Back to Journals » Clinical and Experimental Gastroenterology » Volume 7
Golimumab for the treatment of ulcerative colitis
Authors Löwenberg M, de Boer N, Hoentjen F
Received 10 January 2014
Accepted for publication 3 February 2014
Published 12 March 2014 Volume 2014:7 Pages 53—59
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CEG.S48741
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Mark Löwenberg,1 Nanne KH de Boer,2 Frank Hoentjen3
1Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, the Netherlands; 2Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, VU University Medical Centre, Amsterdam, the Netherlands; 3Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center, Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen, the Netherlands
Abstract: The introduction of therapeutic antibodies against tumor necrosis factor (TNF) had a major impact on the treatment of ulcerative colitis (UC). Infliximab and adalimumab are powerful agents that are used for remission induction and maintenance therapy in UC and have an acceptable safety profile. However, a proportion of UC patients for whom therapy with anti-TNF agents is indicated fail or become intolerant to treatment with infliximab or adalimumab. Hence, there remains an unmet need for novel anti-TNF agents. Golimumab (Simponi®), a human anti-TNF antibody that is administered by monthly subcutaneous injections, is the most recently introduced TNF blocker for the treatment of UC. Here, we will discuss recent literature on clinical efficacy and safety of golimumab induction and maintenance treatment in patients with UC. Furthermore, we will discuss the positioning of golimumab for UC in current treatment algorithms.
Keywords: ulcerative colitis, UC, antitumor necrosis factor, TNF, antibodies, golimumab
Introduction
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the colon characterized by mucosal ulceration, leading to symptoms of bloody diarrhea and abdominal pain. Although the underlying mechanism of inflammation in UC is incompletely understood, preclinical and clinical studies demonstrated that tumor necrosis factor (TNF) plays an important role in the pathogenesis of UC.1 Various therapeutic antibodies that target TNF are used in the field of gastroenterology, rheumatology, and dermatology. Anti-TNF agents have drastically changed the therapeutic arsenal for UC. Infliximab and adalimumab were the first anti-TNF agents that were successfully approved for induction and maintenance of remission in UC.2–4 Golimumab (Simponi®, Janssen Biotech, Inc., Horsham, PA, USA) is a novel anti-TNF antibody that represents a new treatment option for patients suffering from moderate to severe UC failing conventional treatment. Administration is by 4-weekly subcutaneous injection. Golimumab was approved for the treatment of UC by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in May 2013. More recently, in October 2013, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) approved golimumab for the treatment of patients with active UC who have an inadequate response to conventional therapy or intolerance for such therapies. Here, we will give an overview of the available literature about golimumab treatment for UC.
Conventional anti-TNF agents for UC
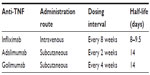
Infliximab (a chimeric anti-TNF antibody that is administered intravenously) and adalimumab (a fully human antibody against TNF that is administered subcutaneously) have significantly improved the treatment armamentarium for patients with UC. Infliximab and adalimumab are powerful agents that are used for remission induction and maintenance treatment in patients suffering from moderate to severe UC (Table 1).2–4 Infliximab and adalimumab are generally safe and well tolerated. Unfortunately, a significant proportion of UC patients do not respond to induction therapy (primary nonresponders) or require dose escalation due to loss of response over time (secondary nonresponders).5 Optimization of the dosing regimen by either increasing the dose or shortening the treatment interval can be efficacious to overcome resistance to these drugs. Coadministration of an immunosuppressive drug (such as thiopurines) can be efficacious to overcome resistance to these agents, especially when antibodies against the given biological have developed. If this strategy in secondary nonresponders is unsuccessful, or if adverse events require discontinuation of infliximab or adalimumab, switching to another anti-TNF agent is generally recommended. Hence, there remains an unmet need for novel anti-TNF agents for UC patients in whom therapy with anti-TNF agents is indicated but who fail or become intolerant to infliximab or adalimumab.
Novel anti-TNF agent: golimumab
Golimumab is the latest addition to the anti-TNF treatment regimen and is different from other available anti-TNF antibodies with regard to affinity for TNF and protein stability (Table 1). Golimumab is a transgenic fully human monoclonal immunoglobulin G1 antibody that targets a unique epitope on the TNF molecule. It was originally synthesized from TNF-immunized transgenic mice expressing human immunoglobulin G.6,7 Preclinical work showed that the affinity of golimumab for soluble and transmembrane TNF and its ability to neutralize TNF is superior to both infliximab and adalimumab.8 This work also demonstrated that golimumab is superior in terms of its conformational stability and its ability to inhibit TNF-induced cytotoxicity and human endothelial cell activation compared with infliximab and adalimumab. Moreover, treatment with golimumab resulted in potent clinical, biochemical, and histological anti-inflammatory effects employing a murine model of TNF-mediated arthritis.8 Treatment with 1 mg/kg golimumab significantly delayed disease progression in this particular model, whereas infliximab was effective only at 10 mg/kg.
Golimumab for rheumatologic diseases
Golimumab has been approved by the FDA and EMA for the treatment of various chronic immune-mediated inflammatory disorders in which TNF plays an important role, including rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. The first report that described efficacy and safety of golimumab in humans was a dose-ranging study in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.9 It was shown that treatment with golimumab in combination with methotrexate was able to reduce disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Besides data on efficacy, this small study also demonstrated that golimumab was well tolerated. Pharmacokinetic analysis showed consistent (detectable) serum drug concentrations after either subcutaneous or intravenous administration of golimumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.10 Subsequently, safety and efficacy of golimumab treatment were assessed in methotrexate-naive patients suffering from active rheumatoid arthritis. Subcutaneously administered golimumab (with or without methotrexate) effectively reduced clinical signs of active rheumatoid arthritis, although the primary end point (the so-called American College of Rheumatology 50 scale, which is used to measure change in rheumatoid arthritis symptoms) was not reached.11
A Phase III trial examined efficacy and safety of golimumab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite treatment with methotrexate.12 This study showed that the addition of golimumab to methotrexate resulted in a significant reduction of clinical signs and improved physical function in these patients. Another trial demonstrated efficacy of golimumab treatment in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis who had previously received one or more anti-TNF agents.13 A total of 58% of patients had discontinued previous treatment with anti-TNF antibodies because of lack of efficacy, and 53% of them stopped earlier treatment with anti-TNF therapy due to other reasons, such as intolerance to these drugs. Hence, this work suggested that switching rheumatoid arthritis patients from a TNF inhibitor to golimumab might be an effective and safe therapeutic strategy. Moreover, golimumab proved to be effective and well tolerated in patients with ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic arthritis.14,15
So far, clinical studies have shown that golimumab is an effective and safe therapeutic option for various rheumatologic diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis.
Golimumab in UC: efficacy and safety data
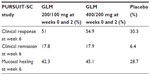
Golimumab was approved in 2013 by the FDA and EMA for the treatment of adult patients with moderately to severely active UC. The Program of Ulcerative Colitis Research Studies Utilizing an Investigational Treatment (PURSUIT) clinical studies were the pivotal trials that led to regulatory approval of golimumab for UC.16,17 The PURSUIT-SC induction study and PURSUIT-Maintenance withdrawal trial evaluated anti-TNF-naive patients with moderately to severely active UC (defined by a Mayo Clinic score18 of 6–12 points with an endoscopy subscore of ≥2) who demonstrated corticosteroid dependence or who had an inadequate response to or failed to tolerate at least one of the following drugs: oral 5-aminosalicylate acid, oral corticosteroids, or a thiopurine (azathioprine or mercaptopurine). Safety and efficacy of golimumab induction therapy was studied in the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled PURSUIT-SC study, which consisted of a Phase II dose-ranging study and a Phase III trial.17 Patients were randomized to receive subcutaneous administration with 400 mg and 200 mg or 200 mg and 100 mg golimumab at weeks 0 and 2, respectively, or placebo. The primary end point of the induction study was the proportion of patients who had a clinical response at week 6, defined by a decrease in the Mayo Clinic score of at least 30% and at least three points from baseline, with either a decrease in the rectal bleeding subscore of at least one point from baseline or a rectal bleeding subscore of 0 or 1. This end point was met by 51.0% and 54.9% of patients receiving golimumab 200/100 mg or 400/200 mg, respectively, and 30.3% of patients in the placebo arm (P<0.0001 for both comparisons versus placebo). Patients who received treatment with golimumab exhibited a clinical response as early as week 2. This trial also met its secondary endpoints, including clinical remission (defined as a Mayo Clinic score ≤2 with no individual subscore >1), mucosal healing (ie, Mayo Clinic endoscopic subscore of 0 or 1), and change from baseline in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire score, all assessed at week 6. The proportion of patients who achieved clinical remission at week 6 was 17.8% in the 200/100 mg golimumab group, 17.9% in the 400/200 mg golimumab group, and 6.4% in the placebo group (P<0.0001 for both comparisons versus placebo). Mucosal healing rates at week 6 were 45.1%, 42.3%, and 28.7% in patients who received 400/200 mg golimumab, 200/100 golimumab, or placebo, respectively (differences were statistically significant for both dosing regimens compared with placebo). Finally, the mean change from baseline in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire19 scores at week 6 was 14.8 points in the placebo arm versus 27.0 points and 26.9 points in the 200/100 mg and 400/200 mg golimumab groups, respectively (P<0.0001 for both golimumab groups versus placebo). Based on the outcomes of the PURSUIT-SC induction study, it was concluded that induction treatment with golimumab is effective and safe for patients with moderate to severe active UC. Pharmacokinetic analysis showed consistent (detectable) dose-proportional golimumab serum concentrations after subcutaneous and intravenous administration in UC patients.17
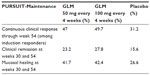
In addition, a placebo-controlled Phase III maintenance trial was completed that evaluated safety and efficacy of subcutaneous golimumab maintenance treatment in patients with moderately to severely active UC.16 Patients who achieved a clinical response with golimumab induction therapy were subsequently randomized to treatment with 50 mg or 100 mg golimumab every 4 weeks or placebo, with a 54-week follow-up. The complex study design consisted of monthly assessments in order to ensure clinical response using the partial Mayo Clinic score and the full Mayo Clinic score (including the endoscopic subscore) at week 30 and week 54. Patients who did not respond to golimumab induction treatment received open-label treatment with 100 mg golimumab at 4-week treatment intervals. It was shown that treatment with golimumab was able to maintain clinical responses through week 54 (primary end point: continuous clinical response among golimumab induction responders through week 54) in 47.0% and 49.7% of patients who received 50 mg or 100 mg golimumab every 4 weeks, respectively, versus 31.2% in the placebo group (P=0.010 and P<0.001, respectively). Clinical remission and mucosal healing at week 30 and week 54 (secondary end points) among golimumab induction responders were seen in a significantly higher percentage of patients receiving active treatment with 50 mg and 100 mg golimumab versus placebo. Clinical remission at week 30 and week 54 was 15.6%, 23.2%, and 27.8% in the placebo, golimumab 50 mg, and golimumab 100 mg groups, respectively (P=0.122 and P=0.004 for 50 mg and 100 mg golimumab-treated patients versus placebo). Based on these outcomes, the FDA advised golimumab maintenance therapy every 4 weeks at a dose of 100 mg.
Furthermore, mucosal healing rates at weeks 30 and 54 were seen in 26.6%, 41.7%, and 42.4% of patients receiving placebo, 50 mg golimumab, or 100 mg golimumab, respectively (differences between placebo and the two golimumab doses reached statistical significance: P<0.05). With regard to safety, the percentages of (serious) adverse events for all patients were not significantly different among subjects receiving placebo, 50 mg, or 100 mg golimumab, except for injection site reactions, which were seen in 7.1% of patients receiving 100 mg golimumab in the PURSUIT-Maintenance trial versus 1.9% in the 50 mg golimumab group and 1.9% in the placebo group. Hence, the PURSUIT-Maintenance trial revealed an attractive safety profile of golimumab, which seems to be consistent with the other two anti-TNF agents (infliximab and adalimumab) that are available for the treatment of UC. The results from the PURSUIT trials are shown in Tables 2 and 3.
Optimization of golimumab therapy in UC
Therapeutic efficacy of infliximab can be improved in UC patients by combining infliximab treatment with a thiopurine. The UC SUCCESS trial revealed that combination treatment with infliximab and azathioprine in UC patients resulted in higher remission rates compared with infliximab or azathioprine monotherapy.20 Steroid-free remission at week 16 (primary end point) was seen in 40%, 22%, and 24% in the infliximab–azathioprine combination group, the infliximab monotherapy group, and the azathioprine monotherapy group, respectively (P<0.05 compared with infliximab; P<0.05 compared with azathioprine). However, the follow-up period of 16 weeks was relatively short, as the optimal effect of thiopurines can be observed only after 2–4 months of therapy. If therapeutic drug monitoring would have been performed, the benefit of both azathioprine and infliximab would probably become more pronounced. Of note, this trial was discontinued prematurely due to slow patient recruitment. Whether efficacy outcomes can also be improved in UC patients receiving treatment with golimumab combined with an immunomodulator needs to be further explored.
Evidence suggests that there is an association between infliximab trough levels (eg, serum drug level measured just before the next administration) and clinical outcomes in UC patients. It has been demonstrated that detectable infliximab trough levels are associated with endoscopic improvement and a lower colectomy risk in UC patients.21 On the other hand, this work showed that undetectable trough levels, irrespective of antidrug antibody levels, are associated with less favorable clinical outcomes. Whether this also holds true for golimumab needs additional investigation. Noteworthy is that higher serum golimumab concentrations have been associated with improved clinical outcomes at week 6 in the PURSUIT-SC induction study. In this trial, an exposure–response relationship was observed in patients in the highest serum golimumab concentration quartiles in the 200/100 mg and 400/200 mg golimumab group versus those in lower quartiles.17 The PURSUIT-Maintenance trial provided additional evidence that clinical response and remission rates were better in patients with high golimumab trough levels.16 Prospective studies are needed in order to determine the clinical benefit of therapeutic drug monitoring in UC patients receiving golimumab treatment and to assess the optimal therapeutic window for golimumab trough levels. Clinical studies with larger patient cohorts should be conducted in order to verify whether an association can be found between golimumab trough levels, clinical outcomes, and adverse effects.
Infliximab and adalimumab have the potential to induce neutralizing antidrug antibodies, which can complicate clinical management.22 Future research should investigate whether antigolimumab antibodies can be detected in patients receiving golimumab treatment and whether this affects treatment outcomes.
What is the position of golimumab in current UC treatment?
In most inflammatory bowel disease clinics, infliximab is the anti-TNF agent of choice as rescue therapy for hospitalized patients with severe UC. However, the question needs to be answered how golimumab should be positioned in respect of infliximab and adalimumab for the treatment of moderate to severe UC. Up to now, no prospective head to head comparison has been performed in UC between infliximab, adalimumab, and golimumab, although most clinical experience has been gained with infliximab. Based on indirect evidence, golimumab and adalimumab seem to be more or less comparable in terms of mode of delivery, efficacy, and safety. Infliximab leads to higher remission rates and mucosal healing, at least in the short term.3,4 An advantage of golimumab over infliximab (which is intravenously administered) might be the subcutaneous route of administration. An advantage of golimumab over adalimumab is the 4-week dosing schedule for maintenance treatment compared with the 2-week dosing interval that is being used for adalimumab. The decision on which anti-TNF agent to use in daily practice for the treatment of moderate to severe UC will be dependent on long-term real-life results, center and physician’s personal experience, the pricing and reimbursement of the different products, and patients’ preferences. With time, long-term clinical efficacy and adverse events of the different anti-TNF agents will help to determine which drug will be most suitable for long-term care in UC patients.
Practical issues with regard to golimumab treatment
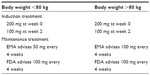
Recent trials showed that golimumab is effective in UC as remission induction and maintenance therapy.16,17 Induction treatment with golimumab for patients with UC consists of 200 mg subcutaneously injected at week 0 and then 100 mg at week 2. The FDA advises to use 100 mg every 4 weeks as maintenance treatment for all patients (ie, independent of body weight). In contrast, the EMA advice is to use 50 mg or 100 mg every 4 weeks in patients with a body weight of less than 80 kg or more than 80 kg, respectively (Table 4). Depending on the national guidelines, golimumab treatment may be intensified in cases of persistent disease activity or disease relapse and when the drug is well tolerated (eg, by increasing the dose from 50 mg to 100 mg every 4 weeks). Golimumab trough levels can be measured at certain laboratories, including the Sanquin laboratory in Amsterdam, the Netherlands, where a home-based test has recently been developed. However, additional studies are required in order to determine the benefit of measuring golimumab trough levels in daily practice and how it should influence clinical management. Moreover, UC patients in need of golimumab should preferably receive combination treatment with an immunomodulator in order to reduce the risk of developing immunogenicity, although there are no data to support this yet.
Screening should take place in order to exclude active or latent tuberculosis prior to treatment initiation with golimumab.23 The recommended method to diagnose latent tuberculosis infection is the tuberculin skin test and interferon gamma assay.24 In positively screened patients, the pulmonologist should be consulted and preventive treatment should be offered before initiating treatment with golimumab, according to the recommendations of the American Thoracic Society.25,26 Screening should take place for viral infections, including hepatitis B, cytomegalovirus, and, in cases of high-risk populations, human immunodeficiency virus.23 The varicella zoster virus (VZV) antibody test should be performed when prior VZV infection is unknown. The vaccination status should be up to date in patients who will start with golimumab. Hepatitis B virus vaccination may be considered in seronegative patients, antiviral treatment is recommended in hepatitis B surface antigen-positive patients, and VZV vaccination should be considered in patients without prior VZV infection before treatment initiation with golimumab. In patients on golimumab, live vaccines are contraindicated; hence, ideally, they should be administered prior to starting this therapy. Vaccination with a pneumococcal vaccine and annual vaccination against seasonal influenza are recommended, along with tetanus and meningococcus vaccine in the appropriate setting.27 Human papilloma virus vaccination is recommended in young females, depending on national guidelines.28 During maintenance treatment with golimumab, it is advised to perform routine laboratory tests every 4 months, including serum chemistry and hematology. Finally, treatment with golimumab should be reconsidered in cases of a malignant disease within 5 years prior to treatment initiation.29
Summary and conclusions
A growing number of anti-TNF agents are entering the clinical arena for chronic inflammatory diseases, including UC. Golimumab is the latest addition to the anti-TNF class of drugs and is registered for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and psoriatic arthritis. Based on the outcomes of two recent trials, golimumab has recently been approved by the FDA and EMA for the treatment of moderate to severe UC for those failing conventional treatment. It was shown that induction therapy with golimumab resulted in a significantly greater proportion of patients achieving clinical response, clinical remission, and mucosal healing at week 6 compared with placebo.17 In addition, it was demonstrated that treatment with golimumab maintained clinical responses in a significantly greater proportion of patients up to week 54 compared with placebo-treated patients.16 Based on the outcomes of these two trials, golimumab is likely to offer an additional choice for the treatment of moderate to severe UC. Induction treatment with golimumab for UC consists of 200 mg and 100 mg subcutaneously injected at week 0 and week 2. The FDA advises to use 100 mg every 4 weeks as maintenance treatment, whereas the EMA advice is to administer 50 mg or 100 mg at a 4-week dosing interval in patients with a body weight of less than or more than 80 kg, respectively. A possible advantage of golimumab compared with infliximab might be the subcutaneous route of administration (Table 1). An advantage of golimumab over adalimumab is the 4-week dosing interval. Although the safety profile of golimumab seems to be comparable with the other available TNF inhibitors, long-term data in UC and other inflammatory diseases are warranted in order to identify potential cumulative adverse effects.
Disclosure
Mark Löwenberg has served as speaker for Abbott/AbbVie, Dr Falk, Ferring Pharmaceuticals, Merck Sharp and Dohme, and Tramedico. Nanne KH de Boer has served as speaker for Abbott/AbbVie and Merck Sharp and Dohme. Frank Hoentjen reports no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
Danese S, Fiocchi C. Ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:1713–1725. | |
Reinisch W, Sandborn WJ, Hommes DW, et al. Adalimumab for induction of clinical remission in moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis: results of a randomised controlled trial. Gut. 2011;60:780–787. | |
Rutgeerts P, Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, et al. Infliximab for induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2462–2476. | |
Sandborn WJ, van AG, Reinisch W, et al. Adalimumab induces and maintains clinical remission in patients with moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 2012;142:257–265. | |
Armuzzi A, Pugliese D, Nardone OM, Guidi L. Management of difficult-to-treat patients with ulcerative colitis: focus on adalimumab. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2013;7:289–296. | |
Hutas G. Golimumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody against TNFalpha. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2008;10:393–406. | |
Lonberg N. Human antibodies from transgenic animals. Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23:1117–1125. | |
Shealy D, Cai A, Staquet K, et al. Characterization of golimumab, a human monoclonal antibody specific for human tumor necrosis factor alpha. MAbs. Epub July 8, 2010;2(4). | |
Kay J, Matteson EL, Dasgupta B, et al. Golimumab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite treatment with methotrexate: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58:964–975. | |
Zhuang Y, Xu Z, Frederick B, et al. Golimumab pharmacokinetics after repeated subcutaneous and intravenous administrations in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and the effect of concomitant methotrexate: an open-label, randomized study. Clin Ther. 2012;34:77–90. | |
Emery P, Fleischmann RM, Moreland LW, et al. Golimumab, a human anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody, injected subcutaneously every four weeks in methotrexate-naive patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: twenty-four-week results of a phase III, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of golimumab before methotrexate as first-line therapy for early-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60:2272–2283. | |
Keystone EC, Genovese MC, Klareskog L, et al. Golimumab, a human antibody to tumour necrosis factor {alpha} given by monthly subcutaneous injections, in active rheumatoid arthritis despite methotrexate therapy: the GO-FORWARD Study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68:789–796. | |
Smolen JS, Kay J, Doyle MK, et al. Golimumab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis after treatment with tumour necrosis factor alpha inhibitors (GO-AFTER study): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial. Lancet. 2009;374:210–221. | |
Inman RD, Davis JC Jr, Heijde D, et al. Efficacy and safety of golimumab in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58:3402–3412. | |
Kavanaugh A, McInnes I, Mease P, et al. Golimumab, a new human tumor necrosis factor alpha antibody, administered every four weeks as a subcutaneous injection in psoriatic arthritis: twenty-four-week efficacy and safety results of a randomized, placebo-controlled study. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60:976–986. | |
Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, Marano C, et al. Subcutaneous golimumab maintains clinical response in patients with moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 2014;146:96–109. | |
Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, Marano C, et al. Subcutaneous golimumab induces clinical response and remission in patients with moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 2014;146:85–95. | |
Schroeder KW, Tremaine WJ, Ilstrup DM. Coated oral 5-aminosalicylic acid therapy for mildly to moderately active ulcerative colitis. A randomized study. N Engl J Med. 1987;317:1625–1629. | |
Irvine EJ, Feagan B, Rochon J, et al. Canadian Crohn’s Relapse Prevention Trial Study Group. Quality of life: a valid and reliable measure of therapeutic efficacy in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1994;106:287–296. | |
Panaccione R,Ghosh S, Middleton S, et al. Combination therapy with Infliximab and Azathioprine is superior to monotherapy with either agent in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 2013. [Epub ahead of print]. | |
Seow CH, Newman A, Irwin SP, Steinhart AH, Silverberg MS, Greenberg GR. Trough serum infliximab: a predictive factor of clinical outcome for infliximab treatment in acute ulcerative colitis. Gut. 2010;59:49–54. | |
Peyrin-Biroulet L. Anti-TNF therapy in inflammatory bowel diseases: a huge review. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 2010;56:233–243. | |
Rahier JF, Ben-Horin S, Chowers Y, et al. European evidence-based consensus on the prevention, diagnosis and management of opportunistic infections in inflammatory bowel disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2009;3:47–91. | |
Lalvani A, Millington KA. Screening for tuberculosis infection prior to initiation of anti-TNF therapy. Autoimmun Rev. 2008;8:147–152. | |
Blumberg HM, Burman WJ, Chaisson RE, et al. American Thoracic Society/Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/Infectious Diseases Society of America: treatment of tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;167:603–662. | |
Theis VS, Rhodes JM. Review article: minimizing tuberculosis during anti-tumour necrosis factor-alpha treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008;27:19–30. | |
Kornbluth A, Sachar DB. Ulcerative colitis practice guidelines in adults: American College of Gastroenterology, Practice Parameters Committee. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105:501–523. | |
Magro F, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Sokol H, et al. Extra-intestinal malignancies in inflammatory bowel disease: results of the 3rd ECCO Pathogenesis Scientific Workshop (III). J Crohns Colitis. 2014;8:31–44. | |
Nordgaard-Lassen I, Dahlerup JF, Belard E, et al. Guidelines for screening, prophylaxis and critical information prior to initiating anti-TNF-alpha treatment. Dan Med J. 2012;59:C4480. |
 © 2014 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.
© 2014 The Author(s). This work is published and licensed by Dove Medical Press Limited. The full terms of this license are available at https://www.dovepress.com/terms.php and incorporate the Creative Commons Attribution - Non Commercial (unported, v3.0) License.
By accessing the work you hereby accept the Terms. Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. For permission for commercial use of this work, please see paragraphs 4.2 and 5 of our Terms.