Back to Journals » Journal of Inflammation Research » Volume 14
Inducing Apoptosis and Suppressing Inflammatory Reactions in Synovial Fibroblasts are Two Important Ways for Guizhi-Shaoyao-Zhimu Decoction Against Rheumatoid Arthritis
Authors Zhang Q, Duan HX, Li RL, Sun JY, Liu J, Peng W, Wu CJ , Gao YX
Received 16 October 2020
Accepted for publication 2 December 2020
Published 26 January 2021 Volume 2021:14 Pages 217—236
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JIR.S287242
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Ning Quan
Qing Zhang,1 Hu-Xinyue Duan,1 Ruo-Lan Li,1 Jia-Yi Sun,2 Jia Liu,1 Wei Peng,1 Chun-Jie Wu,1 Yong-Xiang Gao3
1School of Pharmacy, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 611130, People’s Republic of China; 2Innovation Research Institute, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, People’s Republic of China; 3School of Basic Medicine, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, People’s Republic of China
Correspondence: Chun-Jie Wu
School of Pharmacy, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 611137, People’s Republic of China
Tel +86-28-61801001
Email [email protected]
Yong-Xiang Gao
School of Basic Medicine, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, People’s Republic of China
Tel +86-28-61801001
Email [email protected]
Background and Objectives: Guizhi-Shaoyao-Zhimu decoction (GSZD) is often applied to control rheumatoid arthritis (RA), gout, osteoarthritis, etc. In this study, bioinformatic analysis and experimental verification were used to uncover the integral mechanism profile of GSZD against RA.
Materials and Methods: The chemical compositions of GSZD were identified by UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS. MH7A cell model was established to screen active compounds in GSZD, and potential targets of these compounds were predicted through online database retrieval. The differential expression genes (DEGs) in synovial tissue of RA patients and normal controls were retrieved from the GEO database. DEGs and the predicated compounds targets were overlapped, and the overlapped genes were subsequently enriched by GO and KEGG analysis. The pathways with significant enrichments were further experimentally verified.
Results: A total of 19 constituents were identified from GSZD, and 11 compounds showed obviously antiproliferative effects on MH7A cells with IC50 < 100 μg/mL. Bioinformatic analysis indicated that IL-1β, IL-6, MAPK8, JAK2, CXCL8, and CASP3 were the main targets of GSZD, and the integral pharmacological mechanisms profile of GSZD might be related to anti-inflammation and proapoptosis. GSZD can promote the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (MOMP) and induce apoptosis in MH7A cells. Furthermore, in vitro experiments showed GSZD can not only downregulate mRNA expressions of IL-1β (p< 0.05), IL-6 (p< 0.05), MMPs (p< 0.05) and CCL5 (p< 0.05) but also inhibit the nuclear transcription of NF-κB. GSZD also reduced the expressions of Bcl-2 (p< 0.05), JAK2 (p< 0.05), STAT-3 (p< 0.05), whereas increase Bax (p< 0.05), Caspase-3 (p< 0.05) and caspase-9 (p< 0.05).
Conclusion: Collectively, inducing synovial fibroblast apoptosis and inhibiting inflammatory response are two important ways for GSZD to RA, and our study proved bioinformatic analysis combined with experimental verification is a feasible method to explore the drug targets and mechanism of actions of TCMs.
Keywords: apoptosis, anti-inflammatory, bioinformatic analysis, rheumatoid arthritis, Guizhi-Shaoyao-Zhimu decoction
Introduction
As a chronic invasive autoimmune disease, rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is characterized by joint involvement, proliferative synovitis and bone and cartilage destruction. Currently, the pathological mechanisms of RA are not clear. However, the rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synovial cells (RA-FLSs) are generally believed to be one of the main causes of RA.1 Previous scientific researchers have confirmed that RA-FLSs could release excessive pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokine, and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP), resulting in synovial hyperplasia, inflammatory reactions, pannus formation and bone and cartilage destruction. In addition, the activated RA-FLSs possess the tumor-like abnormal proliferation without inadequate apoptosis.1 Apoptosis, also known as programmed cell death, is an important form of cell death, which is of great significance to the growth and development of the organism. In addition, the study found that apoptosis did not cause inflammation in the surrounding environment. Consequently, effective induction of apoptosis in RA-FLSs appears to be a feasible method for the control and treatment of RA. Furthermore, increasing evidence has suggested that natural herbal medicines are a good resource when searching for new available candidate drugs for treating RA and its related diseases, in particular the traditional Chinese medicines (TCMs) and their clinically proven recipes.2–4
As is well-known, TCMs and their formulations have good therapeutic effects on many diseases, but their features of “multiple components act on multiple targets and multiple pathways” bring great difficulties to reveal their potential mechanisms.5 Network pharmacology is a novel way for investigation of active ingredients, pharmacological mechanism, drug targets of TCMs and TCM formulas.5 Furthermore, network pharmacology can explain the mechanism of drug action from a holistic perspective, which coincides with the holistic thinking of TCM theory. Currently, systematical biology is widely applied to study the mechanisms of pathological action of various diseases. In addition, microarray assays and bioinformatic study were comprehensively carried out to analyze the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) under diseases and enrichment functional terms.6 In our present study, we aimed to uncover the possible molecular mechanisms of Guizhi-Shaoyao-Zhimu decoction (GSZD) for treating RA using an integrated approach based on network pharmacology, bioinformatics and vivo experiments.
Materials and Methods
Chemicals, Reagents, and Materials
Reference substances including malic acid, citric acid, gallic acid, ephedrine, pseudoephedrine, neomangiferin, mangiferin, albiflorin, paeoniflorin, prim-O-glucosylcimifugin, liquiritin, 5-O-β-D-glucosyl-5-O-methylcisamminol, anemarsaponin E1, anemarsaponin BII, liquiritigenin, anemarsaponin C, licorice saponin G2, glycyrrhizic acid and anemarspaonin I were acquired from the Chengdu Desite Co. Ltd (Chengdu, China), and the purity of these compounds was ≥98%. Annexin V-FITC/PI assay kit was obtained from Multisciences (Lianke) Biotechnology Corporate Limited (Hangzhou, China). CCK8 detection kit and JC-1 probe was obtained from US Everbright®Inc (Suzhou, China). Enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) luminescence reagent was purchased from Beijing 4A Biotech Co (Beijing, China). NF-κB activity assay kits were purchased from Beyotime Biotech (Haimen, China), and the human tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α was obtained from Pepro Tech (Rocky Hill, NJ, China). BCA protein quantitative kit and primary antibodies for JAK2, STAT3, Bcl-2, Bax were bought from BOSTER biological technology company (Wuhan, China). C-caspase-9, C-caspase-3, p-JNK1/2, JNK1/2, β-actin, and the IgG-HRP were obtained from Cell Signaling technology (Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo, Japan). The QuickEasy™ Cell Direct RT-qPCR Kit-SYBR Green I kit was obtained from Chengdu Foregene Company Limited.
Prepare the GSZD Extracts
According to the previous method to prepare the freeze-dried powder of GSZD extract.2 Briefly, the nine herbs including Cinnamomi ramulus (12g), Paeoniae radix alba (9 g), Glycyrrhizae radix et rhizoma (6 g), Ephedrae herba (6 g), Zingiberis rhizoma recens (15 g), Atractylodis macrocephalae rhizoma (15 g), Anemarrhenae rhizoma (12 g), Saposhnikoviae radix (12 g), and processed Aconiti lateralis radix praeparata (6 g) are mixed with purified water and soaked for half an hour, then boiled for an hour. Filtrate was collected, vacuum-concentrated at 60°C, and finally freeze-dried to obtain the freeze-dried powder of GSZD water extract. The powder was stored in a dryer for subsequent testing.
Qualitative UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS Analysis
The main chemical composition of GSZD water extract was analyzed by UPLC-QTOF-MS. Chromatographic separation was carried out applying an Agilent 1290 system (Santa Clara, CA, USA). The XBridge BEH C18 (2.1×100 mm, i.d.; 2.5 μm, Waters, MA, USA) was applied for sample separation at 45°C using a gradient elution. Acetonitrile (A) and 0.1% formic acid-water (B) were used as mobile phase.
The gradient program was set as: 0–0.2 min, 3% A; 0.2–1.5 min, 3%-10% B; 1.5–2.2 min, 10% A; 2.2–2.9 min, 10–15% A; 2.9–3.3 min, 15% A; 3.3–4.2 min, 15–22% A; 4.2–4.6 min, 22–25% A; 4.6–5.4 min, 25–35% A; 5.4–8.0 min, 35–40% A; 8.0–10.0 min, 40–45% A; 10.0–11.0 min, 45% A; 11.0–13.0 min, 45–3% A. The flow rate and injection volume were set as 0.4 mL/min and 1.0 μL, respectively. Mass analysis was performed on the 6538 UHD Accurate-Mass Q-TOF LC-MS (Agilent Technologies Inc, Santa Clara, CA, USA) equipped with electrospray ionization (ESI). Nitrogen was applied as auxiliary gas and sheath gas with the flow rate of 12 L/min. The mass determination was carried out based on positive and negative scanning mode with the m/z ranging from 100 to 1000.
Cell Culture
MH7A cells are a novel immortalized rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocyte (FLS) line established by Miyazawa et al in 1998, which have highly consistent pathological characteristics with parental FLSs.7 At present, MH7A cells as a mature pathological model cells have been widely used in the study of RA.2,8,9 Human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synovial cell line of MH7A was obtained from the Beina Biological Company (Beijing, China), sub-cultured in DMEM (high glucose) containing 10% FBS at 37°C. Cells were passed through every 3–4 days, and only 3–5 generations of MH7A cells were used in the experiment.
Preliminary Screening of Anti-RA Compounds in GSZD
To screen the possible active constituents against RA in GSZD, we used cell counting kit-8 (CCK8) method to detect the effects of the main compounds in GSZD on MH7A cell viability.10 Briefly, MH7A cells (5×103/well) suspension was placed in 96-well plates and cultured for 24 h. After this, as previously described, the compound at different concentrations (0–100 μg/mL) was used to intervene in the cells for 24 h. At the end of treatment, 20 μL CCK8 was added into the cell culture wells and cultured for another half hour. The OD value of the 96-well plate was recorded at 450 nm by a microporous counter plate and the cell viability of each group was calculated.
Data Collection and Data Preprocessing
To Establish GSZD Compound Target Library
All the chemical structures of the screened active compounds by CCK8 assays were drawn by ChemDraw professional 15.0 and saved as Mol. format files, and the Mol. format files of potential active compounds were imported into the PharmMapper (http://www.lilab-ecust.cn/pharmmapper/) and SwissTargetPrediction (http://www.swisstargetprediction.ch/) online databases to forecast the action targets. Targets of these compounds were collected through high-throughput screening and reverse docking. In addition, compound target libraries were also supplemented the reported targets of GSZD in previous literature.11–19
To Establish RA Targets Library
As a common data platform, the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo) allows open access to gene expression data of arrays, chips and microarrays. We focused only on the comparison of gene expression data sets between synovial tissue samples from patients with RA and normal synovial tissue. At the same time, in order to ensure the stability and credibility of the analysis results, only data sets with a sample size larger than 10 were selected. Finally, the three data sets of RA were downloaded from the GEO database, dataset GSE55457 performed on the (HG-U133A) Affymetrix Human Genome U133A Array (GPL96 platform), and in this gene expression dataset, synovial tissue samples from 13 RA patients and 10 healthy human samples were included, dataset GSE55235 performed on the (HG-U133A) Affymetrix Human Genome U133A Array (GPL96 platform), and in this gene expression dataset, synovial tissue samples from 10 RA patients and 10 healthy human samples (control) were included, dataset GSE1919 performed on the (HG-U95A) Affymetrix Human Genome U95A Array (GPL91 platform), and in this gene expression dataset, synovial tissue samples from five RA patients and five healthy human samples were included.
The data sets downloaded from the GEO library are imported into the R language (3.6.3), and according to the relevant annotation information on the platform, the probes are transformed into corresponding gene symbols. In the case of a gene symbol with multiple probes, the average value is taken as the final expression value. At the same time, the data is preprocessed by background correction, quantile normalization, base 2 logarithm conversions and so on, and finally the difference analysis of gene expression between normal human and RA patients was realized. In this study, logFC (fold change) ≥2 and adjusted p-values <0.01 considered that the difference was statistically significant, and the corresponding genes were identified as DEGs, combining these DEGs is the RA target library. In addition, some important targets reported in previous literatures regarding the treatment of GSZD on RA are also supplemented in the RA target library.2,20–22
Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI)
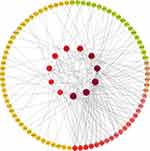
The overlapping genes (OGs) obtained from the intersection of RA target library and compound target library are the objective targets of this study. The protein-protein interaction (PPI) analysis of the OGs was performed using the search tool for the retrieval of interacting genes/proteins (STRING) online database (http://string.embl.de/). Furthermore, Cytoscape software (3.6.0) was used to visualize these interactions and construct PPI network diagram. Each node in the diagram represents a target, and the edge represents the interrelationships between targets. In addition, cytoHubba tool was used to analyze the hub genes in PPI.
Construct Drug-Target Network Diagram (DTN)
Collected target compound data pairs were introduce into Cytoscape software to construct drug-target network diagram (DTN). In this network chart, nodes show compounds and proteins, while edges show the interrelationships between compounds and proteins. In addition, the average shortest path length, betweenness centrality, closeness centrality, degree, and other network topology parameters in DTN were analyzed to evaluate the importance of each node in the network graph.
Bioinformatic Analysis
In order to comprehensively analyze the basic functions and participating pathways of these OGs, gene ontology (GO) term function annotation and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis were employed with the Clusterprofiler package in R language. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant in this study.
Detection of the Activity of Transcription Factor NF-κB
The cells were inoculated in laser confocal plates (1×104/well) and treated with TNF-α (20 ng/mL) and GSZD (0.8, 1.6, 3.2 mg/mL) for 24 h. Subsequently, immunofluorescence staining was performed, following the detailed instruction of the commercial kit, to determine the activation and transfer of the primary NF-κB subunit p65 to the nucleus under a laser confocal microscope. The NF-κB P65 staining shows red fluorescence, and the DAPI staining of the nucleus shows blue fluorescence.
qRT-PCR Analysis
The cells were inoculated in a six-well plate (2×105/well) and treated with TNF-α (20 ng/mL) and GSZD (0.8, 1.6, 3.2 mg/mL) for 24 h, and the PCR experiment was conducted according to the previously established experimental method. The total RNA of the cells was extracted with the QuickEasyTM Cell Direct RT-qPCR Kit-SYBR Green I kit according the standard steps in the instructions of kit, the cDNA was synthesized using Direct RT Mix in the kit, and the Direct qPCR Mix-SYBR of kit was used to amplify cDNA, and the primers used in this qRT-PCR test were shown in Table 1.23–28 The 2–ΔΔct method was applied to analyze the mRNA expressions of target genes.29
 |
Table 1 Sequences of Primers Used for qRT-PCR |
Flow Cytometry Analysis
The cells were inoculated in a six-well plate (2×105/well) and treated with different concentrations of GSZD (0.8, 1.6, 3.2 mg/mL) for 24 h. After treatment, the cells were collected and washed with PBS. Following the standard steps of the instructions of commercial kit, cells were re-suspended with 500 μL binding buffer, and stained with 5 μL of annexin V-FITC and PI at 37°C in dark for 30 min. Finally, the cell apoptosis rate was detected by flow cytometry (BD Company, Franklin Lakes, NY, USA).
Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MOMP) Detection
The decrease of mitochondrial membrane potential (MOMP, ΔΨm) occurred before phosphorylated serine ectropion and activation of caspase hydrolase, which is an important marker of early cell apoptosis. JC-1 is a fluorescent probe that can reflect MOMP changes in cells. In normal condition, JC-1 commonly gathers in the mitochondrial matrix in the form of polymers with red fluorescence under 590 nm. With the reduced MOMP, the JC-1 would exist as monomer with green fluorescence at 530 nm. Therefore, compared with normal cells, the fluorescence intensity ratio of red/green in apoptotic or necrotic cells was reduced. The cells were inoculated in laser confocal plates (1×104/well) and treated with different concentrations of GSZD (0.8, 1.6, 3.2 mg/mL) for 24 h. After treatment, an appropriate amount of JC-1 probe was added to the laser confocal plate and incubated in dark for 20 min. Laser confocal microscopy was used to observe the intensity of red and green fluorescence in cells at 530 nm and 590 nm, and the intensity ratio of red/green was photographed and calculated.
Western Blotting (WB) Assay
The cells were treated in the same way as described before. In short, the cells were inoculated in six-well plates (2×105/well) and incubated for 12 h, followed by different concentrations of GSZD (0.8, 1.6, 3.2 mg/mL) and/or TNF-α (20 ng/mL) for 24 h. At the end of the treatment, 100 μL RIPA cell lysate were added to extract the total cell protein. Then, the SDS-PAGE was used to separate the protein, and the separated protein was transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane. Then, 3% BSA/Tris buffered saline-Tween-20 (TBS-T) buffer was applied to block the PVDF membrane (two hours), and then the PVDF membrane was probed with primary antibodies of JAK2 (dilution of 1:300), STAT3 (dilution of 1:300), Bcl-2 (dilution of 1:300), Bax (dilution of 1:300), C-caspase-9 (dilution of 1:1000), C-caspase-3 (dilution of 1:1000), p-JNK1/2 (dilution of 1:1000), and JNK1/2 (dilution of 1:1000) at 4°C for overnight and then incubated with HPR-conjugated antibody at 37°C for one hour. Finally, enhanced ECL solution was used to develop the protein bands and record the images, and β-actin was used as the internal reference. Image J software was used to conduct normalized analysis and processing of the collected protein bands.
Statistical Analysis
Each experiment was repeated three times, and the data were expressed as the average of the results of the three experiments. Results were expressed as mean ±SD. Significant differences between means were compared using the Duncan’s multi-range test with the p-value <0.05.
Results
Chemical Composition of GSZD Extract
The main components in extracts of GSZD were analyzed qualitatively based on UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS. The analysis results were shown in the Figure 1 and Table 2, including the total ion chromatogram of UPLC-QTOF-MS, as well as the structural formula of main chemical components in GSZD.
 |
Table 2 Precursor and Product Ions of Constituents in Guizhi-Shaoyao-Zhimu Decoction |
Within 13 min, the UPLC-QTOF-MS system detected more than 20 major component peaks from the GSZD water extract. By comparing with the known chemical constituents in GSZD established by us (a total of 1200 compounds; data are not shown) and the reported literature data,30–35 19 main compounds were finally identified and deduced according to their mass spectrometry behavior and fragment ion characteristics. Finally, by comparing these components with the compound standard reference, the 19 main compounds were identified to be malic acid (1), citric acid (2), gallic acid (3), ephedrine (4), pseudoephedrine (5), neomangiferin (6), mangiferin (7), albiflorin (8), paeoniflorin (9), prim-O-glucosyl-cimifugin (10), liquiritin (11), 5-O-β-D-glucosyl-5-O-methylcisamminol (12), anemarsaponin E1 (13), anemarsaponin BII (14), liquiritigenin (15), anemarsaponin C (16), licorice saponin G2 (17), glycyrrhizic acid (18), anemarsaponin I (19) respectively. Interestingly, these 19 monomers have been described in the previous literature on GSZD. Among these monomers, compounds 13, 14, 16, 17, 18, and 19 are triterpenoid saponins and steroidal saponins, and followed by flavonoids (including 6, 7, 11, and 15), and the diterpenes (including compounds 8 and 9) and phenylpropanoids (including 10 and 12). Besides, there are three organic acid (compounds 1–3) and two alkaloids (compounds 4 and 5).
Target Prediction of GSZD Against RA
Complete the experiment of this study according to the flow chart in Figure 2A. In short, the effects of 19 compounds in GSZD on the growth activity of MH7A cells were detected by CCK8 experiment. Results as shown in Figure 3, 11 compounds including anemarsaponin I, gallic acid, paeoniflorin could significantly inhibit the activity of cells, suggesting that these compounds are the potential material basis for GSZD to play an anti-RA role. Subsequently, the targets of these compounds were predicted by means of reverse docking, supplemented by literature mining, and 653 targets of GSZD were finally obtained.
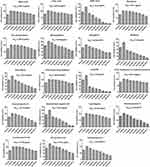 |
Figure 3 Effects of the main constituents in GSZD on proliferation of MH7A cells. Data were expressed as mean ±SD (n=3). |
After normalization of three data sets (GSE55457, GSE55235, and GSE1919) downloaded from the GEO database, the volcano map and hot spot map of gene expression were obtained (Figure 2B and C). Finally, 549 differentially expressed genes were obtained in the synovial tissue of RA patients and normal controls, among which 237 genes were upregulated and 312 genes were downregulated. At the same time, existing studies have shown that GSZD can play a role in RA treatment by regulating the expression of JAK2, CASPA3, BAX, BCL2 and other genes or proteins.2,16–18 Therefore, these targets are also taken into account in the construction of RA target library. Finally, the RA target library containing 574 genes was obtained. In the end, the intersection of the target of the compound and the target of RA was taken to obtain 83 potential targets (OGs) of GSZD for anti-RA (Figure 2D).
Results of PPI Analysis
The PPI network of GSZD anti-RA target gene was constructed by STRING database. The analysis results showed that many target genes had interaction relationships (Figure 2E), and the top 20 hub genes were selected according to node degree, namely IL6, TNF, MAPK8, JUN, MYC, CXCL8, CASP3, EGFR, IL1B, HSP90AA1, STAT1, CCL5, JAK2, NFKB1, CD40, PTPRC, NFKBIA, AR, CASP9, IL17A. Among them, IL6, TNF, MAPK8, CXCL8, CASP3, etc, showed high degree, suggesting these genes might be the potential drug targets of GSZD (Figure 2F).
KEGG and GO Enrichment Analyses of OGs
In order to analyze the biological classification of OGs, functional and pathway enrichment analysis was performed using Clusterprofiler toolkit in R language. The analysis results showed that the accumulation of these OGs into biological processes (BPs) were mainly in response to lipopolysaccharide, positive regulation of cytokine production, leukocyte proliferation, cellular response to biotic stimulus, multicellular organismal homeostasis. The main concentration of the molecular functions (MFs) were the cytokine receptor binding, hormone binding, cytokine activity, ubiquitin like protein ligase binding, protein tyrosine kinase activity, growth factor receptor binding, cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in the apoptotic process. Enriched cellular components (CCs) mainly include membrane raft, membrane microdomain, membrane region, external side of plasma membrane, nuclear envelope (Figure 4 and Table 3).
 |
Table 3 GO Enrichment Analysis Results of Overlapping Genes (OGs) |
 |
Figure 4 GO functional enrichment analysis represented in bar chart (A), bubble diagram (B) and clustering dendrogram (C). Log FC means fold change of log value. |
Enrichment analysis of KEGG pathway found that these OGs are mainly concentrated in the apoptosis, IL-17 signaling pathway, MAPK signaling pathway, NF-κB signaling pathway, RA, Toll-like receptor signaling pathway, the advanced glycation endproducts (AGE)—receptor of advanced glycation endproducts (RAGE) signaling pathway in diabetic complications, TNF signaling pathway (Figure 5 and Table 4). It is undeniable that inflammation plays an important role in the process of autoimmune diseases such as RA, and how to effectively control inflammation is also the feasible direction for the development of anti-RA drugs at present.30,36 At the same time, more and more evidence shows that tumor-like proliferation and apoptosis defects of FLSs are one of the root causes of RA. Inadequate apoptosis of FLSs can lead to synovium hyperplasia and promote pannus formation, while too many FLSs can increase the release of MMPs and various chemokines, degrade extracellular matrix (ECM), enhance inflammatory response, damage joints and cause inflammatory infiltration. Combined with previous PPI analysis, our current study results suggest that TNF, STAT1, PARP1, NFKBIA, NFKB1, MMP3, MMP2, MMP1, MAPK8, JAK2, IL6, IL1B, IL8, CCL5, CASP9, CASP3, CASP1, BAX and other genes are involved in the anti-inflammatory and proapoptotic activities of GSZD, thus playing a pharmacological role in the treatment of RA. Therefore, we established a cell model of RA in vitro to further explore and study the anti-inflammatory and proapoptotic effects of GSZD.
 |
Table 4 KEGG Enrichment Analysis Results of Overlapping Genes (OGs) |
 |
Figure 5 KEGG functional enrichment analysis represented in bar chart (A), bubble diagram (B) and clustering dendrogram (C). |
The Main Potential Active Component Against RA in GSZD
As shown the DTN in Figure 6, 11 chemical components in GSZD can act on multiple similar or different targets at the same time, indicating that GSZD has therapeutic effects on RA through the multi-component and multi-target mechanism. Through in-depth analysis of the network diagram, it is found that GZ-19, GZ-3, GZ-9 and GZ-8 have the most targets, 26, 25, 24, 20, respectively, suggesting that these compounds have made a significant contribution to anti-RA action of GSZD, and these compounds also seem to be able to be used as quality-marker (Q-marker) components of GSZD for its future quality control (Table 5).
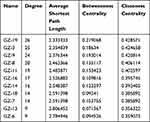 |
Table 5 Network Topology Parameters of Active Compounds in GSZD |
Anti-inflammation is the Important Way for the Anti-RA Effects of GSZD
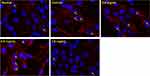
The results of KEGG suggested that NF-κB signaling was a key pathway for anti-RA effects of GSZD, and NF-κB1, NF-κIA was also considered as the joint target of GSZD. Therefore, the effect of GSZD on nuclear translocation of the NF-κB was researched using immunofluorescence assay. The results showed that the nuclear translocation of NF-κB subunit P65 increased sharply in TNF-α-induced cells, and the nuclear transcription of NF-κB was significantly inhibited when GSZD was added (Figure 7).
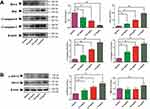
In addition, the qRT-PCR was applied to explore the role of GSZD in regulating the expression of inflammation-related genes in TNF-α-induced MH7A cells. As shown in Figure 8A, TNF-α stimulation significantly upregulated the expression of IL-6, IL-1, MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-3, and CCL5 in MH7A cells, but the upregulation was reversed after GSZD treatment. Interestingly, GSZD can dose-dependently reduce the expression of these inflammatory factors and chemokines.
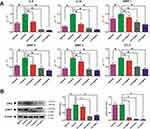 |
Figure 8 Effects of GSZD on the inflammation related genes (A) and proteins (B) in TNF-α stimulated MH7A cells. Data were expressed as mean ±SD (n=3), *p<0.01, vs control. |
Furthermore, the expressions of JAK2 and STAT3 in MH7A cells was analyzed by Western blot, and it was found that TNF-α could increase the JAK2 and STAT3 in MH7A cells (Figure 8B). Fortunately, GSZD treatment can reverse this expression abnormality. Although the effect of GSZD on JAK2 expression does not appear to be a dose-dependent inhibition, each dose of GSZD significantly inhibited JAK2 expression. In conclusion, the above results indicate that inhibition of inflammatory response is an important way for GSZD to treat RA.
Proapoptosis is Another Crucial Way for GSZD to Treat RA
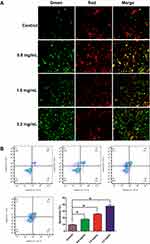
As shown in Figure 9A, compared with normal cells, using GSZD intervention after 24 h, the green fluorescence of MH7A cells increased significantly, suggesting ΔΨ loss in cells. At the same time, the promotion effect of GSZD was dose-dependent, indicating that GSZD could dose-dependently induce MOMP decline in MH7A cells. Subsequently, flow cytometry was used to detect the apoptosis of cells after GSZD intervention. As shown in Figure 9B, GSZD can induce the apoptosis of MH7A cells in a dose-dependent manner. Further studies showed that GSZD could affect the expression of apoptosis-related proteins. Briefly, GSZD can induce MMOP loss in MH7A cells and lead to apoptosis by upregulating the expressions of BAX, C-caspase-3 and C-caspase-9 and downregulating the expression of Bcl-2 (Figure 10A). In addition, GSZD of 0.4 mg/mL and 0.8 mg/mL can increase the expression of p-JNK1/2 without changing the expression of prototype JNK1/2. Although high dose of GSZD can also increase the expression of prototype JNK1/2, it has a significant promoting effect on the expression of P-JNK1/2 (Figure 10B).
Discussion
Guizhi-Shaoyao-Zhimu decoction (GSZD) is a classic prescription first recorded in the “Synopsis of the Golden Chamber” and usually used to treat “arthromyodynia”, such as RA, osteoarthritis, gout, etc.20 In previous works, it is reported that GSZD can effectively treat RA in vivo and in vitro, and the research also revealed that GSZD can affect a lot of cytokines, genes and proteins.2,20–22 However, these works only supplied scattered evidence for the mechanisms of this TCM formula. In this paper, our object is to systematically study the overall mechanism of GSZD using integrated approach of bioinformatic analysis combined with experimental verification.
In our present study, we systemically analyzed the chemical compositions of GSZD using the HPLC-QTOF-MS/MS assay, which is a comprehensively used way for component analysis of drugs. In the results, 19 constituents were identified, including six triterpenoid saponins and steroidal saponins, four flavonoids, two diterpenes, two phenylpropanoids, three organic acid and two alkaloids. Subsequently, we investigated the antiproliferative activities of these 19 compounds on MH7A cells, and found that 11 of them had potential antiproliferative activities on MH7A cells with the IC50 values less than 100 μg/mL. Currently, the online target prediction databases, such as PharmMapper and SwissTarget, become useful tools for investigating the action targets of candidate drugs. The PharmMapper web server could be applied to identify the potential drug targets of candidate drugs via reversed pharmacophore matching, and similarly, the SwissTarget Prediction is an online tool could be used to predict the possible protein targets of candidate drugs based on similarity principle via reverse screening.37,38 Then, we imported the chemical structures of the 11 compounds of GSZD into the online target prediction database to predict the potential targets via PharmMapper and SwissTarget Prediction (GSZD compounds target library). Furthermore, the GEO, an open public data platform for the acquisition of various high-throughput experimental data, is also a useful online tool for screening the DEGs between normal people and patients, and these DEGs might be the potential targets for disease therapies.5 Therefore, we downloaded the microarray data sets of GSE55457, GSE1919, GSE55235 from the GEO database to construct the DEGs and collected the reported cytokines, genes and proteins that could be affected by GSZD from previous literature; then we combined these targets as the RA target library. Subsequently, as shown in Figure 3, we analyzed the overlapped targets as the possible targets of GSZD for treating RA.
KEGG (http://www.kegg.jp/) and GO (http://geneontology.org/) are two useful online web tools for analysis of the molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways of drug therapies.39,40 Combined with KEGG and GO assays, our results revealed that most of the pathways enriched with GSZD’s potential targets were closely related to inflammation and apoptosis, suggesting that inflammation control and apoptosis regulation may be the main approaches for GSZD to treat RA. Interestingly, the present results are in accord with the scattered evidence in previous research. In addition, based on the results of PPI network analysis, the top hub genes were selected according to node degree, which were also closely related to inflammation and apoptosis.
Consequently, we carried out further actual in vitro experiments based on MH7A cells to confirm the virtual bioinformatic analysis. Subsequently, we determined the mRNA expression levels of cytokines and mediums (IL-6, IL-1β, MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-1 and CCL-5) related to inflammation in TNF-α stimulated MH7A, and the results turned out that GSZD could significantly reduce the levels of these cytokines/mediums. Current evidence from the literature indicates that the JAK/STAT signaling pathway is involved in inflammatory responses in a non-negligible capacity, and JAK inhibitors are also considered as potential drugs for RA treatment.41,42 Our current study found that GSZD significantly inhibited the expression of JAK2 and STAT3, suggesting that the anti-inflammatory effect of GSZD is related to the regulation of the JAK/STAT pathway. Furthermore, it is generally recognized that the nuclear transcription of NF-κB contributes significantly to the development of inflammatory responses. Interestingly, the present study also suggested that GSZD significantly reduced the nuclear transcription of NF-κB in cells.
Mitochondrial function is important for the survival of cells, and the decreased mitochondrial membrane potential (MMOP, ΔΨ) could induce the apoptosis of cells.43,44 In addition, the flow cytometry analysis with fluorescent double staining is another important way for determining the apoptosis in cells.45 The results of this study showed that GSZD could reduce the MOMP in MH7A cells, and increase the level of apoptosis. Furthermore, our results also revealed that GSZD increased the expression level of proapoptotic proteins (Bax, caspase-3 and -9), while it reduced the expression level of anti-apoptotic proteins (Bcl-2). In addition, the MAPK pathway is closely related to the apoptosis of synovial cells of joints, and many drugs can promote the apoptosis of synovial cells of RA by regulating the MAPK pathway to play a role in the treatment of RA.1 MAPKs mainly include extracellular regulated protein kinases (ERK), P38 and C-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). Studies have shown that JNK is the main executor of the MAPK pathway involved in apoptosis.46 As is well-known, JNK1/2 is an evolutionarily conserved serine and threonine protein kinase, and only the activated JNK1/2 can play a role in promoting cell apoptosis. Therefore, we investigated the effect of GSZD on the expression of JNK1/2 and phosphorylated JNK1/2 (p-JNK1/2) in synovial cells. The results showed that except for the high dose of GSZD (1.6 mg/mL), the expression of prototype JNK1/2 was promoted to a certain extent, and other doses of GSZD could not change the expression of JNK1/2 in MH7A cells. On the contrary, it was significantly observed that the expression of p-JNK1/2 was increased by different doses of GSZD. Taken together, the in vitro cell experimental results confirmed the bioinformatic analysis above.
In conclusion, induction of apoptosis and suppression of inflammatory reactions in synovial fibroblasts are two important ways for GSZD to treat RA, and the integrated approach based on bioinformatic analysis combined with experimental verification is a feasible way for exploration of the drug targets and pharmacological mechanisms of TCMs and its formulas. However, there are also some limitations in our present study due to the limited time and funds. In the subsequent investigations, more work should be devoted to study the activities and molecular mechanisms of the screened potential active components in the Guizhi-Shaoyao-Zhimu decoction.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (grant number 2019JDRC0074), National Science and Technology Major Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (grant number 2018ZX09721004-009-002), Xinglin Scholar Discipline Promotion Talent Program of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (no. BSH2018006) and the Sate Key Laboratory of Characteristic Chinese Medicine Resources in Southwest China (grant number 2020XSGG021).
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
1. Zhang Q, Liu J, Zhang M, et al. Apoptosis induction of fibroblast-like synoviocytes is an important molecular-mechanism for herbal medicine along with its active components in treating rheumatoid arthritis. Biomolecules. 2019;9(12):795. doi:10.3390/biom9120795
2. Zhang Q, Peng W, Wei S, et al. Guizhi-Shaoyao-Zhimu decoction possesses anti-arthritic effects on type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats via suppression of inflammatory reactions, inhibition of invasion & migration and induction of apoptosis in synovial fibroblasts. Biomed Pharm. 2019;118:109367. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109367
3. Long Y, Yang Q, Xiang Y, et al. Nose to brain drug delivery - a promising strategy for active components from herbal medicine for treating cerebral ischemia reperfusion. Pharm Res. 2020;159:104795. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104795
4. Peng W, Wang L, Qiu XH, et al. Therapeutic effects of Caragana pruinosa Kom. roots extract on type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016;191:1–8. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2016.06.028
5. Liao ML, Shang HH, Li YZ, et al. An integrated approach to uncover quality marker underlying the effects of Alisma orientale on lipid metabolism, using chemical analysis and network pharmacology. Phytomedicine. 2018;45:93–104.
6. Barrett T, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P, et al. NCBI GEO: archive for functional genomics data sets–update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41(Database issue):D991–D995.
7. Miyazawa K, Mori A, Okudaira H. Establishment and characterization of a novel human rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocyte line, MH7A, immortalized with SV40 T antigen. J Biochem. 1998;6:1153–1162.
8. Chen Y, Wang YS, Liu M, Zhou BK, Yang GJ. Diosmetin exhibits anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory effects on TNF-α-stimulated human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes through regulating the Akt and NF-κB signaling pathways. Phytother Res. 2020;6:1310–1319.
9. Yang JL, Li YX, Wang LL, Zhang ZC, Li ZZ, LncRNA JQ. H19 aggravates TNF-α-induced inflammatory injury via TAK1 pathway in MH7A cells. Biofactors. 2020;5:813–820.
10. Wang S-N, Xie G-P, Qin C-H, et al. Aucubin prevents interleukin-1 beta induced inflammation and cartilage matrix degradation via inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway in rat articular chondrocytes.Int Immunopharm. 2015;24(2):408–415. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2014.12.029
11. Gong W-G, Lin J-L, Niu Q-X, et al. Paeoniflorin diminishes ConA-induced IL-8 production in primary human hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells in the involvement of ERK1/2 and Akt phosphorylation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015;62:93–100. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2015.02.017
12. Hu PF, Chen WP, Bao JP, Wu LD. Paeoniflorin inhibits IL-1β-induced chondrocyte apoptosis by regulating the Bax/Bcl-2/caspase-3 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17:6194–6200.
13. Li XY, Wang Y, Wang K, Wu YG. Renal protective effect of Paeoniflorin by inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in diabetic mice. Biosci Trends. 2018;12(2):168–176. doi:10.5582/bst.2018.01009
14. Lima KG, Krause GC, Schuster AD, et al. Gallic acid reduces cell growth by induction of apoptosis and reduction of IL-8 in HepG2 cells. Biomed Pharm. 2016;84:1282–1290. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2016.10.048
15. Szandruk M, Merwid-Ląd A, Szeląg A. The impact of mangiferin from Belamcanda chinensis on experimental colitis in rats. Inflammopharmacology. 2018;26(2):571–581. doi:10.1007/s10787-017-0337-0
16. Tian XH, Liu Y, Liu XL, Gao SJ, Sun XF. Glycyrrhizic acid ammonium salt alleviates Concanavalin A-induced immunological liver injury in mice through the regulation of the balance of immune cells and the inhibition of hepatocyte apoptosis. Biomed Pharm. 2019;120:109481. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109481
17. Yu JH, Xiao ZC, Zhao RZ, Lu CJ, Zhang YM. Paeoniflorin suppressed IL-22 via p38 MAPK pathway and exerts anti-psoriatic effect. Life Sci. 2017;180:17–22. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2017.04.019
18. Zeng Z, Lin C, Wang S, et al. Suppressive activities of mangiferin on human epithelial ovarian cancer. Phytomedicine. 2020;15:76.
19. Zhou D, Yang Q, Tian T, et al. Gastroprotective effect of gallic acid against ethanol-induced gastric ulcer in rats: involvement of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling and anti-apoptosis role. Biomed Pharm. 2020;126:110075. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110075
20. Guo Q, Mao X, Zhang Y, et al. Guizhi-Shaoyao-Zhimu decoction attenuates rheumatoid arthritis partially by reversing inflammation-immune system imbalance. J Trans Med. 2016;14(1):165. doi:10.1186/s12967-016-0921-x
21. Chen LY, Liu H, Wang CQ, Duan M, Luo YY, Liu RH. Effect of Guizhi Shaoyao Zhimu Decoction on acute swelling and its inflammatory mediators at different time points. J Jiangxi Univ TCM. 2013;25:66–68.
22. Wang YH, Fang SB, Li YY, Zhou R. Research on mechanism of Guizhi Shaoyao Zhimu Tang in treatment of gouty arthritis based on Toll-MyD88 signaling pathway. Chin J Exp Trad Med Formul. 2016;22:121–126.
23. Matsui S, Ogata Y. Effects of miR-223 on expression of IL-1β and IL-6 in human gingival fibroblasts. J Oral Sci. 2016;58(1):101–108. doi:10.2334/josnusd.58.101
24. Kim S, You D, Jeong Y, et al. Berberine down-regulates IL-8 expression through inhibition of the EGFR/MEK/ERK pathway in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Phytomedicine. 2018;50:43–49. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2018.08.004
25. Sun HB, Yokota H. Reduction of cytokine-induced expression and activity of MMP-1 and MMP-13 by mechanical strain in MH7A rheumatoid synovial cells. Matrix Biol. 2002;21(3):263–270. doi:10.1016/S0945-053X(02)00003-3
26. Jiang JX, Ma ZN, Hu XH, Dong NZ, Ruan CG. Real-time PCR analysis of the expression of MT1-MMP/TIMP-2/MMP-2 in human vascular endothelial cell lines with different Origin. Chin J Hemorh. 2007;17:7–10.
27. Hanabayashi M, Takahashi N, Sobue Y, Hirabara S, Ishiguro N, Kojima T. Hyaluronan oligosaccharides induce MMP-1 and −3 via transcriptional activation of NF-κB and p38 MAPK in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. PLoS One. 2016;11(8):e0161875. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0161875
28. Shimada T, Imaizumi T, Shirai K, et al. CCL5 is induced by TLR 3 signaling in HuCCT1 human biliary epithelial cells: possible involvement in the pathogenesis of biliary. Biomed Res. 2017;38(5):269–276. doi:10.2220/biomedres.38.269
29. Shabani N, Sheikholeslami S, Paryan M, et al. An investigation on the expression of miRNAs including miR-144 and miR-34a in plasma samples of RET-positive and RET-negative medullar thyroid carcinoma patients. J Cell Phys. 2020;235(2):1366–1373. doi:10.1002/jcp.29055
30. Chen Y, Qian J, Wang B, Sha X. Analysis of components absorbed into plasma of the drug pair of Ramulus Cinnamomi and Paeoniae Radix Alba by UPLC-Q/TOF-MS. Chin J Mod Appl Pharm. 2017;34:1707–1711.
31. Kim J-H, Ha W-R, Park J-H, et al. Influence of herbal combinations on the extraction efficiencies of chemical compounds from Cinnamomum cassia, Paeonia lactiflora, and Glycyrrhiza uralensis, the herbal components of Gyeji-tang, evaluated by HPLC method. J Pharm Biomed Analysis. 2016;129:50–59. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2016.06.044
32. Yan Y, Chai C-Z, Wang D-W, Yue X-Y, Zhu D-N, Yu B-Y. HPLC-DAD-Q-TOF-MS/MS analysis and HPLC quantitation of chemical constituents in traditional Chinese medicinal formula Ge-Gen Decoction.J Pharm Biomed Analysis. 2013;80:192–202. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2013.03.008
33. Shao Y, Yang YP, Li JY, Zhou YJ, Chen L, Shen BBHPLC-Q. TOF-MS/MS analysis of chemical constituents of Fangfeng Shaoyaotang. Chin J Exp Trad Med Formul. 2018;24:54–59.
34. Xia Y-G, Guo X-D, Liang J, Yang B-Y, Kuang H-X. Screening and identification of steroidal saponins from Anemarrhena asphodeloides employing UPLC tandem triple quadrupole linear ion trap mass spectrometry. Steroids. 2017;125:67–80. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2017.06.011
35. Wang Y-H, Avula B, Nanayakkara NP, Zhao J, Khan IA. Cassia cinnamon as a source of coumarin in cinnamon-flavored food and food supplements in the United States. J Agri Food Chem. 2013;61(18):4470–4476. doi:10.1021/jf4005862
36. Abbasi M, Mousavi MJ, Jamalzehi S, et al. Strategies toward rheumatoid arthritis therapy; the old and the new. J Cell Physiol. 2019;7:10018–10031.
37. Daina A, Michielin O, Zoete V. SwissTargetPrediction: updated data and new features for efficient prediction of protein targets of small molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(W1):W357–W364. doi:10.1093/nar/gkz382
38. Wang X, Shen Y, Wang S, et al. PharmMapper 2017 update: a web server for potential drug target identification with a comprehensive target pharmacophore database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(W1):W356–W360. doi:10.1093/nar/gkx374
39. Kanehisa M, Furumichi M, Tanabe M, Sato Y, Morishima K. KEGG: new perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(D1):D353–D361. doi:10.1093/nar/gkw1092
40. Liu W, Liu J, Rajapakse JC. Gene ontology enrichment improves performances of functional similarity of genes. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):12100. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-30455-0
41. Scott DL, Stevenson MD. Treating active rheumatoid arthritis with Janus kinase inhibitors. Lancet. 2017;390(10093):431–432. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31659-8
42. Taylor PC, Abdul Azeez M, Kiriakidis S. Filgotinib for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, Expert Opin. Investig Drugs. 2017;26:1181–1187.
43. Sakamuru S, Attene-Ramos MS, Xia M. Mitochondrial membrane potential assay. Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1473:17–22.
44. Li RL, Zhang Q, Liu J, et al. Hydroxy-α-sanshool possesses protective potentials on H2O2-stimulated PC12 cells by suppression of oxidative stress-induced apoptosis through regulation of PI3K/Akt signal pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:3481758.
45. Wang JN, Guo N. Techniques and methods of identifying apoptosis. Chin J Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005;19:466–470.
46. Wang JZ, Lian JR, Kong XY, Lin N. Effect of triptolide on cell proliferation and regulation of RAS MAPKs pathway in synoviocytes induces by tumor necrosis factor. Chin J Chin Mater Med. 2010;35:888–891.
 © 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2021 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.