive surgery. Ophthalmology. 2001;108:1266–1268. doi:10.1016/S0161-6420(01)00600-5
5. Malecha MA. Fungal keratitis caused by Scopulariopsis brevicaulis treated successfully with natamycin. Cornea. 2004;23:201–203. doi:10.1097/00003226-200403000-00015
6. Ragge NK, Hart JC, Easty DL, Tyers AG. A case of fungal keratitis caused by Scopulariopsis brevicaulis: treatment with antifungal agents and penetrating keratoplasty. Br J Ophthalmol. 1990;74:561–562. doi:10.1136/bjo.74.9.561
7. Cuenca-Estrella M, Gomez-Lopez A, Mellado E, Buitrago MJ, Monzón A, Rodriguez-Tudela JL. Scopulariopsis brevicaulis, a fungal pathogen resistant to broad-spectrum antifungal agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003;47:2339–2341. doi:10.1128/AAC.47.7.2339-2341.2003
8. Sridhar MS, Garg P, Bansal AK, Sharma S. Fungal keratitis after laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000;26:613–615. doi:10.1016/S0886-3350(99)00459-9
9. Karp KO, Hersh PS, Epstein RJ. Delayed keratitis after laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000;26:925–928. doi:10.1016/S0886-3350(99)00413-7
10. Peng Q, Holzer MP, Kaufer PH, Apple DJ, Solomon KD. Interface fungal infection after laser in situ keratomileusis presenting as diffuse lamellar keratitis. A clinicopathological report. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002;28:1400. doi:10.1016/S0886-3350(02)01241-5
11. Donnenfeld ED, Kim T, Holland EJ, et al. ASCRS white paper: management of infectious keratitis following laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005;31:2008–2011. doi:10.1016/j.jcrs.2005.10.030
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
